Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Advantages and Pitfalls for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Graph Theory Concepts and Metrics
2.2. Pathway Connectivity and Human/Non-Human Native Considerations
2.3. TPA Impact Score Calculation
2.4. ORA Probability Calculation
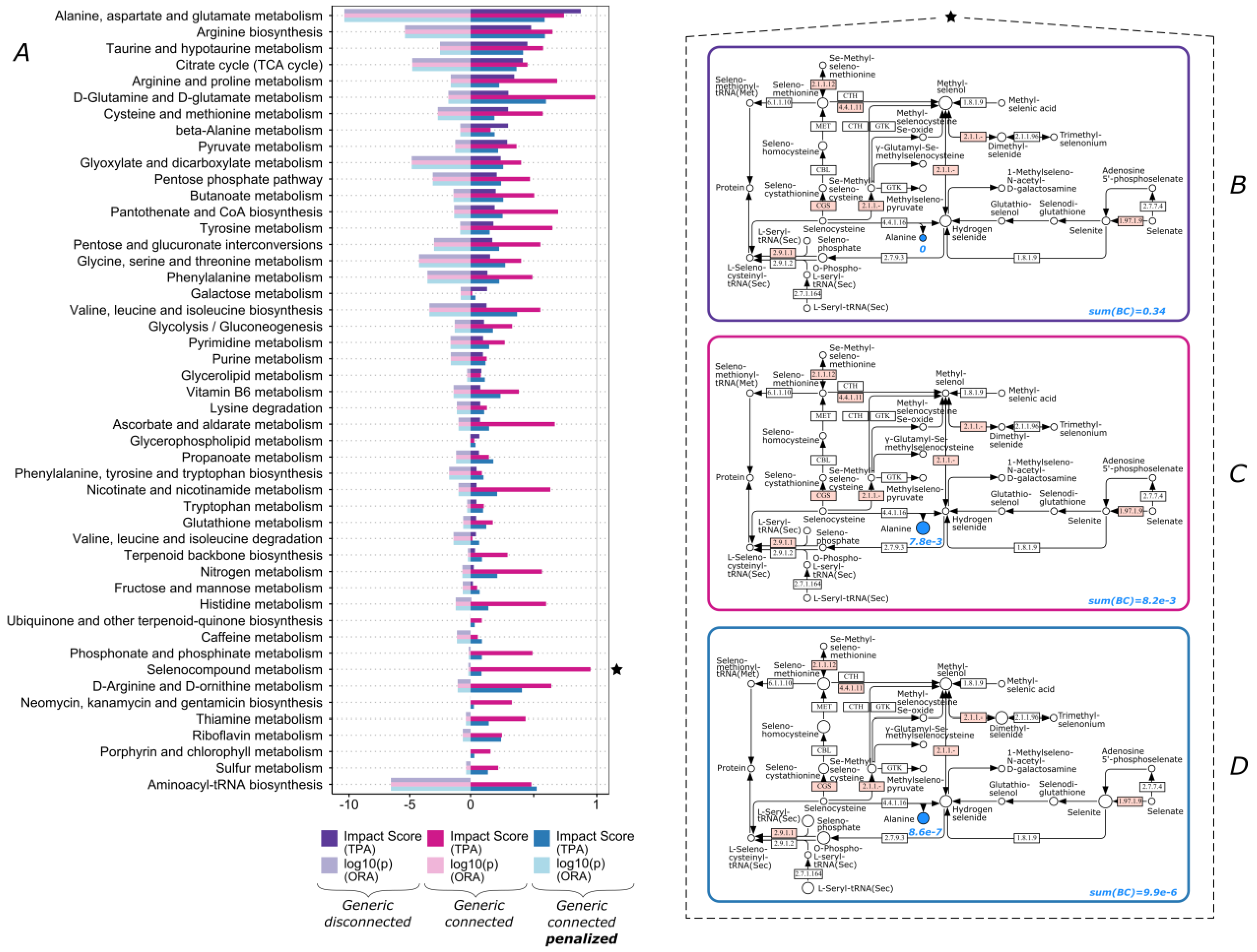
2.5. Hyper Parameter Hub Penalization Scheme
2.6. Software
3. Results
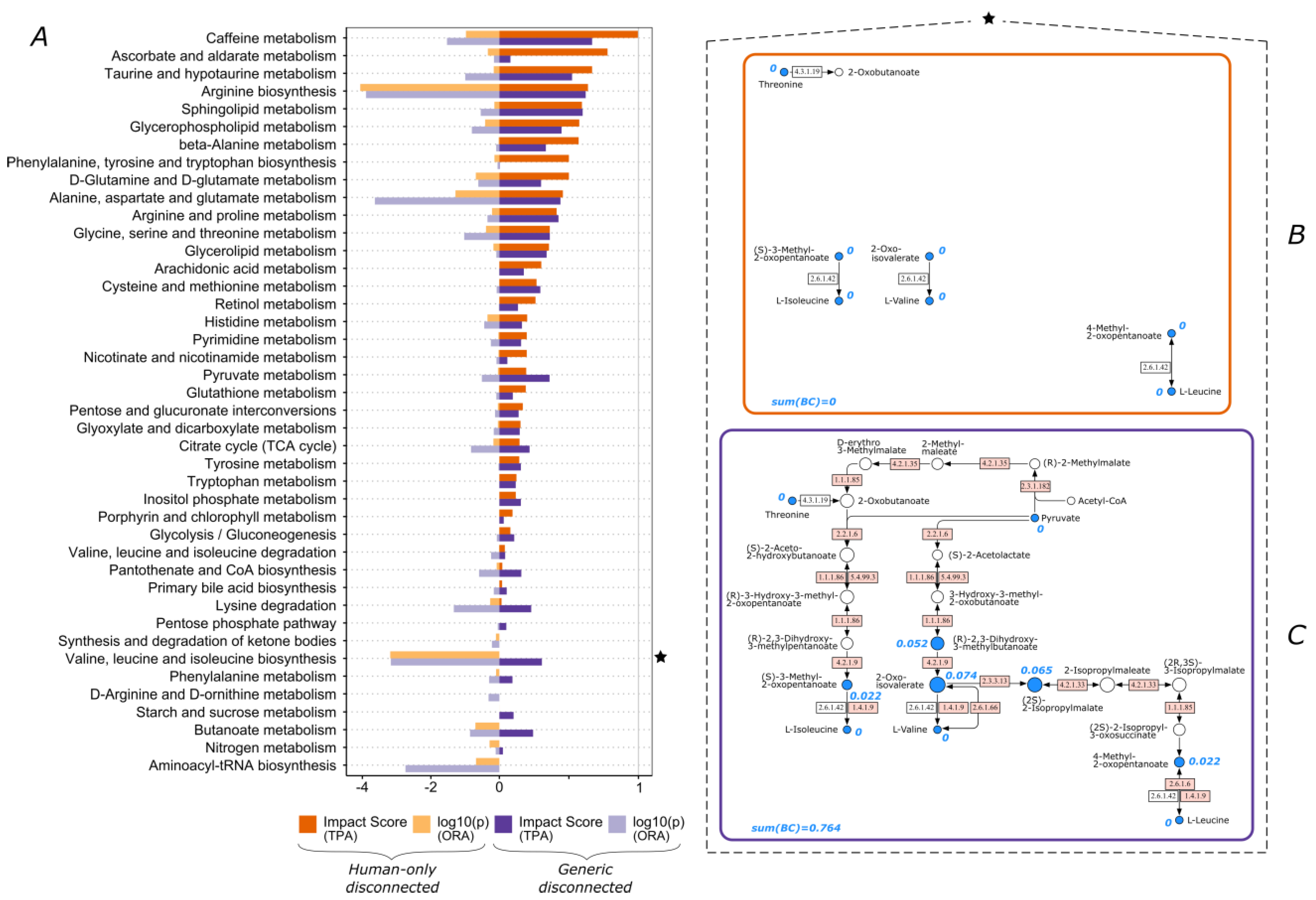
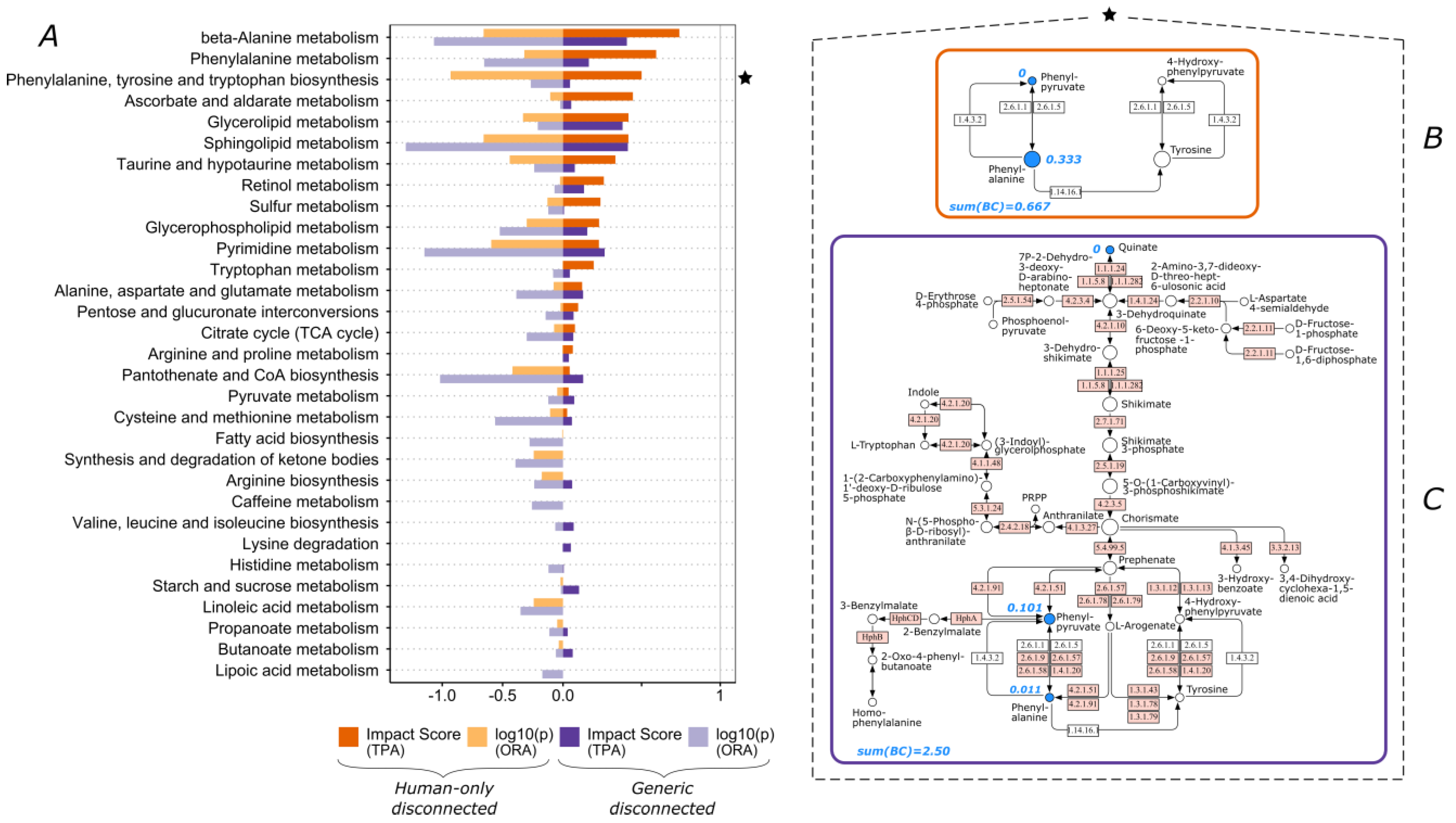
3.1. The Functional Importance of Valine and Tryptophan Biosynthesis Is Highly Impacted by Consideration of Non-Human Enzymes
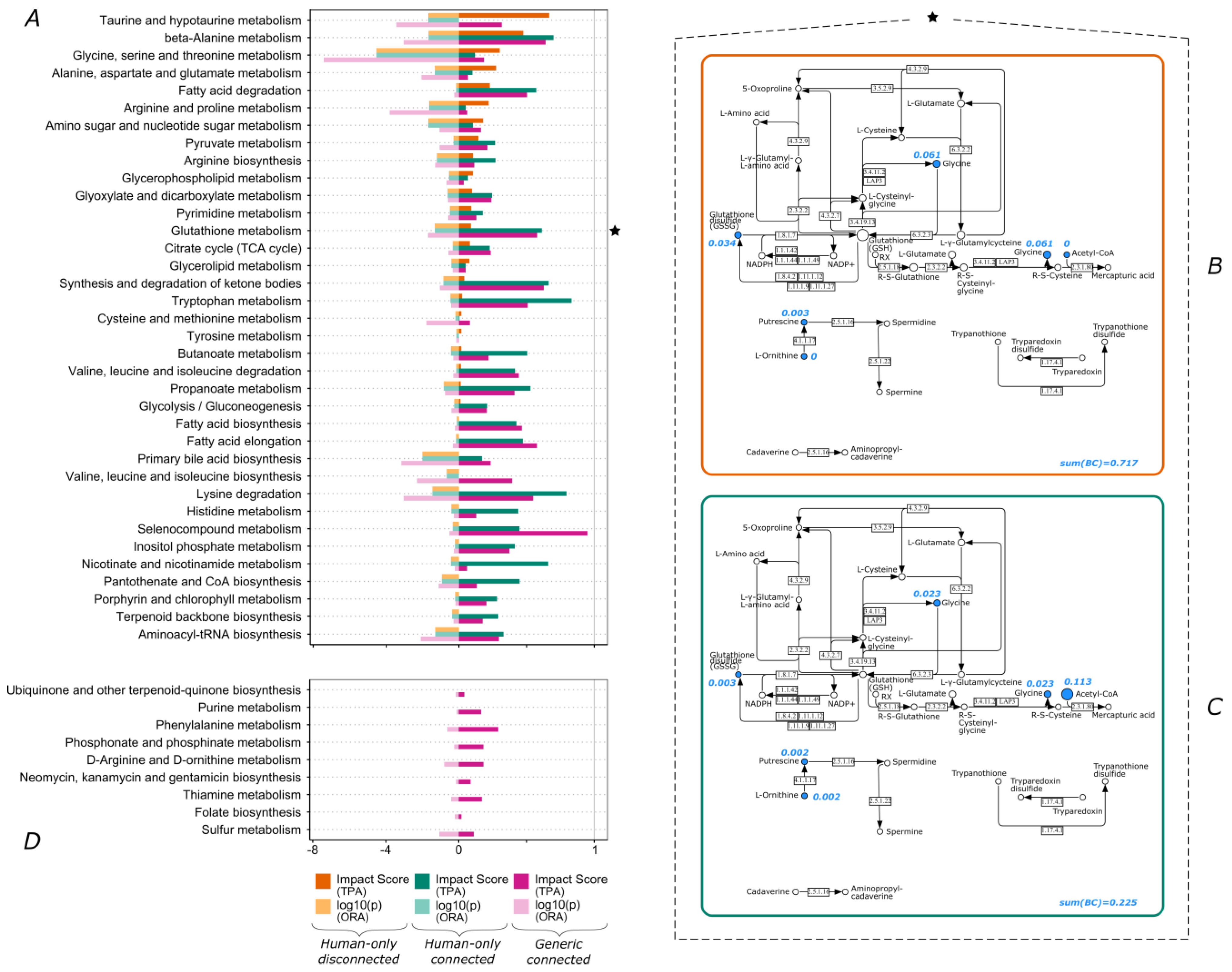
3.2. Lipid Metabolism and Amino Acid Metabolism Pathway Are Highly Impacted by Connectivity
3.3. Over-Representation Analysis vs. Topological Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wieder, C.; Frainay, C.; Poupin, N.; Rodríguez-Mier, P.; Vinson, F.; Cooke, J.; Lai, R.P.J.; Bundy, J.G.; Jourdan, F.; Ebbels, T. Pathway analysis in metabolomics: Recommendations for the use of over-representation analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, P.; Sirota, M.; Butte, A.J. Ten years of pathway analysis: Current approaches and outstanding challenges. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, S.C.; Weljie, A.M.; Turner, R.J. Computational tools for the secondary analysis of metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatri, P.; Draghici, S.; Ostermeier, G.C.; Krawetz, S.A. Profiling gene expression using onto-express. Genomics 2002, 79, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draghici, S.; Khatri, P.; Martins, R.P.; Ostermeier, G.C.; Krawetz, S.A. Global functional profiling of gene expression. Genomics 2003, 81, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Huang, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Ramell, A.; Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Alay, A.; Tulipani, S.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Evaluation and comparison of bioinformatic tools for the enrichment analysis of metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goeman, J.J.; van de Geer, S.A.; de Kort, F.; van Houwelingen, H.C. A global test for groups of genes: Testing association with a clinical outcome. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaab, E.; Baudot, A.; Krasnogor, N.; Valencia, A. TopoGSA: Network topological gene set analysis. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draghici, S.; Khatri, P.; Tarca, A.L.; Amin, K.; Done, A.; Voichita, C.; Georgescu, C.; Romero, R. A systems biology approach for pathway level analysis. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellstern, M.; Ma, J.; Yue, K.; Shojaie, A. netgsa: Fast computation and interactive visualization for topology-based pathway enrichment analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihnatova, I.; Popovici, V.; Budinska, E. A critical comparison of topology-based pathway analysis methods. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MetPA: A web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visualization. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Djukovic, D.; Raftery, D. Distinguishing NASH Histological Severity Using a Multiplatform Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites 2020, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Garcia-Barrera, T.; Gomez-Ariza, J.L. Metabolite profiling for the identification of altered metabolic pathways in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, Y.; Salehzadeh-Yazdi, A.; Schreiber, F.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Controllability in cancer metabolic networks according to drug targets as driver nodes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Fell, D.A. The small world inside large metabolic networks. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2001, 268, 1803–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.W.; Zeng, A.P. The connectivity structure, giant strong component and centrality of metabolic networks. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R.; Palsson, B.O. Properties of metabolic networks: Structure versus function. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, L07–L09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barabasi, A.L.; Gulbahce, N.; Loscalzo, J. Network medicine: A network-based approach to human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Tombor, B.; Albert, R.; Oltvai, Z.N.; Barabasi, A.L. The large-scale organization of metabolic networks. Nature 2000, 407, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, A.P. Reconstruction of metabolic networks from genome data and analysis of their global structure for various organisms. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laniau, J.; Frioux, C.; Nicolas, J.; Baroukh, C.; Cortes, M.P.; Got, J.; Trottier, C.; Eveillard, D.; Siegel, A. Combining graph and flux-based structures to decipher phenotypic essential metabolites within metabolic networks. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, K.R.; Nielsen, J. Uncovering transcriptional regulation of metabolism by using metabolic network topology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2685–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsesia, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Hager, J.; Langin, D.; Saris, W.H.M.; Astrup, A.; Blaak, E.E.; Viguerie, N.; Masoodi, M. Integrative phenotyping of glycemic responders upon clinical weight loss using multi-omics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Lin, W.H.; Davis, A.J.; Jordan, F.; Yang, H.T.; Hwang, M.J. A network perspective on the topological importance of enzymes and their phylogenetic conservation. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M. KEGG mapping tools for uncovering hidden features in biological data. Protein Sci. 2022, 31, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Garapati, P.; Gillespie, M.; Hausmann, K.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Jupe, S.; Korninger, F.; McKay, S.; et al. The Reactome pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D481–D487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, M.; Jassal, B.; Stephan, R.; Milacic, M.; Rothfels, K.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Griss, J.; Sevilla, C.; Matthews, L.; Gong, C.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D687–D692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, R.; Billington, R.; Ferrer, L.; Foerster, H.; Fulcher, C.A.; Keseler, I.M.; Kothari, A.; Krummenacker, M.; Latendresse, M.; Mueller, L.A.; et al. The MetaCyc database of metabolic pathways and enzymes and the BioCyc collection of pathway/genome databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D471–D480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.E.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, S.; Mizutani, S.; Shiroma, H.; Shiba, S.; Nakajima, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Watanabe, H.; Masuda, K.; Nishimoto, Y.; Kubo, M.; et al. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses reveal distinct stage-specific phenotypes of the gut microbiota in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, M.; Keski-Rahkonen, P.; Kiss, A.; Robinot, N.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Murphy, N.; Perlemuter, G.; Viallon, V.; Tjonneland, A.; Rostgaard-Hansen, A.L.; et al. Metabolic perturbations prior to hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: Findings from a prospective observational cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Claria, J.; Aguilar, F.; Fenaille, F.; Lozano, J.J.; Junot, C.; Colsch, B.; Caraceni, P.; Trebicka, J.; Pavesi, M.; et al. Blood metabolomics uncovers inflammation-associated mitochondrial dysfunction as a potential mechanism underlying ACLF. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, A.; Daza, E. Metabolic networks: Beyond the graph. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2011, 7, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderi Yeganeh, P.; Richardson, C.; Saule, E.; Loraine, A.; Taghi Mostafavi, M. Revisiting the use of graph centrality models in biological pathway analysis. BioData Min. 2020, 13, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, L.C. Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Netw. 1978, 1, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croes, D.; Couche, F.; Wodak, S.J.; van Helden, J. Inferring meaningful pathways in weighted metabolic networks. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, M. The metabolic world of Escherichia coli is not small. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoodi, M.; Peschka, M.; Schmiedel, S.; Haddad, M.; Frye, M.; Maas, C.; Lohse, A.; Huber, S.; Kirchhof, P.; Nofer, J.R.; et al. Disturbed lipid and amino acid metabolisms in COVID-19 patients. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Wang, P.; Lin, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, Y. Synergistic Effect in Core Microbiota Associated with Sulfur Metabolism in Spontaneous Chinese Liquor Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01475-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, T.A. Metabolic differences underlying two distinct rat urinary phenotypes, a suggested role for gut microbial metabolism of phenylalanine and a possible connection to autism. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Li, Y.; Yun, H.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yan, H.; Wei, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Lactobacillus maintains healthy gut mucosa by producing L-Ornithine. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Morra, C.N.; Roth, D.; Engevik, K.; Spinler, J.K.; Devaraj, S.; Crawford, S.E.; Estes, M.K.; Kalkum, M.; Versalovic, J. Microbial Metabolic Capacity for Intestinal Folate Production and Modulation of Host Folate Receptors. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobbe, M.D.; Houten, S.M.; Jansen, G.A.; van Kampen, A.H.; Moerland, P.D. Critical assessment of human metabolic pathway databases: A stepping stone for future integration. BMC Syst. Biol. 2011, 5, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, P.D.; Midford, P.E.; Caspi, R.; Khodursky, A. Pathway size matters: The influence of pathway granularity on over-representation (enrichment analysis) statistics. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Condition | Comparison | # of Statistically Significant Compounds | # of Significant Compounds Matched to KEGG IDs | ID of Dataset in This Work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Curation | Online Tool | |||||
| [35] | COVID-19 | Non-severe vs. Healthy | 474 (p < 0.05) | 253 | 143 | 1a |
| Non-COVID-19 vs. Healthy | 272 (p < 0.05) | 135 | 73 | 1b | ||
| [36] | Colorectal cancer | History of colorectal surgery vs. Healthy | 81 (p < 0.10) | 81 * | 81 * | 2 |
| [37] | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Development risk factors | 43 (p < 0.05) | 31 | 25 | 3 |
| [38] | Acute-on-chronic liver failure | Any stage markers vs. Acute decompensation | 149 (p < 0.05) | 131 | 120 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsouka, S.; Masoodi, M. Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Advantages and Pitfalls for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Data. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020244
Tsouka S, Masoodi M. Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Advantages and Pitfalls for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Data. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(2):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020244
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsouka, Sofia, and Mojgan Masoodi. 2023. "Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Advantages and Pitfalls for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Data" Biomolecules 13, no. 2: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020244
APA StyleTsouka, S., & Masoodi, M. (2023). Metabolic Pathway Analysis: Advantages and Pitfalls for the Functional Interpretation of Metabolomics and Lipidomics Data. Biomolecules, 13(2), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020244







