Targeting the Reactive Proteome: Recent Advances in Activity-Based Protein Profiling and Probe Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ABPP and Its Advanced Platforms
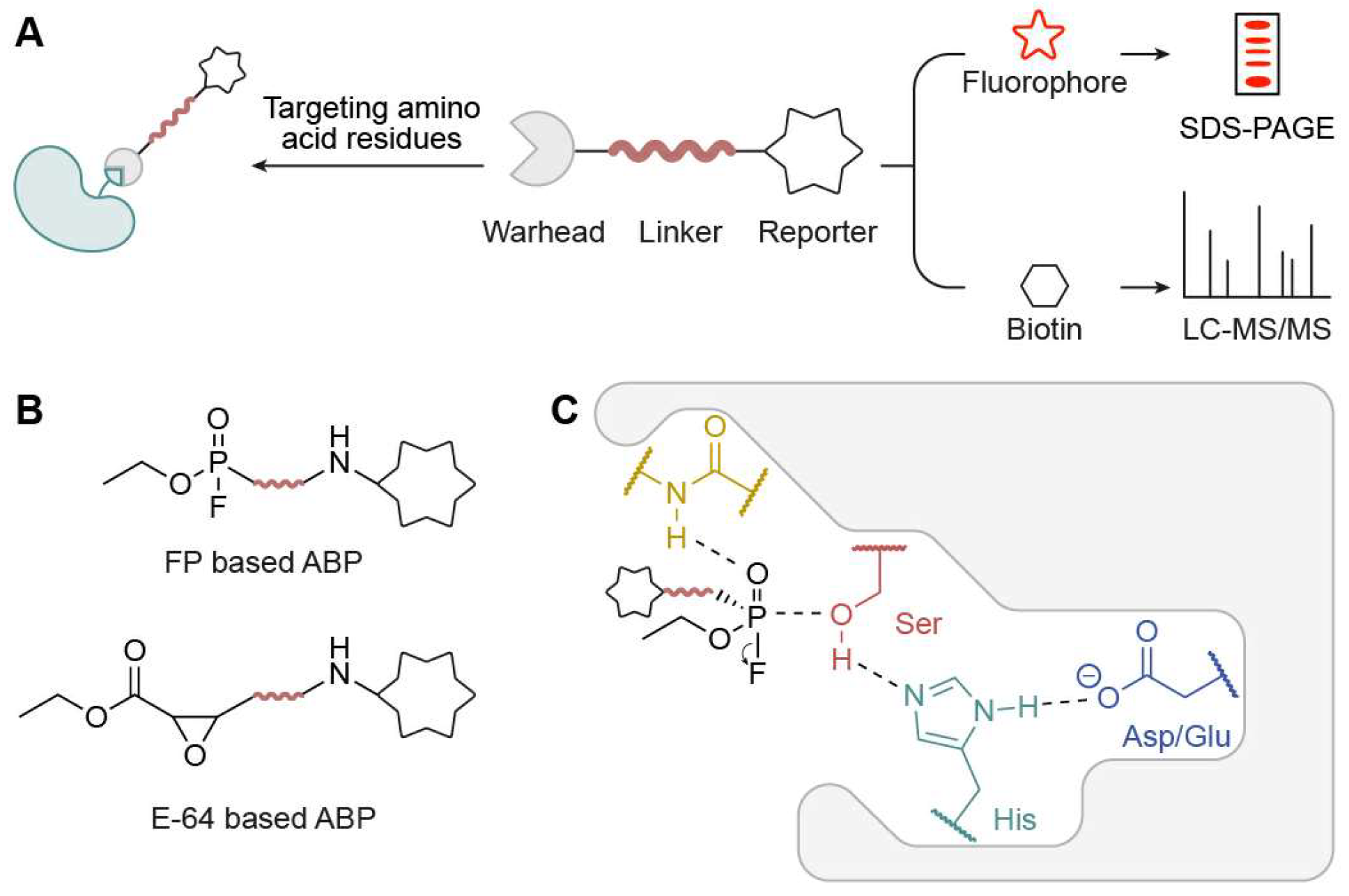
2.1. Basic Form of ABPP
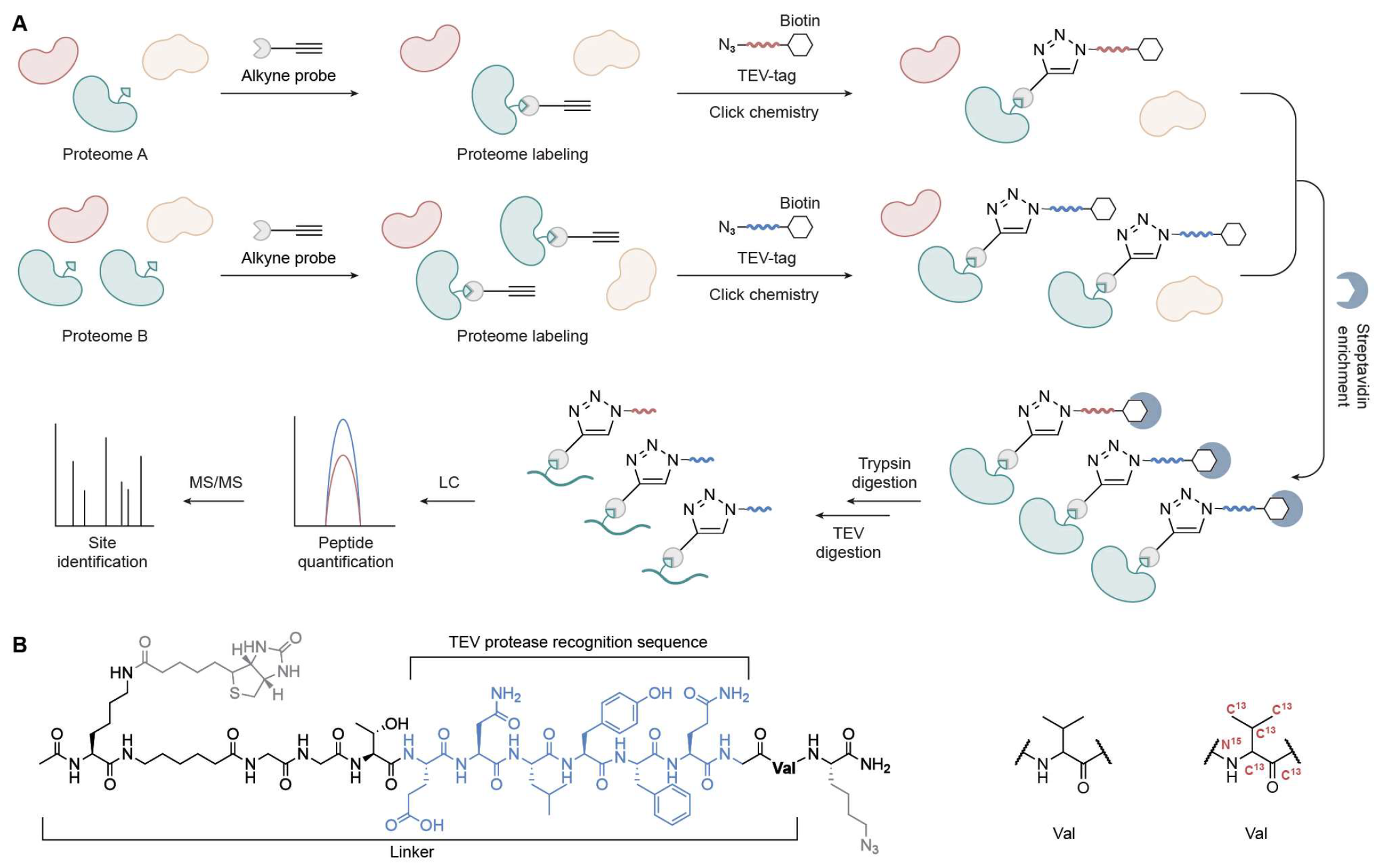
2.2. TOP-ABPP
2.3. IsoTOP-ABPP and Competitive IsoTOP-ABPP
2.4. Other Platforms
3. Design of Reactive Warheads
3.1. Design of Residue-Specific Activity-Based Warheads
3.1.1. Cysteine (Cys)-Specific Warheads
Nucleophilic-Substitution-Based Warheads
Nucleophilic-Addition-Based Warheads
Disulfide-Bond-Based Warheads
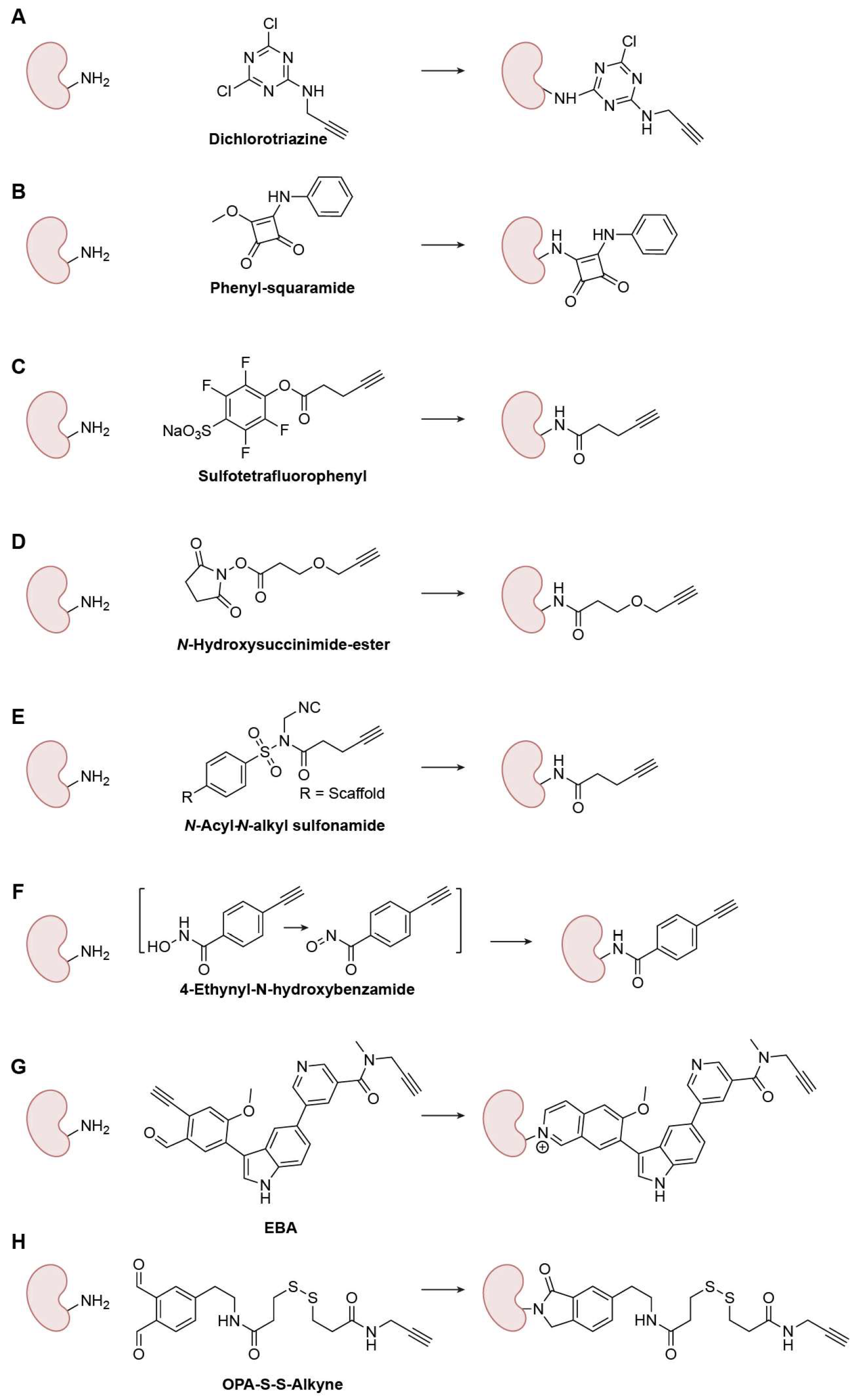
3.1.2. Lysine (Lys)-Specific Warheads
Nucleophilic-Substitution-Based Warheads
Amide-Bond-Based Warheads
Imine-Based Warheads
3.1.3. Histidine (His)-Specific Warheads
Nucleophilic-Substitution-Based Warheads
Nucleophilic-Addition-Based Warheads
Oxidation-Based Warheads
3.1.4. Glutamic Acid (Glu)/Aspartic Acid (Asp)-Specific Warheads
3.1.5. Warheads Specific to Other Amino Acids
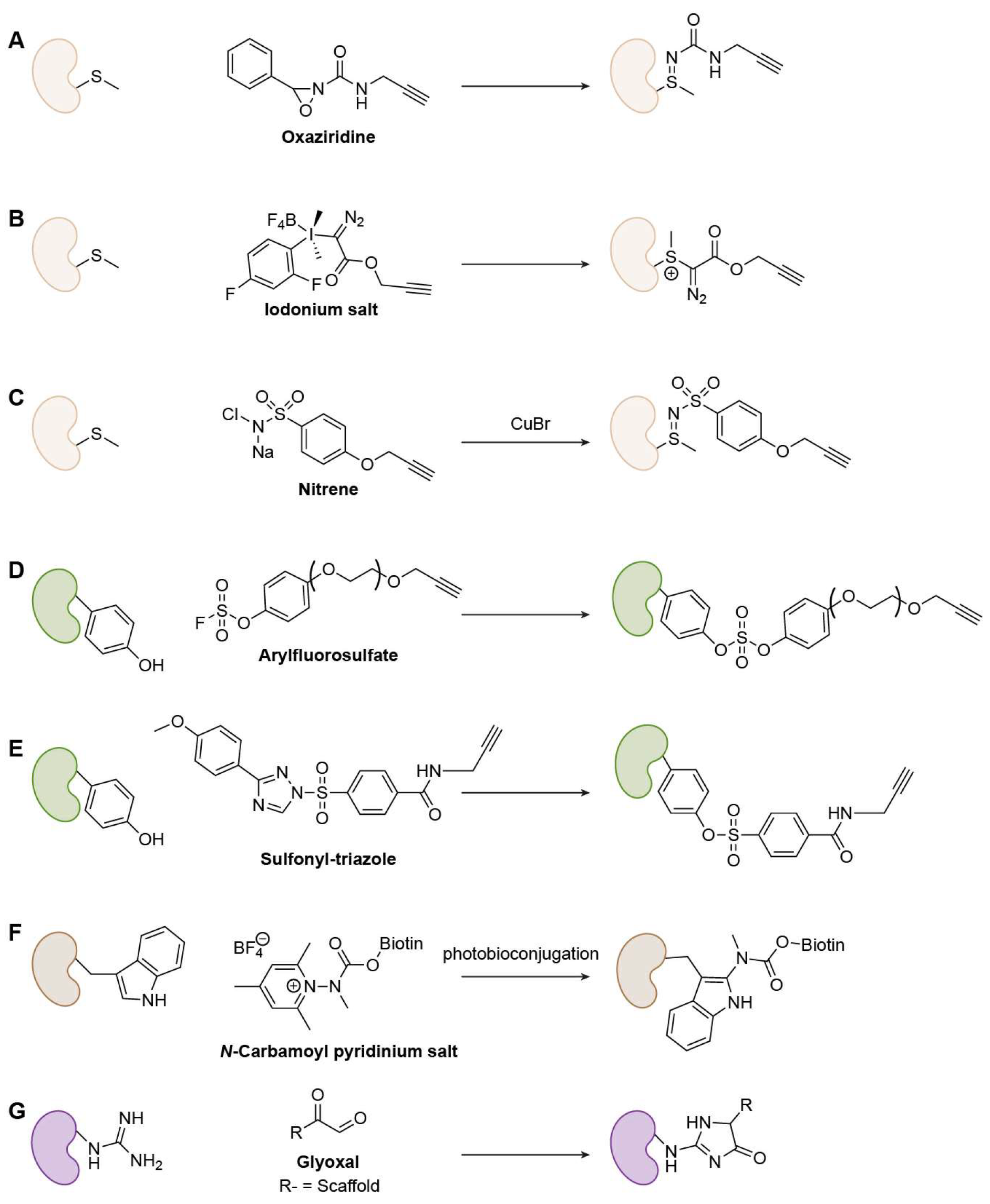
Methionine (Met)-Specific Warheads
Tyrosine (Tyr)-Specific Warheads
Tryptophan (Trp)-Specific Warheads
Arginine (Arg)-Specific Warheads
3.1.6. Outlook for Amino-Acid-Specific Warheads
3.2. Design of Photoaffinity-Labelling (PAL) Probe
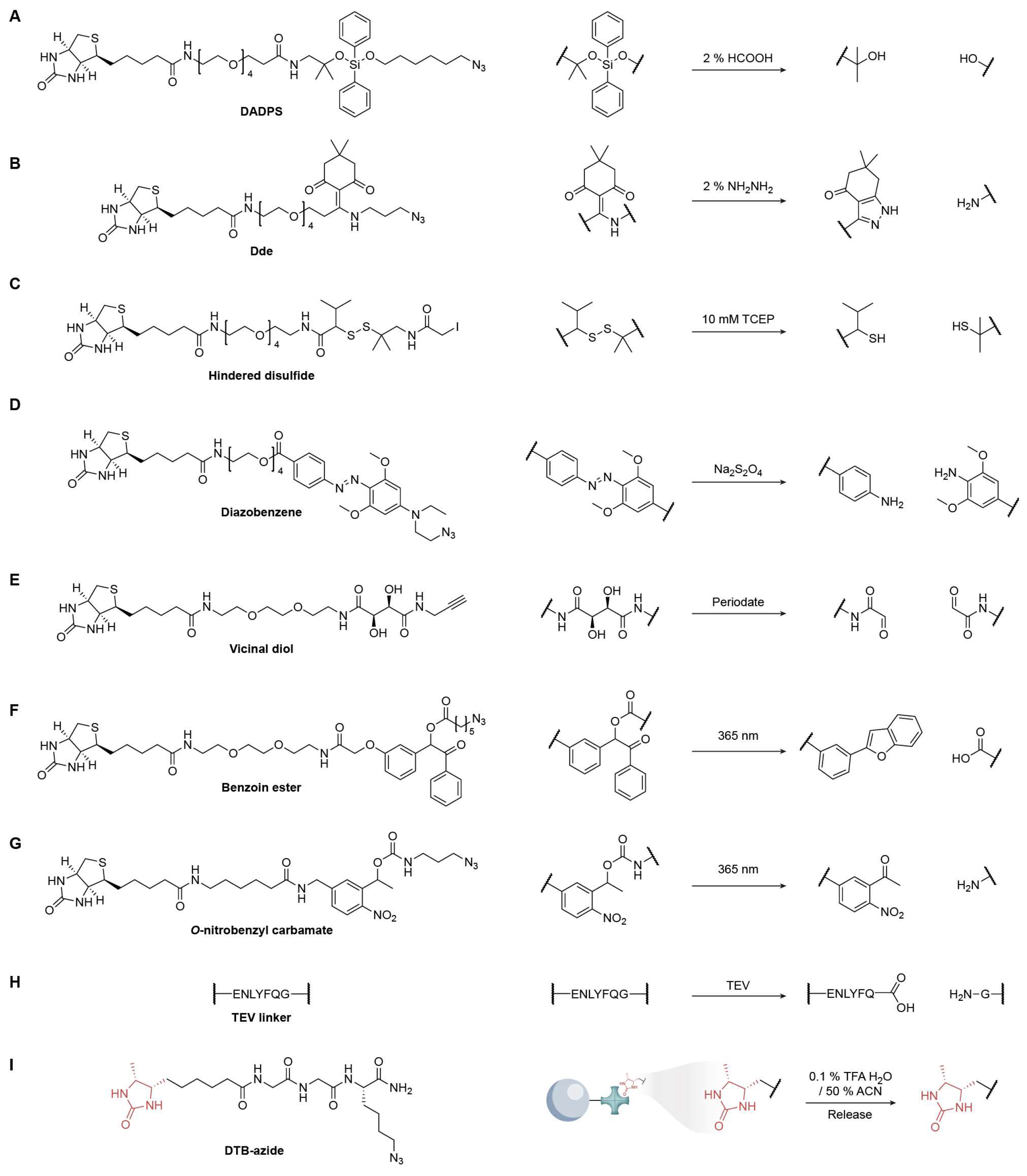
4. Design of Cleavable Linkers
4.1. Acid/Base-Mediated Cleavable Linkers
4.2. Reduction/Oxidation-Mediated Cleavable Linkers
4.3. Photo-Irradiation-Mediated Cleavable Linkers
4.4. Chemoenzymatic Cleavage Linkers
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABPP | Activity-Based Protein Profiling |
| ABP | Activity-Based Probe |
| AI/ML | Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning |
| TOP-ABPP | Tandem Orthogonal Proteolysis–ABPP |
| IsoTOP-ABPP | Isotopic Tandem Orthogonal Proteolysis–ABPP |
| CuAAC | Copper-Catalyzed Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition |
| TEV | Tobacco Etch Virus Protease |
| PAL | Photoaffinity Labeling |
| AfBP(s) | Affinity-Based Probe(s) |
| DADPS | Dialkoxydiphenylsilane |
| Dde | [1-(4,4-Dimethyl-2,6-dioxocyclohex-1-ylidene)ethyl] (Removable Linker) |
| Lev | Levulinoyl (Hydrazine-Cleavable Linker) |
| TCEP | Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine |
| DTT | Dithiothreitol |
| oNB | o-Nitrobenzyl (photocage/linker) |
| HNE | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
| ReACT | Redox-Activated Chemical Tagging |
| CuNiP | Cu(I)-Nitrene Platform |
| SuFEx | Sulfur Fluoride Exchange |
| SuTEx | Sulfur–Triazole Exchange |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| IA-alkyne | Iodoacetamide–alkyne |
| LDE(s) | Lipid-Derived Electrophile(s) |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic Acid |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| PALBOX | Cyclobutane Diazirine Photoaffinity Tag |
| R (ratio) | Light/Heavy Intensity Ratio in IsoTOP-ABPP Quantification |
References
- Go, Y.-M.; Chandler, J.D.; Jones, D.P. The Cysteine Proteome. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, D.K.; Dix, M.M.; Cravatt, B.F. Activity-Based Protein Profiling for Biochemical Pathway Discovery in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.M.; Ward, C.C.; Nomura, D.K. Activity-based protein profiling for mapping and pharmacologically interrogating proteome-wide ligandable hotspots. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speers, A.E.; Cravatt, B.F. A Tandem Orthogonal Proteolysis Strategy for High-Content Chemical Proteomics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 10018–10019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravatt, B.F.; Wright, A.T.; Kozarich, J.W. Activity-Based Protein Profiling: From Enzyme Chemistry to Proteomic Chemistry. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 383–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerapana, E.; Speers, A.E.; Cravatt, B.F. Tandem Orthogonal Proteolysis-Activity-Based Protein Profiling (TOP-ABPP)—A General Method for Mapping Sites of Probe Modification in Proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Whitehouse, R.L.; Dawson, S.L.; Zhang, L.; Martin, J.G.; Johnson, D.S.; Paulo, J.A.; Gygi, S.P.; Yu, Q. Accelerating multiplexed profiling of protein–ligand interactions: High-throughput plate-based reactive cysteine profiling with minimal input. Cell Chem. Biol. 2024, 31, 565–576.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærsgaard, N.L.; Jensen, P.F.; Jørgensen, M.; Bøggild, A.; Nielsen, T.E.; Daugaard, M.; Diness, F. Chemical Conjugation to Less Targeted Proteinogenic Amino Acids. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202200245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, N.R.; Kim, P.; Backus, K.M. Photoaffinity Labelling Strategies for Mapping the Small Molecule–Protein Interactome. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 7792–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Patricelli, M.P.; Cravatt, B.F. Activity-Based Protein Profiling: The Serine Hydrolases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14694–14699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Burlingame, A.; Bogyo, M. Epoxide Electrophiles as Activity-Dependent Cysteine Protease Profiling and Discovery Tools. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise Huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2596–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornøe, C.W.; Christensen, C.; Meldal, M. Peptidotriazoles on solid phase: [1,2,3]-triazoles by regiospecific copper(I)-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions of terminal alkynes to azides. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoopes, C.R.; Garcia, F.J.; Sarkar, A.M.; Kuehl, N.J.; Barkan, D.T.; Collins, N.L.; Meister, G.E.; Bramhall, T.R.; Hsu, C.-H.; Jones, M.D.; et al. Donor–Acceptor Pyridinium Salts for Photo-Induced Electron-Transfer-Driven Modification of Tryptophan in Peptides, Proteins, and Proteomes Using Visible Light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6227–6236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derks, Y.H.W.; Rijpkema, M.; Amatdjais-Groenen, H.I.V.; Loeff, C.C.; de Roode, K.E.; Kip, A.; Laverman, P.; Lütje, S.; Heskamp, S.; Löwik, D.W.P.M. Strain-Promoted Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition-Based PSMA-Targeting Ligands for Multimodal Intraoperative Tumor Detection of Prostate Cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.L.; Guo, Z.; Bernardes, G.J.L. Inverse Electron Demand Diels–Alder Reactions in Chemical Biology. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4895–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerapana, E.; Wang, C.; Simon, G.M.; Richter, F.; Khare, S.; Dillon, M.B.D.; Bachovchin, D.A.; Mowen, K.; Baker, D.; Cravatt, B.F. Quantitative reactivity profiling predicts functional cysteines in proteomes. Nature 2010, 468, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Weerapana, E.; Blewett, M.M.; Cravatt, B.F. A chemoproteomic platform to quantitatively map targets of lipid-derived electrophiles. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Gao, J.; Che, J.; Jia, G.; Wang, C. A Dimethyl-Labeling-Based Strategy for Site-Specifically Quantitative Chemical Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9576–9582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Li, Q.; Cai, L.; Wang, C.; Lei, X. Chemoproteomic profiling of bile acid interacting proteins. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Jia, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Quantitative chemoproteomic profiling with data-independent acquisition-based mass spectrometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, W.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, X. Quantitative Profiling of Protein O-GlcNAcylation Sites by an Isotope-Tagged Cleavable Linker. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, W.P.; Dang, T.H.T.; Tate, E.W. Activity-Based Probes: Discovering New Biology and New Drug Targets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Peng, B.; Ong, S.-Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, L.; Yao, S.Q. Recent Advances in Activity-Based Probes (ABPs) and Affinity-Based Probes (AfBPs) for Profiling of Enzymes. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 8288–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backus, K.M.; Correia, B.E.; Lum, K.M.; Forli, S.; Horning, B.D.; González-Páez, G.E.; Chatterjee, S.; Lanning, B.R.; Teijaro, J.R.; Olson, A.J.; et al. Proteome-Wide Covalent Ligand Discovery in Native Biological Systems. Nature 2016, 534, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.-F.; Yan, B.-C.; Yang, Q.; Long, X.-Y.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Luo, R.-H.; Wang, H.-Y.; Sun, H.-D.; Xue, X.-S.; Zheng, Y.-T.; et al. Harnessing Natural Products by a Pharmacophore-Oriented Semisynthesis Approach for the Discovery of Potential Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridoon; Ng, R.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.J. An Update on the Discovery and Development of Reversible Covalent Inhibitors. Med. Chem. Res. 2023, 32, 1039–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bálint, D.; Póti, Á.L.; Alexa, A.; Sok, P.; Albert, K.; Torda, L.; Földesi-Nagy, D.; Csókás, D.; Turczel, G.; Imre, T.; et al. Reversible Covalent c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitors Targeting a Specific Cysteine by Precision-Guided Michael-Acceptor Warheads. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, N.; Chouchani, E.T. A new era of cysteine proteomics—Technological advances in thiol biology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 79, 102435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boatner, L.M.; Palafox, M.F.; Schweppe, D.K.; Backus, K.M. CysDB: A human cysteine database based on experimental quantitative chemoproteomics. Cell Chem. Biol. 2023, 30, 683–698.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.E.H.; Gil, J.; Tate, E.W. Proteome-wide structural analysis identifies warhead- and coverage-specific biases in cysteine-focused chemoproteomics. Cell Chem. Biol. 2023, 30, 828–838.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Byun, D.P.; Thakur, K.; Ritchie, J.; Xie, Y.; Holewinski, R.; Suazo, K.F.; Stevens, M.; Liechty, H.; Tagirasa, R.; et al. Discovery of a Tunable Heterocyclic Electrophile 4-Chloropyrazolopyridine That Defines a Unique Subset of Ligandable Cysteines. ACS Chem. Biol. 2024, 19, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegg, D.; Tomanik, M.; Qiu, N.; Pechalrieu, D.; Shuster, A.; Commare, B.; Togni, A.; Herzon, S.B.; Adibekian, A. Chemoproteomic Profiling by Cysteine Fluoroalkylation Reveals Myrocin G as an Inhibitor of the Nonhomologous End Joining DNA Repair Pathway. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20332–20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambaldo, C.; Vinogradova, E.V.; Qi, X.; Iaconelli, J.; Suciu, R.M.; Koh, M.; Senkane, K.; Chadwick, S.R.; Sanchez, B.B.; Chen, J.S.; et al. 2-Sulfonylpyridines as Tunable, Cysteine-Reactive Electrophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8972–8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, C.; Yang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T.; Ruan, Z.; Dai, C.; Xing, Y.; Yin, F.; Wang, R.; Li, Z. β-Carbonyl sulfonium enables cysteine-specific bioconjugation for activity-based protein profiling in live cells. Chem. Commun. 2024, 60, 3725–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, D.P.; Ritchie, J.; Jung, Y.; Holewinski, R.; Kim, H.-R.; Tagirasa, R.; Ivanic, J.; Weekley, C.M.; Parker, M.W.; Andresson, T.; et al. Covalent Inhibition by a Natural Product-Inspired Latent Electrophile. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11097–11109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, D.G.; Abegg, D.; Adibekian, A. Cysteine-reactive probes and their use in chemical proteomics. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.-Y.; Lai, H.; Nomura, D.K.; Chung, C.Y.-S. N-Acryloylindole-Alkyne (NAIA) Enables Imaging and Profiling New Ligandable Cysteines and Oxidized Thiols by Chemoproteomics. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, D.; Tian, T.; An, Y.; Wan, C.; Chang, Q.; Liang, M.; Hou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Low-Toxicity Sulfonium-Based Probes for Cysteine-Specific Profiling in Live Cells. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4366–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abegg, D.; Gasparini, G.; Hoch, D.G.; Shuster, A.; Bartolami, E.; Matile, S.; Adibekian, A. Strained cyclic disulfides enable cellular uptake by reacting with the transferrin receptor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, K.M. Applications of Reactive Cysteine Profiling. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 420, 375–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, A.; Taunton, J. Lysine-Targeted Inhibitors and Chemoproteomic Probes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, D.A.; Banerjee, R.; Webster, E.R.; Bak, D.W.; Wang, C.; Weerapana, E. Investigating the Proteome Reactivity and Selectivity of Aryl Halides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3330–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.I.; Ho, J.S.; Trial, H.O.; Carter, A.W.; Kiessling, L.L. Assessing Squarates as Amine-Reactive Probes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 25056–25060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, S.M.; Backus, K.M.; Lazear, M.R.; Forli, S.; Correia, B.E.; Cravatt, B.F. Global Profiling of Lysine Reactivity and Ligandability in the Human Proteome. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, C.C.; Kleinman, J.I.; Nomura, D.K. NHS-Esters as Versatile Reactivity-Based Probes for Mapping Proteome-Wide Ligandable Hotspots. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yang, D.; Song, C.; Liang, M.; An, Y.; Lian, C.; Dai, C.; Ye, Y.; Yin, F.; Wang, R.; et al. A pyridinium-based strategy for lysine-selective protein modification and chemoproteomic profiling in live cells. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 5340–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, B.J.; Ellman, J.A. An alkanesulfonamide “safety-catch” linker for solid-phase synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Ueda, T.; Goto, T.; Tsukidate, T.; Shapira, Y.; Nishikawa, Y.; Fujisawa, A.; Hamachi, I. Rapid Labelling and Covalent Inhibition of Intracellular Native Proteins Using Ligand-Directed N-Acyl-N-Alkyl Sulfonamide. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Tan, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, Z. Global Profiling Lysine Reactivity and Ligandability with Oxidant-Triggered Bioconjugation Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202418473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Tang, G.; Zhu, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Xiang, M.; Huang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.-M.; et al. 2-Ethynylbenzaldehyde-Based, Lysine-Targeting Irreversible Covalent Inhibitors for Protein Kinases and Nonkinases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 3844–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.-R.; Lai, N.C.-H.; Kung, K.K.-Y.; Yang, B.; Chung, S.-F.; Leung, A.S.-L.; Choi, M.-C.; Leung, Y.-C.; Wong, M.-K. N-Terminal Selective Modification of Peptides and Proteins Using 2-Ethynylbenzaldehydes. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, S.; Ji, G.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. A chemical proteomics approach for global mapping of functional lysines on cell surface of living cell. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Khan, S.; Jiang, H.; Antonyak, M.A.; Chen, X.; Spiegelman, N.A.; Shrimp, J.H.; Cerione, R.A.; Lin, H. Identifying the functional contribution of the defatty-acylase activity of SIRT6. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; He, D.; Chang, C.J. Bioinspired Thiophosphorodichloridate Reagents for Chemoselective Histidine Bioconjugation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 7294–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, H.; Tian, K.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G.; Gong, Z.; Qin, H.; et al. ACR-Based Probe for the Quantitative Profiling of Histidine Reactivity in the Human Proteome. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 5252–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peciak, K.; Laurine, E.; Tommasi, R.; Choi, J.; Brocchini, S. Site-Selective Protein Conjugation at Histidine. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z.; Yan, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Global Profiling of Functional Histidines in Live Cells Using Small-Molecule Photosensitizer and Chemical Probe Relay Labelling. Nat. Chem. 2024, 16, 1546–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Sato, S.; Niwa, T.; Tsushima, M.; Tomoshige, S.; Taguchi, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Nakamura, H. Proximity Histidine Labeling by Umpolung Strategy Using Singlet Oxygen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7726–7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, K.; Nagasawa, H.; Fujimura, C.; Koyanagi, E.; Tomoshige, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Sato, S. Switching of Photocatalytic Tyrosine/Histidine Labeling and Application to Photocatalytic Proximity Labeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Fan, Y.; Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, K.; Ye, W.; et al. 2H-Azirine-Based Reagents for Chemoselective Bioconjugation at Carboxyl Residues Inside Live Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6051–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.; Lee, J.-S.; Hao, P.; Yao, S.Q.; Ding, K.; Li, Z. Tetrazole-Based Probes for Integrated Phenotypic Screening, Affinity-Based Proteome Profiling, and Sensitive Detection of a Cancer Biomarker. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15044–15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach, K.; Beerkens, B.L.H.; Zanon, P.R.A.; Hacker, S.M. Light-Activatable, 2,5-Disubstituted Tetrazoles for the Proteome-Wide Profiling of Aspartates and Glutamates in Living Bacteria. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Schürmann, M.; Janning, P.; Hedberg, C.; Waldmann, H. Activity-Based Proteome Profiling Probes Based on Woodward’s Reagent K with Distinct Target Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7766–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Gago, P.; Fansa, E.K.; Winzker, M.; Murarka, S.; Janning, P.; Schultz-Fademrecht, C.; Baumann, M.; Wittinghofer, A.; Waldmann, H. Covalent Protein Labeling at Glutamic Acids. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 589–597.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Sun, P.; Li, Z. Ynamide Coupling Reagent for the Chemical Cross-Linking of Proteins in Live Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; He, X.; Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, K.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z. Simultaneous Covalent Modification of K-Ras(G12D) and K-Ras(G12C) with Tunable Oxirane Electrophiles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 20403–20411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, X.; Jia, S.; Weeks, A.M.; Hornsby, M.; Lee, P.S.; Nichiporuk, R.V.; Iavarone, A.T.; Wells, J.A.; Toste, F.D.; et al. Redox-Based Reagents for Chemoselective Methionine Bioconjugation. Science 2017, 355, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.T.; Nelson, J.E.; Suero, M.G.; Gaunt, M.J. A Protein Functionalization Platform Based on Selective Reactions at Methionine Residues. Nature 2018, 562, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.; Emenike, B.; Beusch, C.M.; Bagchi, P.; Gordon, D.E.; Raj, M. Copper(I)-nitrene platform for chemoproteomic profiling of methionine. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dong, J.; Plate, L.; Mortenson, D.E.; Brighty, G.J.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Galmozzi, A.; Lee, P.S.; Hulce, J.J.; et al. Arylfluorosulfates Inactivate Intracellular Lipid Binding Protein(s) through Chemoselective SuFEx Reaction with a Binding-Site Tyr Residue. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7353–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, H.S.; Toroitich, E.K.; Borne, A.L.; Brulet, J.W.; Libby, A.H.; Yuan, K.; Ware, T.B.; McCloud, R.L.; Ciancone, A.M.; Hsu, K.-L. Global Targeting of Functional Tyrosines Using Sulfur Triazole Exchange Chemistry. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tower, S.J.; Hetcher, W.J.; Myers, T.E.; Kuehl, N.J.; Zakharov, L.N.; Yates, M.V.; Mayer, J.M.; Devaraj, N.K.; Taylor, M.T. Selective Modification of Tryptophan Residues in Peptides and Proteins Using a Biomimetic Electron Transfer Process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9112–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Miao, F.; Wang, Z.; Yang, F.; Xiang, M.; Gu, M.; Li, S.; et al. Cell-Active, Arginine-Targeting Irreversible Covalent Inhibitors for Non-Kinases and Kinases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202422372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, L.; Emenike, B.; Sihag, P.; Shirke, R.; Raj, M. Chemical Carbonylation of Arginine in Peptides and Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 10139–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, P.R.A.; Yu, F.; Musacchio, P.Z.; Lewald, L.; Zollo, M.; Krauskopf, K.; Mrdović, D.; Raunft, P.; Maher, T.E.; Cigler, M.; et al. Profiling the Proteome-Wide Selectivity of Diverse Electrophiles. Nat. Chem. 2025, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo, M.; Weerapana, E. A Caged Electrophilic Probe for Global Analysis of Cysteine Reactivity in Living Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7087–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooden, E.J.; Florea, B.I.; Deng, H.; Baggelaar, M.P.; van Esbroeck, A.C.M.; Zhou, J.; Overkleeft, H.S.; van der Stelt, M. Mapping In Vivo Target Interaction Profiles of Covalent Inhibitors Using Chemical Proteomics with Label-Free Quantification. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, F.; Konno, S.; Uchida, C.; Dairi, T.; Kato, N.; Sato, M. Chemoproteomics Profiling of Surfactin-Producing Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetases in Living Bacterial Cells. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 145–156.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Keller, L.J.; Cordasco, E.; Bogyo, M.; Lentz, C.S. Fluorescent Triazole Urea Activity-Based Probes for the Single-Cell Phenotypic Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, F.; Gu, L.; Wong, Y.K.; Shi, Q.; et al. STEP: Profiling Cellular-Specific Targets and Pathways of Bioactive Small Molecules in Tissues via Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomics and Chemoproteomics. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 4313–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrelly, L.A.; Thompson, R.E.; Zhao, S.; Lepack, A.E.; Lyu, Y.; Bhanu, N.V.; Zhang, B.; Loh, Y.-H.E.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Vadodaria, K.C.; et al. Histone Serotonylation Is a Permissive Modification That Enhances TFIID Binding to H3K4me3. Nature 2019, 567, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guiley, K.Z.; Shokat, K.M. Chemical Acylation of an Acquired Serine Suppresses Oncogenic Signaling of K-Ras(G12S). Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaj, E.; Sindi, S.H.; Tillekeratne, L.M.V. Photoaffinity Labeling and Bioorthogonal Ligation: Two Critical Tools for Designing “Fish Hooks” to Scout for Target Proteins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 62, 116721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinsky, L.; Krom, B.P.; Meijler, M.M. Diazirine Based Photoaffinity Labeling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, E.; Usui, K.; Oonuma, K.; Koshino, H.; Nishiyama, S.; Hirai, G.; Sodeoka, M. Thienyl-Substituted α-Ketoamide: A Less Hydrophobic Reactive Group for Photo-Affinity Labeling. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Qi, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Wang, R.; Liu, Z.; Meng, L.; Ma, N.; et al. Developing Isoxazole as a Native Photo-Cross-Linker for Photoaffinity Labeling and Chemoproteomics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202209947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.V.; Amako, Y.; Woo, C.M. Design and Evaluation of a Cyclobutane Diazirine Alkyne Tag for Photoaffinity Labeling in Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21174–21183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szychowski, J.; Mahdavi, A.; Hodas, J.J.L.; Bagert, J.D.; Ngo, J.T.; Landgraf, P.; Dieterich, D.C.; Schuman, E.M.; Tirrell, D.A. Cleavable Biotin Probes for Labeling of Biomolecules via Azide–Alkyne Cycloaddition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18351–18360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, P.; Yang, J. Benchmarking Cleavable Biotin Tags for Peptide-Centric Chemoproteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Verhelst, S.H.L. Cleavable Trifunctional Biotin Reagents for Protein Labelling, Capture and Release. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 5366–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geurink, P.P.; Florea, B.I.; Li, N.; Witte, M.D.; Verasdonck, J.; Kuo, C.-L.; van der Marel, G.A.; Overkleeft, H.S. A Cleavable Linker Based on the Levulinoyl Ester for Activity-Based Protein Profiling. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6802–6805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustarini, D.; Dalle-Donne, I.; Colombo, R.; Milzani, A.; Rossi, R. Is ascorbate able to reduce disulfide bridges? A cautionary note. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wender, P.A.; Goun, E.A.; Jones, L.R.; Pillow, T.H.; Rothbard, J.B.; Shinde, R.; Contag, C.H. Real-time analysis of uptake and bioactivatable cleavage of luciferin–transporter conjugates in transgenic reporter mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10340–10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellogg, B.A.; Garrett, L.; Kovtun, Y.; Lai, K.C.; Leece, B.; Miller, M.; Payne, G.; Steeves, R.; Whiteman, K.R.; Widdison, W.C.; et al. Disulfide-Linked Antibody–Maytansinoid Conjugates: Optimization of In Vivo Activity by Varying the Steric Hindrance at Carbon Atoms Adjacent to the Disulfide Linkage. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-Y.; Grammel, M.; Raghavan, A.S.; Charron, G.; Hang, H.C. Comparative Analysis of Cleavable Azobenzene-Based Affinity Tags for Bioorthogonal Chemical Proteomics. Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 1212–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hahne, H.; Kuster, B.; Verhelst, S.H.L. A Simple and Effective Cleavable Linker for Chemical Proteomics Applications. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomplun, S.; Shugrue, C.R.; Schmitt, A.M.; Schissel, C.K.; Farquhar, C.E.; Pentelute, B.L. Secondary Amino Alcohols: Traceless Cleavable Linkers for Use in Affinity Capture and Release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11566–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.H.; Tallman, K.A.; Liebler, D.C.; Porter, N.A. An Azido-Biotin Reagent for Use in the Isolation of Protein Adducts of Lipid-Derived Electrophiles by Streptavidin Catch and Photorelease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanon, P.R.A.; Lewald, L.; Hacker, S.M. Isotopically Labeled Desthiobiotin Azide (isoDTB) Tags Enable Global Profiling of the Bacterial Cysteinome. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, C. A Simplified and Ultrafast Pipeline for Site-Specific Quantitative Chemical Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 3360–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, S.; Jia, X.; Gong, Q.; Wen, X.; Lu, W.; Yang, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Suo, Y.; et al. ABPP-CoDEL: Activity-Based Proteome Profiling-Guided Discovery of Tyrosine-Targeting Covalent Inhibitors from DNA-Encoded Libraries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 25283–25292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamata, Y.; Ryu, K.A.; Hermann, G.N.; Sandahl, A.; Vantourout, J.C.; Olow, A.K.; Adams, L.T.A.; Rivera-Chao, E.; Roberts, L.R.; Gnaim, S.; et al. An Electroaffinity Labelling Platform for Chemoproteomic-Based Target Identification. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-F.; Yuan, S.; Ma, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, C. Chemical Proteomic Profiling of Lysine Crotonylation Using Minimalist Bioorthogonal Probes in Mammalian Cells. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Fu, L.; Yang, J.; Carroll, K.S. Wittig Reagents for Chemoselective Sulfenic Acid Ligation Enables Global Site Stoichiometry Analysis and Redox-Controlled Mitochondrial Targeting. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.B.; Fu, L.; Jung, Y.; Yang, J.; Carroll, K.S. Reaction-Based Fluorogenic Probes for Detecting Protein Cysteine Oxidation in Living Cells. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Jung, Y.; Tian, C.; Ferreira, R.B.; Cheng, R.; He, F.; Yang, J.; Carroll, K.S. Nucleophilic Covalent Ligand Discovery for the Cysteine Redoxome. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Carroll, K.S. Activity-Based Sensing for Site-Specific Proteomic Analysis of Cysteine Oxidation. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Buuh, Z.Y.; Gorman, N.; Goldman, A.R.; Islam, M.S.; Tang, H.-Y.; Wang, R.E. Steric-Free Bioorthogonal Labeling of Acetylation Substrates Based on a Fluorine–Thiol Displacement Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Peng, T. A Bioorthogonal Chemical Reporter for the Detection and Identification of Protein Lactylation. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 6019–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufleitner, M.; Haiber, L.M.; Li, S.; Surendran, H.; Mayer, T.U.; Zumbusch, A.; Wittmann, V. Next-Generation Metabolic Glycosylation Reporters Enable Detection of Protein O-GlcNAcylation in Living Cells without S-Glyco Modification. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202320247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gladysz, K.; Fung, Y.M.E.; Tian, G.; Xiong, Y.; Wong, J.W.H.; Yuen, K.W.Y.; Li, X.D. Glutarylation of Histone H4 Lysine 91 Regulates Chromatin Dynamics. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Qin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, W.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, B.; Peng, L.; Chen, N.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; et al. S-Glycosylation-Based Cysteine Profiling Reveals Regulation of Glycolysis by Itaconate. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wei, Q.; Governa, P.; Llanos, M.; Chiu, T.-Y.; Wozniak, J.M.; Jadhav, A.M.; Gathmann, C.; Cravatt, J.; Dongre, A.; et al. Post-Translational Modifications Remodel Proteome-Wide Ligandability. bioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, M.E.; Horning, B.D.; Khattri, R.; Roy, N.; Lu, J.P.; Whitby, L.R.; Ye, E.; Brannon, J.C.; Parker, A.; Chick, J.M.; et al. Selective Inhibitors of JAK1 Targeting an Isoform-Restricted Allosteric Cysteine. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Clayton, J.; Shen, M.; Bhatnagar, S.; Shen, J. Machine Learning Models to Interrogate Proteome-Wide Covalent Ligandabilities Directed at Cysteines. JACS Au 2024, 4, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W. Proteome-Wide Profiling of the Covalent-Druggable Cysteines with a Structure-Based Deep Graph Learning Network. Research 2022, 2022, 9873564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonus, M.; Greb, J.; Majmudar, J.D.; Boehm, M.; Korczynska, M.; Nazemi, A.; Mathiowetz, A.M.; Gohlke, H. TopCysteineDB: A Cysteinome-Wide Database Integrating Structural and Chemoproteomics Data for Cysteine Ligandability Prediction. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 169196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, O.; Gu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, F.; Li, D.; Hou, T.; Pan, P. CovalentInDB 2.0: An Updated Comprehensive Database for Structure-Based and Ligand-Based Covalent Inhibitor Design and Screening. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1322–D1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Y.-F.; Zhang, L.; Niu, Z.L.; Wang, Z.A. Targeting the Reactive Proteome: Recent Advances in Activity-Based Protein Profiling and Probe Design. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121699
Zhou Y-F, Zhang L, Niu ZL, Wang ZA. Targeting the Reactive Proteome: Recent Advances in Activity-Based Protein Profiling and Probe Design. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(12):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121699
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Yuan-Fei, Ling Zhang, Zhuoyi L. Niu, and Zhipeng A. Wang. 2025. "Targeting the Reactive Proteome: Recent Advances in Activity-Based Protein Profiling and Probe Design" Biomolecules 15, no. 12: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121699
APA StyleZhou, Y.-F., Zhang, L., Niu, Z. L., & Wang, Z. A. (2025). Targeting the Reactive Proteome: Recent Advances in Activity-Based Protein Profiling and Probe Design. Biomolecules, 15(12), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15121699





