Absolute Quantitative Metagenomic Analysis Provides More Accurate Insights for the Anti-Colitis Effect of Berberine via Modulation of Gut Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Meta-Analysis of BBR-Regulated Gut Microbiota
2.2. Animal Research
2.3. Calculation of Disease Activity Index (DAI)
2.4. Histological Examination
2.5. ELISA Assay
2.6. Full Length 16 S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. AI Usage Statement
3. Result
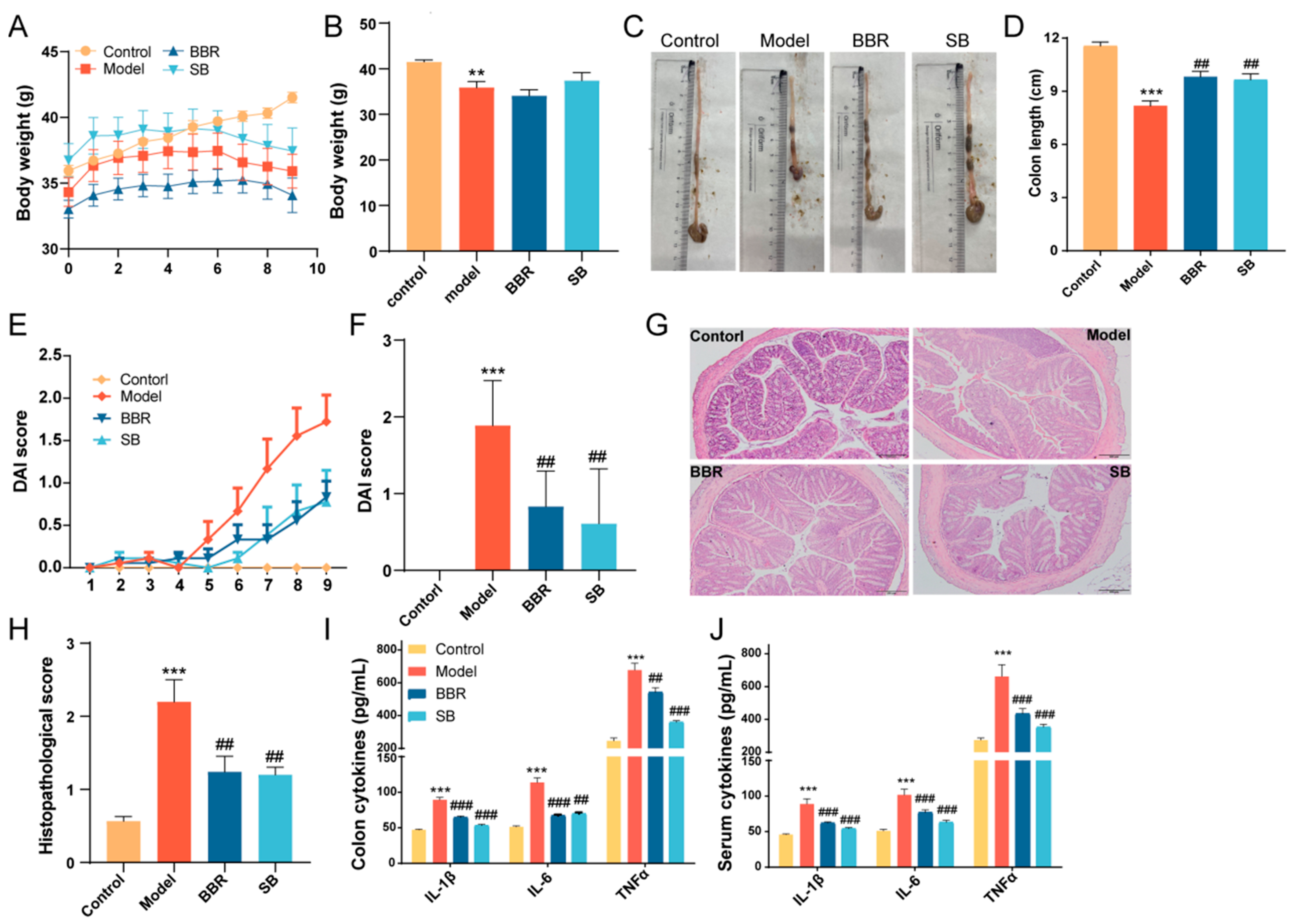
3.1. BBR and SB Administration Ameliorated the Symptoms of DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice
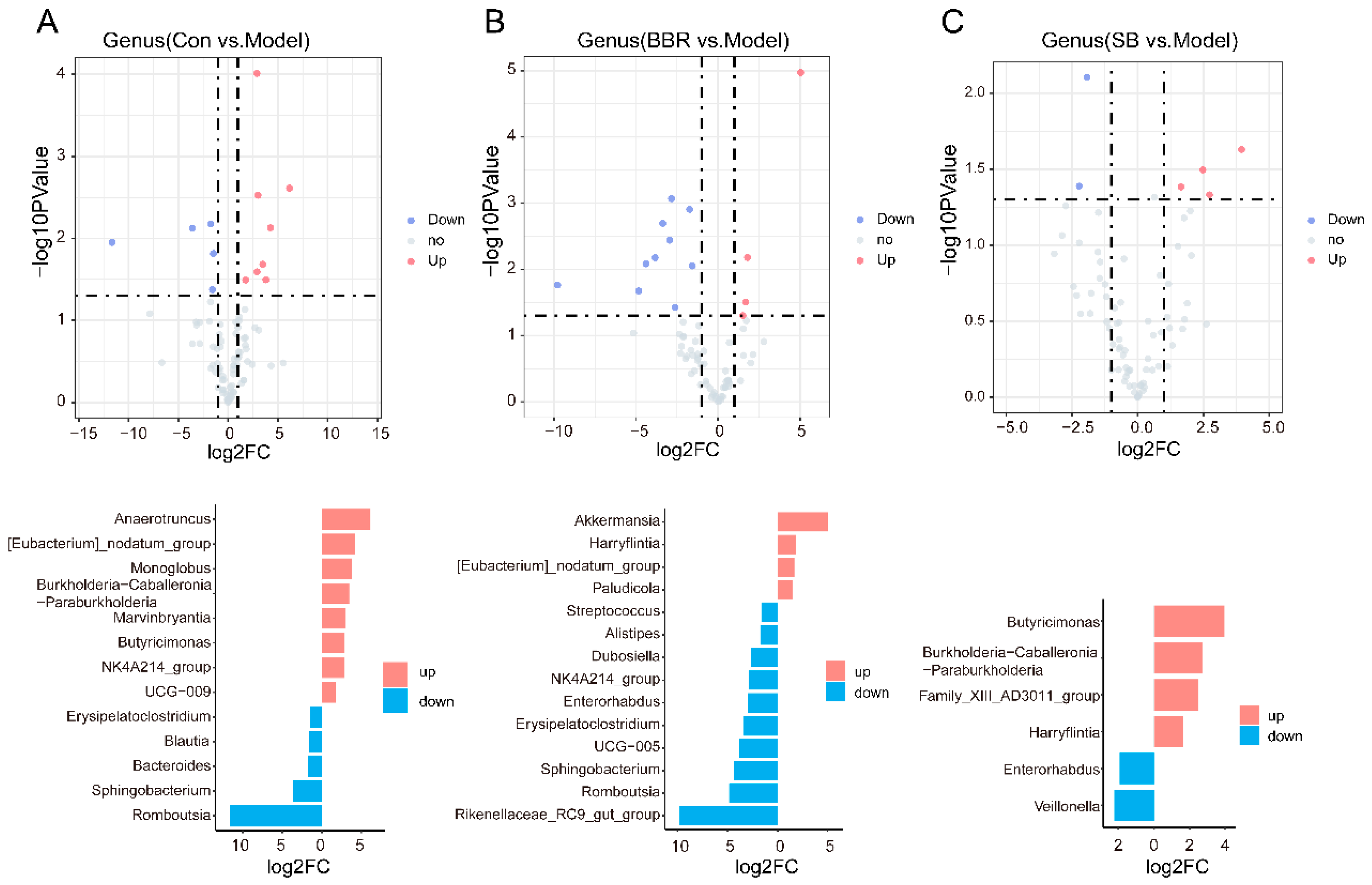
3.2. Relative Quantitative Sequencing-Based Observation of the Effects of SB and BBR on the Gut Microbiota of DSS Mice
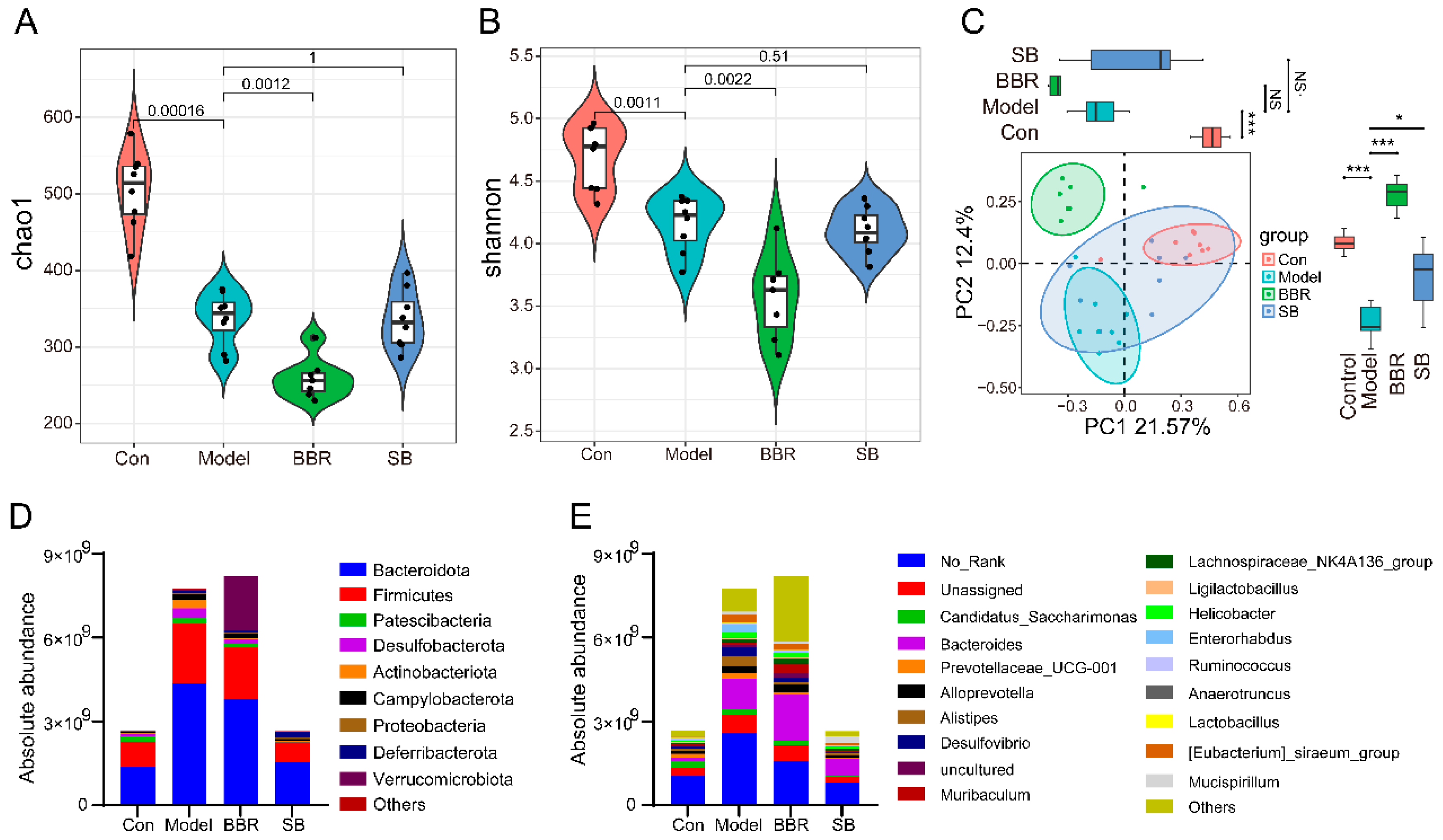
3.3. Absolute Quantitative Sequencing-Based Observation of the Effects of SB and BBR on the Gut Microbiota of DSS Mice
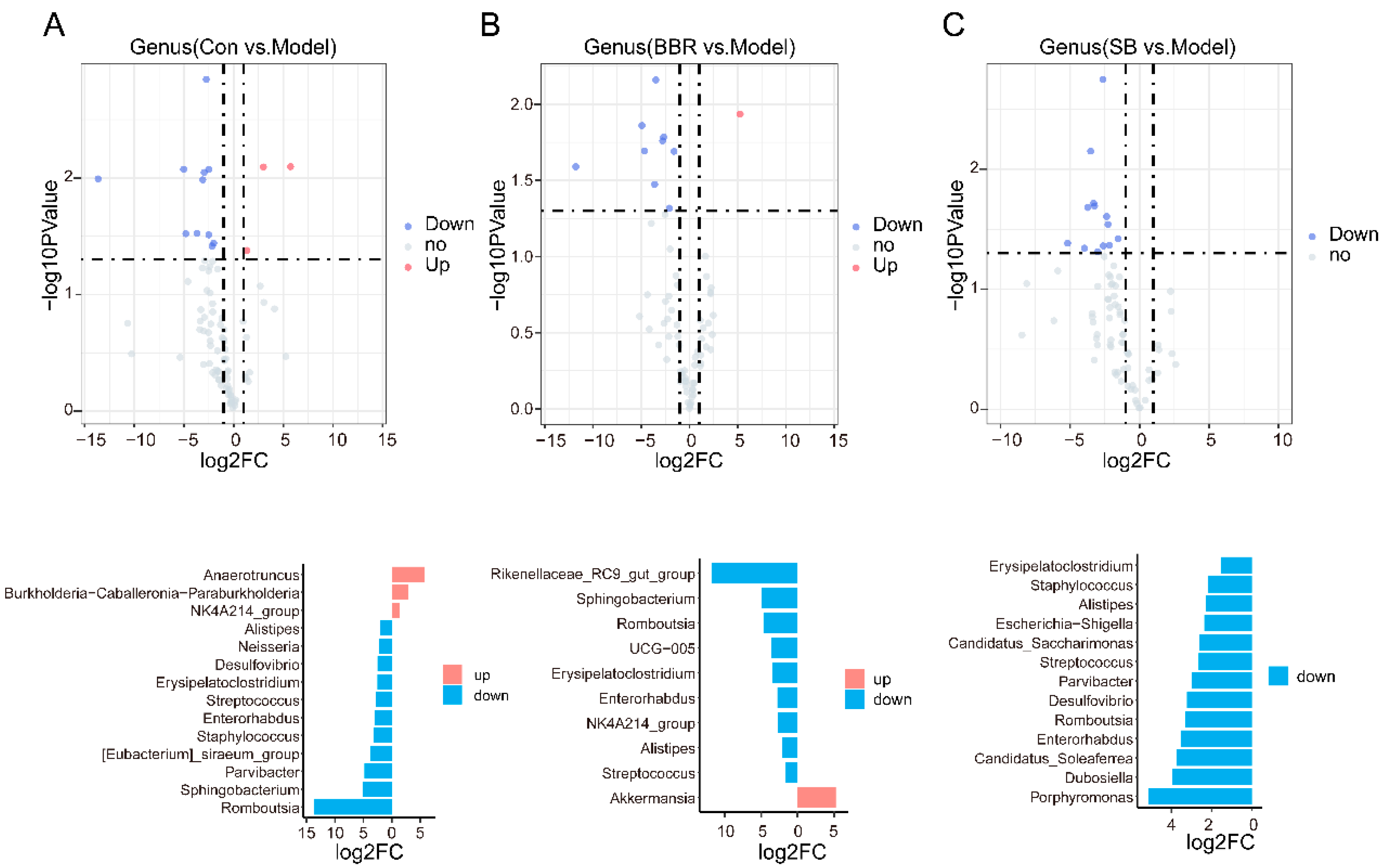
3.4. Difference Between Absolute Quantification and Relative Quantification
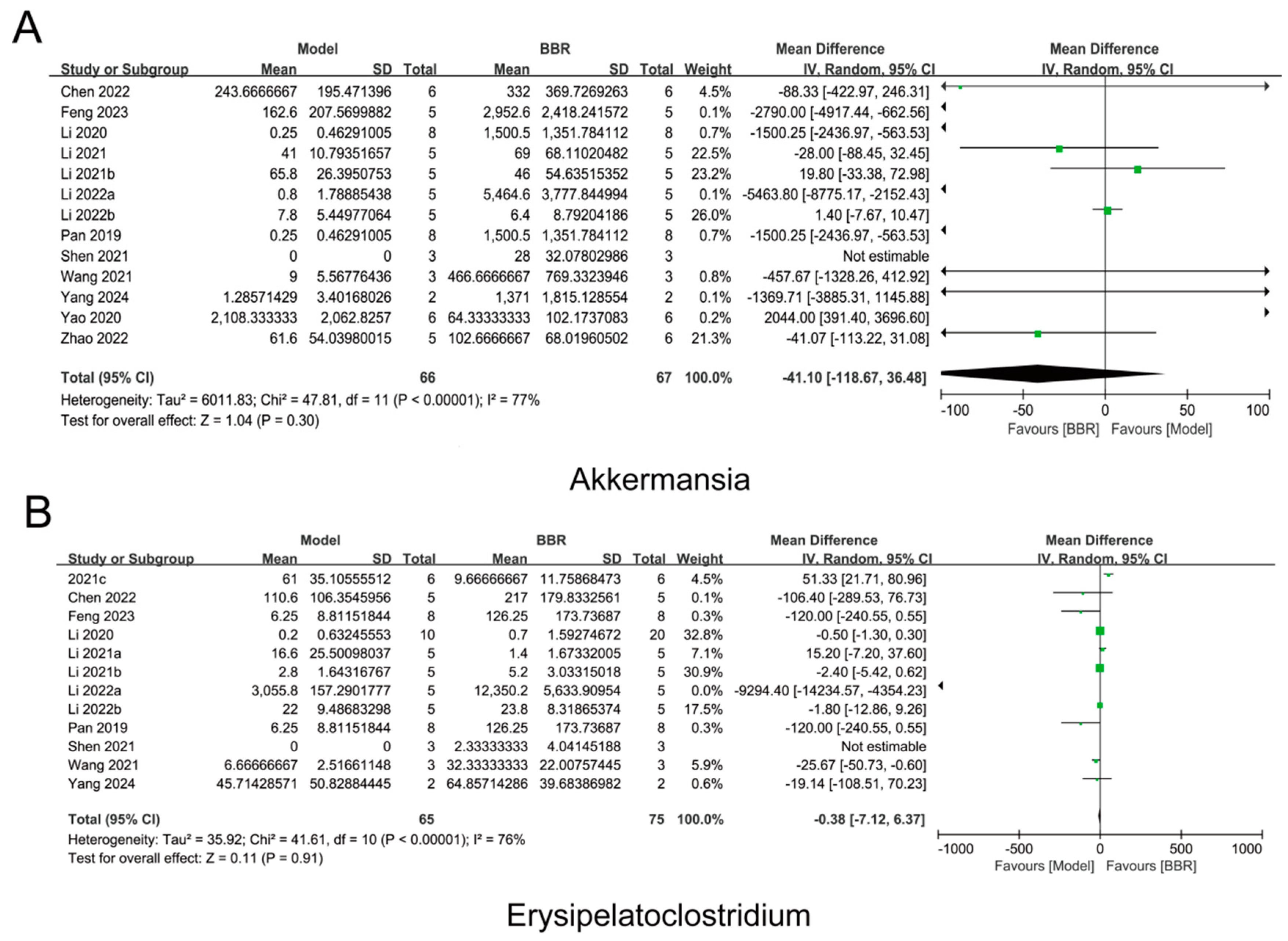
3.5. Individual-Based Meta-Analysis of BBR-Regulated Gut Microbiota Across 13 Cohorts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Gut microbiota combined with metabolites reveals unique features of acute myocardial infarction patients different from stable coronary artery disease. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 46, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraimi, N.; Ross, T.; Pujo, J.; De Palma, G. The gut microbiome in disorders of gut–brain interaction. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2360233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkacz, A.; Hortala, M.; Poole, P.S. Absolute quantitation of microbiota abundance in environmental samples. Microbiome 2018, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandeputte, D.; Kathagen, G.; D’hoe, K.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Sabino, J.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; De Commer, L.; Darzi, Y.; et al. Quantitative microbiome profiling links gut community variation to microbial load. Nature 2017, 551, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruijning, M.; Ayroles, J.F.; Henry, L.P.; Koskella, B.; Meyer, K.M.; Metcalf, C.J.E. Relative abundance data can misrepresent heritability of the microbiome. Microbiome 2023, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghini, D.G.; Dvorak, M.; Dahlen, A.; Roos, M.; Doyle, B.; Kuersten, S.; Bhatt, A.S. Quantifying bias introduced by sample collection in relative and absolute microbiome measurements. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 42, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Song, D.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.; Chi, C.; Jia, S.; Lin, M.; He, C.; Jiang, C.; Gong, F.; et al. Polygonatum cyrtonema polysaccharides reshape the gut microbiota to ameliorate dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1424328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Li, P.; Du, X.; Feng, X.; Qiu, F. Berberine alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting inflammation through targeting IRGM1. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, M.; Deng, L.; Luo, D.; Ma, R.; Lu, Q. Oxyberberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats through suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, M.A.F.; Magalhães, H.I.R.; Duarte, J.R.L.; Conceição, L.B.; Castelucci, P. Butyrate Protects Myenteric Neurons Loss in Mice Following Experimental Ulcerative Colitis. Cells 2023, 12, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qian, Y.; Jiang, C.; Tang, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, G. Butyrate ameliorated ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through modulating Nrf2/GPX4 signal pathway and improving intestinal barrier. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1870, 166984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wei, P.; Li, W.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Hu, C.; Guo, X.; Ma, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y. Pharmacological effects of berberine on models of ulcerative colitis: A meta-analysis and systematic review of animal studies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 937029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, L.; Hu, H.; Liu, H. Berberine improves DSS-induced colitis in mice by modulating the fecal-bacteria-related bile acid metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.-E.; Yang, Y.-N.; Zhan, J.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C. Gut microbiota-based discovery of Houttuyniae Herba as a novel prebiotic of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron with anti-colitis activity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 172, 116302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Jin, M.; Jiang, S.; Shang, P.; Dong, X.; Li, L. Research progress on pharmacological effects and bioavailability of berberine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 8485–8514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Xia, W.; Dai, S.; Wang, C.; Shi, R.; Yang, Y.; Guo, C.; Xu, X.L.; Luo, J. Berberine: An inspiring resource for the treatment of colorectal diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Su, W.; Fan, Q.; Wu, C.; Wu, S. Berberine, a potential prebiotic to indirectly promote Akkermansia growth through stimulating gut mucin secretion. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.; Wu, M.; Chen, T.; Tang, W.; Li, P.; Chen, J. Berberine Attenuates Hyperuricemia by Regulating Urate Transporters and Gut Microbiota. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 2199–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Zheng, T.; Ye, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Dong, Z. Rhubarb polysaccharide and berberine co-assembled nanoparticles ameliorate ulcerative colitis by regulating the intestinal flora. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1184183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, H.; Kang, X.; Tian, H.; Kang, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Ren, P.; Kuang, X.; et al. Berberine alleviates concanavalin A–induced autoimmune hepatitis in mice by modulating the gut microbiota. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Chen, M.; Xu, R.; Guo, M. Therapeutic Mechanisms of Berberine to Improve the Intestinal Barrier Function via Modulating Gut Microbiota, TLR4/NF-κ B/MTORC Pathway and Autophagy in Cats. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 961885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Ye, C.; Cai, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yao, Q. Berberine inhibits intestinal carcinogenesis by suppressing intestinal pro-inflammatory genes and oncogenic factors through modulating gut microbiota. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, S.; Wen, C.; Wang, L. Berberine ameliorates aGVHD by gut microbiota remodelling, TLR4 signalling suppression and colonic barrier repairment for NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Ni, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, J.; Wu, G.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Berberine Relieves Metabolic Syndrome in Mice by Inhibiting Liver Inflammation Caused by a High-Fat Diet and Potential Association with Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 752512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhou, W.; Ji, G.; Zhang, L. Berberine Alleviates Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota Mediated Intestinal FXR Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 750826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-R.; Xu, X.; Ye, D.; Li, X.-L. Berberine Improves the Symptoms of DHEA-Induced PCOS Rats by Regulating Gut Microbiotas and Metabolites. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2021, 86, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, M.; Yang, Y.; Ren, H.; Kong, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Berberine Slows the Progression of Prediabetes to Diabetes in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats by Enhancing Intestinal Secretion of Glucagon-Like Peptide-2 and Improving the Gut Microbiota. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 609134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Su, C.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Berberine attenuates choline-induced atherosclerosis by inhibiting trimethylamine and trimethylamine-N-oxide production via manipulating the gut microbiome. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Lei, L.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Sun, S.; Liu, S.; Huan, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Q.; et al. Berberine combined with stachyose induces better glycometabolism than berberine alone through modulating gut microbiota and fecal metabolomics in diabetic mice. Phytotherapy Res. 2019, 34, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Berberine alleviates type 2 diabetic symptoms by altering gut microbiota and reducing aromatic amino acids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cao, H.; Huan, Y.; Ji, W.; Liu, S.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q.; Lei, L.; Liu, M.; Gao, X.; et al. Berberine combined with stachyose improves glycometabolism and gut microbiota through regulating colonic microRNA and gene expression in diabetic rats. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-D.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Yu, C.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Wang, S.-H.; Yang, D.; Guo, C.-L.; Du, X.; Zhang, W.-J.; et al. Effect of berberine on hyperglycaemia and gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Su, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota specifically mediates the anti-hypercholesterolemic effect of berberine (BBR) and facilitates to predict BBR’s cholesterol-decreasing efficacy in patients. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 37, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baars, D.P.; Fondevila, M.F.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Nieuwdorp, M. The central role of the gut microbiota in the pathophysiology and management of type 2 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1280–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castells-Nobau, A.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Unlocking the mind-gut connection: Impact of human microbiome on cognition. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 1248–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhernakova, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Schirmer, M.; Vatanen, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Vila, A.V.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science 2016, 352, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Props, R.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Rubbens, P.; De Vrieze, J.; Sanabria, E.H.; Waegeman, W.; Monsieurs, P.; Hammes, F.; Boon, N. Absolute quantification of microbial taxon abundances. ISME J. 2016, 11, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshier, F.A.T.; Srinivasan, S.; Lopez, A.; Hoffman, N.G.; Proll, S.; Fredricks, D.N.; Schiffer, J.T. Complementing 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing with Total Bacterial Load To Infer Absolute Species Concentrations in the Vaginal Microbiome. mSystems 2020, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.-Y.; Yao, F.; Zhou, C.-R.; Huang, X.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Long, H.; Wu, Q.-M. Role of gut microbiome in regulating the effectiveness of metformin in reducing colorectal cancer in type 2 diabetes. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 6213–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.-Y.; Driscoll, M.; Gratalo, D.; Jarvie, T.; Weinstock, G.M. Improved DNA Extraction and Amplification Strategy for 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon-Based Microbiome Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsen, J.; Brejnrod, A.; Mortensen, M.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Stokholm, J.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sørensen, S.; Bisgaard, H.; Waage, J. Large-scale benchmarking reveals false discoveries and count transformation sensitivity in 16S rRNA gene amplicon data analysis methods used in microbiome studies. Microbiome 2016, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaura, E.; Pappalardo, V.Y.; Buijs, M.J.; Volgenant, C.M.C.; Brandt, B.W. Optimizing the quality of clinical studies on oral microbiome: A practical guide for planning, performing, and reporting. Periodontology 2000 2020, 85, 210–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Body Weight Loss | Stool Character | Bloody Feces |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | normal | no hematochezia |
| 1–5% | slightly loose | no obvious hematochezia |
| 6–10% | semi-formed dilute stool | darken feces |
| 11–15% | mucoid stool | blood anus + darken feces |
| >15% | fluid stool | gross rectal bleeding |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, J.; Cheng, J.; Chang, W.; Su, Y.; Yue, X.; Wu, C. Absolute Quantitative Metagenomic Analysis Provides More Accurate Insights for the Anti-Colitis Effect of Berberine via Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030400
Zhan J, Cheng J, Chang W, Su Y, Yue X, Wu C. Absolute Quantitative Metagenomic Analysis Provides More Accurate Insights for the Anti-Colitis Effect of Berberine via Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030400
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Jiaguo, Jiale Cheng, Wenhui Chang, Yuying Su, Xixin Yue, and Chongming Wu. 2025. "Absolute Quantitative Metagenomic Analysis Provides More Accurate Insights for the Anti-Colitis Effect of Berberine via Modulation of Gut Microbiota" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030400
APA StyleZhan, J., Cheng, J., Chang, W., Su, Y., Yue, X., & Wu, C. (2025). Absolute Quantitative Metagenomic Analysis Provides More Accurate Insights for the Anti-Colitis Effect of Berberine via Modulation of Gut Microbiota. Biomolecules, 15(3), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030400





