Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL-3: A Key Player in Cancer Signaling
Abstract
1. Brief Introduction of Protein Phosphatases
2. PRL Family
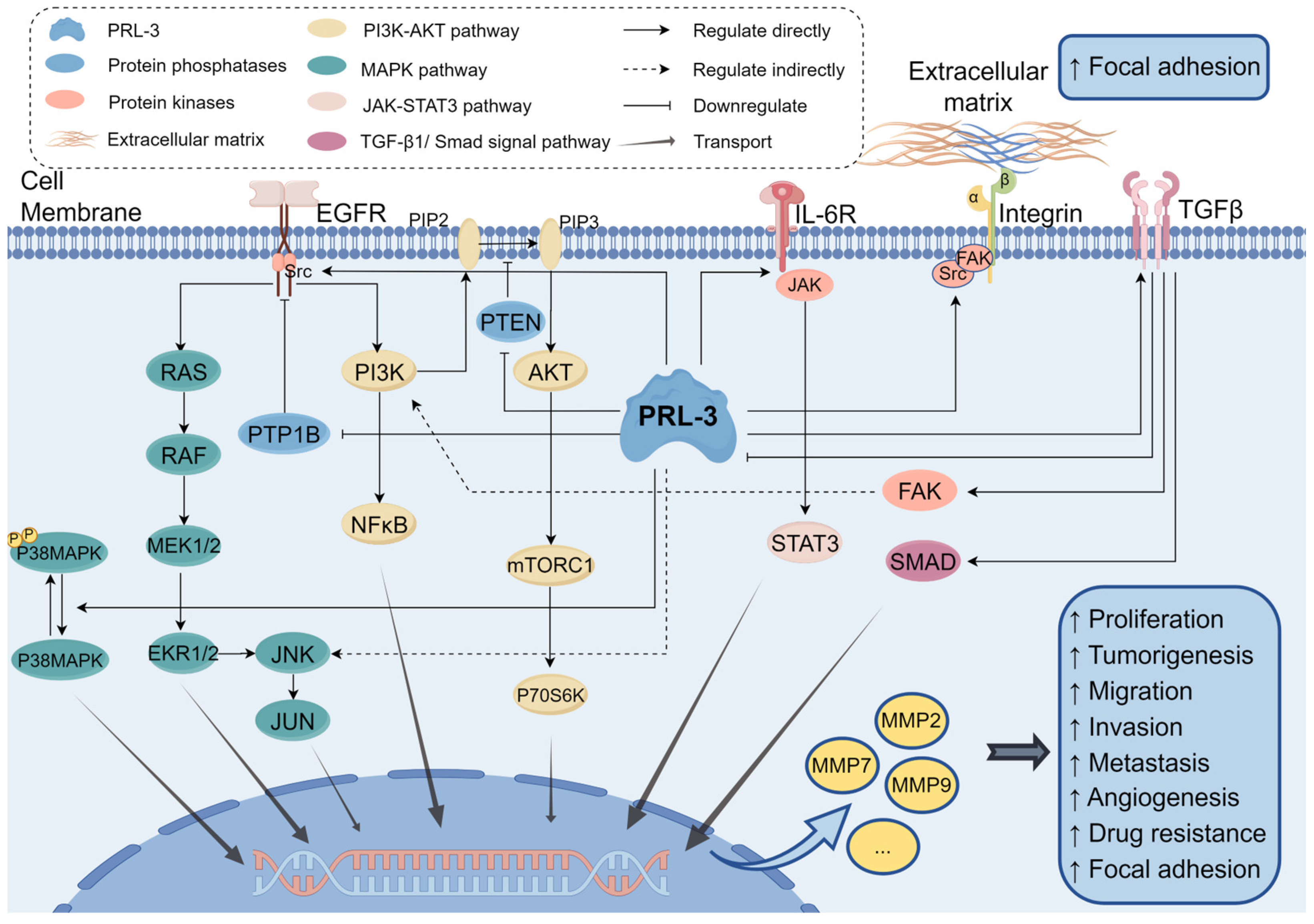
3. Regulatory Mechanisms of PRL-3
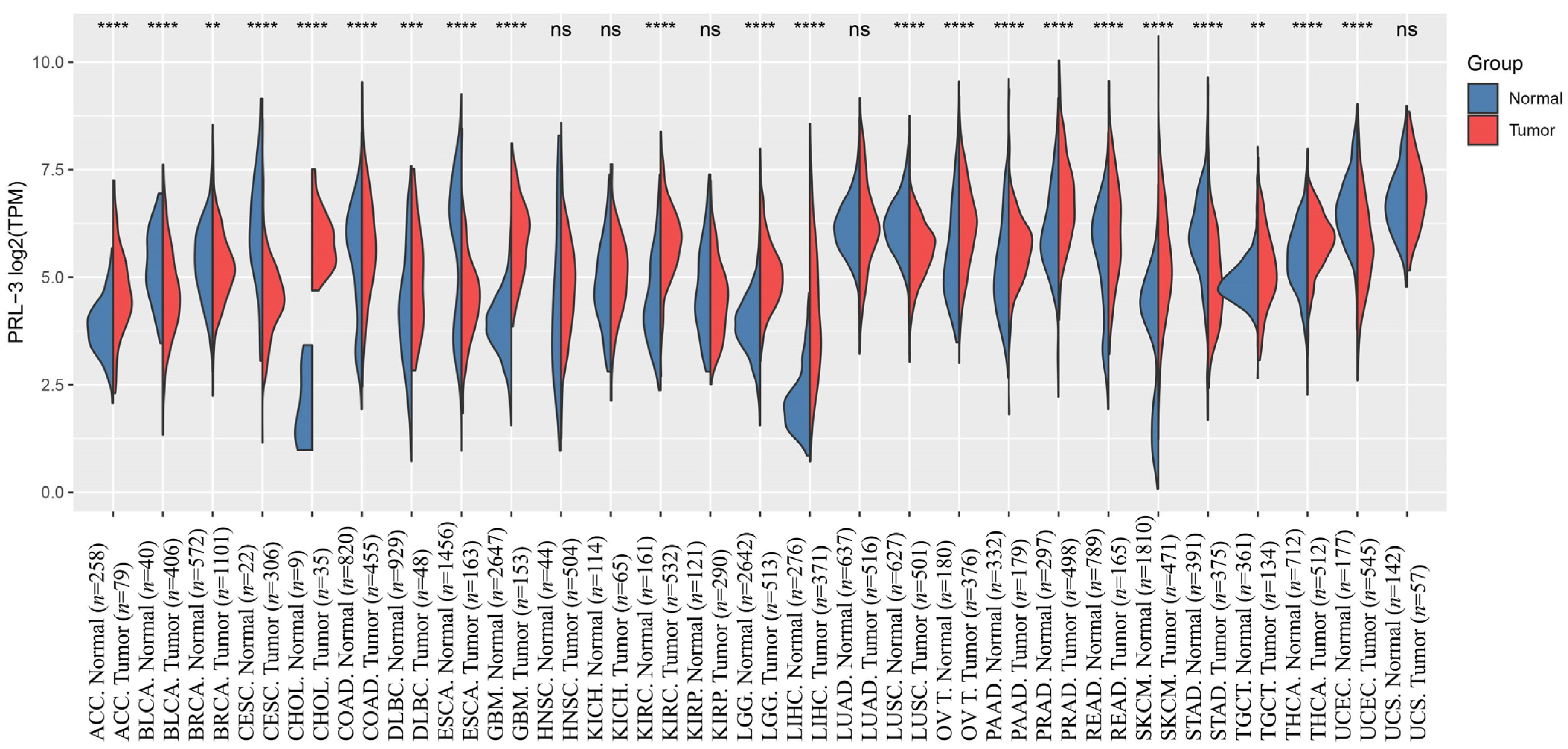
4. PRL-3 in Cancer
4.1. Proliferation and Tumorigenesis
4.2. Migration, Invasion and Metastasis
4.3. Inducing Angiogenesis
4.4. Promoting Focal Adhesion
4.5. Other Functions
5. The Relationship between PRL-3 and Drug Resistance
6. Drug Discovery
| Year | Drug | Discovery | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Pentamidine | The first reported drug has anticancer activity via inhibiting PTPs | [144] |
| 2006 | Biflavonoids | The first natural products reported to have inhibitory effects on PRL. | [145] |
| 2008–2017 | Thienopyridone, JMS-053, NRT-870-59 | Selective PRLs inhibitor. | [80,151,154] |
| 2016 | PRL-3-zumab | A humanized antibody drug against PRL-3 | [156] |
| 2023 | anti-PRL-3 nanobodies | The first alpaca-derived single-domain antibodies against PRL-3 | [159] |
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, G.; Kennedy, E.P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 211, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbrough, T.; Piemontese, E.; Seitz, O. Dissecting the role of protein phosphorylation: A chemical biology toolbox. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5691–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E127–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. Serine/threonine phosphatases: Mechanism through structure. Cell 2009, 139, 468–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewang, P.M.; Hsu, N.M.; Peng, S.Z.; Li, W.R. Protein tyrosine phosphatases and their inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Sasin, J.; Bottini, N.; Friedberg, I.; Friedberg, I.; Osterman, A.; Godzik, A.; Hunter, T.; Dixon, J.; Mustelin, T. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in the human genome. Cell 2004, 117, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, L.; Aricescu, A.R.; Jones, E.Y.; Szedlacsek, S.E. Protein tyrosine phosphatases: Structure-function relationships. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, G.; Cheng, J.; Ziomek, E.; Banville, D.; Gehring, K.; Ekiel, I. Structural insights into molecular function of the metastasis-associated phosphatase PRL-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11882–11889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.M.; Stoker, A.W. A Review of DUSP26: Structure, Regulation and Relevance in Human Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, B.; Janssens, V. Tumor suppressive protein phosphatases in human cancer: Emerging targets for therapeutic intervention and tumor stratification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 98–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Gorska, M.; Knap, N.; Cappello, F.; Wozniak, M. Protein tyrosine phosphatases in pathological process. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, C.M.; Davidson, D.; Rhee, I.; Gratton, J.P.; Davis, E.C.; Veillette, A. The phosphatase PTP-PEST/PTPN12 regulates endothelial cell migration and adhesion, but not permeability, and controls vascular development and embryonic viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43180–43190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giménez-Mascarell, P.; Oyenarte, I.; Hardy, S.; Breiderhoff, T.; Stuiver, M.; Kostantin, E.; Diercks, T.; Pey, A.L.; Ereño-Orbea, J.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; et al. Structural Basis of the Oncogenic Interaction of Phosphatase PRL-1 with the Magnesium Transporter CNNM2. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 786–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Funato, Y.; Miki, H. Phosphatase of regenerating liver maintains cellular magnesium homeostasis. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, S.; Zolotarov, Y.; Coleman, J.; Roitman, S.; Khursheed, H.; Aubry, I.; Uetani, N.; Tremblay, M.L. PRL-1/2 phosphatases control TRPM7 magnesium-dependent function to regulate cellular bioenergetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2221083120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, S.; Kostantin, E.; Wang, S.J.; Hristova, T.; Galicia-Vázquez, G.; Baranov, P.V.; Pelletier, J.; Tremblay, M.L. Magnesium-sensitive upstream ORF controls PRL phosphatase expression to mediate energy metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessette, D.C.; Qiu, D.; Pallen, C.J. PRL PTPs: Mediators and markers of cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiordalisi, J.J.; Keller, P.J.; Cox, A.D. PRL tyrosine phosphatases regulate rho family GTPases to promote invasion and motility. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3153–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, R.H.; Cressman, D.E.; Laz, T.M.; Abrams, C.S.; Taub, R. PRL-1, a unique nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase, affects cell growth. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 3752–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumaual, C.M.; Sandusky, G.E.; Crowell, P.L.; Randall, S.K. Cellular localization of PRL-1 and PRL-2 gene expression in normal adult human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2006, 54, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Sánchez, P.; Ramirez-Munoz, R.; Martín-Cófreces, N.B.; Aguilar-Sopeña, O.; Alegre-Gomez, S.; Hernández-Pérez, S.; Reyes, R.; Zeng, Q.; Cabañas, C.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; et al. Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-1 (PRL-1) Regulates Actin Dynamics During Immunological Synapse Assembly and T Cell Effector Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacchetti, C.; Bai, Y.; Stanford, S.M.; Di Benedetto, P.; Cipriani, P.; Santelli, E.; Piera-Velazquez, S.; Chernitskiy, V.; Kiosses, W.B.; Ceponis, A.; et al. PTP4A1 promotes TGFβ signaling and fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Z.; He, Y.Z.; Dong, P.P.; Ma, L.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Duan, M.; Yang, L.X.; Shi, J.Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP4A1 promotes proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75210–75220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Si, W.; Wei, B.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. PTP4A1 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) metastasis through altered mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kirby, C.E.; Herbst, R. The tyrosine phosphatase PRL-1 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and the mitotic spindle and is required for normal mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 46659–46668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, R.; Hadar, S.; Davidson, B. Expression and clinical role of protein of regenerating liver (PRL) phosphatases in ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Bai, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Gao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yoder, M.C.; Kapur, R.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. PRL2/PTP4A2 phosphatase is important for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1956–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, M.; Sirois, J.; Boyé, K.; Uetani, N.; Hardy, S.; Daubon, T.; Dubrac, A.; Tremblay, M.L.; Bikfalvi, A. PRL-2 phosphatase is required for vascular morphogenesis and angiogenic signaling. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, S.; Wong, N.N.; Muller, W.J.; Park, M.; Tremblay, M.L. Overexpression of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL-2 correlates with breast tumor formation and progression. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8959–8967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bai, Y.; Lyle, L.T.; Yu, G.; Amarasinghe, O.; Nguele Meke, F.; Carlock, C.; Zhang, Z.Y. Mechanism of PRL2 phosphatase-mediated PTEN degradation and tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 20538–20548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlock, C.; Bai, Y.; Paige-Hood, A.; Li, Q.; Nguele Meke, F.; Zhang, Z.Y. PRL2 inhibition elevates PTEN protein and ameliorates progression of acute myeloid leukemia. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e170065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjort, M.A.; Abdollahi, P.; Vandsemb, E.N.; Fenstad, M.H.; Lund, B.; Slørdahl, T.S.; Børset, M.; Rø, T.B. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 is expressed in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and mediates leukemic cell adhesion, migration and drug resistance. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 3549–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.G.; Veloso, A.; Oliveira, M.L.; Allen, J.R.; Loontiens, S.; Brunson, D.; Do, D.; Yan, C.; Morris, R.; Iyer, S.; et al. PRL3 enhances T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia growth through suppressing T-cell signaling pathways and apoptosis. Leukemia 2021, 35, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, K.C.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.; Tong, J.H.M.; Chan, A.W.H.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Yu, J. Increased expression of GATA zinc finger domain containing 1 through gene amplification promotes liver cancer by directly inducing phosphatase of regenerating liver 3. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2302–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, W.F.; Estridge, T.; Zhang, C.; Belagaje, R.; Stancato, L.; Dixon, J.; Johnson, B.; Bloem, L.; Pickard, T.; Donaghue, M.; et al. Role of PRL-3, a human muscle-specific tyrosine phosphatase, in angiotensin-II signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 283, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Osato, M.; Tang, J.P.; Quah, S.Y.; Gan, B.Q.; Zeng, Q. PRL-3 initiates tumor angiogenesis by recruiting endothelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9625–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polato, F.; Codegoni, A.; Fruscio, R.; Perego, P.; Mangioni, C.; Saha, S.; Bardelli, A.; Broggini, M. PRL-3 phosphatase is implicated in ovarian cancer growth. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6835–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Valet, F.; Planque, N.; Silveri, L.; Maacha, S.; Anezo, O.; Hupe, P.; Plancher, C.; Reyes, C.; Albaud, B.; et al. High PTP4A3 phosphatase expression correlates with metastatic risk in uveal melanoma patients. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, S.; Meng, L.; Yao, Q.; Li, Z.; Lian, S. PTP4A3 Is a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated With Immune Infiltrates in Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 717688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, J.S.; Sharlow, E.R.; Cornelison, R.; Hart, D.J.; Llaneza, D.C.; Mendelson, A.J.; Rastelli, E.J.; Tasker, N.R.; Landen, C.N., Jr.; Wipf, P. Credentialing and Pharmacologically Targeting PTP4A3 Phosphatase as a Molecular Target for Ovarian Cancer. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hollander, P.; Rawls, K.; Tsimelzon, A.; Shepherd, J.; Mazumdar, A.; Hill, J.; Fuqua, S.A.; Chang, J.C.; Osborne, C.K.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; et al. Phosphatase PTP4A3 Promotes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth and Predicts Poor Patient Survival. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.; Yan, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; He, C.; Mao, K.; Wang, J.; et al. PRL-3 facilitates Hepatocellular Carcinoma progression by co-amplifying with and activating FAK. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10345–10359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerli, U.M.; Holt, R.U.; Holien, T.; Vaatsveen, T.K.; Zhan, F.; Egeberg, K.W.; Barlogie, B.; Waage, A.; Aarset, H.; Dai, H.Y.; et al. Overexpression and involvement in migration by the metastasis-associated phosphatase PRL-3 in human myeloma cells. Blood 2008, 111, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, J.A.; Marie, K.L.; Lu, Y.; Brombin, A.; Santoriello, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zich, J.; Gautier, P.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Brunsdon, H.; et al. PRL3-DDX21 Transcriptional Control of Endolysosomal Genes Restricts Melanocyte Stem Cell Differentiation. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 317–332.e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basak, S.; Jacobs, S.B.; Krieg, A.J.; Pathak, N.; Zeng, Q.; Kaldis, P.; Giaccia, A.J.; Attardi, L.D. The metastasis-associated gene Prl-3 is a p53 target involved in cell-cycle regulation. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Cao, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, R.; Chen, G.; Xu, Q. VEGF promotes the transcription of the human PRL-3 gene in HUVEC through transcription factor MEF2C. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.S.Y.; Zhou, J.; Lim, J.S.L.; Hee, Y.T.; Chooi, J.Y.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, Z.T.; Zeng, Q.; Waller, D.D.; Sebag, M.; et al. IL6 Promotes a STAT3-PRL3 Feedforward Loop via SHP2 Repression in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4679–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Yuen, H.F.; Zhou, J.B.; Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.; Guo, K.; Valk, P.J.; Zhang, S.D.; Chng, W.J.; Hong, C.W.; Mills, K.; et al. Oncogenic roles of PRL-3 in FLT3-ITD induced acute myeloid leukaemia. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, C.; Chng, W.J.; Cheong, L.L.; Liu, S.C.; Mahara, S.; Tay, K.G.; Zeng, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, K.; et al. PRL-3, a metastasis associated tyrosine phosphatase, is involved in FLT3-ITD signaling and implicated in anti-AML therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Lu, X.X.; Guo, P.D.; Shen, T.; Zhang, S.; He, X.S.; Gan, W.J.; Li, X.M.; Wang, J.R.; Zhao, Y.Y.; et al. Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 4-Mediated Deubiquitination and Stabilization of PRL-3 Is Required for Potentiating Colorectal Oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, G.; Cheng, J.; Lievre, C.; Banville, D.; Gehring, K.; Ekiel, I. 1H, 13C and 15N resonance assignments of the human phosphatase PRL-3. J. Biomol. NMR 2002, 24, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Gao, Y.; Zhangyuan, G.; Xu, X.; Xue, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C.; Sun, B.; Qin, X. lncRNA PCBP1-AS1 Aggravates the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Regulating PCBP1/PRL-3/AKT Pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5395–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Vardy, L.A.; Tan, C.P.; Loo, J.M.; Guo, K.; Li, J.; Lim, S.G.; Zhou, J.; Chng, W.J.; Ng, S.B.; et al. PCBP1 suppresses the translation of metastasis-associated PRL-3 phosphatase. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.K.; Xu, C. Insights into the post-translational modification and its emerging role in shaping the tumor microenvironment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, A.; Linder, M.E. Identification of a novel prenyl and palmitoyl modification at the CaaX motif of Cdc42 that regulates RhoGDI binding. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Si, X.; Horstmann, H.; Xu, Y.; Hong, W.; Pallen, C.J. Prenylation-dependent association of protein-tyrosine phosphatases PRL-1, -2, and -3 with the plasma membrane and the early endosome. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21444–21452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay-Alfaguter, I.; Strazza, M.; Mor, A. Chaperone-mediated specificity in Ras and Rap signaling. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, G.; Luo, X.; Li, K.; Jie, Z.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. PRL-3 promotes gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9069–9074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; You, W. The Deubiquitinating Enzyme USP4 Functions as an Oncoprotein in Gastric Cancer and Mediates NF-κB Signaling by Regulating PRL-3 Expression. Front. Biosci 2022, 27, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xiong, J.B.; Zhang, G.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jie, Z.G.; Li, Z.R. Long Noncoding RNA UCA1 Regulates PRL-3 Expression by Sponging MicroRNA-495 to Promote the Progression of Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Semba, S.; Miskad, U.A.; Seo, Y.; Kasuga, M.; Yokozaki, H. High expression of PRL-3 promotes cancer cell motility and liver metastasis in human colorectal cancer: A predictive molecular marker of metachronous liver and lung metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7318–7328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Lazenby, A.J.; Smith, L.M.; Brattain, M.G.; Black, J.D.; Wang, J.; Are, C. Correlation of PRL3 expression with colorectal cancer progression. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 123, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuncman, W.; Orzechowska, M.; Kuncman, Ł.; Kordek, R.; Taran, K. Intertumoral Heterogeneity of Primary Breast Tumors and Synchronous Axillary Lymph Node Metastases Reflected in IHC-Assessed Expression of Routine and Nonstandard Biomarkers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 660318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Hu, C.; Gao, D.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, X. Phosphatase regenerating liver 3 participates in Integrinβ1/FAK-Src/MAPK signaling pathway and contributes to the regulation of malignant behaviors in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Qin, C. Expression and prognostic value of PRL-3 in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2010, 16, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, S.; Ngoi, N.Y.L.; Zeng, Q.; Ye, Z. PRL-3 dephosphorylates p38 MAPK to promote cell survival under stress. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Y.; Sun, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Sun, X.; Tang, Z.; Feng, Y.; et al. Comprehensive analyses unveil novel genomic and immunological characteristics of micropapillary pattern in lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 931209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, X.; Wen, J.; Xie, L.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, G.; Chen, J.; Fan, M. Integrated Genome-Wide Analysis of Gene Expression and DNA Copy Number Variations Highlights Stem Cell-Related Pathways in Small Cell Esophageal Carcinoma. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 3481783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, S.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Ding, Y. Over-expression of phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Lin, F.; Sheng, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; et al. Nomogram of uveal melanoma as prediction model of metastasis risk. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, J.S.; Isbell, K.N.; Vasa, S.A.; Llaneza, D.C.; Rastelli, E.J.; Wipf, P.; Sharlow, E.R. Disruption of Ovarian Cancer STAT3 and p38 Signaling with a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of PTP4A3 Phosphatase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2023, 384, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Chen, J.; Deng, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhu, J.; Feng, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhao, Z. Identification of NDRG1-regulated genes associated with invasive potential in cervical and ovarian cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 408, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Patel, R.; Kirsch, D.G.; Lewis, C.A.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Locasale, J.W. Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zeng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sha, H.; Ge, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X.; Xu, Q. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promotes motility and metastasis of mouse melanoma cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, N.; Gu, J.; Liu, N.; Xue, X.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Huang, T.; Chu, C.; Zhang, W.; Gong, L.; et al. PRL-3 is a potential glioblastoma prognostic marker and promotes glioblastoma progression by enhancing MMP7 through the ERK and JNK pathways. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, F.; Liang, J.; Wang, W.Q.; Sun, J.P.; Udho, E.; Zhang, Z.Y. PRL3 promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down-regulation of Csk leading to Src activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5413–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueeney, K.E.; Salamoun, J.M.; Burnett, J.C.; Barabutis, N.; Pekic, P.; Lewandowski, S.L.; Llaneza, D.C.; Cornelison, R.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Targeting ovarian cancer and endothelium with an allosteric PTP4A3 phosphatase inhibitor. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8223–8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Liu, B.; Guo, X.; Shi, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; Tong, X.; Wang, H. Independent oncogenic and therapeutic significance of phosphatase PRL-3 in FLT3-ITD-negative acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2014, 120, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Walls, C.D.; Liang, J.; Jiang, H.Y.; Sanford, J.R.; Wek, R.C.; Zhang, Z.Y. Translational control of C-terminal Src kinase (Csk) expression by PRL3 phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10339–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.X.; Mai, S.J.; Huang, X.X.; Wang, F.W.; Liao, Y.J.; Lin, M.C.; Kung, H.F.; Zeng, Y.X.; Xie, D. MiR-29c mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human colorectal carcinoma metastasis via PTP4A and GNA13 regulation of β-catenin signaling. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2196–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, Z.; Lai, D.; Sun, J.; He, C.; Chu, Z.; Ye, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, J. miR-21, miR-17 and miR-19a induced by phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promote the proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, S.; Saghari, S.; Bassiri, F.; Raesi, R.; Zarrabi, A.; Hushmandi, K.; Sethi, G.; Tergaonkar, V. NF-κB as a regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: A focus on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 2770–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.; Chen, S.; Wu, H.; Guan, Y.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, J.; Chu, Z. PRL-3 promotes the proliferation of LoVo cells via the upregulation of KCNN4 channels. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Lei, S.; Yuan, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z. Celecoxib attenuates hepatocellular proliferative capacity during hepatocarcinogenesis by modulating a PTEN/NF-κB/PRL-3 pathway. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20624–20632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Qu, L.; Lian, S.; Meng, L.; Min, L.; Liu, J.; Song, Q.; Shen, L.; Shou, C. PRL-3 Promotes Ubiquitination and Degradation of AURKA and Colorectal Cancer Progression via Dephosphorylation of FZR1. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 928–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xue, Y.; Hu, J.; Lin, D. PRL-3 exerts oncogenic functions in myeloid leukemia cells via aberrant dephosphorylation of stathmin and activation of STAT3 signaling. Aging 2019, 11, 7817–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; You, Q.; Zhai, J.; Shen, L. Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived HAPLN1 promotes tumour invasion through extracellular matrix remodeling in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer Off. J. Int. Gastric Cancer Assoc. Jpn. Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2022, 25, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.F.; He, J.; Li, Y.L.; Zhu, G.B.; Zhang, L.H.; Li, Y.L. Expression of the human phosphatases of regenerating liver (PRLs) in colonic adenocarcinoma and its correlation with lymph node metastasis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2007, 22, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xing, X.; Li, W.; Qu, L.; Meng, L.; Lian, S.; Jiang, B.; Wu, J.; Shou, C. PRL-3 promotes the motility, invasion, and metastasis of LoVo colon cancer cells through PRL-3-integrin beta1-ERK1/2 and-MMP2 signaling. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardelli, A.; Saha, S.; Sager, J.A.; Romans, K.E.; Xin, B.; Markowitz, S.D.; Lengauer, C.; Velculescu, V.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. PRL-3 expression in metastatic cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5607–5615. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, M.; Nan, L.; Guocheng, J.; Qingfu, Z.; Xueshan, Q.; Enhua, W. Downregulating PRL-3 inhibit migration and invasion of lung cancer cell via RhoA and mDia1. Tumori 2012, 98, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Lee, Y.X.; Yu, S.L.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, J.J. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 inhibits invasiveness and proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21799–21811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, D.; Patni, P.; Bishayee, A.; Sah, A.N.; Bishayee, A. Natural products targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway in cancer: A novel therapeutic strategy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvandi, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guan, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Song, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, C.; Gao, P. PTPN14 promotes gastric cancer progression by PI3KA/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Luo, X.; Jie, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Le, Z.; et al. PRL-3 promotes the peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by regulating PTEN. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Toh, S.H.; Chan, Z.L.; Quah, J.Y.; Chooi, J.Y.; Tan, T.Z.; Chong, P.S.Y.; Zeng, Q.; Chng, W.J. A loss-of-function genetic screening reveals synergistic targeting of AKT/mTOR and WTN/β-catenin pathways for treatment of AML with high PRL-3 phosphatase. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.; Yuen, H.F.; Zhang, S.D.; Shen, H.M.; Rozycka, E.; McCrudden, C.M.; Tergaonkar, V.; Gupta, A.; Lin, Y.B.; et al. A role of autophagy in PTP4A3-driven cancer progression. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; López, J.M. Understanding MAPK Signaling Pathways in Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, X.; Chu, Q.; Bao, Z.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slørdahl, T.S.; Abdollahi, P.; Vandsemb, E.N.; Rampa, C.; Misund, K.; Baranowska, K.A.; Westhrin, M.; Waage, A.; Rø, T.B.; Børset, M. The phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 (PRL-3) is important for IL-6-mediated survival of myeloma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27295–27306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, M.A.; Hov, H.; Abdollahi, P.; Vandsemb, E.N.; Fagerli, U.M.; Lund, B.; Slørdahl, T.S.; Børset, M.; Rø, T.B. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 (PRL-3) is overexpressed in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and promotes survival and migration. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobin, E.; Bagwell, K.; Wagner, J.; Mysona, D.; Sandirasegarane, S.; Smith, N.; Bai, S.; Sharma, A.; Schleifer, R.; She, J.X. A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases (MMP) gene expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Ma, J.; Ruan, F.; Bedaiwy, M.A.; Peng, B.; Wu, R.; Lin, J. Elevated phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL-3) promotes cytoskeleton reorganization, cell migration and invasion in endometrial stromal cells from endometrioma. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, X. Evaluation of PRL-3 expression, and its correlation with angiogenesis and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 22, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, M.A.; Sun, W.; Kim, R.; He, A.R.; Abada, P.B.; Mynderse, M.; Finn, R.S. The Role of Angiogenesis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Liu, N.; Gu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Wang, E.H. PRL-3 facilitates angiogenesis and metastasis by increasing ERK phosphorylation and up-regulating the levels and activities of Rho-A/C in lung cancer. Pathology 2009, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.; Yuen, H.F.; Guo, K.; Zhang, S.D.; Chung, T.H.; Chng, W.J.; Zeng, Q. Metastasis-associated PRL-3 induces EGFR activation and addiction in cancer cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3459–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zheng, H. Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 induces angiogenesis by increasing extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation in endometrial adenocarcinoma. Pathobiol. J. Immunopathol. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, S.M.; Francis, H. Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Orsatti, L.; Talamo, F.; Barbato, G.; De Francesco, R.; Tomei, L. Ezrin is a specific and direct target of protein tyrosine phosphatase PRL-3. Biochim. Et. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueeney, K.E.; Salamoun, J.M.; Ahn, J.G.; Pekic, P.; Blanco, I.K.; Struckman, H.L.; Sharlow, E.R.; Wipf, P.; Lazo, J.S. A chemical genetics approach identifies PTP4A3 as a regulator of colon cancer cell adhesion. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2018, 32, 5661–5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csoboz, B.; Gombos, I.; Tatrai, E.; Tovari, J.; Kiss, A.L.; Horvath, I.; Vigh, L. Chemotherapy induced PRL3 expression promotes cancer growth via plasma membrane remodeling and specific alterations of caveolae-associated signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2018, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, M.; Anézo, O.; Saule, S.; Planque, N. PRL-3/PTP4A3 phosphatase regulates integrin β1 in adhesion structures during migration of human ocular melanoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 353, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playford, M.P.; Schaller, M.D. The interplay between Src and integrins in normal and tumor biology. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7928–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanchanawong, P.; Calderwood, D.A. Organization, dynamics and mechanoregulation of integrin-mediated cell-ECM adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 142–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walls, C.D.; Iliuk, A.; Bai, Y.; Wang, M.; Tao, W.A.; Zhang, Z.Y. Phosphatase of regenerating liver 3 (PRL3) provokes a tyrosine phosphoproteome to drive prometastatic signal transduction. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2013, 12, 3759–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, S.; Meng, L.; Yang, Y.; Ma, T.; Xing, X.; Feng, Q.; Song, Q.; Liu, C.; Tian, Z.; Qu, L.; et al. PRL-3 promotes telomere deprotection and chromosomal instability. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6546–6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, T.; Weyershaeuser, J.; Montero, M.G.; Hoffmann, A.; Lujan, P.; Jechlinger, M.; Sotillo, R.; Köhn, M. The phosphatase PRL-3 affects intestinal homeostasis by altering the crypt cell composition. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kozlov, G.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Gulerez, I.; Gehring, K. PRL3 phosphatase active site is required for binding the putative magnesium transporter CNNM3. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, J.T.; Cheatham, T.C.; Blackburn, J.S. Phosphatase and Pseudo-Phosphatase Functions of Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver 3 (PRL-3) Are Insensitive to Divalent Metals In Vitro. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 30578–30589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funato, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Hirata, Y.; Hashizume, O.; Yamazaki, D.; Miki, H. The Oncogenic PRL Protein Causes Acid Addiction of Cells by Stimulating Lysosomal Exocytosis. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 387–397.e388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakács, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marine, J.C.; Dawson, S.J.; Dawson, M.A. Non-genetic mechanisms of therapeutic resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Luo, Q.; Xu, L.; Chen, F. An efficient method to isolate lemon derived extracellular vesicles for gastric cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtetsion, T.; Ding, Z.C.; Pi, W.; Li, T.; Lu, C.; Chen, T.; Xi, C.; Spartz, H.; Liu, K.; Hao, Z.; et al. Alteration of Tumor Metabolism by CD4+ T Cells Leads to TNF-α-Dependent Intensification of Oxidative Stress and Tumor Cell Death. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 228–242.e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Ren, L.; Gupta, P.; Wei, L.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Modulating ROS to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer. Chemother. 2018, 41, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, L.; Gao, Q.; Jin, S.; Lan, Q.; Lai, W.; Luo, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, Y.; et al. PRL-3 improves colorectal cancer cell proliferation and invasion through IL-8 mediated glycolysis metabolism. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Sun, F.; Sun, R.; Man, Z.; Ji, S.; Xu, K.; Yin, L.; Zhang, J.; Pu, Y. PTP4A3, A Novel Target Gene of HIF-1alpha, Participates in Benzene-Induced Cell Proliferation Inhibition and Apoptosis through PI3K/AKT Pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasek-Gajda, E.; Jurkowska, H.; JasiŃska, M.; Litwin, J.A.; Lis, G.J. Combination of ERK2 and STAT3 Inhibitors Promotes Anticancer Effects on Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Anand, U.; Pandey, S.K.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Chen, Z.S.; Dey, A. Therapeutic strategies to overcome taxane resistance in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates Rev. Comment. Antimicrob. Anticancer. Chemother. 2021, 55, 100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nami, B.; Wang, Z. Genetics and Expression Profile of the Tubulin Gene Superfamily in Breast Cancer Subtypes and Its Relation to Taxane Resistance. Cancers 2018, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Vianay, B.; Roca, V.; Farrugia, A.J.; De Pascalis, C.; Boëda, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Bershadsky, A.; et al. Microtubules tune mechanosensitive cell responses. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namee, N.M.; O’Driscoll, L. Extracellular vesicles and anti-cancer drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Gu, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.S.; Fang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, X. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Drug Resistance: Roles, Mechanisms, and Implications. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thura, M.; Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.; Gupta, A.; Chee, C.E.; Lee, S.C.; Hui, K.M.; Li, J.; Guan, Y.K.; Yong, W.P.; So, J.; et al. PRL3-zumab as an immunotherapy to inhibit tumors expressing PRL3 oncoprotein. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; Qiao, Q.; et al. Cytoplasmic SIRT1 promotes paclitaxel resistance in ovarian carcinoma through increased formation and survival of polyploid giant cancer cells. J. Pathol. 2023, 261, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thura, M.; Ye, Z.; Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.; Xiong, Q.; Ong, J.Y.; Gupta, A.; Li, J.; Guo, K.; Ang, K.H.; Zeng, Q. PRL3 induces polypoid giant cancer cells eliminated by PRL3-zumab to reduce tumor relapse. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Yang, K. Chemotherapy targeting cancer stem cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 880–893. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, M.K.; Dhawan, D.; Lindner, D.J.; Borden, E.C.; Farver, C.; Yi, T. Pentamidine is an inhibitor of PRL phosphatases with anticancer activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 1255–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.K.; Oh, H.M.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, D.G.; Ryu, S.E.; Son, K.H.; Han, D.C.; Sung, N.D.; Baek, N.I.; Kwon, B.M. Biflavonoids inhibited phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 (PRL-3). Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Song, R.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q. An anticancer effect of curcumin mediated by down-regulating phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 expression on highly metastatic melanoma cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, M.K.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, L.H.; Yang, J.H.; Kwon, B.M.; Kim, D.K. Inhibitory activities of anthraquinones from Rubia akane on phosphatase regenerating liver-3. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2010, 33, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Lee, S.K.; Jeong, D.G.; Ryu, S.E.; Han, D.C.; Kim, D.K.; Kwon, B.M. Emodin inhibits migration and invasion of DLD-1 (PRL-3) cells via inhibition of PRL-3 phosphatase activity. Bioorg.. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Park, W.S.; Cho, S.Y.; Ha, J.D.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, S.K.; Jeong, D.G.; Jung, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of rhodanine derivatives as PRL-3 inhibitors. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2996–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, G.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.N.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, R.H.; Jeong, D.G.; Han, D.C.; Kwon, B.M. Rhodanine-based PRL-3 inhibitors blocked the migration and invasion of metastatic cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3769–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daouti, S.; Li, W.H.; Qian, H.; Huang, K.S.; Holmgren, J.; Levin, W.; Reik, L.; McGady, D.L.; Gillespie, P.; Perrotta, A.; et al. A selective phosphatase of regenerating liver phosphatase inhibitor suppresses tumor cell anchorage-independent growth by a novel mechanism involving p130Cas cleavage. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, N.R.; Rastelli, E.J.; Blanco, I.K.; Burnett, J.C.; Sharlow, E.R.; Lazo, J.S.; Wipf, P. In-flow photooxygenation of aminothienopyridinones generates iminopyridinedione PTP4A3 phosphatase inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 2448–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooki, A.; Yamashita, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Sakuramoto, S.; Katada, N.; Waraya, M.; Kawamata, H.; Nishimiya, H.; Nakamura, K.; Watanabe, M. Therapeutic potential of PRL-3 targeting and clinical significance of PRL-3 genomic amplification in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, J.S.; Blanco, I.K.; Tasker, N.R.; Rastelli, E.J.; Burnett, J.C.; Garrott, S.R.; Hart, D.J.; McCloud, R.L.; Hsu, K.L.; Wipf, P.; et al. Next-Generation Cell-Active Inhibitors of the Undrugged Oncogenic PTP4A3 Phosphatase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 371, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.L.; Ang, K.H.; Thura, M.; Zeng, Q. PRL3 as a therapeutic target for novel cancer immunotherapy in multiple cancer types. Theranostics 2023, 13, 1876–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thura, M.; Al-Aidaroos, A.Q.O.; Yong, W.P.; Kono, K.; Gupta, A.; Lin, Y.B.; Mimura, K.; Thiery, J.P.; Goh, B.C.; Tan, P.; et al. PRL3-zumab, a first-in-class humanized antibody for cancer therapy. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e87607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Meng, L.; Xing, X.; Li, N.; Song, Q.; Qiao, D.; Qu, L.; Liu, C.; An, G.; Li, Z.; et al. Anti-PRL-3 Monoclonal Antibody inhibits the Growth and Metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2023, 14, 2585–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, C.E.; Ooi, M.; Lee, S.C.; Sundar, R.; Heong, V.; Yong, W.P.; Ng, C.H.; Wong, A.; Lim, J.S.J.; Tan, D.S.P.; et al. A Phase I, First-in-Human Study of PRL3-zumab in Advanced, Refractory Solid Tumors and Hematological Malignancies. Target. Oncol. 2023, 18, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.N.; Kihn, K.; Williamson, Z.A.; Chow, K.M.; Hersh, L.B.; Korotkov, K.V.; Deredge, D.; Blackburn, J.S. Development and characterization of nanobodies that specifically target the oncogenic Phosphatase of Regenerating Liver-3 (PRL-3) and impact its interaction with a known binding partner, CNNM3. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Liu, S.; Ye, Y.; et al. PTPN3 acts as a tumor suppressor and boosts TGF-β signaling independent of its phosphatase activity. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e99945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, X.K.; Szklarczyk, D.; Gábor, A.; Dobberstein, N.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Saez-Rodriguez, J.; von Mering, C.; Bodenmiller, B. Analysis of the Human Kinome and Phosphatome by Mass Cytometry Reveals Overexpression-Induced Effects on Cancer-Related Signaling. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 1086–1102.e1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; He, Q.M.; Chen, J.W.; Li, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.F.; Ren, X.Y.; Sun, Y.; Mai, H.Q.; Shao, J.Y.; Jia, W.H.; et al. Overexpression of CIP2A is an independent prognostic indicator in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its depletion suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabinger, S.C.; Li, X.J.; Ramdas, B.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, L.; Richine, B.; Bowling, J.D.; Fukuda, S.; Goenka, S.; et al. The protein tyrosine phosphatase, Shp2, positively contributes to FLT3-ITD-induced hematopoietic progenitor hyperproliferation and malignant disease in vivo. Leukemia 2013, 27, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Radke, I.; Götte, M.; Kersting, C.; Mattsson, B.; Kiesel, L.; Wülfing, P. Expression and prognostic impact of the protein tyrosine phosphatases PRL-1, PRL-2, and PRL-3 in breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Shi, H.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; Shi, X. Characterizing PTP4A3/PRL-3 as the Potential Prognostic Marker Gene for Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 2717056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.C.; Liang, Q.L.; Chen, M.; Yang, H.X.; Huang, J.; Yi, S.L.; Wang, Z.W.; Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Huang, Z.Y. PRL-3 and MMP9 Expression and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers in Circulating Tumor Cells From Patients With Colorectal Cancer: Potential Value in Clinical Practice. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 878639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Ye, Z.; Cheng, X. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL-3: A Key Player in Cancer Signaling. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030342
Liu H, Li X, Shi Y, Ye Z, Cheng X. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL-3: A Key Player in Cancer Signaling. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(3):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030342
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haidong, Xiao Li, Yin Shi, Zu Ye, and Xiangdong Cheng. 2024. "Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL-3: A Key Player in Cancer Signaling" Biomolecules 14, no. 3: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030342
APA StyleLiu, H., Li, X., Shi, Y., Ye, Z., & Cheng, X. (2024). Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase PRL-3: A Key Player in Cancer Signaling. Biomolecules, 14(3), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030342






