Sequence-Based Viscosity Prediction for Rapid Antibody Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Analysis
2.2. Viscosity Prediction
2.3. Protein Production
2.4. Viscosity Measurement
2.5. Functional Assessment
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Lu, H.; Li, H.; Tang, M.; Tong, A. Development of therapeutic antibodies for the treatment of diseases. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplon, H.; Chenoweth, A.; Crescioli, S.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2022. mAbs 2022, 14, 2014296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, M.; Mieczkowski, C.; Juan, V.; Metwally, E.; Tomazela, D.; Baker, J.; Uchida, M.; Kofman, E.; Raoufi, F.; Motlagh, S.; et al. Predicting Antibody Developability Profiles Through Early Stage Discovery Screening. mAbs 2020, 12, 1743053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Jiskoot, W.; Schöneich, C.; Rathore, A.S. Oxidation and Deamidation of Monoclonal Antibody Products: Potential Impact on Stability, Biological Activity, and Efficacy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatsa, S. In silico prediction of post-translational modifications in therapeutic antibodies. mAbs 2022, 14, 2023938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badkar, A.V.; Gandhi, R.B.; Davis, S.P.; LaBarre, M.J. Subcutaneous Delivery of High-Dose/Volume Biologics: Current Status and Prospect for 335 Future Advancements. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, B.; Richter, W.; Schmidt, J. Subcutaneous Administration of Biotherapeutics: An Overview of 337 Current Challenges and Opportunities. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geoghegan, J.C.; Fleming, R.; Damschroder, M.; Bishop, S.M.; Sathish, H.A.; Esfandiary, R. Mitigation of reversible self-association and viscosity in a human IgG1 monoclonal antibody by rational, structure-guided Fv engineering. mAbs 2016, 8, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, K.; Krystek, S.R., Jr.; Carl, S.M.; Day, T.; Maier, J.K.X. AggScore: Prediction of aggregation-prone regions in proteins based on the distribution of surface patches. Proteins 2018, 86, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilegenova, C.; Izadi, S.; Yin, J.; Huang, C.S.; Wu, J.; Ellerman, D.; Hymowitz, S.G.; Walters, B.; Salisbury, C.; Carter, P.J. Dissecting the molecular basis of high viscosity of monospecific and bispecific IgG antibodies. mAbs 2020, 12, 1692764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Patapoff, T.W.; Kabakoff, B.; Pai, S.; Hilario, E.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Borisov, O.; Kelley, R.F.; Chorny, I.; et al. In silico selection of therapeutic antibodies for development: Viscosity, clearance, and chemical stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18601–18606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomar, D.S.; Li, L.; Broulidakis, M.P.; Luksha, N.G.; Burns, C.T.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S. In-silico prediction of concentration-dependent viscosity curves for monoclonal antibody solutions. mAbs 2017, 9, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apgar, J.R.; Tam, A.S.P.; Sorm, R.; Moesta, S.; King, A.C.; Yang, H.; Kelleher, K.; Murphy, D.; D’Antona, A.M.; Yan, G.; et al. Modeling and mitigation of high-concentration antibody viscosity through structure-based computer-aided protein design. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, B.K.; Apgar, J.R.; Bennett, E.M. Low-data interpretable deep learning prediction of antibody viscosity using a biophysically meaningful representation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.J.; Helk, B.; Kumar, S.; Mody, N.; Sathish, H.A.; Samra, H.S.; Buck, P.M.; Li, L.; Trout, B.L. Computational tool for the early screening of monoclonal antibodies for their viscosities. mAbs 2016, 8, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.K.; Fernando, A.; Cloutier, T.K.; Gokarn, Y.; Zhang, J.; Schwenger, W.; Chari, R.; Calero-Rubio, C.; Trout, B.L. Machine Learning Applied to Determine the Molecular Descriptors Responsible for the Viscosity Behavior of Concentrated Therapeutic Antibodies. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, P.K.; Gallegos, A.; Mody, N.; Sathish, H.A.; Trout, B.L. Machine learning prediction of antibody aggregation and viscosity for high concentration formulation development of protein therapeutics. mAbs 2022, 14, 2026208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.K.; Ghag, G.; Yu, Y.; Juan, V.; Fayadat-Dilman, L.; Trout, B.L. Differences in human IgG1 and IgG4 S228P monoclonal antibodies viscosity and self-interactions: Experimental assessment and computational predictions of domain interactions. mAbs 2021, 13, 1991256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, P.K.; Swan, J.W.; Trout, B.L. Calculation of therapeutic antibody viscosity with coarse-grained models, hydrodynamic calculations and machine learning-based parameters. mAbs 2021, 13, 1907882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mock, M.; Jacobitz, A.W.; Langmead, C.J.; Sudom, A.; Yoo, D.; Humphreys, S.C.; Alday, M.; Alekseychyk, L.; Angell, N.; Bi, V.; et al. Development of in silico models to predict viscosity and mouse clearance using a comprehensive analytical data set collected on 83 scaffold-consistent monoclonal antibodies. mAbs 2023, 15, 2256745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.L. Antibody engineering via genetic engineering of the mouse: XenoMouse strains are a vehicle for the facile generation of therapeutic human monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 1999, 231, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foltz, I.N.; Gunasekaran, K.; King, C.T. Discovery and bio-optimization of human antibody therapeutics using the XenoMouse® transgenic mouse platform. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 270, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielczewska, A.; D’Angelo, I.; Amador, M.S.; Wang, T.; Sudom, A.; Min, X.; Rathanaswami, P.; Pigott, C.; Foltz, I.N. Development of a potent high-affinity human therapeutic antibody via novel application of recombination signal sequence-based affinity maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Day, T.; Warshaviak, D.; Murrett, C.; Friesner, R.; Pearlman, D. Antibody structure determination using a combination of homology modeling, energy-based refinement, and loop prediction. Proteins 2014, 82, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, N.K.; Adzhigirey, M.; Sherman, W.; Pearlman, D.A. Structure-based approach to the prediction of disulfide bonds in proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, H.; Cholleti, A.; Pearlman, D.; Sherman, W.; Loving, K.A. Applying physics-based scoring to calculate free energies of binding for single amino acid mutations in protein-protein complexes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrodinger, L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.8; Schrödinger, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Engler, C.; Gruetzner, R.; Kandzia, R.; Marillonnet, S. Golden gate shuffling: A one-pot DNA shuffling method based on type IIs restriction enzymes. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, C.; Kandzia, R.; Marillonnet, S. A one pot, one step, precision cloning method with high throughput capability. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

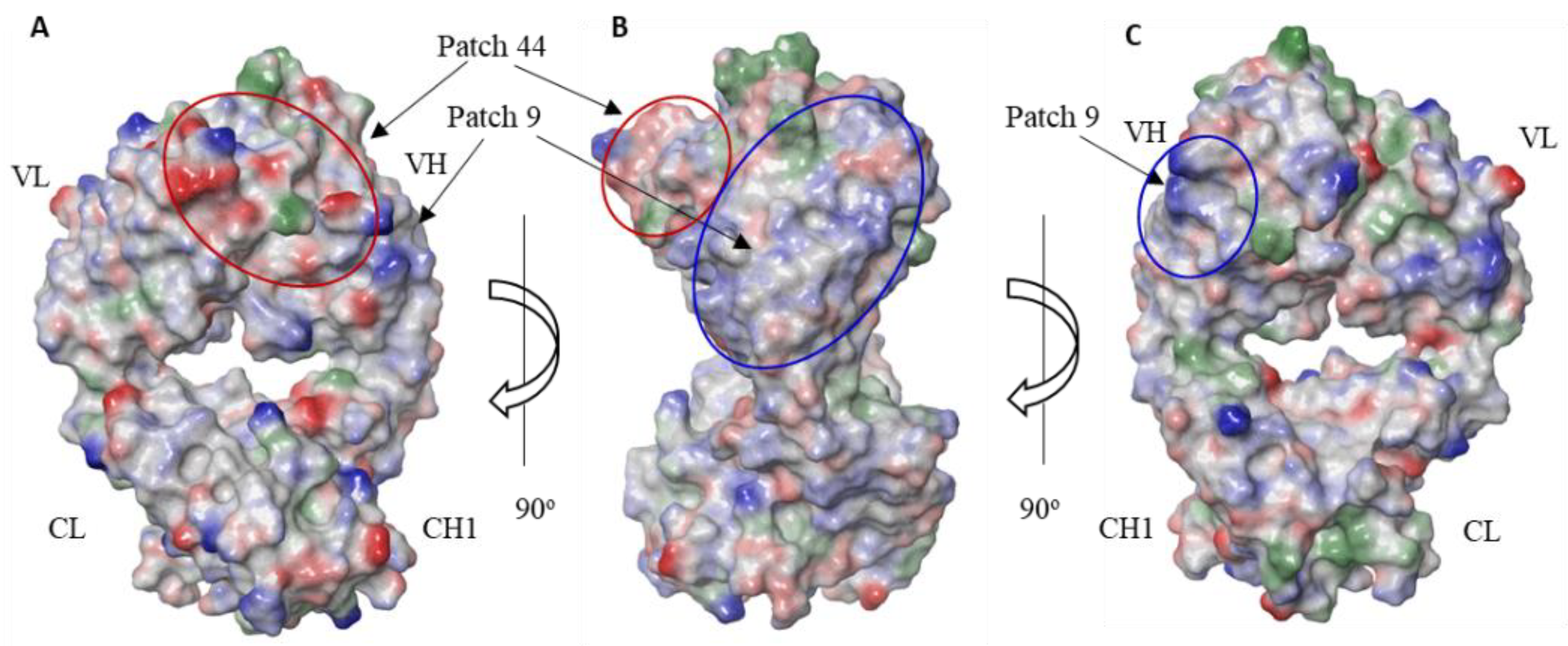
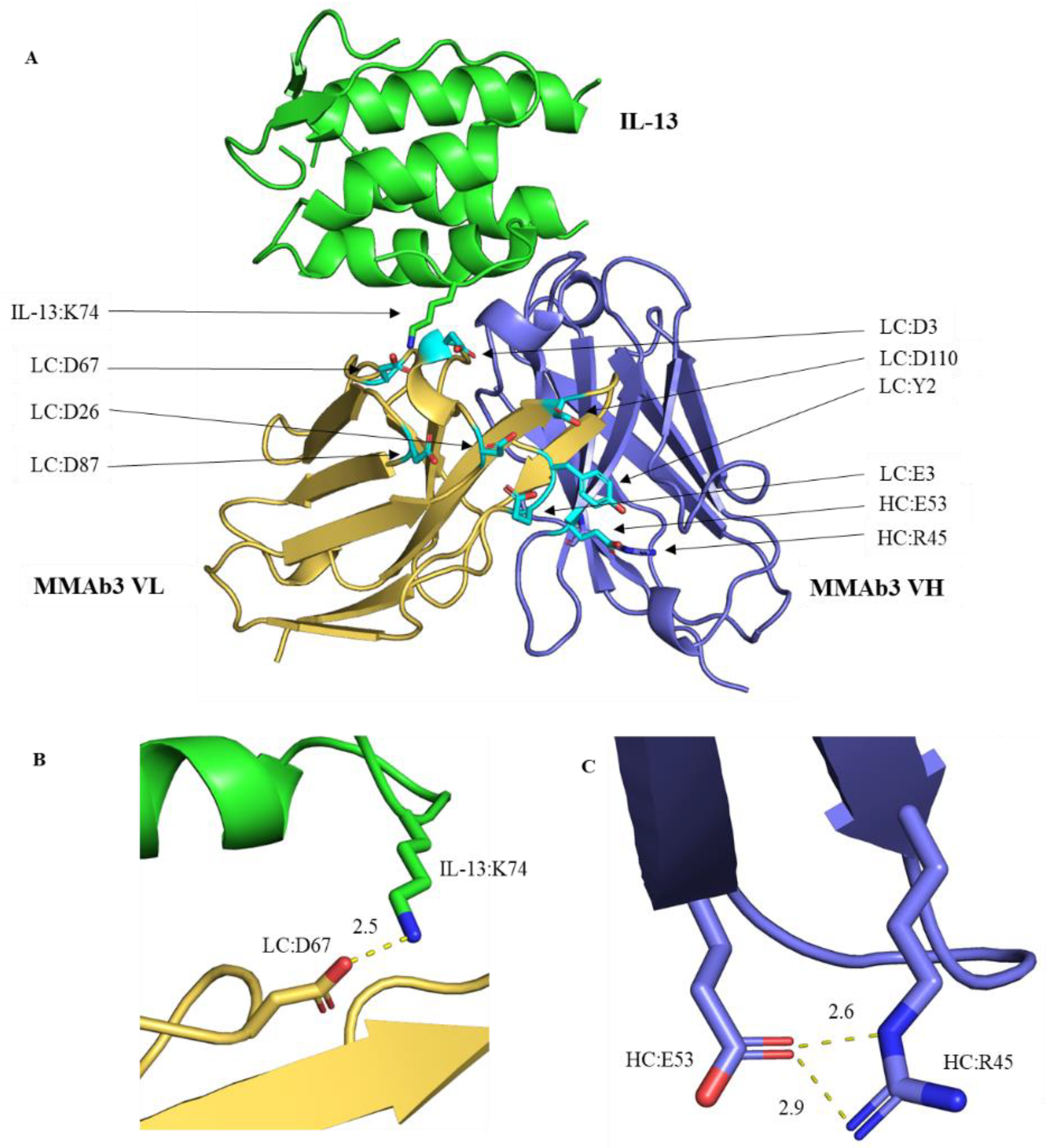

| HC:R20 | HC:K86 | HC:R97 | Predicted Viscosity |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIGH | |||
| S | HIGH | ||
| E | HIGH | ||
| S | HIGH | ||
| S | HIGH | ||
| E | HIGH | ||
| S | S | HIGH | |
| E | E | HIGH | |
| S | S | HIGH | |
| S | S | HIGH | |
| S | S | S | HIGH |
| E | HIGH | ||
| E | E | HIGH | |
| E | E | HIGH | |
| E | E | E | HIGH |
| LC:Y2 | LC:E3 | LC:D26 | LC:D33 | LC:D87 | LC:D110 | Predicted Viscosity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIGH | ||||||
| S | HIGH | |||||
| V | HIGH | |||||
| K | HIGH | |||||
| K | HIGH | |||||
| N | HIGH | |||||
| K | HIGH | |||||
| S | K | HIGH | ||||
| S | K | HIGH | ||||
| S | N | HIGH | ||||
| S | K | HIGH | ||||
| S | K | HIGH | ||||
| V | K | HIGH | ||||
| V | N | HIGH | ||||
| V | S | HIGH | ||||
| V | K | HIGH | ||||
| V | S | HIGH | ||||
| V | N | HIGH | ||||
| V | K | HIGH | ||||
| V | K | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| N | K | HIGH | ||||
| K | S | HIGH | ||||
| K | N | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| N | N | HIGH | ||||
| K | T | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| K | N | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| S | N | HIGH | ||||
| K | T | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| N | K | HIGH | ||||
| K | K | HIGH | ||||
| S | K | K | HIGH | |||
| S | K | N | HIGH | |||
| S | K | K | HIGH | |||
| S | K | N | HIGH | |||
| S | K | K | HIGH | |||
| S | N | K | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | LOW | |||
| V | N | K | HIGH | |||
| V | S | K | HIGH | |||
| V | K | S | HIGH | |||
| V | N | S | HIGH | |||
| V | K | N | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | LOW | |||
| V | K | N | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | LOW | |||
| V | N | K | HIGH | |||
| V | K | K | HIGH | |||
| K | K | N | LOW | |||
| N | K | N | HIGH | |||
| K | S | N | HIGH | |||
| K | K | T | LOW | |||
| N | S | T | HIGH | |||
| K | K | K | LOW | |||
| K | N | K | LOW | |||
| K | K | K | LOW | |||
| K | N | K | LOW | |||
| K | K | K | LOW | |||
| V | K | N | K | LOW | ||
| V | K | K | K | LOW | ||
| V | K | N | K | LOW | ||
| V | K | K | K | LOW | ||
| V | K | K | K | LOW | ||
| V | K | K | N | LOW | ||
| V | K | K | K | LOW | ||
| K | K | K | K | LOW | ||
| K | K | N | K | LOW | ||
| K | K | K | K | LOW |
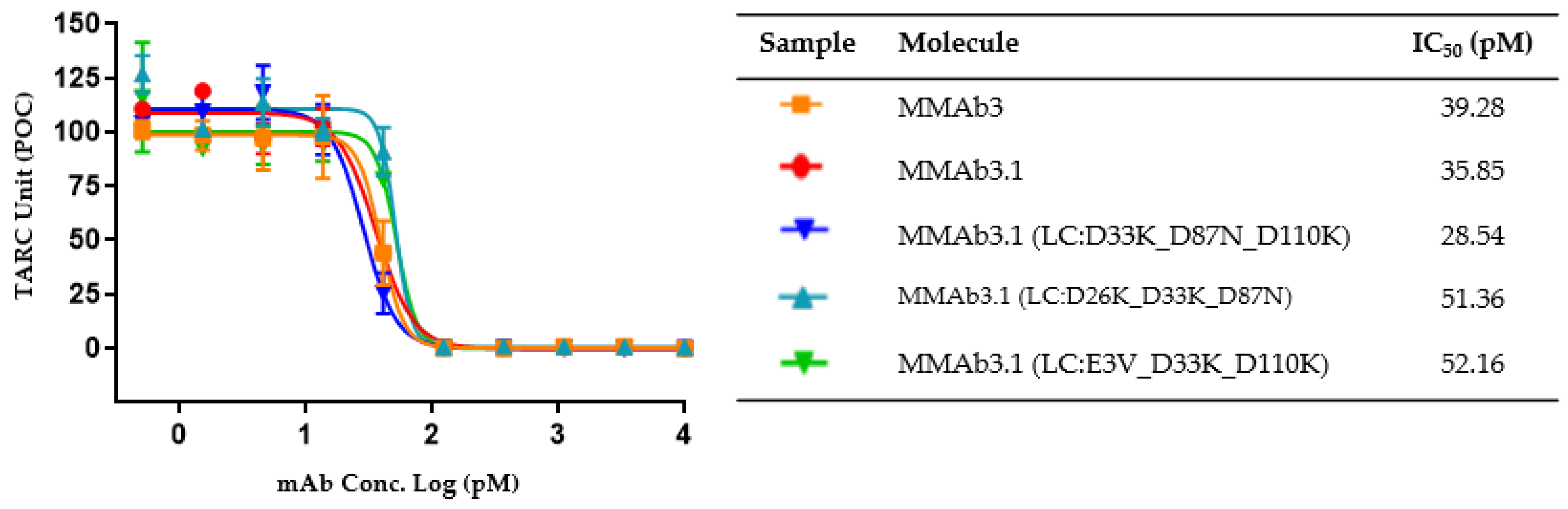
| LC:D26 | LC:D33 | LC:D87 | LC:D110 | Visc. Prediction | Conc. (mg/mL) | Visc. (cP) | TARC IC50 Ave. (pM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIGH | 150 | 33.8 | 39.28 | ||||
| HIGH | 150 | 30.7 | |||||
| K | HIGH | 157 | 32.6 | ||||
| N | HIGH | 150 | 34 | ||||
| K | HIGH | 145 | 25 | ||||
| K | N | K | LOW | 150 | 14.3 | 51.36 | |
| K | N | K | LOW | 150 | 13.1 | ||
| K | K | K | LOW | 150 | 13.7 | ||
| K | K | N | LOW | 151 | 13.8 | 28.54 | |
| N | K | HIGH | 150 | 21.6 | |||
| K | K | LOW | 145 | 13.1 | 52.16 | ||
| K | N | HIGH | 154 | 19.8 | |||
| K | K | LOW | 150 | 25.2 | |||
| K | N | HIGH | 153 | 28.8 | |||
| K | N | K | LOW | 150 | 14.9 | ||
| K | N | K | LOW | 155 | 20.9 |
| Metrics | Formulae | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | (TP + TN)/(TP + TN + FP + FN) | 81.25% |
| Precision | TP/(TP + FP) | 1 |
| Recall | TP/(TP + FN) | 0.73 |
| F1-score | 2 × (Precision × Recall)/(Precision + Recall) | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estes, B.; Jain, M.; Jia, L.; Whoriskey, J.; Bennett, B.; Hsu, H. Sequence-Based Viscosity Prediction for Rapid Antibody Engineering. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060617
Estes B, Jain M, Jia L, Whoriskey J, Bennett B, Hsu H. Sequence-Based Viscosity Prediction for Rapid Antibody Engineering. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(6):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060617
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstes, Bram, Mani Jain, Lei Jia, John Whoriskey, Brian Bennett, and Hailing Hsu. 2024. "Sequence-Based Viscosity Prediction for Rapid Antibody Engineering" Biomolecules 14, no. 6: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060617
APA StyleEstes, B., Jain, M., Jia, L., Whoriskey, J., Bennett, B., & Hsu, H. (2024). Sequence-Based Viscosity Prediction for Rapid Antibody Engineering. Biomolecules, 14(6), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14060617







