The Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms of Persistent Firing in Neurogliaform Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Acute Brain Slice Preparation
2.3. Whole-Cell Current-Clamp Recording
2.4. Pharmacology
2.5. Biocytin Labeling, Image Collection and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
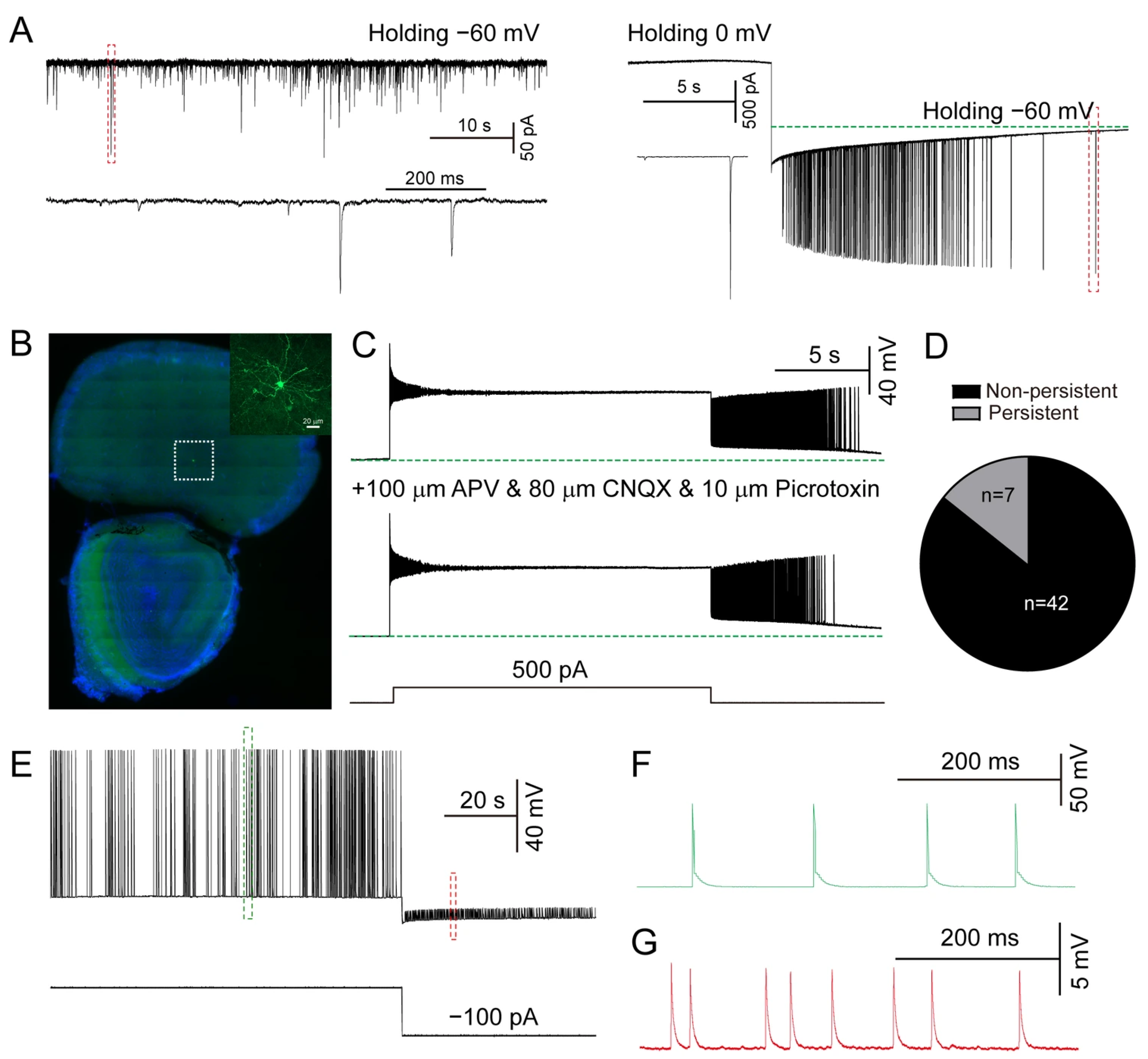
3.1. Persistent Firing in Prefrontal Cortex
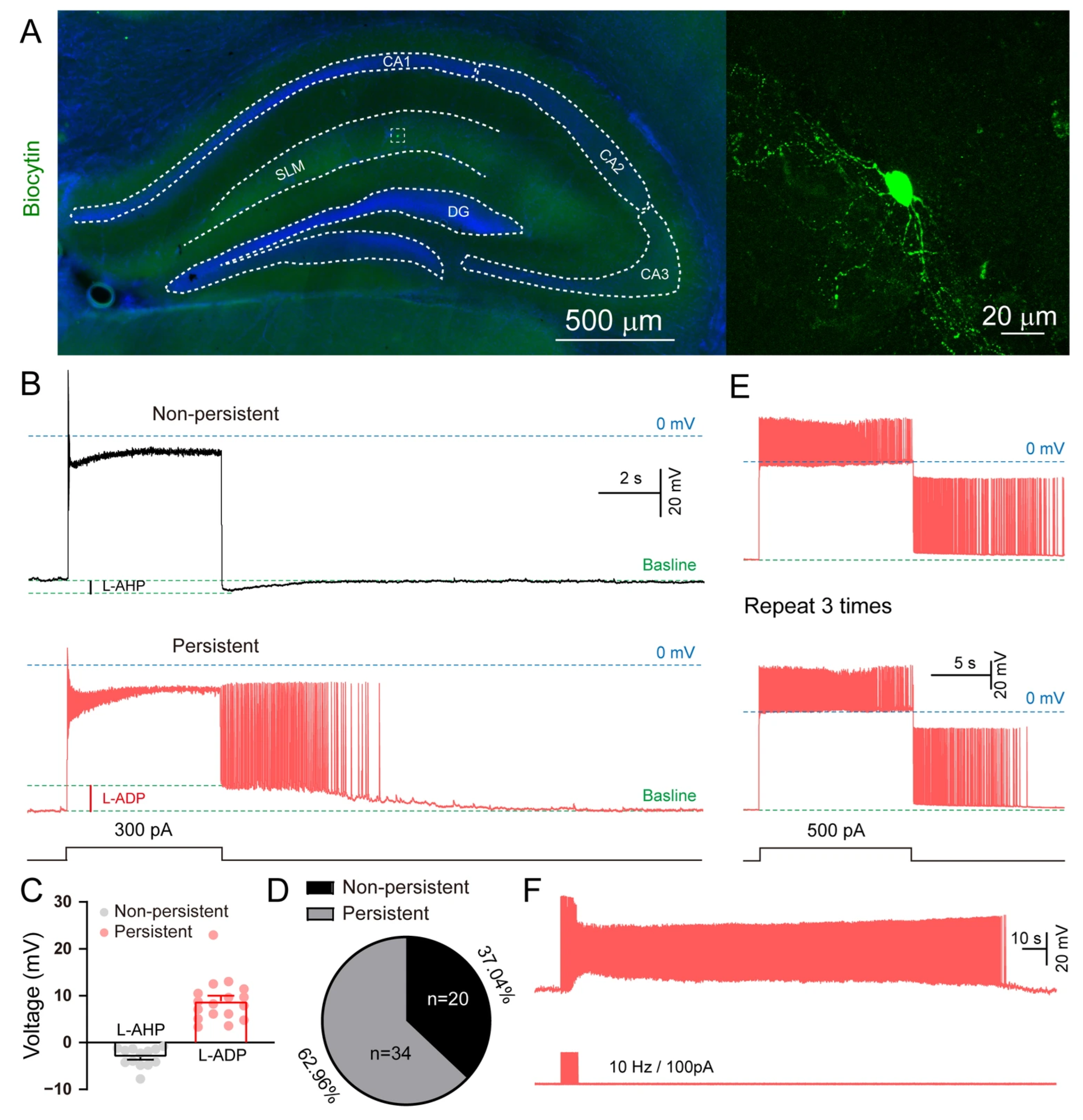
3.2. Persistent Firing in Hippocampal SLM NGFCs
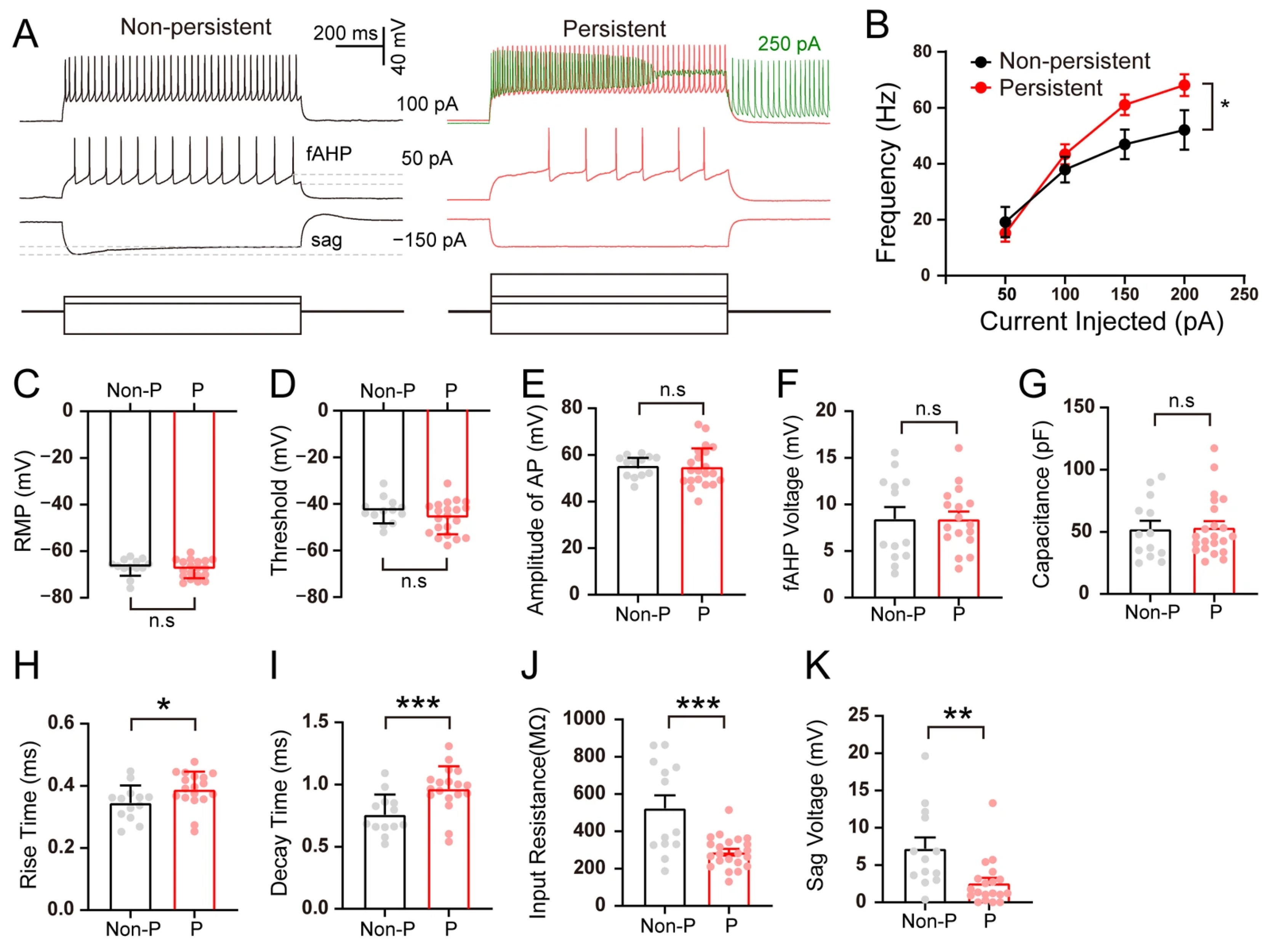
3.3. The Intrinsic Properties of Hippocampal SLM Neurons
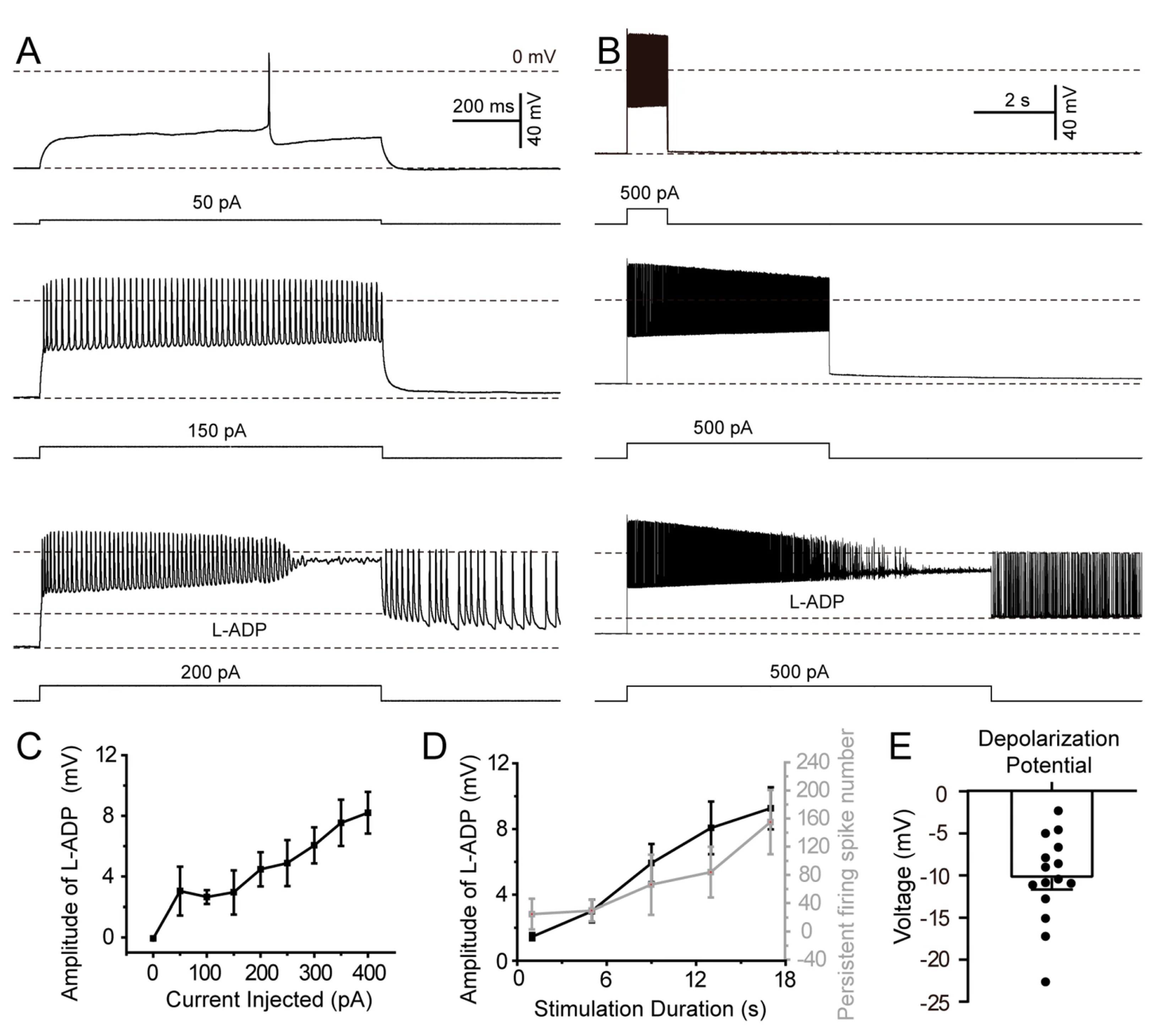
3.4. Induction of Persistent Firing in SLM NGFCs by L-ADP
3.5. The Amplitude of L-ADP in SLM NGFCs Exhibits a Stimulation Intensity-Dependent Relationship
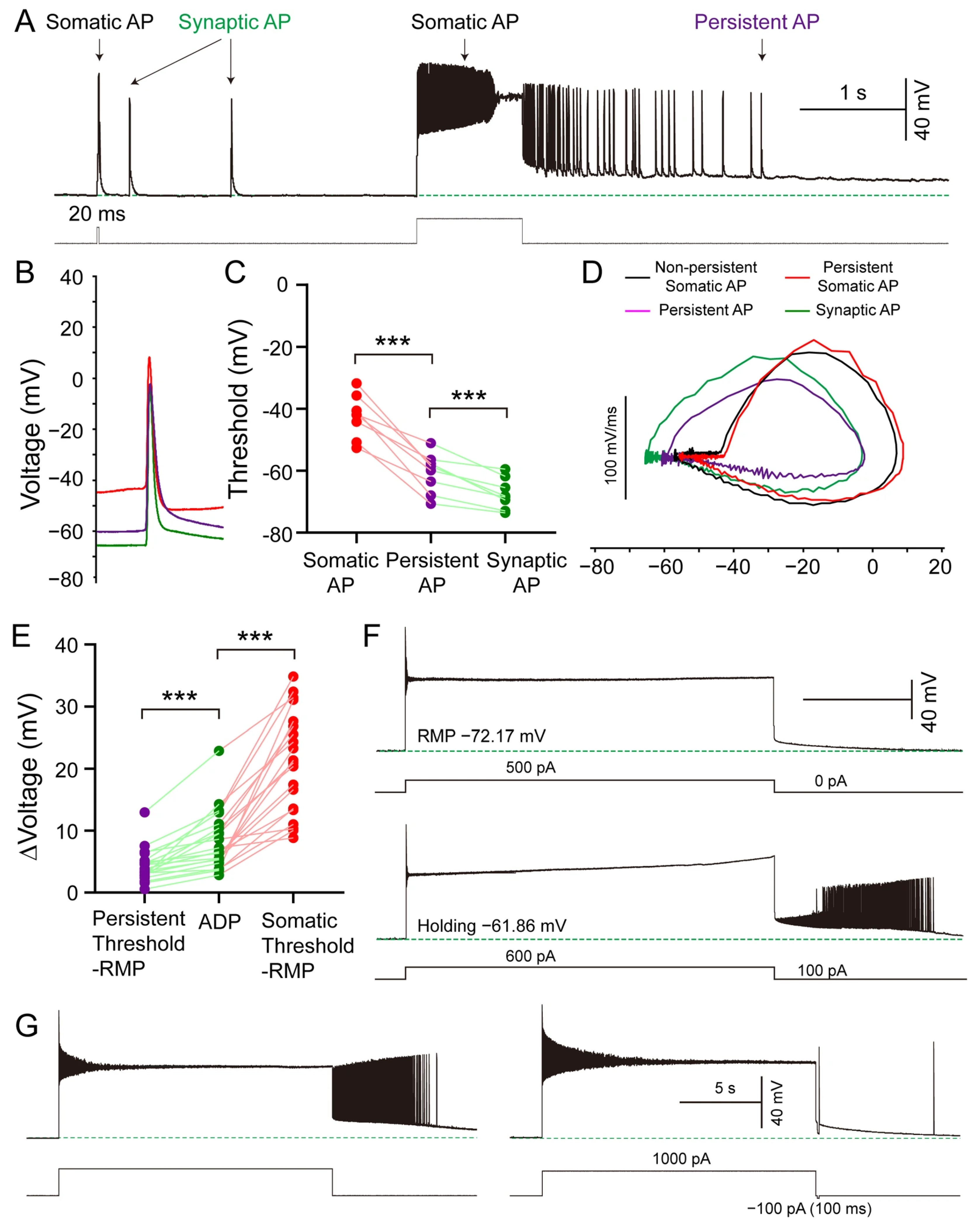
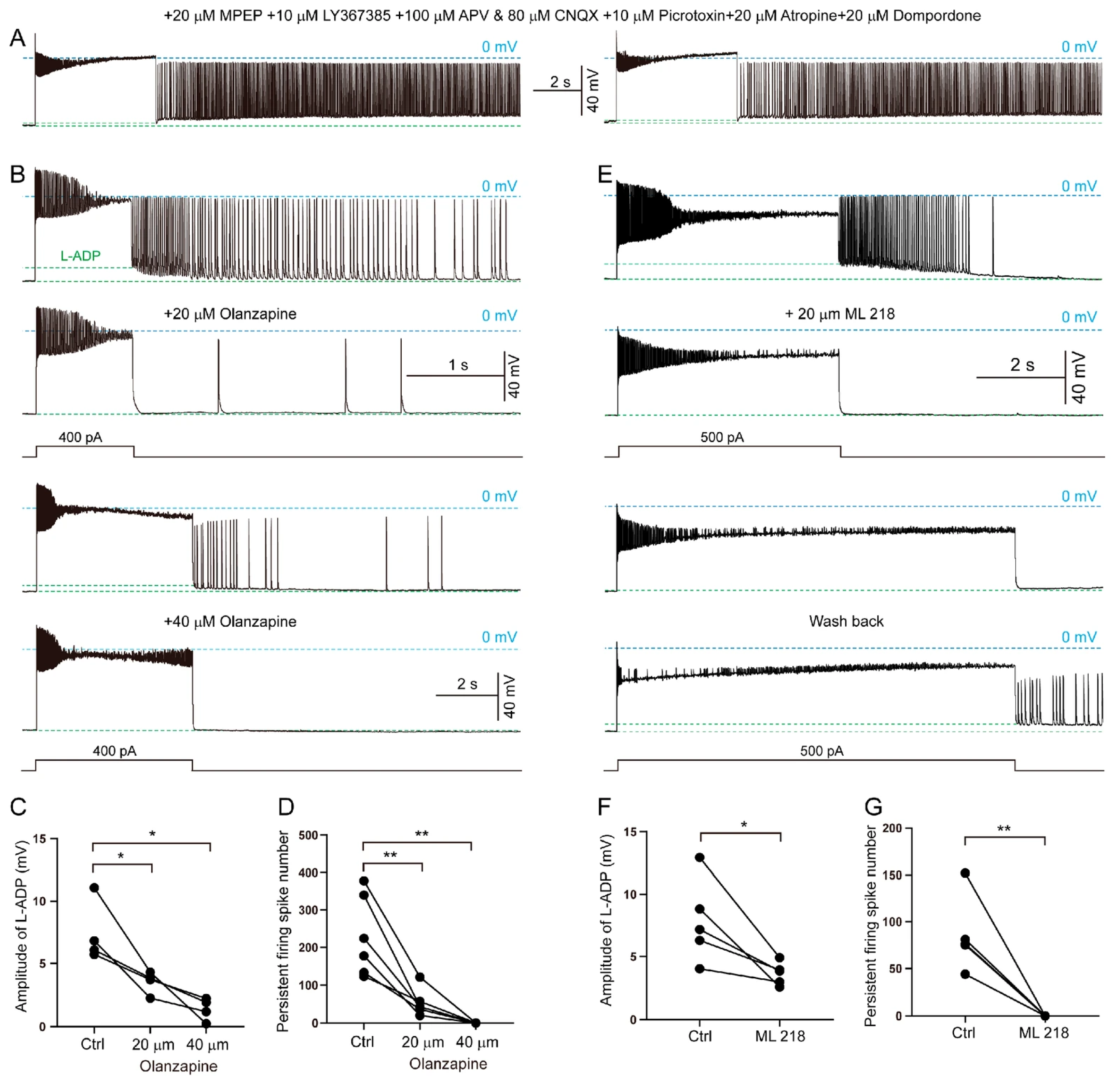
3.6. Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms Underlying Persistent Firing in SLM NGFCs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine |
| ACC | Anterior cingulate cortex |
| aCSF | Artificial cerebrospinal fluid |
| AMPA | Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazolepropionic acid |
| AP | Action potential |
| APV | 2-amino-5-phosphonovalerate |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BAPTA | 1,2-Bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid |
| CCh | Carbachol |
| CNQX | 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione |
| EGTA | Ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid |
| fAHP | Fast afterhyperpolarization |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GTP | Guanosine triphosphate |
| HEPES | 4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid |
| L-ADP | Long-lasting delayed afterdepolarization |
| L-AHP | Long-lasting delayed afterhyperpolarization |
| LY367385 | An inhibitor of metabolic glutamate receptor mGluR1 |
| ML218 | A T-type Ca2+ channel inhibitor |
| MPEP | 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl) pyridine |
| NGFCs | Neurogliaform cells |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NMDG | N-methyl-D-glucamine |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| RMP | Resting membrane potential |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| SLM | Stratum lacunosum-moleculare |
References
- Zeng, H.; Sanes, J.R. Neuronal cell-type classification: Challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 530–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.Y.; Shafiei, G.; Markello, R.D.; Smart, K.; Cox, S.M.L.; Norgaard, M.; Beliveau, V.; Wu, Y.; Gallezot, J.D.; Aumont, E.; et al. Mapping neurotransmitter systems to the structural and functional organization of the human neocortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiorowska, A.; Wydrych, M.; Drapich, P.; Zadrozny, M.; Steczkowska, M.; Niewiadomski, W.; Niewiadomska, G. The biology and pathobiology of glutamatergic, cholinergic, and dopaminergic signaling in the aging brain. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 654931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musall, S.; Sun, X.R.; Mohan, H.; An, X.; Gluf, S.; Li, S.J.; Drewes, R.; Cravo, E.; Lenzi, I.; Yin, C.; et al. Pyramidal cell types drive functionally distinct cortical activity patterns during decision-making. Nat. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, H.G.; Braak, H. Ratio of pyramidal cells versus non-pyramidal cells in sector CA1 of the human Ammon’s horn. Anat. Embryol. 1985, 173, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepecs, A.; Fishell, G. Interneuron cell types are fit to function. Nature 2014, 505, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelkey, K.A.; Chittajallu, R.; Craig, M.T.; Tricoire, L.; Wester, J.C.; McBain, C.J. Hippocampal GABAergic inhibitory interneurons. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1619–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, S.J.; Stacey, J.A.; Teramoto, Y.; Vagnoni, C. A role for GABAergic interneuron diversity in circuit development and plasticity of the neonatal cerebral cortex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 43, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.T.; Tan, Z.L.; Hirjak, D.; Northoff, G. Brain-wide changes in excitation-inhibition balance of major depressive disorder: A systematic review of topographic patterns of GABA- and glutamatergic alterations. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 3257–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboreda, A.; Raouf, R.; Alonso, A.; Seguela, P. Development of cholinergic modulation and graded persistent activity in layer v of medial entorhinal cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Fransen, E.; Hasselmo, M.E. mGluR-dependent persistent firing in entorhinal cortex layer III neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, A.V.; Hamam, B.N.; Fransen, E.; Hasselmo, M.E.; Alonso, A.A. Graded persistent activity in entorhinal cortex neurons. Nature 2002, 420, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalinsky, M.H.; Magistretti, J.; Ma, L.; Alonso, A.A. Muscarinic activation of a cation current and associated current noise in entorhinal-cortex layer-II neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 88, 1197–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Seguela, P. Metabotropic induction of persistent activity in layers II/III of anterior cingulate cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 2948–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, R.; Lee, S.; Rudy, B. GABAergic interneurons in the neocortex: From cellular properties to circuits. Neuron 2016, 91, 260–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, M.E.; Best, T.K.; Mensh, B.D.; Kath, W.L.; Spruston, N. Slow integration leads to persistent action potential firing in distal axons of coupled interneurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet-Wadiche, L.; McBain, C.J. Neurogliaform cells in cortical circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozsa, M.; Toth, M.; Olah, G.; Baka, J.; Lakovics, R.; Barzo, P.; Tamas, G. Temporal disparity of action potentials triggered in axon initial segments and distal axons in the neocortex. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsvar, A.; Sieburg, M.C.; Sietam, M.D.; Hou, W.H.; Capogna, M.A. Combinatory genetic strategy for targeting neurogliaform neurons in the mouse basolateral amygdala. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1254460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.Y.; Jiang, J.X.; Huang, H.X.; Mo, X.P.; Feng, J.R.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Long, C. Neural mechanism underlies CYLD modulation of morphology and synaptic function of medium spiny neurons in dorsolateral striatum. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1107355. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, K.F.; Tan, S.Y.; Chen, X.S.; Li, H.D.; Li, J.J.; Zhou, J.W.; Yang, L.; Long, C. Deubiquitinase CYLD regulates excitatory synaptic transmission and short-term plasticity in the hippocampus. Brain. Res. 2023, 1806, 148313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Mo, X.; Qin, H.; Dong, B.; Zhou, J.; Long, C.; Yang, L. Biocytin-labeling in whole-cell recording: Electrophysiological and morphological properties of pyramidal neurons in CYLD-deficient mice. Molecules 2023, 28, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezaire, M.J.; Soltesz, I. Quantitative assessment of CA1 local circuits: Knowledge base for interneuron-pyramidal cell connectivity. Hippocampus 2013, 23, 751–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, M.E.; Edgerton, G.B.; Heuermann, R.J.; Deemyad, T.; Mensh, B.D.; Spruston, N. Mechanisms of retroaxonal barrage firing in hippocampal interneurons. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 4793–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittajallu, R.; Auville, K.; Mahadevan, V.; Lai, M.; Hunt, S.; Calvigioni, D.; Pelkey, K.A.; Zaghloul, K.A.; McBain, C.J. Activity-dependent tuning of intrinsic excitability in mouse and human neurogliaform cells. Elife 2020, 9, e57571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, G.; Tank, D. Persistent neural activity: Prevalence and mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2004, 14, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattis, B.A.C.; Freitas, A.C.; Oliveira, J.F.; Calandrini-Lima, J.L.A.; Figueiredo, M.J.; Soave, D.F.; Ramos, S.G.; Celes, M.R.N. Effect of verapamil, an L-type calcium channel inhibitor, on caveolin-3 expression in septic mouse hearts. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6667074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergson, P.; Lipkind, G.; Lee, S.P.; Duban, M.E.; Hanck, D.A. Verapamil block of T-type calcium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, S.D.; Fisher, T.A.J.; Wong, E.W.; Lancon, K.; Feighan, K.M.; Beamish, I.V.; Gibon, J.; Seguela, P.; Ruthazer, E.S.; Kennedy, T.E. Acetylcholine synergizes with netrin-1 to drive persistent firing in the entorhinal cortex. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 113812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maricq, A.V.; Peterson, A.S.; Brake, A.J.; Myers, R.M.; Julius, D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science 1991, 254, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Xie, W.; Long, C.; Wu, G. The Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms of Persistent Firing in Neurogliaform Cells. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111603
Chen S, Chen X, Zhou J, Wang J, Li K, Xie W, Long C, Wu G. The Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms of Persistent Firing in Neurogliaform Cells. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111603
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shiyuan, Xiaoshan Chen, Jianwen Zhou, Jinzhao Wang, Kaiyuan Li, Wenyuan Xie, Cheng Long, and Gangyi Wu. 2025. "The Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms of Persistent Firing in Neurogliaform Cells" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111603
APA StyleChen, S., Chen, X., Zhou, J., Wang, J., Li, K., Xie, W., Long, C., & Wu, G. (2025). The Synaptic and Intrinsic Cellular Mechanisms of Persistent Firing in Neurogliaform Cells. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111603




