Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Details
2.1.1. Coarse-Grained (CG) Model of YGZL Peptides
2.1.2. CG Model of Solvent Molecules, Ions, Sphingomyelin, and 1,2-Dipalmitoyllecithin
2.1.3. CG Model for the LTA and LPSs
2.1.4. Self-Assembly of sHDL Nanoparticles
2.1.5. Modeling the Binding Model of sHDL Nanoparticles with LPSs/LTA
2.1.6. Calculation of Binding Free Energies of sHDL Nanoparticles with LPSs/LTA
2.2. Reagents
sHDL Preparation
2.3. Studies in Animals and In Vitro Analysis
2.3.1. In Vivo Efficacy Analysis
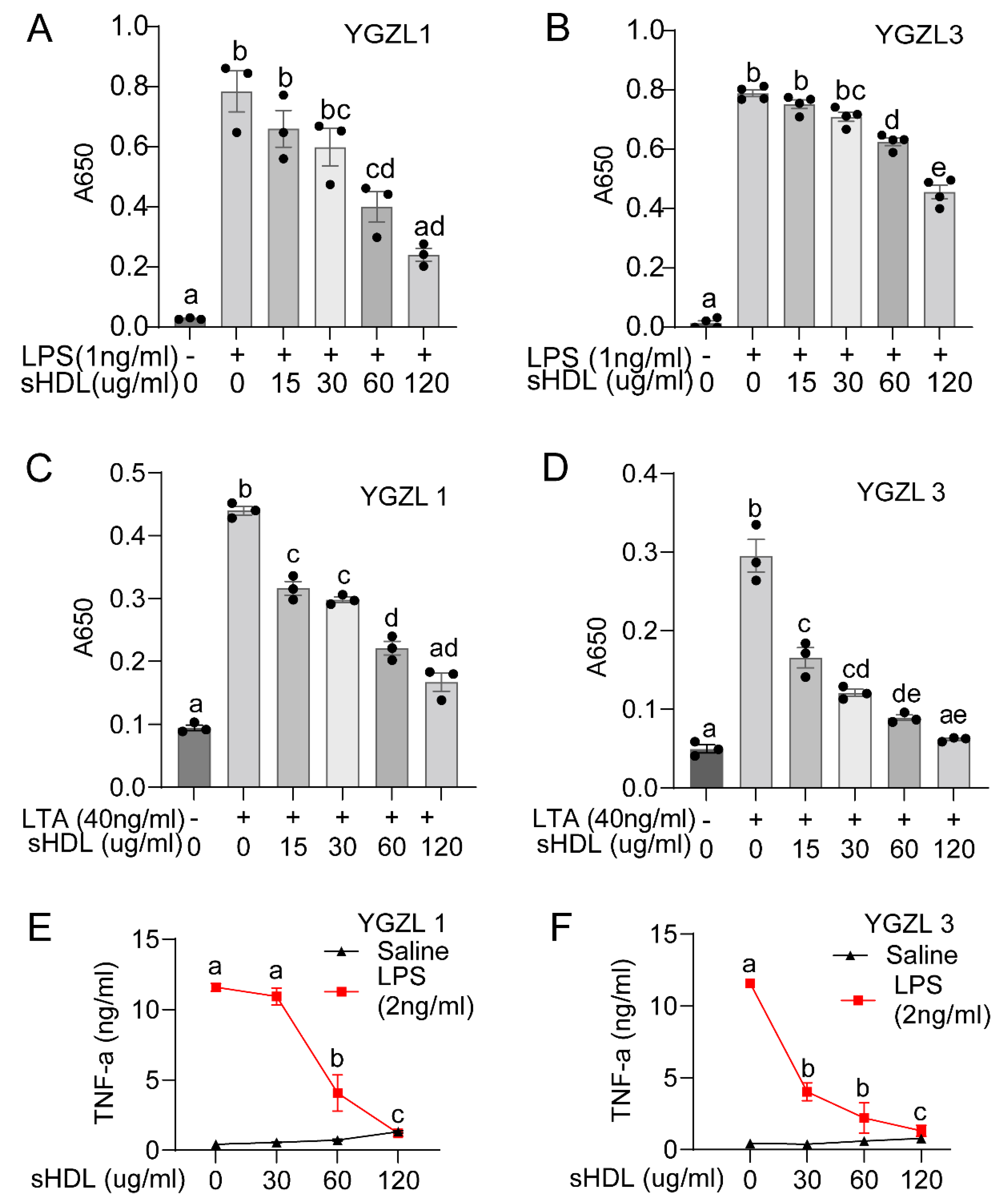
2.3.2. Analysis of NF-κB Expression in HEK-Blue Cells
2.3.3. Analysis of Cytokine Production by RAW264.7 Cells
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. An Efficient Computational Approach to the Design of Novel sHDL Nanoparticles
- (1)
- Simulate the dynamically stable 3D structures of various sHDL nanoparticles associated with different peptides by performing molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. Notably, for the MD simulation of sHDL nanoparticles, all-atomistic simulations are usually constrained to the nanosecond timescale due to the large system size, which is inadequate for studying nanoparticle self-assembly [69]. Therefore, we opted to use a coarse-grained (CG) model for the MD simulations. The CG model has been effectively used in previous studies to investigate the assembly of lipoprotein particles and permits MD simulations on the microsecond timescale [56,69,70,71], offering a more practical and cost-effective approach for simulating sHDL systems. The same CG model was also employed in our subsequent CG MD simulations mentioned below.
- (2)
- Simulate the dynamically stable sHDL-ligand binding structure by performing the CG MD simulation for each sHDL nanoparticle binding with a ligand (the LPSs or LTA concerned in this study).
- (3)
- Estimate the binding free energy of each ligand with a nanoparticle by performing potential of mean force (PMF) calculations based on the CG MD simulations.
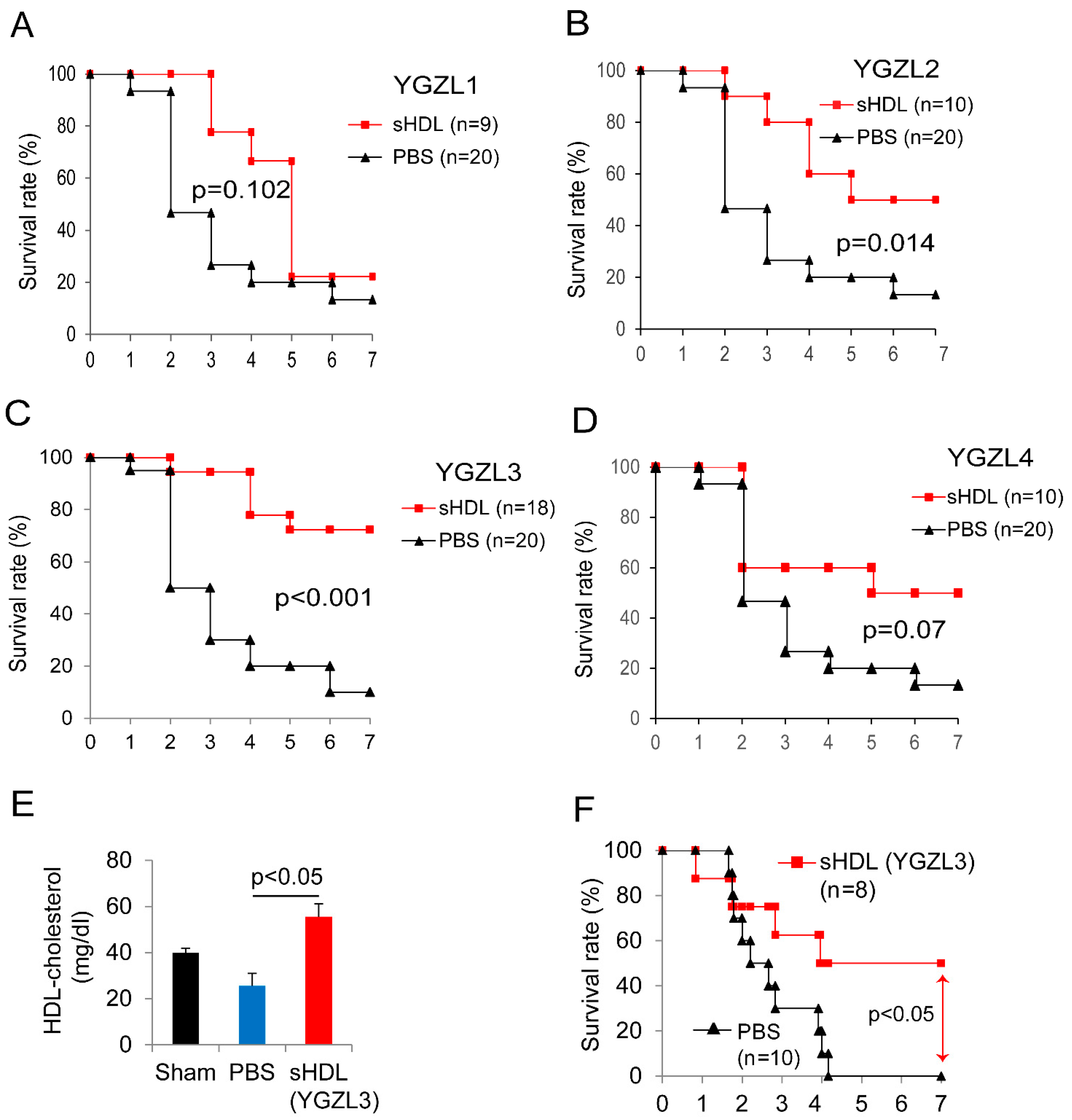
3.2. Targeting HDLs with Synthetic HDLs (sHDLs) for Sepsis Therapy
3.3. sHDLs Suppress Inflammatory Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fleischmann, C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-Treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.E.; Alhazzani, W.; Levy, M.M.; Antonelli, M.; Ferrer, R.; Kumar, A.; Sevransky, J.E.; Sprung, C.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2016. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 486–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.C. Why have clinical trials in sepsis failed? Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachoui, Y.; Kajiwara, Y.; Leaf, I.A.; Mao, D.; Ting, J.P.; Coers, J.; Aderem, A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Miao, E.A. Canonical Inflammasomes Drive IFN-Gamma to Prime Caspase-11 in Defense Against a Cytosol-Invasive Bacterium. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedemann, N.C.; Guo, R.F.; Ward, P.A. The enigma of sepsis. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, D.C.; van der Poll, T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deanfield, J.E.; Halcox, J.P.; Rabelink, T.J. Endothelial Function and Dysfunction: Testing and Clinical Relevance. Circulation 2007, 115, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, W.C. The role of the endothelium in severe sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Blood 2003, 101, 3765–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Morin, E.E.; Yu, M.; Mei, L.; Fawaz, M.V.; Wang, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhan, C.-G.; Standiford, T.J.; Schwendeman, A.; et al. Replenishing HDL with synthetic HDL has multiple protective effects against sepsis in mice. Sci. Signal. 2022, 15, eabl9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Parks, J.S. New roles of HDL in inflammation and hematopoiesis. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2012, 32, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Fogelman, A.M. HDL and cardiovascular disease: Atherogenic and atheroprotective mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, I.M.; Shishehbor, M.H.; Ansell, B.J. High-density lipoprotein as a therapeutic target: A systematic review. JAMA 2007, 298, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, R.J.; Chen, Y.H. Nuclear factor-kappaB: Activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2007, 4, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eggesbo, J.B.; Lyberg, T.; Aspelin, T.; Hjermann, I.; Kierulf, P. Different binding of 125I-LPS to plasma proteins from persons with high or low HDL. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1996, 56, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, W.A.; Wolpl, A.; Mannel, D.N.; Northoff, H. Inhibition of endotoxin-induced activation of human monocytes by human lipoproteins. Infect. Immun. 1989, 57, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenten, B.J.; Fogelman, A.M.; Haberland, M.E.; Edwards, P.A. The role of lipoproteins and receptor-mediated endocytosis in the transport of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2704–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murch, O.; Collin, M.; Hinds, C.J.; Thiemermann, C. Lipoproteins in inflammation and sepsis. I. Basic science. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, T.E.; Harris, H.W.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R.; Calhoun, M.C.; Kane, J.P.; Rapp, J.H. Chylomicrons enhance endotoxin excretion in bile. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.W.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R.; Rapp, J.H. Human very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons can protect against endotoxin-induced death in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, H.W.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R.; Read, T.E.; Kane, J.P.; Jones, A.L.; Eichbaum, E.B.; Bland, G.F.; Rapp, J.H. Chylomicrons alter the fate of endotoxin, decreasing tumor necrosis factor release and preventing death. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulevitch, R.J.; Johnston, A.R.; Weinstein, D.B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Their participation in intravascular reactions of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 64, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulevitch, R.J.; Johnston, A.R.; Weinstein, D.B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 67, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emancipator, K.; Csako, G.; Elin, R.J. In vitro inactivation of bacterial endotoxin by human lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munford, R.S.; Dietschy, J.M. Effects of specific antibodies, hormones, and lipoproteins on bacterial lipopolysaccharides injected into the rat. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 152, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumberger, C.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Dayer, J.M. Modulation of endotoxic activity of lipopolysaccharide by high-density lipoprotein. Pathobiology 1991, 59, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Ji, A.; de Beer, F.C.; Tannock, L.R.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R. SR-BI protects against endotoxemia in mice through its roles in glucocorticoid production and hepatic clearance. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnyakova, T.G.; Bocharov, A.V.; Baranova, I.N.; Chen, Z.; Remaley, A.T.; Csako, G.; Eggerman, T.L.; Patterson, A.P. Binding and internalization of lipopolysaccharide by Cla-1, a human orthologue of rodent scavenger receptor B1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22771–22780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Song, Z.; Li, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, D.; Feng, H.; Bernard, P.; Daugherty, A.; Huang, B.; Li, X.A. Scavenger Receptor BI Protects Against Septic Death through Its Role in Modulating Inflammatory Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19826–19834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ai, J.; Zheng, Z.; Howatt, D.A.; Daugherty, A.; Huang, B.; Li, X.A. High density lipoprotein protects against polymicrobe-induced sepsis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 17947–17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levels, J.H.M.; Abraham, P.R.; van den Ende, A.; van Deventer, S.J.H. Distribution and Kinetics of Lipoprotein-Bound Endotoxin. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunfeld, C.; Marshall, M.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Moser, A.H.; Tobias, P.; Feingold, K.R. Lipoproteins inhibit macrophage activation by lipoteichoic acid. J. Lipid Res. 1999, 40, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, E.E.; Guo, L.; Schwendeman, A.; Li, X.A. HDL in sepsis—Risk factor and therapeutic approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, J.Y.; Jerng, J.S.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, P.C. Low serum level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a poor prognostic factor for severe sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 33, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.H.; Peng, Y.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lien, J.M.; Tian, Y.C.; Fang, J.T.; Weng, H.H.; Chen, P.C.; Yang, C.W.; Wu, C.S. Low serum concentration of apolipoprotein A-I is an indicator of poor prognosis in cirrhotic patients with severe sepsis. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Datta, G.; Zhang, Z.; Gupta, H.; Patel, R.; Honavar, J.; Modi, S.; Wyss, J.M.; Palgunachari, M.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; et al. The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide 4F prevents defects in vascular function in endotoxemic rats. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubsch, A.P.; Powell, F.S.; Lerch, P.G.; Doran, J.E. A reconstituted, apolipoprotein A-I containing lipoprotein reduces tumor necrosis factor release and attenuates shock in endotoxemic rabbits. Circ. Shock 1993, 40, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cue, J.I.; DiPiro, J.T.; Brunner, L.J.; Doran, J.E.; Blankenship, M.E.; Mansberger, A.R.; Hawkins, M.L. Reconstituted high density lipoprotein inhibits physiologic and tumor necrosis factor alpha responses to lipopolysaccharide in rabbits. Arch. Surg. 1994, 129, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.-Z.; Wu, M.-P. Apolipoprotein A-I inhibits chemotaxis, adhesion, activation of THP-1 cells and improves the plasma HDL inflammatory index. Cytokine 2010, 49, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezado, Z.M.; Natanson, C.; Banks, S.M.; Alling, D.W.; Koev, C.A.; Danner, R.L.; Elin, R.J.; Hosseini, J.M.; Parker, T.S.; Levine, D.M. Therapeutic trial of reconstituted human high-density lipoprotein in a canine model of gram-negative septic shock. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 604–611. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Datta, G.; Zhang, Y.; Miller, A.P.; Mochon, P.; Chen, Y.F.; Chatham, J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; White, C.R. Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide treatment inhibits inflammatory responses and improves survival in septic rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H866–H873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolo, B.A.; Nicholls, S.J.; Bao, S.; Rye, K.A.; Heather, A.K.; Barter, P.J.; Bursill, C. The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide ETC-642 exhibits anti-inflammatory properties that are comparable to high density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis 2011, 217, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bartolo, B.A.; Vanags, L.Z.; Tan, J.T.; Bao, S.; Rye, K.A.; Barter, P.J.; Bursill, C.A. The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, ETC-642, reduces chronic vascular inflammation in the rabbit. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasseux, J.-L.; Schwendeman, A.S.; Zhu, L. Apolipoprotein A-I Mimics. U.S. Patent 8,378,068, 19 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Lalwani, N.D.; Drake, S.L.; Crockatt, J.G.; Dasseux, J.L.H. Single-dose intravenous infusion of ETC-642, a 22-Mer ApoA-I analogue and phospholipids complex, elevates HDL-C in atherosclerosis patients. Circulation 2003, 108, 563–564. [Google Scholar]
- Schrodinger, L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 1.3r1; Scientific Research Publishing: Irvine, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Monticelli, L.; Kandasamy, S.K.; Periole, X.; Larson, R.G.; Tieleman, D.P.; Marrink, S.-J. The MARTINI coarse-grained force field: Extension to proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2008, 4, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrink, S.J.; Risselada, H.J.; Yefimov, S.; Tieleman, D.P.; de Vries, A.H. The MARTINI force field: Coarse grained model for biomolecular simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 7812–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrink, S.J.; De Vries, A.H.; Mark, A.E. Coarse grained model for semiquantitative lipid simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; Glück, T. Endotoxin as a drug target. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, S57–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.A. Towards a rational development of anti-endotoxin agents: Novel approaches to sequestration of bacterial endotoxins with small molecules. J. Mol. Recognit. 2001, 14, 370–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Markwitz, S.; Labischinski, H. Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering Analysis of Pneumococcal Lipoteichoic Acid Phase Structure. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 244, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, C.A.; Sovova, Z.; van Eerden, F.J.; de Vries, A.H.; Marrink, S.J. Martini force field parameters for glycolipids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, I.; Grinkova, Y.; Lazarides, A.; Sligar, S. Directed self-assembly of monodisperse phospholipid bilayer Nanodiscs with controlled size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segrest, J.P.; Jones, M.K.; Klon, A.E.; Sheldahl, C.J.; Hellinger, M.; De Loof, H.; Harvey, S.C. A detailed molecular belt model for apolipoprotein AI in discoidal high density lipoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31755–31758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.Y.; Denisov, I.G.; Phillips, J.C.; Sligar, S.G.; Schulten, K. Molecular dynamics simulations of discoidal bilayers assembled from truncated human lipoproteins. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klon, A.E.; Segrest, J.P.; Harvey, S.C. Molecular dynamics simulations on discoidal HDL particles suggest a mechanism for rotation in the apo AI belt model. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 324, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, S.; Páll, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; van der Spoel, D. GROMACS 4.5: A high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Rosenberg, J.M.; Bouzida, D.; Swendsen, R.H.; Kollman, P.A. The weighted histogram analysis method for free-energy calculations on biomolecules. I. The method. J. Comput. Chem. 1992, 13, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hub, J.S.; de Groot, B.L.; van der Spoel, D. g_wham—A Free Weighted Histogram Analysis Implementation Including Robust Error and Autocorrelation Estimates. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2010, 6, 3713–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, G.A.; Strachan, A.F.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R.; Hoppe, H.C.; Jeenah, M.S.; de Beer, F.C. Serum amyloid A-containing human high density lipoprotein 3. Density, size, and apolipoprotein composition. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 9644–9651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beer, M.C.; Ji, A.; Jahangiri, A.; Vaughan, A.M.; de Beer, F.C.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R.; Webb, N.R. ATP binding cassette G1-dependent cholesterol efflux during inflammation. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayburt, T.H.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Sligar, S.G. Self-assembly of discoidal phospholipid bilayer nanoparticles with membrane scaffold proteins. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Hilliard, G.M. The spatial organization of apolipoprotein AI on the edge of discoidal high density lipoprotein particles A mass spectrometry study. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27199–27207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.; Sorci-Thomas, M.G.; Alexander, E.T.; Samuel, M.P.; Thomas, M.J. Intermolecular Contact Between Globular N-Terminal Fold and C-Terminal Domain of ApoA-I Stabilizes Its Lipid-Bound Conformation Studies Employing Chemical Cross-Linking and Mass Spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33015–33025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Mishra, V.K.; Kurtz, J.A.; Cao, D.; Klon, A.E.; Harvey, S.C.; Anantharamaiah, G.; Segrest, J.P. Double belt structure of discoidal high density lipoproteins: Molecular basis for size heterogeneity. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharamaiah, G.; Jones, J.; Brouillette, C.; Schmidt, C.; Chung, B.H.; Hughes, T.A.; Bhown, A.; Segrest, J. Studies of synthetic peptide analogs of the amphipathic helix. Structure of complexes with dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 10248–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufteland, M.; Pesavento, J.B.; Bermingham, R.L.; Hoeprich, P.D.; Ryan, R.O. Peptide stabilized amphotericin B nanodisks. Peptides 2007, 28, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shih, A.Y.; Arkhipov, A.; Freddolino, P.L.; Schulten, K. Coarse grained protein-lipid model with application to lipoprotein particles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3674–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, A.Y.; Freddolino, P.L.; Arkhipov, A.; Schulten, K. Assembly of lipoprotein particles revealed by coarse-grained molecular dynamics simulations. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 157, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catte, A.; Patterson, J.C.; Bashtovyy, D.; Jones, M.K.; Gu, F.; Li, L.; Rampioni, A.; Sengupta, D.; Vuorela, T.; Niemelä, P. Structure of spheroidal HDL particles revealed by combined atomistic and coarse-grained simulations. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 2306–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

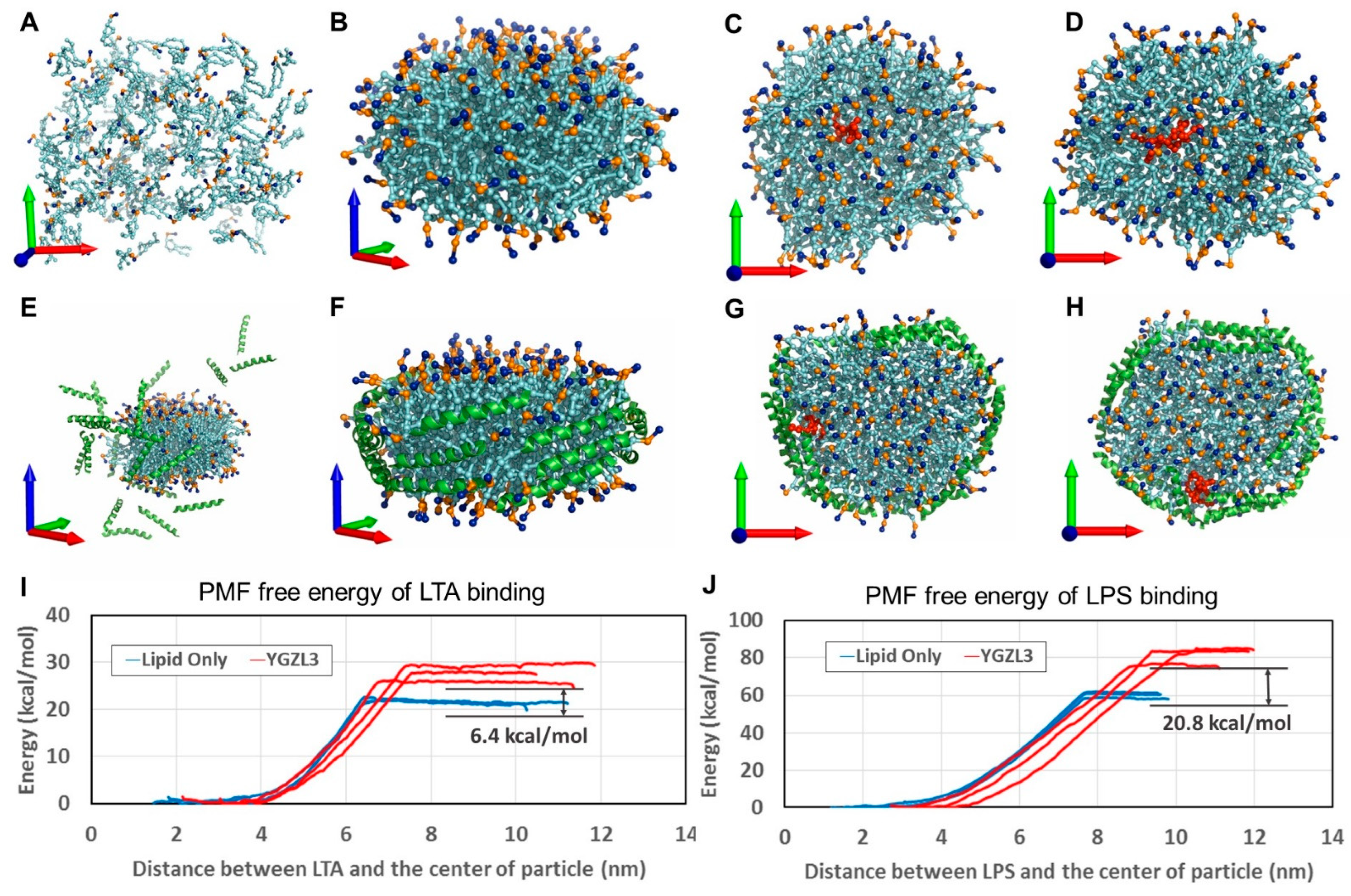
| Particle | Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | Binding Energy Improvement (kcal/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPS | LTA | ∆LPS (sHDL—Lipid) | ∆LTA (sHDL—Lipid) | |
| Lipid-Only | −59.9 | −20.7 | N/A | N/A |
| ETC-642 | −77.6 | −25.1 | −17.7 | −4.4 |
| YGZL1 sHDL | −72.2 | −23.2 | −12.3 | −2.5 |
| YGZL2 sHDL | −76.1 | −24.4 | −16.2 | −3.7 |
| YGZL3 sHDL | −80.7 | −27.1 | −20.8 | −6.4 |
| YGZL4 sHDL | −76.2 | −25.0 | −16.3 | −4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, L.; Yuan, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhan, C.; Li, X. Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030397
Guo L, Yuan Y, Zheng F, Zhan C, Li X. Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030397
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Ling, Yaxia Yuan, Fang Zheng, Changguo Zhan, and Xiangan Li. 2025. "Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030397
APA StyleGuo, L., Yuan, Y., Zheng, F., Zhan, C., & Li, X. (2025). Computational Design and In Vitro and In Vivo Characterization of an ApoE-Based Synthetic High-Density Lipoprotein for Sepsis Therapy. Biomolecules, 15(3), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030397






