Regional Conservation and Transcriptional Regulation of Tumor-Associated Genes by macroH2A1 Deposition in Mammalian Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Cell Cycle Synchronization
2.2. Nucleosome Preparation and Nchip-Seq
2.3. nChIP-Seq Data Processing
2.4. RNA Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Human Histone Variant mH2A1 Exhibits Widespread Genome Occupancy During Both G1/S and Mitotic Phases
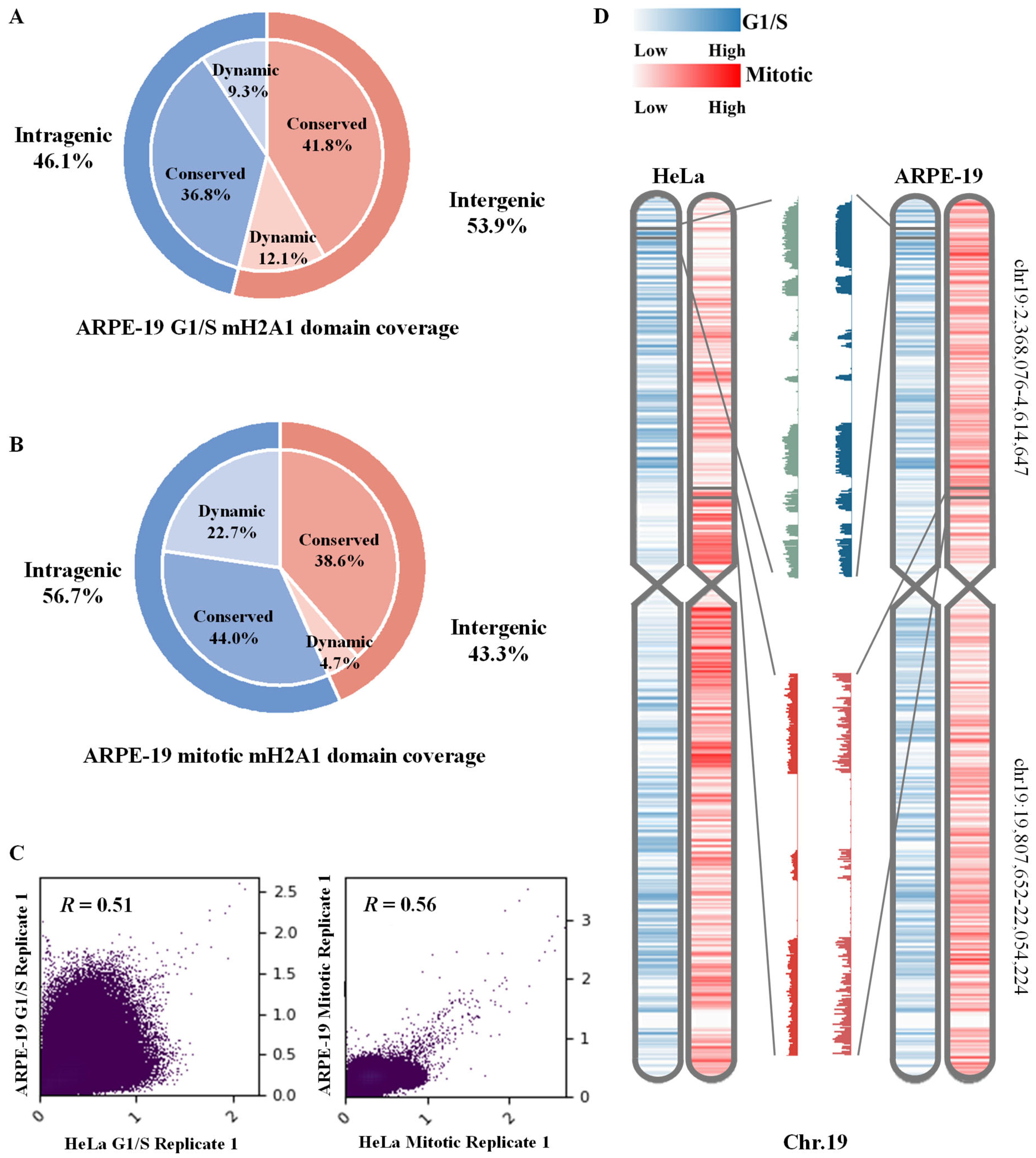
3.2. Dynamic of mH2A1-Enriched Domains Are Conserved from Mouse to Human
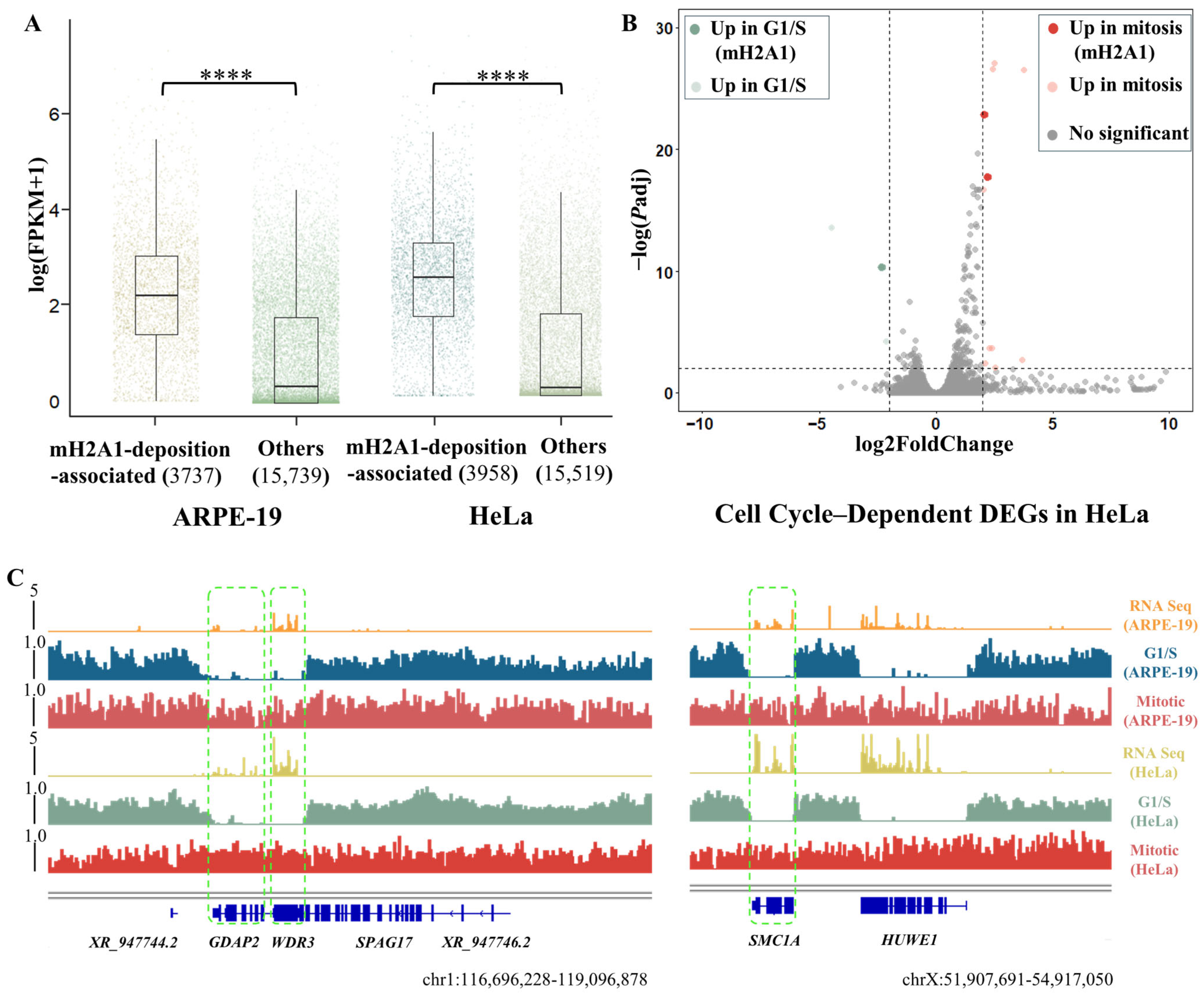
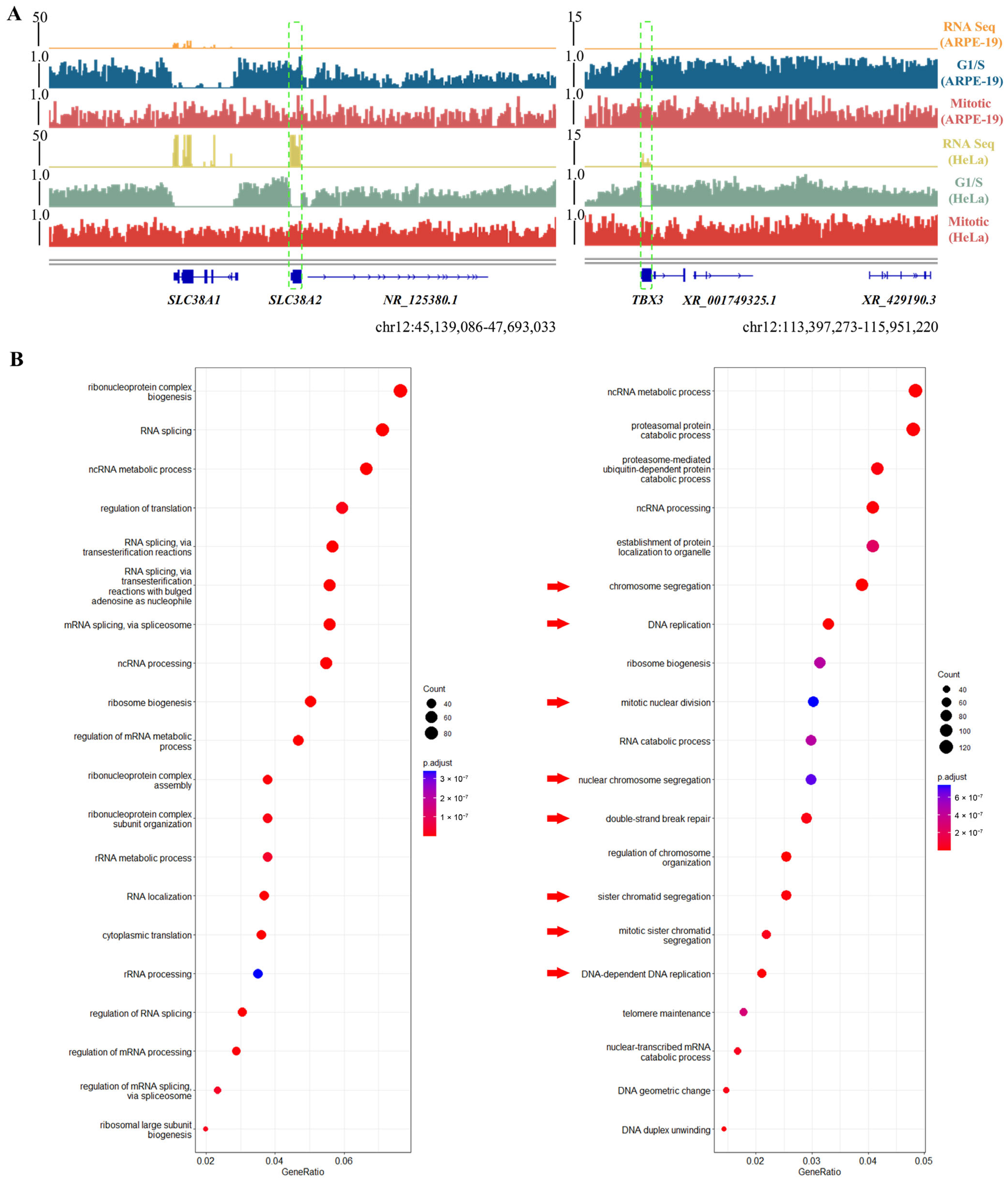
3.3. Dynamic mH2A1 Domains Are Implicated in Tumorigenesis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cutter, A.R.; Hayes, J.J. A brief review of nucleosome structure. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jia, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Fang, D. Overview of Histone Modification. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 1283, pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biterge, B.; Schneider, R. Histone variants: Key players of chromatin. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 356, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Bernstein, E. Histone variant macroH2A: From chromatin deposition to molecular function. Essays Biochem. 2019, 63, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changolkar, L.N.; Singh, G.; Cui, K.; Berletch, J.B.; Zhao, K.; Disteche, C.M.; Pehrson, J.R. Genome-Wide Distribution of MacroH2A1 Histone Variants in Mouse Liver Chromatin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 5473–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasijevic, B.; Rasmussen, T.P. X Chromosome Inactivation and Differentiation Occur Readily in ES Cells Doubly-Deficient for MacroH2A1 and MacroH2A2. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar-Maia, A.; Qadeer, Z.A.; Hasson, D.; Ratnakumar, K.; Leu, N.A.; Leroy, G.; Liu, S.; Costanzi, C.; Valle-Garcia, D.; Schaniel, C.; et al. MacroH2A histone variants act as a barrier upon reprogramming towards pluripotency. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douet, J.; Corujo, D.; Malinverni, R.; Renauld, J.; Sansoni, V.; Marjanović, M.P.; Cantariño, N.; Valero, V.; Mongelard, F.; Bouvet, P.; et al. MacroH2A histone variants maintain nuclear organization and heterochromatin architecture. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1570–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; D.M., C.; Shao, Z. Genome-wide identification of mammalian cell-cycle invariant and mitotic-specific macroH2A1 domains. Biosci. Trends 2023, 17, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.M.; Gong, X.; Chan, K.M. Roles of Histone H2B, H3 and H4 Variants in Cancer Development and Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, A.; Goldberg, M.S.; Cumberland, L.K.; Ratnakumar, K.; Segura, M.F.; Emanuel, P.O.; Menendez, S.; Vardabasso, C.; LeRoy, G.; Vidal, C.I.; et al. The histone variant macroH2A suppresses melanoma progression through regulation of CDK8. Nature 2010, 468, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporn, J.C.; Jung, B. Differential regulation and predictive potential of macroH2A1 isoforms in colon cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 180, 2516–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novikov, L.; Park, J.W.; Chen, H.; Klerman, H.; Jalloh, A.S.; Gamble, M.J. QKI-Mediated Alternative Splicing of the Histone Variant MacroH2A1 Regulates Cancer Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4244–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardenne, E.; Pierredon, S.; Driouch, K.; Gratadou, L.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Espinoza, M.P.; Zonta, E.; Germann, S.; Mortada, H.; Villemin, J.-P.; et al. Splicing switch of an epigenetic regulator by RNA helicases promotes tumor-cell invasiveness. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Parmar, N.; Bhella, G.K.; Robinson, I.K. A simple filtration technique for obtaining purified human chromosomes in suspension. BioTechniques 2014, 56, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, C.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Ye, B.; Li, X.; Czajkowsky, D.M.; Shao, Z. Quantitative catalogue of mammalian mitotic chromosome-associated RNAs. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—FelixKrueger/TrimGalore: A Wrapper Around Cutadapt and FastQC to Consistently Apply Adapter and Quality Trimming to FastQ Files, with Extra Functionality for RRBS Data. Available online: https://github.com/FelixKrueger/TrimGalore (accessed on 29 July 2025).
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Vilella, A.J.; Cuppen, E.; Nijman, I.J.; Prins, P. Sambamba: Fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2032–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, F.; Dündar, F.; Diehl, S.; Grüning, B.A.; Manke, T. deepTools: A flexible platform for exploring deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W187–W191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmuth, J.; Li, N.; Arrigoni, L.; Gianmoena, K.; Cadenas, C.; Gasparoni, G.; Sinha, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Walter, P.; Hengstler, P.G.; et al. normR: Regime enrichment calling for ChIP-seq data. bioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galieva, A.; Egorov, A.; Malogolovkin, A.; Brovin, A.; Karabelsky, A. RNA-Seq Analysis of Trans-Differentiated ARPE-19 Cells Transduced by AAV9-AIPL1 Vectors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.A.; Hitz, B.C.; Sloan, C.A.; Chan, E.T.; Davidson, J.M.; Gabdank, I.; Hilton, J.A.; Jain, K.; Baymuradov, U.K.; Narayanan, A.K.; et al. The Encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): Data portal update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D794–D801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, D.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Weatheritt, R.; Wang, Y.; Blencowe, B.J.; Wang, Z. An extensive program of periodic alternative splicing linked to cell cycle progression. eLife 2016, 5, e10288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general-purpose read summarization program. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, M.; Casas-Delucchi, C.S.; Pabba, M.K.; Prorok, P.; Pradhan, S.K.; Rausch, C.; Lehmkuhl, A.; Maiser, A.; Buschbeck, M.; Pasque, V.; et al. Histone variant macroH2A1 regulates synchronous firing of replication origins in the inactive X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 11659–11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Shim, J.W.; Park, H.S.; Eum, D.-Y.; Park, M.-T.; Yi, J.M.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, S.D.; Son, T.G.; Lu, W.; et al. MacroH2A1 downregulation enhances the stem-like properties of bladder cancer cells by transactivation of Lin28B. Oncogene 2015, 35, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier-Coles, G.; Bröer, A.; McLeod, M.D.; George, A.J.; Hannan, R.D.; Bröer, S. Identification and characterization of a novel SNAT2 (SLC38A2) inhibitor reveals synergy with glucose transport inhibition in cancer cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 963066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, M.; Zois, C.E.; El-Ansari, R.; Craze, M.L.; Rakha, E.A.; Fan, S.-J.; Valli, A.; Haider, S.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; Green, A.R.; et al. Increased expression of glutamine transporter SNAT2/SLC38A2 promotes glutamine dependence and oxidative stress resistance, and is associated with worse prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmer, T.; Hare, S.; Peres, J.; Prince, S. The T-box transcription factor TBX3 drives proliferation by direct repression of the p21WAF1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Cell Div. 2016, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliwaini, S.; Lubbad, A.M.; Shourfa, A.; Hamada, H.A.; Ayesh, B.; Abu Tayem, H.E.M.; Abu Mustafa, A.; Abu Rouk, F.; Redwan, M.M.; Al-Najjar, M. Overexpression of TBX3 transcription factor as a potential diagnostic marker for breast cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 10, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamasbi, E.; Hamelian, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Varmira, K. The cell cycle, cancer development and therapy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 10875–10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, W.K.; Paules, R.S. DNA damage and cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branzei, D.; Foiani, M. Regulation of DNA repair throughout the cell cycle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada, A. Cohesin in cancer: Chromosome segregation and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.L.; Compton, D.A. Chromosomes and cancer cells. Chromosom. Res. 2011, 19, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, M.J.; Frizzell, K.M.; Yang, C.; Krishnakumar, R.; Kraus, W.L. The histone variant macroH2A1 marks repressed autosomal chromatin, but protects a subset of its target genes from silencing. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Qian, J. EnhancerAtlas 2.0: An updated resource with enhancer annotation in 586 tissue/cell types across nine species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D58–D64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Chen, C.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Y.; et al. Inter3D: Capture of TAD Reorganization Endows Variant Patterns of Gene Transcription. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2024, 22, qzae034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Xu, J.; Sun, R.; Mumbach, M.R.; Carter, A.C.; Chen, Y.G.; Yost, K.E.; Kim, J.; He, J.; Nevins, S.A.; et al. Promoter of lncRNA Gene PVT1 Is a Tumor-Suppressor DNA Boundary Element. Cell 2018, 173, 1398–1412.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagnocchi, L.; Poli, V.; Zippo, A. Enhancer reprogramming in tumor progression: A new route towards cancer cell plasticity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2537–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Arensbergen, J.; van Steensel, B.; Bussemaker, H.J. In search of the determinants of enhancer-promoter interaction specificity. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Han, D.; Wei, C.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Chen, L.; Sha, M.; Cao, Y.; Huang, F.; et al. Mesencephalic Astrocyte-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Inhibits Liver Cancer Through Small Ubiquitin-Related Modifier (SUMO)ylation-Related Suppression of NF-κB/Snail Signaling Pathway and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Lee, K.T.; Jang, H.R.; Kim, J.H.; Noh, S.M.; Song, K.S.; Cho, J.S.; Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoo, H.S.; et al. Epigenetic down-regulation and suppressive role of DCBLD2 in gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Kabotyanski, E.B.; Shepherd, J.H.; Villegas, E.; Acosta, D.; Hamor, C.; Sun, T.; Montmeyor-Garcia, C.; He, X.; Dobrolecki, L.E.; et al. Tumor suppressor PLK2 may serve as a biomarker in triple-negative breast cancer for improved response to PLK1 therapeutics. Cancer Res. Commun. 2021, 1, 178–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, G.; Filetti, V.; Ieni, A.; Rapisarda, V.; Ledda, C.; Vitale, E.; Varricchio, S.; Russo, D.; Lombardo, C.; Tuccari, G.; et al. MacroH2A1 Immunoexpression in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kuang, J.; Shen, Y.; Majer, M.M.; Nelson, C.C.; Parsawar, K.; Heichman, K.A.; Kuwada, S.K. The atypical histone macroH2A1.2 interacts with HER-2 protein in cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 23171–23183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corujo, D.; Buschbeck, M. Post-translational modifications of H2A histone variants and their role in cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; Shao, Z.; Li, X. Regional Conservation and Transcriptional Regulation of Tumor-Associated Genes by macroH2A1 Deposition in Mammalian Cells. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101386
Deng Y, Xu Z, Zhang L, Ye B, Shao Z, Li X. Regional Conservation and Transcriptional Regulation of Tumor-Associated Genes by macroH2A1 Deposition in Mammalian Cells. Biomolecules. 2025; 15(10):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101386
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Yongzhuo, Zeqian Xu, Le Zhang, Bishan Ye, Zhifeng Shao, and Xinhui Li. 2025. "Regional Conservation and Transcriptional Regulation of Tumor-Associated Genes by macroH2A1 Deposition in Mammalian Cells" Biomolecules 15, no. 10: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101386
APA StyleDeng, Y., Xu, Z., Zhang, L., Ye, B., Shao, Z., & Li, X. (2025). Regional Conservation and Transcriptional Regulation of Tumor-Associated Genes by macroH2A1 Deposition in Mammalian Cells. Biomolecules, 15(10), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15101386




