Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. HDAC Inhibitors in Fibrotic Diseases
2.1. HDAC Inhibitors in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
2.1.1. Class I HDAC Inhibitors in IPF
2.1.2. Class II HDAC Inhibitors in IPF
2.1.3. Pan-HDAC Inhibitors in IPF
2.2. HDAC Inhibitors in Cardiac Fibrosis
2.3. HDAC Inhibitors in Renal Fibrosis
2.4. HDAC Inhibitors in Liver Fibrosis

3. HDAC Inhibitors as Anti-Inflammatory Agents
3.1. HDAC Classes I and II Inhibitor
3.2. Selective HDAC8 Inhibitor
3.3. Selective HDAC Class IIa Inhibitor
3.4. Selective HDAC Class IIb Inhibitors
3.5. Pan-HDAC Inhibitor
4. Challenges in the Application of HDAC Inhibitors for the Treatment of Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of Histone Acetylation: The Histone Deacetylase Enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Sun, Z.; Kuang, P.; Chen, J. Recent progress on HDAC inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for cancer treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 208, 112831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Seto, E. HDACs and HDAC Inhibitors in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Cohen, M.H.; Justice, R.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Vorinostat for Treatment of Advanced Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Oncologist 2007, 12, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrich, A.; Nabhan, C. Use of class I histone deacetylase inhibitor romidepsin in combination regimens. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, R.M. Belinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2014, 74, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raedler, L.A. Farydak (Panobinostat): First HDAC Inhibitor Approved for Patients with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2016, 9, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Raouf, Y.S. Targeting histone deacetylases: Emerging applications beyond cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 104094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, Y.N. Givinostat: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Hu, M.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Sanders, Y.Y. HDAC inhibitors as antifibrotic drugs in cardiac and pulmonary fibrosis. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319862697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Hu, X.; Yin, H. Molecular mechanisms of histone deacetylases and inhibitors in renal fibrosis progression. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 986405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Qian, S.; Sun, Z. Targeting histone deacetylase in cardiac diseases. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1405569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-P.; Jiang, S.-H.; Cai, J.; Luo, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-H.; Feng, D.-D. Histone deacetylases: potential therapeutic targets for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1426508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, R.S.; Maloney, M.E.; Lucas, R.; Fulton, D.J.R.; Patel, V.; Bagi, Z.; Kovacs-Kasa, A.; Kovacs, L.; Su, Y.; Verin, A.D. Zinc-Dependent Histone Deacetylases in Lung Endothelial Pathobiology. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, D.J.; Martinez, F.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1811–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, S.; Monari, M.; Guerrieri, A.; Donatelli, P.; Bassi, I.; Garuti, M.; Luppi, F.; Betti, S.; Bandelli, G.; Carpano, M.; et al. Real-life comparison of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A 24-month assessment. Respir. Med. 2019, 159, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfei, M.; Mahavadi, P.; Guenther, A. Targeting Histone Deacetylases in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Future Therapeutic Option. Cells 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korfei, M.; Skwarna, S.; Henneke, I.; MacKenzie, B.; Klymenko, O.; Saito, S.; Ruppert, C.; von der Beck, D.; Mahavadi, P.; Klepetko, W.; et al. Aberrant expression and activity of histone deacetylases in sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Son, E.S.; Lee, Y.E.; Kyung, S.Y.; Park, J.-W.; Kim, S.-H. Histone deacetylase 3 promotes alveolar epithelial–mesenchymal transition and fibroblast migration under hypoxic conditions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Geng, B.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Hao, B.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. Histone deacetylase 3 deletion in alveolar type 2 epithelial cells prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvaez, M.; McQuown, S.C.; Rogge, G.A.; Astarabadi, M.; Jacques, V.; Carreiro, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Wood, M.A. HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Deng, H.; Zheng, L.; Yang, H.; Lv, X. The Role of Nrf2 in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Treatment Approaches. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, W. Inhibiting HDAC3 (Histone Deacetylase 3) Aberration and the Resultant Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Derived 2-Related Factor-2) Repression Mitigates Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hypertension 2021, 78, E15–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano-Marquez, F.; Romero, Y.; Espina-Ordoñez, M.; Cisneros, J. Absence of HDAC3 by Matrix Stiffness Promotes Chromatin Remodeling and Fibroblast Activation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cells 2023, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerokonstantis, D.T.; Mantzourani, C.; Gkikas, D.; Wu, K.-C.; Hoang, H.N.; Triandafillidi, I.; Barbayianni, I.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Kokotos, A.C.; Moutevelis-Minakakis, P.; et al. N-(2-Aminophenyl)-benzamide Inhibitors of Class I HDAC Enzymes with Antiproliferative and Antifibrotic Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 14357–14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ota, Y.; Bateman, M.E.; Alkhatib, A.L.; Morris, G.F.; Lasky, J.A. HDAC8 inhibition ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2019, 316, L175–L186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Gu, X. A narrative review of the role of HDAC6 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-C.; Yeh, T.-Y.; Ye, C.-H.; Chong, P.C.T.; Ho, Y.-H.; So, D.K.; Yap, K.Y.; Peng, G.-R.; Shao, C.-H.; Jagtap, A.D.; et al. Discovery of HDAC6, HDAC8, and 6/8 Inhibitors and Development of Cell-Based Drug Screening Models for the Treatment of TGF-β-Induced Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 10528–10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiani, G.; Cavella, C.; Osko, J.D.; Brindisi, M.; Relitti, N.; Brogi, S.; Saraswati, A.P.; Federico, S.; Chemi, G.; Maramai, S.; et al. Harnessing the Role of HDAC6 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Design, Synthesis, Structural Analysis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9960–9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; Cui, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Qian, R.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of a novel TRAIL-activated HDAC6 inhibitor for the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2024, 113, 117924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Quan, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, E.; Ma, C. Discovery of novel pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-3,11-dione (PBD) derivatives as selective HDAC6 inhibitors for the efficient treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 275, 116608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Liou, J.-P.; Hua, H.-S.; Cheng, W.-H.; Yuliani, F.S.; Chen, B.-C.; Lin, C.-H. MPT0E028, a novel pan-HDAC inhibitor, prevents pulmonary fibrosis through inhibition of TGF-β-induced CTGF expression in human lung fibroblasts: Involvement of MKP-1 activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 977, 176711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, T.; Schmull, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H. Dual inhibition of HDAC and tyrosine kinase signaling pathways with CUDC-907 attenuates TGFβ1 induced lung and tumor fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Kee, H.J.; Kee, S.-J.; Jeong, M.H. Hdac8 Inhibitor Alleviates Transverse Aortic Constriction-Induced Heart Failure in Mice by Downregulating Ace1. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Ramos, J.; Luo, W.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Buggy, J.J. A novel histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8)-specific inhibitor PCI-34051 induces apoptosis in T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Kee, H.J.; Bai, L.; Kim, M.-K.; Kee, S.-J.; Jeong, M.H. Selective HDAC8 Inhibition Attenuates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy and Fibrosis via p38 MAPK Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 677757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travers, J.G.; Wennersten, S.A.; Peña, B.; Bagchi, R.A.; Smith, H.E.; Hirsch, R.A.; Vanderlinden, L.A.; Lin, Y.-H.; Dobrinskikh, E.; Demos-Davies, K.M.; et al. HDAC Inhibition Reverses Preexisting Diastolic Dysfunction and Blocks Covert Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Circulation 2021, 143, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, D.M.; Fahlbusch, P.; de Wiza, D.H.; Jacob, S.; Kettel, U.; Al-Hasani, H.; Krüger, M.; Ouwens, D.M.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S.; et al. Rhein, a novel Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor with antifibrotic potency in human myocardial fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.H.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, I.J.; Cha, H.; Cho, J.M.; Ma, S.K.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, E.H. CG200745, a Novel HDAC Inhibitor, Attenuates Kidney Fibrosis in a Murine Model of Alport Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, W.-C.; Tsai, M.-T.; Chen, N.-J.; Tarng, D.-C. Trichostatin A Alleviates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis Through Modulation of the M2 Macrophage Subpopulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zou, J.; Tolbert, E.; Zhao, T.C.; Bayliss, G.; Zhuang, S. Identification of histone deacetylase 8 as a novel therapeutic target for renal fibrosis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7295–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rettig, I.; Koeneke, E.; Trippel, F.; Mueller, W.C.; Burhenne, J.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Fabian, J.; Schober, A.; Fernekorn, U.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Selective inhibition of HDAC8 decreases neuroblastoma growth in vitro and in vivo and enhances retinoic acid-mediated differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, M.; Baskol, M.; Akalın, H.; Baskol, G. Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA) Reduces Fibrosis Markers and Deactivates Human Stellate Cells via the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition (EMT). Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 79, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-M.; Fan, S.-J.; Zhou, X.-R.; Liu, Y.-J.; Li, X.; Liao, L.-P.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.-C.; Yu, L.; Fu, R.; et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitor givinostat attenuates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 43, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuvel, D.J.; Lemasters, J.J.; Chou, C.J.; Zhong, Z. LP340, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, decreases liver injury and fibrosis in mice: role of oxidative stress and microRNA-23a. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1386238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, J.; Yue, K.; Huang, C.; Qin, M.; Chi, D.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, T.; et al. Potent Hydrazide-Based HDAC Inhibitors with a Superior Pharmacokinetic Profile for Efficient Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia In Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 65, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, T.; Lafforgue, P.; Pham, T. NSAID: Current limits to prescription. Jt. Bone Spine 2023, 91, 105685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, J.B.; White, A.G.; Scarpati, L.M.; Wan, G.; Nelson, W.W. Long-term Systemic Corticosteroid Exposure: A Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, Y.; Khan, H. Immunosuppressive Drugs. Encycl. Infect. Immun. 2022, 4, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoui, Y.; Guillot, X.; Sélambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Ralandison, S.; Gasque, P. Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Khan, M.; Singh, I. HDAC inhibitor SAHA normalizes the levels of VLCFAs in human skin fibroblasts from X-ALD patients and downregulates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in Abcd1/2-silenced mouse astrocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobreva, Z.G.; Grigorov, B.G.; Stanilova, S.A. Suppression of IL-12p40-related regulatory cytokines by suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid an inhibitor of histone deacetylases. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.N.; Choijookhuu, N.; Takagi, H.; Srisowanna, N.; Huynh, M.N.N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Oo, P.S.; Kyaw, M.T.H.; Sato, K.; Yamaguchi, R.; et al. The HDAC Inhibitor, SAHA, Prevents Colonic Inflammation by Suppressing Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in DSS-induced Colitis. Acta Histochem. ET Cytochem. 2018, 51, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhaecke, T.; Papeleu, P.; Elaut, G.; Rogiers, V. Trichostatin A - like Hydroxamate Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents: Toxicological Point of View. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1629–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-F.; Sheu, J.-R.; Lin, C.-H.; Chen, W.-C.; Hsiao, G.; Ou, G.; Chiu, P.-T.; Hsu, M.-J. MAPK phosphatase-1 contributes to trichostatin A inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gen. Subj. 2011, 1810, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleophas, M.C.P.; Crişan, T.O.; Klück, V.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Netea-Maier, R.T.; Dinarello, C.A.; Netea, M.G.; Joosten, L.A.B. Romidepsin suppresses monosodium urate crystal-induced cytokine production through upregulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 expression. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pojani, E.; Barlocco, D. Romidepsin (FK228), A Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor and its Analogues in Cancer Chemotherapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, M.; McClatchy, D.B.; Diedrich, J.K.; Olmer, M.; Johnson, K.A.; Yates, J.R.; Lotz, M.K. Mocetinostat activates Krüppel-like factor 4 and protects against tissue destruction and inflammation in osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 8, e170513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wen, R.; Yang, N.; Zhang, T.-N. Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in inflammatory diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, D.-X.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.-M.; Cui, Y.-M.; Shen, T.-Z.; Li, X.-L.; Sun, H.-D.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, W.-L. Synthesis of nigranoic acid and manwuweizic acid derivatives as HDAC inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 109, 104728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Oehme, I.; Witt, O.; Oliveira, G.; Sippl, W.; Romier, C.; Pierce, R.J.; Jung, M. HDAC8: a multifaceted target for therapeutic interventions. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, J.; Shin, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, H.; Yu, J.H.; Jeon, Y.H.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Discovery of organosulfur-based selective HDAC8 inhibitors with anti-neuroblastoma activity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 203, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-I.; Cho, H.; Jeon, R.; Sung, M.-K. Therapeutic Efficacy of Novel HDAC Inhibitors SPA3052 and SPA3074 against Intestinal Inflammation in a Murine Model of Colitis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, E.K.; Liu, L.; Wu, K.; Lim, J.; Sweet, M.J.; Lohman, R.; Iyer, A.; Fairlie, D.P. A novel inhibitor of class IIa histone deacetylases attenuates collagen-induced arthritis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 181, 4804–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strowig, T.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Flavell, R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. Nature 2012, 481, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangan, M.S.J.; Olhava, E.J.; Roush, W.R.; Seidel, H.M.; Glick, G.D.; Latz, E. Targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magupalli, V.G.; Negro, R.; Tian, Y.; Hauenstein, A.V.; Di Caprio, G.; Skillern, W.; Deng, Q.; Orning, P.; Alam, H.B.; Maliga, Z.; et al. HDAC6 mediates an aggresome-like mechanism for NLRP3 and pyrin inflammasome activation. Science 2020, 369, eaas8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T. The Role of HDAC6 in Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 763831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Gan, H.; Chen, H.; Zhai, X.; Liang, P.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Histone Deacetylation 10 Alleviates Inflammation After Intracerebral Hemorrhage via the PTPN22/NLRP3 Pathway in Rats. Neuroscience 2020, 432, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, F.B.; Enns, J.; Honin, I.; Engelhardt, J.; Schöler, A.; Smith, S.T.; Meiler, J.; Schäker-Hübner, L.; Weindl, G.; Hansen, F.K. Groebke Blackburn Bienaymé-mediated multi-component synthesis of selective HDAC6 inhibitors with anti-inflammatory properties. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 143, 107072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Sun, S.; Jia, G.; Qin, M.; Hou, X.; Chou, C.J.; Huang, C.; Li, X. First-in-Class Hydrazide-Based HDAC6 Selective Inhibitor with Potent Oral Anti-Inflammatory Activity by Attenuating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12140–12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Mondal, P.; Sang, N.; Li, Z.; Ding, W.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Birar, V.C.; Gomm, A.; Tanzi, R.E.; et al. Design, synthesis, and anti-inflammatory activity characterization of novel brain-permeable HDAC6 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 254, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindisi, M.; Barone, S.; Rossi, A.; Cassese, E.; Del Gaudio, N.; Morel, J.F.; Filocamo, G.; Alberico, A.; De Fino, I.; Gugliandolo, D.; et al. Efficacy of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibition in mouse models of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: A new glimpse for reducing inflammation and infection in cystic fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 936, 175349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.-M.; Lee, C.; Min, J.; Ha, N.; Bae, D.; Nam, G.; Park, H.-J. Development of a tetrahydroindazolone-based HDAC6 inhibitor with in-vivo anti-arthritic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2024, 99, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, K.; Shinojima, N.; Hayashi, M.; Nakano, T.; Ichimura, K.; Mukasa, A. Histone deacetylase inhibition enhances the therapeutic effects of methotrexate on primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldecker, M.; Kautenburger, T.; Daumann, H.; Busch, C.; Schrenk, D. Inhibition of histone-deacetylase activity by short-chain fatty acids and some polyphenol metabolites formed in the colon. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 19, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Dash, D.; Singh, R. An antioxidant ameliorates allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting HDAC 1 via HIF-1α/VEGF axis suppression in mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mitra, P.; Lahiri, A.; Das, T.; Sarkar, J.; Paul, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Butyrate limits inflammatory macrophage niche in NASH. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, P.; Bai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Butyrate suppresses atherosclerotic inflammation by regulating macrophages and polarization via GPR43/HDAC-miRNAs axis in ApoE−/− mice. PLOS ONE 2023, 18, e0282685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R. Safety and Tolerability of Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors in Oncology. Drug Saf. 2019, 42, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberland, M.; Montgomery, R.L.; Olson, E.N. The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, J.; Macarak, E.; Piera-Velazquez, S.; Jimenez, S.A. Human Fibrotic Diseases: Current Challenges in Fibrosis Research. In Fibrosis; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1627, pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

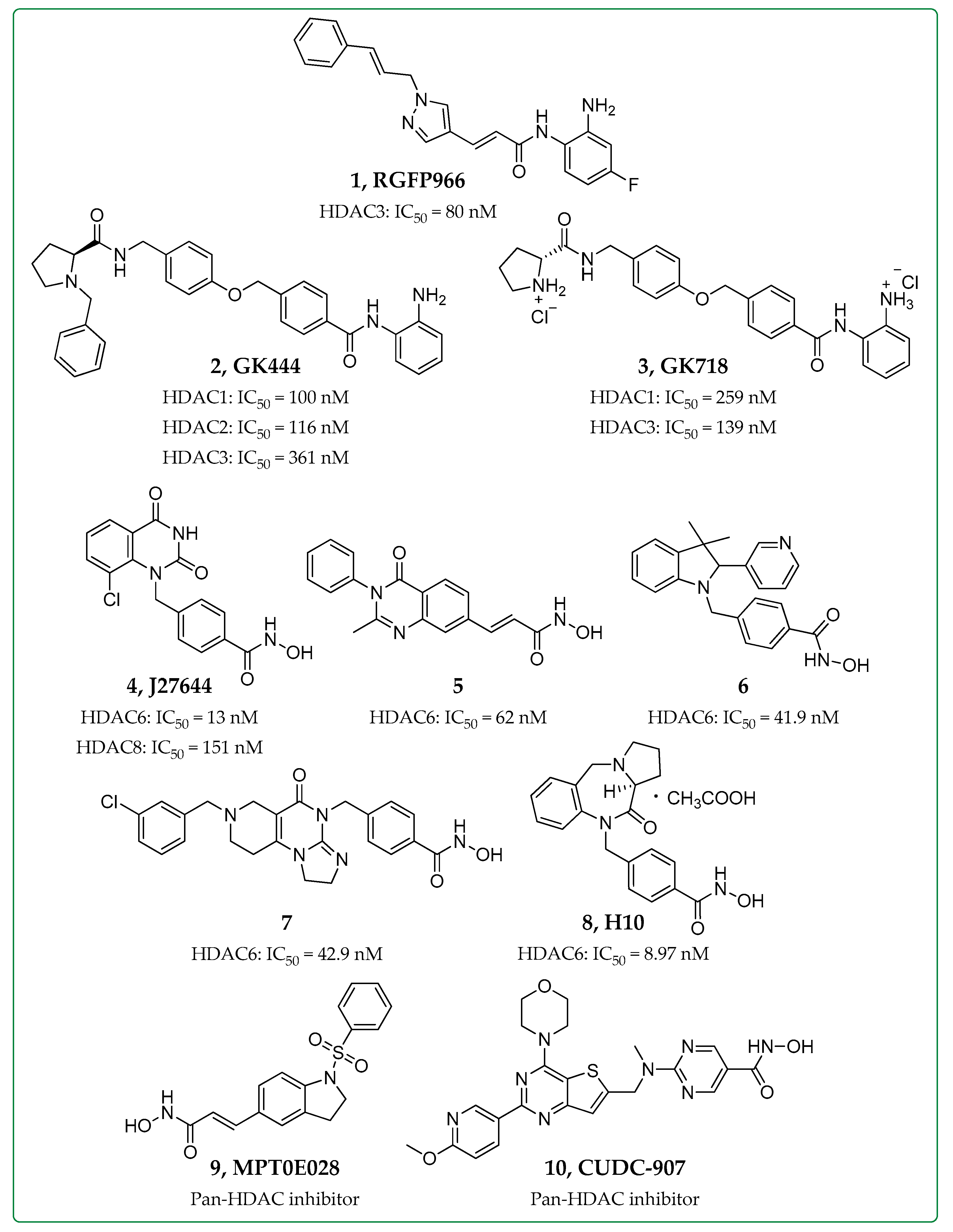
| Inhibitor | HDAC Inhibition | Biological Evaluation In Vitro or In Vivo | Anti-Fibrotic Activity | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGFP966 (1) | HDAC3 | Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | ↑ Nrf2 expression, ↑ Inflammatory cytokines | [20,23] |
| GK444 (2), GK718 (3) | HDAC1,2,3 | Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | ↓ Col1a1 expression, ↓ Fibrotic masses, ↓ Collagen deposition | [25] |
| J27644 (4) | HDAC6,8 | TGF-β-treated human pulmonary fibroblasts (HPFs) | ↓ Pulmonary fibrosis, ↓ α-SMA, ↓ Col1a1 levels | [28] |
| Compound 5 | HDAC6 | |||
| Compound 6 | HDAC6 | Organoid cultures of airway basal cells derived from IPF patients | ↓ Proliferation, ↓ Fibrotic sphere formation | [29] |
| Ex vivo cultures of human lung tissues | ↓ TGF-β dependent fibrogenesis, ↓ Expression of ECM genes | |||
| Compound 7 | HDAC6-TRAIL activation | Bleomycin-induced and silica suspension-induced mice | ↓ Proliferation (Fibroblast cell lines NIH/3T3 and HPF)↓ Inflammation, ↓ Collagen deposition | [30] |
| H10 (8) | HDAC6 | Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | ↓ TGF-β1-dependent fibrogenesis, ↓ Collagen deposition | [31] |
| MPT0E028 (9) | Pan-HDAC | Human lung fibroblasts | ↑ MKP-1, ↓ p38 + ERK phosphorylation, ↓ Smad3 + AP-1 activation, ↓ CTGF expression | [32] |
| Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | ↓ Fibrosis score, ↓ Fibronectin, ↓ Collagen, ↓ α-SMA expression | |||
| CUDC-907 (10) | Pan-HDAC- PI3K/AKT | Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis mice | ↓ Collagen levels | [33] |
| Inhibitor | HDAC Inhibition | Biological Evaluation In Vitro or In Vivo | Anti-Fibrotic Activity | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCI34051 (11) | HDAC8 | Isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy mouse model | ↓ Cardiac fibrosis, ↓ TGF-β1/Smad2/3 pathway (Rat cardiac fibroblasts), ↓ Cardiac hypertrophy, ↓ Collagen type I, ↓ Fibronectin, ↓ CTGF | [34,36,41] |
| Unilateral ureteral obstruction murine model | ↑ Contactin acetylation, ↓ Phosphorylation of Smad3, STAT3, β-catenin, ↓ Snail expression | |||
| Givinostat (12) | Pan-HDAC | Mouse model of diastolic dysfunction | ↓ Extracellular matrix deposition ↓ Cardiac fibroblast activation | [37,44] |
| Mice receiving methionine- and choline-deficient diet | ↓ Inflammation, ↓ Hepatic fibrosis | |||
| Rhein (13) | Classes I/II HDACs | Hypoxia-treated or TGF-β1-stimulated primary human ventricular cardiac fibroblasts | ↓ Collagen contraction, ↑ Smad7 levels, ↑ Smad-specific E3 ubiquitin ligase SMURF2 | [38] |
| CG200745 (14) | Pan-HDAC | Col4a3−/− mice, a murine model of Alport syndrome | ↓ Kidney fibrosis, ↓ TGF-β-Smad signaling | [39] |
| TSA (15) | Pan-HDAC | Unilateral ureteral obstruction murine model | ↓ Interstitial macrophages, ↑ M2c macrophages, ↓ Myofibroblast activation, ↓ Fibrosis | [40] |
| Vorinostat (16) | Pan-HDAC | LX2 cells isolated from human hepatic stellate cells | ↓ Cell viability, ↓ Migration, ↓ Colony formation, ↓ Expression of Col1a1, Col3a1, α-SMA and TGF-β genes | [43] |
| LP340 (17) | Class I HDACs | Mouse models of liver fibrosis induced by CCl4 treatment or bile duct ligationImmortal human hepatic stellate cells | ↓ Liver injury, ↓ Inflammation, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ miR23a,↓ TGF-β/Smad signaling | [45] |
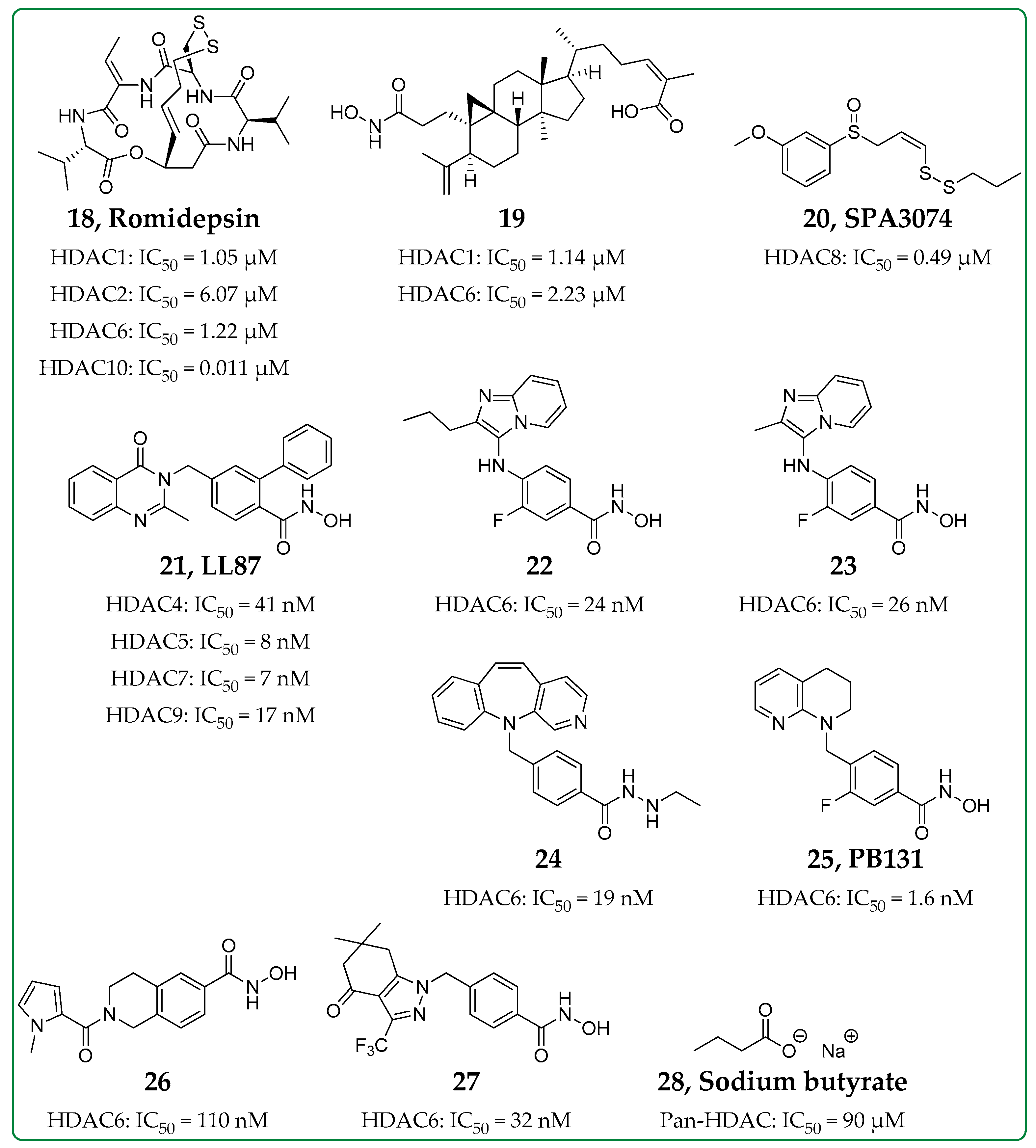
| Inhibitor | HDAC Inhibition | Biological Evaluation In Vitro or In Vivo | Anti-Inflammatory Activity | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 19 | Class I and Class II (not HDAC8) | In vitro in murine macrophage J774A.1 cells | ↓LDH, blocks NLRP3 inflammasome activation => ↓IL-1β and ↓caspase-1 | [60] |
| SPA3074 (20) | HDAC8 | In vivo colitis mouse model | ↑SOCS1 expression => ↓p-Akt and ↑ERK1/2, ↑p-IκBα, ↓IL-13 | [63] |
| LL87 (21) | Class IIa | In vitro in HMDMsIn vivo in rat CIA model | ↓IL-1α, ↓MCP-1, ↓GM-CSF, ↓IL-6↓p-Akt, ↓p-ERK1/2 | [64] |
| Compounds 22 and 23 | HDAC6 | In vitro in human THP-1 macrophages | ↑Acetylation of α-tubulin, ↓LPS-induced IL1β mRNA expression, ↓TNF | [70] |
| Compound 24 | HDAC6 | In vitro in murine macrophage J774A.1 cellsIn vivo endotoxic shock mouse model | ↓ATP/LPS-induced IL-1β release | [71] |
| PB131 (25) | HDAC6 | In vitro in mouse microglia BV2 cellsIn vivo neuroinflammation mouse model | ↓IL-10, ↓IFN-γ, ↓IL-1β, ↓IL-2, ↓IL-5, ↑Acetylation of α-tubulin | [72] |
| Compound 26 | HDAC6 | In vivo chronic respiratory infection mouse model | ↓IL-1α, ↓IL-1β, ↓IL-4, ↓IL-6, ↓IL-12, ↓IL-17A, ↓IFN-γ | [73] |
| Compound 27 | HDAC6 | In vitro in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma cells and in THP-1 cellsIn vivo in rat AIA model and in mouse CIA model | ↑Acetylation of tubulin, ↓TNF-α secretion | [74] |
| Sodium butyrate (28) | Pan-HDAC | In vivo asthmatic mouse model | ↓LDH, ↓GATA-3 => ↓IL-5, ↓HIF-1α, ↓VEGF-α, ↓p-PI3K, ↓p-Akt | [77,78,79] |
| In vitro in liver macrophages, BMDM and RAW264.7 cells | ↓TNF-α, ↓IL-6, ↓Inflammasome activation | |||
| In vivo atherosclerosis inflammation mouse model | ↓TNF-α, ↓IL-1β, ↓IL-6, ↓IL-7A, ↓IFN-γ, ↑IL-10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Theodoropoulou, M.A.; Mantzourani, C.; Kokotos, G. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121605
Theodoropoulou MA, Mantzourani C, Kokotos G. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules. 2024; 14(12):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121605
Chicago/Turabian StyleTheodoropoulou, Maria A., Christiana Mantzourani, and George Kokotos. 2024. "Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases" Biomolecules 14, no. 12: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121605
APA StyleTheodoropoulou, M. A., Mantzourani, C., & Kokotos, G. (2024). Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Novel Therapeutic Option Against Fibrotic and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules, 14(12), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14121605