The Efficacy of an Active Medicinal Alkaloid, Berbamine, in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in a Retinyl Acetate-Induced Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
- -
- a group of animals that was administered with saline (the control group, CON)
- -
- a group of animals that was administered with retinyl acetate (RA)
- -
- a group of animals that was administered with berbamine (BBM; 25 mg/kg/day i.p.)
- -
- a group that received of animals that was administered with retinyl acetate plus berbamine (RA + BBM).
2.2. Drugs
- -
- Retinyl acetate (Sigma-Aldrich Fluka, St. Louis, MO, USA): diluted to 0.75% solution with a mixture of Polysorbate 80 and saline and administered intravesically due to the bladder detrusor overactivity induction.
- -
2.3. Surgical Procedures
2.3.1. Conscious Cystometry
2.3.2. Bladder Urothelium Tissue and Detrusor Muscle Preparation
2.4. Bladder Blood Flow (BBF)
2.5. The Assessment of Cardiovascular Parameters and Diuresis
2.6. Determining the Expression Levels of cFos in Central Micturition Areas
2.7. Biochemical Analyses
2.8. The Research Project
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Urodynamic Parameters
3.2. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the BBF
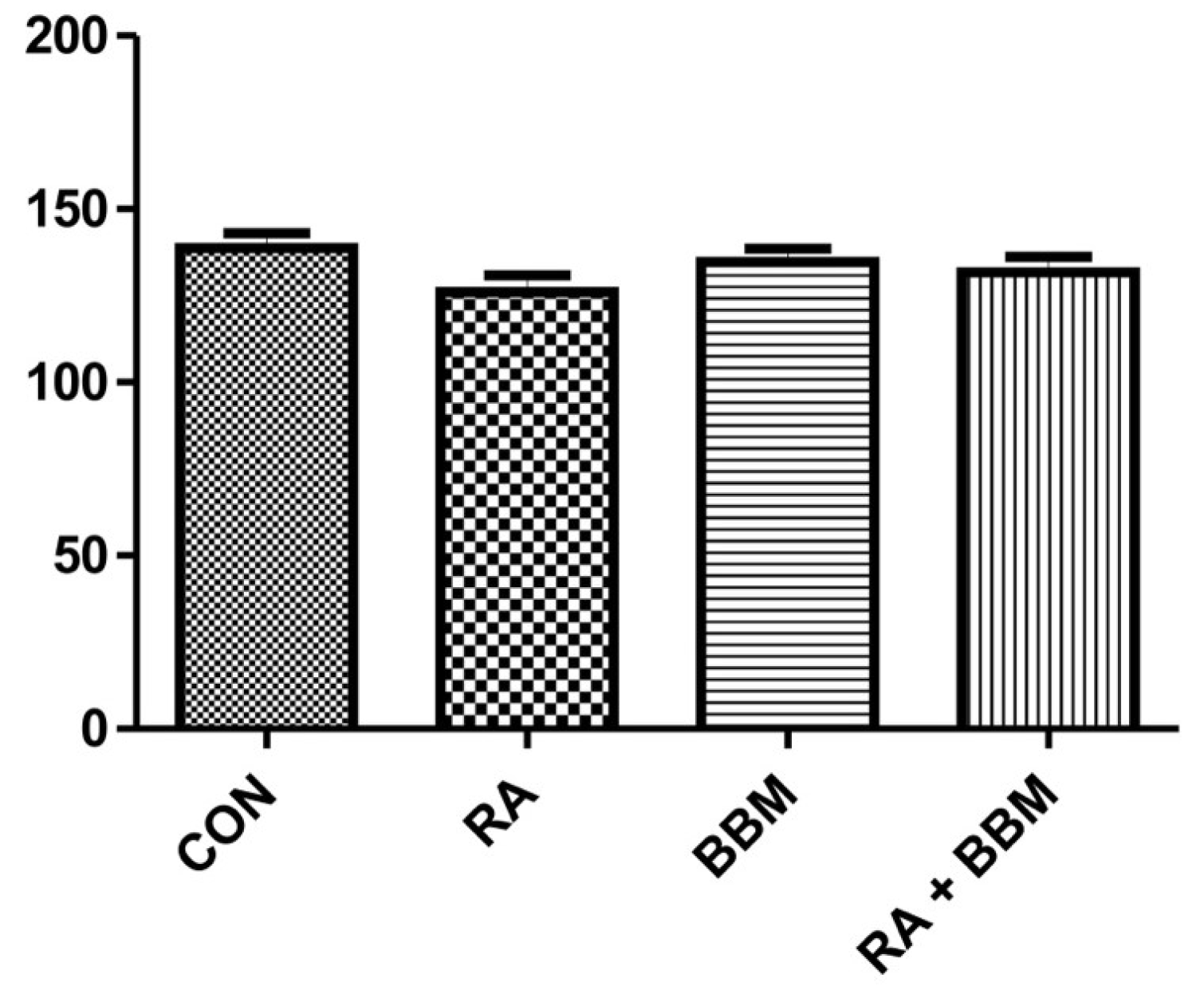
3.3. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Cardiovascular Parameters and Diuresis
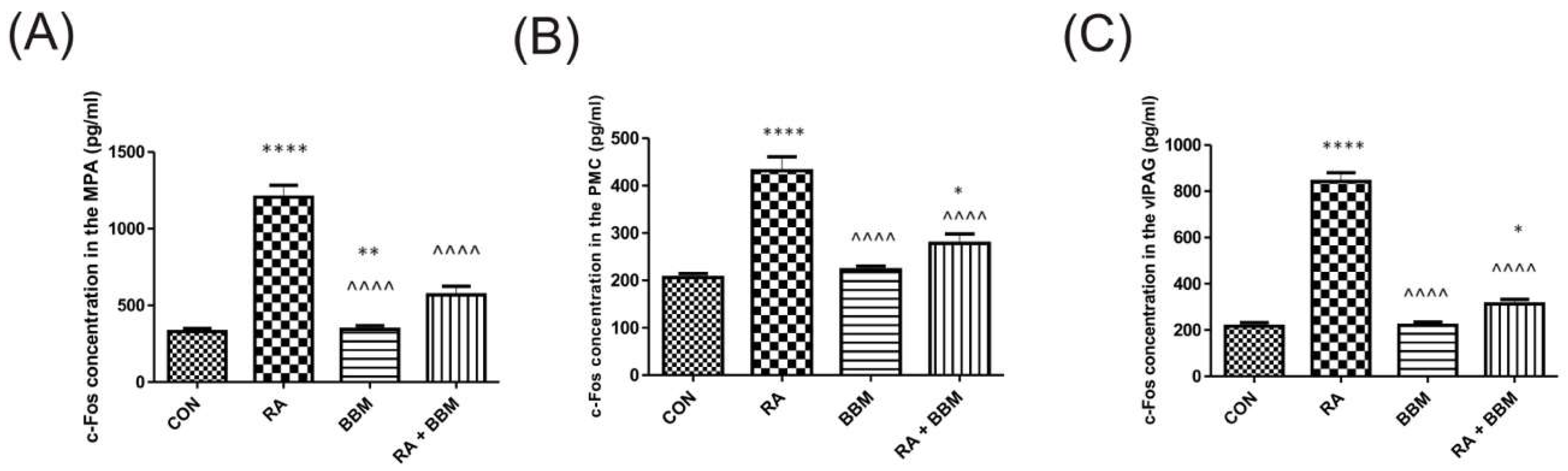
3.4. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Expression Levels of c-Fos in Central Micturition Areas
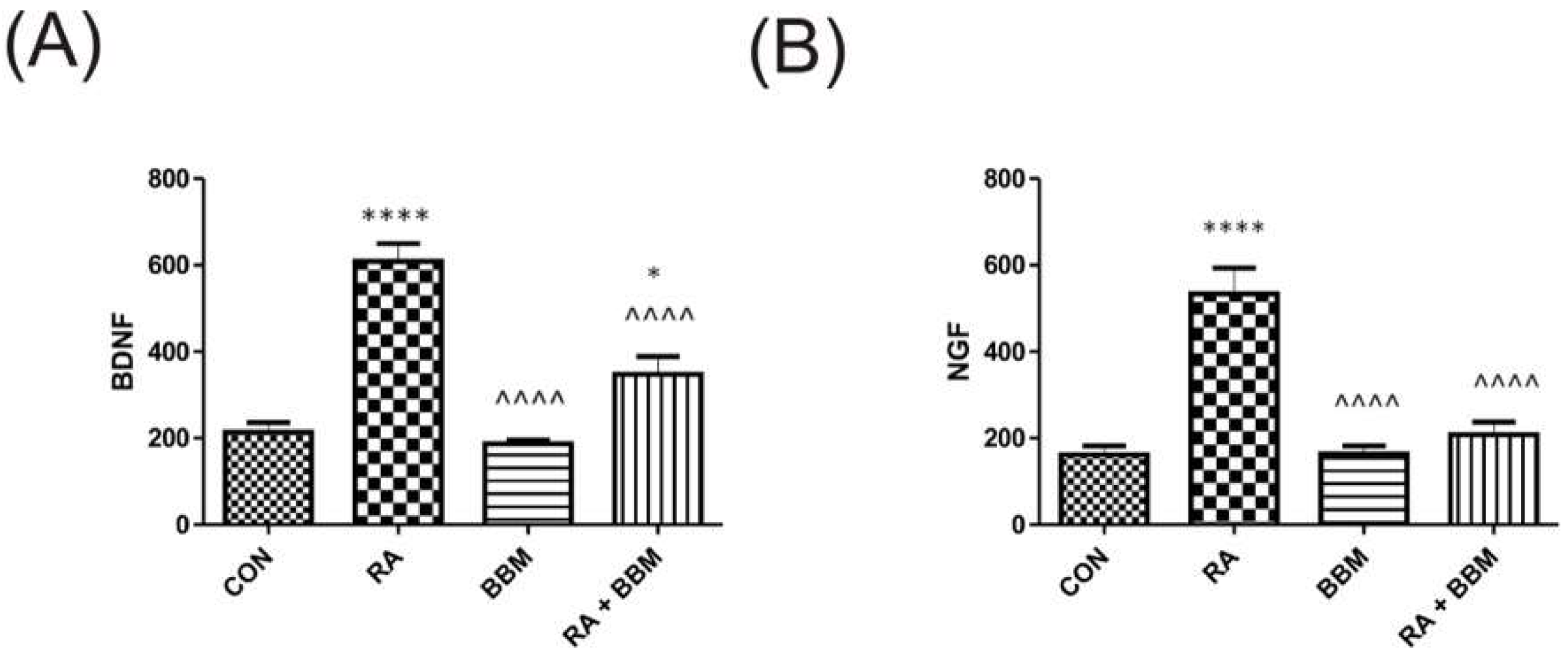
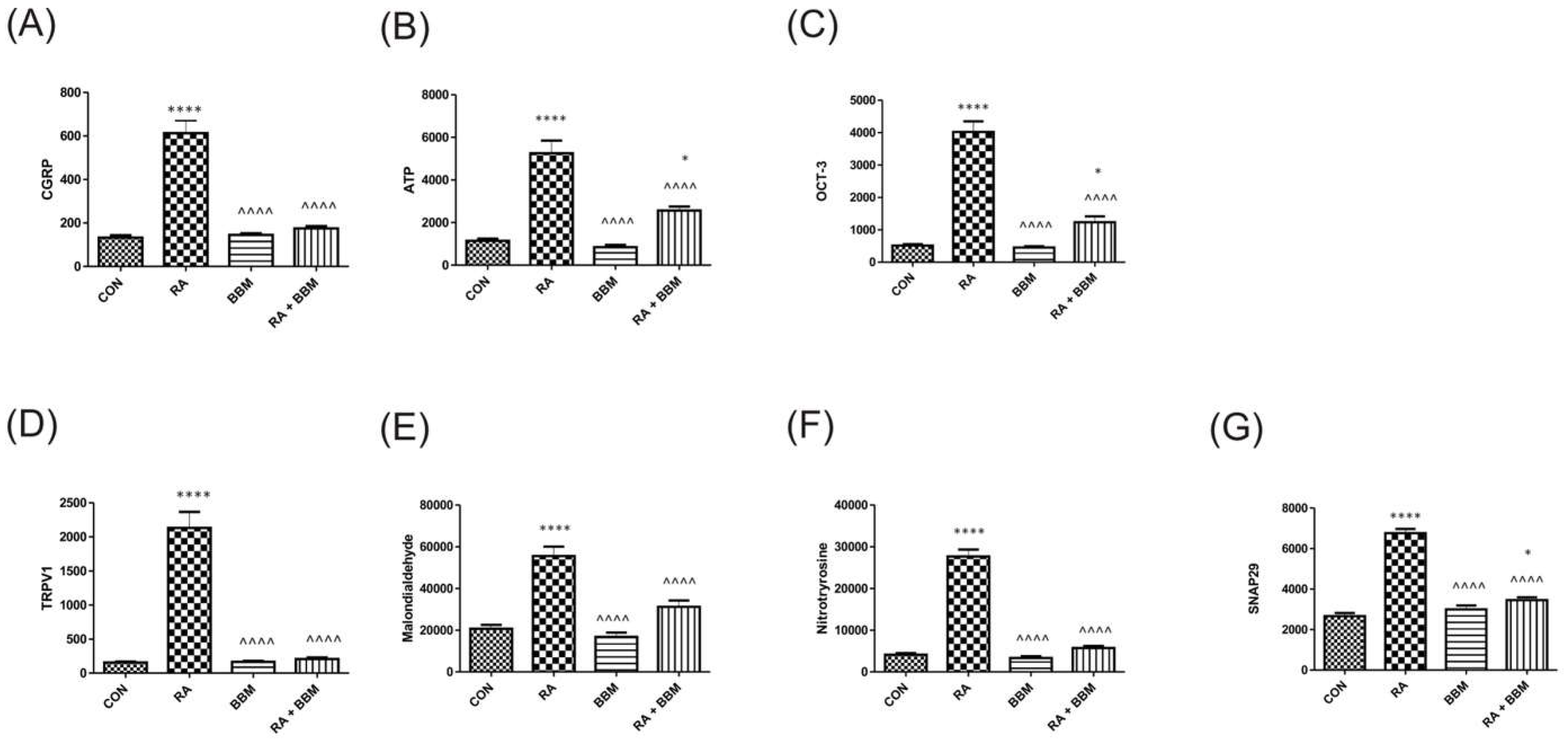
3.5. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Biochemical Analyses of Biomarkers in Urine
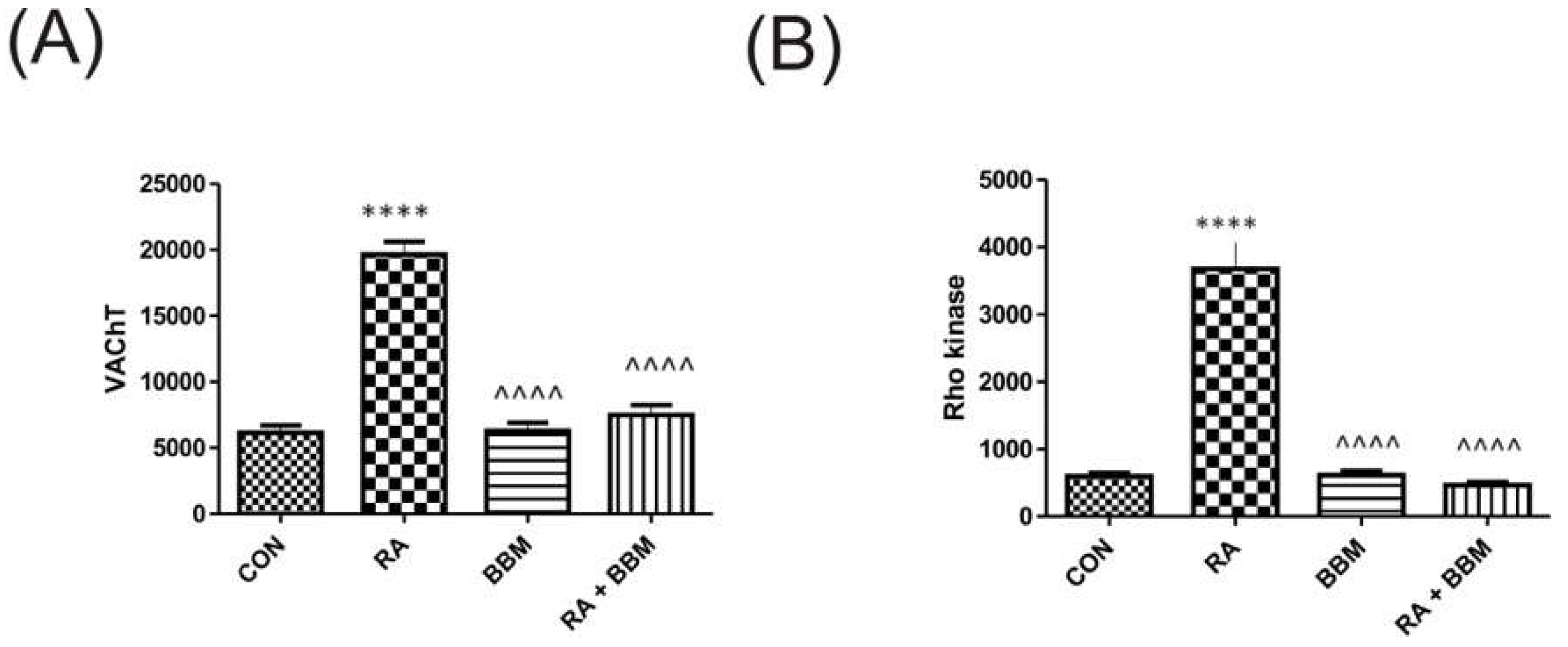
3.6. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Biochemical Analyses of Biomarkers in the Bladder Detrusor Muscle
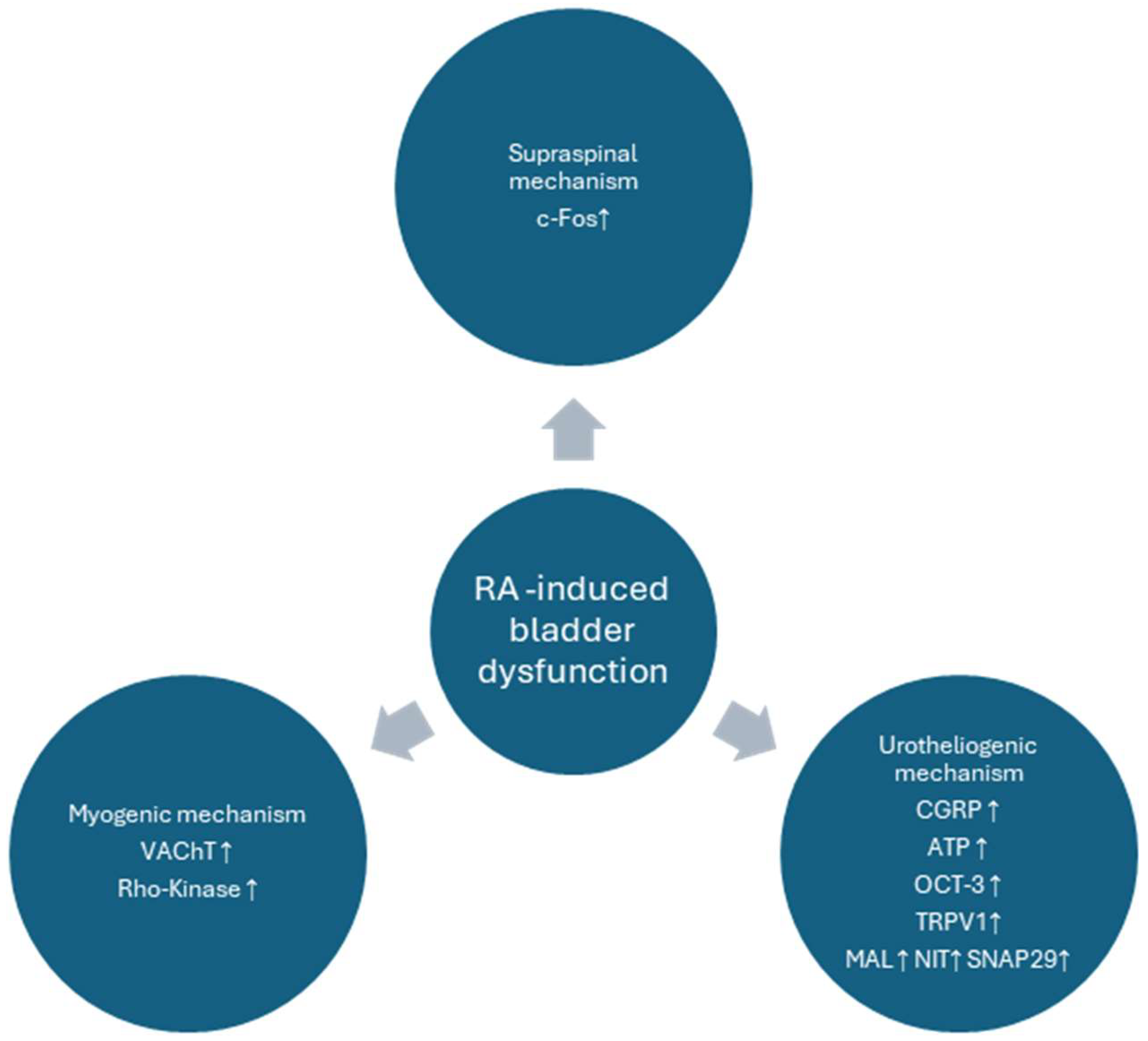
3.7. The Effects of BBM on RA-Induced Changes in the Biochemical Analyses of Biomarkers in the Bladder Urothelium
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANVC | nonvoiding contractions amplitude (cm H2O) |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate (pg/mL) |
| AUC | the area under the pressure curve (cm H2O/s) |
| BBF | bladder blood flow (color scale) |
| BBM | berbamine |
| BC | bladder compliance (mL/cm H2O) |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor (pg/mL) |
| BP | basal pressure (cm H2O) |
| c-Fos | AP-1 transcription factor subunit (pg/mL) |
| CGRP | Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (pg/mL) |
| DO | detrusor overactivity |
| DOI | detrusor overactivity index (cm H2O/mL) |
| FNVC | nonvoiding contractions frequency (times/filling phase) |
| HR | heart rate (beats/min) |
| ICI | intercontraction interval (s) |
| MAL | Malondialdehyde (pg/mL) |
| MAP | arterial pressure (mm Hg) |
| MPA | medial preoptic area |
| MVP | micturition voiding pressure (cm H2O) |
| NGF | nerve growth factor (pg/mL) |
| NIT | 3-Nitrotyrosine (pg/mL) |
| OAB | overactive bladder syndrome |
| OCT3 | Organic Cation Transporter 3 (pg/mL) |
| PMC | pontine micturition center |
| PVR | post-void residual (mL) |
| ROCK | rho kinase (pg/mL) |
| SNAP-29 | Rat Synaptosome Associated Protein 29 |
| TP | threshold pressure (cm H2O) |
| TRPV1 | Transient Receptor Potential Cation Channel Subfamily V, Member 1 |
| UP | urine production (mL/day) |
| VAChT | vesicular acetylcholine transporter (pg/mL) |
| vlPAG | ventrolateral periaqueductal gray |
| VTNVC | volume threshold to elicit NVC (%) |
| VV | voided volume (mL) |
References
- Irwin, D.E.; Milsom, I.; Hunskaar, S.; Reilly, K.; Kopp, Z.; Herschorn, S.; Coyne, K.; Kelleher, C.; Hampel, C.; Artibani, W.; et al. Population-based survey of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and other lower urinary tract symptoms in five countries: Results of the EPIC study. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 1306–1314; discussion 1314–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milsom, I.; Kaplan, S.A.; Coyne, K.S.; Sexton, C.C.; Kopp, Z.S. Effect of bothersome overactive bladder symptoms on health-related quality of life, anxiety, depression, and treatment seeking in the United States: Results from EpiLUTS. Urology 2012, 80, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, M.P.; Ciortea, R.; Malutan, A.M.; Doumouchtsis, S.K.; Bucuri, C.E.; Clim, A.; Roman, A.; Mihu, D. The profile of urinary biomarkers in overactive bladder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, P.; Wagg, A. Overactive bladder: Strategies to ensure treatment compliance and adherence. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lua, L.L.; Pathak, P.; Dandolu, V. Comparing anticholinergic persistence and adherence profiles in overactive bladder patients based on gender, obesity, and major anticholinergic agents. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, B.; Kavaler, E.; Lee, R.; Te, A.; Kaplan, S.A.; Lowe, F. Use of herbal supplements for overactive bladder. Rev. Urol. 2013, 15, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Ma, J.; Chen, K.; Wang, K.; Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Berbamine ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by inhibiting peptidyl-arginine deiminase 4-dependent neutrophil extracellular traps formation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 975, 176634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Anand, S.K.; Singh, N.; Dwivedi, U.N.; Kakkar, P. Berbamine induced AMPK activation regulates mTOR/SREBP-1c axis and Nrf2/ARE pathway to allay lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in steatotic HepG2 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 882, 173244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Barclay, D.; Zamora, R.; Yoshimura, N.; Peters, K.; Vodovotz, Y.; Chancellor, M. Urine cytokines suggest an inflammatory response in the overactive bladder: A pilot study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2010, 42, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Shen, X.; Yu, B.; Tao, L.; Wang, S. Proliferation, migration and invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells are suppressed by berbamine via the PI3K/Akt/MDM2/p53 and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, T.; Fu, R.; Peng, Y.; Jing, P.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Shu, Z.; Yin, Y.; et al. Combination of Detoxified Pneumolysin Derivative DeltaA146Ply and Berbamine as a Treatment Approach for Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2020, 18, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampogu, S.; Balasubramaniyam, T.; Lee, J.H. Phytotherapeutic applications of alkaloids in treating breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 155, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooqi, A.A.; Wen, R.; Attar, R.; Taverna, S.; Butt, G.; Xu, B. Regulation of Cell-Signaling Pathways by Berbamine in Different Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Kang, W.; Wei, C.; Ma, H.; Wang, M.; Jin, X. Berbamine Suppresses the Progression of Bladder Cancer by Modulating the ROS/NF-kappaB Axis. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 8851763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Abdel Aziz, I.; Cheng, W.; Liu, H. Iron oxide-alginate-berbamine nanocomposites trigger reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of PI3K/AKT signaling in human bladder cancer cells. Process Biochem. 2022, 122, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virginio, C.; Graziani, F.; Terstappen, G.C. Differential inhibition of rat alpha3* and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by tetrandrine and closely related bis-benzylisoquinoline derivatives. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 381, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toler, S.M.; Yohannes, D.; Lippiello, P.M.; Chancellor, M.B. Anticholinergic therapy for overactive bladder: A nicotinic modality? Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, A.; Lancut, M.; Rechberger, T. A new model of detrusor overactivity in conscious rats induced by retinyl acetate instillation. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2015, 74, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, A.; Juszczak, K.; Adamowicz, J.; Drewa, T.; Dudka, J. The influence of Potentilla chinensis aqueous extract on urinary bladder function in retinyl acetate-induced detrusor overactivity in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.W.; Seow, W.K.; Thong, Y.H. Comparative effects of tetrandrine and berbamine on acute and relapsing experimental allergic encephalitis in Lewis rats. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1992, 97, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, S.; Baskaran, R.; Poornima, P.; Vijaya Padma, V. Berbamine ameliorates isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction by inhibiting mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in rats. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 3101–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, A.; Rechberger, T. The effect of combined treatment with a beta3 AR agonist and a ROCK inhibitor on detrusor overactivity. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.C.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, S.I.; Lee, S.Y.; Tak, Y.K.; Choi, C.W.; Yun, S.; Park, J.; Lee, M.; Chung, H.K.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Urothelium of Rats with Detrusor Overactivity Induced by Bladder Outlet Obstruction. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2018, 17, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.E.; Shin, M.S.; Kim, C.J.; Park, J.H.; Chung, K.J.; Jung, H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, I.G. Effects of Tamsulosin on Urinary Bladder Function and Neuronal Activity in the Voiding Centers of Rats with Cyclophosphamide-induced Overactive Bladder. Int. Neurourol. J. 2012, 16, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, B.A.; Drake, M.J. Animal models in overactive bladder research. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2011, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyronnet, B.; Mironska, E.; Chapple, C.; Cardozo, L.; Oelke, M.; Dmochowski, R.; Amarenco, G.; Game, X.; Kirby, R.; Van Der Aa, F.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Overactive Bladder Pathophysiology: On the Way to Tailored Treatment. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camoes, J.; Coelho, A.; Castro-Diaz, D.; Cruz, F. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Aging: The Impact of Chronic Bladder Ischemia on Overactive Bladder Syndrome. Urol. Int. 2015, 95, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.G.; Robertson, H.A. Activation of c-fos in the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1996, 50, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstege, G. Micturition and the soul. J. Comp. Neurol. 2005, 493, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontani, H.; Ueda, Y. A method for producing overactive bladder in the rat and investigation of the effects of GABAergic receptor agonists and glutamatergic receptor antagonists on the cystometrogram. J. Urol. 2005, 173, 1805–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Lopes, T.; Cruz, F. Urinary Biomarkers in Overactive Bladder: Revisiting the Evidence in 2019. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochodnicky, P.; Cruz, C.D.; Yoshimura, N.; Cruz, F. Neurotrophins as regulators of urinary bladder function. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2012, 9, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Chancellor, M.B.; Kuo, H.C. Decrease of urinary nerve growth factor levels after antimuscarinic therapy in patients with overactive bladder. BJU Int. 2009, 103, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.S.; Jen, P.Y.; Gosling, J.A. The distribution of vesicular acetylcholine transporter in the human male genitourinary organs and its co-localization with neuropeptide Y and nitric oxide synthase. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2000, 19, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Fleming, L.L.; Wood, C.; Vaughan, S.K.; Gomes, M.P.; Camargo, W.; Naves, L.A.; Prado, V.F.; Prado, M.A.; Guatimosim, C.; et al. VAChT overexpression increases acetylcholine at the synaptic cleft and accelerates aging of neuromuscular junctions. Skelet. Muscle 2016, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, M.P.; Pore, S.K.; de Groat, W.C.; Chermansky, C.J.; Yoshimura, N.; Tyagi, P. BDNF overexpression in the bladder induces neuronal changes to mediate bladder overactivity. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 315, F45–F56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, H.; Borsodi, K.; Orsy, P.; Horvath, B.; Molnar, P.J.; Lenart, A.; Kosztelnik, M.; Ruisanchez, E.; Wess, J.; Offermanns, S.; et al. Intracellular signaling pathways of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated detrusor muscle contractions. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2023, 325, F618–F628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, K.E.; de Groat, W.C.; McVary, K.T.; Lue, T.F.; Maggi, M.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Wyndaele, J.J.; Melby, T.; Viktrup, L. Tadalafil for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: Pathophysiology and mechanism(s) of action. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2011, 30, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnama’i, M.S.; Biallosterski, B.T.; Van Kerrebroeck, P.E.; van Koeveringe, G.A.; Gillespie, J.I.; de Wachter, S.G. Distribution and sub-types of afferent fibre in the mouse urinary bladder. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 79, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnegelsberg, B.; Sun, T.T.; Cain, G.; Bhattacharya, A.; Nunn, P.A.; Ford, A.P.; Vizzard, M.A.; Cockayne, D.A. Overexpression of NGF in mouse urothelium leads to neuronal hyperinnervation, pelvic sensitivity, and changes in urinary bladder function. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R534–R547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna-Mitchell, A.T.; Beckel, J.M.; Barbadora, S.; Kanai, A.J.; de Groat, W.C.; Birder, L.A. Non-neuronal acetylcholine and urinary bladder urothelium. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 2298–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Masunaga, K.; Satoji, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Nagata, T.; Inadome, A. Basic and clinical aspects of non-neuronal acetylcholine: Expression of non-neuronal acetylcholine in urothelium and its clinical significance. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 106, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birder, L.A.; Wolf-Johnston, A.S.; Sun, Y.; Chai, T.C. Alteration in TRPV1 and Muscarinic (M3) receptor expression and function in idiopathic overactive bladder urothelial cells. Acta Physiol. 2013, 207, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.; Chueh, K.S.; Chuang, S.M.; Long, C.Y.; Lu, J.H.; Juan, Y.S. Bladder Hyperactivity Induced by Oxidative Stress and Bladder Ischemia: A Review of Treatment Strategies with Antioxidants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ArnsrudGodtman, R.; Hallsberg, L.; Lof-Ohlin, Z.; Peeker, R.; Delbro, D. Constitutive expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in healthy rat urothelium? Scand. J. Urol. 2021, 55, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.Y.; Lu, J.H.; Lin, R.J.; Chueh, K.S.; Juan, T.J.; Mao, J.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Chuang, S.M.; Shen, M.C.; Sun, T.W.; et al. Effects of Nitric Oxide on Bladder Detrusor Overactivity through the NRF2 and HIF-1alpha Pathways: A Rat Model Induced by Metabolic Syndrome and Ovarian Hormone Deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Chen, S.H.; Chancellor, M.B.; Kuo, H.C. Presence of Cleaved Synaptosomal-Associated Protein-25 and Decrease of Purinergic Receptors P2X3 in the Bladder Urothelium Influence Efficacy of Botulinum Toxin Treatment for Overactive Bladder Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Emoto, M.; Fukuda, N.; Nomiyama, R.; Yamada, K.; Tanizawa, Y. SNARE-binding protein synaptosomal-associated protein of 29 kDa (SNAP29) regulates the intracellular sequestration of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) vesicles in adipocytes. J. Diabetes Investig. 2023, 14, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| CONTROL | RA | BBM | RA + BBM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage phase | ||||
| BP | 3.0 ± 0.62 | 5.6 ± 1.3 **** | 2.9 ± 0.73 ^^^^ | 3.3 ± 1.3 ^^^^ |
| TP | 9 ± 2.4 | 5.3 ± 1.6 **** | 8.8 ± 1.9 ^^^^ | 7.9 ± 2.1 ^^ |
| DOI | 38 ± 22 | 320 ± 150 **** | 41 ± 17 ^^^^ | 131 ± 30 *^^^^ |
| FNVC | 0.41 ± 0.25 | 4.7 ± 1.6 **** | 0.57 ± 0.3 ^^^^ | 1.3 ± 0.72 *^^^^ |
| VTNC | 63 ± 14 | 32 ± 6.7 **** | 66 ± 20 ^^^^ | 45 ± 12 ** |
| ANVC | 2.8 ± 0.65 | 5.6 ± 1.5 **** | 3.1 ± 0.79 ^^^^ | 4.3 ± 1.2 **^^ |
| BC | 0.53 ± 0.17 | 0.32 ± 0.11 ** | 0.47 ± 0.11 | 0.52 ± 0.17 ^^^^ |
| Voiding phase | ||||
| MVP | 45 ± 6.5 | 42 ± 8.8 | 41 ± 9.5 | 43 ± 8.9 |
| ICI | 1110 ± 172 | 693 ± 159 *** | 1089 ± 174 ^^^^ | 914 ± 181 *^^ |
| VV | 0.90 ± 0.059 | 0.57 ± 0.19 *** | 0.90 ± 0.13 ^^^^ | 0.84 ± 0.19 ^^^^ |
| PVR | 0.078 ± 0.012 | 0.082 ± 0.012 | 0.072 ± 0.017 | 0.078 ± 0.016 |
| AUC | 16 ± 4.0 | 23 ± 3.3 **** | 18 ± 3.9 ^^ | 19 ± 4.1 ^ |
| CON | RA | BBM | RA + BBM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAP (mm Hg) | 139 ± 14 | 149 ± 16 | 136 ± 16 | 143 ± 8.8 |
| HR (beats/min) | 236 ± 19 | 218 ± 24 | 222 ± 33 | 234 ± 30 |
| UP (mL/day) | 21 ± 2.7 | 20 ± 2.7 | 23 ± 4.0 | 22 ± 2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wróbel, J.; Zapała, Ł.; Niemczyk, G.; Poleszak, E.; Dobrowolski, P.; Kluz, T.; Bogaczyk, A.; Jasielski, P.; Wdowiak, A.; Bojar, I.; et al. The Efficacy of an Active Medicinal Alkaloid, Berbamine, in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in a Retinyl Acetate-Induced Model. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020190
Wróbel J, Zapała Ł, Niemczyk G, Poleszak E, Dobrowolski P, Kluz T, Bogaczyk A, Jasielski P, Wdowiak A, Bojar I, et al. The Efficacy of an Active Medicinal Alkaloid, Berbamine, in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in a Retinyl Acetate-Induced Model. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(2):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020190
Chicago/Turabian StyleWróbel, Jan, Łukasz Zapała, Grzegorz Niemczyk, Ewa Poleszak, Piotr Dobrowolski, Tomasz Kluz, Anna Bogaczyk, Patryk Jasielski, Artur Wdowiak, Iwona Bojar, and et al. 2025. "The Efficacy of an Active Medicinal Alkaloid, Berbamine, in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in a Retinyl Acetate-Induced Model" Biomolecules 15, no. 2: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020190
APA StyleWróbel, J., Zapała, Ł., Niemczyk, G., Poleszak, E., Dobrowolski, P., Kluz, T., Bogaczyk, A., Jasielski, P., Wdowiak, A., Bojar, I., Misiek, M., & Wróbel, A. (2025). The Efficacy of an Active Medicinal Alkaloid, Berbamine, in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in a Retinyl Acetate-Induced Model. Biomolecules, 15(2), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15020190









