Research Progress on Quinone Compounds for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
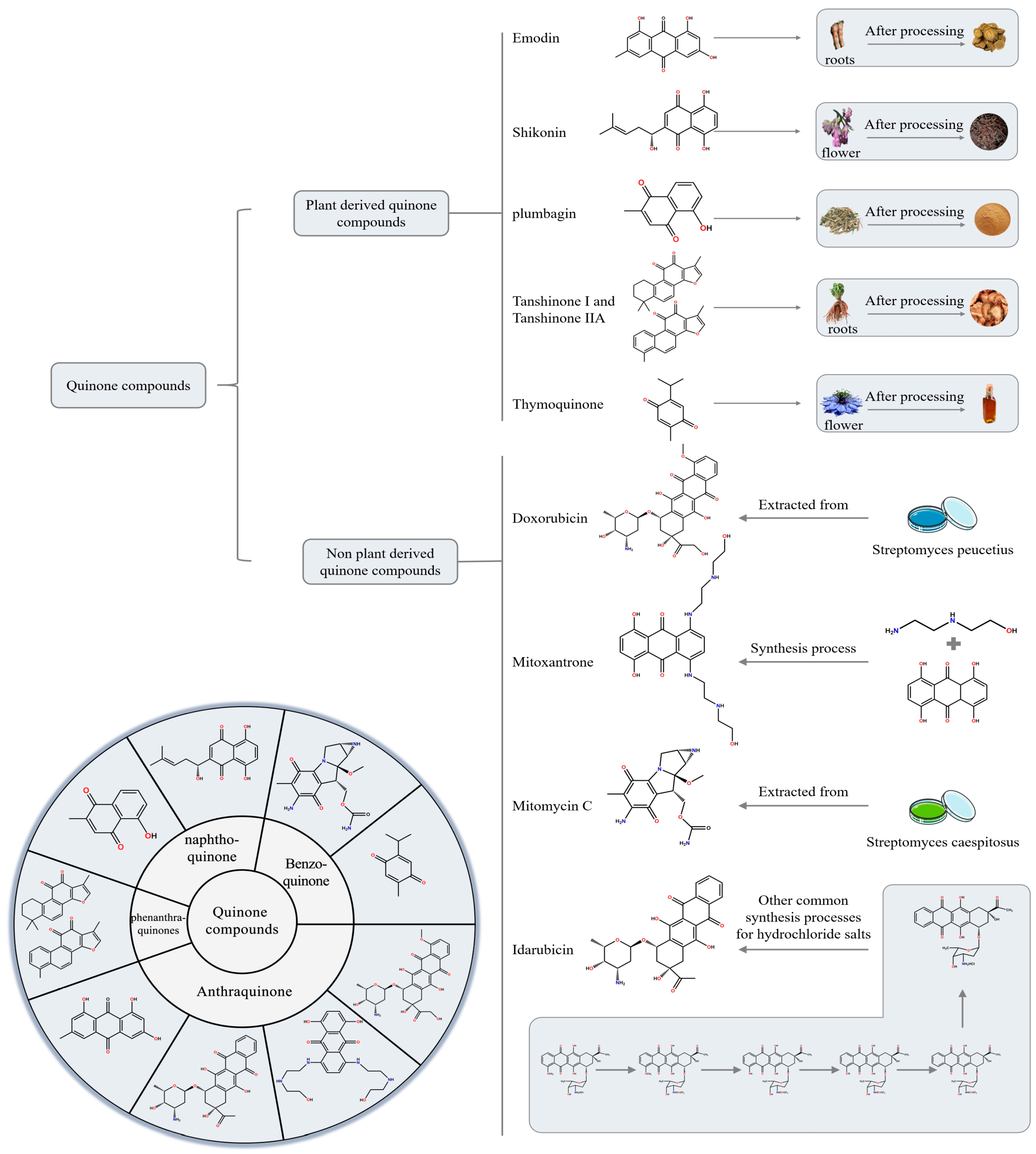
2. Quinone Compounds
3. Research Progress of Plant-Derived Quinonoid Compounds in the Treatment of HCC
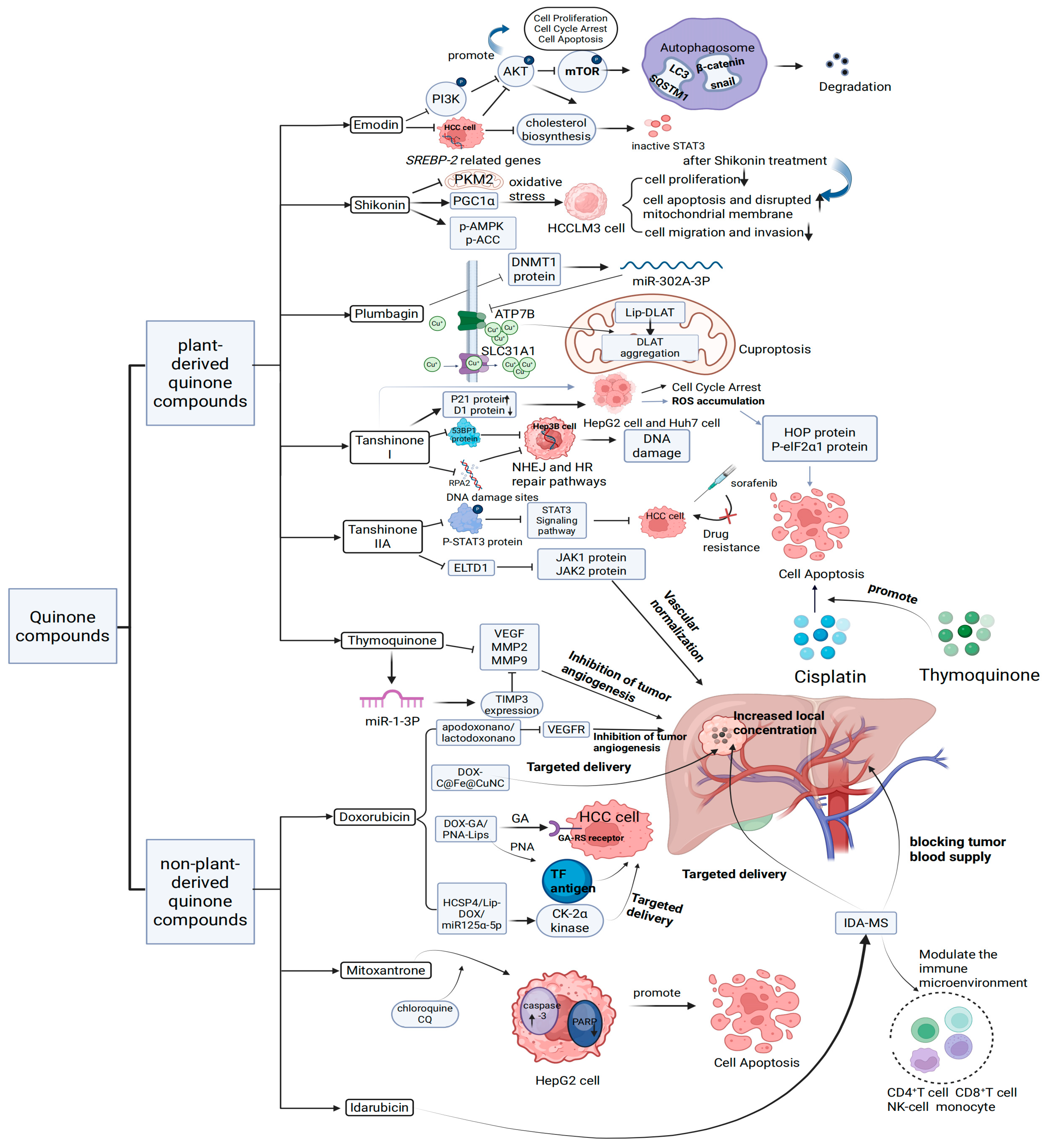
3.1. Experimental Studies of Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds in the Field of Anti-HCC
3.2. Clinical Studies on Plant-Derived Quinonoid Compounds
3.3. Adverse Reactions of Plant-Derived Quinonoid Compounds
4. Research Progress of Non-Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds in the Field of Anti-HCC
4.1. Experimental Studies of Non-Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds in the Field of Anti-HCC
4.2. Clinical Studies of Non-Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds in the Field of Anti-HCC
4.3. Adverse Reactions and Toxicity of Non-Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds
5. Investigation of the Attenuation Effects of Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds on the Toxicity of the Non-Plant-Derived Quinone Compound Dox
6. Clinical Translation of Quinonoid Compounds—Challenges and Limitations
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Tan IIA | Tanshinone IIA |
| Tan I | Tanshinone I |
| PLB | Plumbagin |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| MTX | Mitoxantrone |
| IDA | Idarubicin |
| MMC | Mitomycin |
| PKC | Protein Kinase C |
| ERK5 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 |
| ADAMTS4 | A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase With Thrombospondin 4 |
| MMP3 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 3 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| SREBP-2 | Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 2 |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PKM2 | Pyruvate kinase isozyme type M2 |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha |
| ZO-1 | Zona Occludens 1 |
| ELTD1 | EGF, latrophilin and seven transmembrane domain containing 1 |
| JAK1 | Janus Kinase 1 |
| JAK2 | Janus Kinase 2 |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| AFP | Alpha-Fetoprotein |
| AFP-L3 | Alpha-Fetoprotein isoform L3 |
| GPC3 | Glypican 3 |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma-2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2 associated X protein |
| TACE | Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| TBIL | Total Bilirubin |
| DHAD | Dihydroxyanthracenedione |
| DHAD-loaded PBCA nanoparticles | Mitoxantrone-loaded Polybutylcyanacrylate Nanoparticles |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| RNS | Reactive Nitrogen Species |
| MnSOD | Manganese Superoxide Dismutase |
| PTP | Permeability Transition Pore |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| GPX | Glutathione Peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| IKK | IκB kinase |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| HSP90 | Heat Shock Protein 90 |
| TAS | Total Antioxidant Status |
| TQ | Thymoquinone |
| UGT | Uridine 5′-diphosphate Glucuronosyltransferase |
| MDR | Multidrug Resistance |
| IDA-MS | Biodegradable Microsphere Loaded with Idarubicin |
| PLD | Pegylated Liposomal Doxorubicin |
| RFA | Radiofrequency Ablation |
| LTLD | Lyso-thermosensitive Liposomal Doxorubicin |
| EF | Ejection FractionES: End-systolic Volume |
| CK-MB | Creatine Kinase-MB |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| GRP78 | Glucose Regulated Protein 78 |
| AKT | Oncogenic protein kinase B |
| EMT | Epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| NHEJ | Non-homologous end joining |
| HR | Homologous recombination |
| TILs | Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes |
| GA | Glycyrrhetinic acid |
| PNA | Peanut agglutininCQ: Chloroquine |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| DLAT | Lipoylated dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase |
| DNMT1 | DNA methyltransferase 1 |
| Amr | Amrubicin |
| Epi | Epirubicin |
| Hepa1-6-R cells | DOX-resistant Hepa1-6 cells |
| BCLC | Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| MMP-2 | Matrix metalloproteinase-2 |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| p53 | Tumor protein p53 |
| MSP | Methylation-specific PCR |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| 2D Echo | Two-dimensional echocardiography |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Ma, X.; Fan, D. Ginsenoside Rk3 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development through Targeting the Gut-Liver Axis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 10121–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, A. Evolving Global Etiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Insights and Trends for 2024. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2025, 15, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature reviews. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Ming, X.; Xiang, T.; Feng, N.; Zhang, M.; Ye, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Q. Recent research on the physicochemical properties and biological activities of quinones and their practical applications: A comprehensive review. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 8973–8997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, A. Reactions of Quinones-Mechanisms, Structures, and Prospects for Food Research. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 13051–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, T.L.; Monte, F.J.; Santos, A.K.; Fonseca, A.M.; Santos, H.S.; Oliveira, M.F.; Costa, S.M.; Pessoa, O.D.; Braz-Filho, R. Quinones from plants of northeastern Brazil: Structural diversity, chemical transformations, NMR data and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2007, 21, 529–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes de Carvalho, N.K.; Wellisson da Silva Mendes, J.; Martins da Costa, J.G. Quinones: Biosynthesis, Characterization of (13) C Spectroscopical Data and Pharmacological Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 20, e202301365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ding, X.; Feng, S.X.; Guan, Q.; Zhang, X.P.; Du, C.; Di, Y.T.; Chen, T. Seven New Tetrahydroanthraquinones from the Root of Prismatomeris connata and Their Cytotoxicity against Lung Tumor Cell Growth. Molecules 2015, 20, 22565–22577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Hou, H. Novel anthraquinone compounds as anticancer agents and their potential mechanism. Future Med. Chem. 2020, 12, 627–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.L.; Chang, F.R.; Yen, M.H.; Yu, D.; Liu, Y.N.; Bastow, K.F.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Lee, K.H. Cytotoxic phenanthrenequinones and 9,10-dihydrophenanthrenes from Calanthe arisanensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, R. Naphthohydroquinones, naphthoquinones, anthraquinones, and a naphthohydroquinone dimer isolated from the aerial parts of Morinda parvifolia and their cytotoxic effects through up-regulation of p53. Phytochemistry 2016, 130, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, F.; Li, H.; Jin, X. Regulation of apoptosis by ubiquitination in liver cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 4832–4871. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Zha, W.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Gan, J. The Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development and Therapeutic Intervention of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2023, 23, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, G.; Koudelkova, P.; Dituri, F.; Mikulits, W. Role of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Tian, T.; Jin, A.; Liu, Y.; Huo, R.; Liu, T.; Pan, B.; Guo, W.; et al. Plumbagin Triggers Cuproptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) via the DNA-Methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1)/microRNA-302a-3p (miR-302a-3p)/ATPase Copper Transporting Beta (ATP7B) Axis. MedComm 2025, 6, e70312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Shangwen, J.; Ye, Z.J.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Peng, G.; Wang, Q.; Gu, W.; et al. Emodin inhibits invasion and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via regulating autophagy-mediated degradation of snail and β-catenin. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.M.; Hamdan, A.M.; Alattar, A.; Alshaman, R.; Bahattab, O.; Al-Gayyar, M.M.H. Evaluating anticancer activity of emodin by enhancing antioxidant activities and affecting PKC/ADAMTS4 pathway in thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2024, 29, 2365590. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Oh, T.I.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kan, S.Y.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.M.; Yim, W.J.; et al. Emodin Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to the Anti-Cancer Effect of Sorafenib through Suppression of Cholesterol Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilin, E.; Simoni, E.; Candito, M.; Cazzador, D.; Astolfi, L. Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Updates on Molecular Targets. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, I.; Ragazzi, E.; Pasut, G.; Montopoli, M. The Pentose Phosphate Pathway and Its Involvement in Cisplatin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Cui, R.; Wang, L. Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR increased the sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to cisplatin via interference with mitochondrial-lysosomal crosstalk. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xiong, Z.; Deng, H.; Chen, X.; Lai, Q.; Wang, H.; Leng, Y. Effect of emodin combined with cisplatin on the invasion and migration of HepG2 hepatoma cells. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2023, 74, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J. Synthesis, biological function and evaluation of Shikonin in cancer therapy. Fitoterapia 2019, 134, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, L.; Jiang, M.; Xie, C. Shikonin exerts antitumor activity by causing mitochondrial dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma through PKM2-AMPK-PGC1α signaling pathway. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, J.; Hou, L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y. Shikonin differentially regulates glucose metabolism via PKM2 and HIF1α to overcome apoptosis in a refractory HCC cell line. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L.; Liu, S.; Liang, L.; Wei, Y. Plumbagin Exhibits Genotoxicity and Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest via ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Activation of ATM-p53 Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Yan, D.; Jiang, B.; Xue, Q.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Qi, L.; Tang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, J. Plumbagin is a novel GPX4 protein degrader that induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 203, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Q.; Yuan, B.; Ye, Y.X.; Zhou, F.L.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.J.; Wei, Y.F. Plumbagin Regulates Snail to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in vivo and in vitro. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2024, 11, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, F.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Y.; Tang, F.; Li, H.; et al. Nano co-delivery of doxorubicin and plumbagin achieves synergistic chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 661, 124424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wen, H.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, D. Tanshinone I improves renal fibrosis by promoting gluconeogenesis through upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α. Ren. Fail. 2024, 46, 2433710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, H.; Shen, Q.K.; Quan, Z.S. Tanshinone IIA: Pharmacology, Total Synthesis, and Progress in Structure-modifications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 1959–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J. Tanshinone I induces cell apoptosis by reactive oxygen species-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and by suppressing p53/DRAM-mediated autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Feng, N.; Geng, A. Tanshinone I suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cells growth through targeting DNA double-strand break repair. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2023, 24, 2229958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Ma, H.; Cao, L. Identification of the molecular mechanisms of Salvia miltiorrhiza relevant to the treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology. Discov. Med. 2020, 30, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, E.; Cai, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zeng, G.; Yin, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; et al. Combined Treatment of Tanshinone I and Epirubicin Revealed Enhanced Inhibition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 3197–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, M.; Rizzo, A.; Mollica, V.; Matrana, M.R.; Rosellini, M.; Faloppi, L.; Marchetti, A.; Battelli, N.; Massari, F. The impact of gender on The efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients: The MOUSEION-01 study. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2022, 170, 103596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Q.; Liu, L.; Sun, H.C.; Fu, Y.L.; Xu, H.X.; Chai, Z.T.; Zhang, Q.B.; Kong, L.Q.; Zhu, X.D.; Lu, L.; et al. Tanshinone IIA inhibits metastasis after palliative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma and prolongs survival in part via vascular normalization. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Che, X.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Huo, J.; Chen, Y. Tanshinone IIA normalized hepatocellular carcinoma vessels and enhanced PD-1 inhibitor efficacy by inhibiting ELTD1. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 123, 155191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.M.; Huang, S.Y.; Chang, S.F.; Liao, K.F.; Chiu, S.C. Synergistic antitumor effects of tanshinone IIA and sorafenib or its derivative SC-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, N.K.; Abd Manap, M.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Alhelli, A.M.; Meor Hussin, A.S. The Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Antioxidant Properties, Chemical Composition, and Thermal Behavior of Black Seed (Nigella sativa L.) Oil. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. eCAM 2016, 2016, 6273817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entok, E.; Ustuner, M.C.; Ozbayer, C.; Tekin, N.; Akyuz, F.; Yangi, B.; Kurt, H.; Degirmenci, I.; Gunes, H.V. Anti-inflammatuar and anti-oxidative effects of Nigella sativa L.: 18FDG-PET imaging of inflammation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 2827–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Fahim, S.A.; Tadros, S.A.; Badary, O.A. Suppressive effects of thymoquinone on the initiation stage of diethylnitrosamine hepatocarcinogenesis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, S.A.; Attia, Y.M.; Maurice, N.W.; Fahim, S.A.; Abdelwahed, F.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Badary, O.A. Thymoquinone Suppresses Angiogenesis in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting miR-1-3p. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, M.E.; Khowailed, A.A.; Aboulhoda, B.E.; Rashed, L.A.; Gaber, S.S.; Ashour, H. Thymoquinone Potentiated the Anticancer Effect of Cisplatin on Hepatic Tumorigenesis by Modulating Tissue Oxidative Stress and Endoplasmic GRP78/CHOP Signaling. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.S.; Wang, H.F.; XU, H.J.; Tan, Z.X.; Zhan, W.Y.; Song, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.M.; Liu, X. Effect of Rhubarb Aphid Fanghe Xiaoyaofang Decoction on Postoperative TACE Syndrome of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Med. Inf. 2018, 31, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.X.; Liu, W. Effects of Dahuang Zhechong Pill on liver function and immune function after interventional therapy for liver cancer. Chin. J. Mod. Drug Appl. 2022, 16, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.F.; Zhao, C. Clinical Observation of Rheum officinale Soda Tablets for treating advanced primary liver cancer. J. Pract. Med. 2007, 11, 1750–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Yi, F.T. The effect of γ knife the combined application of danshen injections on immune function in patients with primary liver cancer. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Liver Dis. 2020, 30, 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Shao, X.W. The clinical efficacy of compound Danshen injection in liver cancer patients and its impact on T cell subsets. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Liver Dis. 2004, 3, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Semwal, R.B.; Semwal, D.K.; Combrinck, S.; Viljoen, A. Emodin—A natural anthraquinone derivative with diverse pharmacological activities. Phytochemistry 2021, 190, 112854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshida, K.; Hirakata, M.; Maeda, A.; Miyoshi, T.; Miyamoto, Y. Toxicological effect of emodin in mouse testicular gene expression profile. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2011, 31, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Hou, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X. Toxicity induced by emodin on zebrafish embryos. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 35, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.H.; Chang, S.C.; Chan, W.H. Injurious effects of emodin on maturation of mouse oocytes, fertilization and fetal development via apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13911–13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Tang, S.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Evaluation of the inhibition risk of shikonin on human and rat UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) through the cocktail approach. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 312, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figat, R.; Zgadzaj, A.; Geschke, S.; Sieczka, P.; Pietrosiuk, A.; Sommer, S.; Skrzypczak, A. Cytotoxicity and antigenotoxicity evaluation of acetylshikonin and shikonin. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 44, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Chen, A.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Assessment of the inhibition risk of shikonin on cytochrome P450 via cocktail inhibition assay. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 281, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakor, N.; Janathia, B. Plumbagin: A Potential Candidate for Future Research and Development. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2022, 23, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Patil, P.A.; Roy, S.; Kholkute, S.D.; Hegde, H.V.; Nair, V. Comparative toxicity profiles of Plumbago zeylanica L. root petroleum ether, acetone and hydroalcoholic extracts in Wistar rats. AYU 2015, 36, 329–334. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, C.; Kim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Yu, J.W.; Song, M.H.; Kim, Y.; Son, J.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.E. Plumbagin, a natural derivative of 1,4-naphthoquinone, induces cyclopic phenomenon via increased apoptosis and ROS generation in the early stage of zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuKhader, M.M.; Khater, S.H.; Al-Matubsi, H.Y. Acute effects of thymoquinone on the pregnant rat and embryo-fetal development. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 36, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Zhong, C.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Wu, Q.; Yao, H. Tanshinone I: Pharmacological activities, molecular mechanisms against diseases and future perspectives. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 110, 154632. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Yu, S.H.; Zhen, W.X.; Cheng, T.; Wang, D.; Lin, J.B.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Shu, L.P.; et al. Tanshinone I, a new EZH2 inhibitor restricts normal and malignant hematopoiesis through upregulation of MMP9 and ABCG2. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6891–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, K.; Chen, J.; Lan, Y.; Qin, Y.; Mei, W.; Wang, B. Evaluation of Tanshinone IIA Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish Embryos. Molecules 2017, 22, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, R.; Ilari, A.; Colotti, B.; Mosca, L.; Fazi, F.; Colotti, G. Doxorubicin and other anthracyclines in cancers: Activity, chemoresistance and its overcoming. Mol. Asp. Med. 2023, 93, 101205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K. The Roles of Doxorubicin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ADMET DMPK 2013, 1, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, K.; Bhaskar, C.; Ahmed, F.; Kondapi, A.K. A target-specific oral formulation of Doxorubicin-protein nanoparticles: Efficacy and safety in hepatocellular cancer. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddik, M.S.; Elsayed, M.M.A.; Abdel-Rheem, A.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Mosa, E.S.; Al-Hakkani, M.F.; Al-Shelkamy, S.A.; Khames, A.; Daha, M.A.; Abdel-Aleem, J.A. A Novel C@Fe@Cu Nanocomposite Loaded with Doxorubicin Tailored for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Alrbyawi, H.; Poudel, I.; Arnold, R.D.; Babu, R.J. Co-delivery of Doxorubicin and Ceramide in a Liposomal Formulation Enhances Cytotoxicity in Murine B16BL6 Melanoma Cell Lines. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Lin, L.; Chen, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhu, K.; Shuai, X. Codelivery of sorafenib and GPC3 siRNA with PEI-modified liposomes for hepatoma therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 2468–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Diao, W.; Xue, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Jiang, B.; Bai, J.; Lian, B.; Feng, W.; Sun, T.; et al. Improved efficacy of doxorubicin delivery by a novel dual-ligand-modified liposome in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Cheng, S.; Bai, X.; Zhang, D.; Fang, H.; Che, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, W.; Liang, Q.; et al. Development of an efficient liposomal DOX delivery formulation for HCC therapy by targeting CK2α. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 19, e2400050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.J. Mechanism of action of mitoxantrone. Neurology 2004, 63 (Suppl. S6), S15–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Sato, Y.; Furuse, J.; Mitsunaga, S.; Ueno, H.; Morizane, C.; Inaba, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Arai, Y. A Phase I/II trial of continuous hepatic intra-arterial infusion of 5-fluorouracil, mitoxantrone and cisplatin for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 47, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mizushima, N.; Yoshimori, T.; Levine, B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell 2010, 140, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; He, X.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, Y. High-throughput screening identified mitoxantrone to induce death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells with autophagy involvement. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 521, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcamone, F.; Bernardi, L.; Giardino, P.; Patelli, B.; Marco, A.; Casazza, A.M.; Pratesi, G.; Reggiani, P. Synthesis and antitumor activity of 4-demethoxydaunorubicin, 4-demethoxy-7,9-diepidaunorubicin, and their beta anomers. Cancer Treat. Rep. 1976, 60, 829–834. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, M. Oral idarubicin--an anthracycline derivative with unique properties. Ann. Hematol. 1993, 66, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, M.; Han, X.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Kang, J.; Kong, X.; Sun, G.; et al. Idarubicin-loaded biodegradable microspheres enhance sensitivity to anti-PD1 immunotherapy in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Biomater. 2023, 157, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Wu, P.C.; Chan, G.C.; Lok, A.S.; Lin, H.J. Doxorubicin versus no antitumor therapy in inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma. A prospective randomized trial. Cancer 1988, 62, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, J.W.; Dangoor, A.; Beech, J.; Sherlock, D.J.; Lee, S.M.; Scarffe, J.H.; Swindell, R.; Ranson, M. Treatment of inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD): Results of a phase II study. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, W.Y.; Lin, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Vecchione, A.; Park, S.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Wong, S.; Xu, R.; Peng, C.Y.; et al. Phase III HEAT Study Adding Lyso-Thermosensitive Liposomal Doxorubicin to Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Lesions. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, F.A.; Evans, W.K.; Blackstein, M.E.; Fine, S.; Heathcote, J.; Langer, B.; Taylor, B.; Habal, F.; Kutas, G.; Pritchard, K.I.; et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of mitoxantrone in the treatment of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1987, 5, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Farrés, M.T.; de Baere, T.; Lagrange, C.; Ramirez, L.; Rougier, P.; Munck, J.N.; Roche, A. Percutaneous mitoxantrone injection for primary and secondary liver tumors: Preliminary results. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 1998, 21, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Sun, X.; Zeng, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z. A randomized multicenter phase II clinical trial of mitoxantrone-loaded nanoparticles in the treatment of 108 patients with unresected hepatocellular carcinoma. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 419–423. [Google Scholar]
- Mitomycin. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012.
- Cheirsilpa, A.; Leelasethakul, S.; Auethaveekiat, V.; Maoleekulpriroj, S.; Kangsumrit, N.; Thanakaravit, P.; Phanthumjida, P. High-dose mitomycin C: Activity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 24, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulin, M.; Guiu, S.; Chauffert, B.; Aho, S.; Cercueil, J.P.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Krause, D.; Fagnoni, P.; Hillon, P.; Bedenne, L.; et al. Screening of anticancer drugs for chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2011, 22, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulin, M.; Hillon, P.; Cercueil, J.P.; Bonnetain, F.; Dabakuyo, S.; Minello, A.; Jouve, J.L.; Lepage, C.; Bardou, M.; Wendremaire, M.; et al. Idarubicin-loaded beads for chemoembolisation of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the IDASPHERE phase I trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.S.; Teyssier, Y.; Abousalihac, M.; Seigneurin, A.; Ghelfi, J.; Sengel, C.; Decaens, T. Idarubicin vs doxorubicin in transarterial chemoembolization of intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, C.; Santos, R.X.; Cardoso, S.; Correia, S.; Oliveira, P.J.; Santos, M.S.; Moreira, P.I. Doxorubicin: The good, the bad and the ugly effect. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 3267–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciarrino, E.; Simonetti, R.G.; Le Moli, S.; Pagliaro, L. Adriamycin treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Experience with 109 patients. Cancer 1985, 56, 2751–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Tommasini, M.A.; Del Ninno, E.; Rumi, M.G.; De Fazio, C.; Dioguardi, M.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Italy: Report of a clinical trial with intravenous doxorubicin. Liver 1985, 5, 336–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dunk, A.A.; Scott, S.C.; Johnson, P.J.; Melia, W.; Lok, A.S.; Murray-Lyon, I.; Williams, R.; Thomas, H.C. Mitozantrone as single agent therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. A phase II study. J. Hepatol. 1985, 1, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, R.M.; Moura, D.J.; Viau, C.M.; Caceres, R.A.; Henriques, J.A.P.; Saffi, J. Pathways of cardiac toxicity: Comparison between chemotherapeutic drugs doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 2063–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, J.; Pinedo, H.M. Mitomycin C: Mechanism of action, usefulness and limitations. Anti-Cancer Drugs 1990, 1, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Nakayama, T.; Hiyama, Y.; Iwama, S.; Goto, N.; Takashi, M.; Ohtsuki, T.; Kono, K.; Nakajima, Y.; et al. Arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with mitomycin C microcapsules. Radiology 1984, 152, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, S.M.; Koeller, J.M. Idarubicin: A second-generation anthracycline. DICP Ann. Pharmacother. 1991, 25, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X.; Han, J.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, W.; Su, L.; et al. Emodin attenuates cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by directly binding to GSDMD. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 121, 155105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, H.; Li, W.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Li, D.; Jin, L. Shikonin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via Mst1/Nrf2 pathway in mice. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, D.; Ozturk, E.; Kaymak, E.; Akin, A.T.; Yakan, B. Thymoquinone attenuates doxorubicin-cardiotoxicity in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymak, E.; Öztürk, E.; Akİn, A.T.; Karabulut, D.; Yakan, B. Thymoquinone alleviates doxorubicin induced acute kidney injury by decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Biotech. Histochem. Off. Publ. Biol. Stain Comm. 2022, 97, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E.; Kaymak, E.; Akin, A.T.; Karabulut, D.; Ünsal, H.M.; Yakan, B. Thymoquinone is a protective agent that reduces the negative effects of doxorubicin in rat testis. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2020, 39, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Hong, Y.; et al. Tanshinone I inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating Nrf2 signaling pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 106, 154439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, D.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y. Tanshinone IIA inhibits cardiomyocyte apoptosis and rescues cardiac function during doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by activating the DAXX/MEK/ERK1/2 pathway. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2022, 107, 154471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.Y.; Wang, P.F.; Lin, H.Y.; Tang, C.Y.; Zhu, H.L.; Yang, Y.H. Naphthoquinones: A continuing source for discovery of therapeutic antineoplastic agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Singh, A.; Negi, P.; Kapoor, V.K. Thymoquinone: A small molecule from nature with high therapeutic potential. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2716–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fan, W.; Li, H.; Qiao, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Guo, J.; Huang, K.; Tang, Y.; Wen, J.; et al. Idarubicin versus Epirubicin in Transarterial Chemoembolization for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage B Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Open-label, Randomized, Phase IV Trial. Radiology 2025, 315, e242315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yan, H.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Huang, M. Idarubicin versus epirubicin in drug-eluting beads-transarterial chemoembolization for treating hepatocellular carcinoma: A real-world retrospective study. Investig. New Drugs 2023, 41, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.W.; Kim, H.C.; Han, J.; Jang, M.J.; Chung, J.W. Transarterial Chemoembolization Using Idarubicin Versus Doxorubicin Chemoemulsion in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (IDADOX): Protocol for a Randomized, Non-inferiority, Double-Blind Trial. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 47, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Medicine | Model | Administration and Relevant Experiments | Therapeutic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emodin | SD rats | Administration: Oral gavage at 40 mg/kg/day. Relevant experiments: Liver morphology and nodule formation, and histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses were examined. Oxidative stress levels and antioxidant activity were also evaluated. In addition, the expression of angiogenesis- and oxidative stress–related proteins, such as ADAMTS-4 and MMP3, was assessed using Western blotting and RT-PCR. | The treatment significantly reduced the number of hepatic nodules and improved the structural integrity of hepatocytes in HCC-bearing rats. It also downregulated the mRNA and protein expression levels of PKCδ, ERK5, ADAMTS-4, MMP3, and VEGF in the liver, suggesting a potential inhibitory effect on angiogenesis in HCC. | [19] |
| Hep-G2 cells | Administration: 60 μM Relevant experiments: Transwell migration and invasion assays, Ad-mCherry-GFP-LC3B transfection assay, validation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway, RNA sequencing, and other cell-based experiments. | Emodin significantly inhibits the proliferation of Hep-G2 cells and reduces the migration and invasion abilities of Hep-G2 cells. Moreover, emodin regulates the expression of proteins related to EMT, autophagy, and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. | [18] | |
| Emodin + Sorafenib | nude mice | Administration: Emodin was administered via intraperitoneal injection at 10 mg/kg/day, and sorafenib at 5 mg/kg/day. Relevant experiments: Tumor size was measured using calipers, and protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry. | Emodin can enhance the anticancer efficacy of sorafenib by inhibiting tumor growth and inducing apoptosis in tumor cells. | [20] |
| Hep-G2 cells | Administration: 20 μM Emodin, 2 μM Sorafenib Relevant experiments: The main experiments conducted included cell cycle analysis, Ki67 cell proliferation assay, Western blotting, apoptosis detection, intracellular cholesterol measurement, and qRT-PCR. | Emodin synergistically enhances the inhibitory effect of sorafenib on liver cancer cells. Moreover, the combination treatment more effectively suppresses cholesterol synthesis, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and inhibits both the STAT3 and AKT signaling pathways. | ||
| Emodin + Cisplatin | Hep-G2 cells | Administration: Emodin at 6.25, 25, and 50 μg/mL; cisplatin at 2.5 μg/mL. Relevant experiments: The main experiments conducted included wound healing assay, Transwell assay, gelatin zymography to detect the activities of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), ELISA, and immunofluorescence analysis of E-cadherin and vimentin expression. | When combined with cisplatin, emodin can inhibit the EMT process in Hep-G2 cells by downregulating the protein expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and upregulating E-cadherin, thereby suppressing cell migration. | [24] |
| Shikonin | HCCLM3 cells Hep-G2 cells | Administration: Shikonin at 0.5, 2 μM Relevant experiments: The main assessments include apoptosis detection, mitochondrial membrane potential and mass assay, cellular oxygen consumption measurement, and ATP quantification. | Shikonin can induce oxidative stress in HCCLM3 cells and downregulate the expression of Bcl-2 and p53, thereby promoting apoptosis. Additionally, it inhibits cancer cell metabolism by regulating energy metabolism. | [26,27] |
| PLB | nude male BALB/c mice | Administration: PLB was administered via intravenous injection at 2 mg/kg/day. Relevant experiments: Tumor weight in mice was monitored, and the expression levels of GPX4, ubiquitin, and cleaved caspase-3 were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. | PLB inhibits tumor growth by promoting GPX4 degradation and inducing apoptosis, demonstrating a good safety profile. | [29] |
| PLB | nude male BALB/c mice | Administration: Intraperitoneal injection of PLB (4 mg/kg/day). Relevant experiments: Observation of metastatic nodules in the lungs and liver via in vivo imaging and HE staining. Immunohistochemical analysis to assess the expression of relevant proteins in liver tissue. | PLB can inhibit the progression of liver cancer and its pulmonary metastasis. Additionally, PLB effectively suppresses the EMT in liver cancer. | [30] |
| Huh-7 cells | Administration: 2 μM, 4 μM, 8μM PLB Relevant experiments: The main experiments focused on investigating the effects of PLB on TGF-β–induced EMT in Huh-7 cells and the regulatory effects of PLB on the mRNA expression of EMT-related markers. | PLB effectively inhibits EMT in HCC cells, and this therapeutic effect is concentration-dependent. | ||
| PLB | nude male BALB/c mice | Administration: Intraperitoneal injection of PLB 2 mg/kg/day, TTM: 10 mg/kg/day. Relevant experiments: Tumor volume changes were assessed, and tumor cell distribution was observed via hematoxylin and eosin staining. Molecular analyses included protein profiling, nucleic acid analysis, copper ion concentration measurement, and quantification of oxidative stress-related markers. | PLB can significantly inhibit tumor growth and trigger the Cuproptosis mechanism in liver cancer cells, enhancing cellular oxidative stress. | [17] |
| Huh-7 cells PLC cells | Administration: 6 µM PLB Relevant experiments: The main experiments included cell cycle analysis, copper ion detection assays, immunofluorescence staining, transfection experiments, luciferase reporter assays, and methylation-specific PCR (MSP). | PLB inhibits the proliferation of HCC cells in a dose-dependent manner. At the same time, TTM mitigates the PLB-induced reduction in cell viability, indicating that PLB primarily suppresses HCC cell growth through cuproptosis. | ||
| PLB + DOX | C57BL/6 mice | Administration: Intravenous injection of DOX (12 mg/kg) and PLB (2 mg/kg). Relevant experiments: Histopathological analysis of tumor tissues, Western blot analysis, and detection of apoptotic cells. | The targeted formulation prepared by combining PLB and DOX can inhibit the growth of drug-resistant tumors. | [31] |
| Tan I + EADM | C57BL/6J mice | Administration: Tail vein injection of Tan I (15 mg/kg) and EADM (3 mg/kg). Relevant experiments: Biochemical analysis of mouse serum, urine, and other samples. Immunohistochemical staining of xenograft tumor sections. | The combination treatment of Tan I and EADM significantly reduces tumor volume more effectively than monotherapy and induces apoptosis to a greater extent. | [37] |
| Hep-G2 cells Huh-7 cells | Administration: Tan I at (40 μM); EADM at (0.25 μM) Relevant experiments: The main experiments included cell transfection, evaluation of drug combination synergy, and apoptosis analysis. | Tan I can act synergistically with EADM to enhance the inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α signaling pathway and reverse HIF-1α–mediated drug resistance. | ||
| Tan IIA | C57BL6/J mice | Administration: Oral gavage of Tan IIA (low dose: 45 mg/kg, high dose: 90 mg/kg) and RMP1-14 (5 mg/kg). Relevant experiments: Conducted fluorescence scanning of mouse abdominal tumors, tumor cell apoptosis detection (flow cytometry analysis), immunofluorescence staining, and ultrasound Doppler blood flow measurement. | Tan IIA can significantly inhibit tumor growth, improve the immune microenvironment, enhance the therapeutic efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors, and simultaneously improve tumor vascular function and promote vascular normalization. | [40] |
| Tan IIA + Sorafenib/SC-1 | Huh-7 cells Hep-G2 cells | Administration: Tan IIA (1.5 μg/mL), sorafenib (2.5 μM; 5 μM), and SC-1 (5 μM) Relevant experiments: The main experiments included flow cytometry analysis (for apoptosis detection and sub-G1 cell population analysis), cell migration, and invasion assays. | The combination of Tan IIA with sorafenib or SC-1 significantly enhanced the induction of the mitochondrial extrinsic apoptotic pathway in HCC cells, inhibited their migration and invasion, and markedly suppressed the STAT3 signaling pathway by downregulating the expression of phosphorylated STAT3 | [41] |
| TQ | Adult male rats | Administration: Add TQ (5 mg/kg/day) to drinking water. Relevant experiments: Performed immunohistochemical staining, qRT-PCR analysis, and other assessments. | TQ significantly downregulated the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2, thereby promoting apoptosis. Additionally, TQ ameliorated multiple histopathological alterations in the hepatic parenchyma induced by DEN. | [44] |
| TQ + Cisplatin | Wistar rats | Administration: Oral gavage of TQ (20 mg/kg) and intraperitoneal injection of cisplatin (2 mg/kg). Relevant experiments: Performed biomarker assays (ALT, AST, AFP, etc.), detection of oxidative stress-related markers, and histological analysis. | The combination therapy group demonstrated superior liver function to the disease control and monotherapy groups, as evidenced by significantly improved ALT, AST, and other liver function markers. Moreover, the hepatic structural architecture in the combination group was markedly improved. | [46] |
| Compound Drug | Study Group Size | Treatment Protocol | Therapeutic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Da Huang Zhe Chong Formula combined with Xiao Yao Formula | The study included 60 patients with primary HCC in stages II–III who were ineligible for surgery. After obtaining approval from the hospital’s ethics committee, the patients were divided into a treatment group and a control group, each consisting of 30 patients. | After undergoing TACE, the control group received supportive treatment including glucose and electrolyte supplementation, second-generation cephalosporins for infection prevention, and routine hepatoprotective therapy. Based on this regimen, the treatment group additionally received oral administration of a combined decoction of Xiaoyao Formula and Da Huang Zhe Chong Formula. | Significantly reduces the incidence of post-TACE syndrome in primary HCC. | [47] |
| Da Huang Zhe Chong Pill | In this study, 90 patients who had undergone interventional therapy for liver cancer were selected as the research subjects. Using the random number table method, they were randomly assigned to the experimental and control groups, with 45 patients in each group. | The control group received hepatoprotective treatment with compound glycyrrhizin injection. On this basis, the experimental group was additionally treated with oral administration of Da Huang Zhe Chong pills at 3 g per administration, twice daily. | Significantly improves liver function after interventional liver cancer therapy while enhancing patients’ immune function. | [48] |
| Da Huang Soda Tablets | In this study, a total of 76 patients with advanced primary liver cancer were enrolled, including 64 cases complicated by cirrhosis following hepatitis and 8 cases who had previously undergone transarterial embolization and chemotherapy. There were 38 patients in the treatment group and 38 in the control group. No significant differences were observed between the two groups regarding gender, age, clinical condition, disease duration, or other baseline characteristics. | Both groups received hepatoprotective, supportive, and symptomatic treatment; additionally, the treatment group was administered 2 to 5 tablets of Da Huang Soda Tablets daily for a duration of two months. | It improves symptoms such as abdominal distension and fatigue and reduces the incidence of complications, including ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and upper gastrointestinal bleeding. | [49] |
| Danshen Injection | A total of 40 patients with primary liver cancer who underwent Gamma Knife radiosurgery were included in this study. They were randomly divided into two groups, the experimental group and the control group, based on a random number table method. No statistically significant differences were found in the clinical data between the two groups. | From the first day of Gamma Knife treatment, patients in the experimental group were simultaneously administered 20 mL of Compound Danshen Injection diluted in 250 mL of 5% glucose injection via intravenous infusion once daily, continuing until the completion of Gamma Knife therapy. In contrast, patients in the control group did not receive this intervention during the course of Gamma Knife treatment. | The treatment effectively increased the levels of immunoglobulins in patients with primary liver cancer, stimulated the proliferation of CD3+ T cells and CD4+ T cells, and inhibited the production of CD8+ T cells. This, in turn, enhanced the overall immune function. | [50] |
| Danshen Injection | A total of 64 patients with HCC were included in this study, with 34 patients in the treatment group and 30 in the control group. No significant differences were observed between the two groups regarding age, gender, disease duration, or symptoms and signs. None of the patients in either group received chemotherapy. All cases were characterized by multiple nodular tumors, making catheter-based treatments unfeasible. | Both groups received 15 mL of Huachansu Injection once daily via intravenous infusion. On this basis, the treatment group was additionally administered 60 mL of Compound Danshen Injection diluted in 500 mL of 10% glucose solution via intravenous infusion once daily. The treatment course lasted for 30 days. | The treatment enhanced cellular immunity, improved clinical symptoms and signs, and prolonged the survival time of patients. | [51] |
| Quinone Compounds | Model | Administration and Relevant Experiments/Relevant Tests | Toxicity and Adverse Reactions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emodin | Male ICR mice Zebrafish Female ICR mice | Administration: Emodin: Oral administration at 1000 mg/kg (Male ICR mice); Oral administration at 0–40 μM (Female ICR mice); 0–2 μg/mL (Zebrafish) Relevant experiments: The study primarily included histopathological analysis, DNA microarray profiling qPCR, assessment of embryo sac developmental potential, evaluation of the in vivo effects of emodin exposure, analysis of anti-apoptotic effects, as well as observation and documentation of zebrafish embryonic development. | It causes testicular toxicity in mice, reduces the maturation of mouse oocytes and in vitro fertilization rates, leads to early embryonic developmental damage, and adversely affects the hatching of zebrafish embryos. | [53,54,55] |
| Shikonin | SD rats Conventional V79 cell line Human liver microsomes | Administration: Shikonin: 0.05, 0.1 mg/L (Conventional V79 cell line); intravenous injection 4 or 8 mg/kg (SD rats); 0.2–20 μM (Human liver microsomes) Relevant experiments: The study primarily involved cytotoxicity assays, micronucleus tests, CYP enzyme activity assays, and enzyme inhibition kinetics analyses. | It possesses cytotoxicity, dermal toxicity, and hepatotoxicity, with a potential inhibitory effect on cytochrome P450, which may affect metabolism and lead to drug–drug and food–drug interaction toxicities. | [56,57,58] |
| PLB | Wistar rats | Administration: PZPE, PZAC, PZHY: A single oral dose of 2000 mg/kg was administered for each of the three extracts (Acute toxicity study). Apart from the control group, the remaining three groups were each further divided into three subgroups. The PZPE group received oral administration of the extract at doses of 2.75 mg/kg, 5.5 mg/kg, and 11.0 mg/kg, respectively. The other two groups were treated with their respective extracts at doses 10 times those used in the corresponding PZPE subgroups. (Subacute toxicity study) Relevant experiments: The study primarily evaluated biochemical parameters such as AST and ALT, hematological indicators including hemoglobin (Hb), and conducted histopathological examinations of the liver and kidneys in each group. | Various PLB extracts led to elevated biochemical markers such as AST and urea levels in experimental animals and induced congestion in both the liver and kidneys. In addition, the petroleum ether extract (PZPE) specifically caused a reduction in hemoglobin (Hb) levels and hematocrit. | [60] |
| PLB | Zebrafish embryo | Administration: PLB: 0.13, 0.26, 0.40 and 0.53 μM (Acute toxicity study); 0.4 μM PLB (RT-qPCR analysis); 0.13, 0.26 μM (In situ hybridization (ISH) analysis) Relevant experiments: The study primarily included acute toxicity assessment, evaluation of neurodevelopmental impairment, gene expression analysis (targeting genes such as gsc, pax2a, and foxb1a), micro-CT imaging to assess ocular morphology, and metabolomic analysis. | PLB exposure significantly impaired brain differentiation in zebrafish embryos and induced severe developmental abnormalities, including spinal curvature, pericardial edema, tail malformations, and pronounced cyclopia. | [61] |
| TQ | Pregnant Wistar rats | Administration: TQ: Except for the control group, each of the other three groups was further divided into two subgroups, which received intraperitoneal injections of thymoquinone (TQ) at doses of 15 mg/kg, 35 mg/kg, and 50 mg/kg on gestational Day 11 and Day 14, respectively. Relevant experiments: This study primarily involved measuring serum α-amylase levels, histopathological examinations, and external and skeletal evaluations of fetuses. | Pregnant mice administered 35 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg of thymoquinone (TQ) on gestational Day 11 exhibited signs of toxicity, including abdominal distension and vaginal bleeding. Fat necrosis and inflammation around the pancreas were observed in the transverse mesocolon or mesentery. However, no external or skeletal abnormalities were detected in the fetuses. | [62] |
| Tan IIA | Zebrafish Zebrafish embryos | Administration: Both the chorionic embryo group and the dechorionated embryo group were treated with tanshinone IIA at concentrations of 1.0 μM, 5.0 μM, 10.0 μM, 20.0 μM, and 50.0 μM. Relevant experiments: Crystallographic analysis and assessments of lethal and teratogenic effects were conducted in this study. | Zebrafish embryos with developmental defects exhibited pericardial edema, spinal curvature, and tail loss. | [65] |
| Quinone Compounds | Model | Processing Method/Therapy | Administration and Relevant Experiments | Therapeutic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOX | Wistar rats | Apo-transferrin and nanolactoferrin particles loaded with doxorubicin | Administration: Oral administration of DOX at a dose of 4 mg/kg or protein nanoparticles loaded with an equivalent dose of DOX. Relevant experiments: Liver nodules were counted, and pathological assessments were performed using H&E staining. In addition, RT-PCR and WB analyses were conducted to evaluate the mRNA and protein expression levels of tumor-related markers associated with angiogenesis and apoptosis, including p53 and VEGFR1. | Reduction in the number of liver nodules, increased intrahepatic DOX concentration, and upregulated expression of cancer control-related proteins. | [68] |
| DOX | BALB/C-nu mice | DOX-loaded liposomes modified with glycyrrhetinic acid and peanut agglutinin as ligands. | Administration: Cy7, Cy7-Lips, Cy7-GA-Lips, Cy7-PNA-Lips, and Cy7-GA/PNA-Lips were administered via tail vein injection at a dose of 10 mg (For the in vivo imaging experiments); Normal saline (NS), DOX, DOX-Lips, DOX-GA-Lips, DOX-PNA-Lips, and DOX-GA/PNA-Lips were administered via intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 5 mg/kg (For the anti-tumor efficacy experiments) Relevant experiments: The study primarily involved in vivo imaging, assessment of anti-tumor efficacy, and histopathological analysis to evaluate the formulation’s therapeutic performance and biological effects. | Cy7-GA/PNA-Lips exhibited excellent targeting ability in in vivo imaging. Moreover, this formulation achieved more than twice the tumor inhibition rate compared to free DOX, while inducing significantly lower systemic toxicity. | [72] |
| DOX | Hep-G2 cells | Combined with C@Fe@Cu nanocomposite materials | Administration:0.04–80 µg/mL(DOX/DOX-C@Fe@Cu NC) Relevant experiments: MTT assay was performed to evaluate cytotoxicity, and flow cytometry was used for apoptosis analysis. | Exhibits greater cytotoxicity compared to the DOX-only group. | [69] |
| MTX | Hep-G2 cells | In combination with the autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (CQ) | Administration: MTX: 0 to 10 μM (MTX dose–response experiment) MTX: 5 μM; CQ: 20 μM (the combination treatment experiment) MTX: 5, 7.5 and, 10 μM (MTX-induced autophagy experiment) Relevant experiments: Dose–response experiments, cell-killing specificity assays, Western blot analysis, autophagic flux detection, and apoptosis assays were performed. | By inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway, autophagy was activated, leading to specific suppression of the growth and proliferation of HCC cells. | [77] |
| IDA | VX2 rabbits | Preparation of biodegradable microspheres loaded with IDA (IDA-MS) in combination with TACE | Administration: IDA-MS: 0.5 mg Relevant experiments: The main experiments included angiography, PET-CT imaging, and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining analysis. | Inhibits tumor growth and improves histopathological conditions. | [81] |
| C57BL/6 mice | Combination of IDA-MS-TACE with anti-PD-1 immunotherapy | Administration: IDA-MS/IDA: 4 mg/kg Relevant experiments: The main experiments included periodic measurement of tumor size, histological analysis via hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, immunohistochemistry, and mass cytometry analysis. | Enhances CD8+ T cell expression and improves the tumor microenvironment. |
| Quinone Compounds and Administration Methods | Study Group Size | Treatment Protocol | Therapeutic Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intravenous injection of DOX | This study included a total of 106 patients with HCC who were not candidates for surgery. Among them, 60 patients were randomly assigned to receive intravenous doxorubicin injection, while the remaining 46 patients did not receive any antitumor treatment. | In the treatment group, patients received intravenous administration of doxorubicin once every three weeks. The initial dose was 60 mg/m2, which was increased to 75 mg/m2 if well tolerated. If patients exhibited poor tolerance, the dose of doxorubicin was reduced by one-third or one-half, depending on the severity of adverse reactions. Patients in the control group did not receive any antitumor therapy and were followed up once a month, with hospitalization provided if necessary. | The median survival time was improved compared to the control group, and tumor volume was somewhat reduced. However, some patients died due to fatal complications induced by DOX. | [81] |
| Intravenous injection of PLD in glucose solution | As a Phase II clinical study, this research included 16 patients with HCC, who underwent 47 treatment cycles with pegylated liposomal doxorubicin. | On Day 1 of each 28-day treatment cycle, patients received an intravenous infusion of 50 mg/m2 pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) diluted in 250–500 mL of glucose solution. | DOX-induced side effects were alleviated. | [82] |
| LTLD combined with radiofrequency ablation | As part of the Phase III HEAT Study, this study enrolled a total of 701 patients. Among them, 347 patients received radiofrequency ablation (RFA) treatment, while 354 patients were treated with a combination of RFA and laparoscopic transabdominal liver decompression (LTLD). | To prevent hypersensitivity reactions, patients in the RFA + LTLD group were premedicated with dexamethasone, diphenhydramine, and chlorpheniramine, administered either orally or intravenously prior to drug infusion. In contrast, patients in the control group received placebo capsules and an intravenous infusion of either 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% dextrose in water (D5W). Subsequently, patients in the RFA + LTLD group received an intravenous infusion of LTLD at 50 mg/m2, while the control group received D5W. Fifteen minutes after the start of drug infusion, both groups underwent radiofrequency ablation (RFA). | RFA + LTLD did not demonstrate a significant benefit in the general population. However, in the subgroup of patients with a single tumor and an RFA ablation time of ≥45 min, an improvement in overall survival (OS) was observed. | [83] |
| Hepatic artery infusion of MTX | This study enrolled 23 patients with HCC and underwent hepatic arterial infusion of MTX every four weeks. | A catheter was percutaneously inserted into the hepatic artery via the femoral artery, followed by continuous infusion of mitoxantrone. The initial dose was 6 mg/m2/day for 3 consecutive days. Due to the absence of significant toxicity, the dose was subsequently increased to 10 mg/m2/day for 3 days. The treatment was repeated every four weeks. | The treatment demonstrated strong efficacy with relatively low toxicity. | [84] |
| Minimally invasive intratumoral injection of MTX | A total of 9 HCC patients who experienced treatment failure or developed severe complications were included in this study, and they were treated with mitoxantrone-based contrast agent injection therapy. | Under CT guidance, percutaneous intratumoral injection of mitoxantrone was performed. (A 50 mL intravenous contrast agent was administered, and the liver was scanned with a 10 mm collimation thickness during both the arterial and portal venous phases. The puncture site was marked based on the imaging findings. After local anesthesia, a 22-gauge needle was inserted into the center of the lesion for drug delivery). | Percutaneous injection of mitoxantrone was safe and feasible in patients with malignant liver lesions. The chemotherapeutic agent was effectively delivered to the tumor site, and biopsy confirmed tumor necrosis. | [85] |
| Intravenous injection of DHAD-PBCA-NPs | As a phase II clinical study, this research included 108 Chinese patients with HCC. Among them, 57 patients were assigned to the DHAD-PBCA-NPs group for treatment, while 51 were assigned to the DHAD group for treatment. | Patients in the treatment group received an intravenous injection of DHAD-PBCA-NPs at a dose of 12 mg/m2. The control group received an intravenous injection of free DHAD at the same dose of 12 mg/m2. Treatment was administered once every three weeks, and each patient received at least two treatment cycles. | Regarding disease progression and leukopenia rate, it was superior to the DHAD group. | [86] |
| High-dose intravenous injection of MMC | The study included 30 patients, of whom only 23 were histologically or cytologically confirmed to have HCC. Subsequently, these 23 patients received periodic intravenous infusions of MMC and follow-up visits. | Patients received MMC at 20–25 mg/m2 via intravenous infusion on the first day. At Week 6, toxicity was reassessed. Patients with normal blood counts and urinalysis were re-treated with MMC at 50% of the initial dose. Chemotherapy was repeated every 6 weeks at the second dose level until disease progression occurred. | It has a certain degree of tumor inhibitory effect, with toxicity and side effects milder than DOX. | [88] |
| Treatment with IDA microspheres combined with TACE | As a phase I, single-center, open-label, dose-escalation study, this research enrolled 21 patients with HCC. After administering a single session of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), each patient received idarubicin-eluting bead injection therapy, with the idarubicin dosage increasing according to the modified continuous reassessment method. | Idarubicin-loaded microspheres with varying drug loads were selectively administered into each tumor-feeding artery. The microspheres were loaded with idarubicin at five doses: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, and 25 mg. Among the 21 patients enrolled, 9 received a dose of 5 mg, 6 received 10 mg, and 6 received 15 mg of idarubicin. | The median survival time was longer than that of conventional TACE treatment. | [90] |
| Combined treatment with IDA-TACE | In this study, a total of 90 patients with HCC who underwent transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) were enrolled. Among them, 30 received IDA-TACE treatment, while 60 underwent DOX-TACE treatment. | A mixture of 50 mg lyophilized doxorubicin (DOX) or 10 mg lyophilized idarubicin (IDA) with lipiodol was prepared and administered via intra-arterial injection. Embolization was then performed using gelatin sponge particles until arterial blood flow ceased for at least 10 min. Alternatively, 100μM drug-eluting beads (DEBs) loaded with DOX or IDA were infused until saturation of the tumor-feeding artery was achieved. | IDA-TACE has the potential to replace Dox-TACE. | [91] |
| Quinone Compounds | Study Participants | Administration and Relevant Experiments/Relevant Tests | Toxicity and Adverse Reactions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOX | HCC patients | Administration: Doxorubicin was administered via intravenous injection at a dose of 60 mg/m2. Relevant tests: Serum AFP levels, liver imaging, liver biopsy, liver function, electrocardiography (ECG), and two-dimensional echocardiography (2D Echo) tests were performed. | Nausea and vomiting, stomatitis, hair loss, gastrointestinal disturbances, cardiotoxicity, neurotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity. | [81,93,94] |
| MTX | HCC patients | Administration: Methotrexate (MTX) was administered via intravenous injection at a dose of 12 mg/m2. Relevant tests: Complete blood count (CBC), electrocardiography (ECG), and radionuclide ventriculography were performed. In addition, all adverse events occurring during the treatment process were recorded. | Vomiting, hair loss, bone marrow suppression, cardiotoxicity. | [84,86,95] |
| MMC | HCC patients | Administration: Nine patients received a single infusion of 20 mg of mitomycin C microcapsules, while eleven patients received a total dose ranging from 20 to 60 mg. Relevant tests: Complete blood count, urinalysis, liver function tests, electrocardiography (ECG), echocardiography, chest X-ray examination, and histological analysis were performed. | Delayed bone marrow suppression, diarrhea, anorexia, and hair loss. Occasional rash, peritonitis, rare hemolytic uremic syndrome, interstitial pneumonia, and heart failure. | [88,97,98] |
| IDA | HCC patients | Administration: Intravenous administration at a dose of 10–12.5 mg/m2 Relevant tests: Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) assessment, and blood cell count analysis were conducted. Additionally, gastrointestinal and dermatological adverse reactions, including the severity of vomiting, diarrhea, and skin ulceration, were systematically recorded. | Bone marrow suppression, gastrointestinal toxicity, skin toxicity, cardiotoxicity, tissue ulceration, and necrosis caused by extravasation and pain. Rare cases of liver failure and fatal arrhythmias. | [99] |
| Plant-Derived Quinone Compounds | Model | Administration and Relevant Experiments | Attenuation Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emodin | Male C57BL/6 mice | Administration: DOX: 5 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal injection); Emodin: 10, 20 mg/kg (Oral gavage) Relevant experiments: Echocardiography, detection of myocardial injury biomarkers, and histopathological examinations (including HE staining, Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining, and TUNEL assay) were performed. | Alleviate DOX-induced myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction. | [100] |
| Shikonin | Male C57BL/6 mice | Administration: DOX: 4 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal injection); Shikonin: 4 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal injection) Relevant experiments: Echocardiographic examination, hemodynamic monitoring, gene knockdown experiments (targeting Nrf2 expression), detection of cardiac injury biomarkers (such as CK-MB, ALT, and AST), and TUNEL staining were performed. | Shikonin can alleviate DOX-induced myocardial injury, which is associated with reduced inflammation and apoptosis. | [101] |
| Primary cardiomyocytes from SD rats | Administration: DOX: 0.1 μM; Shikonin: 0.1 μM Relevant experiments: Western blotting (WB), RT-PCR analysis, measurement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, and detection of inflammation- and apoptosis-related markers were primarily performed. | Nrf2 is involved in the protective effect of shikonin against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (following Nrf2 silencing, the protective effects of shikonin—such as the regulation of Bax and Bcl-2 expression and the reduction of caspase-3 activity—were all abolished). At the same time, Mst1 plays a key negative regulatory role in shikonin-mediated activation of Nrf2. | ||
| TQ | Male Wistar rats | Administration: TQ group: TQ: 10 mg/kg/day (intraperitoneal injection) for 14 consecutive days; DOX group: DOX: 15 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection on day 7); DOX+TQ group: Mice received both the TQ treatment regimen and the DOX administration as described above. Relevant experiments: The main experiments included histopathological examination, immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis, and TUNEL staining. | Alleviate DOX-induced myocardial and renal tissue damage and increase testicular weight. | [102,103,104] |
| Tan I | Male C57BL/6 mice | Administration: DOX: 5 mg/kg (Tail vein injection); Tan I: 5, 10 mg/kg (Oral gavage) Relevant experiments: The main evaluations included cardiac function monitoring, histopathological examination, serum biomarker analysis, oxidative stress assessment, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation, Western blotting (WB), and apoptosis detection. | It improved cardiac function, alleviated myocardial injury, reduced oxidative stress, and inhibited apoptosis, thereby protecting mitochondria from damage. | [105] |
| H9C2 cells | Administration: DOX: 1 μM; Tan I: 10 μM Relevant experiments: The main experiments included oxidative stress assessment, mitochondrial membrane potential detection, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) measurement, apoptosis analysis, immunofluorescence staining, Western blotting (WB), and Nrf2 knockdown experiments. | Tan I can attenuate oxidative stress, reduce apoptosis, and preserve mitochondrial function, partially through activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. | ||
| Tan IIA | Male C57BL/6 mice | Administration: DOX: 3 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal injection); Tan IIA: 2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg (Low-, medium-, and high-dose groups; Intraperitoneal injection) Relevant experiments: The main experiments included echocardiographic assessment, hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, TUNEL staining, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation, and Western blot (WB) analysis. | Tan IIA alleviated DOX-induced heart failure and reversed structural alterations in the myocardium. Meanwhile, Tan IIA inhibited cardiomyocyte apoptosis by activating the DAXX/MEK/ERK1/2 signaling pathway through upregulating p-ERK1/2 and p-MEK expression. | [106] |
| H9C2 cells | Administration: DOX: 60 μM/L; Tan IIA: 10, 20, 40 μM/L (TUNEL staining); 40 μM/L (RNA extraction) Relevant experiments: The main experiments included Hoechst 33342 and TUNEL staining for detecting apoptosis, RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, qRT-PCR, and Western blotting, among others. | Tan IIA significantly reduces the level of caspase-3, downregulates the mRNA expression of MDR1 and MRP1, upregulates the expression of DAXX, and markedly decreases the percentage of apoptotic cells. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Y.; Liu, M.; Miao, Y.; Pei, K.; Lin, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, G. Research Progress on Quinone Compounds for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101400
Ye Y, Liu M, Miao Y, Pei K, Lin Z, Liu S, Huang X, Wang Y, Lv G. Research Progress on Quinone Compounds for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(10):1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101400
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Yaowu, Mengmeng Liu, Yukang Miao, Ke Pei, Zhe Lin, Songyan Liu, Xiaowei Huang, Yuchen Wang, and Guangfu Lv. 2025. "Research Progress on Quinone Compounds for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Biomolecules 15, no. 10: 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101400
APA StyleYe, Y., Liu, M., Miao, Y., Pei, K., Lin, Z., Liu, S., Huang, X., Wang, Y., & Lv, G. (2025). Research Progress on Quinone Compounds for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomolecules, 15(10), 1400. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101400




