The Emerging Role and Clinical Significance of PI3K-Akt-mTOR in Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
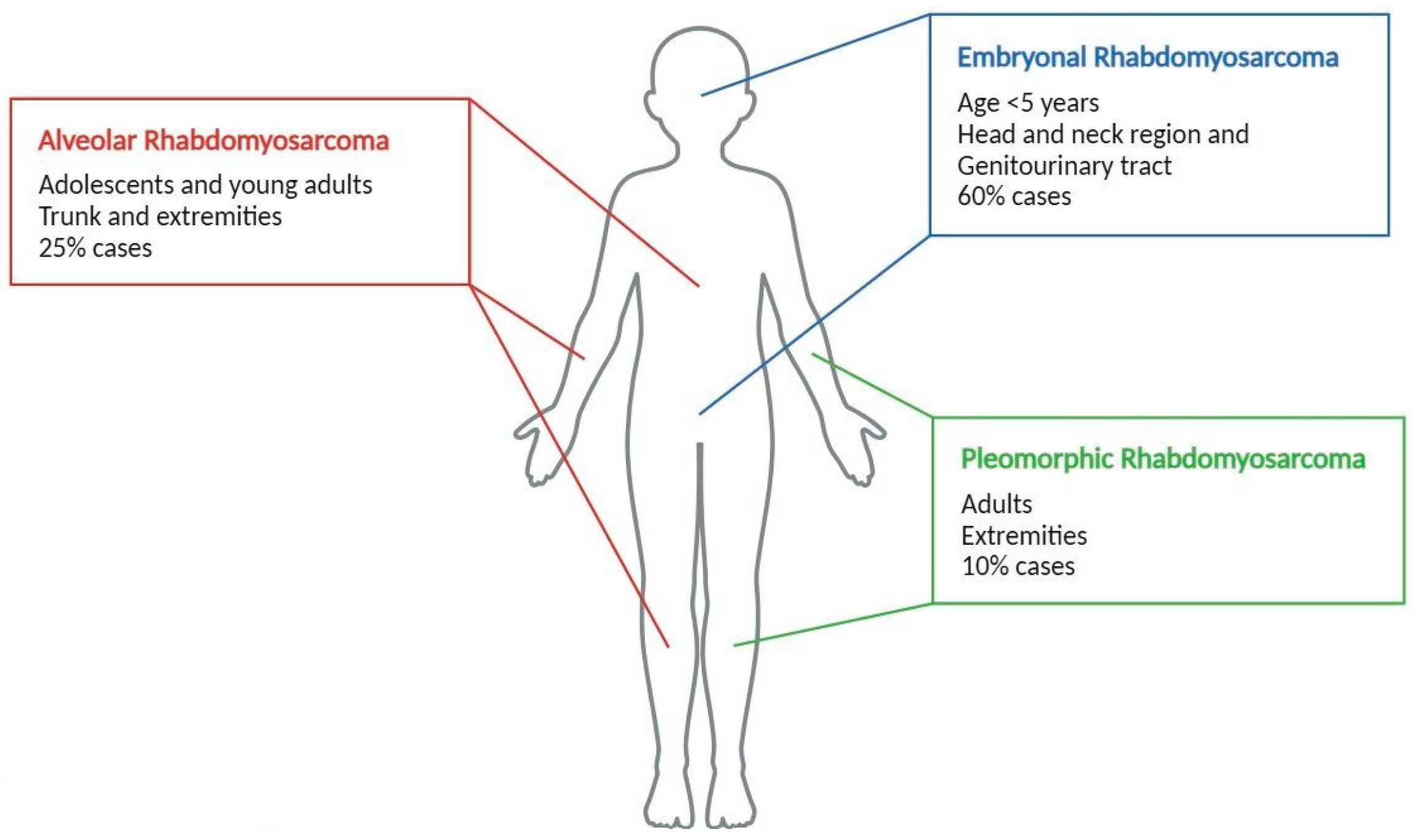
1. Introduction: Rhabdomyosarcoma Features
2. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR Pathway: Structure, Components, and Activity
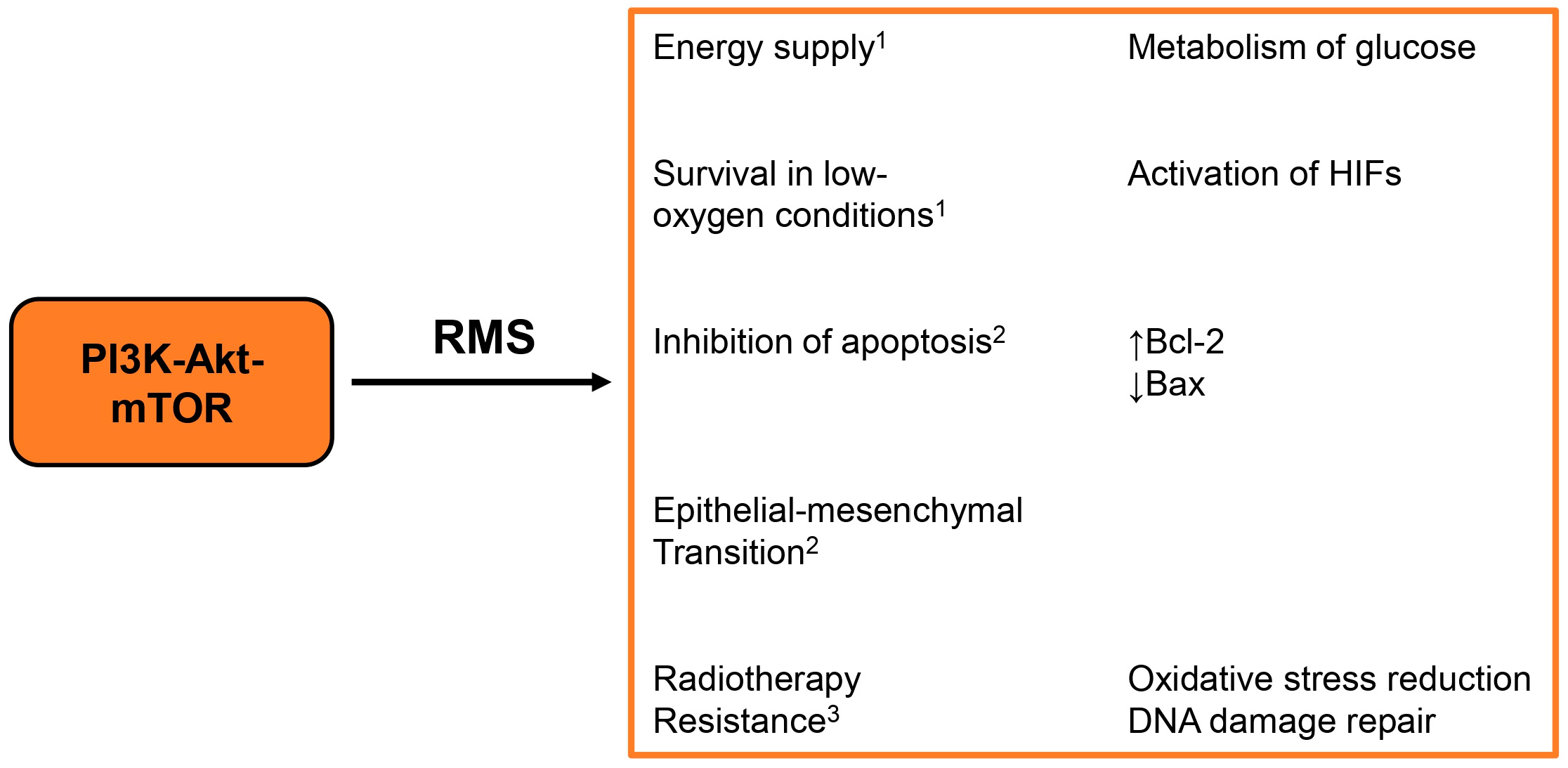
3. The PI3K-Akt-mTOR Pathway in Rhabdomyosarcoma
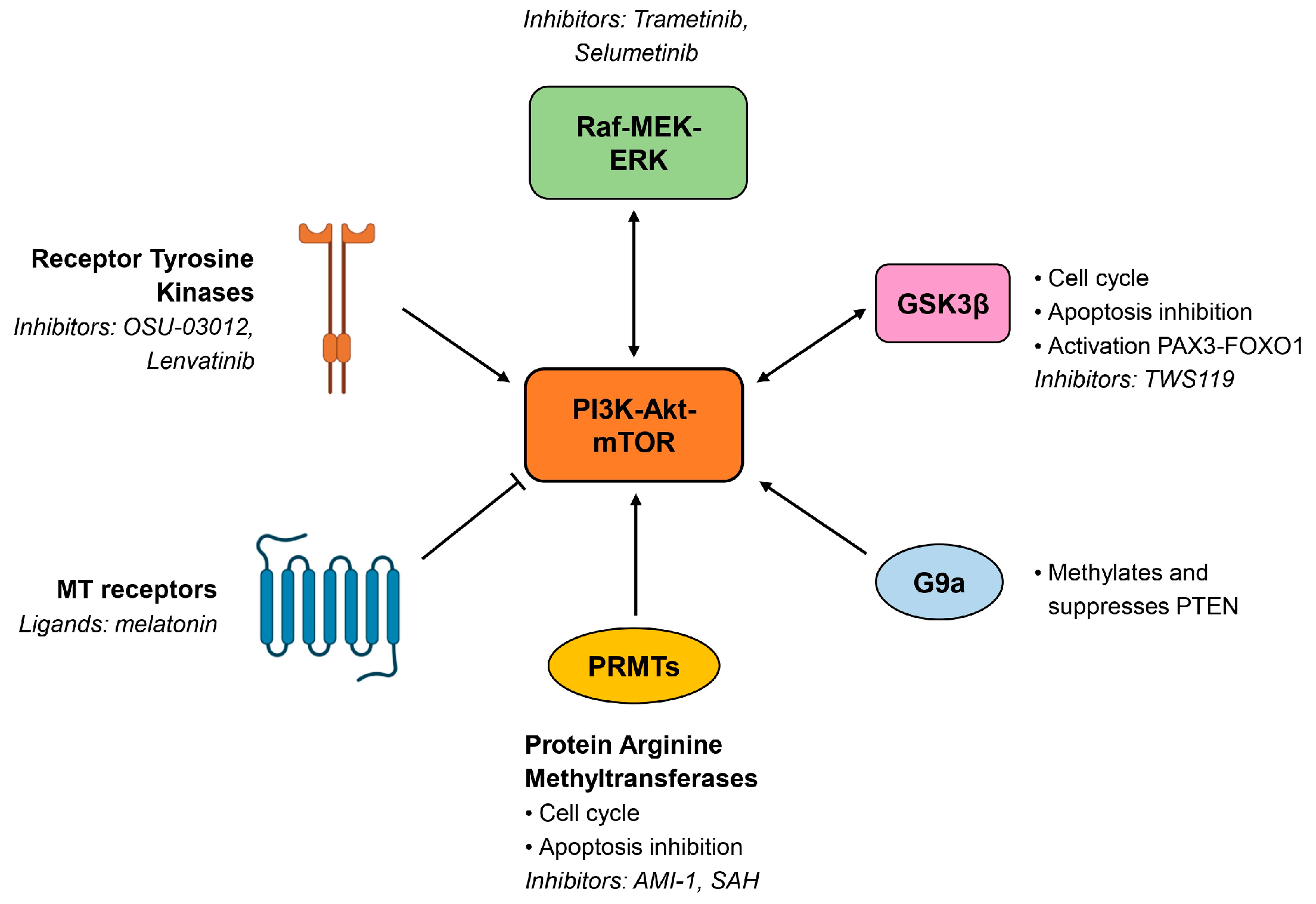
4. Treatments Targeting the Pathway in RMS
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skapek:, S.X.; Ferrari, A.; Gupta, A.A.; Lupo, P.J.; Butler, E.; Shipley, J.; Barr, F.G.; Hawkins, D.S. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseb, H.; Kuhn, J.; Babiker, H.M. Rhabdomyosarcoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Oberlin, O.; Rey, A.; Lyden, E.; Bisogno, G.; Stevens, M.C.; Meyer, W.H.; Carli, M.; Anderson, J.R. Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Rhabdomyosarcomas: Results of a Pooled Analysis From United States and European Cooperative Groups. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, W.W.; Skapek, S.X. Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma: New Insight on Biology and Treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 12, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, D.M.; Barr, F.G. Classification of Rhabdomyosarcoma and Its Molecular Basis. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2013, 20, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanzani, A.; Monti, E.; Donato, R.; Sorci, G. Muscular dystrophies share pathogenetic mechanisms with muscle sarcomas. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiner, J.; Le Loarer, F. The current landscape of rhabdomyosarcomas: An update. Virchows Arch. 2019, 476, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, E.; Fanzani, A. Uncovering metabolism in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, F.; Fahs, A.; Ghayad, S.E.; Saab, R. Signaling pathways in Rhabdomyosarcoma invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, R.; Takita, J.; Sato-Otsubo, A.; Kato, M.; Koh, K.; Hanada, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, K.; Maeda, D.; Fukayama, M.; et al. Characterization of genetic lesions in rhabdomyosarcoma using a high-density single nucleotide polymorphism array. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Barr, F.G. Therapeutic Approaches Targeting PAX3-FOXO1 and Its Regulatory and Transcriptional Pathways in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Molecules 2018, 23, 2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Odaka, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, B.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Shang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; et al. Dihydroartemisinin Inhibits mTORC1 Signaling by Activating the AMPK Pathway in Rhabdomyosarcoma Tumor Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, P.H.; Lynch, J.C.; Qualman, S.J.; Tirabosco, R.; Lim, J.F.; Maurer, H.M.; Bridge, J.A.; Crist, W.M.; Triche, T.J.; Barr, F.G. PAX3-FKH and PAX7-FKHR Gene Fusions Are Prognostic Indicators in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; Missiaglia, E.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Oberlin, O.; Shipley, J.M.; Delattre, O.; De Reyniès, A.; Pierron, G.; Thuille, B.; Palenzuela, G.; et al. Fusion Gene-Negative Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma is Clinically and Molecularly Indistinguishable from Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase–AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Cheng, H.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J. Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Yuzugullu, H.; Zhao, J.J. PI3K in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.L.; Park, A.; Akiyama, R.; Tap, W.D.; Denny, C.T.; Federman, N. Evaluation of In Vitro Activity of the Class I PI3K Inhibitor Buparlisib (BKM120) in Pediatric Bone and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, B.T.; Smith, D.L.; Ram, P.T.; Lu, Y.; Mills, G.B. Exploiting the PI3K/AKT Pathway for Cancer Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmings, B.A.; Restuccia, D.F. PI3K-PKB/Akt Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, E.; Hugle, M.; Reimann, R.; Schlecht, M.; Fulda, S. Pan-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Inhibitor AZD8055 Primes Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells for ABT-737-induced Apoptosis by Down-regulating Mcl-1 Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35287–35296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A. Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Kong, Y.; Yan, H.; Duan, J.; Wang, C.; Sha, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, C. Perfluorooctanoic acid induces migration and invasion and inhibits apoptosis through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Ameur, N.; Yilmaz, I.; Nafa, K.; Lau, C.-Y.; Marchetti, A.; Borsu, L.; Barr, F.G.; Ladanyi, M. Oncogene Mutation Profiling of Pediatric Solid Tumors Reveals Significant Subsets of Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma and Neuroblastoma with Mutated Genes in Growth Signaling Pathways. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shern, J.F.; Chen, L.; Chmielecki, J.; Wei, J.S.; Patidar, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Ambrogio, L.; Auclair, D.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.K.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma reveals a landscape of alterations affecting a common genetic axis in fusion-positive and fusion-negative tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seki, M.; Nishimura, R.; Yoshida, K.; Shimamura, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Kato, M.; Chiba, K.; Tanaka, H.; Hoshino, N.; et al. Integrated genetic and epigenetic analysis defines novel molecular subgroups in rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.M.; Kumar, S.; Parker, C.; Slevin, M.; Kumar, P. PAX3 and PAX3-FKHR promote rhabdomyosarcoma cell survival through downregulation of PTEN. Cancer Lett. 2007, 253, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crose, L.E.S.; Linardic, C.M. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases as Therapeutic Targets in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 756982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codenotti, S.; Zizioli, D.; Mignani, L.; Rezzola, S.; Tabellini, G.; Parolini, S.; Giacomini, A.; Asperti, M.; Poli, M.; Mandracchia, D.; et al. Hyperactive Akt1 Signaling Increases Tumor Progression and DNA Repair in Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma RD Line and Confers Susceptibility to Glycolysis and Mevalonate Pathway Inhibitors. Cells 2022, 11, 2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, T.; Venier, R.; Yohe, M.; Sindiri, S.; Gryder, B.E.; Shern, J.F.; Kabaroff, L.; Dickson, B.; Schleicher, K.; Chouinard-Pelletier, G.; et al. Functional screening of FGFR4-driven tumorigenesis identifies PI3K/mTOR inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2630–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielecki, J.; Bailey, M.; He, J.; Elvin, J.; Vergilio, J.-A.; Ramkissoon, S.; Suh, J.; Frampton, G.M.; Sun, J.X.; Morley, S.; et al. Genomic Profiling of a Large Set of Diverse Pediatric Cancers Identifies Known and Novel Mutations across Tumor Spectra. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Davie, J.K. New insights into signalling-pathway alterations in rhabdomyosarcoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 112, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petricoin, E.F.; Espina, V.; Araujo, R.P.; Midura, B.; Yeung, C.; Wan, X.; Eichler, G.S.; Johann, D.J.; Qualman, S.; Tsokos, M.; et al. Phosphoprotein Pathway Mapping: Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Activation Is Negatively Associated with Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Survival. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codenotti, S.; Sandrini, L.; Mandracchia, D.; Lorenzi, L.; Corsetti, G.; Poli, M.; Asperti, M.; Salvi, V.; Bosisio, D.; Monti, E.; et al. Statin-Sensitive Akt1/Src/Caveolin-1 Signaling Enhances Oxidative Stress Resistance in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Sellers, W.R. Drug discovery approaches targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5511–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazzi, M.; Bavelloni, A.; Cenni, V.; Salucci, S.; Stella, A.B.; Tomassini, E.; Scotlandi, K.; Blalock, W.L.; Faenza, I. Combined Treatment with PI3K Inhibitors BYL-719 and CAL-101 Is a Promising Antiproliferative Strategy in Human Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, K.E.; Rojo, F.; She, Q.-B.; Solit, D.; Mills, G.B.; Smith, D.; Lane, H.; Hofmann, F.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ludwig, D.L.; et al. mTOR Inhibition Induces Upstream Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling and Activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotkin, E.K.; Patwardhan, P.P.; Vasudeva, S.D.; de Stanchina, E.; Tap, W.D.; Schwartz, G.K. MLN0128, an ATP-Competitive mTOR Kinase Inhibitor with Potent In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Activity, as Potential Therapy for Bone and Soft-Tissue Sarcoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsley, C.W.; Zhao, Z.; Leister, W.H.; Robinson, R.G.; Barnett, S.F.; Defeo-Jones, D.; Jones, R.E.; Hartman, G.D.; Huff, J.R.; Huber, H.E.; et al. Allosteric Akt (PKB) inhibitors: Discovery and SAR of isozyme selective inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, N.C.; Kasamon, Y.; Pazdur, R.; Gormley, N. The saga of PI3K inhibitors in haematological malignancies: Survival is the ultimate safety endpoint. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttwak, E.; Smith, M.R.; Zelenetz, A.D. Is there a pathway for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta inhibitors to be approved therapeutics for B-cell lymphoma therapy. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2023, 24, 1331–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Gupta, A.; Xue, W.; Harrison, D.J.; Hawkins, D.S.; Dasgupta, R.; Wolden, S.; Shulkin, B.; Qumseya, A.; Routh, J.C.; MacDonald, T.; et al. Addition of temsirolimus to chemotherapy in children, adolescents, and young adults with intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma (ARST1431): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial from the Children’s Oncology Group. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, L.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Hingorani, P.; Anderson, J.R.; Lyden, E.R.; Rodeberg, D.A.; Indelicato, D.J.; Kao, S.C.; Dasgupta, R.; Spunt, S.L.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Bevacizumab or Temsirolimus in Combination With Chemotherapy for First Relapse Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koscielniak, E.; Klingebiel, T. Randomised trials in children with rhabdomyosarcoma: Time for a change? Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 828–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Janeway, K.A.; Patton, D.R.; Winter, C.L.; Coffey, B.; Williams, P.M.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Routbort, M.; Ramirez, N.C.; et al. Actionable Tumor Alterations and Treatment Protocol Enrollment of Pediatric and Young Adult Patients With Refractory Cancers in the National Cancer Institute–Children’s Oncology Group Pediatric MATCH Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janisiak, J.; Kopytko, P.; Tkacz, M.; Rogińska, D.; Perużyńska, M.; Machaliński, B.; Pawlik, A.; Tarnowski, M. Protein Arginine Methyltransferase (PRMT) Inhibitors—AMI-1 and SAH Are Effective in Attenuating Rhabdomyosarcoma Growth and Proliferation in Cell Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, L.; Hsieh, F.-C.; Lin, H.-J.; Chen, C.-S.; Qualman, S.J.; Lin, J. PDK-1/AKT pathway as a novel therapeutic target in rhabdomyosarcoma cells using OSU-03012 compound. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 97, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, C.; Chen, M.; Long, Q.; Xu, Z.; Lv, D.; Rong, Y.; et al. Melatonin inhibits fibroblast cell functions and hypertrophic scar formation by enhancing autophagy through the MT2 receptor-inhibited PI3K/Akt /mTOR signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1870, 166887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihanfar, A.; Yousefi, B.; Azizzadeh, B.; Majidinia, M. Interactions of melatonin with various signaling pathways: Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codenotti, S.; Battistelli, M.; Burattini, S.; Salucci, S.; Falcieri, E.; Rezzani, R.; Faggi, F.; Colombi, M.; Monti, E.; Fanzani, A. Melatonin decreases cell proliferation, impairs myogenic differentiation and triggers apoptotic cell death in rhabdomyosarcoma cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burattini, S.; Battistelli, M.; Codenotti, S.; Falcieri, E.; Fanzani, A.; Salucci, S. Melatonin action in tumor skeletal muscle cells: An ultrastructural study. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.V.; Kala, M.P.; Rao, V.K.; Pignata, L.; Lim, H.J.; Suriyamurthy, S.; Chang, K.T.E.; Lee, V.K.; Guccione, E.; Taneja, R. Epigenetic Regulation of the PTEN–AKT–RAC1 Axis by G9a Is Critical for Tumor Growth in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2232–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renshaw, J.; Taylor, K.R.; Bishop, R.; Valenti, M.; Brandon, A.D.H.; Gowan, S.; Eccles, S.A.; Ruddle, R.R.; Johnson, L.D.; Raynaud, F.I.; et al. Dual Blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR (AZD8055) and RAS/MEK/ERK (AZD6244) Pathways Synergistically Inhibits Rhabdomyosarcoma Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5940–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, M.K.; Graab, U.; Fulda, S. Synthetic lethal interaction between PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/MEK/ERK pathway inhibition in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erp, A.E.; Versleijen-Jonkers, Y.M.; van der Graaf, W.T.; Fleuren, E.D. Targeted Therapy–based Combination Treatment in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1365–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, A.D.; DuBois, S.G.; Macy, M.E.; de Rojas, T.; Donoghue, M.; Weiner, S.; Knoderer, H.; Bernardi, R.; Buenger, V.; Canaud, G.; et al. Paediatric strategy forum for medicinal product development of PI3-K, mTOR, AKT and GSK3β inhibitors in children and adolescents with cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 207, 114145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.-Y.; Dong, H.; Cui, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, T. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 regulates PAX3–FKHR-mediated cell proliferation in human alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 391, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Giacalone, B.A.; Li, H.; Scheurer, M.E.; Casey, D.L.; Dugan-Perez, S.; Marquez-Do, D.A.; Muzny, D.; Gibbs, R.A.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Hall, D.; et al. Germline Genetic Testing and Survival Outcomes Among Children With Rhabdomyosarcoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e244170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beevers, C.S.; Li, F.; Liu, L.; Huang, S. Curcumin inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated signaling pathways in cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beevers, C.S.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Webster, N.J.; Huang, S. Curcumin Disrupts the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin-Raptor Complex. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salucci, S.; Bavelloni, A.; Stella, A.B.; Fabbri, F.; Vannini, I.; Piazzi, M.; Volkava, K.; Scotlandi, K.; Martinelli, G.; Faenza, I.; et al. The Cytotoxic Effect of Curcumin in Rhabdomyosarcoma Is Associated with the Modulation of AMPK, AKT/mTOR, STAT, and p53 Signaling. Nutrients 2023, 15, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugle, M.; Fulda, S. Dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 synergizes with chloroquine to induce apoptosis in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoroddu, S.; Lucariello, A.; De Luca, A.; Bagella, L. Dysregulation of miRNAs in Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cells 2024, 13, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocelli, M.; Sampaolesi, M. The mesmiRizing complexity of microRNAs for striated muscle tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 88, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, E.; Giarratana, N.; Sassi, G.; Elmastas, M.; Killian, T.; Wang, C.-C.; Marini, V.; Ronzoni, F.; Yustein, J.; Uyttebroeck, A.; et al. Upregulation of miR181a/miR212 Improves Myogenic Commitment in Murine Fusion-Negative Rhabdomyosarcoma. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 701354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, E.; Yedigaryan, L.; Giarratana, N.; Wang, C.-C.; Garrido, G.M.; Degreef, E.; Marini, V.; Rinaldi, G.; van der Veer, B.K.; Sassi, G.; et al. miR-449a/miR-340 reprogram cell identity and metabolism in fusion-negative rhabdomyosarcoma. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megiorni, F.; Cialfi, S.; McDowell, H.P.; Felsani, A.; Camero, S.; Guffanti, A.; Pizer, B.; Clerico, A.; De Grazia, A.; Pizzuti, A.; et al. Deep Sequencing the MicroRNA Profile in Rhabdomyosarcoma Reveals Down-regulation of miR-378 Family Members. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, A.L.; Li, L.; Subramanian, S. MicroRNA miR-183 Functions as an Oncogene by Targeting the Transcription Factor EGR1 and Promoting Tumor Cell Migration. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9570–9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-André, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-Enhancers in the Control of Cell Identity and Disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryder, B.E.; Yohe, M.E.; Chou, H.-C.; Zhang, X.; Marques, J.; Wachtel, M.; Schaefer, B.; Sen, N.; Song, Y.; Gualtieri, A.; et al. PAX3–FOXO1 Establishes Myogenic Super Enhancers and Confers BET Bromodomain Vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 884–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hewitt, S.M.; Wright, H.; Keller, C.; Barr, F.G. DNA methylation patterns are influenced by Pax3::Foxo1 expression and developmental lineage in rhabdomyosarcoma tumours forming in genetically engineered mouse models. J. Pathol. 2025, 265, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, C.A.; Bernasconi, A.; Lasalvia, P.; Bisogno, G.; Milano, G.M.; Trama, A.; Chiaravalli, S.; Bergamaschi, L.; Casanova, M.; Massimino, M.; et al. Being diagnosed with a rhabdomyosarcoma in the era of artificial intelligence: Whom can we trust? Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2024, 71, e31256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Agent | Molecular Target | Approved for | Clinical Trial Phase (RMS) | Usage | Status | Clinical Trial Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Everolimus | mTOR | Breast Cancer Pancreatic NETs NETs of the Lung NETs of the Gut Advanced RCC | Phase I Phase II Phase I/II | Monotherapy Monotherapy Combination | Completed Unknown Completed | NCT00187174 NCT01216839 NCT03245151 |
| Lenvatinib | RTKs | Thyroid Carcinoma Hepatocellular Carcinoma Endometrial Carcinoma | Phase I/II | Combination | Completed | NCT03245151 |
| Samotolisib | PI3K | N.A. | Phase II | Monotherapy | Completed | NCT03213678 |
| Sirolimus | mTOR | Transplant medication S-LAM | Phase I Phase II | Combination Combination | Completed Recruiting | NCT01135563 NCT02574728 |
| Temsirolimus | mTOR | Advanced RCC Mantle Cell Lymphoma | Phase I Phase I/II Phase II Phase II Phase III | Combination Combination Combination Combination Combination | Terminated Completed Completed Completed Active | NCT01204450 NCT00949325 NCT01614795 NCT01222715 NCT02567435 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Versari, I.; Salucci, S.; Bavelloni, A.; Battistelli, M.; Traversari, M.; Wang, A.; Sampaolesi, M.; Faenza, I. The Emerging Role and Clinical Significance of PI3K-Akt-mTOR in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030334
Versari I, Salucci S, Bavelloni A, Battistelli M, Traversari M, Wang A, Sampaolesi M, Faenza I. The Emerging Role and Clinical Significance of PI3K-Akt-mTOR in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleVersari, Ilaria, Sara Salucci, Alberto Bavelloni, Michela Battistelli, Mirko Traversari, Ashley Wang, Maurilio Sampaolesi, and Irene Faenza. 2025. "The Emerging Role and Clinical Significance of PI3K-Akt-mTOR in Rhabdomyosarcoma" Biomolecules 15, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030334
APA StyleVersari, I., Salucci, S., Bavelloni, A., Battistelli, M., Traversari, M., Wang, A., Sampaolesi, M., & Faenza, I. (2025). The Emerging Role and Clinical Significance of PI3K-Akt-mTOR in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Biomolecules, 15(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15030334










