Obesity-Linked PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation Promotes Beneficial Effects on the Liver, despite Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Generation of PPARy S273A Knockin Mice and Genotyping
2.2. Animals
2.3. Diets and Experimental Design
2.4. Insulin Tolerance Test (ITT) and Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
2.5. Plasma Biochemical Analysis
2.6. Liver Histology
2.7. eWAT Histology
2.8. Hepatic Triglyceride Content Quantification
2.9. Hepatic Glycogen Measurement
2.10. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
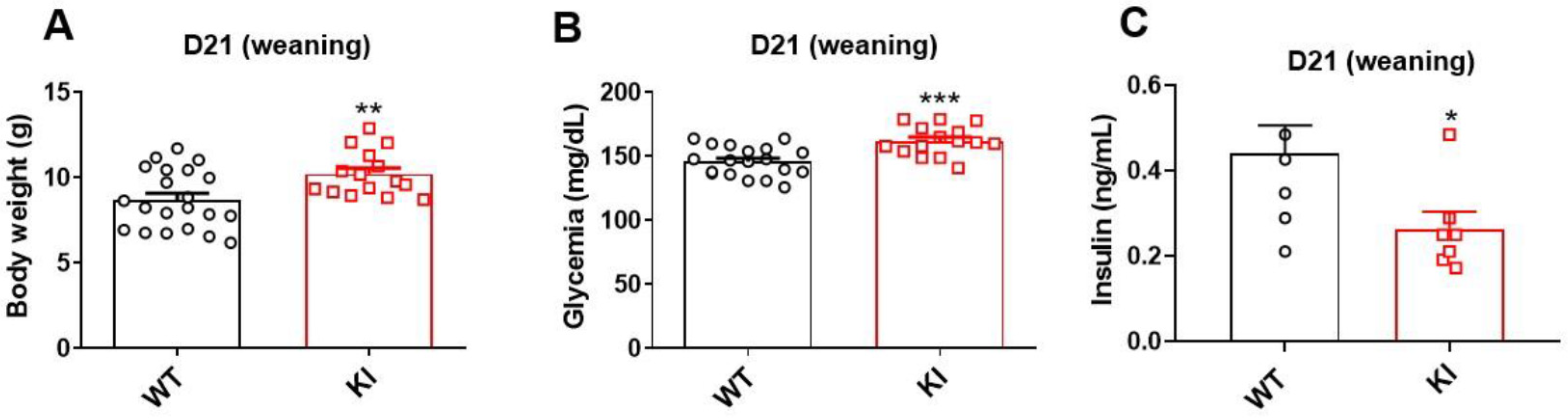
3.1. Knockin Lineage Had Higher Body Weight, Hyperglycemia, and Low Insulin Levels at Weaning
3.2. 8 Weeks of MNT Diet Increased Food Intake, Altered Plasma Metabolites, and Promoted Liver Modification
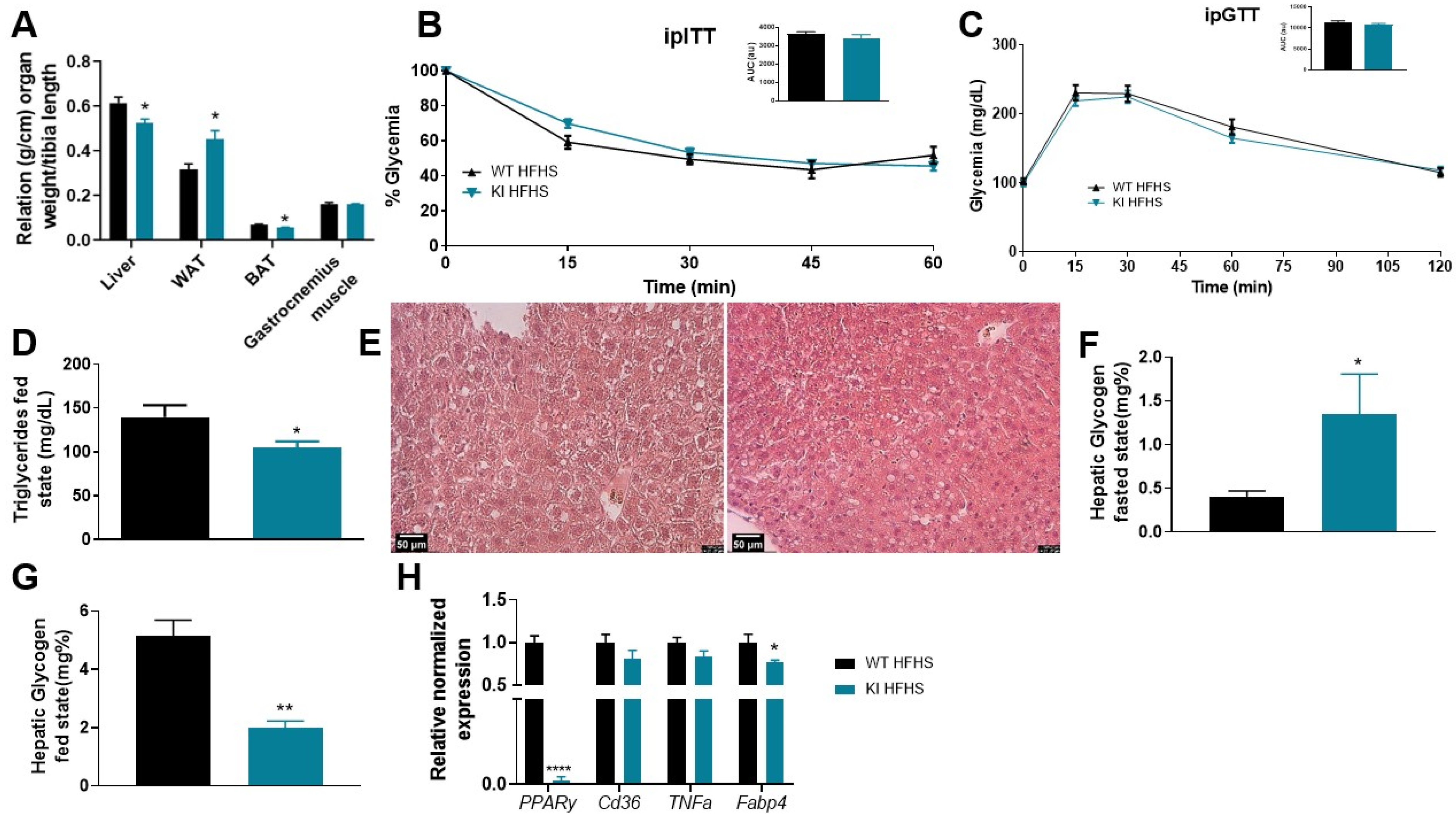
3.3. 8 Weeks of HFHS Increased WAT, Promotes Liver Damage, but Was Not Sufficient to Promote Insulin Resistance and Glucose Intolerance
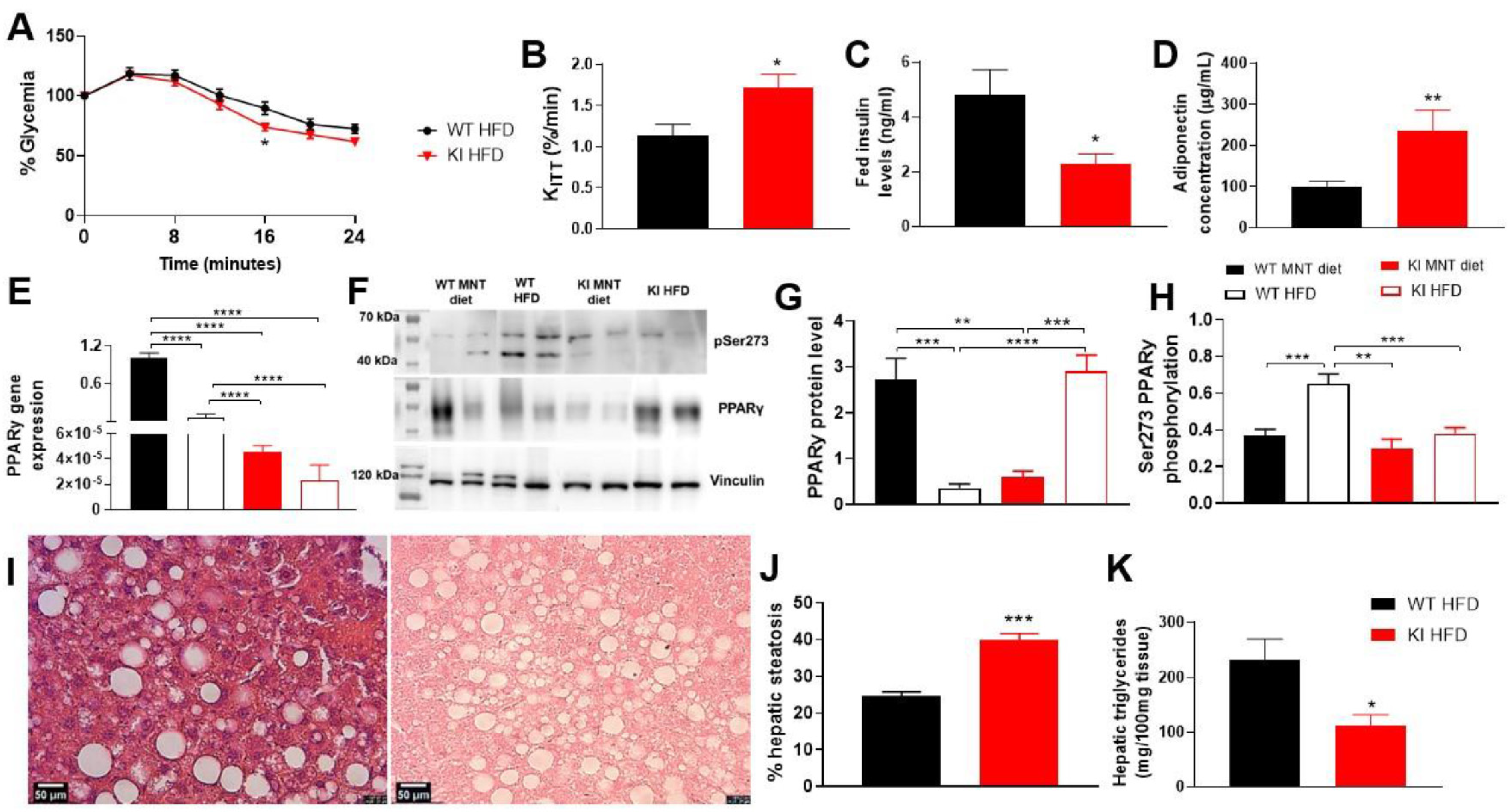
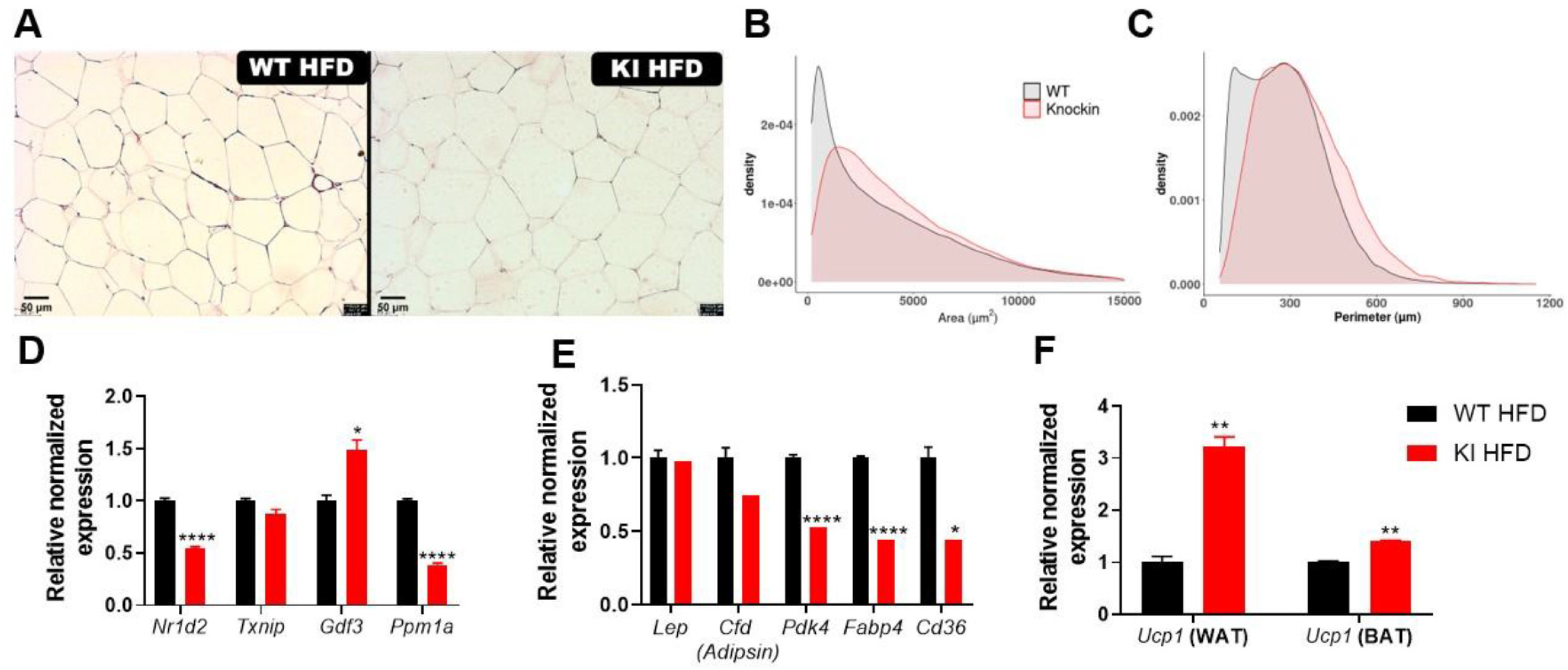
3.4. 16 Weeks of HFD Promoted Less Weight Gain, Insulin Sensitivity, Changes in PPARγ Expression, Liver Injury, and Adipocytes Hypertrophy in KI Animals
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unnikrishnan, R.; Pradeepa, R.; Joshi, S.R.; Mohan, V. Type 2 Diabetes: Demystifying the Global Epidemic. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, V.S.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Global obesity: Trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 9, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Vantyghem, M.-C.; Schoonjans, K.; Pattou, F. Thiazolidinediones in Type 2 Diabetes. Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Gamma (PPARgamma); Annales d’Endocrinologie: Paris, France, 2002; pp. 511–523. [Google Scholar]
- Soccio, R.E.; Chen, E.R.; Lazar, M.A. Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Willson, T.M.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tontonoz, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Fat and beyond: The diverse biology of PPARγ. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 289–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, R.M.; Singh, P.P.; Nesto, R.W. Congestive heart failure and cardiovascular death in patients with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes given thiazolidinediones: A meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Lancet 2007, 370, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesto, R.W.; Bell, D.; Bonow, R.O.; Fonseca, V.; Grundy, S.M.; Horton, E.S.; Le Winter, M.; Porte, D.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Smith, S.J.C. Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: A consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Circulation 2003, 108, 2941–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, A.; Jensen, M.D.; McCann, F.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Joyner, M.J.; Rizza, R.A. Effects of pioglitazone versus glipizide on body fat distribution, body water content, and hemodynamics in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Banks, A.S.; Estall, J.L.; Kajimura, S.; Bostrom, P.; Laznik, D.; Ruas, J.L.; Chalmers, M.J.; Kamenecka, T.M.; Bluher, M. Obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARγ by cdk5 is a direct target of the anti-diabetic PPARγ ligands. Nature 2010, 466, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, H.R.; Guerra, J.; Cagliari, R.; Batista, F.; Le Maire, A.; Oliveira, P.; Figueira, A. Exploring the mechanism of PPARγ phosphorylation mediated by CDK5. J. Struct. Biol. 2019, 207, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.S.; de Lima, C.L.; Royer, C.; Silva, J.B.; Oliveira, F.C.B.; Christ, C.G.; Pereira, S.A.; Bao, S.N.; Lima, M.C.A.; Pitta, M.G.R.; et al. GQ-16, a TZD-derived partial PPARγ agonist, induces the expression of thermogenesis-related genes in brown fat and visceral white fat and decreases visceral adiposity in obese and hyperglycemic mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.C.; de Oliveira, E.M.; Turato, W.M.; Trossini, G.H.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Pitta, M.G.; Pitta, I.R.; de las Heras, B.; Boscá, L.; Rudnicki, M.; et al. GQ-11: A new PPAR agonist improves obesity-induced metabolic alterations in LDLr−/− mice. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terra, M.; García-Arévalo, M.; Avelino, T.; Degaki, K.; Malospirito, C.; de Carvalho, M.; Torres, F.; Saito, Â.; Figueira, A.J.M.O. AM-879, a PPARy non-agonist and Ser273 phosphorylation blocker, promotes insulin sensitivity without adverse effects in mice. Metab. Open 2022, 17, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, G.; Petersen, J.; Ek, M.; Rae, R.; Johansson, C.; Jianming, L.; Prokoph, N.; Bergström, F.; Bamberg, K.; Giordanetto, F.; et al. Discovery by Virtual Screening of an Inhibitor of CDK5-Mediated PPARγ Phosphorylation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, R.; Capelli, D.; Yamamoto, K.; Awaishima, H.; Nishikata, K.; Barendregt, A.; Heck, A.J.R.; Loiodice, F.; Altieri, F.; Paiardini, A.; et al. Insights into PPARγ Phosphorylation and Its Inhibition Mechanism. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4811–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.M.G.; Batista, F.A.H.; Tittanegro, T.H.; De Oliveira, A.G.; Le Maire, A.; Torres, F.R.; Filho, H.V.R.; Silveira, L.R.; Figueira, A.C.M. PPARγ S273 phosphorylation modifies the dynamics of coregulator proteins recruitment. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 561256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Ramachandran, D.; Roh, H.C.; DiSpirito, J.R.; Belchior, T.; Zushin, P.-J.H.; Palmer, C.; Hong, S.; Mina, A.I.; Liu, B.; et al. Obesity-Linked PPARγ S273 Phosphorylation Promotes Insulin Resistance through Growth Differentiation Factor 3. bioRxiv 2020, 32, 665–675.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.D.; Scott, D.A.; Weinstein, J.A.; Ran, F.A.; Konermann, S.; Agarwala, V.; Li, Y.; Fine, E.J.; Wu, X.; Shalem, O.; et al. DNA targeting specificity of RNA-guided Cas9 nucleases. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeussler, M.; Schönig, K.; Eckert, H.; Eschstruth, A.; Mianné, J.; Renaud, J.-B.; Schneider-Maunoury, S.; Shkumatava, A.; Teboul, L.; Kent, J.; et al. Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Ray, G.; DeWitt, M.A.; Curie, G.L.; Corn, J.E. Enhancing homology-directed genome editing by catalytically active and inactive CRISPR-Cas9 using asymmetric donor DNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Hanchuk, T.D.; Colleti, C.; Saito, Â.; Mendes, M.C.S.; Carvalheira, J.B.C.; Vassallo, J.; Kobarg, J.J.O. Intracellular hyaluronic acid-binding protein 4 (HABP4): A candidate tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, S.; Phillips, D.; Vines, S.; Clark, P.; Hales, C. Reproducibility of the short insulin tolerance test. Diabet. Med. 1993, 10, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojibi, N.; Rasouli, M. Comparison of methods to assay liver glycogen fractions: The effects of starvation. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2017, 11, BC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokri-Afra, H.; Ostovar-Ravari, A.; Rasouli, M. Improvement of the classical assay method for liver glycogen fractions: ASG is the main and metabolic active fraction. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4328–4336. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikano, S. Hypothesis testing in the bayesian framework. Swiss Politi-Sci. Rev. 2019, 25, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, D.S.; Williams, D.R. Bayesian alternatives for common null-hypothesis significance tests in psychiatry: A non-technical guide using JASP. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedeskov, C.J. Mechanism of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Physiol. Rev. 1980, 60, 442–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.-M.; Obici, S.; Dong, H.H.; Haas, M.; Lou, D.; Kim, D.H.; Liu, M.; D’Alessio, D.; Woods, S.C.; Tso, P. Impaired insulin secretion and enhanced insulin sensitivity in cholecystokinin-deficient mice. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyot, M.-L.; Pepin, E.; Lamontagne, J.; Latour, M.G.; Zarrouki, B.; Lussier, R.; Pineda, M.; Jetton, T.L.; Madiraju, S.M.; Joly, E.; et al. β-cell failure in diet-induced obese mice stratified according to body weight gain: Secretory dysfunction and altered islet lipid metabolism without steatosis or reduced β-cell mass. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frkic, R.L.; Richter, K.; Bruning, J.B. The therapeutic potential of inhibiting PPARγ phosphorylation to treat type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, M.; Sy, M.; Pavlovich, K.; Leibel, R.L.; Hirsch, J. Leptin reverses weight loss–induced changes in regional neural activity responses to visual food stimuli. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.F.; Carpentier, A.C.; Pereira, S.; Hahn, M.; Giacca, A. Direct and indirect control of hepatic glucose production by insulin. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, P.; Thoppil, D. Hypoglycemia; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.A.; Ataide, T.d.R.; Oliveira, S.L.d.; Sant’Ana, A.E.; Cabral Júnior, C.R.; Balwani, M.d.C.; de Oliveira, F.G.; Santos, M.C. Metabologia, Efeito hepatoprotetor do consumo crônico de dieptanoína e trieptanoína contra a esteatose em ratos. Arq. Bras. De Endocrinol. Metabol. 2008, 52, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.H.; Moreira, C.C.L.; Mario, E.G.; de Souza Cordeiro, L.M.; Avelar, G.F.; Botion, L.M.; Chaves, V.E. Differential modulation of cytosolic lipases activities in liver and adipose tissue by high-carbohydrate diets. Endocrine 2016, 53, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Amaral, M.S.; Oliveira, S.L.; Barbosa, J.P.; Cabral, C.R., Jr.; Melo, I.S.; Bueno, N.B.; Freitas, J.D.; Sant’ana, A.G.; Ataíde, T.R. Dietary intake of AIN-93 standard diet induces fatty liver with altered hepatic fatty acid profile in Wistar rats. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, L.; Mittenbühler, M.J.; Vesting, A.J.; Ostermann, A.L.; Wunderlich, C.M.; Wunderlich, F.T.J.C. Obesity-induced TNFα and IL-6 signaling: The missing link between obesity and inflammation—Driven liver and colorectal cancers. Cancers 2018, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Fan, J.; Huang, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Hepatoprotective effects exerted by Poria Cocos polysaccharides against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.T.; Huang, J.S.; Gao, D.D.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, H. Combined treatment with FABP4 inhibitor ameliorates rosiglitazone-induced liver steatosis in obese diabetic db/db mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 129, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Zhang, C.-L.; Gao, Y.-C.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, C.-P.; Huangfu, J.; Xiao, R. Gene expression and correlation of Pten and Fabp4 in liver, muscle, and adipose tissues of type 2 diabetes rats. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Escoté, X.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Garrido-Sanchez, L.; Miranda, M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Pérez-Pérez, R.; Peral, B.; Cardona, F.; Fernández-Real, J.M.; et al. FABP4 dynamics in obesity: Discrepancies in adipose tissue and liver expression regarding circulating plasma levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rada, P.; González-Rodríguez, Á.; García-Monzón, C.; Valverde, Á.M. Understanding lipotoxicity in NAFLD pathogenesis: Is CD36 a key driver? Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, F.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.J.C. MicroRNA-29a suppresses CD36 to ameliorate high fat diet-induced steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in mice. Cells 2019, 8, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, H.N.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Hernandez-Ono, A. Regulation of plasma triglycerides in insulin resistance and diabetes. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Lima, F.; Monte, T.L.R.G.; de Morais Nascimento, F.A.; Gregório, B.M. Short Exposure to a High-Sucrose Diet and the First ‘Hit’ of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice. Cells Tissues Organs 2016, 201, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes-Santos, C.; Carneiro, R.E.; de Souza Mendonca, L.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. Pan-PPAR agonist beneficial effects in overweight mice fed a high-fat high-sucrose diet. Nutrition 2009, 25, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, C. Ameliorative effect of vanadyl (IV)–ascorbate complex on high-fat high-sucrose diet-induced hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress in mice. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 32, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.; Engles, J.M.; Huso, D.L.; Ishimori, T.; Wahl, R.L. Comparison of uptake of multiple clinical radiotracers into brown adipose tissue under cold-stimulated and nonstimulated conditions. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhao, M.; Wang, M.; Yan, W.; Liu, Y.; Ren, S.; Lu, J.; Wang, B.; Chen, L. Effects of canagliflozin on weight loss in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeuchi, M.; Koyama, T.; Takahashi, J.; Yazawa, K. Effects of astaxanthin in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisler, C.E.; Hepler, C.; Higgins, M.R.; Renquist, B.J. Hepatic adaptations to maintain metabolic homeostasis in response to fasting and refeeding in mice. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavarow, Z.A.; Kang, H.-R.; Waskowicz, L.R.; Bay, B.-H.; Young, S.P.; Yen, P.M.; Koeberl, D.D. Fenofibrate rapidly decreases hepatic lipid and glycogen storage in neonatal mice with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajri, T.; Zaiou, M.; Fungwe, T.V.; Ouguerram, K.; Besong, S.J.C. Epigenetic Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Mediates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwamborn, R.A.J.; Slieker, R.C.; Mulder, P.C.A.; Zoetemelk, I.; Verschuren, L.; Suchiman, H.E.D.; Toet, K.H.; Droog, S.; Slagboom, P.E.; Kooistra, T.; et al. Prolonged high-fat diet induces gradual and fat depot-specific DNA methylation changes in adult mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Qi, C.; Wang, T. Maternal and post-weaning high-fat, high-sucrose diet modulates glucose homeostasis and hypothalamic POMC promoter methylation in mouse offspring. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edillor, C.R.; Parks, B.W.; Mehrabian, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Pellegrini, M. DNA methylation changes more slowly than physiological states in response to weight loss in genetically diverse mouse strains. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.A.; Sommerfeld-Sager, J.M.; Meng, C.-X.; Nagel, S.C.; Shioda, T.; Vom Saal, F.S. Reduced body weight at weaning followed by increased post-weaning growth rate interacts with part-per-trillion fetal serum concentrations of bisphenol A (BPA) to impair glucose tolerance in male mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiki, K.; Kano, F.; Shiota, K.; Murata, M. Expression of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ gene is repressed by DNA methylation in visceral adipose tissue of mouse models of diabetes. BMC Biol. 2009, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yu, J.; Li, G.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W.; Jiang, H.; Hong, Z.J.A. MiR-27a promotes insulin resistance and mediates glucose metabolism by targeting PPAR-γ-mediated PI3K/AKT signaling. Aging 2019, 11, 7510–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.L.; Riching, K.M.; Urh, M. Monitoring and deciphering protein degradation pathways inside cells. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2019, 31, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clague, M.J.; Urbe, S. Ubiquitin: Same Molecule, Different Degradation Pathways. Cell 2010, 143, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, N.B.; Dias, M.M.G.; Terra, M.F.; de Oliveira, V.M.; García-Arévalo, M.; Avelino, T.M.; Torres, F.R.; Batista, F.A.H.; Figueira, A.C.M. PPAR Modulation Through Posttranslational Modification Control. In Nuclear Receptors: The Art and Science of Modulator Design and Discovery; Badr, M.Z., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 537–611. [Google Scholar]
- Kilroy, G.; Kirk-Ballard, H.; Carter, L.E.; Floyd, Z.E. The ubiquitin ligase Siah2 regulates PPARγ activity in adipocytes. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.; Lee, E.; Jang, W.; Seo, J.; Shin, S.; Hwang, K.; Song, J. Suppression of PPARγ through MKRN1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation prevents adipocyte differentiation. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 21, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.M.; Vestergaard, E.T.; Jessen, N.; Kolind-Thomsen, P.; Nellemann, B.; Nielsen, T.S.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Møller, N.; Sharma, R.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Growth hormone acts along the PPARγ-FSP27 axis to stimulate lipolysis in human adipocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 316, E34–E42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwanhäusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khim, K.W.; Choi, S.S.; Jang, H.-J.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, E.; Hyun, J.-M.; Eom, H.-J.; Yoon, S.; Choi, J.-W.; Park, T.-E.; et al. PPM1A controls diabetic gene programming through directly dephosphorylating PPARγ at Ser273. Cells 2020, 9, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, T.; Mounier, R.; Patsalos, A.; Gogolák, P.; Peloquin, M.; Horvath, A.; Pap, A.; Daniel, B.; Nagy, G.; Pintye, E.; et al. Macrophage PPARγ, a lipid activated transcription factor controls the growth factor GDF3 and skeletal muscle regeneration. Immunity 2016, 45, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Dong, X.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Sun, H.; Kim, D.-H.; Kemper, J.K.; Chen, L.-F. Brd4 modulates diet-induced obesity via PPARγ-dependent Gdf3 expression in adipose tissue macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 6, e143379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mu, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Wolfe, V.; Cui, S.-N.; Wang, X.; Peng, T.; Zingarelli, B.; et al. Administration of GDF3 Into Septic Mice Improves Survival via Enhancing LXRα-Mediated Macrophage Phagocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Feng, T.; Zhu, N.; Liu, P.; Han, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.J.S. Identification of a novel selective agonist of PPARγ with no promotion of adipogenesis and less inhibition of osteoblastogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadoudal, T.; Distel, E.; Durant, S.; Fouque, F.; Blouin, J.-M.; Collinet, M.; Bortoli, S.; Forest, C.; Benelli, C.J.D. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4: Regulation by thiazolidinediones and implication in glyceroneogenesis in adipose tissue. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2272–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Terra, M.F.; García-Arévalo, M.; Avelino, T.M.; Degaki, K.Y.; de Carvalho, M.; Torres, F.R.; Saito, A.; Figueira, A.C.M. Obesity-Linked PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation Promotes Beneficial Effects on the Liver, despite Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040632
Terra MF, García-Arévalo M, Avelino TM, Degaki KY, de Carvalho M, Torres FR, Saito A, Figueira ACM. Obesity-Linked PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation Promotes Beneficial Effects on the Liver, despite Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(4):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040632
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerra, Maiara Ferreira, Marta García-Arévalo, Thayná Mendonça Avelino, Karina Y. Degaki, Murilo de Carvalho, Felipe Rafael Torres, Angela Saito, and Ana Carolina Migliorini Figueira. 2023. "Obesity-Linked PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation Promotes Beneficial Effects on the Liver, despite Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Mice" Biomolecules 13, no. 4: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040632
APA StyleTerra, M. F., García-Arévalo, M., Avelino, T. M., Degaki, K. Y., de Carvalho, M., Torres, F. R., Saito, A., & Figueira, A. C. M. (2023). Obesity-Linked PPARγ Ser273 Phosphorylation Promotes Beneficial Effects on the Liver, despite Reduced Insulin Sensitivity in Mice. Biomolecules, 13(4), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13040632





