IL-6 Baseline Values and Dynamic Changes in Predicting Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
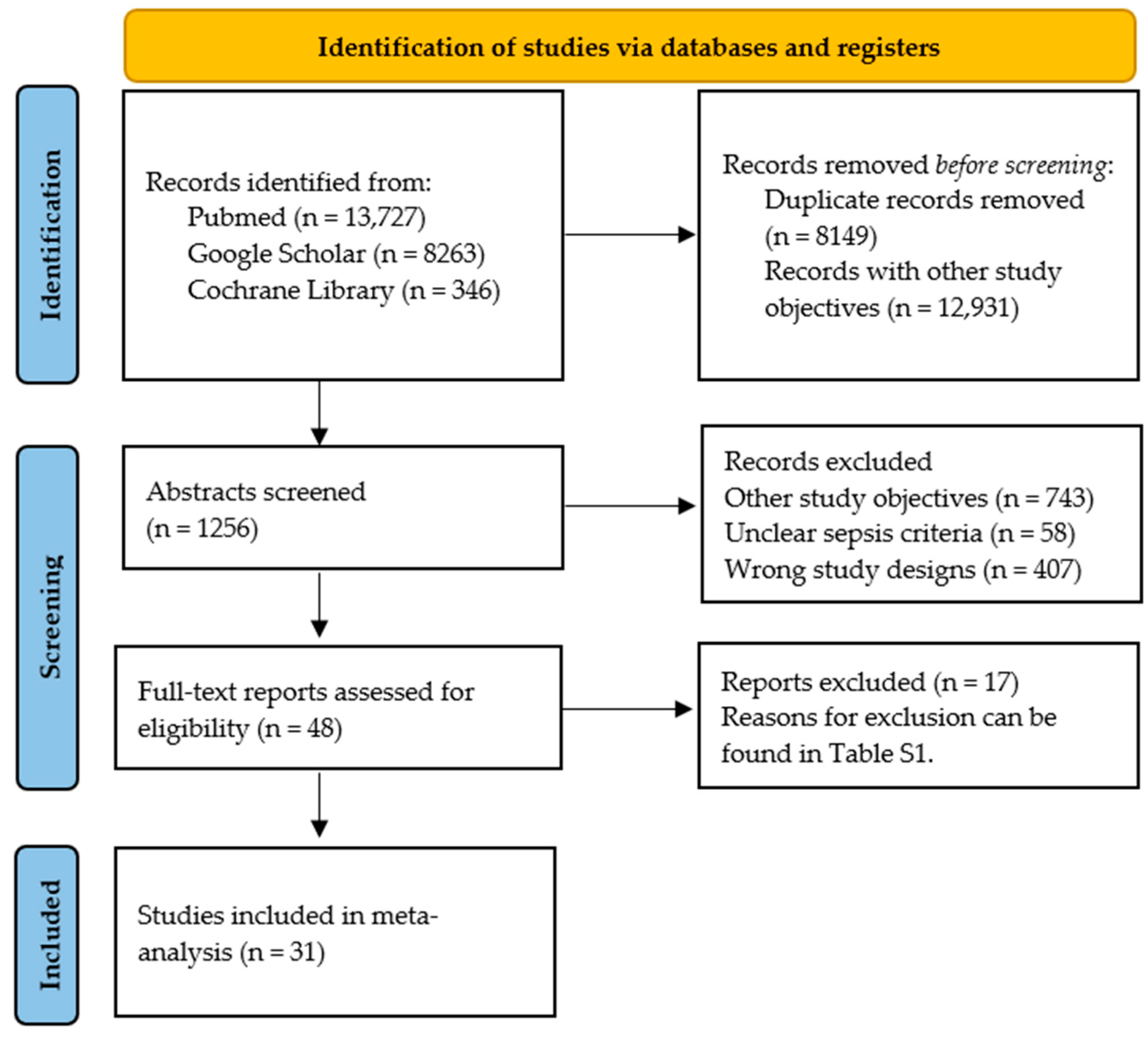
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overview of Selected Studies
3.2. Risk of Bias
3.3. Meta-Analysis
3.3.1. Baseline IL-6 Values and IL-6 Clearance: Effect Measures
3.3.2. Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousterman, B.G.; Swirski, F.K.; Weber, G.F. Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.A.; Vissel, B. The meteorology of cytokine storms, and the clinical usefulness of this knowledge. Semin. Immunopathol. 2017, 39, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ali, M.M.; McGuire, F.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Role of cytokines as a double-edged sword in sepsis. Vivo 2013, 27, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, J. Pathophysiology of sepsis. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2002, 59 (Suppl. S1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, M.; Wiersinga, W.J.; Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Inflammation, endothelium, and coagulation in sepsis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; van der Poll, T. Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb. Res. 2017, 149, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, M.; Aab, A.; Altunbulakli, C.; Azkur, K.; Costa, R.A.; Crameri, R.; Duan, S.; Eiwegger, T.; Eljaszewicz, A.; Ferstl, R.; et al. Interleukins (from IL-1 to IL-38), interferons, transforming growth factor β, and TNF-α: Receptors, functions, and roles in diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 984–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uciechowski, P.; Dempke, W.C. Interleukin-6: A Masterplayer in the Cytokine Network. Oncology 2020, 98, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Interleukin-6 and its receptors: A highly regulated and dynamic system. Cytokine 2014, 70, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, M.; Hashizume, M.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, M.; Shiina, M. IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. 2011, 122, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble il-6 receptor: Importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Huang, D.; Zeng, R.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y. Accuracy of serum interleukin (IL)-6 in sepsis diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 15238–15245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hayden, J.A.; Côté, P.; Steenstra, I.A.; Bombardier, C.; QUIPS-LBP Working Group. Identifying phases of investigation helps planning, appraising, and applying the results of explanatory prognosis studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, J.A.; Van Der Windt, D.A.; Cartwright, J.L.; Côté, P.; Bombardier, C. Assessing bias in studies of prognostic factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 158, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amancio, R.T.; Japiassu, A.M.; Gomes, R.N.; Mesquita, E.C.; Assis, E.F.; Medeiros, D.M.; Grinsztejn, B.; Bozza, P.T.; Castro-Faria, H.C.; Bozza, F.A. The innate immune response in hiv/aids septic shock patients: A comparative study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viallon, A.; Guyomarc’h, S.; Marjollet, O.; Berger, C.; Carricajo, A.; Robert, F.; Laporte, S.; Lambert, C.; Page, Y.; Zéni, F.; et al. Can emergency physicians identify a high mortality subgroup of patients with sepsis: Role of procalcitonin. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 15, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calandra, T.; Gerain, J.; Heumann, D.; Baumgartner, J.-D.; Glauser, M.P. High circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with septic shock: Evolution during sepsis, prognostic value, and interplay with other cytokines. Am. J. Med. 1991, 91, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandaswamy, P.; Hemlata; Singh, G.P.; Ahmad, M.K. Comparative Evaluation of Procalcitonin and Interleukin-6 as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers for Sepsis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2018, 12, UC17–UC21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Kong, L.; Fink, M.P.; Weissfeld, L.A.; Yealy, D.M.; Pinsky, M.R.; Fine, J.; Krichevsky, A.; Delude, R.L.; Angus, D.C. Understanding the inflammatory cytokine response in pneumonia and sepsis: Results of the genetic and inflammatory markers of sepsis (GenIMS) study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschaikowsky, K.; Hedwig-Geissing, M.; Braun, G.G.; Radespiel-Troeger, M. Predictive value of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and C-reactive protein for survival in postoperative patients with severe sepsis. J. Crit. Care 2011, 26, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunder, C.; Eichelbrönner, O.; Roewer, N. Are IL-6, IL-10 and PCT plasma concentrations reliable for outcome prediction in severe sepsis? A comparison with APACHE III and SAPS II. Inflamm. Res. 2004, 53, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, M.; Rekowski, J.; Jánosi, R.A.; Kribben, A.; Canbay, A.; Katsounas, A. Score performance of SAPS 2 and SAPS 3 in combination with biomarkers IL-6, PCT or CRP. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebihara, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Matsubara, T.; Togami, Y.; Nakao, S.; Matsuura, H.; Kojima, T.; Sugihara, F.; Okuzaki, D.; Hirata, H.; et al. Cytokine Elevation in Severe COVID-19 From Longitudinal Proteomics Analysis: Comparison with Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 798338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jekarl, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, S.; Yoo, J.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sepsis Based on Use of Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. Dis. Markers 2019, 1, 1089107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudian, S.; Piovani, D.; Desai, A.; Mapelli, S.N.; Leone, R.; Sironi, M.; Valentino, S.; Silva-Gomes, R.; Stravalaci, M.; Asgari, F.; et al. A cytokine/PTX3 prognostic index as a predictor of mortality in sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 979232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, L.; Martín, M.M.; Pérez-Cejas, A.; Barrios, Y.; Solé-Violán, J.; Ferreres, J.; Labarta, L.; Díaz, C.; Jiménez, A. Association between Interleukin-6 Promoter Polymorphism (-174 G/C), Serum Interleukin-6 Levels and Mortality in Severe Septic Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, A.; Owusu, E.D.A.; Amponsah, J.A.; Obeng-Aboagye, E.; van der Puije, W.; Frempong, A.F.; Kusi, K.A.; Ofori, M.F. Cytokines as Potential Biomarkers for Differential Diagnosis of Sepsis and Other Non-Septic Disease Conditions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 901433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L.F.; Cuenca, A.G.; Vanzant, E.L.; Efron, P.A.; McKinley, B.; Moore, F.; Moldawer, L.L. Is there value in plasma cytokine measurements in patients with severe trauma and sepsis? Methods 2013, 61, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbarth, S.; Holeckova, K.; Froidevaux, C.; Pittet, D.; Ricou, B.; Grau, G.E.; Vadas, L.; Pugin, J.; The Geneva Sepsis Network. Diagnostic value of procalcitonin, interleukin-6, and interleukin-8 in critically ill patients admitted with suspected sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekarl, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Han, K.; Woo, S.H.; Lee, W.J. Diagnosis and evaluation of severity of sepsis via the use of biomarkers and profiles of 13 cytokines: A multiplex analysis. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oda, S.; Hirasawa, H.; Shiga, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Matsuda, K.-I.; Nakamua, M. Sequential measurement of IL-6 blood levels in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)/sepsis. Cytokine 2005, 29, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Bobillo, F.; Iglesias, V.; Almansa, R.; Rico, L.; Gandía, F.; Resino, S.; Tamayo, E.; de Lejarazu, R.O.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F. A combined score of pro- and anti-inflammatory interleukins improves mortality prediction in severe sepsis. Cytokine 2012, 57, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, O.E.; Campolo, J.; Vallerio, P.; Musca, F.; Moreo, A.; Maloberti, A.; Parolini, M.; Bonacchini, L.; Monti, G.; De Gasperi, A.; et al. Biochemical but not imaging parameters are predictive of outcome in septic shock: A pilot study. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2022, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneyto, L.A.P.; Luis, O.R.; Sánchez, C.S.; Simón, O.C.; Rentero, D.B.; Bayarri, V.M. Valor pronóstico de la interleucina 6 en la mortalidad de pacientes con sepsis. Med. Clin. 2016, 147, 281–286, Erratum in Med. Clin. 2017, 148, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidt, M.V.; Nunes, F.B.; Pedrazza, L.; Caeran, G.; Pellegrin, G.; Melo, D.A.; Possuelo, L.; Jost, R.T.; Dias, H.B.; Donadio, M.V.; et al. Biochemical and inflammatory aspects in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: The predictive role of IL-18 in mortality. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 453, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frencken, J.F.; van Vught, L.A.; Peelen, L.M.; Ong, D.S.Y.; Klouwenberg, P.M.C.K.; Horn, J.; Bonten, M.J.M.; van der Poll, T.; Cremer, O.L. An Unbalanced Inflammatory Cytokine Response Is Not Associated with Mortality Following Sepsis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e493–e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jekarl, D.W.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.H.; Wee, J.H.; Choi, S.P. Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker and IL-6 as a prognostic marker for sepsis. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, F.-Q.; Kong, F.; An, M.-M.; Jin, B.-B.; Cao, D.; Gong, P. Inflammatory anemia-associated parameters are related to 28-day mortality in patients with sepsis admitted to the ICU: A preliminary observational study. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamouzos, V.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Velissaris, D.; Gkavogianni, T.; Gogos, C. Cytokine production and outcome in MDR versus non-MDR gram-negative bacteraemia and sepsis. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampela, I.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Kandri, E.; Antonakos, G.; Vogiatzakis, E.; Dimopoulos, G.; Armaganidis, A.; Dalamaga, M. Circulating eNampt and resistin as a proinflammatory duet predicting independently mortality in critically ill patients with sepsis: A prospective observational study. Cytokine 2019, 119, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; She, F.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X. Effects of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Combined with Interleukin-6 in Predicting 28-Day Mortality in Patients with Sepsis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 639735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bai, C.; Li, B.; Shan, A.; Shi, F.; Yao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Xie, M.; et al. Mortality prediction using a novel combination of biomarkers in the first day of sepsis in intensive care units. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Ogura, H.; Shimizu, K.; Ikeda, M.; Hirose, T.; Matsuura, H.; Kang, S.; Takahashi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Shimazu, T. The clinical importance of a cytokine network in the acute phase of sepsis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel-Bayarri, V.; Casanoves-Laparra, E.; Pallás-Beneyto, L.; Sancho-Chinesta, S.; Martín-Osorio, L.; Tormo-Calandín, C.; Bautista-Rentero, D. Prognostic value of the biomarkers procalcitonin, interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in severe sepsis. Med. Intensiv. 2012, 36, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberholzer, A.; Souza, S.M.; Tschoeke, S.K.; Oberholzer, C.; Abouhamze, A.; Pribble, J.P.; Moldawer, L.L. Plasma cytokine measurements augment prognostic scores as indicators of outcome in patients with severe sepsis. Shock 2005, 23, 488–493. [Google Scholar]
- Phua, J.; Koay, E.S.C.; Lee, K.H. Lactate, procalcitonin, and amino-terminal pro-b-type natriuretic peptide versus cytokine measurements and clinical severity scores for prognostication in septic shock. Shock 2008, 29, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricarte-Bratti, J.P.; Jaime-Albarrán, N.; Montrull, H.L.; Brizuela, N.Y. IL-6, MMP 3 and prognosis in previously healthy sepsis patients. Rev. Fac. Cien. Med. Univ. Nac. Cordoba 2017, 74, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Toro, J.-J.; Márquez-Coello, M.; García-Álvarez, J.-M.; Martín-Aspas, A.; Rivera-Fernández, R.; de Benito, A.S.; Girón-González, J.-A. Soluble membrane receptors, interleukin 6, procalcitonin and C reactive protein as prognostic markers in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.; Gurung, R.L.; Liu, S.; Seet, E.C.P.; Lim, S.C. Genetic Polymorphisms and Cytokine Profile of Different Ethnicities in Septic Shock Patients, and their Association with Mortality. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Park, D.W.; Moon, S.; Cho, H.-J.; Park, J.H.; Seok, H.; Choi, W.S. Diagnostic and prognostic value of interleukin-6, pentraxin 3, and procalcitonin levels among sepsis and septic shock patients: A prospective controlled study according to the Sepsis-3 definitions. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, W.; Nakada, T.A.; Yazaki, M.; Oda, S. Interleukin-6 Levels Act as a Diagnostic Marker for Infection and a Prognostic Marker in Patients with Organ Dysfunction in Intensive Care Units. Shock 2016, 46, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thao, P.T.N.; Tra, T.T.; Son, N.T.; Wada, K. Reduction in the IL-6 level at 24 h after admission to the intensive care unit is a survival predictor for Vietnamese patients with sepsis and septic shock: A prospective study. BMC Emerg. Med. 2018, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, Y.B. The role of proadrenomedullin, interleukin 6 and CD64 in the diagnosis and prognosis of septic shock. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivas, M.C.; Villamarin, C.; Guerrero, H.F.V.; Tascon, A.J.; Valderrama-Aguirre, A. Plasma interleukin-6 levels correlate with survival in patients with bacterial sepsis and septic shock. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidhase, L.; Wellhöfer, D.; Schulze, G.; Kaiser, T.; Drogies, T.; Wurst, U.; Petros, S. Is Interleukin-6 a better predictor of successful antibiotic therapy than procalcitonin and C-reactive protein? A single center study in critically ill adults. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C.; Lei, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, J. Interleukin-37 as a biomarker of mortality risk in patients with sepsis. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-P.; Chen, C.-K.; Chung, K.; Jiang, B.-Y.; Yu, T.-J.; Chuang, D.-Y. Plasma transforming growth factor-β1 level in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and association with disease severity. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2009, 108, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, B.; Lin, Y.; Shi, F.; Chen, W.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.; Fei, Y.; Zou, S.; Yao, C. Combining Blood-Based Biomarkers to Predict Mortality of Sepsis at Arrival at the Emergency Department. Med Sci. Monit. 2020, 27, e929527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhuang, D.; Chen, H.; Zou, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y. 28-day sepsis mortality prediction model from combined serial interleukin-6, lactate, and procalcitonin measurements: A retrospective cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 42, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, J. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Interleukin-6 in Emergency Department Sepsis Patients. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, ume 15, 5557–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khalid, S.; Jiang, L. Diagnostic and predictive performance of biomarkers in patients with sepsis in an intensive care unit. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 47, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Jia, Y. Evaluation of the Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis score combined with procalcitonin in septic patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 31, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molano-Franco, D.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, I.; Muriel, A.; del Campo-Albendea, L.; Fernández-García, S.; Alvarez-Méndez, A.; Simancas-Racines, D.; Viteri, A.; Sanchez, G.; Fernandez-Felix, B.; et al. Basal procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and presepsin for prediction of mortality in critically ill septic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagn. Progn. Res. 2023, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Y.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y.-J.; Jiang, Y.-J.; Zhang, Z.-N. Alterations in levels of cytokine following treatment to predict outcome of sepsis: A meta-analysis. Cytokine 2022, 161, 156056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, P.E.; Tinel, C.; Barbar, S.; Aho, S.; Prin, S.; Doise, J.M.; Olsson, N.O.; Blettery, B.; Quenot, J.P. Procalcitonin kinetics within the first days of sepsis: Relationship with the appropriateness of antibiotic therapy and the outcome. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S.; Heikkinen, M.; Pettilä, V.; Alila, S.; Väisänen, S.; Pulkki, K.; Kolho, E.; Ruokonen, E.; the Finnsepsis Study Group. Predictive value of procalcitonin decrease in patients with severe sepsis: A prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, A.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Poddar, B.; Baronia, A. Procalcitonin kinetics as a prognostic marker in severe sepsis/septic shock. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 19, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Maurer, P.; Punjabi, V.; Desai, A.; Amin, D.N.; Gluck, E. Procalcitonin decrease over 72 hours in US critical care units predicts fatal outcome in sepsis patients. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Peng, J.-M.; Hu, X.-Y.; Wang, Y. The utility of initial procalcitonin and procalcitonin clearance for prediction of bacterial infection and outcome in critically ill patients with autoimmune diseases: A prospective observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2015, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nor, M.B.M.; Ralib, A.M. Procalcitonin clearance for early prediction of survival in critically ill patients with severe sepsis. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 819034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pieralli, F.; Vannucchi, V.; Mancini, A.; Antonielli, E.; Luise, F.; Sammicheli, L.; Turchi, V.; Para, O.; Bacci, F.; Nozzoli, C. Procalcitonin Kinetics in the First 72 Hours Predicts 30-Day Mortality in Severely Ill Septic Patients Admitted to an Intermediate Care Unit. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 7, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.J.; Bae, J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.A.R.; Mun, S.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yune, C.J.; Chung, T.N.; Kim, K. Serial Change of Endotoxin Tolerance in a Polymicrobial Sepsis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.-L.; Ramsay, G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershler, W.B.; Keller, E.T. Age-associated increased interleukin-6 gene expression, late-life diseases, and frailty. Annu. Rev. Med. 2000, 51, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzianowska-Kuźnicka, M.; Owczarz, M.; Wieczorowska-Tobis, K.; Nadrowski, P.; Chudek, J.; Slusarczyk, P.; Skalska, A.; Jonas, M.; Franek, E.; Mossakowska, M. Interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein, successful aging, and mortality: The PolSenior study. Immun. Ageing 2016, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya-Ruiz, C.; Jaimes, F.A.; Rugeles, M.T.; López, J.Á.; Bedoya, G.; Velilla, P.A. Variants in LTA, TNF, IL1B and IL10 genes associated with the clinical course of sepsis. Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhang, A.Q.; Yue, C.L.; Gao, J.W.; Zeng, L.; Gu, W.; Jiang, J.X. Association between interleukin-10 polymorphisms and sepsis: A meta-analysis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.-W.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Pan, W.; Yue, C.-L.; Zeng, L.; Gu, W.; Jiang, J. Association between IL-6-174G/C Polymorphism and the Risk of Sepsis and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study ID | Country | Clinical Setting | Patient Recruitment | N | Events/N | Age (years) | Sex (% of Males) | Outcome | Sepsis Criteria | Sepsis Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaluz-Ojeda 2012 [34] | Spain | ICU | Prospective | 29 | 12/29 | 66.1; mean | 58.70% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Belli 2022 [35] | Italy | ICU | Prospective | 35 | 15/35 | 59 (48–60); median (25th–75th) | 60% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Beneyto 2016 [36] | Spain | ICU | Prospective | 203 | 52/203 | 65; mean | 64% | In-hospital mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Eidt 2016 [37] | Brazil | ICU | Prospective | 48 | 21/48 | 61.4 (18.7) in severe sepsis; 65.9 (17.8) in septic shock; mean (SD) | 50% | ICU mortality | Levy 2001 | NR |
| Frencken 2017 [38] | Netherlands | ICU | Prospective | 708 | 226/708 | 63 (53–72); median (25th–75th) | 60% | 4-day, 28-day, and 1-year mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Jekarl 2013 [39] | South Korea | Mixed | Prospective | 78 | 15/78 | 62.1 (19.9); mean (SD) | 45% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Jiang 2019 [40] | China | ICU | Prospective | 198 | 88/198 | 69.9 (28–91) in S vs. 68.7 (18;91) in NS; median (25th–75th) | 81.80% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Karamouzos 2021 [41] | Greece | ICU | Retrospective | 128 | 46/128 | 72.4 (15) in S vs. 77.3 (10) in NS; mean (SD) | 43.80% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Karampela 2022 [42] | Greece | ICU | Prospective | 102 | 30/102 | 64.7 (15.6); mean (SD) | 55.90% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Liu S. 2021 [43] | China | ICU | Retrospective | 264 | 78/264 | 52.9 (12.6); mean (SD) | 64% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Liu J. 2021 [44] | China | ICU | Prospective | 66 | 17/66 | 69 (54–82) in S vs. 77 (63–84) in NS; median (IQR) | 59% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Matsumoto 2018 [45] | Japan | DTACM | Retrospective | 31 | 7/31 | 73.0 (65.0–81.0); median (IQR) | 74% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Miguel-Bayarri 2012 [46] | Spain | ICU | Prospective | 81 | 27/81 | 62, median; no other details | 54% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Oberholzer 2005 [47] | USA | Mixed | Prospective | 124 | 39/124 | 58.3 (17.5); mean (SD) | 55% | 28–30-day mortality | Other | NR |
| Phua 2008 [48] | Singapore | ICU | Prospective | 72 | 30/72 | 55 (16) in S vs. 54 (17) in NS; mean (SD) | 64% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Ricarte-Bratti 2017 [49] | Argentina | ICU | Prospective | 48 | 21/48 | 53.8 (17.1) in S vs. 73.2 (8.9) in NS; mean (SD) | 46% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Rios-Toro 2017 [50] | Spain | ICU | Prospective | 50 | 21/50 | 68 (53–75); median (25th–75th) | 72% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Siddiqui 2019 [51] | Singapore | ICU | Prospective | 198 | NR | 63.0 (49.5;73.5); 54.0 (45.0;64.0); 61.0 (40.0;68.8); mean (SD) | 60.10% | 28–30-day mortality | Other | NR |
| Song 2019 [52] | South Korea | ER | Prospective | 97 | NR | 75 (42;98); median (25th–75th) | 56.00% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Takahashi 2016 [53] | Japan | ICU | Prospective | 85 | 15/85 | 68 (59–77); median (25th–75th) | 62.40% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Thao 2018 [54] | Vietnam | ICU | Prospective | 123 | 75/123 | 62 (46–75) in S; 54 (43–73) in NS; median (25th–75th) | NR | In-hospital mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Turan 2023 [55] | Turkey | ICU | Prospective | 60 | 39/60 | 60 (56–68) in S vs. 74 (62–80) in NS; median (IQR) | 60.00% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Vivas 2021 [56] | Colombia | ICU | Prospective | 62 | 10/62 | 53 (19.47); mean (SD) | 59.67% | In-hospital mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Weidhase 2019 [57] | Germany | ICU | Retrospective | 328 | 118/328 | 64 [54;73] in S vs. 62 [55;69] in NS; median (IQR) | 63.10% | In-hospital mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Wu C.X. 2021 [58] | China | ICU | Prospective | 114 | 51/114 | 71 (60;81); median (25th–75th) | 72.90% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Wu H.P. 2009 [59] | China | Mixed | Prospective | 63 | 14/63 (22.2%) | 70.0 (2.0) in S vs. 69.1 (4.1) in NS; mean (SD) | 63.50% | 28–30-day mortality | Other | Respiratory |
| Xie 2021 [60] | China | ER | Retrospective | 90 | 23/90 | 72 (26–97) in S vs. 77 (50–97) in NS; median (25th–75th) | 64% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Xie 2023 [61] | China | ER | Retrospective | 367 | 53/367 | 71 (19–98) in S vs. 80 (46–97) in NS; median (25th–75th) | 65.90% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Yu 2022 [62] | China | ER | Prospective | 63 | NR | 79 (34–95); median (25th–75th) | 63.50% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | NR |
| Zhang 2019 [63] | China | ICU | Retrospective | 150 | 16/66 in sepsis group and 48/84 in septic shock group | 70 (24–91) in sepsis group vs. 74.5 (24–89) in septic shock group; median (25th–75th) | 63.40% | 28–30-day mortality | Singer 2015 | Mixed |
| Zhao 2013 [64] | China | ER | Prospective | 501 | 134/504 | 73 (58–79) in S vs. 77 (65–83) in NS; median (IQR) | 55.70% | 28–30-day mortality | Levy 2001 | Mixed |
| Study ID | N | Events/N | IL-6 Values and Mortality: Effect Measures (95% CI) | Model Adjusted by |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaluz-Ojeda 2012 [34] | 29 | 12 | Adjusted HR at D3: 1.86 (1.08–3.20); D28: 2.00 (1.22−3.27) | APACHE II, other biomarkers |
| Belli 2022 [35] | 35 | 15 | HR = 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | Univariable |
| Beneyto 2016 [36] | 203 | 52 | Admission: log IL-6 OR = 1.62 (1.24–2.13); D3: log IL-6 OR = 2.69 (1.64–4.40) | Age, sex, APACHE II, SOFA, other biomarkers |
| Eidt 2016 [37] | 48 | 21 | NR | Age, sex, lactate, other biomarkers |
| Frencken 2017 [38] | 708 | 226 | Admission: RR = 1.13 (0.91–1.41); D4: RR = 1.03 (0.86–1.23) | Age, Charlson comorbidity index, immunodeficiency, site of infection |
| Jekarl 2013 [39] | 78 | 15 | NR | Other biomarkers |
| Jiang 2019 [40] | 198 | 88 | OR = 1.033 (1.007–1.061) | SOFA, other biomarkers such as EPO, hepcidin, ferritin, sTfR/log ferritin |
| Karamouzos 2021 [41] | 128 | 46 | OR = 1.002 (0.996–1.008) | Microorganism, MDR status, type of infection, cytokines |
| Karampela 2022 [42] | 102 | 30 | HR = 1.70 (1.05–2.74) | Age, Sex, BMI, APACHE-II, presence of septic shock |
| Liu S. 2021 [43] | 264 | 78 | OR = 1.017 (1.005–1.028) | Age, sex, BMI, SBP, APACHE-II, SOFA |
| Liu J. 2021 [44] | 66 | 17 | OR = 1.001 (1.000–1.001) | Age, SOFA, other biomarkers |
| Matsumoto 2018 [45] | 31 | 7 | Maximum values from three days (D1, D2, D4): 19.62 (3.47–110.80) | SOFA |
| Miguel-Bayarri 2012 [46] | 81 | 27 | Admission: log IL-6 OR = 1.98 (1.27–3.09); D3: log IL-6 OR = 2.6 (1.43–4.71) | Age, sex, development of MOF, other biomarkers, SOFA, APACHE-II |
| Oberholzer 2005 [47] | 124 | 39 | Not significant (p-value) | APACHE-II, age, treatments, baseline MOD |
| Phua 2008 [48] | 72 | 30 | NR | APACHE-II |
| Ricarte-Bratti 2017 [49] | 48 | 21 | NR | Univariable |
| Rios-Toro 2017 [50] | 50 | 21 | NR | Age, SOFA, APACHE II, other biomarkers |
| Siddiqui 2019 [51] | 198 | NR | HR = 1.46 (1.11−1.92) | Age, sex, surgical methods, qSofa |
| Song 2019 [52] | 97 | NR | HR = 1.001 (1.000–1.002) | APACHE-II, SOFA, pentraxin, lactate |
| Takahashi 2016 [53] | 85 | 15 | NR | Age, sex, SOFA |
| Thao 2018 [54] | 123 | 75 | IL-6 clearance in 24 h: ≥86%, OR = 5.67 (1.27–25.3); Il-6 clearance between 85% and 50%, OR = 1.86 (0.44–7.94) | Age, sex, BUN, Creatinine, aPTT, pH |
| Turan 2023 [55] | 60 | 39 | NR | Age, sex, diagnosis, SOFA, APACHE II, other biomarkers |
| Vivas 2021 [56] | 62 | 10 | NR | Age, site of infection |
| Weidhase 2019 [57] | 328 | 118 | NR | NR |
| Wu C.X. 2021 [58] | 114 | 51 | OR = 1.66 (0.67−4.10) | SOFA and IL-37 |
| Wu H.P. 2009 [59] | 63 | 14 | OR = 1.00 (0.99−1.01) | APACHE-II, septic shock, gastrointestinal bleeding, IL-10 and TGF-β1 |
| Xie 2021 [60] | 90 | 23 | OR = 1.000 (1.000–1.001) | Lactate, neutrophil-to-WBC ratio |
| Study | Estimate | Standard Error | Lower Limit of 95% CI | Upper Limit of 95% CI | z | p-Value | Weight (%)—Fixed | Weight (%)—Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frencken 2017 [38] | 1.13 | 0.127 | 0.881 | 1.379 | 0.001 | 0.004 | ||
| Jiang 2019 [40] | 1.033 | 0.014 | 1.006 | 1.060 | 0.082 | 0.33 | ||
| Karamouzos 2021 [41] | 1.002 | 0.003 | 0.996 | 1.008 | 1.79 | 5.32 | ||
| Karampela 2022 [42] | 1.7 | 0.427 | 0.863 | 2.537 | 0.009 | 0.004 | ||
| Liu S. 2021 [43] | 1.017 | 0.006 | 1.005 | 1.029 | 0.45 | 1.68 | ||
| Liu J. 2021 [44] | 1.001 | 0.001 | 0.999 | 1.003 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Siddiqui 2019 [51] | 1.46 | 0.202 | 1.064 | 1.856 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| Song 2019 [52] | 1.001 | 0.001 | 0.999 | 1.003 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Wu C.X. 2021 [58] | 1.66 | 0.828 | 0.0371 | 3.283 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| Wu H.P. 2009 [59] | 1 | 0.005 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.65 | 2.33 | ||
| Xie 2021 [60] | 1 | 0.001 | 0.998 | 1.002 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Xie 2023 [61] | 1 | 0.001 | 0.998 | 1.002 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Yu 2022 [62] | 0.999 | 0.001 | 0.997 | 1.001 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Zhang 2019 [63] | 1.02 | 0.01 | 1 | 1.04 | 0.16 | 0.64 | ||
| Zhao 2013 [64] | 1.002 | 0.001 | 1 | 1.004 | 16.14 | 14.95 | ||
| Total (fixed effects) | 1.001 | 0 | 1 | 1.001 | 2490.434 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
| Total (random effects) | 1.001 | 0.001 | 0.999 | 1.003 | 1230.89 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
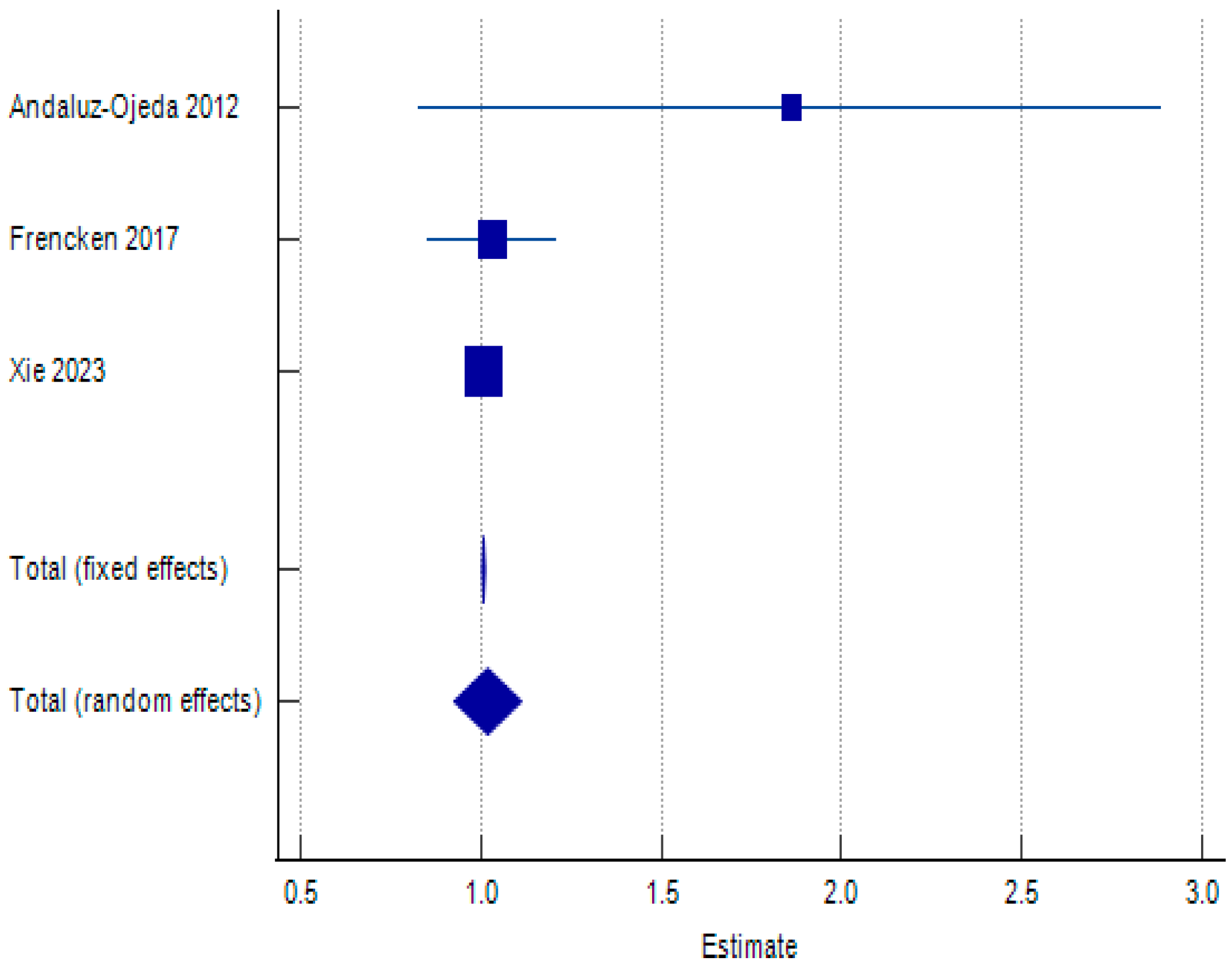
| Study | Estimate | Standard Error | Lower Limit of 95% CI | Upper Limit of 95% CI | z | p-Value | Weight (%)—Fixed | Weight (%)—Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaluz-Ojeda 2012 [34] | 1.86 | 0.525 | 0.831 | 2.889 | 0.001 | 0.82 | ||
| Frencken 2017 [38] | 1.03 | 0.092 | 0.85 | 1.21 | 0.047 | 20.12 | ||
| Xie 2023 [61] | 1.007 | 0.002 | 1.003 | 1.011 | 99.95 | 79.06 | ||
| Total (fixed effects) | 1.007 | 0.002 | 1.003 | 1.011 | 503.634 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
| Total (random effects) | 1.019 | 0.048 | 0.925 | 1.112 | 21.316 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
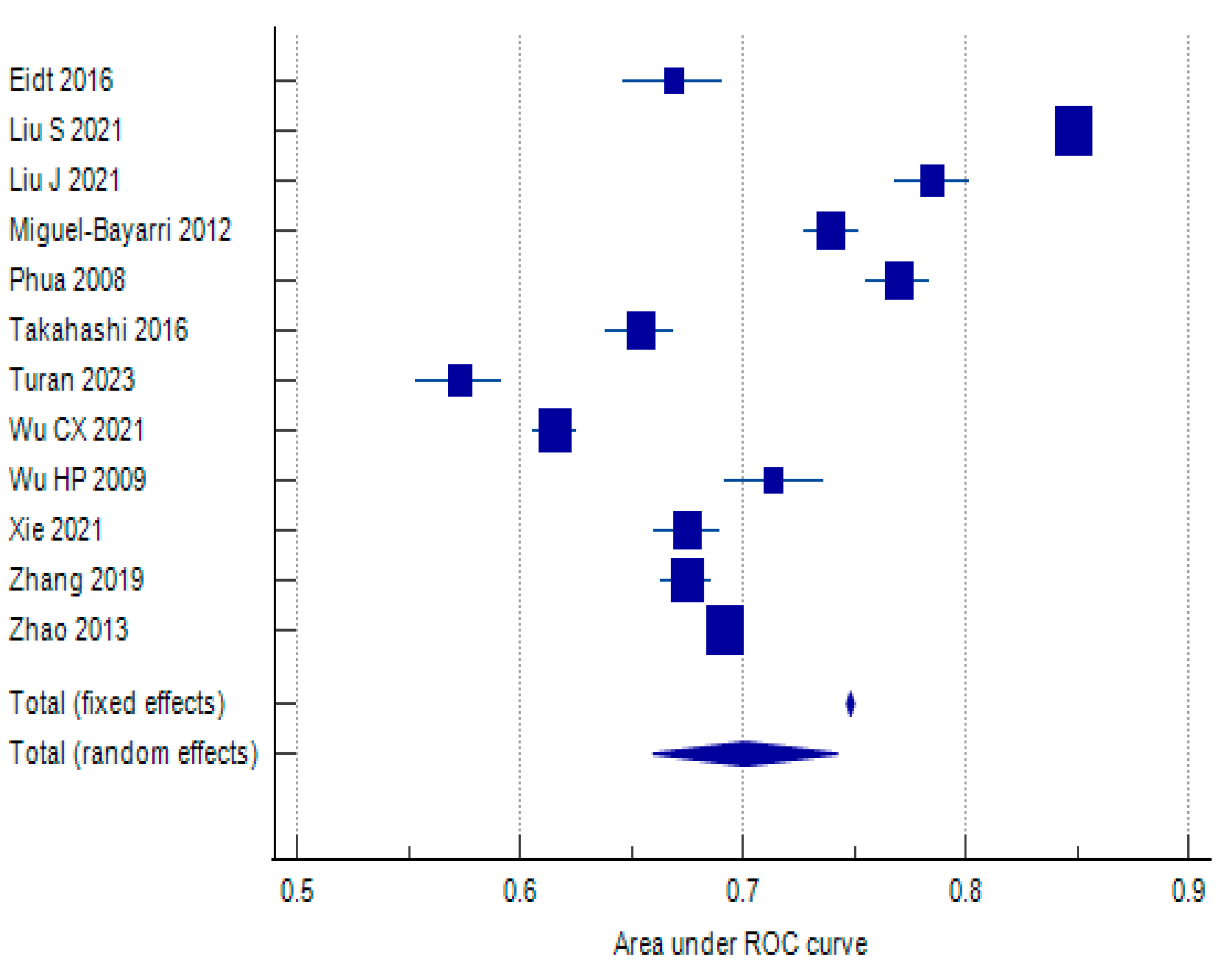
| Study | ROC Area | Standard Error | Lower Limit of 95% CI | Upper Limit of 95% CI | Z | p-Value | Weight (%)—Fixed | Weight (%)—Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eidt 2016 [37] | 0.669 | 0.0115 | 0.646 | 0.692 | 0.54 | 8.22 | ||
| Liu S. 2021 [43] | 0.849 | 0.0014 | 0.846 | 0.852 | 36.72 | 8.42 | ||
| Liu J. 2021 [44] | 0.785 | 0.0086 | 0.768 | 0.802 | 0.97 | 8.31 | ||
| Miguel-Bayarri 2012 [46] | 0.74 | 0.0065 | 0.727 | 0.753 | 1.70 | 8.36 | ||
| Phua 2008 [48] | 0.77 | 0.0072 | 0.756 | 0.784 | 1.39 | 8.34 | ||
| Takahashi 2016 [53] | 0.654 | 0.0078 | 0.639 | 0.669 | 1.18 | 8.33 | ||
| Turan 2023 [55] | 0.573 | 0.0098 | 0.554 | 0.592 | 0.75 | 8.28 | ||
| Wu C.X. 2021 [58] | 0.616 | 0.005 | 0.606 | 0.626 | 2.88 | 8.39 | ||
| Wu H.P. 2009 [59] | 0.714 | 0.0113 | 0.692 | 0.736 | 0.56 | 8.23 | ||
| Xie 2021 [60] | 0.675 | 0.0076 | 0.66 | 0.69 | 1.25 | 8.33 | ||
| Zhang 2019 [63] | 0.675 | 0.0059 | 0.663 | 0.687 | 2.07 | 8.37 | ||
| Zhao 2013 [64] | 0.692 | 0.0012 | 0.69 | 0.694 | 49.98 | 8.42 | ||
| Total (fixed effects) | 0.748 | 0.0008 | 0.747 | 0.75 | 882.121 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
| Total (random effects) | 0.701 | 0.0211 | 0.66 | 0.742 | 33.266 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
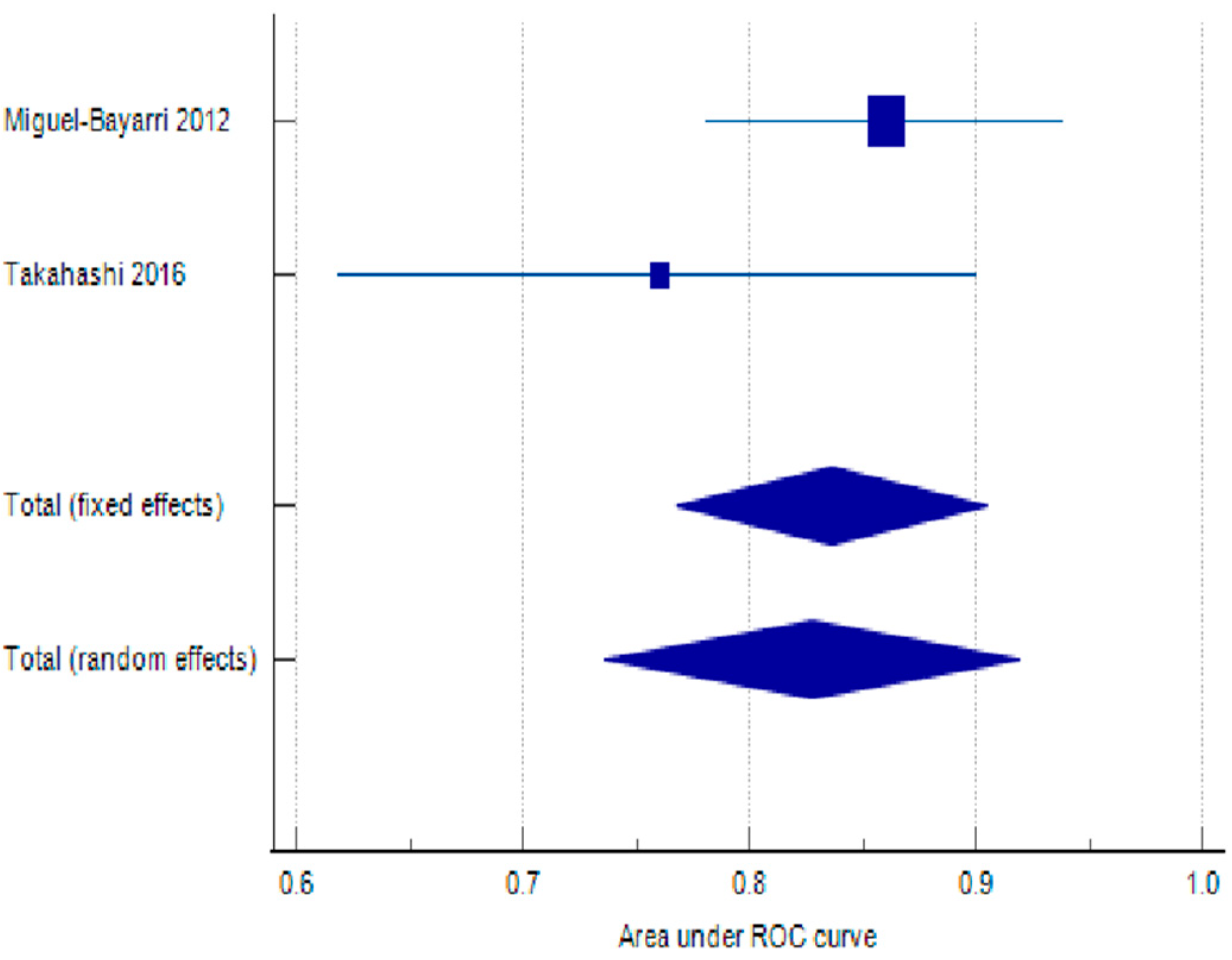
| Study | ROC Area | Standard Error | Lower Limit of 95% CI | Upper Limit of 95% CI | Z | p-Value | Weight (%)—Fixed | Weight (%)—Random |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miguel-Bayarri 2012 [46] | 0.86 | 0.04 | 0.782 | 0.938 | 76.42 | 67.92 | ||
| Takahashi 2016 [53] | 0.76 | 0.072 | 0.619 | 0.901 | 23.58 | 32.08 | ||
| Total (fixed effects) | 0.836 | 0.035 | 0.768 | 0.905 | 23.921 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
| Total (random effects) | 0.828 | 0.0467 | 0.736 | 0.919 | 17.737 | <0.001 | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varga, N.-I.; Bagiu, I.C.; Vulcanescu, D.D.; Lazureanu, V.; Turaiche, M.; Rosca, O.; Bota, A.V.; Horhat, F.G. IL-6 Baseline Values and Dynamic Changes in Predicting Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030407
Varga N-I, Bagiu IC, Vulcanescu DD, Lazureanu V, Turaiche M, Rosca O, Bota AV, Horhat FG. IL-6 Baseline Values and Dynamic Changes in Predicting Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030407
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarga, Norberth-Istvan, Iulia Cristina Bagiu, Dan Dumitru Vulcanescu, Voichita Lazureanu, Mirela Turaiche, Ovidiu Rosca, Adrian Vasile Bota, and Florin George Horhat. 2025. "IL-6 Baseline Values and Dynamic Changes in Predicting Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030407
APA StyleVarga, N.-I., Bagiu, I. C., Vulcanescu, D. D., Lazureanu, V., Turaiche, M., Rosca, O., Bota, A. V., & Horhat, F. G. (2025). IL-6 Baseline Values and Dynamic Changes in Predicting Sepsis Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomolecules, 15(3), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030407








