Hexameric-Based Hierarchy in the Sizes of a Cytolysin Pore-Forming Complex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Expression and Purification of PFO and Its Derivative
2.2. Vesicle Preparation
2.3. Native Gradient PAGE
2.4. Multi-Stack Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Gel Isolation and Imaging
2.6. AFM Sample Preparation and Imaging
2.7. Planar Bilayer Membrane Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Multi-Stack Gel Electrophoresis Resolves a Range of Sizes of PFO Pore Complexes

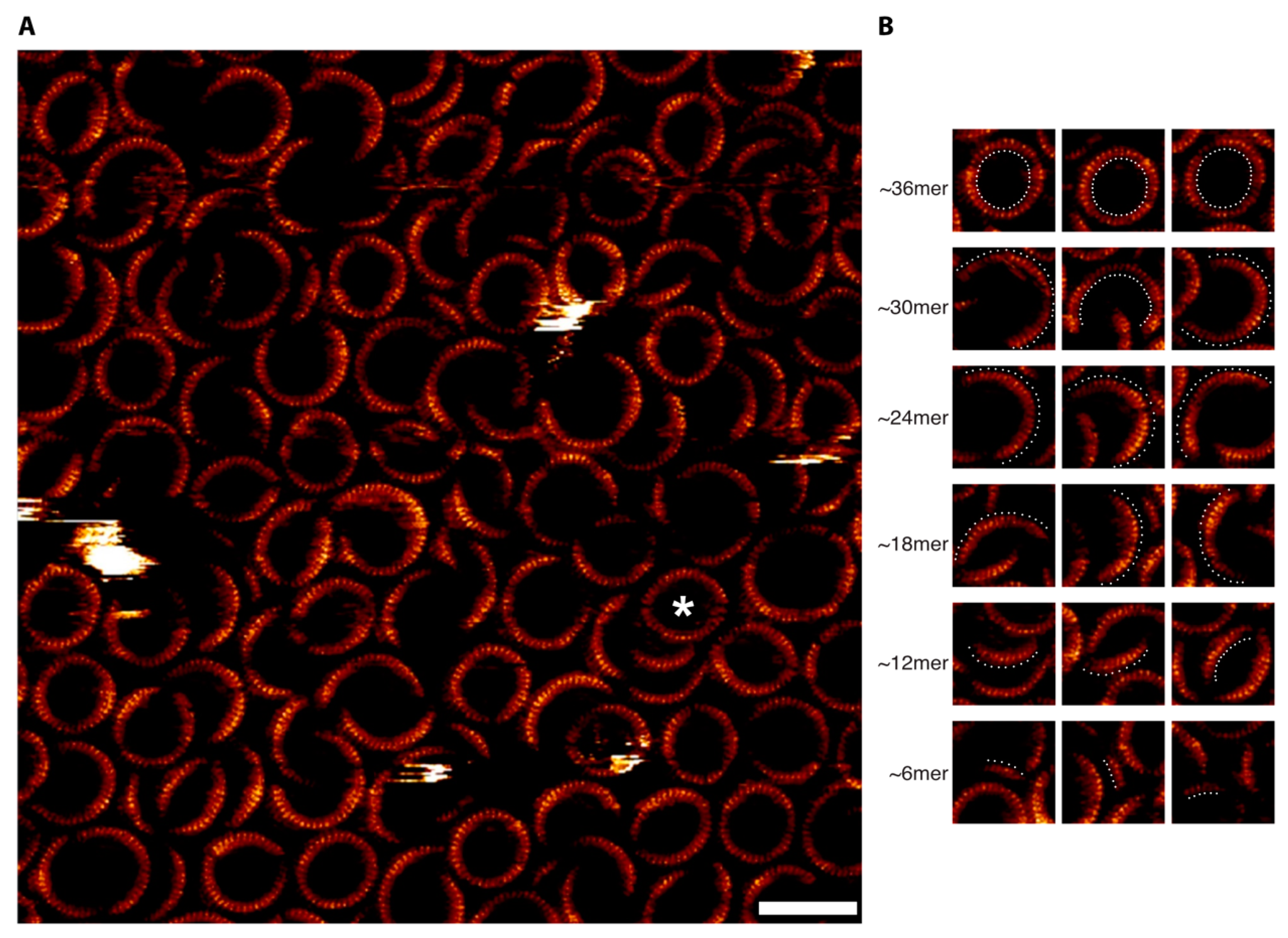
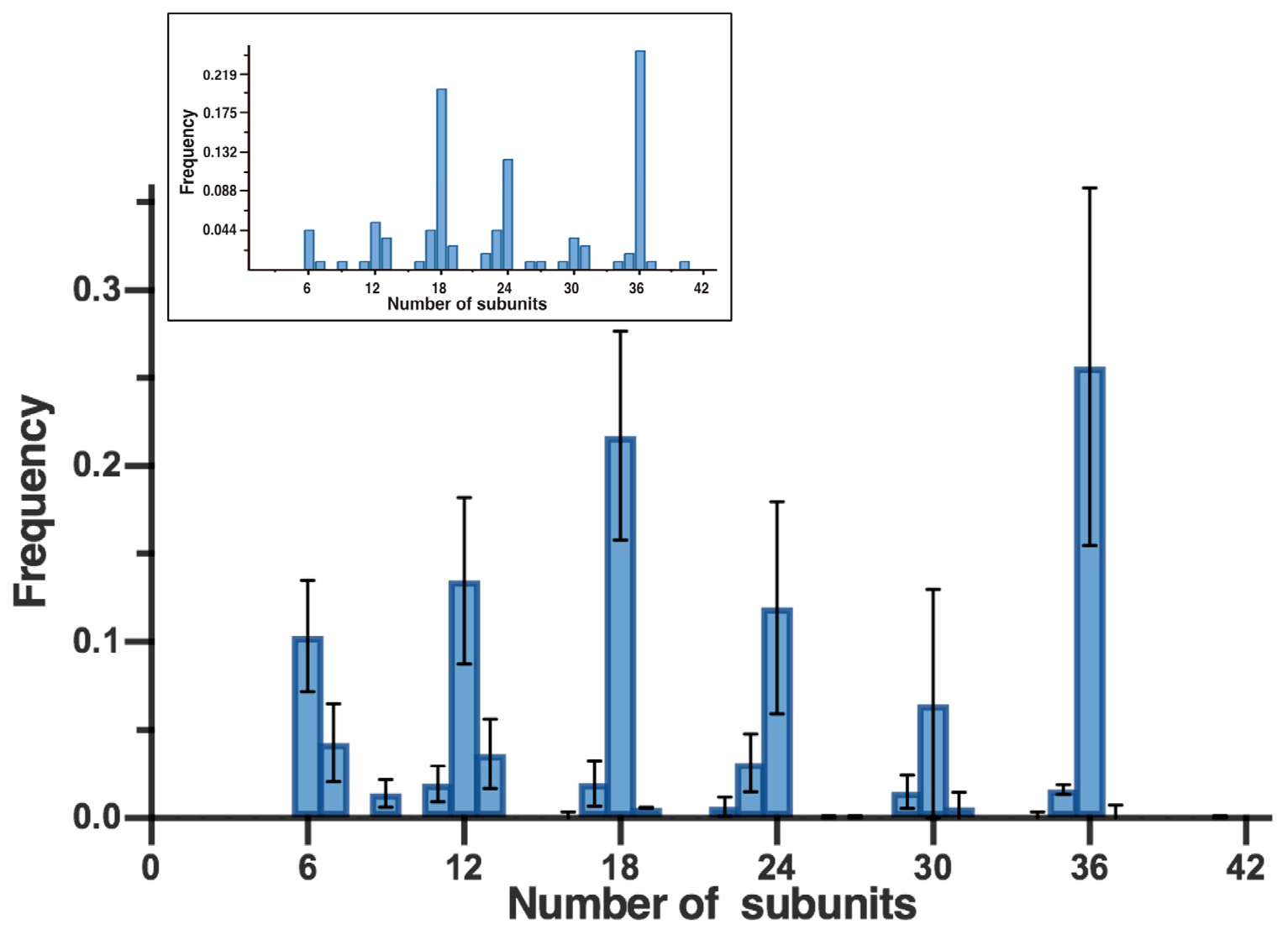
3.2. AFM Suggests That the Predominant Gel-Resolved PFO Pore Complexes Are Multiples of Six Subunits
3.3. Confirmation of the Hexameric-Based Stoichiometry with High-Resolution AFM and Single-Channel Electrophysiology
3.4. Multi-Stack Gel Reveals Hexameric Stoichiometry in Prepore-Trapped PFO Complexes
3.5. Identification of a Mutant That Is Kinetically Trapped at a Hexameric State
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDC | Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins |
| PFT | Pore-forming toxin |
| MACPF | Membrane attack complex/perforin-like protein |
| PFO | Perfringolysin O |
| SDS-AGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-agarose gel electrophoresis |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| Egg-PC | Egg L-α-phosphatidylcholine |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| POPC | 1-Palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| LDS | Lithium dodecyl sulfate |
References
- Christie, M.P.; Johnstone, B.A.; Tweten, R.K.; Parker, M.W.; Morton, C.J. Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins: From Water-Soluble State to Membrane Pore. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1337–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.J.C. Electron Microscopy as a Critical Tool in the Determination of Pore Forming Mechanisms in Proteins. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 649, pp. 71–102. [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone, B.A.; Joseph, R.; Christie, M.P.; Morton, C.J.; McGuiness, C.; Walsh, J.C.; Böcking, T.; Tweten, R.K.; Parker, M.W. Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins: The Outstanding Questions. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukoyanova, N.; Hoogenboom, B.W.; Saibil, H.R. The Membrane Attack Complex, Perforin and Cholesteroldependent Cytolysin Superfamily of Pore-Forming Proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margheritis, E.; Kappelhoff, S.; Cosentino, K. Pore-Forming Proteins: From Pore Assembly to Structure by Quantitative Single-Molecule Imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, K. Chapter Seven—Structures and Functions of the Membrane-Damaging Pore-Forming Proteins. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Donev, R., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 128, pp. 241–288. ISBN 1876-1623. [Google Scholar]
- Tweten, R.K.; Hotze, E.M.; Wade, K.R. The Unique Molecular Choreography of Giant Pore Formation by the Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins of Gram-Positive Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuck, A.P.; Tweten, R.K.; Johnson, A.E. Assembly and Topography of the Prepore Complex in Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins *. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31218–31225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatursky, O.; Heuck, A.P.; Shepard, L.A.; Rossjohn, J.; Parker, M.W.; Johnson, A.E.; Tweten, R.K. The Mechanism of Membrane Insertion for a Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin: A Novel Paradigm for Pore-Forming Toxins. Cell 1999, 99, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, A.; Hebert, H.; Thelestam, M. The Projection Structure of Perfringolysin O (Clostridium perfringens θ-Toxin). FEBS Lett. 1993, 319, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossjohn, J.; Polekhina, G.; Feil, S.C.; Morton, C.J.; Tweten, R.K.; Parker, M.W. Structures of Perfringolysin O Suggest a Pathway for Activation of Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.R.; Voisin, T.B.; Parsons, E.S.; Boyd, C.M.; Hoogenboom, B.W.; Bubeck, D. Structural Basis for Tuning Activity and Membrane Specificity of Bacterial Cytolysins. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, K.R.; Hotze, E.M.; Kuiper, M.J.; Morton, C.J.; Parker, M.W.; Tweten, R.K.; Collier, R.J. An Intermolecular Electrostatic Interaction Controls the Prepore-to-Pore Transition in a Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2204–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, C.H.; Robert, C.H.; Decker, H.; Richey, B.; Gill, S.J.; Wyman, J. Nesting: Hierarchies of Allosteric Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, E.D.; Teichmann, S.A. Chapter Two—Structural, Evolutionary, and Assembly Principles of Protein Oligomerization. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Giraldo, J., Ciruela, F., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 117, pp. 25–51. ISBN 1877-1173. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, L.A.; Shatursky, O.; Johnson, A.E.; Tweten, R.K. The Mechanism of Pore Assembly for a Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin: Formation of a Large Prepore Complex Precedes the Insertion of the Transmembrane β-Hairpins. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 10284–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.M.; Parsons, E.S.; Smith, R.A.G.; Seddon, J.M.; Ces, O.; Bubeck, D. Disentangling the Roles of Cholesterol and CD59 in Intermedilysin Pore Formation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.C.; Johnstone, B.A.; Lawrence, S.L.; Morton, C.J.; Christie, M.P.; Parker, M.W.; Tweten, R.K. A Key Motif in the Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins Reveals a Large Family of Related Proteins. mBio 2020, 11, 02351-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Le, H.M.; Sieber, J.R.; Bruxvoort, C.; McInerney, M.J.; Tweten, R.K. Identification and Characterization of the First Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins from Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.K.; Tweten, R.K.; Johnson, A.E. Disulfide-Bond Scanning Reveals Assembly State and β-Strand Tilt Angle of the PFO β-Barrel. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, K.R.; Lawrence, S.L.; Farrand, A.J.; Hotze, E.M.; Kuiper, M.J.; Gorman, M.A.; Christie, M.P.; Panjikar, S.; Morton, C.J.; Parker, M.W.; et al. The Structural Basis for a Transition State That Regulates Pore Formation in a Bacterial Toxin. mBio 2019, 10, e00538-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Tweten, R.K.; Johnson, A.E. Membrane-Dependent Conformational Changes Initiate Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin Oligomerization and Intersubunit β-Strand Alignment. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakdi, S.; Tranum-Jensen, J.; Sziegoleit, A. Mechanism of Membrane Damage by Streptolysin-O. Infect. Immun. 1985, 47, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowsky, D.M.; Hotze, E.M.; Shao, Z.; Tweten, R.K. Vertical Collapse of a Cytolysin Prepore Moves Its Transmembrane β-Hairpins to the Membrane. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3206–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.; Dudkina, N.V.; Lukoyanova, N.; Hodel, A.W.; Farabella, I.; Pandurangan, A.P.; Jahan, N.; Pires Damaso, M.; Osmanović, D.; Reboul, C.F.; et al. Stepwise Visualization of Membrane Pore Formation by Suilysin, a Bacterial Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin. eLife 2014, 3, e04247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvihill, E.; Van Pee, K.; Mari, S.A.; Müller, D.J.; Yildiz, Ö. Directly Observing the Lipid-Dependent Self-Assembly and Pore-Forming Mechanism of the Cytolytic Toxin Listeriolysin O. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 6965–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnen, A.F.-P.; Plitzko, J.M.; Gilbert, R.J.C. Incomplete Pneumolysin Oligomers Form Membrane Pores. Open Biol. 2014, 4, 140044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.E.; D’Angelo, M.E.; Piantavigna, S.; Tabor, R.F.; Martin, L.L.; Bird, P.I. Assembly of Streptolysin O Pores Assessed by Quartz Crystal Microbalance and Atomic Force Microscopy Provides Evidence for the Formation of Anchored but Incomplete Oligomers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, C.; Walsh, J.C.; Bayly-Jones, C.; Dunstone, M.A.; Christie, M.P.; Morton, C.J.; Parker, M.W.; Bocking, T. Single-Molecule Analysis of the Entire Perfringolysin O Pore Formation Pathway. eLife 2022, 11, e74901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senior, M.J.T.; Monico, C.; Weatherill, E.E.; Gilbert, R.J.; Heuck, A.P.; Wallace, M.I. Single-Molecule Tracking of Perfringolysin O Assembly and Membrane Insertion Uncoupling. FEBS J. 2023, 290, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pee, K.; Neuhaus, A.; D’Imprima, E.; Mills, D.J.; Kühlbrandt, W.; Yildiz, Ö. CryoEM Structures of Membrane Pore and Prepore Complex Reveal Cytolytic Mechanism of Pneumolysin. eLife 2017, 6, e23644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhilocha, S.; Amin, R.; Pandya, M.; Yuan, H.; Tank, M.; LoBello, J.; Shytuhina, A.; Wang, W.L.; Wisniewski, H.G.; de la Motte, C.; et al. Agarose and Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Methods for Molecular Mass Analysis of 5-to 500-KDa Hyaluronan. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 417, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesapogu, S.; Jillepalli, C.M.; Arora, D.K. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis and Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis: Methods and Principles. In Analyzing Microbes: Manual of Molecular Biology Techniques; Arora, D.K., Das, S., Sukumar, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 73–91. ISBN 978-3-642-34410-7. [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowsky, D.M.; Sheng, S.; Shao, Z. Staphylococcal α-Hemolysin Can Form Hexamers in Phospholipid Bilayers. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 276, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyl, Z. Chapter 4 Molecular Size and Shape in Electrophoresis. In Journal of Chromatography Library; Deyl, Z., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979; Volume 18, pp. 45–67. ISBN 0301-4770. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Mou, J.; Czajkowsky, D.M.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.Y. Biological Atomic Force Microscopy: What Is Achieved and What Is Needed. Adv. Phys. 1996, 45, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajkowsky, D.M.; Shao, Z. Submolecular Resolution of Single Macromolecules with Atomic Force Microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, F.; Cannon, K.S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Gladfelter, A.S.; Scheuring, S. The Hierarchical Assembly of Septins Revealed by High-Speed AFM. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, A.; Chipot, C.; Rangl, M.; Scheuring, S. High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy Shows That Annexin V Stabilizes Membranes on the Second Timescale. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, D.J.; Sass, H.-J.; Müller, S.A.; Büldt, G.; Engel, A. Surface Structures of Native Bacteriorhodopsin Depend on the Molecular Packing Arrangement in the Membrane. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1903–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Ruan, Y.; Scheuring, S. High-Speed Atomic Force Microscopy to Study Pore-Forming Proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2021, 649, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karrasch, S.; Hegerl, R.; Hoh, J.H.; Baumeister, W.; Engel, A. Atomic Force Microscopy Produces Faithful High-Resolution Images of Protein Surfaces in an Aqueous Environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Wilson-Kubalek, E.M.; Rossjohn, J.; Parker, M.W.; Johnson, A.E.; Tweten, R.K. Arresting Pore Formation of a Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysin by Disulfide Trapping Synchronizes the Insertion of the Transmembrane β-Sheet from a Prepore Intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8261–8268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaChapelle, S.; Tweten, R.K.; Hotze, E.M. Intermedilysin-Receptor Interactions during Assembly of the Pore Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12719–12726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotze, E.M.; Wilson-Kubalek, E.; Farrand, A.J.; Bentsen, L.; Parker, M.W.; Johnson, A.E.; Tweten, R.K. Monomer-Monomer Interactions Propagate Structural Transitions Necessary for Pore Formation by the Cholesterol-Dependent Cytolysins. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 24534–24543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacprzyk-Stokowiec, A.; Kulma, M.; Traczyk, G.; Kwiatkowska, K.; Sobota, A.; Dadlez, M. Crucial Role of Perfringolysin O D1 Domain in Orchestrating Structural Transitions Leading to Membrane-Perforating Pores. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 28738–28752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Roy, A.; Dutta, S. Cryo-EM-Based Structural Insights into Supramolecular Assemblies of γ-Hemolysin from S. Aureus Reveal the Pore Formation Mechanism. Structure 2023, 31, 651–667.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, G.; Movileanu, L.; Bayley, H. Subunit Composition of a Bicomponent Toxin: Staphylococcal Leukocidin Forms an Octameric Transmembrane Pore. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyama, H. Visualizing the Domino-Like Prepore-to-Pore Transition of Streptolysin O by High-Speed AFM. J. Membr. Biol. 2023, 256, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Qin, X.; Luo, M.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Czajkowsky, D.M.; Shao, Z. Hexameric-Based Hierarchy in the Sizes of a Cytolysin Pore-Forming Complex. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030424
Liu M, Qin X, Luo M, Shen Y, Wang J, Sun J, Czajkowsky DM, Shao Z. Hexameric-Based Hierarchy in the Sizes of a Cytolysin Pore-Forming Complex. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030424
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Meijun, Xintao Qin, Menglin Luo, Yi Shen, Jiabin Wang, Jielin Sun, Daniel M. Czajkowsky, and Zhifeng Shao. 2025. "Hexameric-Based Hierarchy in the Sizes of a Cytolysin Pore-Forming Complex" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030424
APA StyleLiu, M., Qin, X., Luo, M., Shen, Y., Wang, J., Sun, J., Czajkowsky, D. M., & Shao, Z. (2025). Hexameric-Based Hierarchy in the Sizes of a Cytolysin Pore-Forming Complex. Biomolecules, 15(3), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030424






