Comprehensive Data-Driven Assessment of Non-Kinase Targets of Inhibitors of the Human Kinome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Targets, Compounds, and Activity Data
2.2. Protein Classification
2.3. Kinome Tree Mapping and PKI-Based Target Network
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Data Curation
3.2. Protein Kinase Inhibitors with Non-Kinase Targets
3.3. Promiscuity Assessment
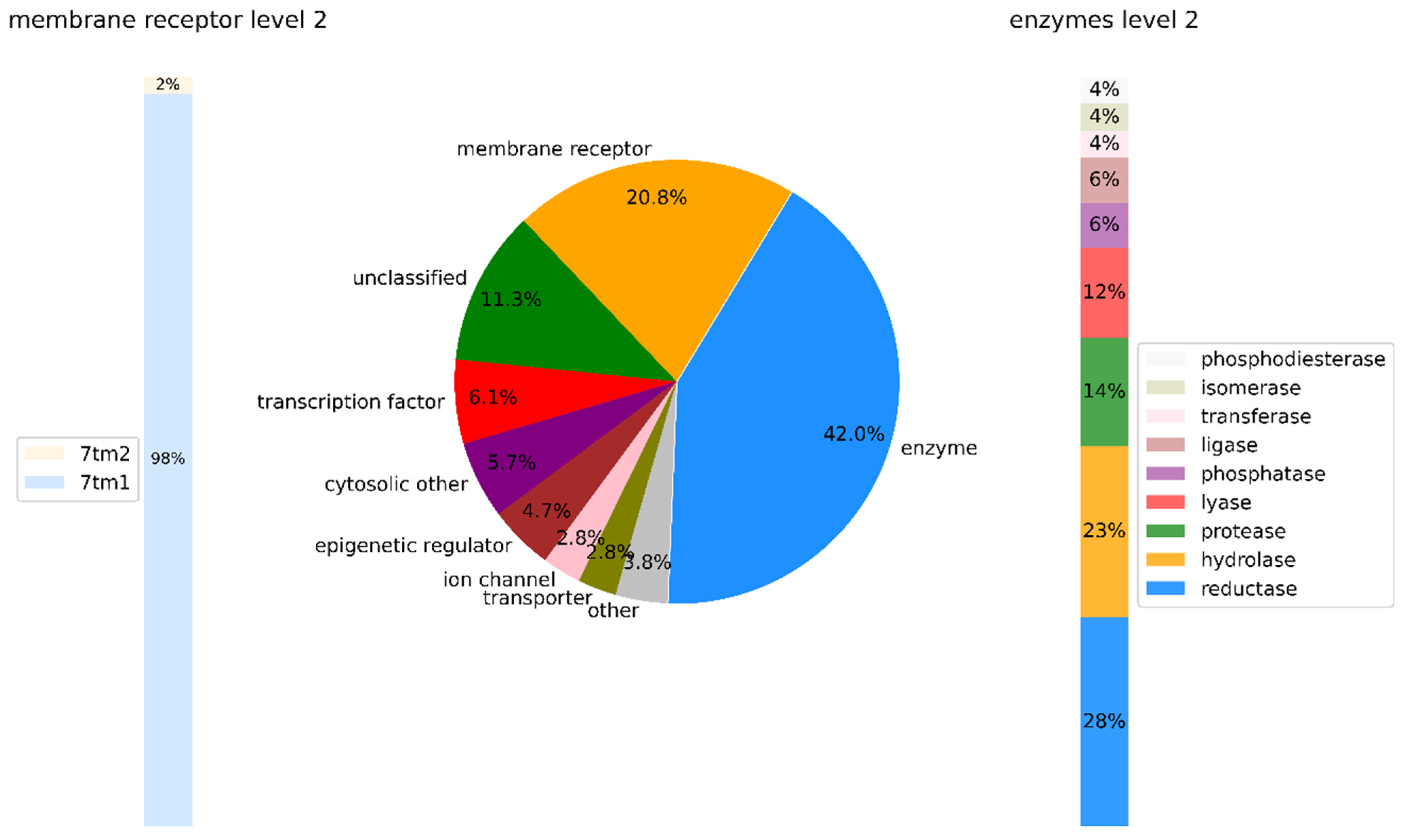
3.4. Distribution of Non-Protein Kinase Targets
3.5. Inhibitor–Target Interactions
3.6. Kinase Targets
3.7. Most Frequent Non-Protein Kinase Targets
3.8. Drugs with Protein Kinase Activity and Largest Numbers of Non-Protein Kinase Targets
3.9. Potency Level Dependence of Protein Kinase Inhibitor–Target Interactions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, F.M.; Gray, N.S. Kinase Inhibitors: The Road Ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors: An Analysis of FDA-Approved Drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrin, L.K.; Saiah, E. Approaches to Discover Non-ATP Site Kinase Inhibitors. Med. Chem. Commun. 2012, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T. Discovering the First Tyrosine Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 7877–7882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Hunter, T. The Eukaryotic Protein Kinase Superfamily: Kinase (Catalytic) Domain Structure and Classification 1. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 576–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitzki, A.; Gazit, A. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition: An Approach to Drug Development. Science 1995, 267, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endicott, J.A.; Noble, M.E.; Johnson, L.N. The Structural Basis for Control of Eukaryotic Protein Kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 587–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baselga, J. Targeting Tyrosine Kinases in Cancer: The Second Wave. Science 2006, 312, 1175–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, Z.A.; Lin, H.; Shokat, K.M. Targeting the Cancer Kinome through Polypharmacology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrin, A.A.; Bao, K.; Lupardus, P.; Vucic, D. Kinase Inhibition in Autoimmunity and Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 39–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuny, G.D. Kinase Inhibitors as Potential Therapeutics for Acute and Chronic Neurodegenerative Conditions. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3919–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, I.; Leiva, M.; Sabio, G. The Role of Stress Kinases in Metabolic Disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2020, 16, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, M.; Buchdunger, E.; Druker, B.J. The Development of Imatinib as a Therapeutic Agent for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2005, 105, 2640–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Cross, D.; Jänne, P.A. Kinase Drug Discovery 20 Years after Imatinib: Progress and Future Directions. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2021, 20, 551–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yang, X.; Duan, Y.; Han, J.; Liao, C. Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Nononcologic Diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 1283–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Properties of FDA-Approved Small Molecule Protein Kinase Inhibitors: A 2024 Update. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Furtmann, N.; Bajorath, J. Current Compound Coverage of the Kinome. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xerxa, E.; Miljković, F.; Bajorath, J. Data-Driven Global Assessment of Protein Kinase Inhibitors with Emphasis on Covalent Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 7657–7665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xerxa, E.; Laufkötter, O.; Bajorath, J. Systematic Analysis of Covalent and Allosteric Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Molecules 2023, 28, 5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regenmortel, M.H.V. Reductionism and Complexity in Molecular Biology: Scientists Now Have the Tools to Unravel Biological Complexity and Overcome the Limitations of Reductionism. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.L. Network Pharmacology. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1110–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overington, J.P.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hopkins, A.L. How Many Drug Targets Are There? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 993–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.U. Polypharmacology—Foe or Friend? J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8955–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anighoro, A.; Bajorath, J.; Rastelli, G. Polypharmacology: Challenges and Opportunities in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolognesi, M.L.; Cavalli, A. Multitarget Drug Discovery and Polypharmacology. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 1190–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proschak, E.; Stark, H.; Merk, D. Polypharmacology by Design: A Medicinal Chemist’s Perspective on Multitargeting Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H., 3rd; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A Small Molecule-Kinase Interaction Map for Clinical Kinase Inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, M.W.; Herrgard, S.; Treiber, D.K.; Gallant, P.; Atteridge, C.E.; Campbell, B.T.; Chan, K.W.; Ciceri, P.; Davis, M.I.; Edeen, P.T.; et al. A Quantitative Analysis of Kinase Inhibitor Selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaeger, S.; Heinzlmeir, S.; Wilhelm, M.; Polzer, H.; Vick, B.; Koenig, P.A.; Reinecke, M.; Ruprecht, B.; Petzoldt, S.; Meng, C.; et al. The Target Landscape of Clinical Kinase Inhibitors. Science 2017, 358, eaan4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonge, P.J. Drug–target kinetics in drug discovery. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug Repurposing: Progress, Challenges and Recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, L. Non-Kinase Targets of Protein Kinase Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.P.; Olesen, S.H.; Georg, G.I.; Schönbrunn, E. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor Dinaciclib Interacts with the Acetyl-Lysine Recognition Site of Bromodomains. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2360–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, P.; Müller, S.; O’Mahony, A.; Fedorov, O.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Hunt, J.P.; Lasater, E.A.; Pallares, G.; Picaud, S.; Wells, C.; et al. Dual Kinase-Bromodomain Inhibitors for Rationally Designed Polypharmacology. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K. The Molecular Basis of G Protein–Coupled Receptor Activation. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 897–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolini, G.V.; Shapland, R.H.; van Hoorn, W.P.; Mason, J.S.; Hopkins, A.L. Global Mapping of Pharmacological Space. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, J.M.; Fedele, V.; Szklarz, M.; Abdul Azeez, K.R.; Salah, E.; Mikolajczyk, J.; Romanov, S.; Sepetov, N.; Huang, X.P.; Roth, B.L.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of the Published Kinase Inhibitor Set. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, D.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; De Veij, M.; Félix, E.; Magariños, M.P.; Mosquera, J.F.; Mutowo, P.; Nowotka, M.; et al. ChEMBL: Towards Direct Deposition of Bioassay Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D930–D940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, Y.; Wen, X.; Jorissen, R.N.; Gilson, M.K. BindingDB: A Web-Accessible Database of Experimentally Determined Protein–Ligand Binding Affinities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D198–D201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar]
- Weininger, D. SMILES, a Chemical Language and Information System. 1. Introduction to Methodology and Encoding Rules. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1988, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baell, J.B.; Holloway, G.A. New Substructure Filters for Removal of Pan Assay Interference Compounds (PAINS) from Screening Libraries and for Their Exclusion in Bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2719–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, R.F.; Watson, I.A. Rules for Identifying Potentially Reactive or Promiscuous Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 9763–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Turk, S.; Volkamer, A.; Rippmann, F.; Fulle, S. KinMap: A Web-Based Tool for Interactive Navigation through Human Kinome Data. BMC Bioinf. 2017, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ChEMBL Target ID | Name | Group | PKIs | Non-PK Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 279 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | TK | 53 | 31 |
| 203 | Epidermal growth factor receptor erbB1 | TK | 51 | 55 |
| 1913 | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | TK | 46 | 35 |
| 5014 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase RIPK2 | TKL | 45 | 46 |
| 4630 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | GAMK | 42 | 11 |
| 1862 | Tyrosine-protein kinase ABL | TK | 41 | 32 |
| 2973 | Rho-associated protein kinase 2 | AGC | 40 | 21 |
| 2185 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Aurora-B | AUR | 38 | 35 |
| 2041 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor RET | TK | 36 | 36 |
| 4439 | TGF-beta receptor type I | TKL | 35 | 17 |
| ChEMBL Target ID | Name | Class | PKIs | PK Targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220 | Acetylcholinesterase | Enzyme | 32 | 45 |
| 4105933 | Uncharacterized protein FLJ45252 | Unclassified | 30 | 353 |
| 3107 | Basic fibroblast growth factor | Secreted protein | 21 | 26 |
| 5465 | Histone deacetylase 6 | Epigenetic regulator | 21 | 3 |
| 3959 | Quinone reductase 2 | Enzyme | 18 | 291 |
| 1947 | Thyroid hormone receptor beta-1 | Transcription factor | 18 | 2 |
| 3879831 | Ferrochelatase, mitochondrial | Enzyme | 18 | 296 |
| 1741176 | X-box-binding protein 1 | Unclassified | 17 | 7 |
| 1795185 | Bromodomain testis-specific protein | Epigenetic regulator | 15 | 179 |
| 5378 | P_selectin | Adhesion | 15 | 33 |
| Compound Name | ChEMBL Compound ID | Non-PK Targets | PKs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aripiprazole | 1112 | 19 | 1 |
| -- | 461571 | 16 | 1 |
| Celecoxib | 118 | 13 | 1 |
| Paroxetine | 490 | 9 | 1 |
| Crenolanib | 2105728 | 9 | 44 |
| Alisertib | 483158 | 7 | 11 |
| Flavone | 275638 | 6 | 1 |
| AZD-5438 | 488436 | 5 | 17 |
| Sorafenib | 1336 | 5 | 59 |
| Erlotinib | 553 | 4 | 44 |
| pPot ≥ 5 | pPot ≥ 6 | pPot ≥ 7 | pPot ≥ 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unique PK targets | 390 | 366 | 275 | 146 |
| Unique non-PK targets | 210 | 134 | 84 | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mobasher, M.; Vogt, M.; Xerxa, E.; Bajorath, J. Comprehensive Data-Driven Assessment of Non-Kinase Targets of Inhibitors of the Human Kinome. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030258
Mobasher M, Vogt M, Xerxa E, Bajorath J. Comprehensive Data-Driven Assessment of Non-Kinase Targets of Inhibitors of the Human Kinome. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(3):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030258
Chicago/Turabian StyleMobasher, Mona, Martin Vogt, Elena Xerxa, and Jürgen Bajorath. 2024. "Comprehensive Data-Driven Assessment of Non-Kinase Targets of Inhibitors of the Human Kinome" Biomolecules 14, no. 3: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030258
APA StyleMobasher, M., Vogt, M., Xerxa, E., & Bajorath, J. (2024). Comprehensive Data-Driven Assessment of Non-Kinase Targets of Inhibitors of the Human Kinome. Biomolecules, 14(3), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14030258








