Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animal Study
2.3. Enzymatic Release of N-Glycans
2.4. Purification, Reduction, and Permethylation of N-Glycans
2.5. LC-MS Analysis
2.6. LC-PRM-MS Data Validation
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
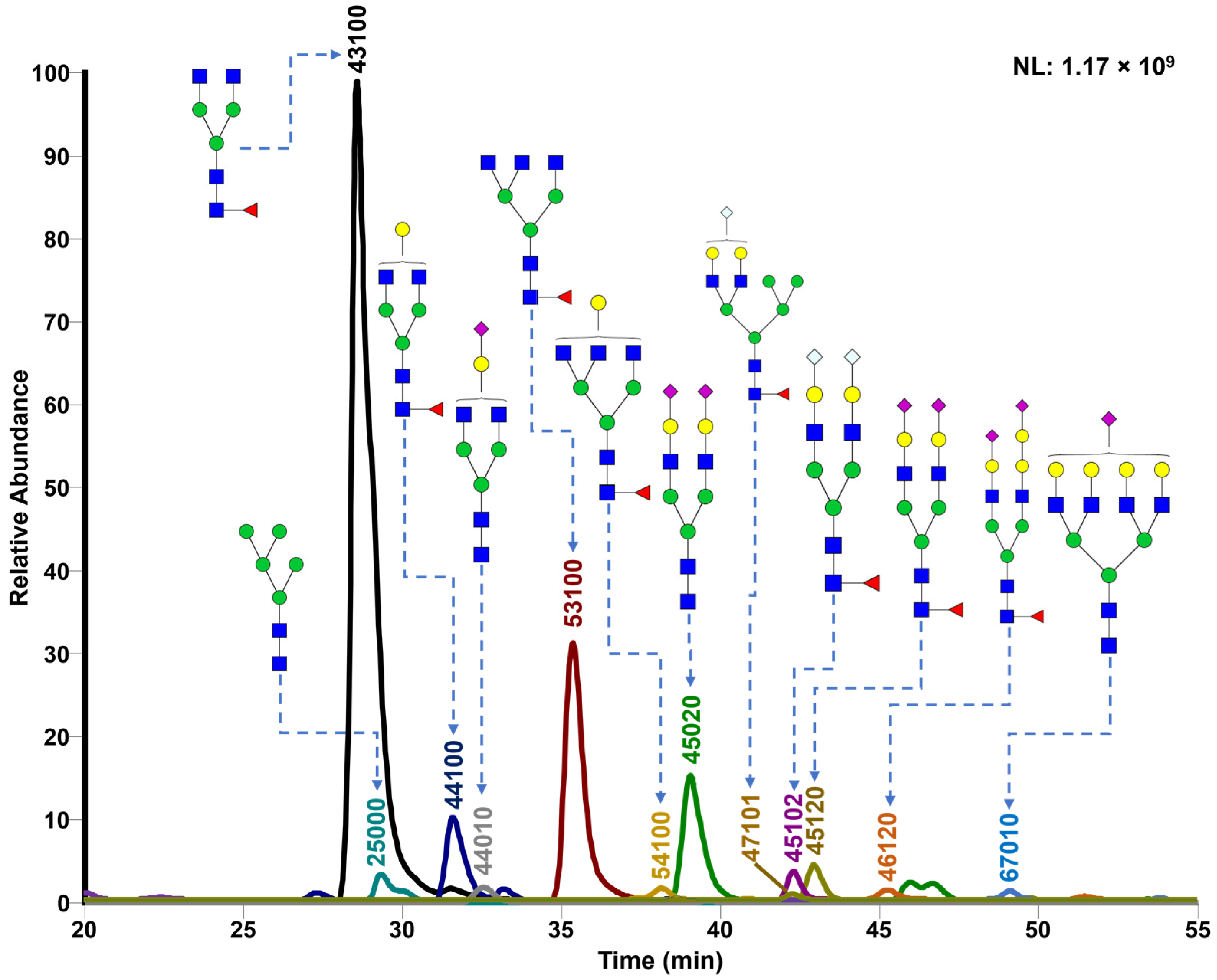
3.1. N-Glycan Profiling in Control and GBH-Exposed Groups
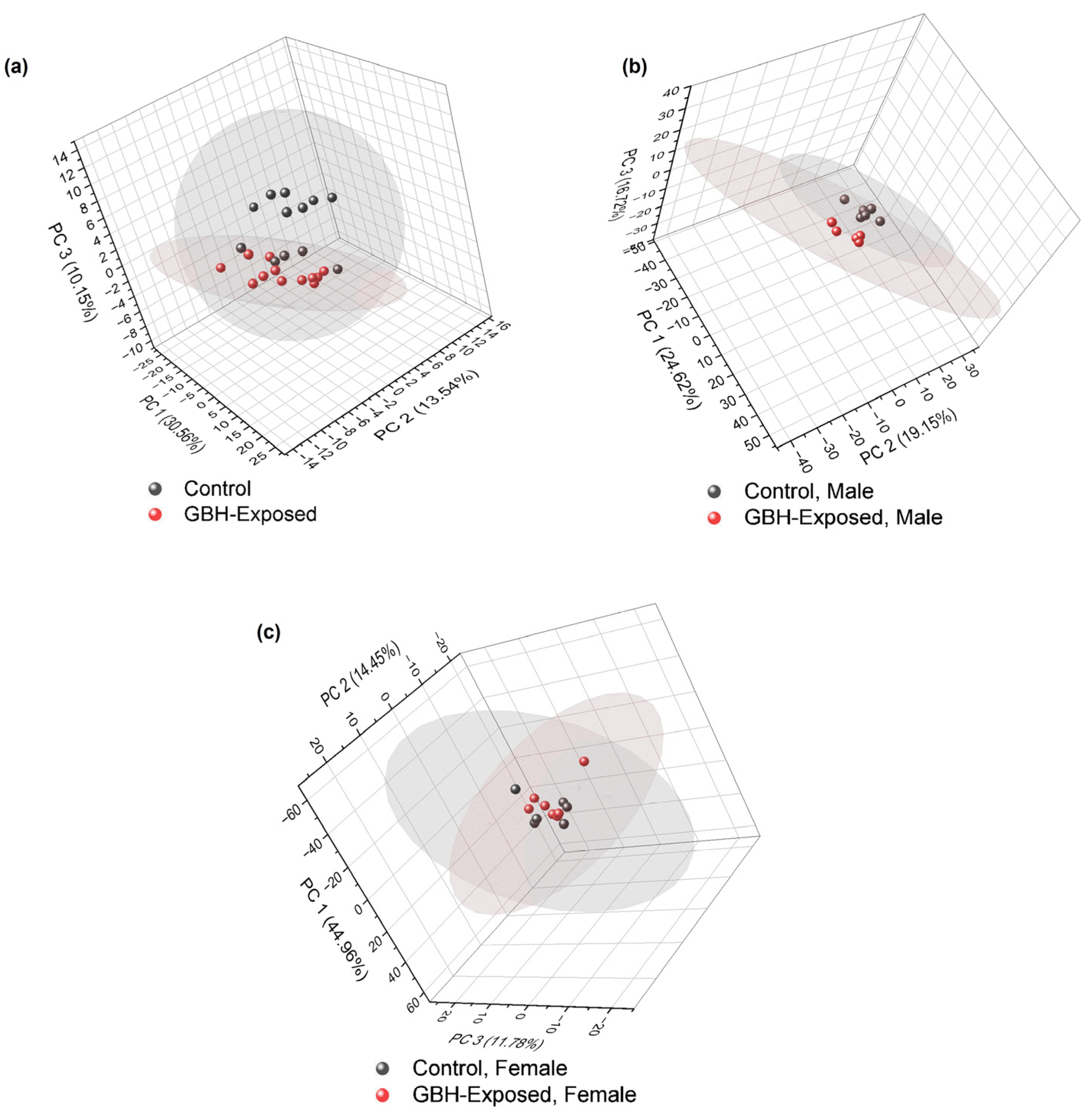
3.2. Unsupervised PCA for Comparative N-Glycomics Analysis
3.3. N-Glycan Heterogeneity
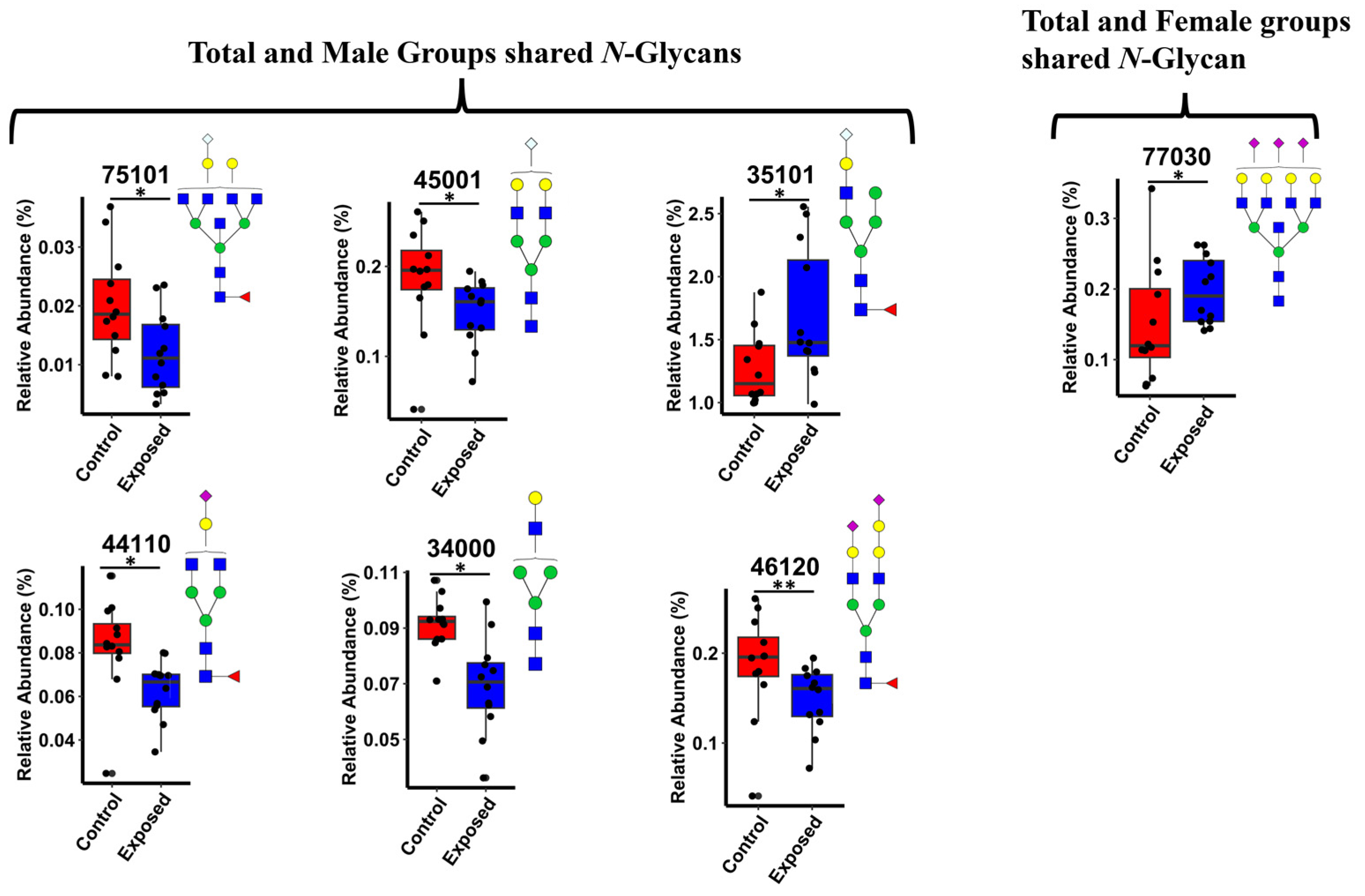
3.4. Differentially Expressed N-Glycans
3.5. PRM Validation
3.6. Expression Analysis/Cluster Heatmaps
3.7. Box Plots and ROC Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dill, G.M.; Sammons, R.D.; Feng, P.C.; Kohn, F.; Kretzmer, K.; Mehrsheikh, A.; Bleeke, M.; Honegger, J.L.; Farmer, D.; Wright, D. Glyphosate: Discovery, development, applications, and properties. Glyphosate Resist. Crops Weeds Hist. Dev. Manag. 2010, 1, 344. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O.; Powles, S.B. Glyphosate: A once-in-a-century herbicide. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 64, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulet-González, A.; Barco-Antoñanzas, M.; Gil-Monreal, M.; Royuela, M.; Zabalza, A. Increased Glyphosate-Induced Gene Expression in the Shikimate Pathway Is Abolished in the Presence of Aromatic Amino Acids and Mimicked by Shikimate. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas-Ferreira, C.; Durán, R.; Faro, L.R.F. Toxic Effects of Glyphosate on the Nervous System: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruggen, A.H.C.; He, M.M.; Shin, K.; Mai, V.; Jeong, K.C.; Finckh, M.R.; Morris, J.G. Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliatto, S.; Ferrero, A.; Vidotto, F. Current and future scenarios of glyphosate use in Europe: Are there alternatives? Adv. Agron. 2020, 163, 219–278. [Google Scholar]
- Duke, S.O. The history and current status of glyphosate. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudsk, P.; Mathiassen, S.K. Pesticide regulation in the European Union and the glyphosate controversy. Weed Sci. 2020, 68, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, K.Z.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Scoccianti, C.; Mattock, H.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of tetrachlorvinphos, parathion, malathion, diazinon, and glyphosate. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 490–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, N.A.; Carpenter, D.O. Effects of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides like Roundup™ on the mammalian nervous system: A review. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, H.; Panin, V.M. The role of protein N-glycosylation in neural transmission. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shental-Bechor, D.; Levy, Y. Effect of glycosylation on protein folding: A close look at thermodynamic stabilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2008, 105, 8256–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, K.B.; Leon, D.R.; Kuang, J.; Meyer, R.D.; Rahimi, N.; Costello, C.E. N-Glycosylation regulates ligand-dependent activation and signaling of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2). J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 13117–13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.; Shyanti, R.K.; Singh, V.; Kale, R.K.; Mishra, J.P.; Singh, R.P. Integrin expression and glycosylation patterns regulate cell-matrix adhesion and alter with breast cancer progression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Coillie, J.; Schulz, M.A.; Bentlage, A.E.; de Haan, N.; Ye, Z.; Geerdes, D.M.; van Esch, W.J.; Hafkenscheid, L.; Miller, R.L.; Narimatsu, Y. Role of N-Glycosylation in FcγRIIIa interaction with IgG. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 987151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, V.K.; Sharma, R.; Prajapati, G.K.; Mohanta, T.K.; Mishra, A.K. N-glycosylation, a leading role in viral infection and immunity development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 8109–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Jin, H.; Wu, Z.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Mao, C.; Hao, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.-F.; Yang, S. Mass Spectrometry-Based Analysis of Serum N-Glycosylation Changes in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizuka, Y.; Kitazume, S.; Taniguchi, N. N-glycan and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 2447–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.M.; Jorwal, P.; Ubilla-Rodriguez, N.C.; Assafa, T.E.; Gatdula, J.R.P.; Vultaggio, J.S.; Harris, D.A.; Millhauser, G.L. N-glycosylation is a potent regulator of prion protein neurotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, A.; Koyama, S.; Kozutsumi, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Suzuki, A. The molecular basis for the absence of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15866–15871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.L.H.; Roth, T.L. Animal Models and Their Contribution to Our Understanding of the Relationship Between Environments, Epigenetic Modifications, and Behavior. Genes 2019, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.F.; Parekh, R.B.; Wing, D.R.; Willis, A.C.; Barclay, A.N.; Dalchau, R.; Fabre, J.W.; Dwek, R.A.; Rademacher, T.W. Comparative analysis of the N-glycans of rat, mouse and human Thy-1. Site-specific oligosaccharide patterns of neural Thy-1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albach, C.; Klein, R.A.; Schmitz, B. Do Rodent and Human Brains Have Different N-Glycosylation Patterns? Biol. Chem. 2001, 382, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, K.C.; Robinson, P.N.; MacRae, C.A. Animal-based studies will be essential for precision medicine. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 352ed12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechref, Y.; Hu, Y.; Desantos-Garcia, J.L.; Hussein, A.; Tang, H. Quantitative glycomics strategies. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 874–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhao, J.; Dong, X.; Banazadeh, A.; Huang, Y.; Hussien, A.; Mechref, Y. Clinical application of quantitative glycomics. Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2018, 15, 1007–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.G.; Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Goli, M.; Gautam, S.; Banazadeh, A.; Mechref, Y. Targeted N-Glycan Analysis with Parallel Reaction Monitoring Using a Quadrupole-Orbitrap Hybrid Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 15215–15222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanni, A.; Goli, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Barsa, C.; El Hayek, S.; Talih, F.; Lanuzza, B.; Kobeissy, F.; Plazzi, G.; et al. LC-MS/MS-Based Proteomics Approach for the Identification of Candidate Serum Biomarkers in Patients with Narcolepsy Type 1. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, M.; Yang, Q.; Zong, G.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; Dhani, H.; Khan, K.; Kroemer, A.; Wang, L.X.; Goldman, R. LC-MS/MS-PRM Quantification of IgG Glycoforms Using Stable Isotope Labeled IgG1 Fc Glycopeptide Standard. J. Proteome Res. 2023, 22, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Reyes, J.; Gutiérrez-Reyes, C.D.; Hernández-Cuellar, E.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A. Neurotoxicity of glyphosate: Focus on molecular mechanisms probably associated with alterations in cognition and behavior. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2024, 106, 104381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Reyes, J.; López-Lariz, C.H.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A. Both acute glyphosate and the aminomethylphosphonic acid intoxication decreased the acetylcholinesterase activity in rat hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and gastrocnemius muscle. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daramola, O.; Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Chávez-Reyes, J.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Nwaiwu, J.; Onigbinde, S.; Adeniyi, M.; Solomon, J.; Bhuiyan, M.M.A.A.; Mechref, Y. Metabolomic Changes in Rat Serum after Chronic Exposure to Glyphosate-Based Herbicide. Metabolites 2024, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayne, K. Revised Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals available. Am. Physiol. Society. Physiol. 1996, 39, 199. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira-Bicca, D.; Chiapinotto-Spiazzi, C.; Bernera-Ramalho, J.; Bucco-Soares, M.; Santos-Cibin, F.W. A subchronic low-dose exposure of a glyphosate-based herbicide induces depressive and anxious-like behavior in mice: Quercetin therapeutic approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67394–67403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Bali, Y.; Kaikai, N.-e.; Ba-M’hamed, S.; Bennis, M. Learning and memory impairments associated to acetylcholinesterase inhibition and oxidative stress following glyphosate based-herbicide exposure in mice. Toxicology 2019, 415, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.G.; Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Mechref, Y. N-Glycomics of Cerebrospinal Fluid: Method Comparison. Molecules 2021, 26, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, C.D.G.; Hakim, M.A.; Atashi, M.; Goli, M.; Gautam, S.; Wang, J.; Bennett, A.I.; Zhu, J.; Lubman, D.M.; Mechref, Y. LC-MS/MS Isomeric Profiling of N-Glycans Derived from Low-Abundant Serum Glycoproteins in Mild Cognitive Impairment Patients. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.; Mechref, Y.; Novotny, M.V. High-throughput solid-phase permethylation of glycans prior to mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass. Spectrom. 2008, 22, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait Bali, Y.; Ba-Mhamed, S.; Bennis, M. Behavioral and Immunohistochemical Study of the Effects of Subchronic and Chronic Exposure to Glyphosate in Mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimatsu, Y.; Joshi, H.J.; Nason, R.; Van Coillie, J.; Karlsson, R.; Sun, L.; Ye, Z.; Chen, Y.H.; Schjoldager, K.T.; Steentoft, C.; et al. An Atlas of Human Glycosylation Pathways Enables Display of the Human Glycome by Gene Engineered Cells. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 394–407.e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, B. Lysosomal metabolism of glycoproteins. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 1r–15r. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Müller, F.-J.; Zenke, M.; Schuppert, A. Principal components analysis and the reported low intrinsic dimensionality of gene expression microarray data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A. Genetic basis for the lack of N-glycolylneuraminic acid expression in human tissues and its implication to human evolution. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2006, 82, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, R. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, O.M.T.; Läubli, H. Sialic acids in cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology 2015, 26, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, G.P.; Colley, K.J. Sialylation of N-glycans: Mechanism, cellular compartmentalization and function. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 147, 149–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A. Loss of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans: Mechanisms, consequences, and implications for hominid evolution. Am. J. Biol. Anthropol. 2001, 33, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, A.; Mann, B.; Giri, A.; Chatterjee, R.; Crandall, K.A. Metabolite, protein, and tissue dysfunction associated with COVID-19 disease severity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.; Caterino, M.; Sotgiu, G.; Ruoppolo, M.; Franconi, F.; Campesi, I. Sex differences in the human metabolome. Biol. Sex Differ. 2022, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.A.; Santos Ferreira, D.L.; Fraser, A.; Soares, A.L.G.; Howe, L.D.; Lawlor, D.A.; Carslake, D.; Davey Smith, G.; O’Keeffe, L.M. Sex differences in systemic metabolites at four life stages: Cohort study with repeated metabolomics. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheys, F.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Smagghe, G. Let’s talk about sexes: Sex-related N-glycosylation in ecologically important invertebrates. Glycoconj. J. 2020, 37, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.E.; Noel, M.; Lehoux, S.; Cetinbas, M.; Xavier, R.J.; Sadreyev, R.I.; Scolnick, E.M.; Smoller, J.W.; Cummings, R.D.; Mealer, R.G. Mammalian brain glycoproteins exhibit diminished glycan complexity compared to other tissues. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, L.R.; Hawkinson, T.R.; Young, L.E.A.; Gentry, M.S.; Sun, R.C. Emerging roles of N-linked glycosylation in brain physiology and disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 980–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazniewska, J.; Weiss, N. Glycosylation of voltage-gated calcium channels in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, I.; Jensen, P.; Schwämmle, V.; Larsen, M.R. Depolarization-dependent Induction of Site-specific Changes in Sialylation on N-linked Glycoproteins in Rat Nerve Terminals. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 1418–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, D.; de Liz Oliveira Cavalli, V.L.; Heinz Rieg, C.E.; Domingues, J.T.; Dal-Cim, T.; Tasca, C.I.; Mena Barreto Silva, F.R.; Zamoner, A. Mechanisms underlying the neurotoxicity induced by glyphosate-based herbicide in immature rat hippocampus: Involvement of glutamate excitotoxicity. Toxicology 2014, 320, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Zhou, J.W. Neuroinflammation in the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia 2019, 67, 1017–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demina, E.P.; Pierre, W.C.; Nguyen, A.L.A.; Londono, I.; Reiz, B.; Zou, C.; Chakraberty, R.; Cairo, C.W.; Pshezhetsky, A.V.; Lodygensky, G.A. Persistent reduction in sialylation of cerebral glycoproteins following postnatal inflammatory exposure. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, D.; Shoji, H.; Duan, C.; Zhang, G.; Isaji, T.; Wang, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Gu, J. Deficiency of α1,6-fucosyltransferase promotes neuroinflammation by increasing the sensitivity of glial cells to inflammatory mediators. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edri-Brami, M.; Rosental, B.; Hayoun, D.; Welt, M.; Rosen, H.; Wirguin, I.; Nefussy, B.; Drory, V.E.; Porgador, A.; Lichtenstein, R.G. Glycans in Sera of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients and Their Role in Killing Neuronal Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Marth, J.D. N-glycan branching requirement in neuronal and postnatal viability. Glycobiology 2004, 14, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Qin, W.; Han, J.; Gu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapeutic efficacy in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer by serum IgG glycomics profiling. Clin. Proteom. 2020, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, C.; Ikenaka, Y.; Ichii, O.; Nakayama, S.M.M.; Nishimura, S.I.; Ohashi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Mizukawa, H.; Ishizuka, M. A glycomics approach to discover novel renal biomarkers in birds by administration of cisplatin and diclofenac to chickens. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F.; Ishihama, Y.; Okuda, S. GlycoPOST realizes FAIR principles for glycomics mass spectrometry data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1523–D1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 , N-acetylglucosamine (HexNAc);
, N-acetylglucosamine (HexNAc);  , mannose (Hex);
, mannose (Hex);  , galactose (Hex);
, galactose (Hex);  , fucose;
, fucose;  , N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc);
, N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc);  , N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc).
, N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc).
 , N-acetylglucosamine (HexNAc);
, N-acetylglucosamine (HexNAc);  , mannose (Hex);
, mannose (Hex);  , galactose (Hex);
, galactose (Hex);  , fucose;
, fucose;  , N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc);
, N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc);  , N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc).
, N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc).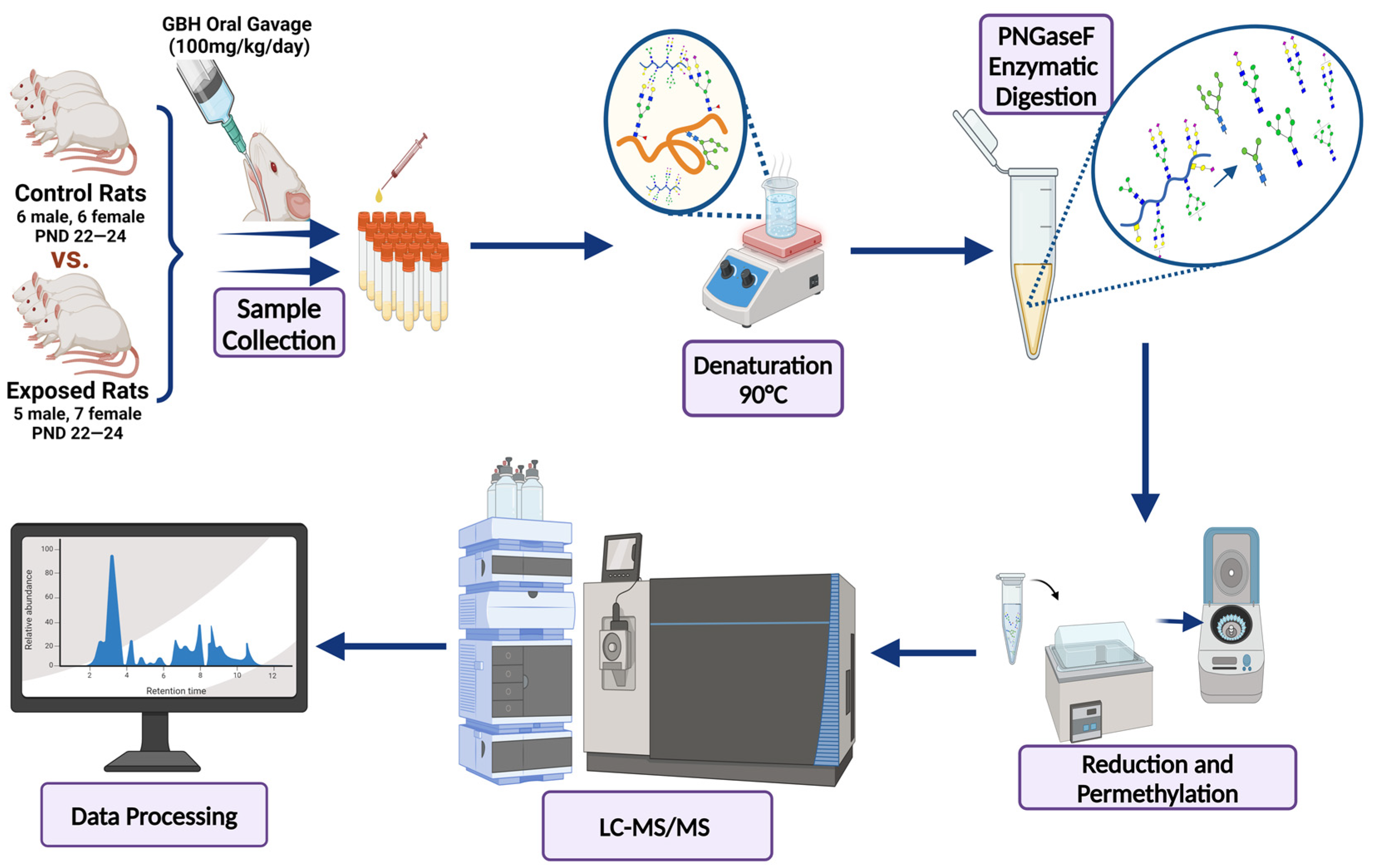

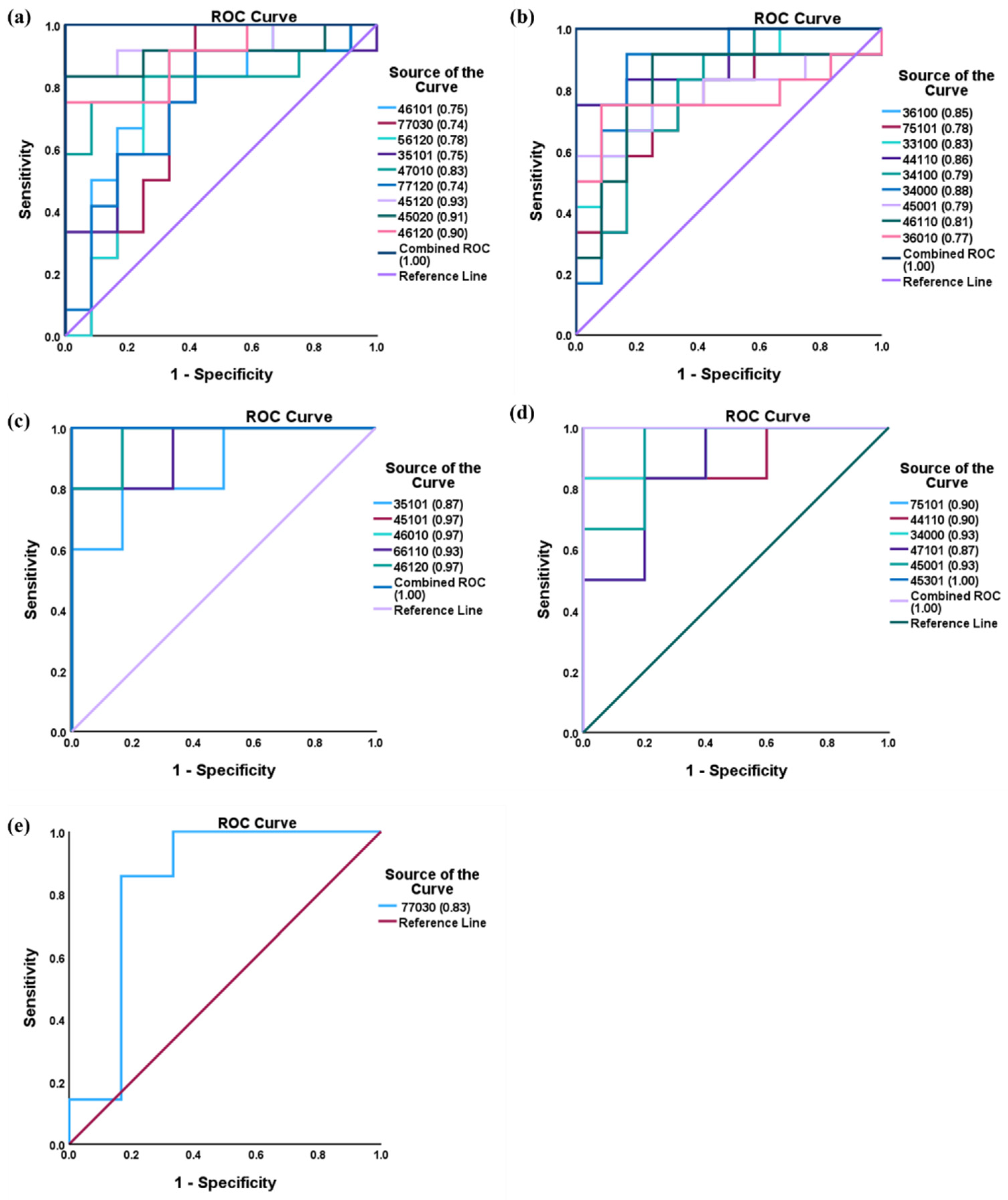
| N-Glycan Composition | Putative N-GLYCAN Structure | Control | GBH- Exposed | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value * | Fold Change (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-5-1-2-0 | 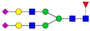 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.0003 | 0.005 | 1.59 |
| 4-5-0-2-0 | 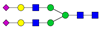 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 4 ± 1 | 0.0007 | 0.006 | 1.68 |
| 4-6-1-2-0 | 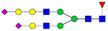 | 0.16 ± 0.06 | 0.27 ± 0.06 | 0.001 | 0.007 | 1.72 |
| 4-7-0-1-0 | 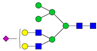 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.04 | 0.007 | 0.01 | 1.36 |
| 5-6-1-2-0 | 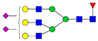 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 1.32 |
| 3-5-1-0-1 | 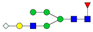 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.33 |
| 4-6-1-0-1 | 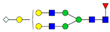 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.24 |
| 7-7-0-3-0 | 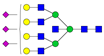 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.30 |
| 7-7-1-2-0 | 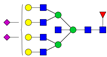 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.46 |
| 3-4-0-0-0 | 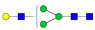 | 0.091 ± 0.009 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.76 |
| 4-4-1-1-0 |  | 0.08 ± 0.03 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.01 | 0.75 |
| 3-6-1-0-0 | 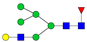 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.59 |
| 3-3-1-0-0 |  | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.7 ± 0.2 | 0.006 | 0.01 | 0.75 |
| 3-4-1-0-0 | 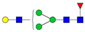 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.75 |
| 4-5-0-0-1 |  | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.80 |
| 4-6-1-1-0 |  | 5 ± 1 | 4.3 ± 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.84 |
| 3-6-0-1-0 |  | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.61 ± 0.09 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.91 |
| 7-5-1-0-1 | 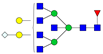 | 0.020 ± 0.009 | 0.012 ± 0.007 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.60 |
| N-Glycan Composition | Putative N-Glycan Structure | Control | GBH- Exposed | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value * | Fold Change (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-5-1-0-1 | 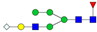 | 1.4 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.45 |
| 4-5-1-0-1 | 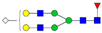 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.65 |
| 4-6-0-1-0 |  | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.67 |
| 4-6-1-2-0 | 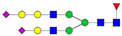 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 0.30 ± 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 1.80 |
| 6-6-1-1-0 | 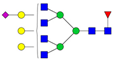 | 0.016 ± 0.006 | 0.029 ± 0.007 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 1.76 |
| 3-4-0-0-0 | 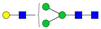 | 0.090 ± 0.009 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.73 |
| 4-5-0-0-1 | 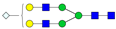 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.77 |
| 4-4-1-1-0 | 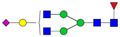 | 0.09 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.71 |
| 7-5-1-0-1 | 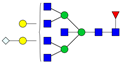 | 0.016 ± 0.006 | 0.008 ± 0.006 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.49 |
| 4-5-3-0-1 | 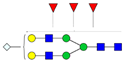 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 0.006 | 0.03 | 0.78 |
| 4-7-1-0-1 | 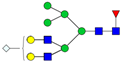 | 0.24 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.74 |
| 7-7-0-3-0 ** | 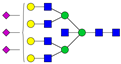 | 0.13 ± 0.06 | 0.18 ± 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeniyi, M.; Gutierrez Reyes, C.D.; Chávez-Reyes, J.; Marichal-Cancino, B.A.; Solomon, J.; Fowowe, M.; Onigbinde, S.; Flores-Rodriguez, J.A.; Bhuiyan, M.M.A.A.; Mechref, Y. Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14091077
Adeniyi M, Gutierrez Reyes CD, Chávez-Reyes J, Marichal-Cancino BA, Solomon J, Fowowe M, Onigbinde S, Flores-Rodriguez JA, Bhuiyan MMAA, Mechref Y. Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(9):1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14091077
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeniyi, Moyinoluwa, Cristian D. Gutierrez Reyes, Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino, Joy Solomon, Mojibola Fowowe, Sherifdeen Onigbinde, Jorge A. Flores-Rodriguez, Md Mostofa Al Amin Bhuiyan, and Yehia Mechref. 2024. "Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides" Biomolecules 14, no. 9: 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14091077
APA StyleAdeniyi, M., Gutierrez Reyes, C. D., Chávez-Reyes, J., Marichal-Cancino, B. A., Solomon, J., Fowowe, M., Onigbinde, S., Flores-Rodriguez, J. A., Bhuiyan, M. M. A. A., & Mechref, Y. (2024). Serum N-Glycan Changes in Rats Chronically Exposed to Glyphosate-Based Herbicides. Biomolecules, 14(9), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14091077







