IGF/mTORC1/S6 Signaling Is Potentiated and Prolonged by Acute Loading of Subtoxicological Manganese Ion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Western Blot
2.3. Cellular Fura-2 Manganese Uptake Assay (CFMEA)
3. Results
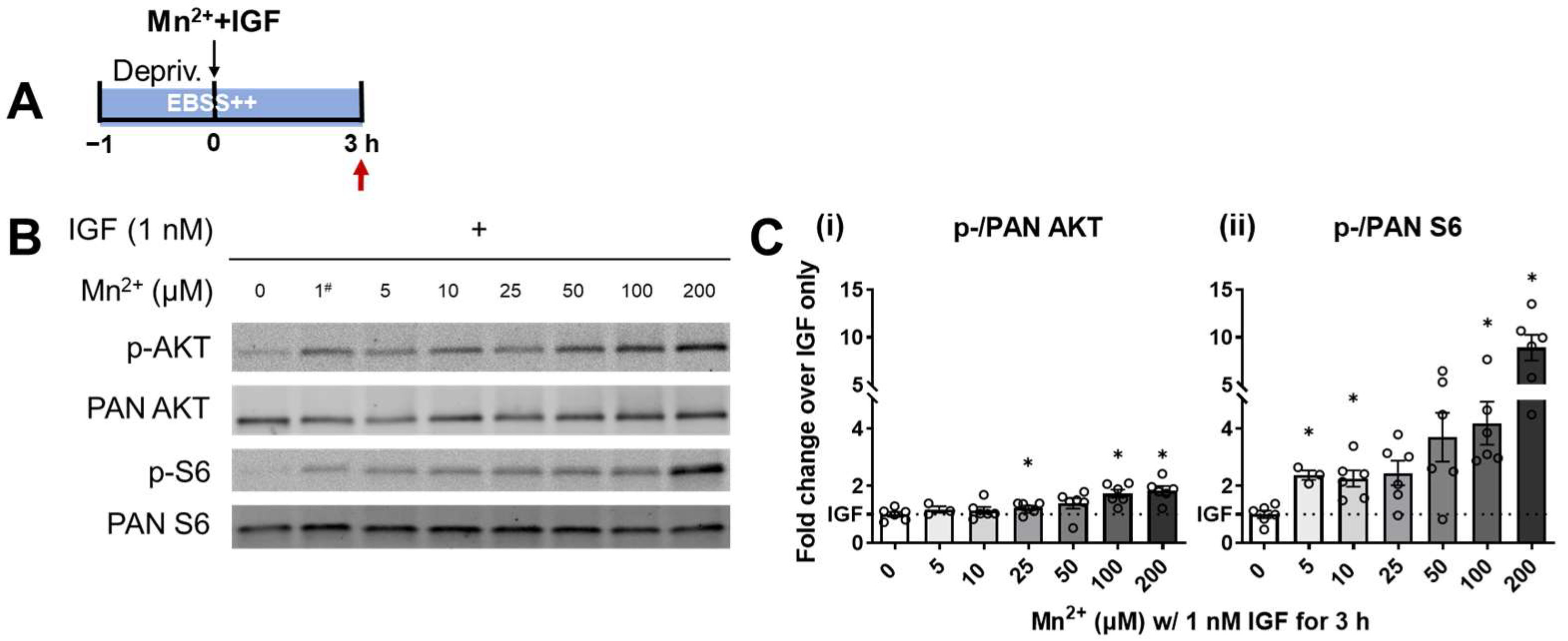
3.1. S6 Phosphorylation Displayed a Higher Sensitivity to Lower Levels of Mn2+ Exposure
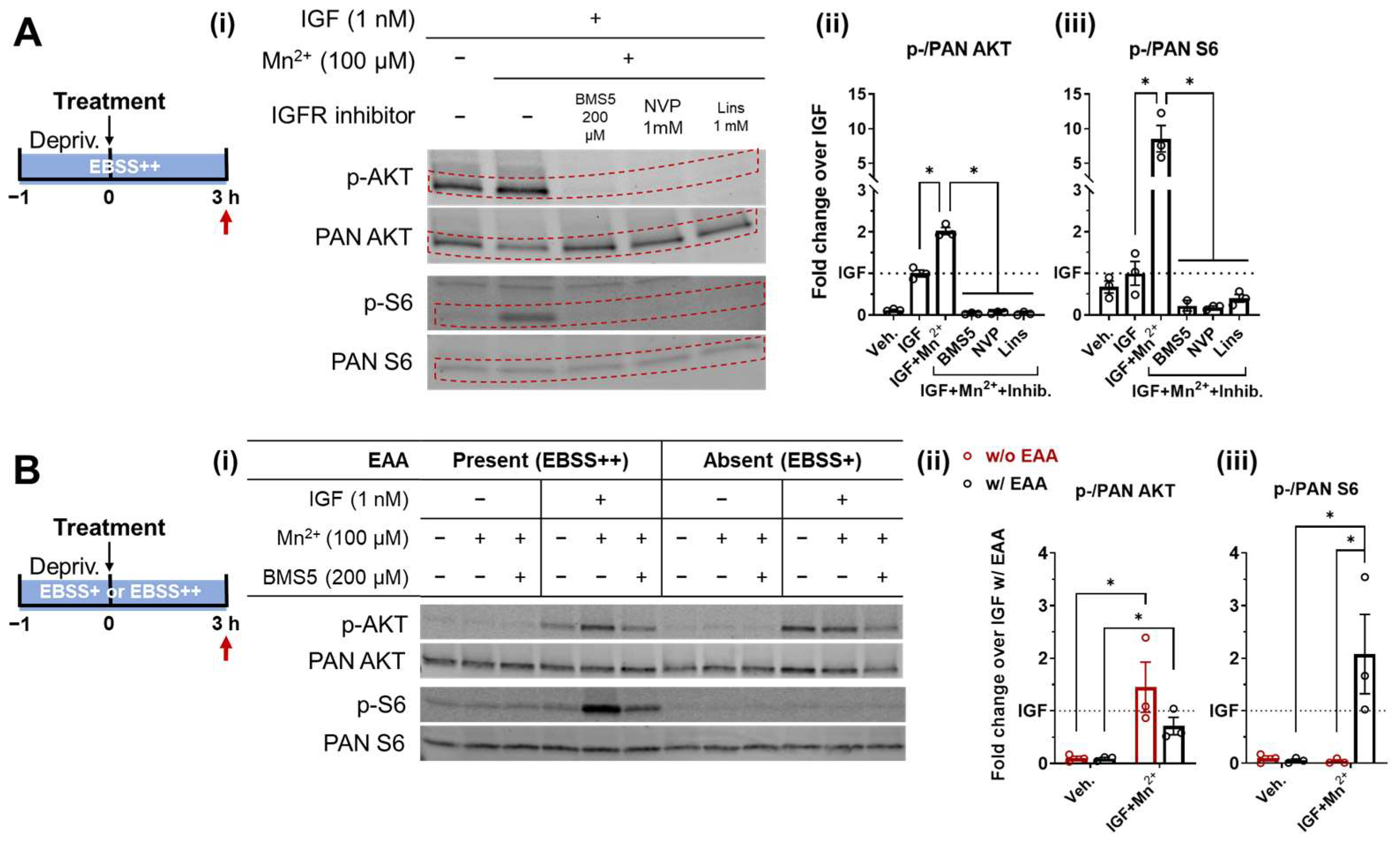
3.2. Essential Amino Acids Supplementation and IGF/Insulin Signaling Are Required for AKT and S6 Response to Low-Level Mn2+ Exposure
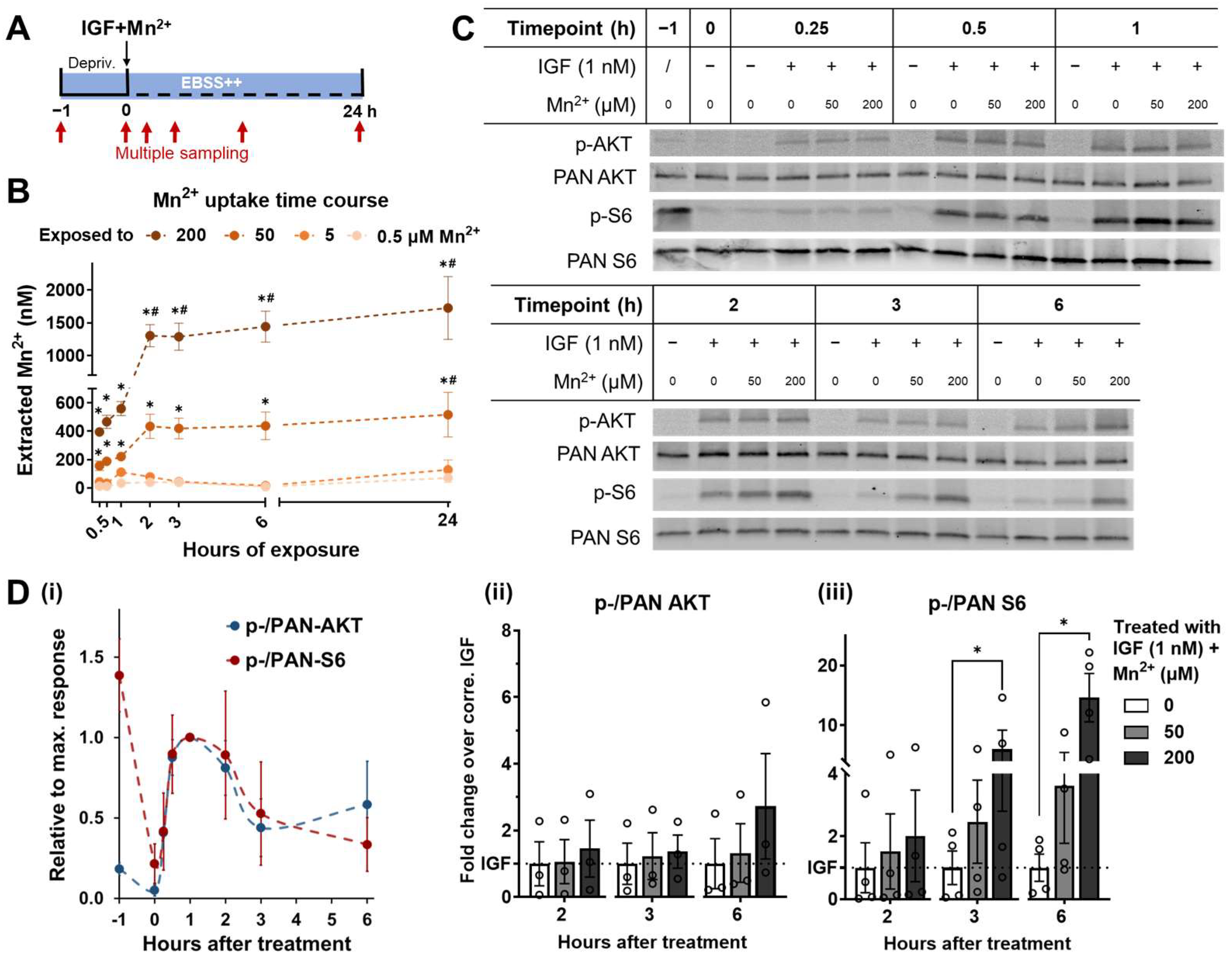
3.3. Mn2+ Exposure Prolongs AKT and S6 Responses to Physiological IGF Stimulation
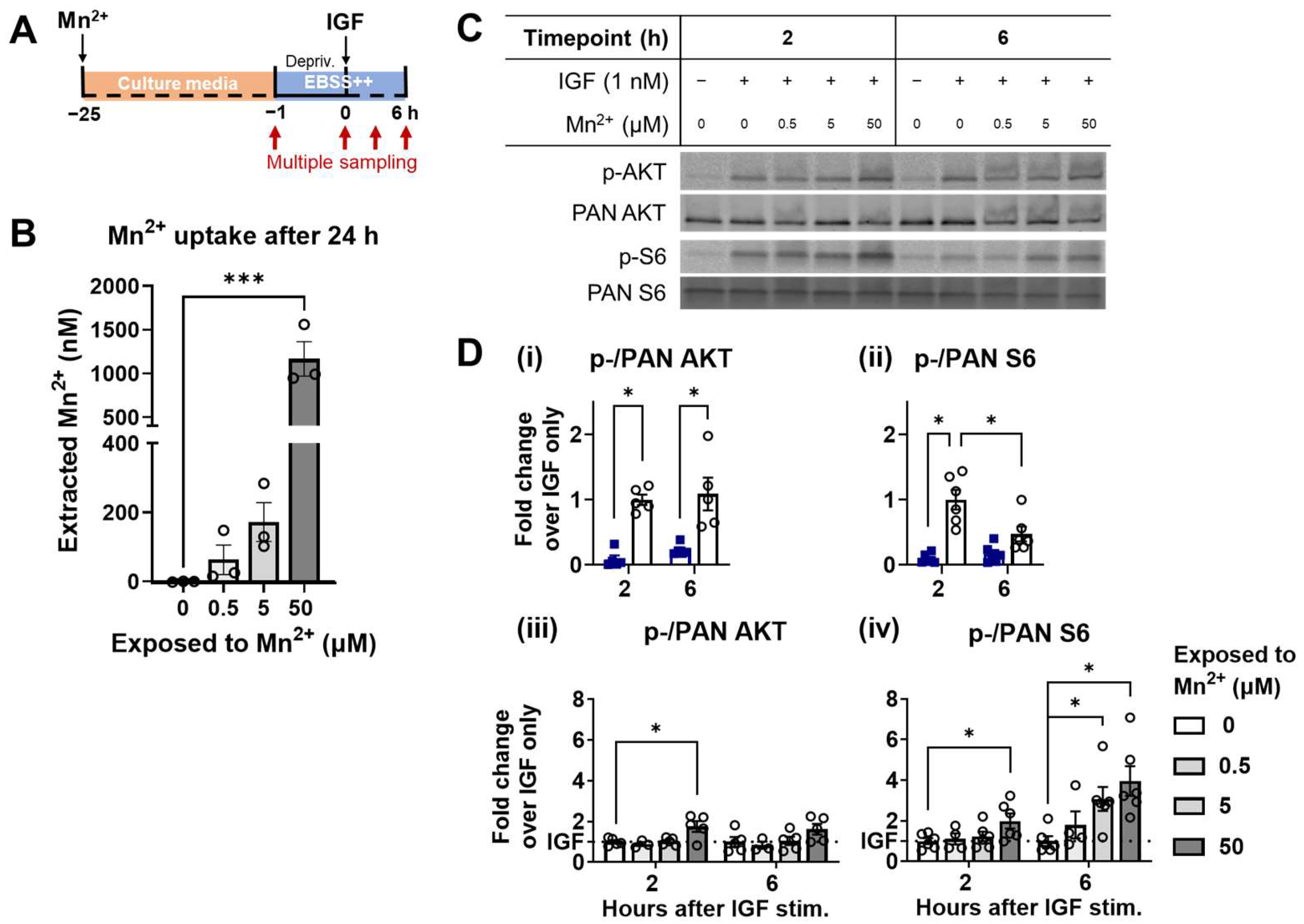
3.4. Higher Responsiveness of S6 Is Recapitulated under a Steady-State Increase of Intracellular Mn2+
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Klein, D.P.; Charles, A.M. Differences between Magnesium- and Manganese-Activated Pyruvate Kinase from Thiobacillus versutus (A2). Curr. Microbiol. 1989, 19, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korennykh, A.V.; Egea, P.F.; Korostelev, A.A.; Finer-Moore, J.; Stroud, R.M.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Walter, P. Cofactor-Mediated Conformational Control in the Bifunctional Kinase/RNase Ire1. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tari, L.W.; Matte, A.; Goldie, H.; Delbaere, L.T.J. Mg2+–Mn2+ Clusters in Enzyme-Catalyzed Phosphoryl-Transfer Reactions. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1997, 4, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovitt, B.; VanderPorten, E.C.; Sheng, Z.; Zhu, H.; Drummond, J.; Liu, Y. Differential Effects of Divalent Manganese and Magnesium on the Kinase Activity of Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2). Biochemistry 2010, 49, 3092–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.W.; Son, S.C.; Block, W.; Ye, R.; Khanna, K.K.; Wold, M.S.; Douglas, P.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Pelley, J.; Taya, Y.; et al. Purification and Characterization of ATM from Human Placenta: A Manganese-Dependent, Wortmannin-Sensitive Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7803–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, R.; Gaillard, H.; Zarzuela, L.; Péli-Gulli, M.-P.; Fernández-García, E.; Tomé, M.; García-Rodríguez, N.; Durán, R.V.; de Virgilio, C.; Wellinger, R.E. Manganese Is a Physiologically Relevant TORC1 Activator in Yeast and Mammals. eLife 2022, 11, e80497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidball, A.M.; Bryan, M.R.; Uhouse, M.A.; Kumar, K.K.; Aboud, A.A.; Feist, J.E.; Ess, K.C.; Neely, M.D.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. A Novel Manganese-Dependent ATM-P53 Signaling Pathway Is Selectively Impaired in Patient-Based Neuroprogenitor and Murine Striatal Models of Huntington’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 1929–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, P.M.; Lierhagen, S.; Flaten, T.P.; Syversen, T.; Vesterberg, O.; Nordberg, M. Manganese in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood Plasma of Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 237, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalke, B.; Berthele, A.; Mistriotis, P.; Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M.; Halbach, S. Manganese Species from Human Serum, Cerebrospinal Fluid Analyzed by Size Exclusion Chromatography-, Capillary Electrophoresis Coupled to Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2007, 21, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Mouri, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Nishiyama, K.; Fujii, N.; Yano, H. Study of Subacute Toxicity of Manganese Dioxide in Monkeys. Tokushima J. Exp. Med. 1975, 22, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Erikson, K.M.; Dorman, D.C.; Lash, L.H.; Aschner, M. Manganese Inhalation by Rhesus Monkeys Is Associated with Brain Regional Changes in Biomarkers of Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 97, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, E.B.; Bryan, M.R.; Morcillo, P.; Hardeman, K.N.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. Manganese-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction Is Not Detectable at Exposures Below the Acute Cytotoxic Threshold in Neuronal Cell Types. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 176, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, M.R.; Uhouse, M.A.; Nordham, K.D.; Joshi, P.; Rose, D.I.R.; O’Brien, M.T.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. Phosphatidylinositol 3 Kinase (PI3K) Modulates Manganese Homeostasis and Manganese-Induced Cell Signaling in a Murine Striatal Cell Line. Neurotoxicology 2018, 64, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, P.; Bodnya, C.; Ilieva, I.; Neely, M.D.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. Huntington’s Disease Associated Resistance to Mn Neurotoxicity Is Neurodevelopmental Stage and Neuronal Lineage Dependent. Neurotoxicology 2019, 75, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Chandler, J.D.; Liu, K.H.; Uppal, K.; Hao, L.; Hu, X.; Go, Y.-M.; Jones, D.P. Metabolomic Responses to Manganese Dose in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 169, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Hao, L.; Bijli, K.M.; Chandler, J.D.; Orr, M.; Hu, X.; Jones, D.P.; Go, Y.-M. From the Cover: Manganese Stimulates Mitochondrial H2O2 Production in SH-SY5Y Human Neuroblastoma Cells Over Physiologic as Well as Toxicologic Range. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 155, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Paoliello, M.M.B.; Mazilina, A.N.; Skalny, A.V.; Martins, A.C.; Voskresenskaya, O.N.; Aaseth, J.; Santamaria, A.; Notova, S.V.; Tsatsakis, A.; et al. Molecular Targets of Manganese-Induced Neurotoxicity: A Five-Year Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, K.; Li, X.-R.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Yan, D.-Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, B. Alpha-Synuclein Is Involved in Manganese-Induced Spatial Memory and Synaptic Plasticity Impairments via TrkB/Akt/Fyn-Mediated Phosphorylation of NMDA Receptors. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mythri, R.B.; Raghunath, N.R.; Narwade, S.C.; Pandareesh, M.D.R.; Sabitha, K.R.; Aiyaz, M.; Chand, B.; Sule, M.; Ghosh, K.; Kumar, S.; et al. Manganese- and 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinium-Induced Neurotoxicity Display Differences in Morphological, Electrophysiological and Genome-Wide Alterations: Implications for Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurochem. 2017, 143, 334–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamm, C.; Sabri, F.; Ceccatelli, S. Mitochondrial-Mediated Apoptosis in Neural Stem Cells Exposed to Manganese. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, M.R.; Nordham, K.D.; Rose, D.I.R.; Brien, M.T.O.; Joshi, P.; Foshage, A.M.; Gonçalves, F.M.; Nitin, R.; Uhouse, M.A.; Aschner, M. Manganese Acts upon Insulin/IGF Receptors to Phosphorylate AKT and Increase Glucose Uptake in Huntington’ s Disease Cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1570–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Ieguchi, K.; Davari, P.; Yamaji, S.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Cross-Talk between Integrin A6β4 and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor (IGF1R) through Direct A6β4 Binding to IGF1 and Subsequent A6β4-IGF1-IGF1R Ternary Complex Formation in Anchorage-Independent Conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 12491–12500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, R.A.; Green, D.A. Insulin Receptor Dephosphorylation in Permeabilized Adipocytes Is Inhibitable by Manganese and Independent of Receptor Kinase Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 162, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Nakashima, A.; Guo, L.; Tamanoi, F. Specific Activation of MTORC1 by Rheb G-Protein In Vitro Involves Enhanced Recruitment of Its Substrate Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12783–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Hiney, J.K.; Dees, W.L. Early Life Manganese Exposure Upregulates Tumor-Associated Genes in the Hypothalamus of Female Rats: Relationship to Manganese-Induced Precocious Puberty. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 136, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Xia, B.; Su, C.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Zou, Y.; Yang, X. PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway and Hsp70 Activate in Hippocampus of Rats with Chronic Manganese Sulfate Exposure. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 50, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye, G.F.; Li, D.; Kabobel, O.A.; Bowman, A.B. Cellular Fura-2 Manganese Extraction Assay (CFMEA). Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2011, 48, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.W.; Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M. Manganese Neurotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1012, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.B.; Kwakye, G.F.; Wegrzynowicz, M.; Li, D.; Aschner, M.; Erikson, K.M.; Bowman, A.B. Altered Manganese Homeostasis and Manganese Toxicity in a Huntington’s Disease Striatal Cell Model Are Not Explained by Defects in the Iron Transport System. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 117, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Peterson, T.R.; Shaul, Y.D.; Lindquist, R.A.; Thoreen, C.C.; Bar-Peled, L.; Sabatini, D.M. The Rag GTPases Bind Raptor and Mediate Amino Acid Signaling to MTORC1. Science 2008, 320, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Goraksha-Hicks, P.; Li, L.; Neufeld, T.P.; Guan, K.-L. Regulation of TORC1 by Rag GTPases in Nutrient Response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Melick, C.H.; Navlani, R.; Frank, A.R.; Jewell, J.L. Glutamine and Asparagine Activate MTORC1 Independently of Rag GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2890–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, T.; Amemiya, Y.; Sugiyama, R.; Maki, M.; Shibata, H. Amino Acid-Dependent Control of MTORC1 Signaling: A Variety of Regulatory Modes. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, A.D.; Gakes, T.; Hogervorst, J.M.A.; de Wit, G.M.J.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Jaspers, R.T. Mechanical Stimulation and IGF-1 Enhance MRNA Translation Rate in Osteoblasts Via Activation of the AKT-MTOR Pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Hiney, J.K.; Dees, W.L. Manganese-Stimulated Kisspeptin Is Mediated by the IGF-1/Akt/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway in the Prepubertal Female Rat. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, H.; Ding, Y.; Slepak, T.; Wu, W.; Sun, Y.; Martinez, Y.; Xu, X.-M.; Lemmon, V.P.; Bixby, J.L. The MTOR Substrate S6 Kinase 1 (S6K1) Is a Negative Regulator of Axon Regeneration and a Potential Drug Target for Central Nervous System Injury. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 7079–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, L.; Tang, S.; Shi, Q.; Wu, B.; Yang, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, X.; Ao, Q.; Meng, L.; et al. Regulation PP2Ac Methylation Ameliorating Autophagy Dysfunction Caused by Mn Is Associated with MTORC1/ULK1 Pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 156, 112441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, R.; Cai, T.; Aschner, M.; Zhao, F.; Yao, T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Z.; Luo, W.; Chen, J. The Role of Autophagy Dysregulation in Manganese-Induced Dopaminergic Neurodegeneration. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 24, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, S.; Wei, F.; Liang, G.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y. Pivotal Role of CAMP-PKA-CREB Signaling Pathway in Manganese-induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2019, 34, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.E.J.; Xie, J.; Gomez, E.; Herbert, T.P. Identification of CAMP-Dependent Kinase as a Third in Vivo Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase in Pancreatic β-Cells. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biever, A.; Valjent, E.; Puighermanal, E. Ribosomal Protein S6 Phosphorylation in the Nervous System: From Regulation to Function. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svenningsson, P.; Nishi, A.; Fisone, G.; Girault, J.-A.; Nairn, A.C.; Greengard, P. DARPP-32: An Integrator of Neurotransmission. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 269–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, M.; Kankipati, H.N.; Kimpe, M.; van Zeebroeck, G.; Zhang, Z.; Thevelein, J.M. The Nutrient Transceptor/PKA Pathway Functions Independently of TOR and Responds to Leucine and Gcn2 in a TOR-Independent Manner. FEMS Yeast Res. 2017, 17, fox048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Litwin, C.; Cheng, R.; Ma, J.-X.; Chen, Y. DARPP32, a Target of Hyperactive MTORC1 in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207489119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Delgado, D.; Puigdellívol, M.; Moreno, E.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.; Botta, J.; Gasperini, P.; Chiarlone, A.; Howell, L.A.; Scarselli, M.; Casadó, V.; et al. Modulation of Dopamine D1 Receptors via Histamine H3 Receptors Is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Huntington’s Disease. eLife 2020, 9, e51093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitman, J.; Barak, B.; Benyair, R.; Shenkman, M.; Ashery, U.; Hartl, F.U.; Lederkremer, G.Z. ER Stress-Induced EIF2-Alpha Phosphorylation Underlies Sensitivity of Striatal Neurons to Pathogenic Huntingtin. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, L.R.; Alton, G.R.; Richter, D.T.; Kath, J.C.; Lingardo, L.; Chapman, J.; Hwang, C.; Alessi, D.R. Characterization of PF-4708671, a Novel and Highly Specific Inhibitor of P70 Ribosomal S6 Kinase (S6K1). Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, G.G.; Abraham, R.T. Phosphorylation of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) at Ser-2448 IsMediated by P70S6 Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25485–25490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, V.C.; Markworth, J.F.; Cameron-Smith, D. Considerations on MTOR Regulation at Serine 2448: Implications for Muscle Metabolism Studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 2537–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Bowman, A.B.; Bryan, M.R.; Singh, R.; Aschner, M. Dysregulation of TFEB Contributes to Manganese-Induced Autophagic Failure and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Astrocytes. Autophagy 2020, 16, 1506–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, Y. 4E-BP1, a Multifactor Regulated Multifunctional Protein. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Yan, D.-Y.; Tan, X.; Liu, K.; Jing, M.-J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, B. Manganese Induces Autophagy Dysregulation: The Role of S-Nitrosylation in Regulating Autophagy Related Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norsted Gregory, E.; Codeluppi, S.; Gregory, J.A.; Steinauer, J.; Svensson, C.I. Mammalian Target of Rapamycin in Spinal Cord Neurons Mediates Hypersensitivity Induced by Peripheral Inflammation. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, E.J.; Nam, H.Y.; Park, J.; Chung, M.A.; Woo, H.A.; Kim, H.-J. PI3K-MTOR-S6K Signaling Mediates Neuronal Viability via Collapsin Response Mediator Protein-2 Expression. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Liimatta, M.B.; Bottum, O.L. Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I Regulates IGF-Binding Protein-5 Gene Expression through the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Protein Kinase B/Akt, and P70 S6 Kinase Signaling Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37147–37153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.M.; Tucker, B.A.; Rahimtula, M.; Mearow, K.M. The Synergistic Effects of NGF and IGF-1 on Neurite Growth in Adult Sensory Neurons: Convergence on the PI 3-Kinase Signaling Pathway. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenal, J.; Pierre, K.; Pellerin, L. Insulin and IGF-1 Enhance the Expression of the Neuronal Monocarboxylate Transporter MCT2 by Translational Activation via Stimulation of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Akt-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Miao, L.; Liang, F.; Huang, H.; Teng, X.; Li, S.; Nuriddinov, J.; Selzer, M.E.; Hu, Y. The MTORC1 Effectors S6K1 and 4E-BP Play Different Roles in CNS Axon Regeneration. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, V.; Lu, Y.; Steinhilb, M.L.; Oldham, S.; Shulman, J.M.; Feany, M.B. TOR-Mediated Cell-Cycle Activation Causes Neurodegeneration in a Drosophila Tauopathy Model. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Du, W.; Wang, W.; Luo, L.; Huang, M.; Wang, H.; Lin, R.; Li, Z.; Shi, H.; Yuan, T.; et al. Persistent Rheb-Induced MTORC1 Activation in Spinal Cord Neurons Induces Hypersensitivity in Neuropathic Pain. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Illades, D.; Chen, P.; Zogzas, C.E.; Hutchens, S.; Mercado, J.M.; Swaim, C.D.; Morrisett, R.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S. SLC30A10 Is a Cell Surface-Localized Manganese Efflux Transporter, and Parkinsonism-Causing Mutations Block Its Intracellular Trafficking and Efflux Activity. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14079–14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horning, K.J.; Caito, S.W.; Tipps, K.G.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese Is Essential for Neuronal Health. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2015, 35, 71–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, C.; Kiely, A.P.; Coakley, M.F.; Manning, S.; Long-Smith, C.M. Insulin and IGF-1 Signalling: Longevity, Protein Homoeostasis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccamo, A.; de Pinto, V.; Messina, A.; Branca, C.; Oddo, S. Genetic Reduction of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Ameliorates Alzheimer’s Disease-Like Cognitive and Pathological Deficits by Restoring Hippocampal Gene Expression Signature. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 7988–7998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Learman, L.N.; Na, C.-H.; Renuse, S.; Chen, K.T.; Chen, P.Y.; Lee, G.-H.; Xiao, B.; Resnick, S.M.; Troncoso, J.C.; et al. Persistently Elevated MTOR Complex 1-S6 Kinase 1 Disrupts DARPP-32–Dependent D1 Dopamine Receptor Signaling and Behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 1058–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M. Brain Insulin Resistance and Deficiency as Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimers Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2012, 9, 35–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrling, J.; Laberge, R.-M. Age-Related Neurodegeneration Prevention Through MTOR Inhibition: Potential Mechanisms and Remaining Questions. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, C.; Iyaswamy, A.; Krishnamoorthi, S.; Sreenivasmurthy, S.G.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Tong, B.C.-K.; Song, J.; Lu, J.; et al. Balancing MTOR Signaling and Autophagy in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hei, C.; Liu, P.; Song, Y.; Thomas, T.; Tshimanga, S.; Wang, F.; Niu, J.; Sun, T.; Li, P.A. Inhibition of MTOR Pathway by Rapamycin Reduces Brain Damage in Rats Subjected to Transient Forebrain Ischemia. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Balachandran, R.C.; Aschner, M.; Bowman, A.B. IGF/mTORC1/S6 Signaling Is Potentiated and Prolonged by Acute Loading of Subtoxicological Manganese Ion. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081229
Tang X, Balachandran RC, Aschner M, Bowman AB. IGF/mTORC1/S6 Signaling Is Potentiated and Prolonged by Acute Loading of Subtoxicological Manganese Ion. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(8):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081229
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xueqi, Rekha C. Balachandran, Michael Aschner, and Aaron B. Bowman. 2023. "IGF/mTORC1/S6 Signaling Is Potentiated and Prolonged by Acute Loading of Subtoxicological Manganese Ion" Biomolecules 13, no. 8: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081229
APA StyleTang, X., Balachandran, R. C., Aschner, M., & Bowman, A. B. (2023). IGF/mTORC1/S6 Signaling Is Potentiated and Prolonged by Acute Loading of Subtoxicological Manganese Ion. Biomolecules, 13(8), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13081229






