Integrating 3D Osteocyte Culture, Microgravity Simulation, and Fluid Flow Reveals Mechanisms of Osteocyte Mechanosensation and Calcium Signaling Altered by Disuse
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line, Scaffold Preparation and 3D Culture Conditions
2.2. Exposure to Microgravity Conditions Simulating Disuse
2.3. RNA Isolation and Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Turbulent Fluid Shear Stress (TFSS) and Osteocyte PMD Formation
2.5. Laminar Fluid Flow Shear Stress (LFSS)
2.6. Calcium Signaling
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
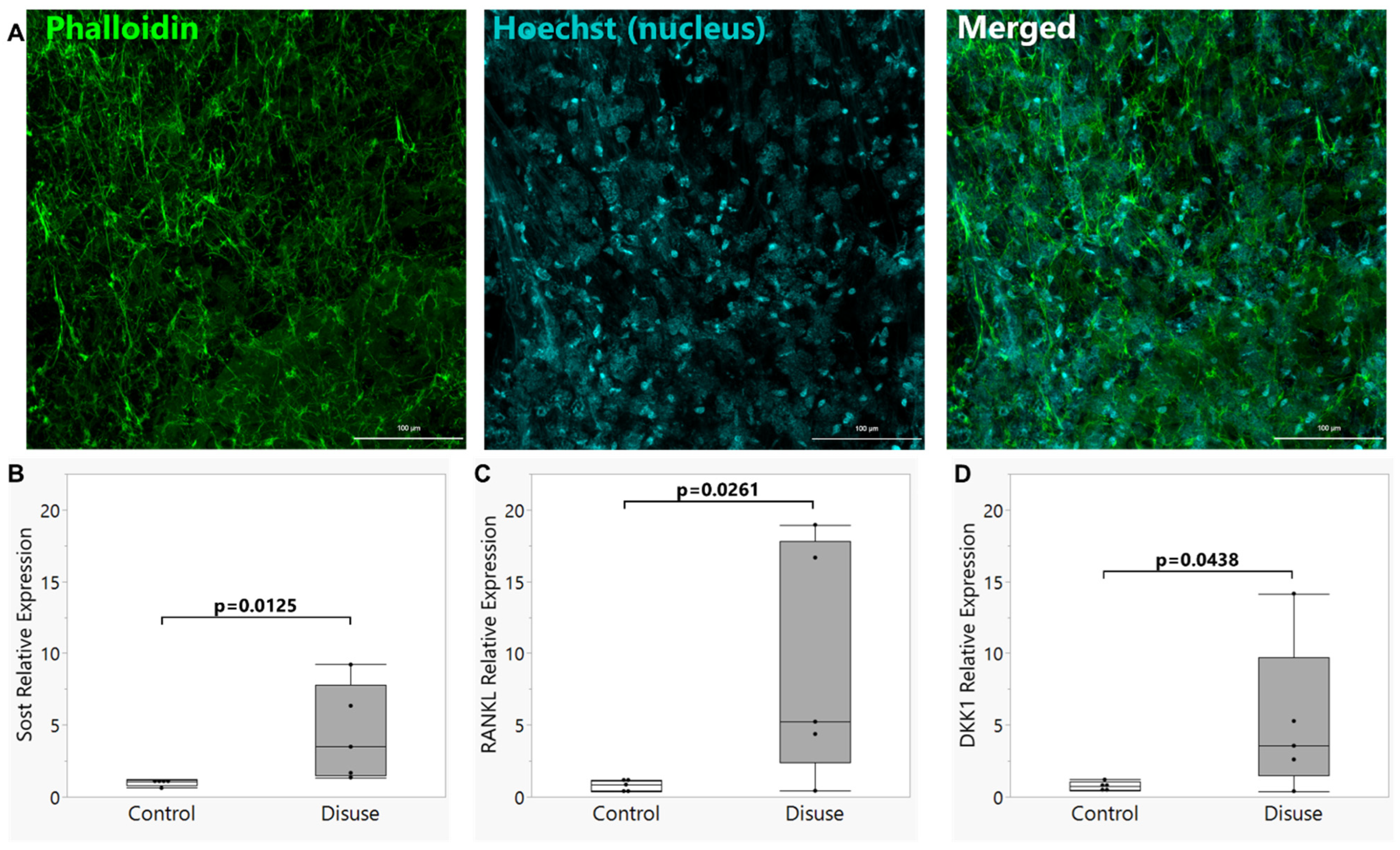
3.1. Establishment of the Disuse Bioreactor Model
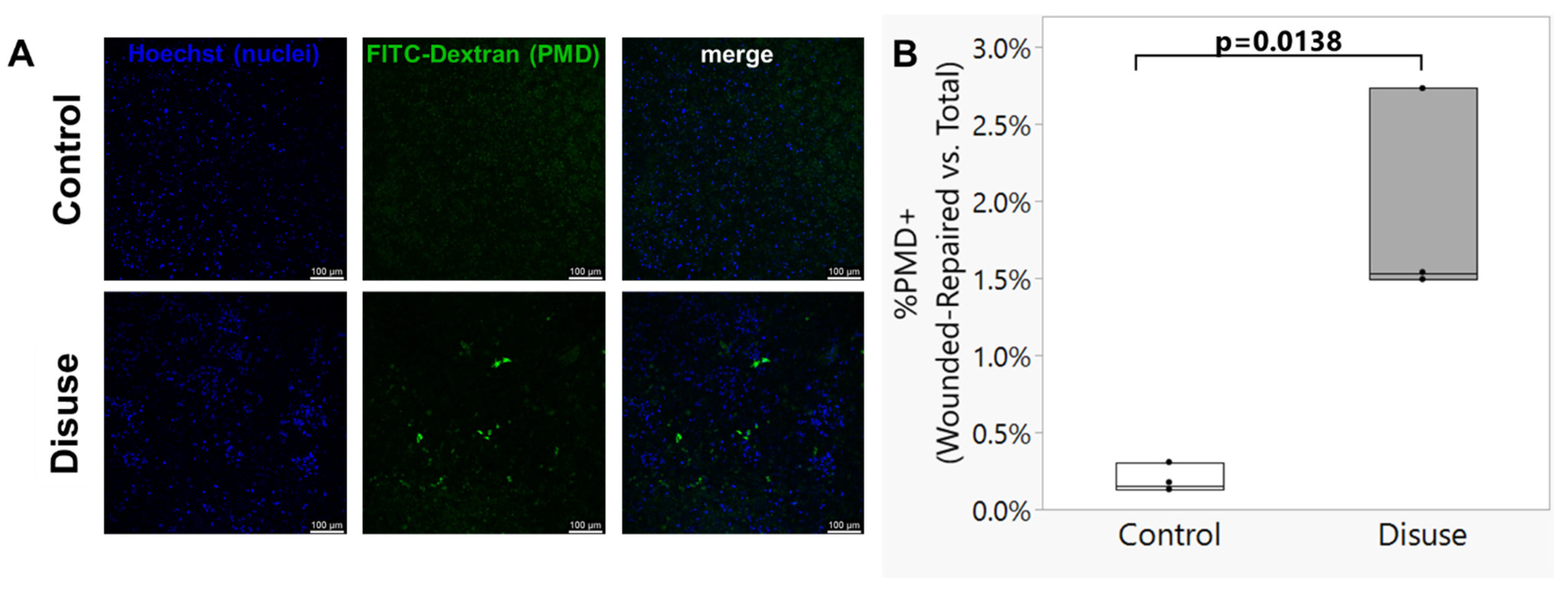
3.2. Exposure to Disuse Sensitizes Osteocytes to the Formation of Membrane Damage upon Reloading
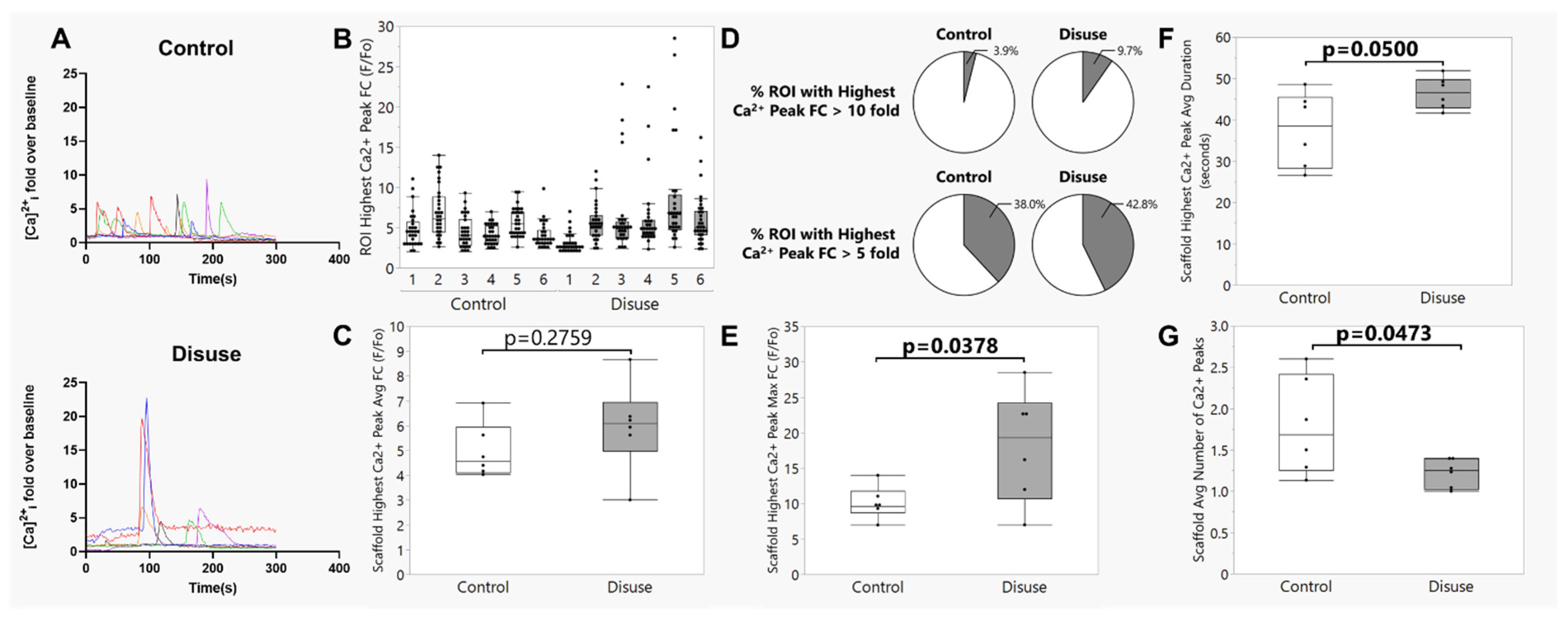
3.3. Exposure to Disuse Amplifies Calcium Signaling Responses upon Reloading
3.4. The Amplified Calcium Signaling Responses in Disuse-Exposed Osteocytes Uniquely Occurred in Cells with Evidence of Membrane Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, T.; LeBlanc, A.; Evans, H.; Lu, Y.; Genant, H.; Yu, A. Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2004, 19, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, A.; Schneider, V.; Shackelford, L.; West, S.; Oganov, V.; Bakulin, A.; Voronin, L. Bone mineral and lean tissue loss after long duration space flight. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2000, 1, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, A.D.; Spector, E.R.; Evans, H.J.; Sibonga, J.D. Skeletal responses to space flight and the bed rest analog: A review. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2007, 7, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Axpe, E.; Chan, D.; Abegaz, M.F.; Schreurs, A.S.; Alwood, J.S.; Globus, R.K.; Appel, E.A. A human mission to Mars: Predicting the bone mineral density loss of astronauts. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibonga, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Jones, J.; Shapiro, J.; Lang, T.; Shackelford, L.; Smith, S.M.; Young, M.; Keyak, J.; Kohri, K.; et al. Resistive exercise in astronauts on prolonged spaceflights provides partial protection against spaceflight-induced bone loss. Bone 2019, 128, 112037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, C.; Simon, C.; Vernikos, J.; Gauquelin-Koch, G.; Blanc, S.; Bergouignan, A. Revisiting the Role of Exercise Countermeasure on the Regulation of Energy Balance During Space Flight. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.L.; Bahraini, A.; Pierce, J.L.; Bass, S.M.; Yu, K.; Elsayed, R.; Elsalanty, M.; Johnson, M.H.; McNeil, A.; McNeil, P.L.; et al. Inhibition of Osteocyte Membrane Repair Activity via Dietary Vitamin E Deprivation Impairs Osteocyte Survival. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 104, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Sellman, D.P.; Bahraini, A.; Hagan, M.L.; Elsherbini, A.; Vanpelt, K.T.; Marshall, P.L.; Hamrick, M.W.; McNeil, A.; McNeil, P.L.; et al. Mechanical loading disrupts osteocyte plasma membranes which initiates mechanosensation events in bone. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajewicz, N.; Zimmermann, E.A.; Willie, B.M.; Komarova, S.V. Mechanically-stimulated ATP release from murine bone cells is regulated by a balance of injury and repair. eLife 2018, 7, e37812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.L.; Yu, K.; Zhu, J.; Vinson, B.N.; Roberts, R.L.; Montesinos Cartagena, M.; Johnson, M.H.; Wang, L.; Isales, C.M.; Hamrick, M.W.; et al. Decreased pericellular matrix production and selection for enhanced cell membrane repair may impair osteocyte responses to mechanical loading in the aging skeleton. Aging Cell 2020, 19, e13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.; Shaver, J.C.; McGee, W.A.; Yu, K.; Dorn, J.; Horne, J.L.; Alhamad, D.W.; Hagan, M.L.; Cooley, M.A.; Zhong, R.; et al. Prkd1 regulates the formation and repair of plasma membrane disruptions (PMD) in osteocytes. Bone 2024, 186, 117147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagan, M.L.; Tuladhar, A.; Yu, K.; Alhamad, D.W.; Bensreti, H.; Dorn, J.; Piedra, V.M.; Cantu, N.; Stokes, E.G.; Blumenthal, D.; et al. Osteocyte Sptbn1 Deficiency Alters Cell Survival and Mechanotransduction Following Formation of Plasma Membrane Disruptions (PMD) from Mechanical Loading. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, E.H.; Klein-Nulend, J. Microgravity and bone cell mechanosensitivity. Bone 1998, 22, 127S–130S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajubi, N.E.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Nijweide, P.J.; Vrijheid-Lammers, T.; Alblas, M.J.; Burger, E.H. Pulsating fluid flow increases prostaglandin production by cultured chicken osteocytes--a cytoskeleton-dependent process. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 225, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabony, J.; Job, D. Gravitational symmetry breaking in microtubular dissipative structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 6948–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodionova, N.V.; Oganov, V.S.; Polkovenko, O.V. Mechanisms of gravity-dependent changes in the bone tissue. J. Gravit. Physiol. 2002, 9, P169–P170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaber, E.A.; Dvorochkin, N.; Lee, C.; Alwood, J.S.; Yousuf, R.; Pianetta, P.; Globus, R.K.; Burns, B.P.; Almeida, E.A. Microgravity induces pelvic bone loss through osteoclastic activity, osteocytic osteolysis, and osteoblastic cell cycle inhibition by CDKN1a/p21. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, J.C.; Mullen, Z.A.; Weins, A.M.; Fisher, L.E.; Lynch, M.E.; Stodieck, L.S.; Ferguson, V.L. Reduced local mechanical stimuli in spaceflight diminishes osteocyte lacunar morphometry and spatial heterogeneity in mouse cortical bone. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uda, Y.; Spatz, J.M.; Hussein, A.; Garcia, J.H.; Lai, F.; Dedic, C.; Fulzele, K.; Dougherty, S.; Eberle, M.; Adamson, C.; et al. Global transcriptomic analysis of a murine osteocytic cell line subjected to spaceflight. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatz, J.M.; Fields, E.E.; Yu, E.W.; Divieti Pajevic, P.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Sibonga, J.D.; Zwart, S.R.; Smith, S.M. Serum sclerostin increases in healthy adult men during bed rest. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1736–E1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatz, J.M.; Wein, M.N.; Gooi, J.H.; Qu, Y.; Garr, J.L.; Liu, S.; Barry, K.J.; Uda, Y.; Lai, F.; Dedic, C.; et al. The Wnt Inhibitor Sclerostin Is Up-regulated by Mechanical Unloading in Osteocytes in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16744–16758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabahug-Zuckerman, P.; Frikha-Benayed, D.; Majeska, R.J.; Tuthill, A.; Yakar, S.; Judex, S.; Schaffler, M.B. Osteocyte Apoptosis Caused by Hindlimb Unloading is Required to Trigger Osteocyte RANKL Production and Subsequent Resorption of Cortical and Trabecular Bone in Mice Femurs. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Shao, X.; Hao, X.; Luo, E.; Guo, X.E.; et al. Glucose- and glutamine-dependent bioenergetics sensitize bone mechanoresponse after unloading by modulating osteocyte calcium dynamics. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e164508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, T.G.; Hammond, J.M. Optimized suspension culture: The rotating-wall vessel. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2001, 281, F12–F25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B.; Lim, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T. Numerical simulation of fluid field and in vitro three-dimensional fabrication of tissue-engineered bones in a rotating bioreactor and in vivo implantation for repairing segmental bone defects. Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Carpio, L.R.; Schulze, R.J.; Pierce, J.L.; McNiven, M.A.; Farr, J.N.; Khosla, S.; Oursler, M.J.; Westendorf, J.J. Hdac3 Deficiency Increases Marrow Adiposity and Induces Lipid Storage and Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Osteochondroprogenitor Cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, S.W.; Vaughan, T.J.; McNamara, L.M. Fluid flow in the osteocyte mechanical environment: A fluid-structure interaction approach. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2014, 13, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Wang, L. Real-time measurement of solute transport within the lacunar-canalicular system of mechanically loaded bone: Direct evidence for load-induced fluid flow. J. Bone Miner. Res. Off. J. Am. Soc. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings-Meuthen, P.; Boehme, G.; Liphardt, A.M.; Baecker, N.; Heer, M.; Rittweger, J. Sclerostin and DKK1 levels during 14 and 21 days of bed rest in healthy young men. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2013, 13, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belavy, D.L.; Baecker, N.; Armbrecht, G.; Beller, G.; Buehlmeier, J.; Frings-Meuthen, P.; Rittweger, J.; Roth, H.J.; Heer, M.; Felsenberg, D. Serum sclerostin and DKK1 in relation to exercise against bone loss in experimental bed rest. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2016, 34, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaki, R.; Mukaibo, T.; Monir, A.; Gao, X.; Munemasa, T.; Nodai, T.; Tamura, A.; Obikane, Y.H.; Kondo, Y.; Masaki, C.; et al. Simulated microgravity environment inhibits matrix mineralization during the osteoblast to osteocyte differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 739, 150963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.J.; Boorman-Padgett, J.F.; Castaneda, M.; Spray, D.C.; Thi, M.M.; Schaffler, M.B. A Fluorescent Intravital Imaging Approach to Study Load-Induced Calcium Signaling Dynamics in Mouse Osteocytes. J. Vis. Exp. 2023, 192, 64366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, K.J.; Cabahug-Zuckerman, P.; Boorman-Padgett, J.F.; Basta-Pljakic, J.; Louie, J.; Stephen, S.; Spray, D.C.; Thi, M.M.; Seref-Ferlengez, Z.; Majeska, R.J.; et al. Estrogen depletion on In vivo osteocyte calcium signaling responses to mechanical loading. Bone 2021, 152, 116072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.J.; Frikha-Benayed, D.; Louie, J.; Stephen, S.; Spray, D.C.; Thi, M.M.; Seref-Ferlengez, Z.; Majeska, R.J.; Weinbaum, S.; Schaffler, M.B. Osteocyte calcium signals encode strain magnitude and loading frequency in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11775–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, W.; Cao, H.; Xiao, G. Molecular mechanosensors in osteocytes. Bone Res. 2020, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kordsmeier, J.; Xiong, J. New Advances in Osteocyte Mechanotransduction. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, M.L.; Balayan, V.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E. Plasma membrane disruption (PMD) formation and repair in mechanosensitive tissues. Bone 2021, 149, 115970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Cao, X. miRNA-132-3p inhibits osteoblast differentiation by targeting Ep300 in simulated microgravity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrell, A.E.; Robinson, S.T.; Silva, M.J.; Guo, X.E. Mechanosensitive Ca2+ signaling and coordination is diminished in osteocytes of aged mice during ex vivo tibial loading. Connect. Tissue Res. 2020, 61, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badley, R.A.; Woods, A.; Carruthers, L.; Rees, D.A. Cytoskeleton changes in fibroblast adhesion and detachment. J. Cell Sci. 1980, 43, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, M.K.; Tan, G.; Fellows, R.E. Trypsin-induced alterations of insulin binding, microfilament organization and cell shape in fibroblastic cultures from non-diabetic and diabetic mice. Exp. Cell Res. 1981, 133, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lordon, B.; Campion, T.; Gibot, L.; Gallot, G. Impact of trypsin on cell cytoplasm during detachment of cells studied by terahertz sensing. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehls, S.; Noding, H.; Karsch, S.; Ries, F.; Janshoff, A. Stiffness of MDCK II Cells Depends on Confluency and Cell Size. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Pan, C.; Starke, A.M.; Matos, A.L.L.; Soehnlein, O.; Gerke, V. Altered shear stress of blood flow causes plasma membrane damage in endothelial cells. Blood Vessel. Thromb. Hemost. 2025, 2, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmaleki, M.; Pachenari, M.; Seyedpour, S.M.; Shahghadami, R.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Impact of Simulated Microgravity on Cytoskeleton and Viscoelastic Properties of Endothelial Cell. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.T.; Yang, X.; Tian, R.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Fan, Y.B.; Sun, L.W. Cells respond to space microgravity through cytoskeleton reorganization. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2022, 36, e22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Fulford, M. Function of the cytoskeleton in gravisensing during spaceflight. Adv. Space Res. 2003, 32, 1585–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guignandon, A.; Vico, L.; Alexandre, C.; Lafage-Proust, M.H. Shape changes of osteoblastic cells under gravitational variations during parabolic flight—Relationship with PGE2 synthesis. Cell Struct. Funct. 1995, 20, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubshet, N.H.; Cai, G.; Chen, S.J.; Sullivan, M.; Reeves, M.; Mays, D.; Harrison, M.; Varnado, P.; Yang, B.; Arreguin-Martinez, E.; et al. Cellular mechanotransduction of human osteoblasts in microgravity. NPJ Microgravity 2024, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.S.; Bamman, M.M.; Feeback, D.L. Bed rest decreases mechanically induced myofiber wounding and consequent wound-mediated FGF release. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1998, 85, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, C.E. Sarcolemmal disruption in reloaded atrophic skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1995, 79, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorf, B.B.; Riley, D.A. Distinguishing unloading- versus reloading-induced changes in rat soleus muscle. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, D.A.; Ellis, S.; Slocum, G.R.; Sedlak, F.R.; Bain, J.L.; Krippendorf, B.B.; Lehman, C.T.; Macias, M.Y.; Thompson, J.L.; Vijayan, K.; et al. In-flight and postflight changes in skeletal muscles of SLS-1 and SLS-2 spaceflown rats. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 1996, 81, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, H.C.; Orr, S.; Murugesh, D.K.; Hsia, A.W.; Osipov, B.; Go, L.; Wu, P.H.; Wong, A.; Loots, G.G.; Kazakia, G.J.; et al. Differential bone adaptation to mechanical unloading and reloading in young, old, and osteocyte deficient mice. Bone 2023, 167, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.; Tuladhar, A.; Dankberg, S.; Dai, C.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E. Integrating 3D Osteocyte Culture, Microgravity Simulation, and Fluid Flow Reveals Mechanisms of Osteocyte Mechanosensation and Calcium Signaling Altered by Disuse. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111534
Yu K, Tuladhar A, Dankberg S, Dai C, McGee-Lawrence ME. Integrating 3D Osteocyte Culture, Microgravity Simulation, and Fluid Flow Reveals Mechanisms of Osteocyte Mechanosensation and Calcium Signaling Altered by Disuse. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(11):1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111534
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kanglun, Anik Tuladhar, Samuel Dankberg, Caihong Dai, and Meghan E. McGee-Lawrence. 2025. "Integrating 3D Osteocyte Culture, Microgravity Simulation, and Fluid Flow Reveals Mechanisms of Osteocyte Mechanosensation and Calcium Signaling Altered by Disuse" Biomolecules 15, no. 11: 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111534
APA StyleYu, K., Tuladhar, A., Dankberg, S., Dai, C., & McGee-Lawrence, M. E. (2025). Integrating 3D Osteocyte Culture, Microgravity Simulation, and Fluid Flow Reveals Mechanisms of Osteocyte Mechanosensation and Calcium Signaling Altered by Disuse. Biomolecules, 15(11), 1534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15111534





