Region-Specific Impact of Repeated Synthetic Cannabinoid Exposure and Withdrawal on Endocannabinoid Signaling, Gliosis, and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. Drug Administration
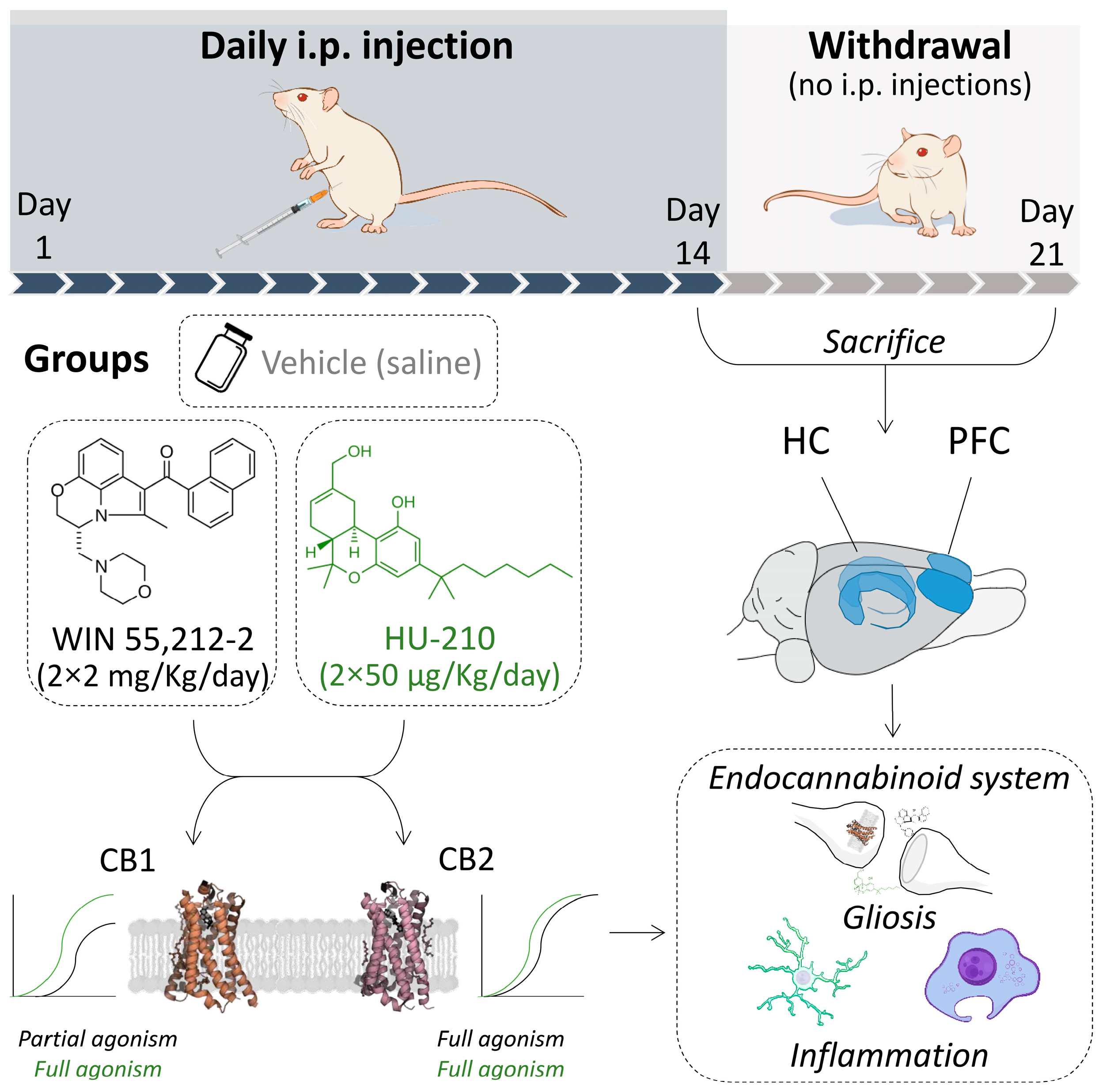
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Tissue Collection
2.6. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR Analysis
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
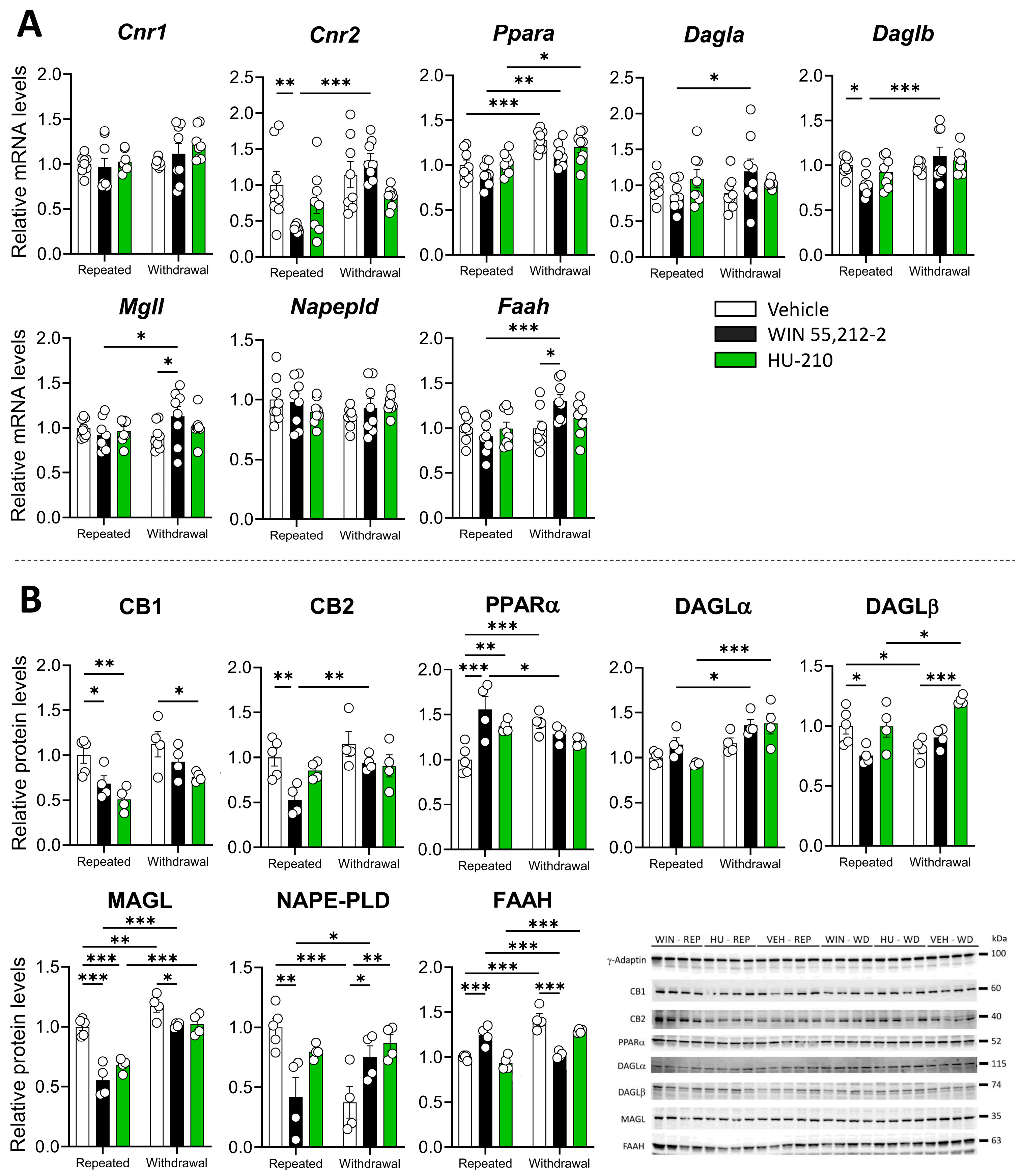
3.1. Repeated Administration and Withdrawal of WIN 55,212-2 and HU-210 Lead to Distinct Effects on the Endocannabinoid System in the Prefrontal Cortex
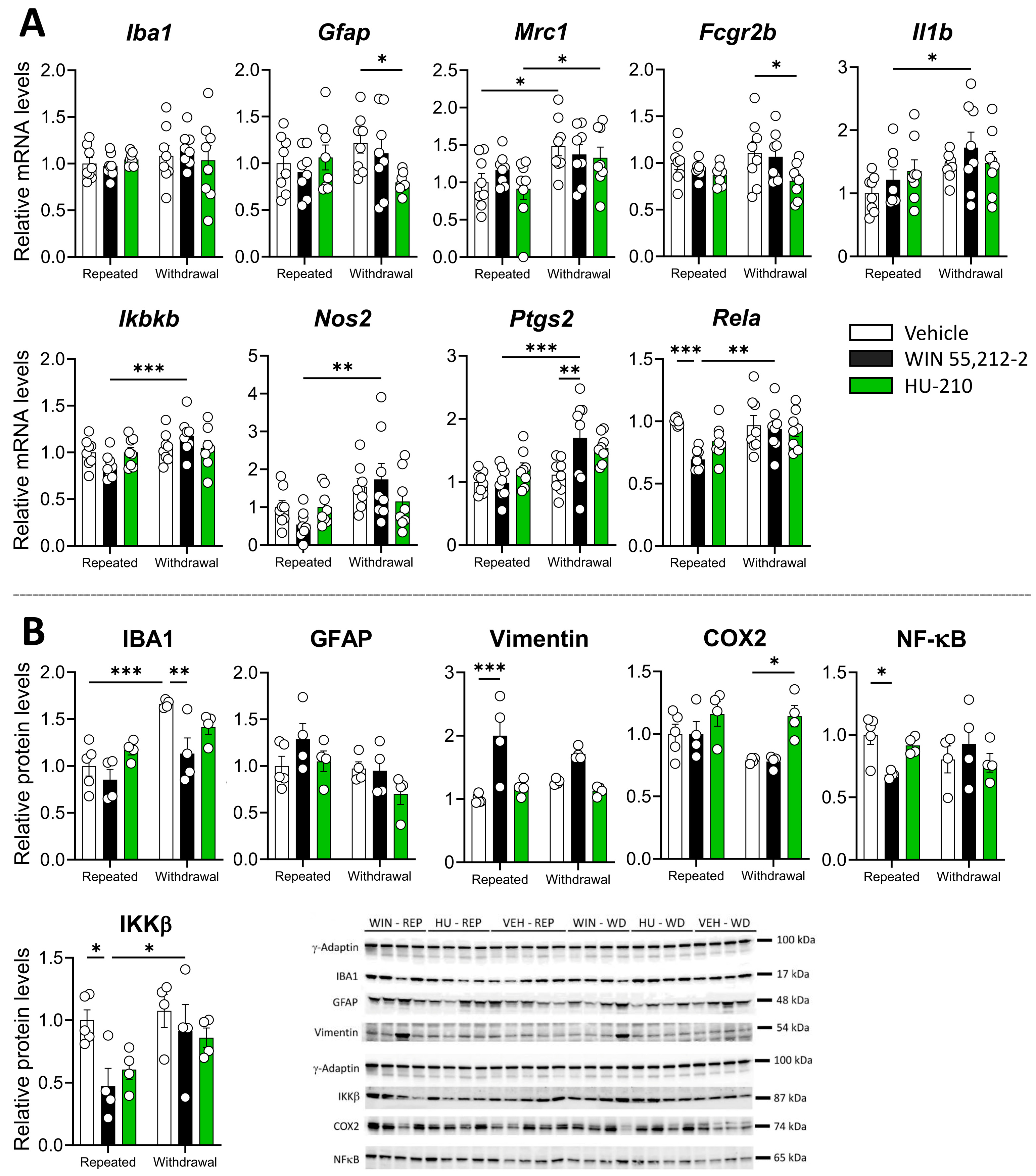
3.2. Repeated Administration and Withdrawal of WIN 55,212-2 and HU-210 Modulate Gliosis and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex
3.3. Repeated Administration and Withdrawal of WIN 55,212-2 and HU-210 Differentially Modify the Endocannabinoid System in Hippocampus
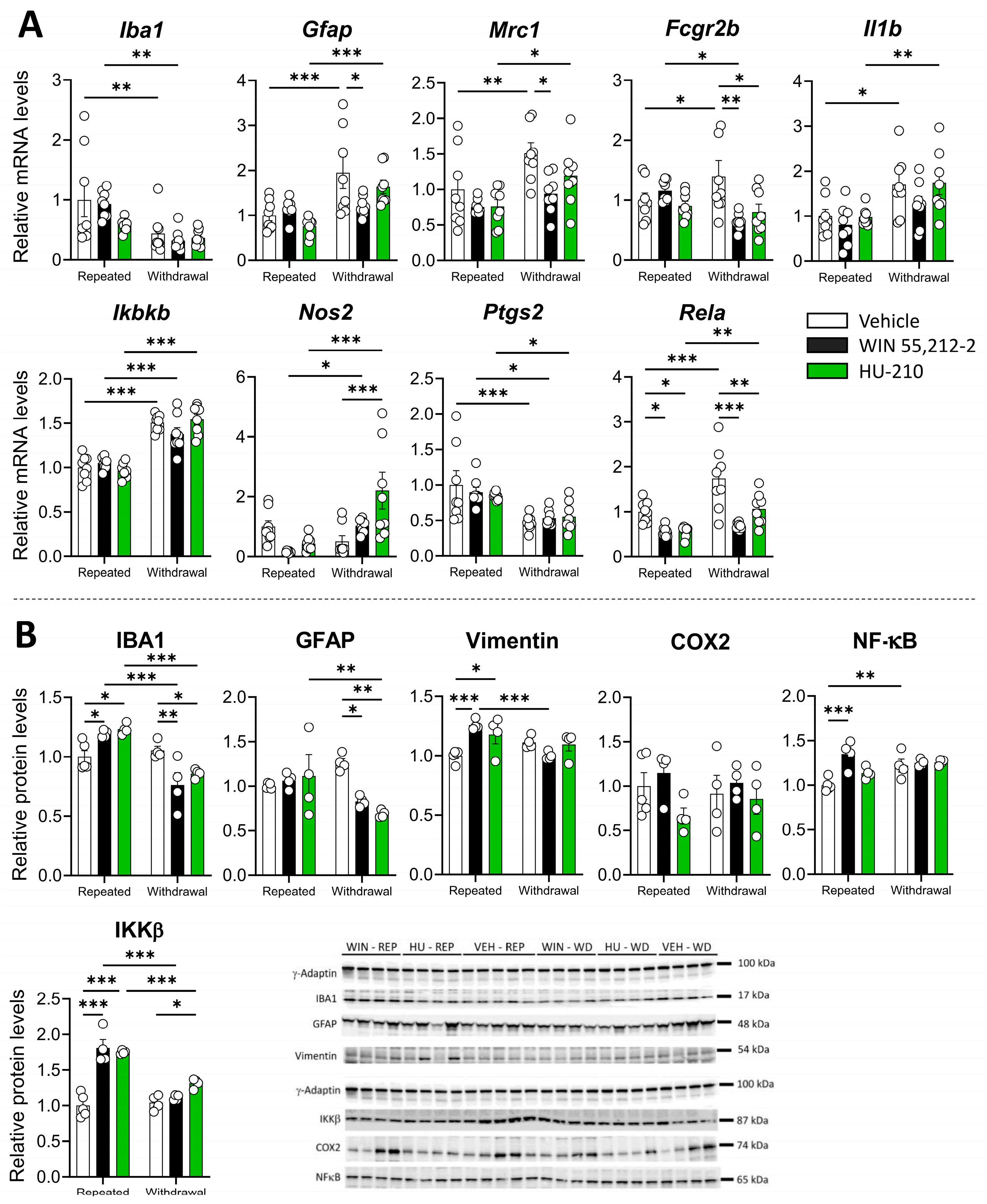
3.4. Repeated Administration of WIN 55,212-2 and HU-210 Increases Markers of Gliosis in the Hippocampus That Are Resolved During Withdrawal
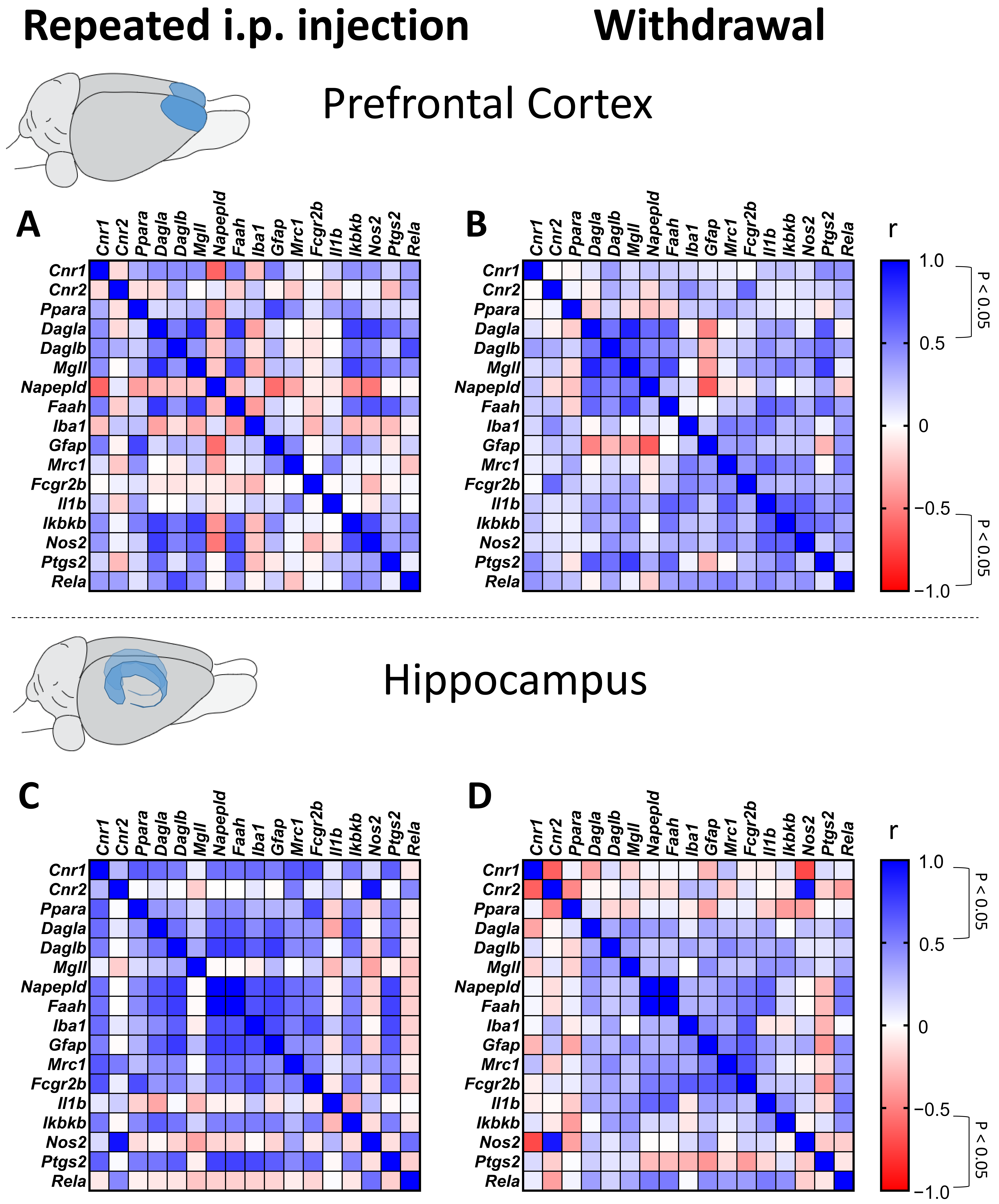
3.5. Relationship Between Gliosis, Inflammation Markers, and Endocannabinoid System During Repeated Administration and Withdrawal of WIN 55,212-2 and HU-210
4. Discussion
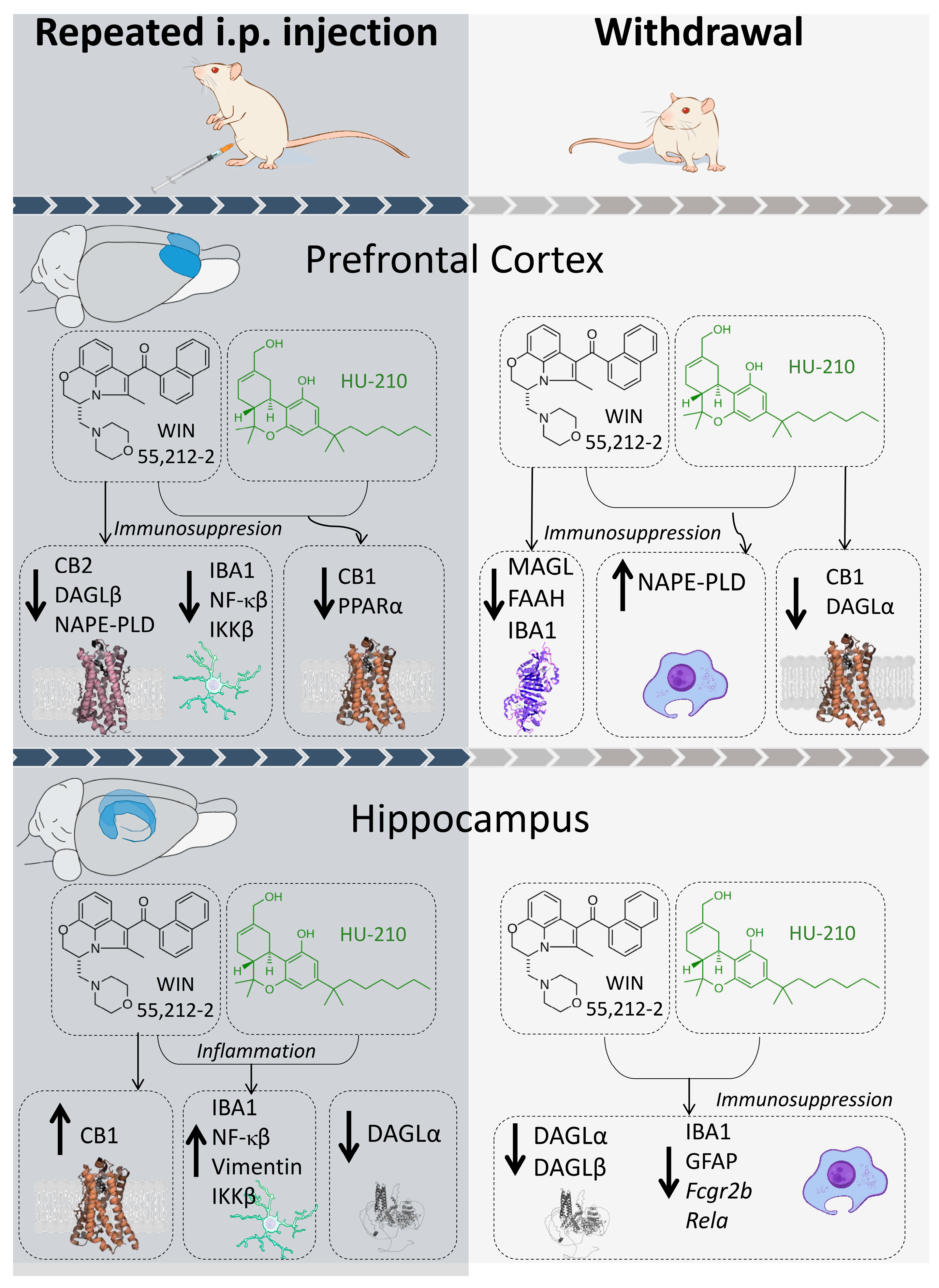
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coelho, M.P.; Duarte, P.; Calado, M.; Almeida, A.J.; Reis, C.P.; Gaspar, M.M. The current role of cannabis and cannabinoids in health: A comprehensive review of their therapeutic potential. Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshell, R.; Kearney-Ramos, T.; Brents, L.; Hyatt, W.; Tai, S.; Prather, P.; Fantegrossi, W. In vivo effects of synthetic cannabinoids JWH-018 and JWH-073 and phytocannabinoid Δ9-THC in mice: Inhalation versus intraperitoneal injection. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-aal, A.; Hemeda, M.S.; Sayed, H.Y. New designer drugs: An emergent community challenge. Med. Updates 2023, 15, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeste-Villalvir, A.; Crouch, C.; Heads, A.M.; Witte, L.; Weaver, M.; Schmitz, J.M.; Isbell, F.; Schick, V. Investigating the Experiences and Effects of Synthetic Cannabinoid (kush/K2/Spice) Use Among Individuals Experiencing Homelessness in Houston, Texas. Tex. Public Health J. 2022, 74, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneto, M.S.; Gorelick, D.A.; Desrosiers, N.A.; Hartman, R.L.; Pirard, S.; Huestis, M.A. Synthetic cannabinoids: Epidemiology, pharmacodynamics, and clinical implications. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 144, 12–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.J.; Banister, S.D.; Irizarry, L.; Trecki, J.; Schwartz, M.; Gerona, R. “Zombie” outbreak caused by the synthetic cannabinoid AMB-FUBINACA in New York. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Synthetic Cannabinoids in Europe—A Review; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shevyrin, V.; Melkozerov, V.; Endres, G.W.; Shafran, Y.; Morzherin, Y. On a new cannabinoid classification system: A sight on the illegal market of novel psychoactive substances. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2016, 1, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar]
- 1Busquets-Garcia, A.; Bains, J.; Marsicano, G. CB1 receptor signaling in the brain: Extracting specificity from ubiquity. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J. Deletion of CB2 cannabinoid receptors reduces synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in the mouse hippocampus. Hippocampus 2016, 26, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayram, O.; Alferink, J.; Pitsch, J.; Piyanova, A.; Neitzert, K.; Poppensieker, K.; Mauer, D.; Michel, K.; Legler, A.; Becker, A. Role of CB1 cannabinoid receptors on GABAergic neurons in brain aging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11256–11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marzo, V.; Stella, N.; Zimmer, A. Endocannabinoid signalling and the deteriorating brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauskela, J.S.; Comas, T.; Hewitt, M.; Aylsworth, A.; Zhao, X.; Martina, M.; Costain, W.J. Effect of synthetic cannabinoids on spontaneous neuronal activity: Evaluation using Ca2+ spiking and multi-electrode arrays. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 786, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdikaris, P.; Tsarouchi, M.; Fanarioti, E.; Natsaridis, E.; Mitsacos, A.; Giompres, P. Long lasting effects of chronic WIN55, 212-2 treatment on mesostriatal dopaminergic and cannabinoid systems in the rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2018, 129, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andó, R.D.; Bíró, J.; Csölle, C.; Ledent, C.; Sperlágh, B. The inhibitory action of exo-and endocannabinoids on [3H] GABA release are mediated by both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the mouse hippocampus. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; Decara, J.; Pavon, F.J.; Stouffer, D.G.; Edwards, S.; Serrano, A.; Suárez, J.; Parsons, L.H.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F. Cannabinoid dependence induces sustained changes in GABA release in the globus pallidus without affecting dopamine release in the dorsal striatum: A dual microdialysis probe study. Addict. Biol. 2018, 23, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.; Ottani, A.; Giuliani, D. Inhibitory effects of the cannabinoid agonist HU 210 on rat sexual behaviour. Physiol. Behav. 2000, 69, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates: Hard Cover Edition; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Decara, J.; Rivera, P.; Arrabal, S.; Vargas, A.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Suárez, J. Cooperative role of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor and β3-adrenergic-mediated signalling on fat mass reduction through the downregulation of PKA/AKT/AMPK signalling in the adipose tissue and muscle of rats. Acta Physiol. 2018, 222, e13008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fonseca, F.R.; Gorriti, M.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.; Palomo, T.; Ramos, J. Downregulation of rat brain cannabinoid binding sites after chronic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol treatment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 47, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, J.; Buzsáki, G.; Eichenbaum, H.; Nadel, L.; Ranganath, C.; Redish, A.D. Viewpoints: How the hippocampus contributes to memory, navigation and cognition. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarante, F.F.; Vila-Verde, C.; Detoni, V.L.; Ferreira-Junior, N.C.; Guimarães, F.S.; Campos, A.C. Cannabinoid modulation of the stressed hippocampus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, T.W. Cannabinoid-based drugs as anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, J.; Llorente, R.; Romero-Zerbo, S.Y.; Mateos, B.; Bermúdez-Silva, F.J.; de Fonseca, F.R.; Viveros, M.P. Early maternal deprivation induces gender-dependent changes on the expression of hippocampal CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors of neonatal rats. Hippocampus 2009, 19, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.F.; Yang, L.Q.; Goschke, A.; Stumm, R.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Liang, Y.J.; Höllt, V.; Koch, T. Role of receptor internalization in the agonist-induced desensitization of cannabinoid type 1 receptors. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim-Selley, L.J.; Martin, B.R. Effect of Chronic Administration ofR-(+)-[2,3-Dihydro-5-methyl-3-[(morpholinyl) methyl] pyrrolo [1,2,3-de]-1,4-benzoxazinyl]-(1-naphthalenyl) methanone Mesylate (WIN55, 212-2) or Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol on Cannabinoid Receptor Adaptation in Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas-Roig, J.; Agbemenyah, H.; Celarain, N.; Quintana, E.; Ramió-Torrentà, L.; Havemann-Reinecke, U. Dose-dependent effect of cannabinoid WIN-55,212-2 on myelin repair following a demyelinating insult. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría, F.; Petrosino, S.; Mestre, L.; Spagnolo, A.; Correa, F.; Hernangómez, M.; Guaza, C.; Di Marzo, V.; Docagne, F. Study of the regulation of the endocannabinoid system in a virus model of multiple sclerosis reveals a therapeutic effect of palmitoylethanolamide. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Shin, W.-H.; Baek, J.Y.; Cho, E.J.; Baik, H.H.; Kim, S.R.; Won, S.-Y.; Jin, B.K. CB2 receptor activation prevents glial-derived neurotoxic mediator production, BBB leakage and peripheral immune cell infiltration and rescues dopamine neurons in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, G.; Li, Q. Activation of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor in Microglia Reduces Neuroinflammation through Inhibiting Aerobic Glycolysis to Relieve Hypertension. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabiyi, B.F.; Schmoele, A.-C.; Beins, E.C.; Zimmer, A. Pharmacological blockade of cannabinoid receptor 2 signaling does not affect LPS/IFN-γ-induced microglial activation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11105. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, B.; Wu, J.; Foss, J.F.; Naguib, M. An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Anesthesiol. 2018, 31, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozzi, A.; Caissutti, D.; Mattei, V.; Gado, F.; Martellucci, S.; Longo, A.; Recalchi, S.; Manganelli, V.; Riitano, G.; Garofalo, T. Anti-inflammatory activity of a CB2 selective cannabinoid receptor agonist: Signaling and cytokines release in blood mononuclear cells. Molecules 2021, 27, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchalant, Y.; Rosi, S.; Wenk, G.L. Anti-inflammatory property of the cannabinoid agonist WIN-55212-2 in a rodent model of chronic brain inflammation. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, J.A.; Swinton, M.K.; Montilla-Perez, P.; Ricciardelli, E.; Telese, F. The cannabinoid receptor agonist, WIN-55212-2, suppresses the activation of proinflammatory genes induced by interleukin 1 beta in human astrocytes. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2022, 7, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puffenbarger, R.A.; Boothe, A.C.; Cabral, G.A. Cannabinoids inhibit LPS-inducible cytokine mRNA expression in rat microglial cells. Glia 2000, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, X. Cannabidiol alleviates neuroinflammation and attenuates neuropathic pain via targeting FKBP5. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 111, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, M.; McDougall, J.J. Cannabinoid control of neurogenic inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4386–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, B.R.; Anyaegbu, C.C.; Hellewell, S.C.; Papini, M.; McGonigle, T.; De Prato, L.; Shales, M.; Fitzgerald, M. Cannabinoids in traumatic brain injury and related neuropathologies: Preclinical and clinical research on endogenous, plant-derived, and synthetic compounds. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, T.E.; Kolb, B. Structural plasticity associated with exposure to drugs of abuse. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbey, F.M.; Dunlop, J.; Myers, U.S. Neural effects of positive and negative incentives during marijuana withdrawal. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.; Nweke, A.; Vincent, V.; Oke, M.; Kulkarni, P.; Ferris, C.F. Chronic exposure to inhaled vaporized cannabis high in Δ9-THC alters brain structure in adult female mice. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1139309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, P.; Bindila, L.; Pastor, A.; Pérez-Martín, M.; Pavón, F.J.; Serrano, A.; de la Torre, R.; Lutz, B.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Suárez, J. Pharmacological blockade of the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) alters neural proliferation, apoptosis and gliosis in the rat hippocampus, hypothalamus and striatum in a negative energy context. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Cowley, T.R.; Blau, C.W.; Dempsey, C.N.; Noonan, J.; Gowran, A.; Tanveer, R.; Olango, W.M.; Finn, D.P.; Campbell, V.A. The fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 exerts anti-inflammatory effects in hippocampus of aged rats and restores an age-related deficit in long-term potentiation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaeili, M.A.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Waggoner, G.R.; Deloach, A.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Beal, M.F.; Kiaei, M. Preferential PPAR-α activation reduces neuroinflammation, and blocks neurodegeneration in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.E. An update on PPAR activation by cannabinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antón, M.; Alén, F.; Gomez de Heras, R.; Serrano, A.; Pavón, F.J.; Leza, J.C.; García-Bueno, B.; Rodriguez de Fonseca, F.; Orio, L. Oleoylethanolamide prevents neuroimmune HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kB danger signaling in rat frontal cortex and depressive-like behavior induced by ethanol binge administration. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 724–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Falkenberg, I.; Martin-Santos, R.; Atakan, Z.; Crippa, J.A.; Giampietro, V.; Brammer, M.; McGuire, P. Cannabinoid modulation of functional connectivity within regions processing attentional salience. Neuropsychopharmacology 2015, 40, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Vadas, E.; Ferrer, B.; Bilbao, A.; Granado, N.; Suárez, J.; Pavon, F.J.; Moratalla, R.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F. Genetic deletion of dopamine D1 receptors increases the sensitivity to cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist-precipitated withdrawal when compared with wild-type littermates: Studies in female mice repeatedly exposed to the Spice cannabinoid HU-210. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Cebeira, M.; Ramos, J.A.; Martín, M.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.J. Cannabinoid receptors in rat brain areas: Sexual differences, fluctuations during estrous cycle and changes after gonadectomy and sex steroid replacement. Life Sci. 1994, 54, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, C.E.; Breivogel, C.S.; Gamage, T.F.; Gay, E.A.; Thomas, B.F.; Craft, R.M.; Wiley, J.L. Sex, THC, and hormones: Effects on density and sensitivity of CB1cannabinoid receptors in rats. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 194, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurikainen, H.; Tuominen, L.; Tikka, M.; Merisaari, H.; Armio, R.L.; Sormunen, E.; Borgan, F.; Veronese, M.; Howes, O.; Haaparanta-Solin, M.; et al. Sex difference in brain CB1 receptor availability in man. Neuroimage 2019, 184, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.D.; Rubin, T.G.; Hunter, R.G.; McEwen, B.S. Hippocampal gene expression changes underlying stress sensitization and recovery. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Cai, D.; Yang, X.; Shang, Y.; Li, X.; Jia, Y.; Yin, C.; Zou, H.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Q. Stress response simulated by continuous injection of ACTH attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in porcine adrenal gland. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vadas, E.; López-Gambero, A.J.; Vargas, A.; Rodríguez-Pozo, M.; Rivera, P.; Decara, J.; Serrano, A.; Martín-de-las-Heras, S.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; Suárez, J. Region-Specific Impact of Repeated Synthetic Cannabinoid Exposure and Withdrawal on Endocannabinoid Signaling, Gliosis, and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030417
Vadas E, López-Gambero AJ, Vargas A, Rodríguez-Pozo M, Rivera P, Decara J, Serrano A, Martín-de-las-Heras S, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Suárez J. Region-Specific Impact of Repeated Synthetic Cannabinoid Exposure and Withdrawal on Endocannabinoid Signaling, Gliosis, and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030417
Chicago/Turabian StyleVadas, Evelin, Antonio J. López-Gambero, Antonio Vargas, Miguel Rodríguez-Pozo, Patricia Rivera, Juan Decara, Antonia Serrano, Stella Martín-de-las-Heras, Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca, and Juan Suárez. 2025. "Region-Specific Impact of Repeated Synthetic Cannabinoid Exposure and Withdrawal on Endocannabinoid Signaling, Gliosis, and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030417
APA StyleVadas, E., López-Gambero, A. J., Vargas, A., Rodríguez-Pozo, M., Rivera, P., Decara, J., Serrano, A., Martín-de-las-Heras, S., Rodríguez de Fonseca, F., & Suárez, J. (2025). Region-Specific Impact of Repeated Synthetic Cannabinoid Exposure and Withdrawal on Endocannabinoid Signaling, Gliosis, and Inflammatory Markers in the Prefrontal Cortex and Hippocampus. Biomolecules, 15(3), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030417









