Therapeutic Effects of Stimulating the Melanocortin Pathway in Regulating Ocular Inflammation and Cell Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. α-MSH Bioavailability in the Eye
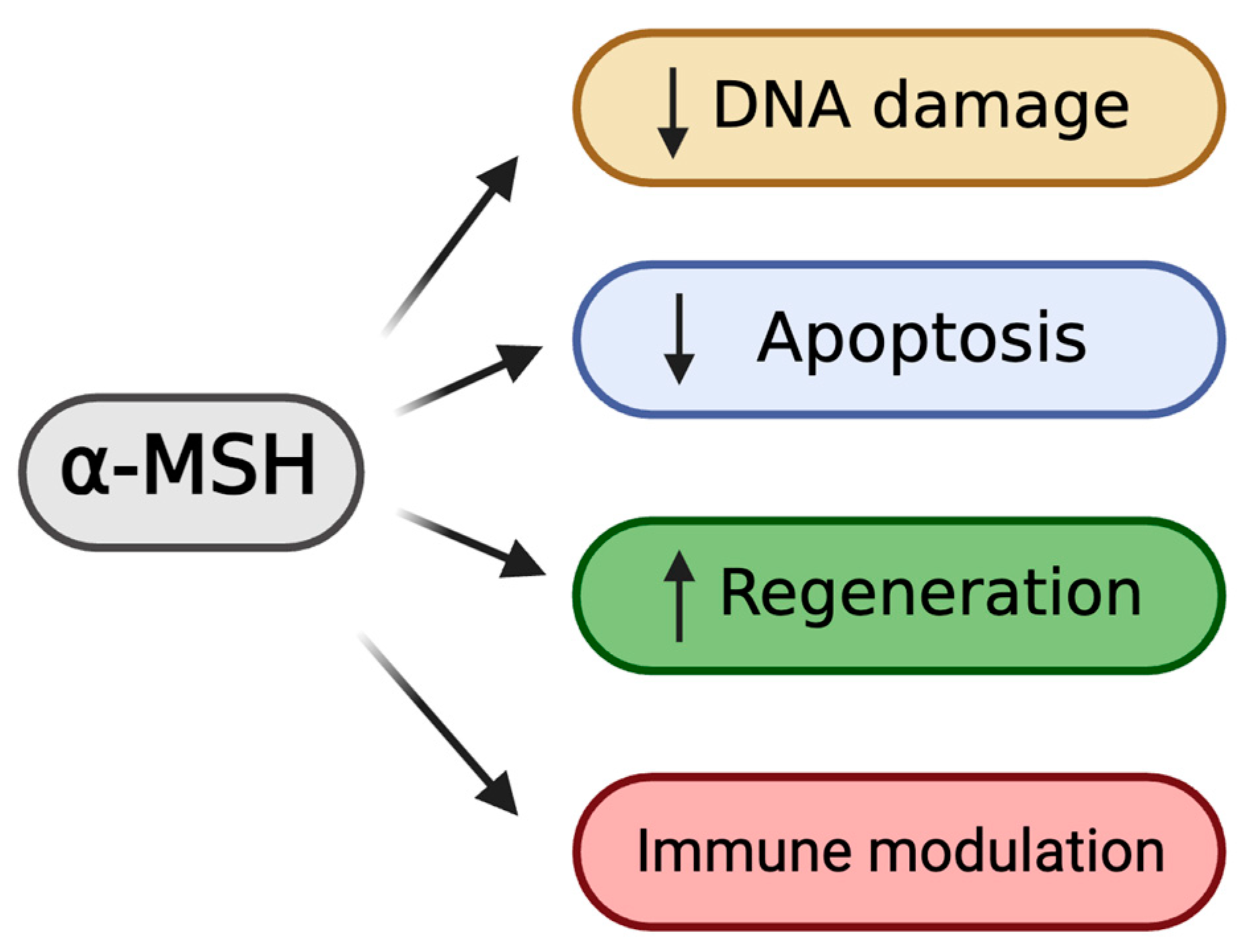
3. Biological Functions of Melanocortin Stimulation
3.1. Cytoprotective Effects of α-MSH
3.2. Pro-Regenerative Effects of α-MSH
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of α-MSH
3.4. Anti-Angiogenic Effects of α-MSH
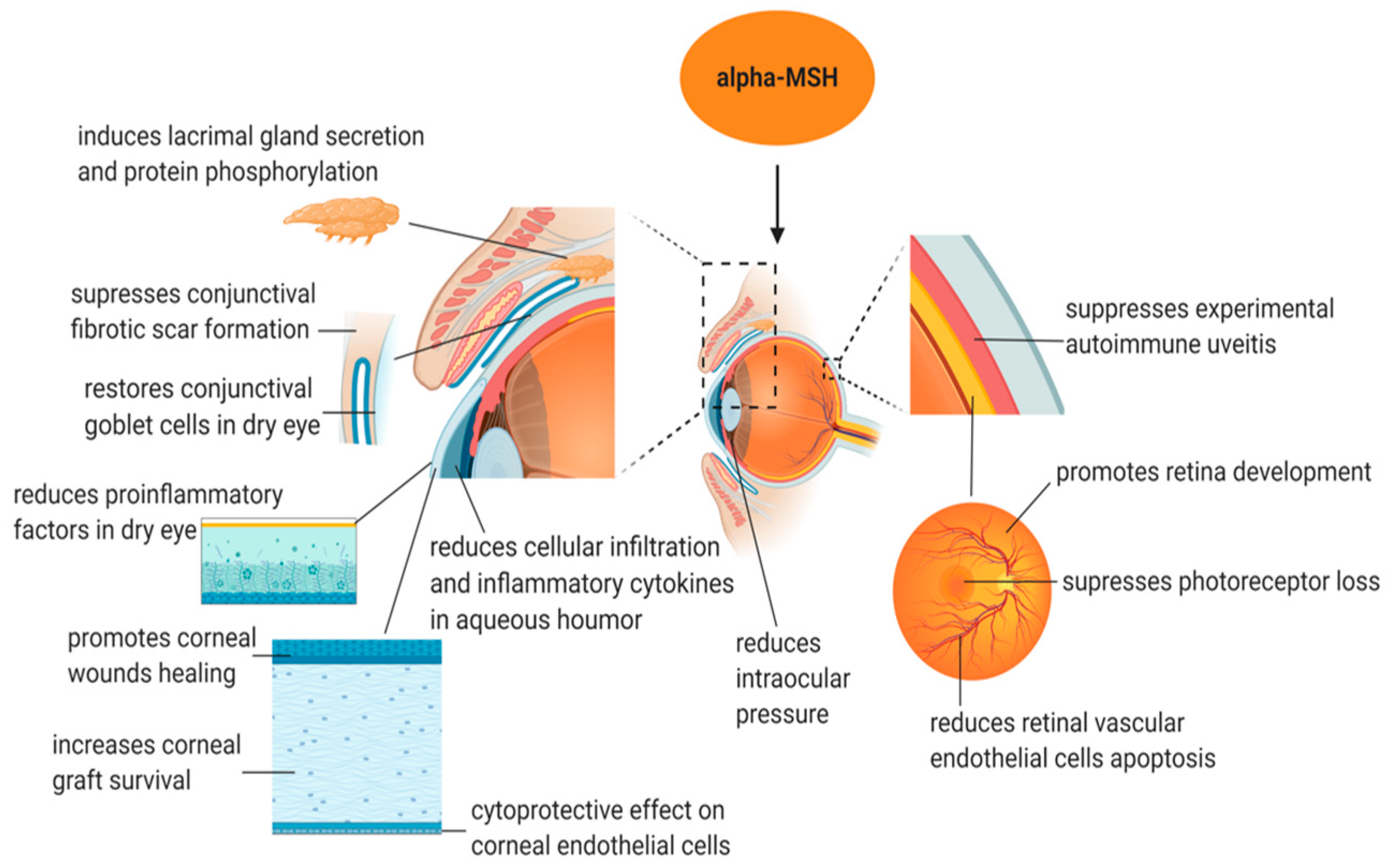
4. Application of α-MSH in Treating Eye Disease (Figure 2 and Table 2)
4.1. α-MSH Application in the Cornea
| Target Tissue | Mechanism of Action | Observed Function | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maintenance of tear production and corneal function |
|
|
|
| Acceleration of corneal wound healing |
|
|
|
| Regulation of Allergic Conjunctivitis |
|
|
|
| Prevention of conjunctival fibrosis |
|
|
|
| Cyto-protection of uveal and retinal tissues |
|
|
|
4.2. α-MSH Application in the Uvea and Retina
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cooray, S.N.; Clark, A.J.L. Melanocortin Receptors and Their Accessory Proteins. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2011, 331, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, G.; Diaz, J.; Murphree, S.; Catania, A.; Lipton, J.M. The Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Inhibits Experimental Arthritis in Rats. Neuroimmunomodulation 1994, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarini, S.; Bazzani, C.; Bertolini, A. Resuscitating Effect of Melanocortin Peptides after Prolonged Respiratory Arrest. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 121, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, J.M.; Ceriani, G.; Macaluso, A.; McCoy, D.; Carnes, K.; Biltz, J.; Catania, A. Antiinflammatory Effects of the Neuropeptide α-MSH in Acute, Chronic, and Systemic Inflammation. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; Volume 741, pp. 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajora, N.; Boccoli, G.; Burns, D.; Sharma, S.; Catania, A.P.; Lipton, J.M. α-MSH Modulates Local and Circulating Tumor Necrosis Factor-α in Experimental Brain Inflammation. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajora, N.; Boccoli, G.; Catania, A.; Lipton, J.M. α-MSH Modulates Experimental Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Peptides 1997, 18, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiba, H.; Garty, N.B.; Schmidt-Sole, J.; Piterman, O.; Azrad, A.; Salomon, Y. The Melanocortin Receptor in the Rat Lacrimal Gland: A Model System for the Study of MSH (Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone) as a Potential Neurotransmitter. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 181, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H.; Du, J.; Meng, Z.; Dou, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, R.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Ameliorates Ocular Surface Dysfunctions and Lesions in a Scopolamine-Induced Dry Eye Model via PKA-CREB and MEK-Erk Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. A-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Protects Retinal Vascular Endothelial Cells From Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis in a Rat Model of Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, F.; Onderka, J.; Braun, G.; Schneider, A.C.; Hos, D.; Bi, Y.; Bachmann, B.O.; Cursiefen, C. Identification of Novel Endogenous Anti(Lymph)Angiogenic Factors in the Aqueous Humor. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 6554–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjiv, N.; Osathanugrah, P.; Fraser, E.; Ng, T.F.; Taylor, A.W. Extracellular Soluble Membranes from Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Mediate Apoptosis in Macrophages. Cells 2021, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, D.N.; Zhao, H.; McCormick, S.A.; Nordlund, J.J.; Boissy, R.E. Uveal Melanocytes Do Not Respond to or Express Receptors for α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4507–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.W.; Yee, D.G.; Nishida, T.; Namba, K. Neuropeptide Regulation of Immunity: The Immunosuppressive Activity of Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (α-MSH). In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; Volume 917, pp. 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.F.; Dawit, K.; Taylor, A.W. Melanocortin Receptor Agonists Suppress Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 218, 108986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.W.; Lee, D. Applications of the Role of α-MSH in Ocular Immune Privilege. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 681, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, T.A.; Griffith, T.S. The Role of Fas Ligand and TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) in the Ocular Immune Response. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2007, 92, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederkorn, J.Y. The Immune Privilege of Corneal Grafts. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 74, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.W. A Review of the Influence of Aqueous Humor on Immunity. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2003, 11, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streilein, J.W.; Masli, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Kezuka, T. The Eye’s View of Antigen Presentation. Hum. Immunol. 2002, 63, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.W.; Streilein, J.W.; Cousins, S.W. Identification of Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone as a Potential Immunosuppressive Factor in Aqueous Humor. Curr. Eye Res. 1992, 11, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Stohl, L.L.; Wagner, J.A.; Granstein, R.D. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Biases Langerhans Cells toward Th2-Type Immunity. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 6020–6026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, M.; Pozo, D.; Ganea, D. The Significance of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide in Immunomodulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 249–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niizeki, H.; Alard, P.; Streilein, J.W. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Is Necessary for Ultraviolet B-Impaired Induction of Contact Hypersensitivity. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5183–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, C.P.; Arleth, A.J.; Aiyar, N.; Bhatnagar, P.K.; Lysko, P.G.; Feuerstein, G. CGRP Stimulates the Adhesion of Leukocytes to Vascular Endothelial Cells. Peptides 1992, 13, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Columbo, M.; Horowitz, E.M.; Kagey-Sobotka, A.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Substance P Activates the Release of Histamine from Human Skin Mast Cells through a Pertussis Toxin-Sensitive and Protein Kinase C-Dependent Mechanism. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1996, 81, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ramnath, R.D.; Zhi, L.; Tamizhselvi, R.; Bhatia, M. Substance P Enhances NF-ΚB Transactivation and Chemokine Response in Murine Macrophages via ERK1/2 and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C1586–C1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.A.; Taylor, A.W. The Neuropeptides α-MSH and NPY Modulate Phagocytosis and Phagolysosome Activation in RAW 264.7 Cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2013, 260, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Rey, E.; Ganea, D.; Delgado, M. Neuropeptides: Keeping the Balance between Pathogen Immunity and Immune Tolerance. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Taylor, A.W. Specific Aqueous Humor Factors Induce Activation of Regulatory T Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.W.; Namba, K. In Vitro Induction of CD25+ CD4+ Regulatory T Cells by the Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (α-MSH). Immunol. Cell Biol. 2001, 79, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, K.; Kitaichi, N.; Nishida, T.; Taylor, A.W. Induction of Regulatory T Cells by the Immunomodulating Cytokines α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone and Transforming Growth Factor-Β2. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.W. Modulation of Regulatory T Cell Immunity by the Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 49, 143–149. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, J.E.; Casanova, I.; Serna-Ojeda, J.C.; Graue-Hernández, E.O.; Quintana, G.; Salazar, A.; Jiménez-Martinez, M.C. Increased Expression of Tlr4 in Circulating Cd4+t Cells in Patients with Allergic Conjunctivitis and in Vitro Attenuation of Th2 Inflammatory Response by Alpha-Msh. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, V.J.; Wilkes, B.C.; Hadley, M.E.; Al-obeidi, F.; Sawyer, T.K.; Staples, D.J.; Devaux, A.E.; Dym, O.; Castrucci, A.M.d.L.; Hintz, M.F.; et al. α-Melanotropin: The Minimal Active Sequence in the Frog Skin Bioassay. J. Med. Chem. 1987, 30, 2126–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, R.J.; Szabo, M.; Wagner, M.J.; Kemp, E.H.; MacNeil, S.; Haycock, J.W. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone, MSH 11-13 KPV and Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Signalling in Human Keratinocyte Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englaro, W.; Rezzonico, R.; Durand-Clément, M.; Lallemand, D.; Ortonne, J.P.; Ballotti, R. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway and AP-1 Are Activated during CAMP-Induced Melanogenesis in B-16 Melanoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 24315–24320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshahi, M.; Mirshahi, A.; Sedighian, R.; Hecquet, C.; Faure, J.P.; Agarwal, M.K. Immunochemical Demonstration of the Mineralocorticoid Receptor in Ocular Tissues. Neuroendocrinology 1997, 65, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Thomas, L.C.; Moustafa, M.; Dawson, R.A.; Wagner, M.; Balafa, C.; Haycock, J.W.; Krauss, A.H.P.; Woodward, D.F.; Macneil, S. Cellular and Hormonal Regulation of Pigmentation in Human Ocular Melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res. 2001, 14, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haycock, J.W.; Wagner, M.; Morandini, R.; Ghanem, G.; Rennie, I.G.; Macneil, S. α-MSH Immunomodulation Acts via Rel/NF-ΚB in Cutaneous and Ocular Melanocytes and in Melanoma Cells. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 885, pp. 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintermann, E.; Erb, C.; Talke-Messerer, C.; Liu, R.; Tanner, H.; Flammer, J.; Eberle, A.N. Expression of the Melanin-Concentrating Hormone Receptor in Porcine and Human Ciliary Epithelial Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 206–209. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.B.; Cheng, L.; Bi, H.E.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Yao, J.; Zhou, X.Z.; Jiang, Q. Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Protects Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells from Oxidative Stress through Activation of Melanocortin 1 Receptor-Akt-MTOR Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lužnik Marzidovšek, Z.; Blanco, T.; Sun, Z.; Alemi, H.; Ortiz, G.; Nakagawa, H.; Chauhan, S.K.; Taylor, A.W.; Jurkunas, U.V.; Yin, J.; et al. The Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte–Stimulating Hormone Is Critical for Corneal Endothelial Cell Protection and Graft Survival after Transplantation. Am. J. Pathol. 2022, 192, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemi, H.; Wang, S.; Blanco, T.; Kahale, F.; Singh, R.B.; Ortiz, G.; Musayeva, A.; Yuksel, E.; Pang, K.; Deshpande, N.; et al. The Neuropeptide α-Melanocyte–Stimulating Hormone Prevents Persistent Corneal Edema Following Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loser, K.; Brzoska, T.; Oji, V.; Auriemma, M.; Voskort, M.; Kupas, V.; Klenner, L.; Mensing, C.; Hauschild, A.; Beissert, S.; et al. The Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Is Critically Involved in the Development of Cytotoxic CD8+ T Cells in Mice and Humans. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriemma, M.; Brzoska, T.; Klenner, L.; Kupas, V.; Goerge, T.; Voskort, M.; Zhao, Z.; Sparwasser, T.; Luger, T.A.; Loser, K. α-MSH-Stimulated Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells Induce Functional Regulatory T Cells and Ameliorate Ongoing Skin Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.; Robinson, S.J.; Pickard, C.; Jackson, C.L.; Friedmann, P.S.; Healy, E. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Suppresses Antigen-Induced Lymphocyte Proliferation in Humans Independently of Melanocortin 1 Receptor Gene Status. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 4806–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spana, C.; Taylor, A.W.; Yee, D.G.; Makhlina, M.; Yang, W.; Dodd, J. Probing the Role of Melanocortin Type 1 Receptor Agonists in Diverse Immunological Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridmanis, D.; Roga, A.; Klovins, J. ACTH Receptor (MC2R) Specificity: What Do We Know about Underlying Molecular Mechanisms? Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, N.; Näpänkangas, U.; Lindblom, J.; Hallböök, F. Proopiomelanocortin and Melanocortin Receptors in the Adult Rat Retino-Tectal System and Their Regulation after Optic Nerve Transection. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 482, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Yang, Q.; Hou, M.; Han, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Qi, C.; Bo, Q.; Ru, Y.; Yang, W.; et al. A-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Protects Early Diabetic Retina from Blood-Retinal Barrier Breakdown and Vascular Leakage via MC4R. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.J.; Taylor, A.W. Both MC5r and A2Ar Are Required for Protective Regulatory Immunity in the Spleen of Post–Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis in Mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Maisto, R.; Gesualdo, C.; Trotta, M.C.; Ferraraccio, F.; Kaneva, M.K.; Getting, S.J.; Surace, E.; Testa, F.; Simonelli, F.; et al. Activation of Melanocortin Receptors MC1 and MC5 Attenuates Retinal Damage in Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 7368389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisto, R.; Gesualdo, C.; Trotta, M.C.; Grieco, P.; Testa, F.; Simonelli, F.; Barcia, J.M.; D’Amico, M.; Di Filippo, C.; Rossi, S. Melanocortin Receptor Agonists MCR1-5 Protect Photoreceptors from High-Glucose Damage and Restore Antioxidant Enzymes in Primary Retinal Cell Culture. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, P.M.; Van der Zee, C.E.E.M.; Verhaagen, J.; Schotman, P.; Jennekens, F.G.I.; Gispen, W.H. Evidence That the Neurotrophic Actions of α-MSH May Derive from Its Ability to Mimick the Actions of a Peptide Formed in Degenerating Nerve Stumps. J. Neurol. Sci. 1984, 64, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Meent, H.; Hamers, F.P.T.; Lankhorst, A.J.; Joosten, E.A.J.; Gispen, W.H. Beneficial Effects of the Melanocortin α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone on Clinical and Neurophysiological Recovery after Experimental Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Wolff, I.; Scholzen, T.E.; Robinson, S.J.; Healy, E.; Luger, T.A.; Schwarz, T.; Schwarz, A. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Protects from Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Apoptosis and DNA Damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 5795–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadekaro, A.L.; Kavanagh, R.; Kanto, H.; Terzieva, S.; Hauser, J.; Kobayashi, N.; Schwemberger, S.; Cornelius, J.; Babcock, G.; Shertzer, H.G.; et al. α-Melanocortin and Endothelin-1 Activate Antiapoptotic Pathways and Reduce DNA Damage in Human Melanocytes. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4292–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.P.; Wheeler, P.; MacNeil, S.; Haycock, J.W. α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Cytoprotective Biology in Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. Peptides 2005, 26, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktar, B.K.; Yüksel, M.; Alican, I. The Role of Cyclooxygenase Inhibition in the Effect of α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone on Reactive Oxygen Species Production by Rat Peritoneal Neutrophils. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 71, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, R.; Carlin, A.; Airaghi, L.; Demitri, M.T.; Meda, L.; Galimberti, D.; Baron, P.; Lipton, J.M.; Catania, A. Melanocortin Peptides Inhibit Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Nitric Oxide by Activated Microglia. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, D.; Baron, P.; Meda, L.; Prat, E.; Scarpini, E.; Delgado, R.; Catania, A.; Lipton, J.M.; Scarlato, G. α-MSH Peptides Inhibit Production of Nitric Oxide and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α by Microglial Cells Activated with β-Amyloid and Interferon γ. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 263, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Star, R.A.; Rajora, N.; Huang, J.; Stock, R.C.; Catania, A.; Lipton, J.M. Evidence of Autocrine Modulation of Macrophage Nitric Oxide Synthase by α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8016–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsatmali, M.; Graham, A.; Szatkowski, D.; Ancans, J.; Manning, P.; McNeil, C.J.; Graham, A.M.; Thody, A.J. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Modulates Nitric Oxide Production in Melanocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Diaz, R.A.; Higham, S.; Kone, B.C. α-MSH Inhibits Induction of C/EBPβ-DNA Binding Activity and NOS2 Gene Transcription in Macrophages. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, C.; Durand, D.; Schiöth, H.B.; Rey, R.; Seilicovich, A.; Lasaga, M. Activation of Melanocortin 4 Receptors Reduces the Inflammatory Response and Prevents Apoptosis Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and Interferon-γ in Astrocytes. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 4918–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.J.; Han, D.J.; Chang, S.H.; Lim, D.G.; Wee, Y.M.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Koo, S.K.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.C. Protective Effect of Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone on Pancreas Islet Cell Against Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity In Vitro. Transplant. Proc. 2007, 39, 1604–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lužnik, Z.; Sun, Z.; Nakagawa, H.; Taylor, A.W.; Jurkunas, U.V.; Yin, J.; Dana, R. Association of α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone with Corneal Endothelial Cell Survival during Oxidative Stress and Inflammation-Induced Cell Loss in Donor Tissue. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020, 138, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahale, F.; Deshpande, N.; Alemi, H.; Naderi, A.; Wang, S.; Blanco, T.; Dohlman, T.H.; Yin, J.; Jurkunas, U.V.; Dana, R. Treatment with Neuropeptide Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Suppresses Progression of Fuchs Dystrophy in a UV-Induced Mouse Model. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 635. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, C.; Huang, Y.; Ru, Y.; Lu, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, K.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. α-MSH Ameliorates Corneal Surface Dysfunction in Scopolamine-Induced Dry Eye Rats and Human Corneal Epithelial Cells via Enhancing EGFR Expression. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 210, 108685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, B.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, W.; Newman, E.; Ammori, J.; Mulholland, M.W. Melanocortin-4 Receptor-Mediated Inhibition of Apoptosis in Immortalized Hypothalamic Neurons via Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase. Peptides 2006, 27, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Jo, S.K.; Cho, W.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Won, N.H. The Effect of α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone on Renal Tubular Cell Apoptosis and Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis in Cyclosporine A Nephrotoxicity. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Hu, X.; Yuen, P.S.T.; Star, R.A. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Inhibits Lung Injury after Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.W.; Wayne Streilein, J.; Cousins, S.W. Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Suppresses Antigen-Stimulated T Cell Production of Gamma-Lnterferon. Neuroimmunomodulation 1994, 1, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Schulte, U.; Kalden, H.; Luger, T.A. Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Modulates Activation of NF-ΚB and AP-1 and Secretion of Interleukin-8 in Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 885, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M.; Schiller, M.; Ständer, S.; Seltmann, H.; Li, Z.; Brzoska, T.; Metze, D.; Schiöth, H.B.; Skottner, A.; Seiffert, K.; et al. Evidence for Expression of Melanocortin-1 Receptor in Human Sebocytes in Vitro and in Situ. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.K.; Sarkar, A.; Sreenivasan, Y. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone down-Regulates CXC Receptors through Activation of Neutrophil Elastase. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandini, R.; Boeynaems, J.M.; Hedley, S.J.; Macneil, S.; Ghanem, C. Modulation of ICAM-1 Expression by α-MSH in Human Melanoma Cells and Melanocytes. J. Cell Physiol. 1998, 175, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.E.; Sunderkötter, C.; Kalden, D.H.; Brzoska, T.; Fastrich, M.; Fisbeck, T.; Armstrong, C.A.; Ansel, J.C.; Luger, T.A. A-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Prevents Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Vasculitis By Down-Regulating Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Expression. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böhm, M.; Eickelmann, M.; Li, Z.; Schneider, S.W.; Oji, V.; Diederichs, S.; Barsh, G.S.; Vogt, A.; Stieler, K.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; et al. Detection of Functionally Active Melanocortin Receptors and Evidence for an Immunoregulatory Activity of α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone in Human Dermal Papilla Cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4635–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.P.; MacNeil, S.; Haycock, J.W. Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Peptides Inhibit TNF-α Signaling in Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. Peptides 2006, 27, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Sreenivasan, Y.; Manna, S.K. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Induces Cell Death in Mast Cells: Involvement of NF-ΚB. FEBS Lett. 2003, 549, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Becher, E.; Mahnke, K.; Hartmeyer, M.; Schwarz, T.; Scholzen, T.; Luger, T.A. Evidence for the Differential Expression of the Functional Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Receptor MC-1 on Human Monocytes. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Barabino, S.; Taylor, A.W.; Dana, M.R. Effect of the Ocular Microenvironment in Regulating Corneal Dendritic Cell Maturation. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2007, 125, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonindard, C.; Goigoux, C.; Hollande, E.; D’Hinterland, L.D. The Administration of an α-MSH Analogue Reduces the Serum Release of IL-1α and TNFα Induced by the Injection of a Sublethal Dose of Lipopolysaccharides in the BALB/c Mouse. Pigment Cell Res. 1996, 9, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, J. Prevention and Treatment of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone-Transduced PLP139-151-Specific T Cells. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktar, B.K.; Ercan, F.; Yegen, B.Ç.; Alican, I. The Effect of α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone on Colonic Inflammation in the Rat. Peptides 2000, 21, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.S.; Schwarz, A.; Becher, E.; Mahnke, K.; Aragane, Y.; Schwarz, T.; Luger, T.A. Pro-Opiomelanocortin-Derived Peptides Induce IL-10 Production in Human Monocytes. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo, P.; García-Foncillas, J.; Okroujnov, I.; Bandrés, E. α-MSH Regulates Interleukin-10 Expression by Human Keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1998, 290, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, S.; Elbasiony, E.; Zidan, A.A.; Yin, J. Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (α-MSH) Suppresses Corneal Angiogenesis and Inflammation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 1729. [Google Scholar]
- Rheins, L.A.; Cotleur, A.L.; Kleier, R.S.; Hoppenjans, W.B.; Saunder, D.N.; Nordlund, J.J. Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Modulates Contact Hypersensitivity Responsiveness in C57/BL6 Mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1989, 93, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabbe, S.; Bhardwaj, R.S.; Mahnke, K.; Simon, M.M.; Schwarz, T.; Luger, T.A. Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Induces Hapten-Specific Tolerance in Mice. J. Immunol. 1996, 156, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamrah, P.; Haskova, Z.; Taylor, A.W.; Zhang, Q.; Ksander, B.R.; Dana, M.R. Local Treatment with Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Reduces Corneal Allorejection. Transplantation 2009, 88, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahvildari, M.; Inomata, T.; Amouzegar, A.; Dana, R. Regulatory T Cell Modulation of Cytokine and Cellular Networks in Corneal Graft Rejection. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2018, 6, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.W.; Dinwoodie, I.R.; Linderman, S.E. Retinal Pigment Epithelium Activation of Alternative Macrophages. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 4599. [Google Scholar]
- Haycock, J.W.; Wagner, M.; Morandini, R.; Ghanem, G.; Rennie, I.G.; Mac Neil, S. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Inhibits NF-ΚB Activation in Human Melanocytes and Melanoma Cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustafa, M.; Szabo, M.; Ghanem, G.E.; Morandini, R.; Kemp, E.H.; MacNeil, S.; Haycock, J.W. Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Stimulated NFκB/P65 in Human Keratinocytes by α-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone and Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Peptides. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teare, K.A.; Pearson, R.G.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Haycock, J.W. α-MSH Inhibits Inflammatory Signalling in Schwann Cells. Neuroreport 2004, 15, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiyama, T.; Zhao, H.; Catania, A.; Furukawa, S.; Lipton, J.M. α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Inhibits NF-ΚB Activation and IκBα Degradation in Human Glioma Cells and in Experimental Brain Inflammation. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 157, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Sato, N.; Kone, B.C. Amelanocyte Stimulating Hormone Protects against H2O 2-Induced Inhibition of Wound Restitution in IEC-6 Cells via a Syk Kinase- and NF-Κβ-Dependent Mechanism. Shock 2004, 22, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Kenyon, B.M.; Hamrah, P. Immunomodulatory Role of Neuropeptides in the Cornea. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, L.; Ye, E.A.; Wang, A.; Li, G.; Chen, L. Aqueous humor induces lymphatic regression on the ocular surface. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.W.; Tsai, P.J.; Tai, M.H.; Bee, Y.S. Therapeutic Effect of α-Msh in Primary Cultured Orbital Fibroblasts Obtained from Patients with Thyroid Eye Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Liu, L.; Pang, K. Corneal Nerves Modulate Angiogenesis via Secreted Neuropeptides. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 881. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Liu, L.; Pang, K. Peripheral Sensory Nerves Inhibit Corneal Angiogenesis via Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 911-A0275. [Google Scholar]
- Gipson, I.K. The Ocular Surface: The Challenge to Enable and Protect Vision. The Friedenwald Lecture. In Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science; ARVO: Rockville, ML, USA, 2007; Volume 48, pp. 4391–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.J.; Marfurt, C.F.; Kruse, F.; Tervo, T.M.T. Corneal Nerves: Structure, Contents and Function. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Kraan, M.; Adan, R.A.H.; Entwistle, M.L.; Gispen, W.H.; Burbach, J.P.H.; Tatro, J.B. Expression of Melanocortin-5 Receptor in Secretory Epithelia Supports a Functional Role in Exocrine and Endocrine Glands. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 2348–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, R.; Padel, U.; Porsch, P.H.; Soling, H.-D. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone and A-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Induce Secretion and Protein Phosphorylation in the Rat Lacrimal Gland by Activation of a CAMP-Dependent Pathway. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 126, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.; Kenyon, K.; Ousler, G.; Watson, M.; Vollmer, P.; McLaurin, E.B.; Torkildsen, G.; Winters, J.; Dodd, J.; Jordan, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Melanocortin Pan-Agonist PL9643 in a Phase 2 Study of Patients with Dry Eye Disease. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 39, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, J.; Lukenda, A.; Štambuk, N.; Konjevoda, P.; Kaštelan, S.; Ćurković, M. Effects of Alpha-MSH on Corneal Epithelial Lesions in Rats. Coll. Antropol. 2012, 36, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naveh, N.; Marshall, J. Melanocortins Are Comparable to Corticosteroids as Inhibitors of Traumatic Ocular Inflammation in Rabbits. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2001, 239, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Yao, K.; Yin, J. Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Suppresses the Proliferation of Human Tenon’s Capsule Fibroblast Proliferation Induced by Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1. Mol. Biol. 2012, 46, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, S.; Braunstahl, G.J.; Rüdrich, U.; Gehring, M.; Eiz-Vesper, B.; Luger, T.A.; Steelant, B.; Seys, S.F.; Kapp, A.; Böhm, M.; et al. Regulation of Melanocortin 1 Receptor in Allergic Rhinitis in Vitro and in Vivo. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webering, S.; Lunding, L.P.; Vock, C.; Schröder, A.; Gaede, K.I.; Herzmann, C.; Fehrenbach, H.; Wegmann, M. The Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone Acts as a Local Immune Homeostasis Factor in Experimental Allergic Asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Biros, D.J.; Taylor, A.W. Injection of an Alpha-Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone Expression Plasmid Is Effective in Suppressing Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2009, 9, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Miyata, S.; Itoh, Y.; Mizuki, N.; Ohgami, K.; Shiratori, K.; Ilieva, I.B.; Ohno, S.; Taylor, A.W. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Alpha-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone against Rat Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis and the Time Course of Inflammatory Agents in Aqueous Humor. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiratori, K.; Ohgami, K.; Ilieva, I.B.; Koyama, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Ohno, S. Inhibition of Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis and Potentiation of Cyclooxygenase-2 Protein Expression by α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ng, T.F.; Kitaichi, N.; Taylor, A.W. In Vitro-Generated Autoimmune Regulatory T Cells Enhance Intravitreous Allogeneic Retinal Graft Survival. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5112–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshigawara, K.; Takahashi, S.; Boswell, T.; Li, Q.; Tanaka, S.; Takeuchi, S. Identification of Avian α-Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone in the Eye: Temporal and Spatial Regulation of Expression in the Developing Chicken. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 168, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Naveh, N. Melanocortins Applied Intravitreally Delay Retinal Dystrophy in Royal College of Surgeons Rats. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2003, 241, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Receptor | Site of Expression | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| MC1R | Uveal Melanocytes | Inhibits cytokine-stimulated NF-κB activity |
| Corneal Endothelial Cells | Cytoprotection Regeneration | |
| RPE | Inhibits apoptosis | |
| T cells | Expands Tregs and suppresses Th17 proliferation | |
| B lymphocytes | Suppresses antigen-induced proliferation | |
| MC3R | B lymphocytes | Suppress antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation |
| Retinal ganglion cells | Stimulates neurite growth from retinal neurons | |
| MC4R | Retinal micro-vessel endothelial cells | Antagonizes hyperpermeability |
| Retinal ganglion cells | Stimulates neurite growth from retinal neurons | |
| MC5R | RPE cells | Mitigates the release of cytokines and angiogenesis |
| Primed T cells | Suppresses INF-γ by activating Treg cells |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Kahale, F.; Naderi, A.; Surico, P.L.; Yin, J.; Dohlman, T.; Chen, Y.; Dana, R. Therapeutic Effects of Stimulating the Melanocortin Pathway in Regulating Ocular Inflammation and Cell Death. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020169
Wang S, Kahale F, Naderi A, Surico PL, Yin J, Dohlman T, Chen Y, Dana R. Therapeutic Effects of Stimulating the Melanocortin Pathway in Regulating Ocular Inflammation and Cell Death. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shudan, Francesca Kahale, Amirreza Naderi, Pier Luigi Surico, Jia Yin, Thomas Dohlman, Yihe Chen, and Reza Dana. 2024. "Therapeutic Effects of Stimulating the Melanocortin Pathway in Regulating Ocular Inflammation and Cell Death" Biomolecules 14, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020169
APA StyleWang, S., Kahale, F., Naderi, A., Surico, P. L., Yin, J., Dohlman, T., Chen, Y., & Dana, R. (2024). Therapeutic Effects of Stimulating the Melanocortin Pathway in Regulating Ocular Inflammation and Cell Death. Biomolecules, 14(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14020169





