Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
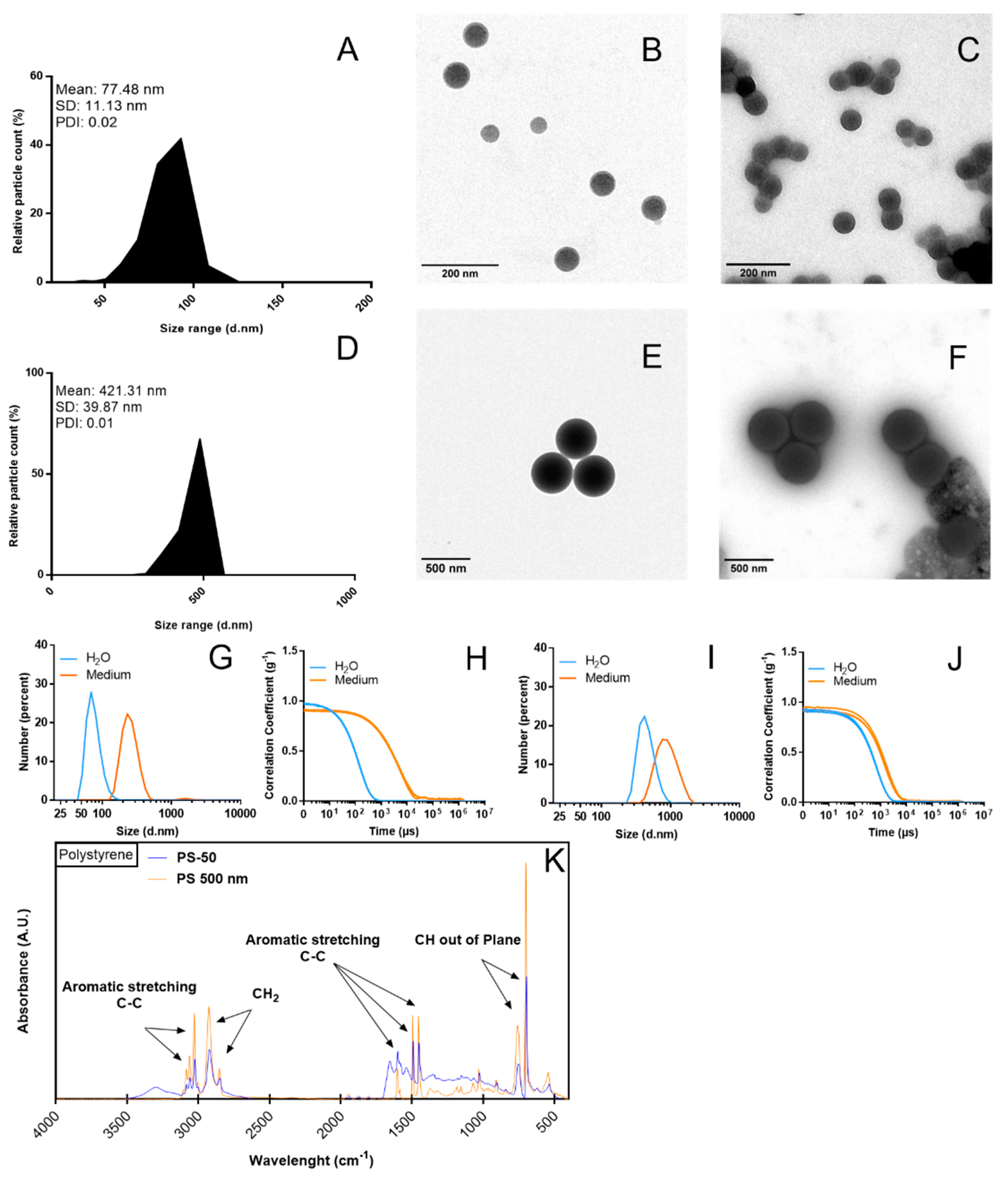
2.1. Characterization of Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PSNPLs)
2.2. Cell Culture
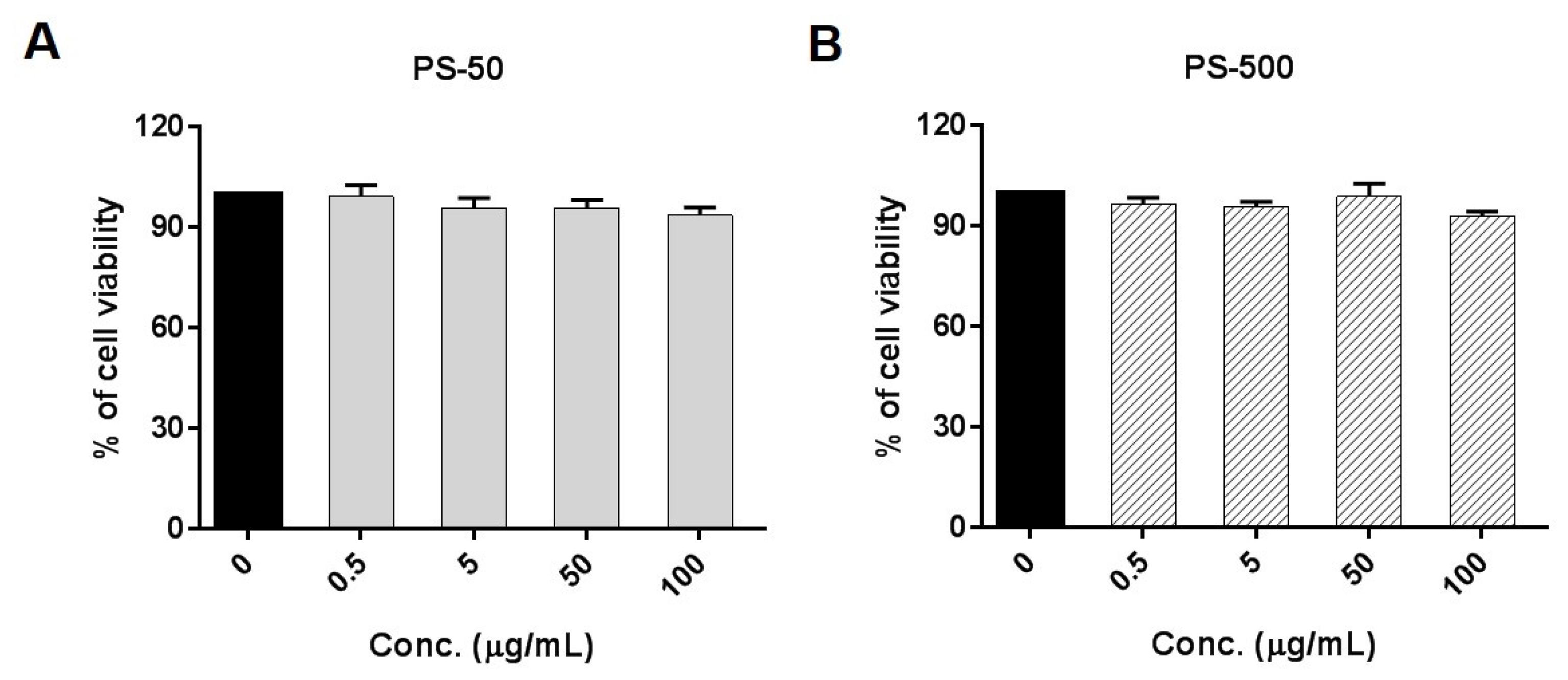
2.3. Cell Viability
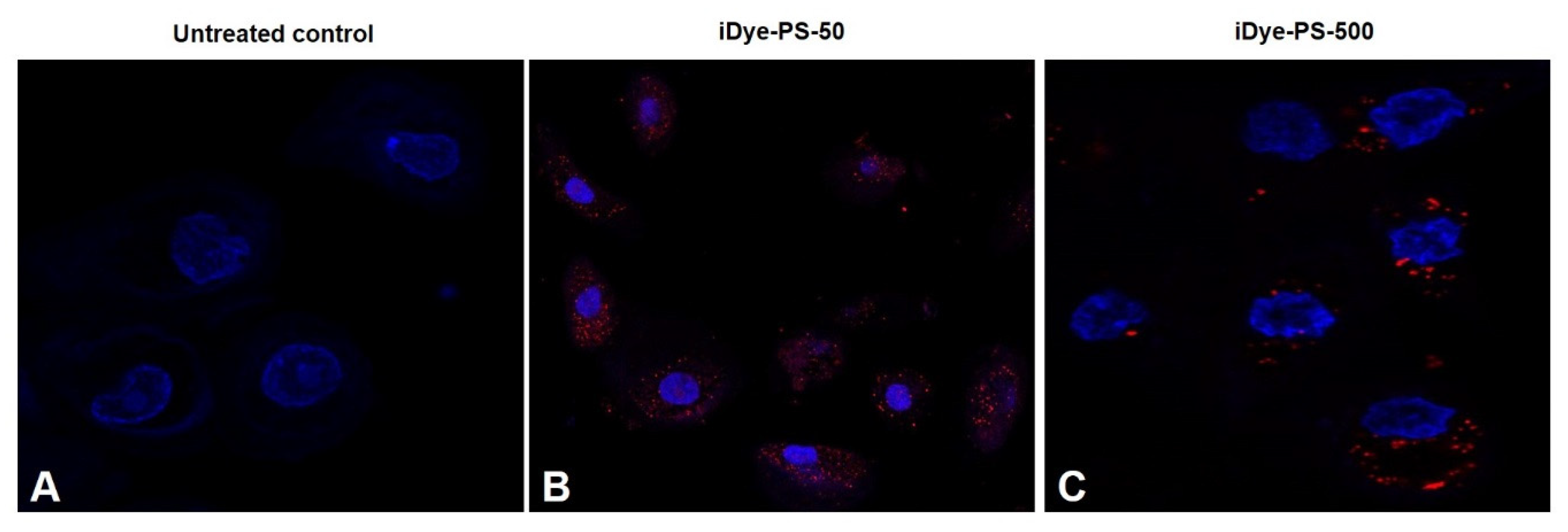
2.4. Intracellular Uptake by Confocal Microscopy
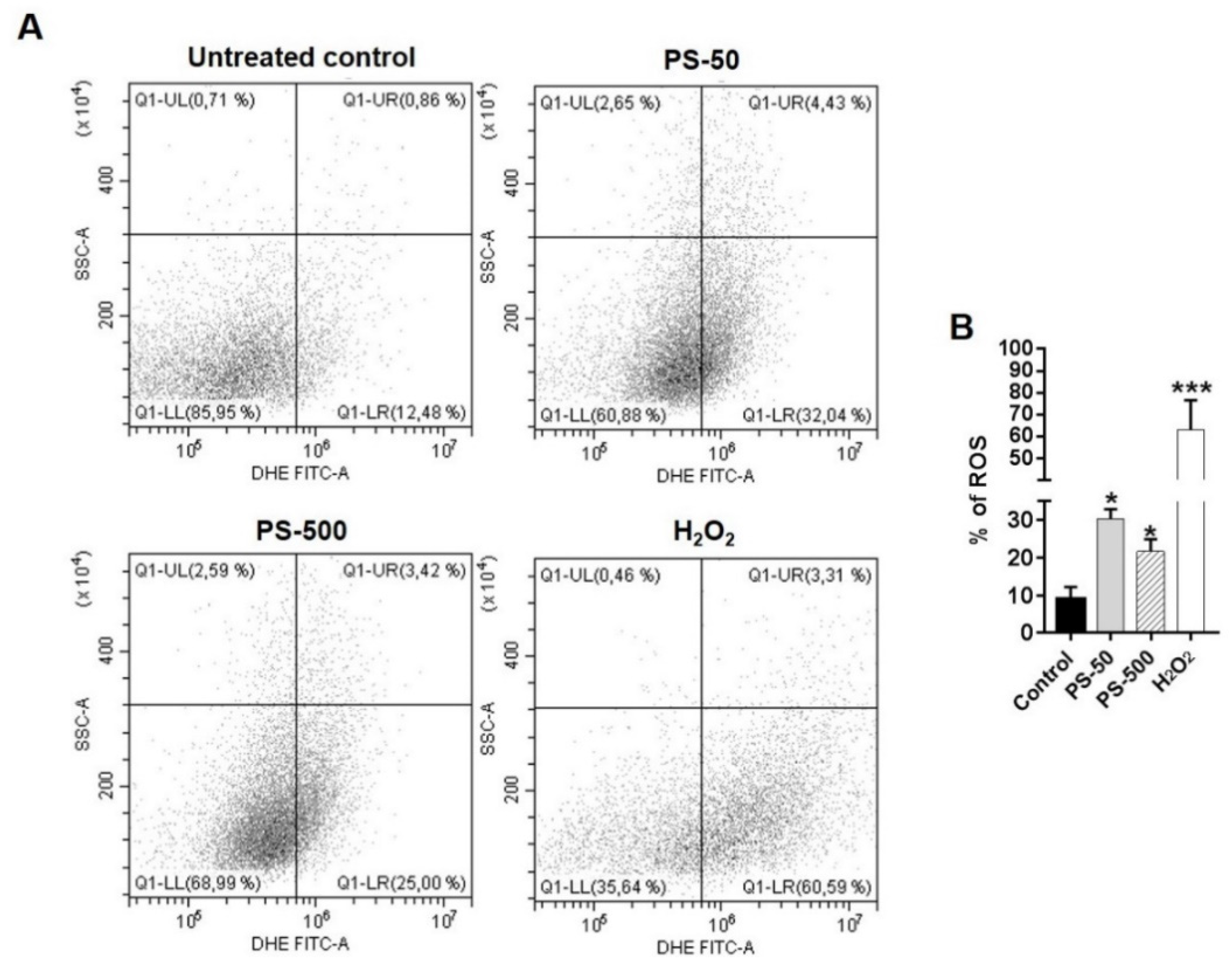
2.5. Estimation of Intracellular ROS Levels by Using the DCFH-DA Assay
2.6. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
2.7. Total Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of the Used PSNPLs
3.2. Cell Viability Assessment
3.3. Intracellular Localization of PSNPLs
3.4. Generation of iROS by PSNPLs Exposure
3.5. Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential by PSNPLs
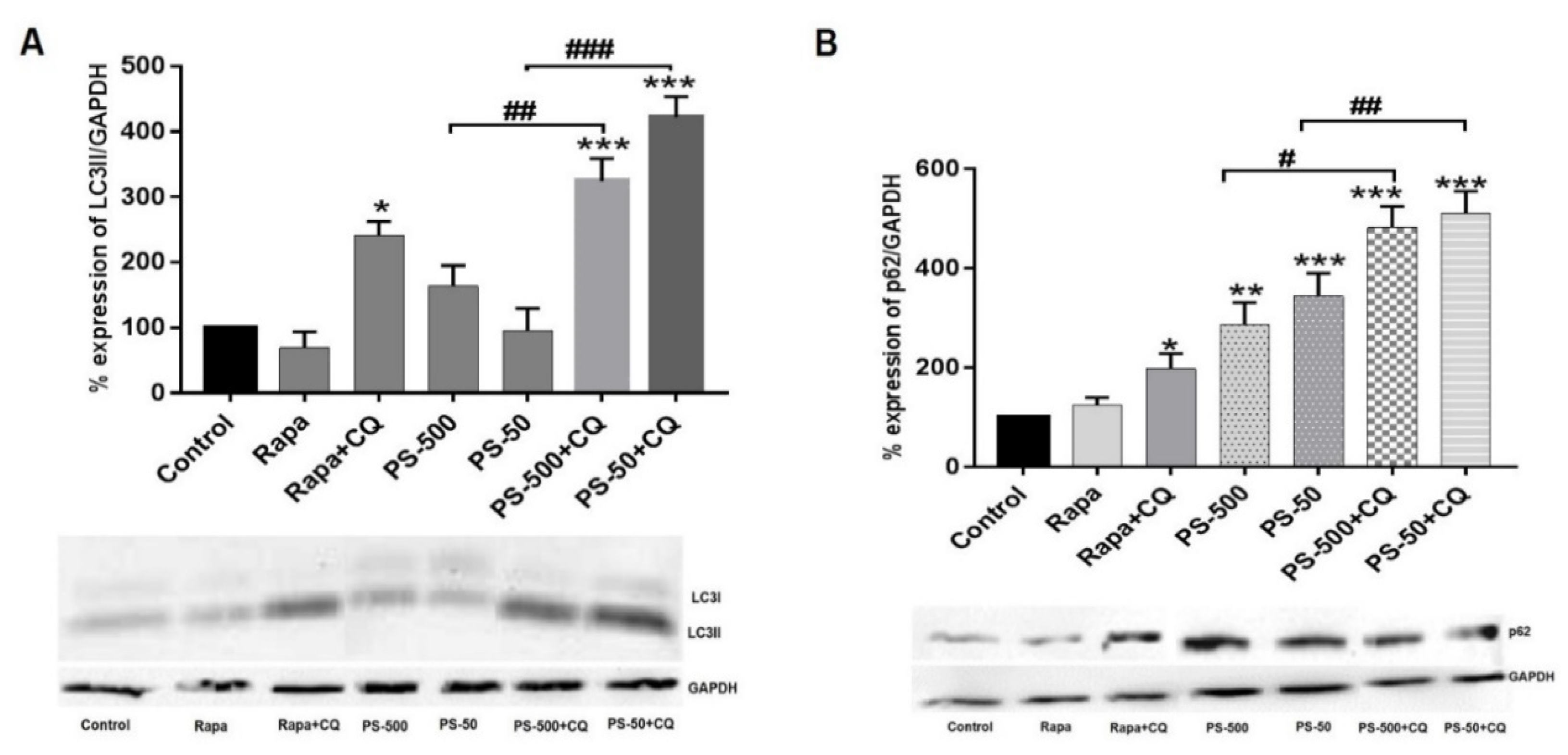
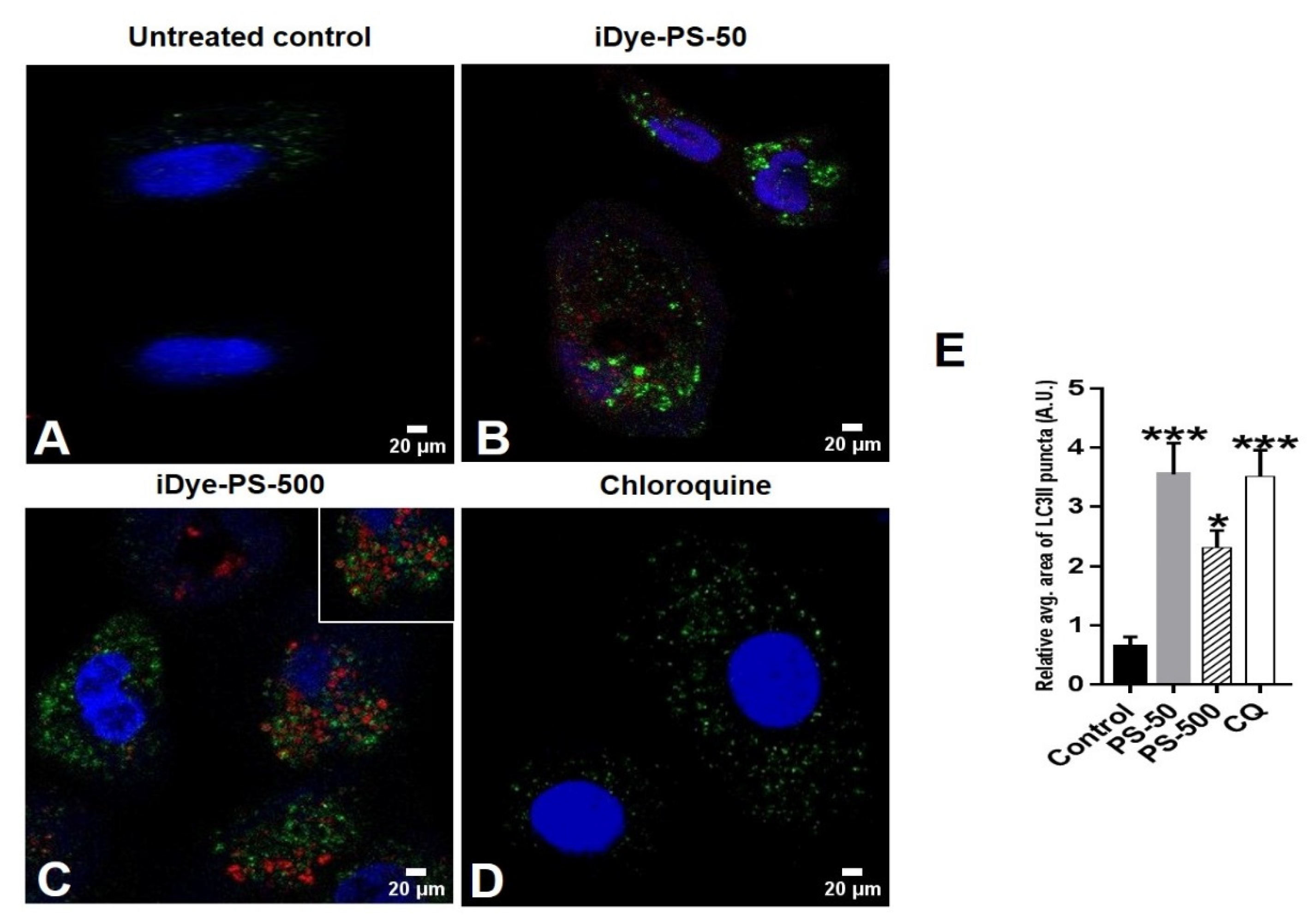
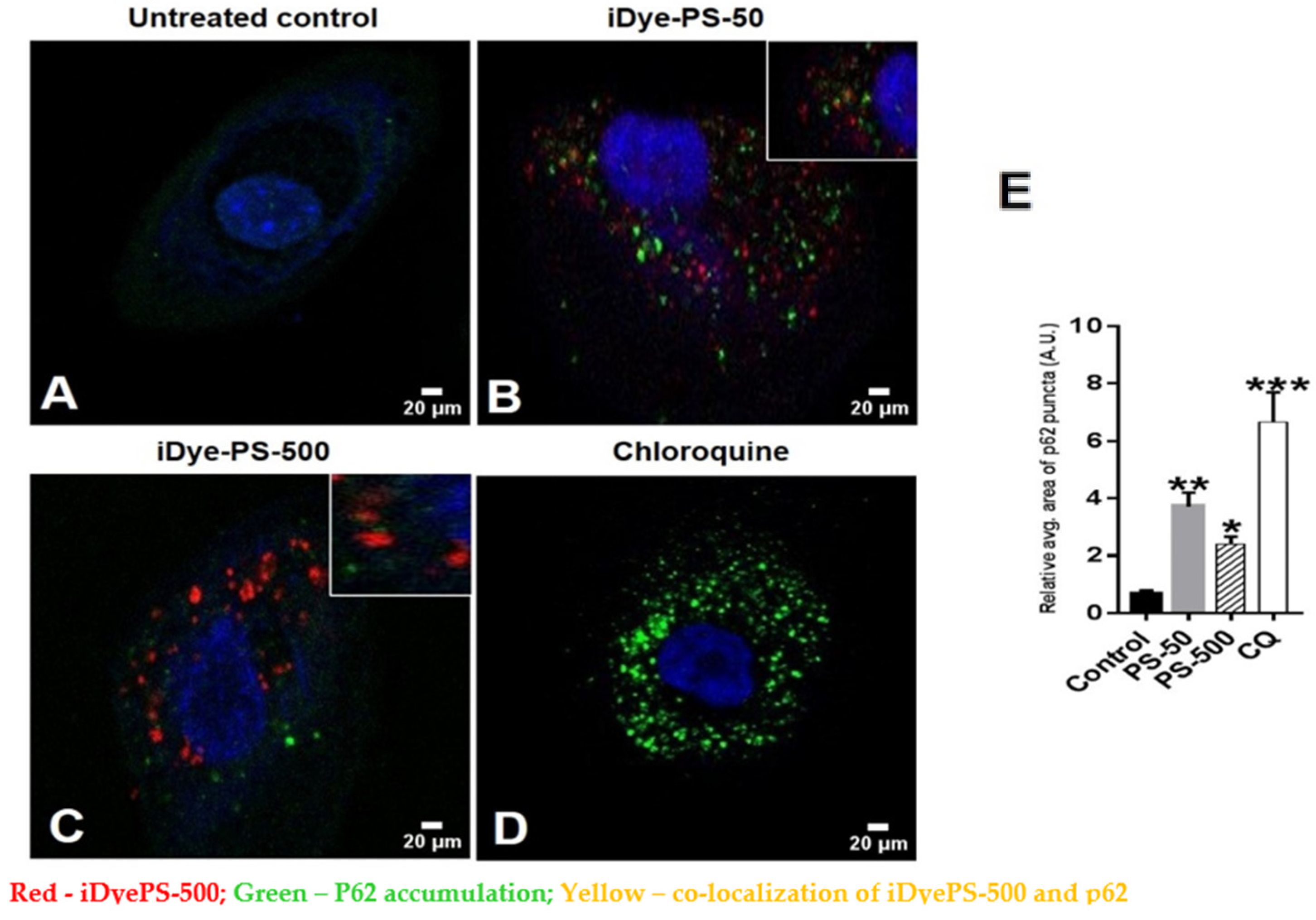
3.6. PSNPLs Cause Defective Autophagy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, X.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Shang, L.; Zhong, R. Microplastic pollution in soils, plants, and animals: A review of distributions, effects, and potential mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 157857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, L.; Barguilla, I.; Domenech, J.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Biological effects, including oxidative stress and genotoxic damage, of polystyrene nanoparticles in different human hematopoietic cell lines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigault, J.; El Hadri, H.; Nguyen, B.; Grassl, B.; Rowenczyk, L.; Tufenkji, N.; Feng, S.; Wiesner, M. Nanoplastics are neither mi-croplastics nor engineered nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Lin, S.; Cao, G.; Wu, J.; Jin, H.; Wang, C.; Wong, M.H.; Yang, Z.; Cai, Z. Absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and toxicity of microplastics in the human body and health implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human health and ocean pollution. Ann. Glob. Health. 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Nag, R.; Cummins, E. Human health concerns regarding microplastics in the aquatic environment -From marine to food systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 823, 153730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, N.; Body-Malapel, M. Immunotoxicity and intestinal effects of nano- and microplastics: A review of the literature. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, J.; Hernández, A.; Rubio, L.; Marcos, R.; Cortés, C. Interactions of polystyrene nanoplastics with in vitro models of the human intestinal barrier. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 2997–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredeck, G.; Halamoda-Kenzaoui, B.; Bogni, A.; Lipsa, D.; Bremer-Hoffmann, S. Tiered testing of micro- and nanoplastics using intestinal in vitro models to support hazard assessments. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, B.; Sadhu, S.D. Microplastic profusion in food and drinking water: Are microplastics becoming a macroproblem? Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2022, 24, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C. Airborne microplastics: Consequences to human health? Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanyange, S.N.; Lyu, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Crittenden, J.C.; Anning, C.; Chen, T.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, H. Does microplastic really represent a threat? A review of the atmospheric contamination sources and potential impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibi, N.; Uddin, S.; Fowler, S.W.; Behbehani, M. Microplastics in the atmosphere: A review. J. Environ. Expo. Assess. 2022, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangeliou, N.; Grythe, H.; Klimont, Z.; Heyes, C.; Eckhardt, S.; Lopez-Aparicio, S.; Stohl, A. Atmospheric transport is a major pathway of microplastics to remote regions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and tear of tyres: A stealthy source of microplastics in the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ageel, H.K.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A. Occurrence, human exposure, and risk of microplastics in the indoor environment. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Jeong, J.; Song, K.; Sung, J.; Oh, S.; Choi, J. Inhalation toxicity of polystyrene micro (nano) plastics using modified OECD TG 412. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Xia, X.; Ji, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, R.; et al. Inhaled tire-wear microplastic particles induced pulmonary fibrotic injury via epithelial cytoskeleton rearrangement. Environ. Int. 2022, 164, 107257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, T.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liang, G. In vitro evaluation of nanoplastics using human lung epithelial cells, microarray analysis and co-culture model. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 226, 112837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Tang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, R.; Giesy, J.P. Combined cytotoxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics and phthalate esters on human lung epithelial A549 cells and its mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Dong, G.; Liang, M.; Wu, X.; Xian, M.; An, Y.; Zhan, J.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Sun, W.; et al. Toxicity of mi-cro(nano)plastics with different size and surface charge on human nasal epithelial cells and rats via intranasal exposure. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Xia, J.; Zhang, R.; Bai, Y.; Liu, S.; Dan, M.; Li, T.; Yan, T.; Chen, L.; Gong, S.; et al. Investigation of the impact of PM2.5 on the ciliary motion of human nasal epithelial cells. Chemosphere 2019, 233, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; An, T. The respiratory cytotoxicity of typical organophosphorus flame retardants on five different respiratory tract cells: Which are the most sensitive one? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoja, S.; Nel, H.A.; Abdallah, M.A.; Harrad, S. Microplastics in freshwater sediments: Analytical methods, temporal trends, and risk of associated organophosphate esters as exemplar plastics additives. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesonen, M.; Vähäkangas, K. Autophagy in exposure to environmental chemicals. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 305, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Duan, Y. Crosstalk between autophagy and nanomaterials: Internalization, activation, termination. Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 1, e1800259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L. Size-dependent effects of polystyrene microplastics on cytotoxicity and efflux pump inhibition in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X. Size-dependent effects of polystyrene nanoplastics on autophagy response in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakolis, E.G.; Nguyen, B.; You, J.B.; Rochman, C.M.; Sinton, D. Fluorescent dyes for visualizing microplastic particles and fibers in laboratory-based studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.; Tufenkji, N. Single-particle resolution fluorescence microscopy of nanoplastics. 768 Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6426–6435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezanpour, M.; Bolt, H.; Psaltis, A.J.; Wormald, P.J.; Vreugde, S. Primary human nasal epithelial cells: A source of poly (I:C) LMW-induced IL-6 production. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherzad, A.; Hagen, R.; Hackenberg, S. Current understanding of nasal epithelial cell mis-differentiation. J. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 12, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.C. The infrared spectra of polymers III: Hydrocarbon polymers. Spectroscopy 2021, 36, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.F.; Xuan, Y.M.; Li, Q. Preparation of polystyrene spheres in different particle sizes and assembly of the PS colloidal crystals. Sci. Chin. Tech. Sci. 2010, 53, 3088–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: An update and review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Palić, D. Micro- and nano-plastics activation of oxidative and inflammatory adverse outcome pathways. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Bum, J.; Eun-Ji, W.; Hye-Min, K.; Min-Chul, L.; Dae-Sik, H.; Un-Ki, H.; Bingsheng, Z.; Sami, S.; Su-Jae, L.; Jae-Seong, L. Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-JNK and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; et al. Toxic effects of na-noplastics with different sizes and surface charges on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in A549 cells and the potential toxicological mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruenraroengsak, P.; Tetley, T.D. Differential bioreactivity of neutral, cationic, and anionic polystyrene nanoparticles with cells from the human alveolar compartment: Robust response of alveolar type 1 epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Fan, M.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Jin, Y. Amino-functionalized polystyrene nano-plastics induce mitochondria damage in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Toxics 2022, 10, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Hou, B.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce mitochondrial damage in mouse GC-2 cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Bai, J.; Ning, B.; Fan, L.; Sun, T.; Fang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Duan, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effects of bisphenol A and nanoscale and microscale polystyrene plastic exposure on particle uptake and toxicity in human Caco-2 cells. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, G.G.; Mariño, G. Autophagy role in environmental pollutants exposure. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 172, 257–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.W.; Choi, J.; Ryu, K.Y. Stress response of mouse embryonic fibroblasts exposed to polystyrene nanoplastics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Amarakoon, D.; Wei, C.I.; Choi, K.Y.; Smolensky, D.; Lee, S.H. Adverse effect of polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) on tube formation and viability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 154, 112356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Lee, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Chiu, I.J.; Huang, C.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chia, Z.C.; Lee, C.P.; Lin, Y.F.; Chiu, H.W. The kidney-related effects of polystyrene microplastics on human kidney proximal tubular epithelial cells HK-2 and male C57BL/6 mice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 57003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Wang, W.X. Differential cascading cellular and subcellular toxicity induced by two sizes of nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wu, D.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Compromised autophagic effect of polystyrene nanoplastics mediated by protein corona was recovered after lysosomal degradation of corona. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11485–11493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Ng, C.T.; Zou, L.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Bay, B.H.; Shen, H.M.; Ong, C.N. Targeted metabolomics reveals differential biological effects of nanoplastics and nanoZnO in human lung cells. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperi, J.; Wright, S.; Dris, R.; Collard, F.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Kelly, F.; Tassin, B. Microplastics in air: Are we breathing it in? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Annangi, B.; Villacorta, A.; López-Mesas, M.; Fuentes-Cebrian, V.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020220
Annangi B, Villacorta A, López-Mesas M, Fuentes-Cebrian V, Marcos R, Hernández A. Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(2):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020220
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnnangi, Balasubramanyam, Aliro Villacorta, Montserrat López-Mesas, Victor Fuentes-Cebrian, Ricard Marcos, and Alba Hernández. 2023. "Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects" Biomolecules 13, no. 2: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020220
APA StyleAnnangi, B., Villacorta, A., López-Mesas, M., Fuentes-Cebrian, V., Marcos, R., & Hernández, A. (2023). Hazard Assessment of Polystyrene Nanoplastics in Primary Human Nasal Epithelial Cells, Focusing on the Autophagic Effects. Biomolecules, 13(2), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020220






