Identification of Inhibitors of Tubulin Polymerization Using a CRISPR-Edited Cell Line with Endogenous Fluorescent Tagging of β-Tubulin and Histone H1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line Development
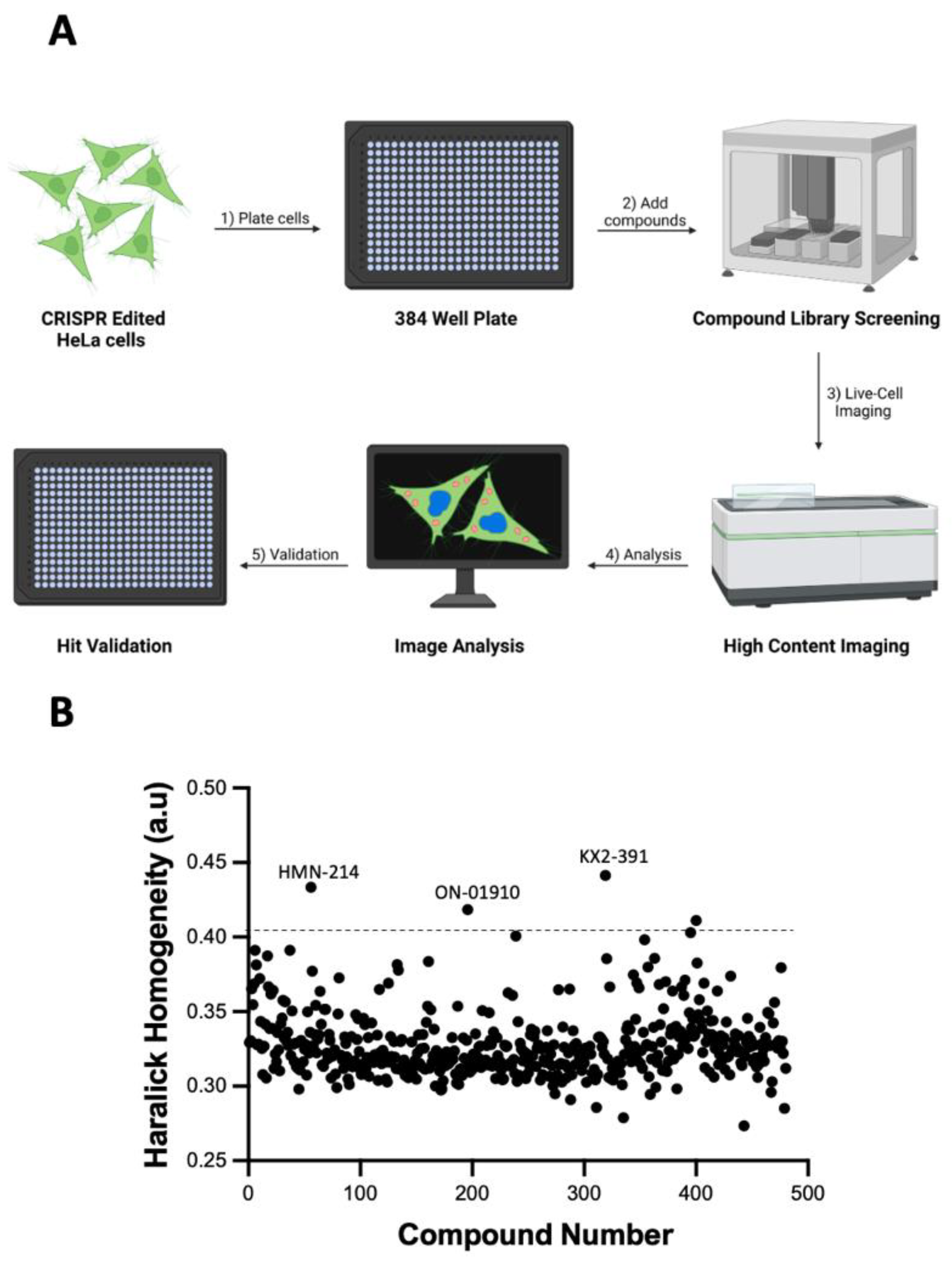
2.2. High-Content Imaging, Compound Screening and Time-Lapsed Microscopy
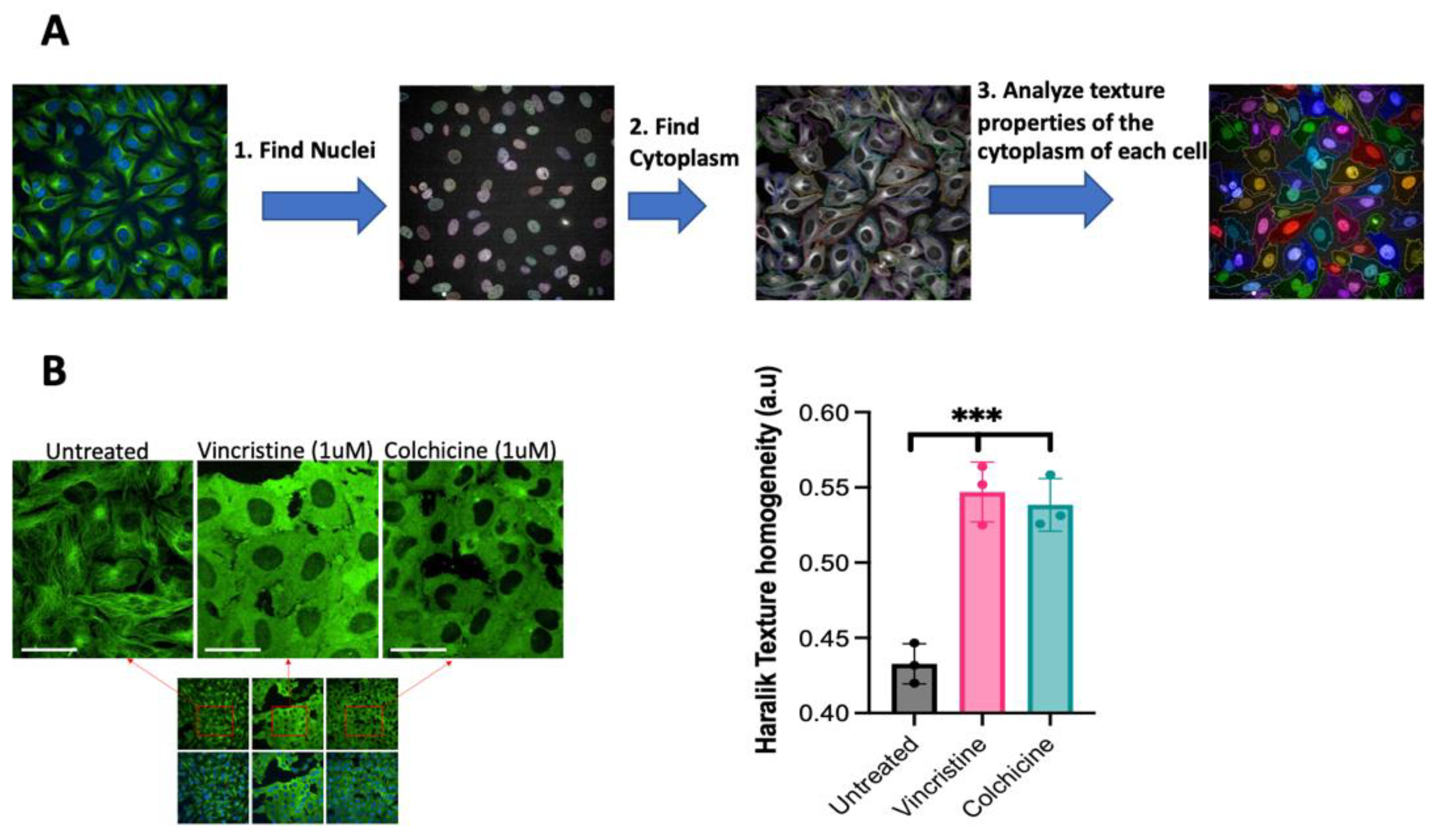
2.3. Image Data Analysis
2.4. Molecular Docking
2.5. Reproducibility and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detecting the Inhibition of Tubulin Polymerization in Live Cells without Using Antibodies or Chemical Staining
3.2. Identifying Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors in a Library of Kinase Inhibitors
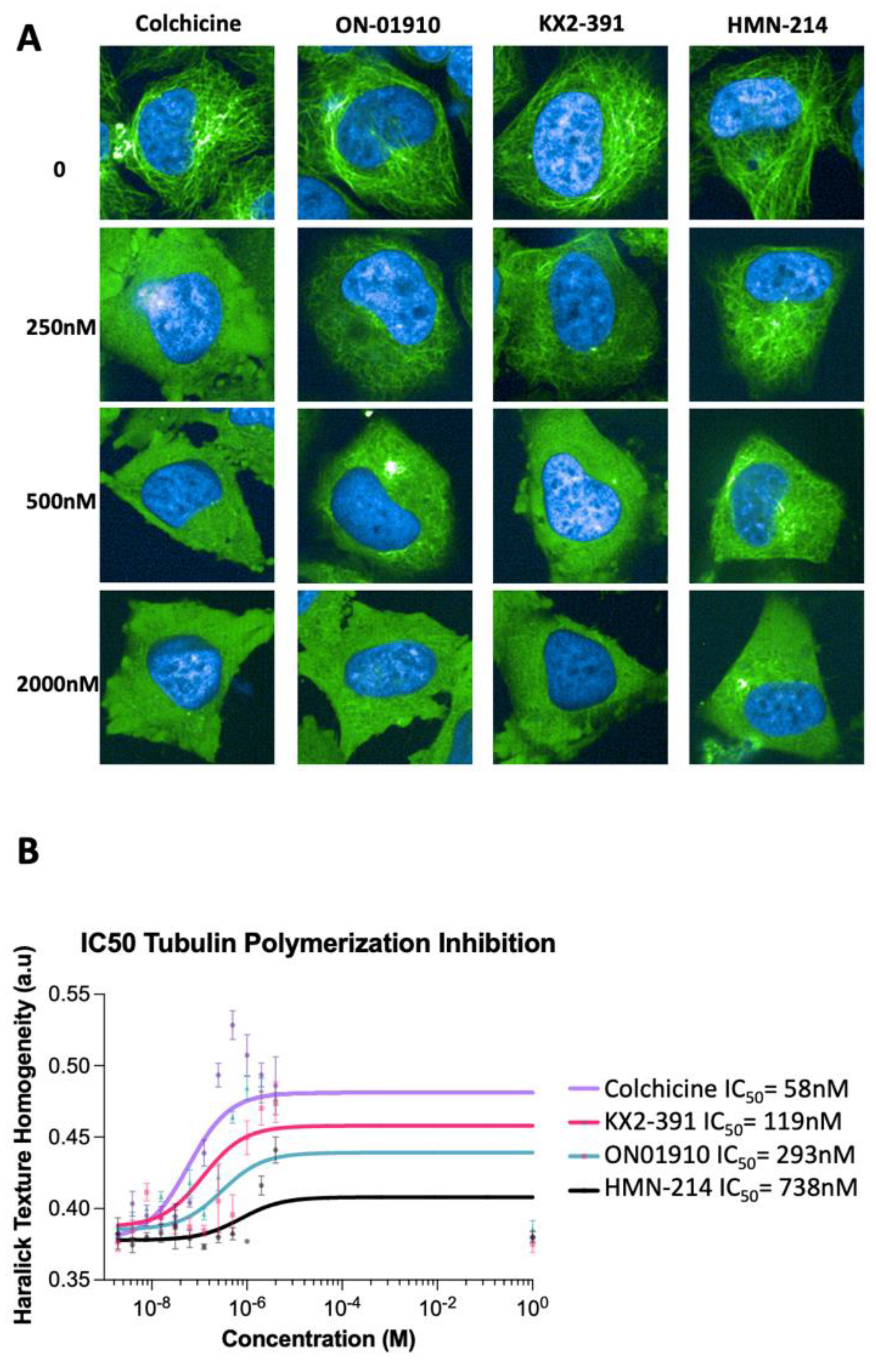
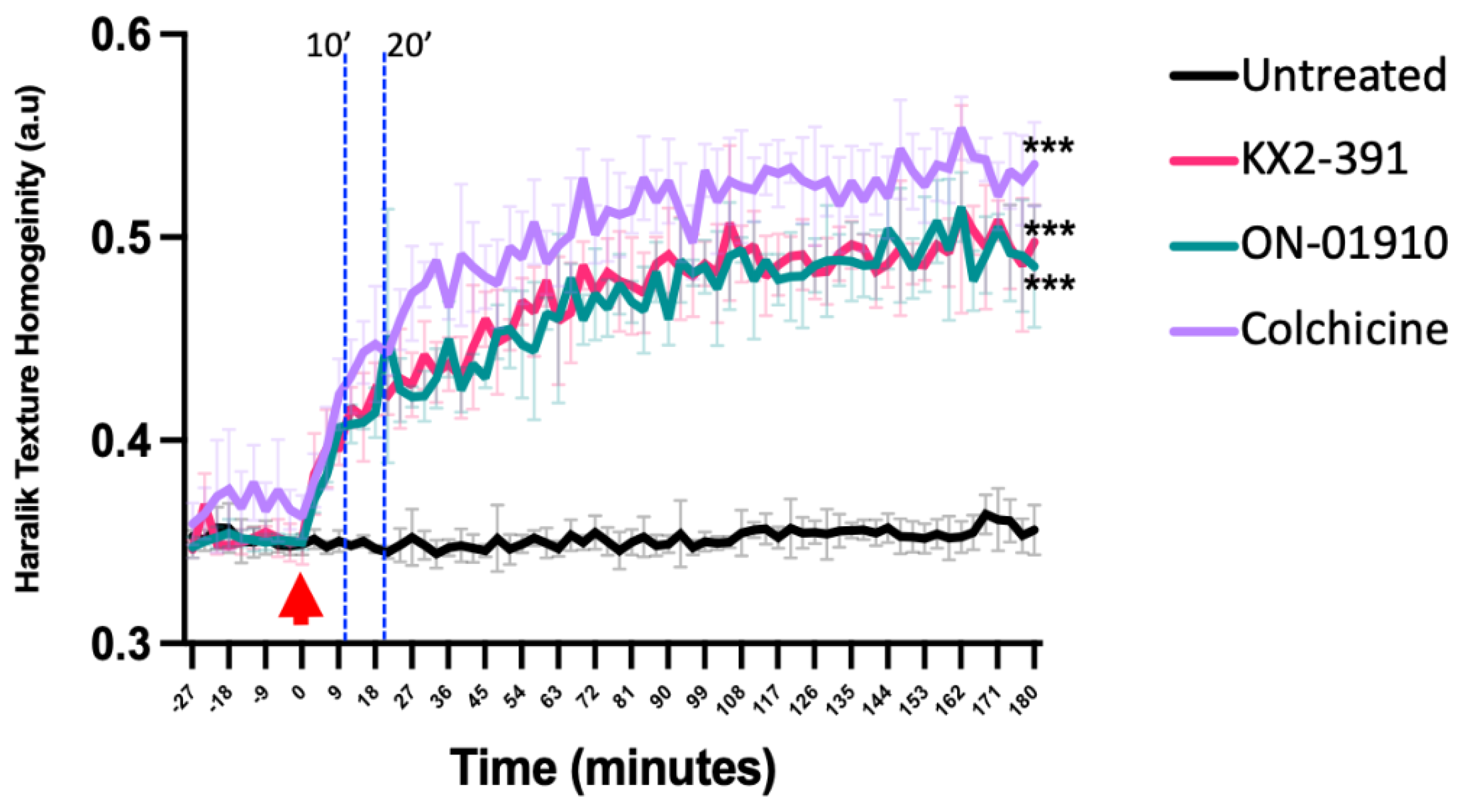
3.3. Validating Kinase Inhibitors as Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors
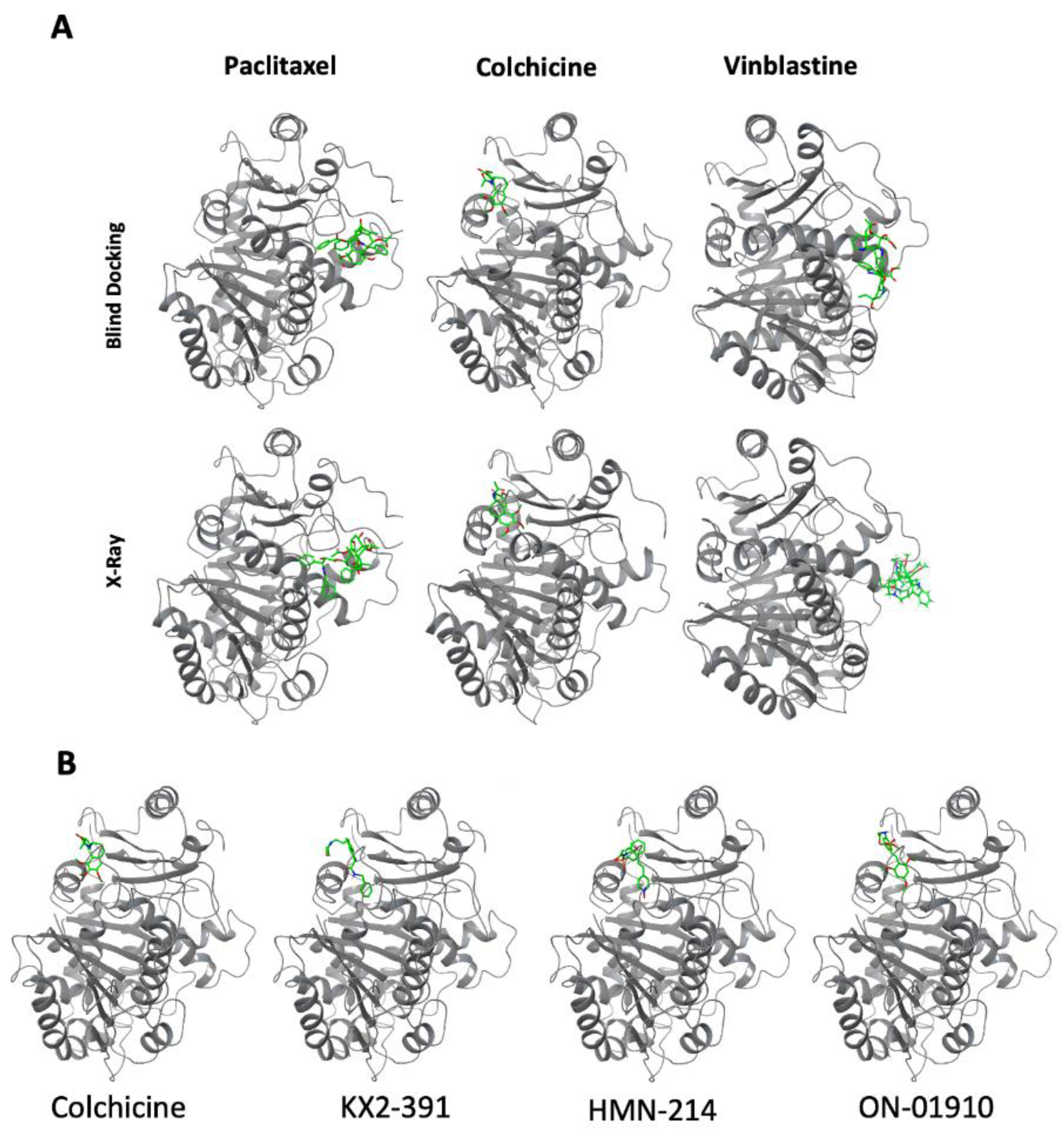
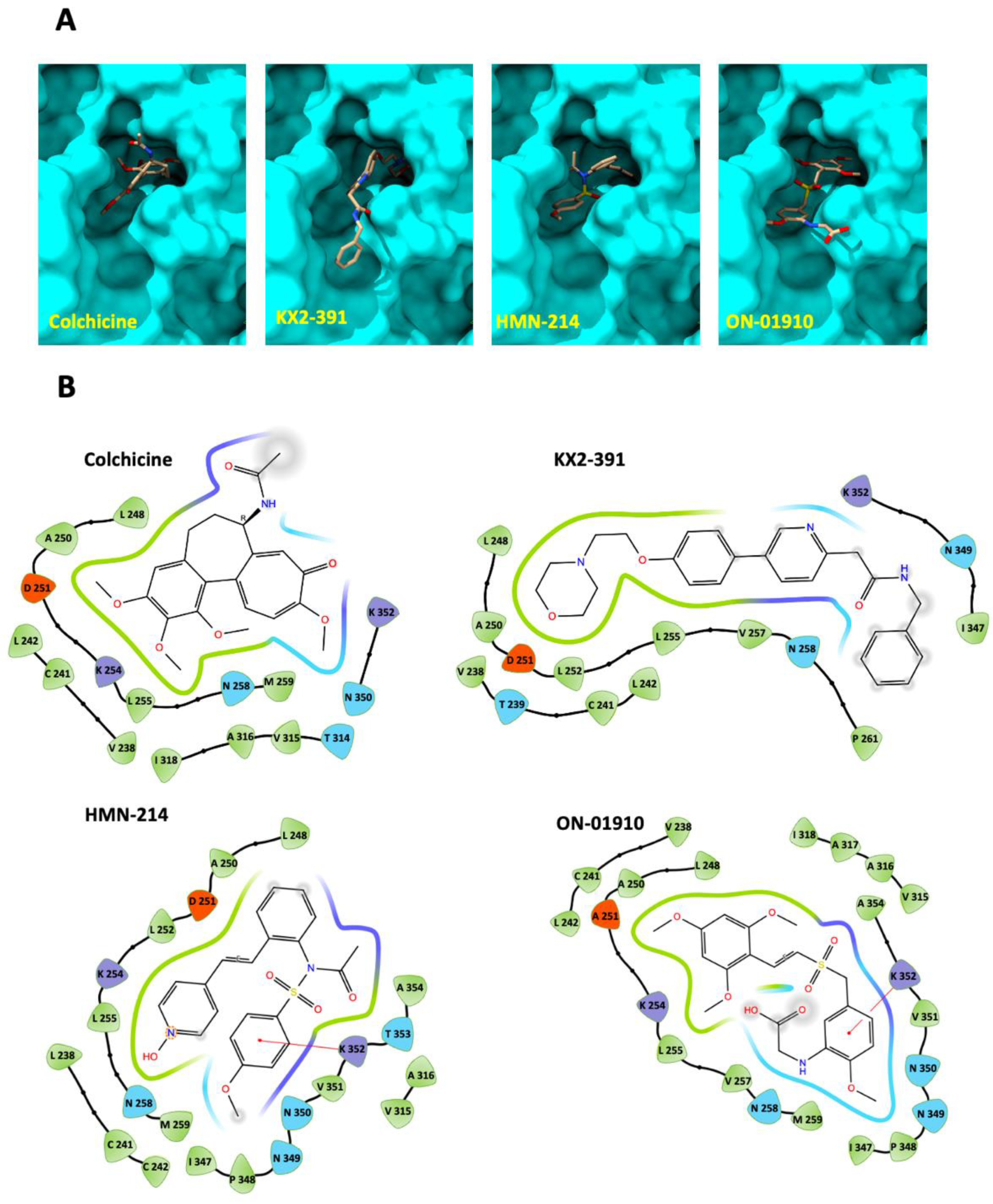
3.4. Molecular Docking of Kinase Inhibitors That Inhibit Tubulin Polymerization
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Current Cancer Epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biemar, F.; Foti, M. Global progress against cancer—challenges and opportunities. Cancer Biol. Med. 2013, 10, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, K.; Rahaman, S.; Yar, M.S.; Kamal, A. Tubulin inhibitors as novel anticancer agents: An overview on patents (2013–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, G.; Gill, R.K.; Soni, R.; Bariwal, J. Recent developments in tubulin polymerization inhibitors: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisy, G.; Heald, R.; Howard, J.; Janke, C.; Musacchio, A.; Nogales, E. Microtubules: 50 years on from the discovery of tubulin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoughlin, E.C.; O’Boyle, N.M. Colchicine-Binding Site Inhibitors from Chemistry to Clinic: A Review. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanathamsan, O.; Pongrakhananon, V. Post-translational modifications of tubulin: Their role in cancers and the regulation of signaling molecules. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.R.; Holen, K.D.; Liu, G. Beyond taxanes: A review of novel agents that target mitotic tubulin and microtubules, kinases, and kinesins. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. H&O 2009, 7, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiao, M.; Li, W.; Miller, D.D. An Overview of Tubulin Inhibitors That Interact with the Colchicine Binding Site. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2943–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumontet, C.; Jordan, M.A. Microtubule-binding agents: A dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, E.; Adhami, V.M.; Mukhtar, H. Targeting Microtubules by Natural Agents for Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Wang, S.-H.; Li, D.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, X.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zhang, S.-Y. Progress of tubulin polymerization activity detection methods. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 37, 127698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ahn, S.; Li, C.-M.; Lu, Y.; Loveless, V.S.; Dalton, J.T.; Miller, D.D.; Li, W. Novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors overcome multidrug resistance and reduce melanoma lung metastasis. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 3040–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asteriti, I.A.; Di Cesare, E.; De Mattia, F.; Hilsenstein, V.; Neumann, B.; Cundari, E.; Lavia, P.; Guarguaglini, G. The Aurora-A inhibitor MLN8237 affects multiple mitotic processes and induces dose-dependent mitotic abnormalities and aneuploidy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6229–6242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; Walter, T.; Hériché, J.-K.; Bulkescher, J.; Erfle, H.; Conrad, C.; Rogers, P.; Poser, I.; Held, M.; Liebel, U.; et al. Phenotypic profiling of the human genome by time-lapse microscopy reveals cell division genes. Nature 2010, 464, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Leal, O.; Nixon-Abell, J.; Barrero, C.; Gordon, J.; Oesterling, J.; Rico, M. Multiplex Gene Tagging with CRISPR-Cas9 for Live-Cell Microscopy and Application to Study the Role of SARS-CoV-2 Proteins in Autophagy, Mitochondrial Dynamics, and Cell Growth. CRISPR J. 2021, 4, 854–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Gan, J.; Chen, S.; Xiao, Z.; Cao, Y. CB-Dock2: Improved protein-ligand blind docking by integrating cavity detection, docking and homologous template fitting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W159–W164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 2017, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Arnst, K.; Banerjee, S.; Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Hwang, D.; Li, W.; Miller, D.D. Current advances of tubulin inhibitors as dual acting small molecules for cancer therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1398–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, A.; Murphy, R.F.; Rohde, G.K. A generative model of microtubule distributions, and indirect estimation of its parameters from fluorescence microscopy images. Cytom. Part A 2010, 77, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynolfsson, P.; Nilsson, D.; Torheim, T.; Asklund, T.; Karlsson, C.T.; Trygg, J.; Nyholm, T.; Garpebring, A. Haralick texture features from apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) MRI images depend on imaging and pre-processing parameters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutcliffe, M.D.; Tan, P.M.; Fernandez-Perez, A.; Nam, Y.-J.; Munshi, N.V.; Saucerman, J.J. High content analysis identifies unique morphological features of reprogrammed cardiomyocytes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunachalam, H.B.; Mishra, R.; Daescu, O.; Cederberg, K.; Rakheja, D.; Sengupta, A.; Leonard, D.; Hallac, R.; Leavey, P. Viable and necrotic tumor assessment from whole slide images of osteosarcoma using machine-learning and deep-learning models. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, A.; Eissa, I.; Belal, A.; El-Sayed, A. Design, eco-friendly synthesis, molecular modeling and anticancer eval-uation of thiazol-5(4H)-ones as potential tubulin polymerization inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2791–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Zhang, H.-X.; Mezei, M.; Cui, M. Molecular Docking: A Powerful Approach for Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, R.; Villarreal, M.A. Vinardo: A Scoring Function Based on Autodock Vina Improves Scoring, Docking, and Virtual Screening. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracheva, I.A.; Shchegravina, E.S.; Schmalz, H.-G.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Fedorov, A.Y. Colchicine Alkaloids and Synthetic Analogues: Current Progress and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10618–10651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilan, Y. Microtubules: From understanding their dynamics to using them as potential therapeutic targets. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 7923–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppens, I.E. Current State of the Art of New Tubulin Inhibitors in the Clinic. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 1, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, M.; Chen, Y.; Gilbert, L.A.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Krenning, L.; Menchon, G.; Rai, A.; Cho, M.Y.; Stern, J.J.; Prota, A.E.; et al. Combined CRISPRi/a-Based Chemical Genetic Screens Reveal that Rigosertib Is a Microtubule-Destabilizing Agent. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 210–223.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinski, M.P.; Bu, Y.; Clements, J.; Gelman, I.H.; Hegab, T.; Cutler, D.L.; Fang, J.W.S.; Fetterly, G.; Kwan, R.; Barnett, A.; et al. Discovery of Novel Dual Mechanism of Action Src Signaling and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors (KX2-391 and KX2-361). J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4704–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.-P.D.; Sahni, V.N.; Sahni, D.R.; Balogh, E.A.; Grada, A.; Feldman, S.R. 1% Tirbanibulin Ointment for the Treatment of Actinic Keratoses. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, M.; Honmura, T.; Watanabe, S.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nogawa, M.; Nishimura, I.; Katoh, F.; Matsuda, M.; Hidaka, H. In vivo antitumor activity of a novel sulfonamide, HMN-214, against human tumor xenografts in mice and the spectrum of cytotoxicity of its active metabolite, HMN-176. Investig. New Drugs 2003, 21, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khachatryan, H.; Olszowy, B.; Barrero, C.A.; Gordon, J.; Perez-Leal, O. Identification of Inhibitors of Tubulin Polymerization Using a CRISPR-Edited Cell Line with Endogenous Fluorescent Tagging of β-Tubulin and Histone H1. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020249
Khachatryan H, Olszowy B, Barrero CA, Gordon J, Perez-Leal O. Identification of Inhibitors of Tubulin Polymerization Using a CRISPR-Edited Cell Line with Endogenous Fluorescent Tagging of β-Tubulin and Histone H1. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhachatryan, Harutyun, Bartlomiej Olszowy, Carlos A. Barrero, John Gordon, and Oscar Perez-Leal. 2023. "Identification of Inhibitors of Tubulin Polymerization Using a CRISPR-Edited Cell Line with Endogenous Fluorescent Tagging of β-Tubulin and Histone H1" Biomolecules 13, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020249
APA StyleKhachatryan, H., Olszowy, B., Barrero, C. A., Gordon, J., & Perez-Leal, O. (2023). Identification of Inhibitors of Tubulin Polymerization Using a CRISPR-Edited Cell Line with Endogenous Fluorescent Tagging of β-Tubulin and Histone H1. Biomolecules, 13(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020249






