An Efficient Lightweight Hybrid Model with Attention Mechanism for Enhancer Sequence Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
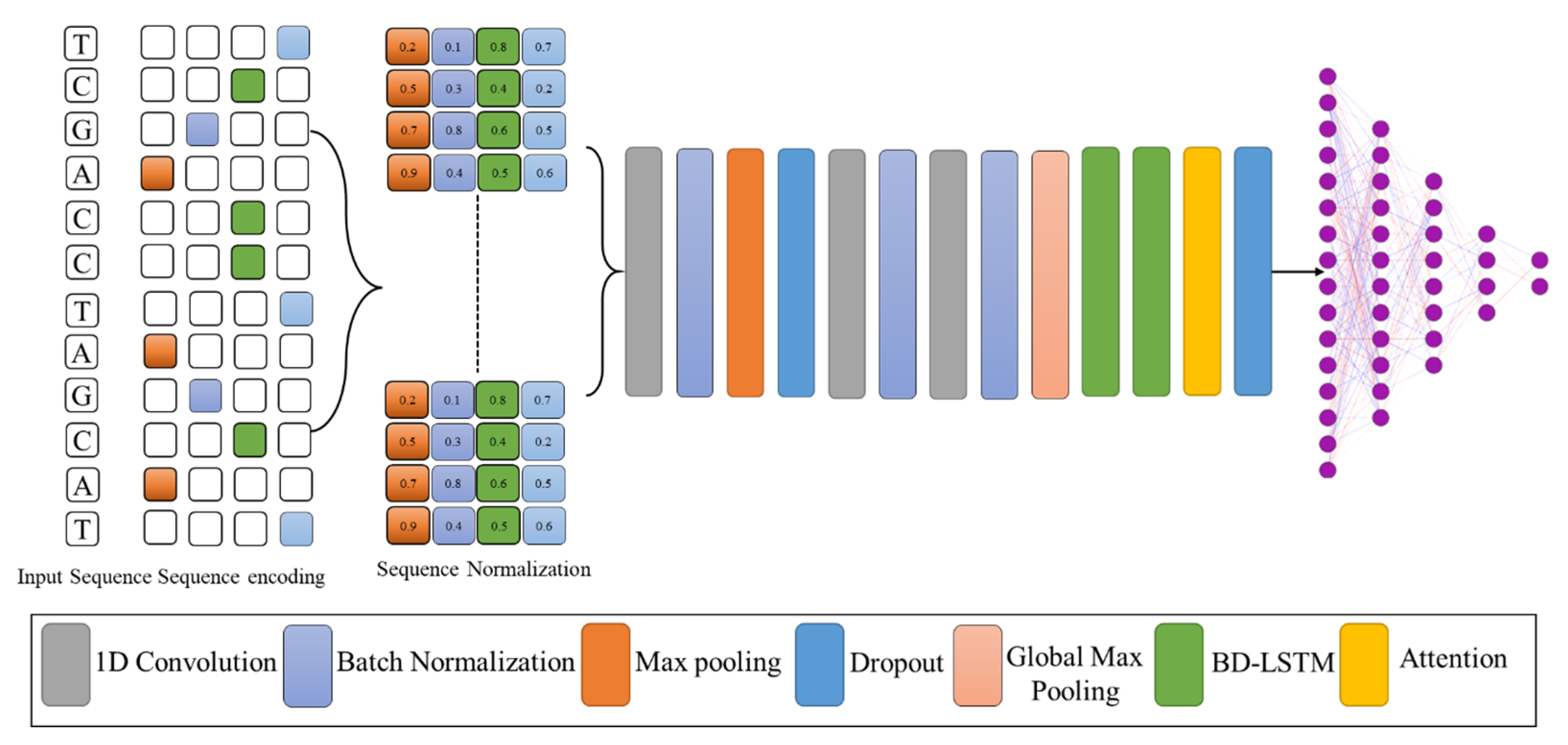
2.2. Sequence Encoding and Proposed Model
2.3. Features Extraction
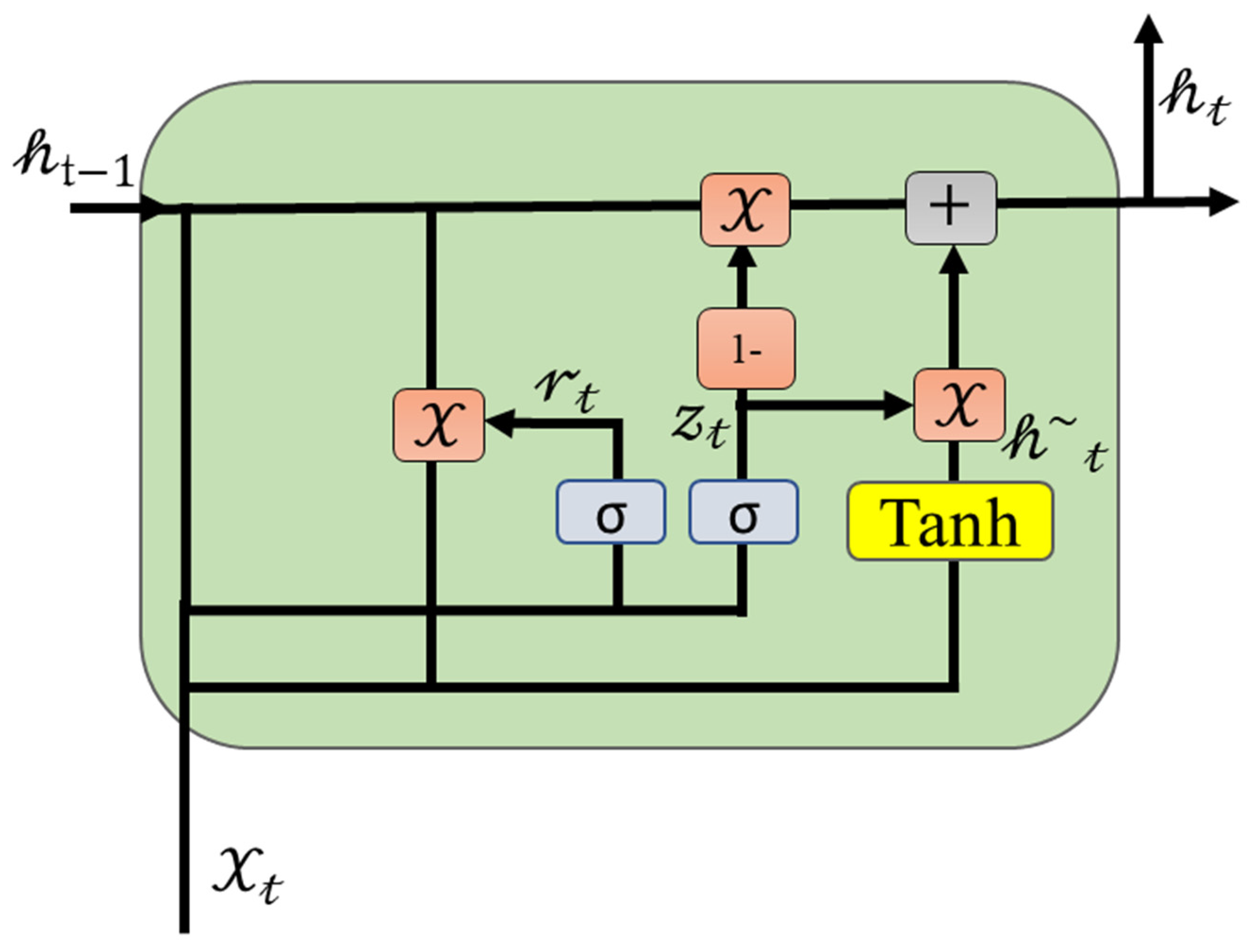
2.4. Multi-Layer Bi Direction Gated Recurrent Units
2.5. Attention Mechanism with GRU
3. Results and Discussion
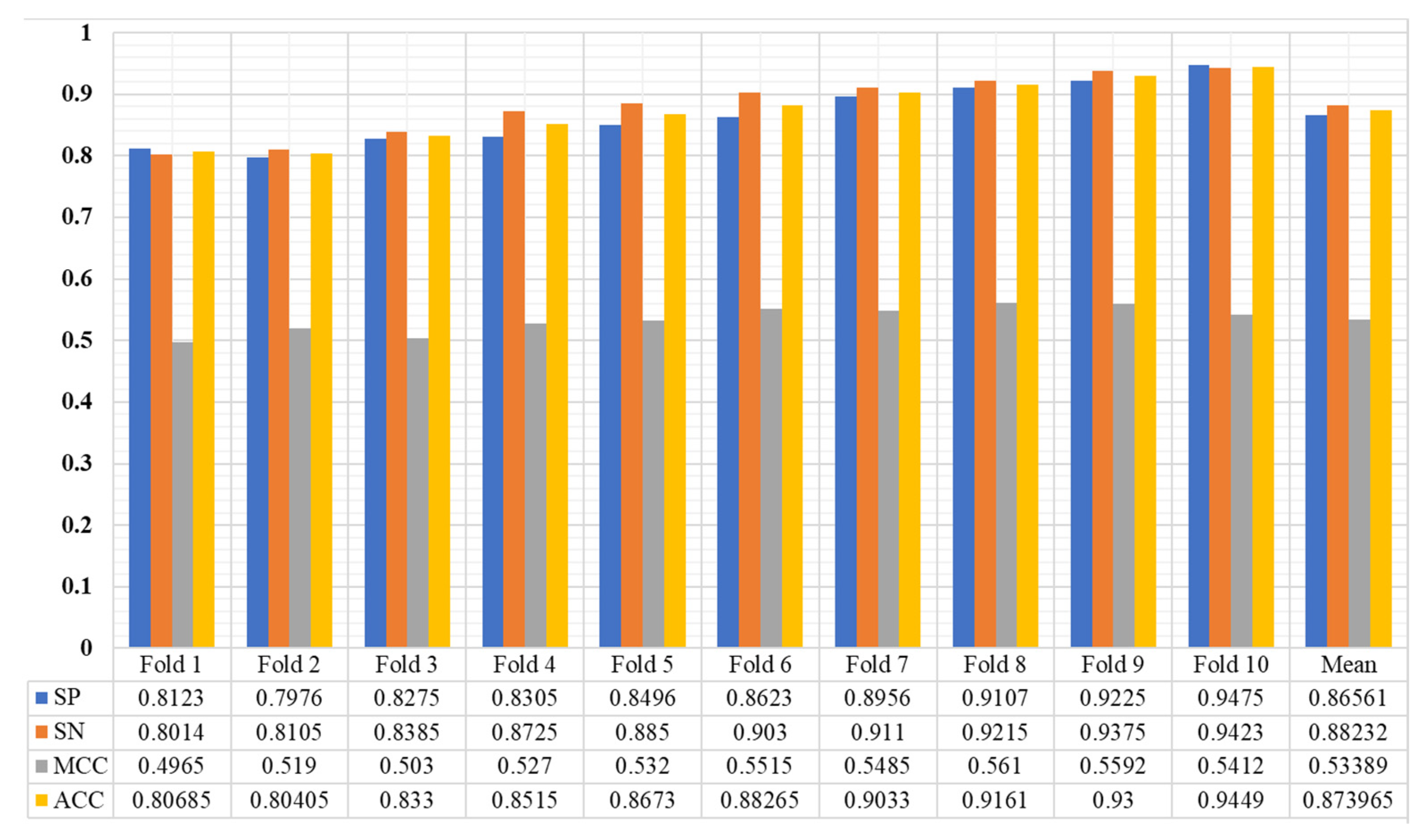
3.1. Training Detail, Cross Validation and Evaluation Metrices
3.2. Results
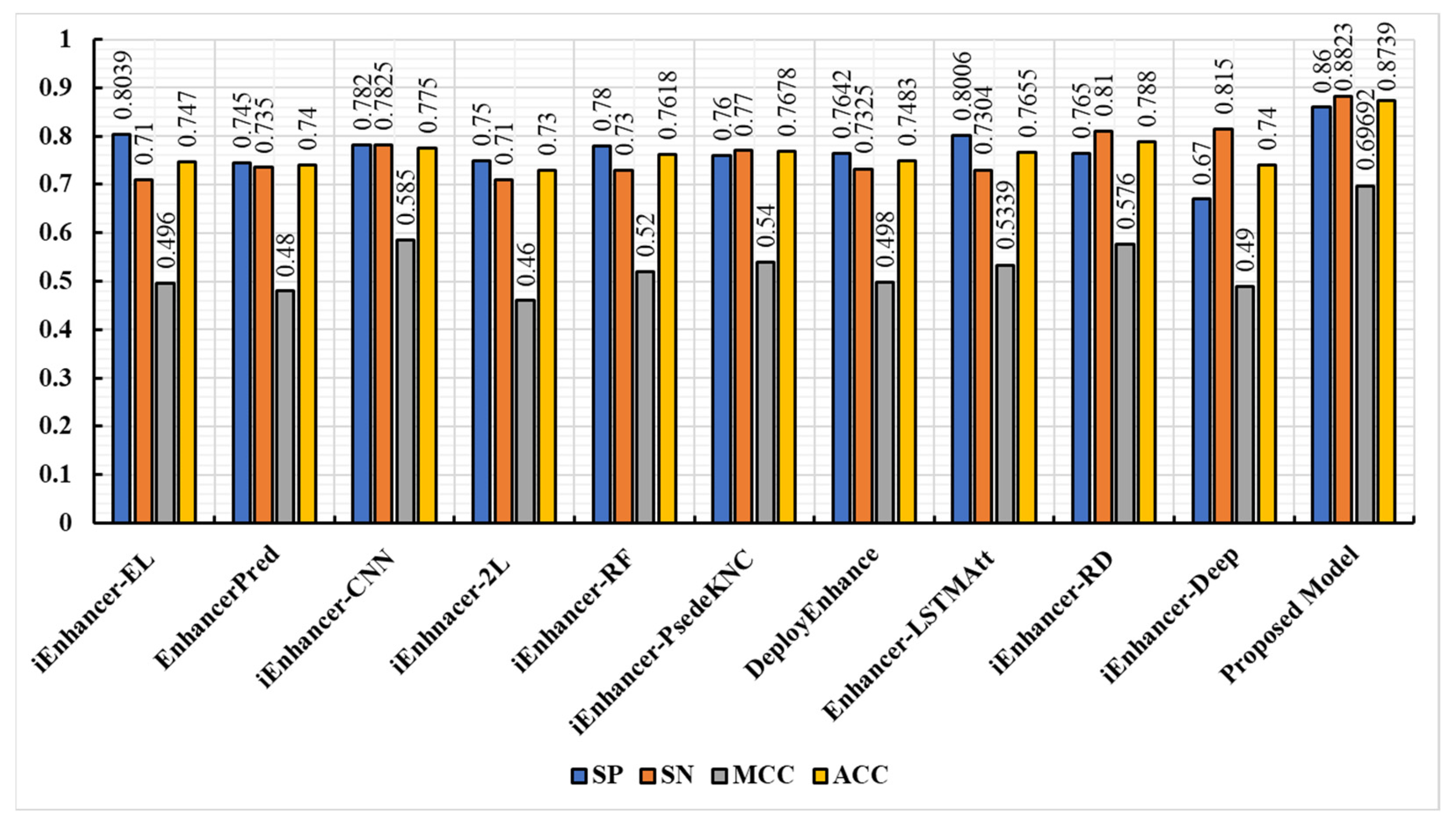
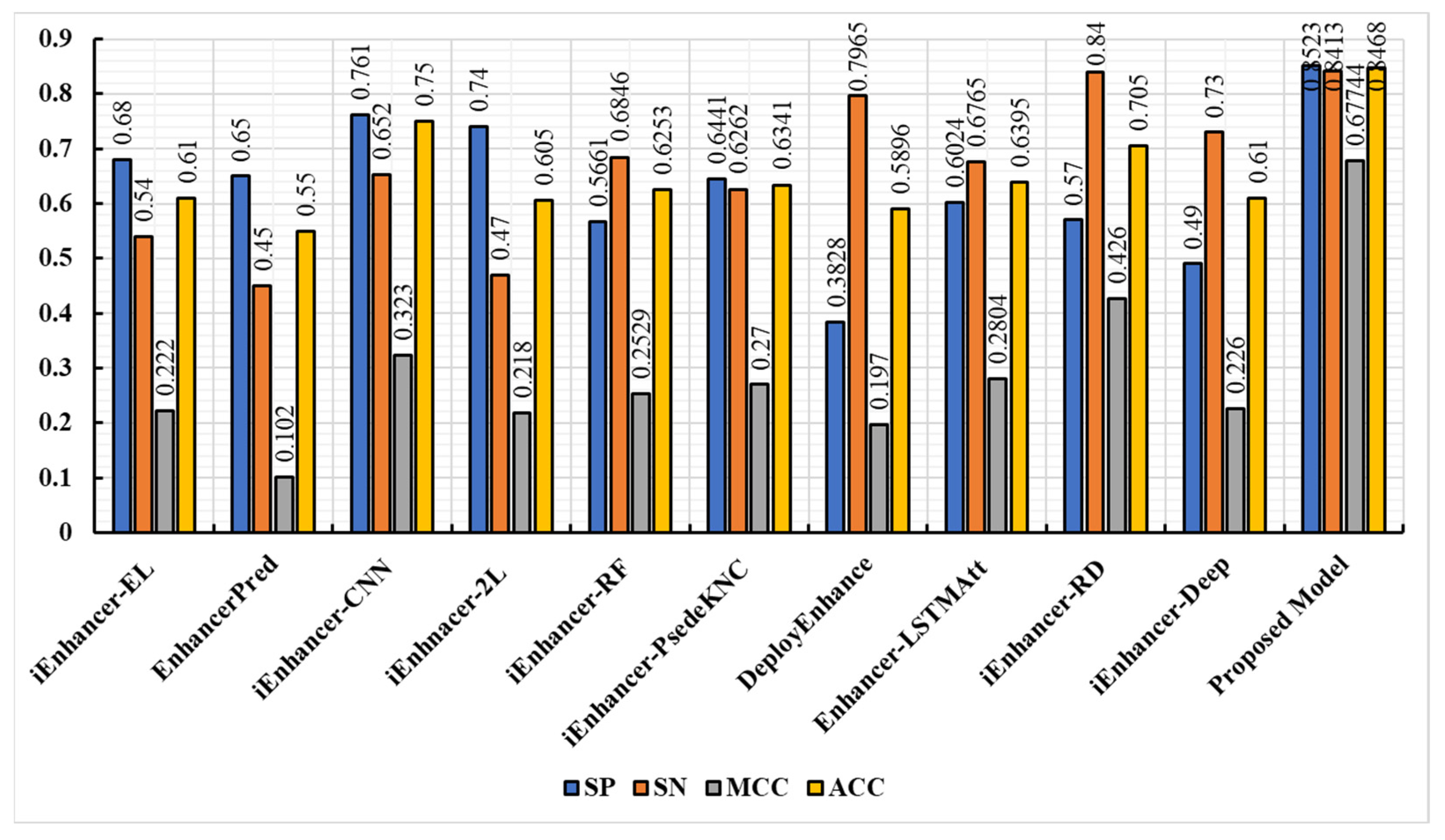
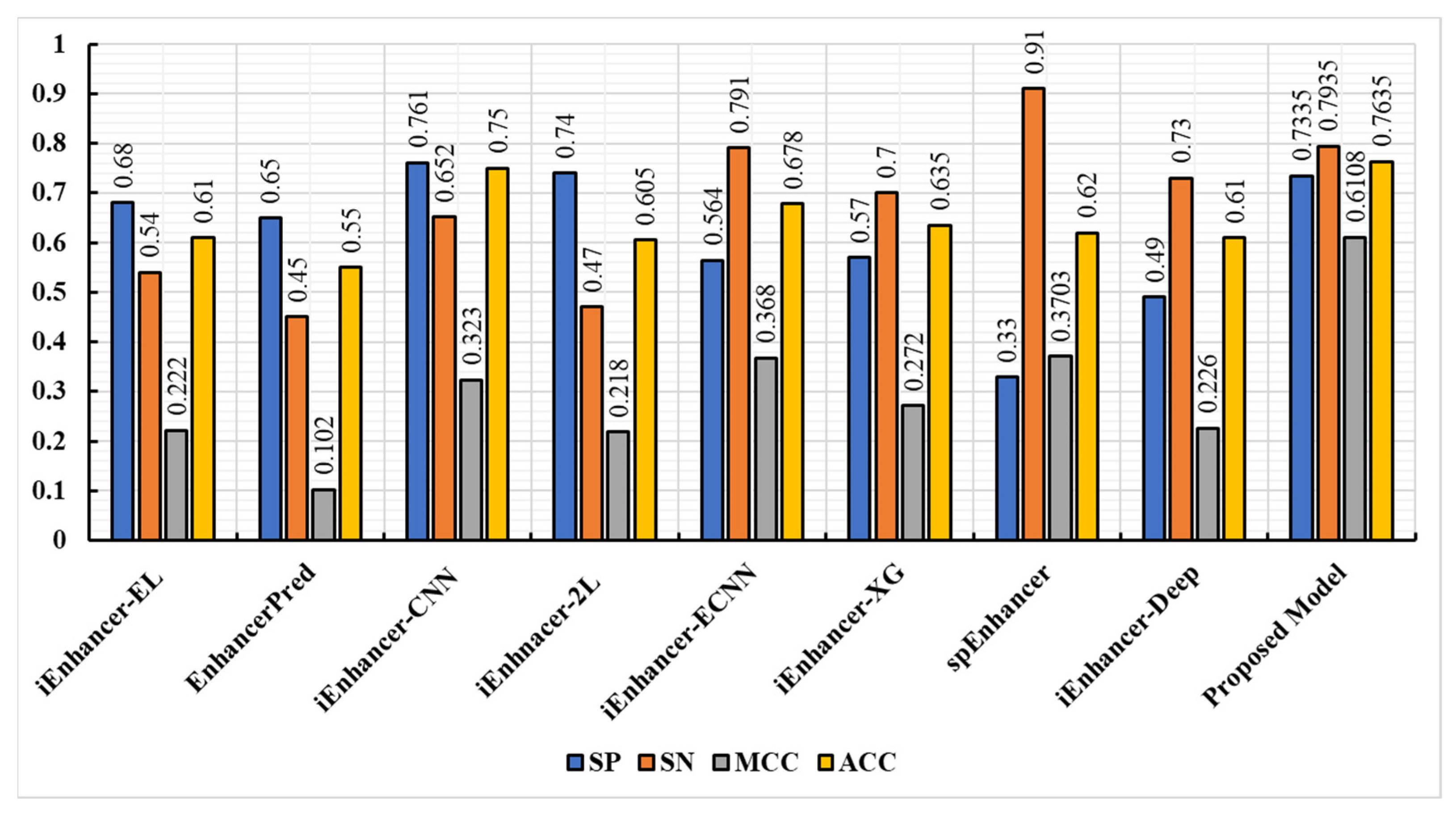
3.3. Comparison of the Proposed Model with Existing Techniques
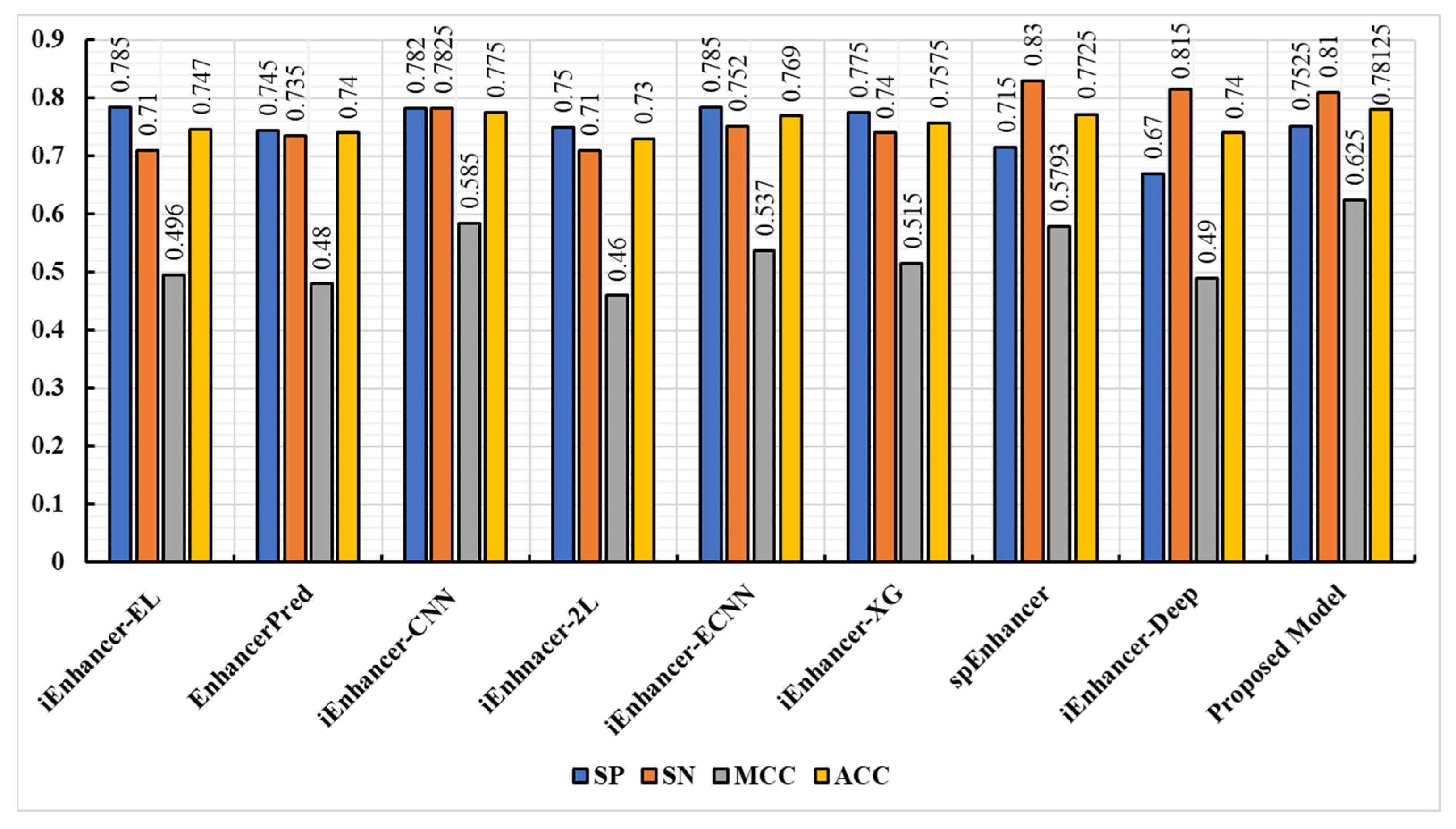
3.4. Experimental Result on Independent Dataset
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pennacchio, L.A.; Bickmore, W.; Dean, A.; Nobrega, M.A.; Bejerano, G. Enhancers: Five essential questions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plank, J.L.; Dean, A. Enhancer function: Mechanistic and genome-wide insights come together. Mol. Cell 2014, 55, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Fang, L.; Long, R.; Lan, X.; Chou, K.-C. iEnhancer-2L: A two-layer predictor for identifying enhancers and their strength by pseudo k-tuple nucleotide composition. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejerano, G.; Pheasant, M.; Makunin, I.; Stephen, S.; Kent, W.J.; Mattick, J.S.; Haussler, D. Ultraconserved elements in the human genome. Science 2004, 304, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.; Thodberg, M.; Vitezic, M.; Bornholdt, J.; Vitting-Seerup, K.; Chen, Y.; Coskun, M.; Li, Y.; Lo, B.Z.S.; Klausen, P.; et al. Characterization of the enhancer and promoter landscape of inflammatory bowel disease from human colon biopsies. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlyueva, D.; Stampfel, G.; Stark, A. Transcriptional enhancers: From properties to genome-wide predictions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, M.; Habib, S.; Khan, N.F.; Alsharekh, M.F.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. A Deep-Learning Model for Real-Time Red Palm Weevil Detection and Localization. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhaib, M.; Shaikh, F.A.; Tanweer, W.; Alnajim, A.M.; Alyahya, S.; Khan, S.; Usman, M.; Islam, M.; Hasan, M.K. Faults Feature Extraction Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Artificial Neural Network for Induction Motor Availability Monitoring—Internet of Things Enabled Environment. Energies 2022, 15, 7888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albattah, W.; Kaka Khel, M.H.; Habib, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Abdul Kadir, K. Hajj Crowd Management Using CNN-Based Approach. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 66, 2183–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Lee, D.; Mohammad-Noori, M.; Beer, M.A. Enhanced regulatory sequence prediction using gapped k-mer features. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleftogiannis, D.; Kalnis, P.; Bajic, V.B. DEEP: A general computational framework for predicting enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Miranda-Saavedra, D. Genome-wide enhancer prediction from epigenetic signatures using genetic algorithm-optimized support vector machines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, N.; Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Wagner, U.; Wang, W.; Stamatoyannopoulos, J.; Ernst, J.; Kellis, M.; Ren, B. RFECS: A random-forest based algorithm for enhancer identification from chromatin state. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Gan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Guan, J. A new method for enhancer prediction based on deep belief network. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, F.; Ren, C.; Ouyang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Bo, X.; Shu, W. BiRen: Predicting enhancers with a deep-learning-based model using the DNA sequence alone. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, K.; Huang, D.S.; Chou, K.C. iEnhancer-EL: Identifying enhancers and their strength with ensemble learning approach. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3835–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Muhammad, K.; Haq, I.U.; Ullah, A.; Khattak, S.U.; Sajjad, M. Splicing sites prediction of human genome using machine learning techniques. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 30439–30460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ikram, S.; Ahmad, J.; Ullah, W.; Hassan, F.; Khattak, S.U.; Rehman, I.U. GASPIDs Versus Non-GASPIDs-Differentiation Based on Machine Learning Approach. Curr. Bioinform. 2020, 15, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Alsanea, M.; Aloraini, M.; Al-Rawashdeh, H.S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. An Efficient and Effective Deep Learning-Based Model for Real-Time Face Mask Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.D.; Alam, W.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K. Identification of functional piRNAs using a convolutional neural network. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2020, 9, 8491–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; He, W. EnhancerPred: A predictor for discovering enhancers based on the combination and selection of multiple features. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Ullah, A.; Haq, I.U.; Muhammad, K.; Sajjad, M.; Baik, S.W. CNN features with bi-directional LSTM for real-time anomaly detection in surveillance networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 16979–16995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Ullah, A.; Hussain, T.; Khan, Z.A.; Baik, S.W. An efficient anomaly recognition framework using an attention residual LSTM in surveillance videos. Sensors 2021, 21, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, W.; Ullah, A.; Hussain, T.; Muhammad, K.; Heidari, A.A.; Del Ser, J.; Baik, S.W.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C. Artificial Intelligence of Things-assisted two-stream neural network for anomaly detection in surveillance Big Video Data. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 129, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Hussain, T.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Gupta, S.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. Randomly Initialized CNN with Densely Connected Stacked Autoencoder for Efficient Fire Detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 116, 105403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, H.; Hussain, T.; Agarwal, M.; Khan, Z.A.; Gupta, S.K.; Baik, S.W. Optimized Dual Fire Attention Network and Medium-Scale Fire Classification Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6331–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.L.; Kuhn, G.M.; Williams, R.J. Dynamic recurrent neural networks: Theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Ullah, A.; Malik, K.M.; Saudagar, A.K.J.; Khan, M.B.; Hasanat, M.H.A.; AlTameem, A.; AlKhathami, M. Multi-Stage Temporal Convolution Network for COVID-19 Variant Classification. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arras, L.; Montavon, G.; Müller, K.-R.; Samek, W. Explaining recurrent neural network predictions in sentiment analysis. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.07206. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, W.; Hussain, T.; Khan, Z.A.; Haroon, U.; Baik, S.W. Intelligent dual stream CNN and echo state network for anomaly detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 253, 109456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, L. Hierarchical recurrent neural network for skeleton based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1110–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.A.; Ullah, A.; Haq, I.U.; Hamdy, M.; Mauro, G.M.; Muhammad, K.; Hijji, M.; Baik, S.W. Efficient short-term electricity load forecasting for effective energy management. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Hussain, T.; Haq, I.U.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Baik, S.W. Towards efficient and effective renewable energy prediction via deep learning. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 10230–10243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami-Namini, S.; Tavakoli, N.; Namin, A.S. The performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in forecasting time series. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 3285–3292. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1259. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Ellis, D.P. Feed-forward networks with attention can solve some long-term memory problems. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.08756. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.; Hussain, A.; Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Albattah, W. Towards Efficient Detection and Crowd Management for Law Enforcing Agencies. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics (CAIDA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–7 April 2021; pp. 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, D.Y.; Khanal, J.; Tayara, H.; Chong, K.T. iEnhancer-RF: Identifying enhancers and their strength by enhanced feature representation using random forest. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2021, 212, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. iEnhancer-PsedeKNC: Identification of enhancers and their subgroups based on Pseudo degenerate kmer nucleotide composition. Neurocomputing 2016, 217, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsharekh, M.F.; Habib, S.; Dewi, D.A.; Albattah, W.; Islam, M.; Albahli, S. Improving the Efficiency of Multistep Short-Term Electricity Load Forecasting via R-CNN with ML-LSTM. Sensors 2022, 22, 6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wang, S.; Xia, X. iEnhancer-RD: Identification of enhancers and their strength using RKPK features and deep neural networks. Anal. Biochem. 2021, 630, 114318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Ren, X.; Fu, X.; Peng, L.; Gao, M.; Zeng, X. iEnhancer-XG: Interpretable sequence-based enhancers and their strength predictor. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.Q.K.; Yapp, E.K.Y.; Ho, Q.-T.; Nagasundaram, N.; Ou, Y.-Y.; Yeh, H.-Y. iEnhancer-5Step: Identifying enhancers using hidden information of DNA sequences via Chou’s 5-step rule and word embedding. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 571, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asim, M.N.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Malik, M.I.; Dengel, A.; Ahmed, S. Enhancer-dsnet: A supervisedly prepared enriched sequence representation for the identification of enhancers and their strength. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, S.; Hussain, A.; Albattah, W.; Islam, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, R.U.; Khan, K. Abnormal Activity Recognition from Surveillance Videos Using Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2021, 21, 8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Khan, I.; Aladhadh, S.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. External Features-Based Approach to Date Grading and Analysis with Image Processing. Emerg. Sci. J. 2022, 6, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| Dataset | |
| Enhancer sequences | |
| Non-enhancer sequence | |
| Reset gate | |
| Update gate | |
| Hidden state | |
| Attention weights | |
| Accuracy | |
| Sensitivity | |
| Matthews’ Correlation Coefficient | |
| Specificity | |
| True Positive | |
| True Negative | |
| False Positive | |
| False Negative |
| Layer | Output Shape | Param |
|---|---|---|
| Input layer | [(DS, NS, Fs)] | 0 |
| conv1d (Conv1D)) | (None, 298, 27) | 459 |
| max_pooling1d (MaxPooling1D) | (None, 99, 27) | 0 |
| dropout (Dropout) | (None, 99, 27) | 0 |
| conv1d_1 (Conv1D) | (None, 99, 27) | 770 |
| bidirectional (Bidirectional GRU) | (None, 256) | 110,592 |
| Attention (None, 64) | (None, 256) | 0 |
| Dropout_1 (Dropout) | (None, 256) | 0 |
| Dense (Dense) | (None, 128) | 32,896 |
| Dense_1 (Dense) | (None, 64) | 8256 |
| Dense_2 (Dense) | (None, 64) | 4160 |
| Dense_3 (Dense) | (None, 16) | 1040 |
| Dense_4 (Dense) | (None, 2) | 34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aladhadh, S.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Habib, S.; Alabdulatif, A.; Khattak, S.U.; Islam, M. An Efficient Lightweight Hybrid Model with Attention Mechanism for Enhancer Sequence Recognition. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010070
Aladhadh S, Almatroodi SA, Habib S, Alabdulatif A, Khattak SU, Islam M. An Efficient Lightweight Hybrid Model with Attention Mechanism for Enhancer Sequence Recognition. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010070
Chicago/Turabian StyleAladhadh, Suliman, Saleh A. Almatroodi, Shabana Habib, Abdulatif Alabdulatif, Saeed Ullah Khattak, and Muhammad Islam. 2023. "An Efficient Lightweight Hybrid Model with Attention Mechanism for Enhancer Sequence Recognition" Biomolecules 13, no. 1: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010070
APA StyleAladhadh, S., Almatroodi, S. A., Habib, S., Alabdulatif, A., Khattak, S. U., & Islam, M. (2023). An Efficient Lightweight Hybrid Model with Attention Mechanism for Enhancer Sequence Recognition. Biomolecules, 13(1), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010070








