Modeling Human Lung Cells Exposure to Wildfire Uncovers Aberrant lncRNAs Signature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture Conditions and Seeding
2.2. Smoke Generation
2.3. Direct Smoke Exposure (DSE) Using Air-Liquid Interface (ALI) Chamber
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Cellular Growth Assay
2.6. RNA Extraction
2.7. Library Preperation and Sequencing
2.8. Quality Control and Read Mapping
2.9. Differential Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Exposure System Setup, System Validation and Optimization, and Smoke Exposure Duration
3.2. Exposure System Setup
3.3. Validation and Optimization of Cell Seeding within ALI Exposure Chambers
3.4. Validation and Optimization of Smoke Exposure Duration and Experimental Setup
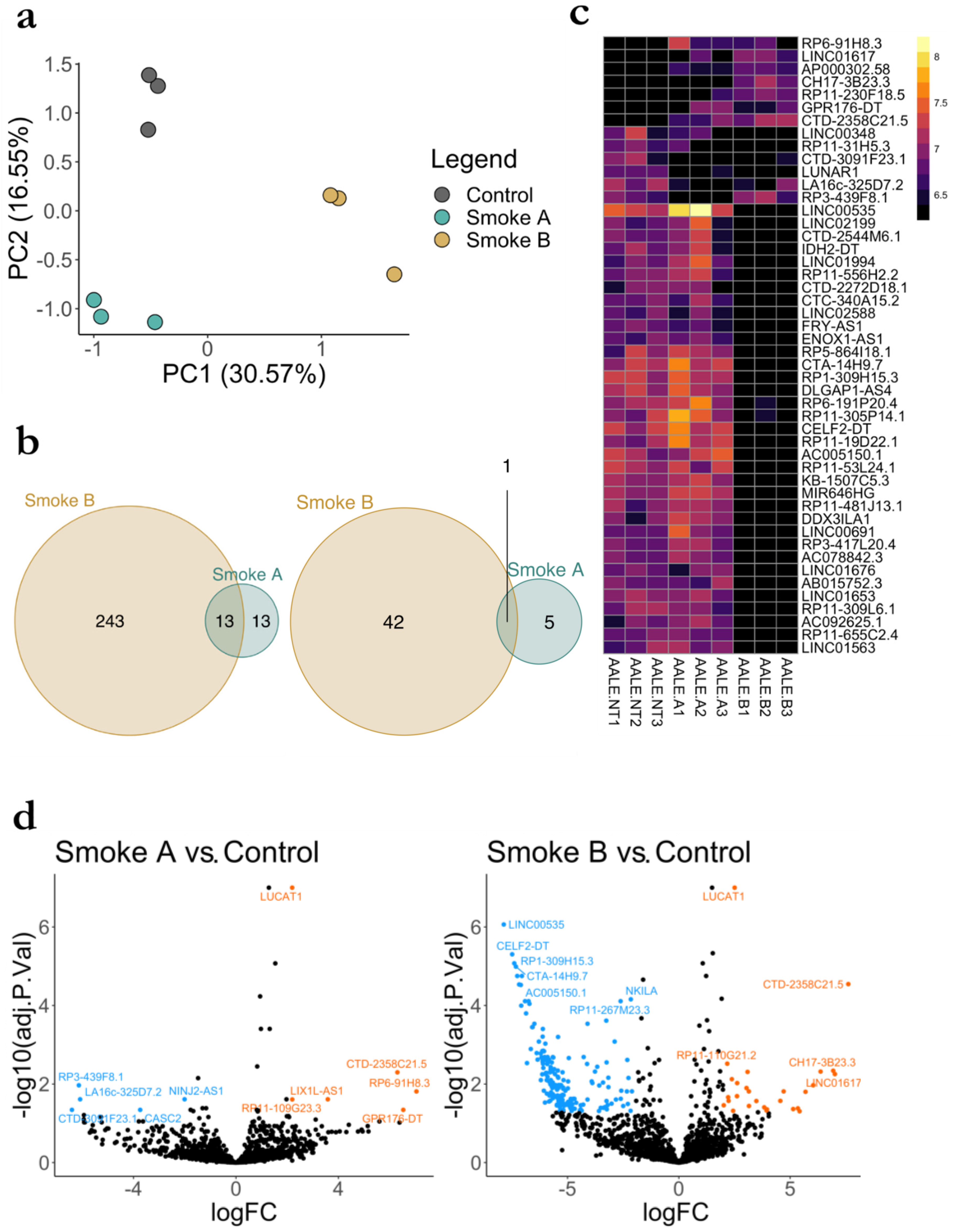
3.5. RNA Seq Analysis of LncRNA
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Williams, A.P. Impact of anthropogenic climate change on wildfire across western US forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11770–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, F.H.; Henderson, S.B.; Yang, C.; Randerson, J.T.; Marlier, M.; Defries, R.S.; Kinney, P.; Bowman, D.M.J.S.; Brauer, M. Estimated Global Mortality Attributable to Smoke from Landscape Fires. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, C.; Samburova, V.; Sengupta, D.; Iaukea-Lum, M.; Watts, A.C.; Moosmüller, H.; Khlystov, A.Y. Physical and chemical characterization of aerosol in fresh and aged emissions from open combustion of biomass fuels. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning—An updated assessment. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 19, 8523–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.C.; Pereira, G.; Uhl, S.A.; Bravo, M.A.; Bell, M.L. A systematic review of the physical health impacts from non-occupational exposure to wildfire smoke. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi, D.; Haswell, L.E.; Foss-Smith, G.; Hewitt, K.; Asquith, N.; Corke, S.; Phillips, G. Evaluation of an air–liquid interface cell culture model for studies on the inflammatory and cytotoxic responses to tobacco smoke aerosols. Toxicol. Vitr. 2015, 29, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mülhopt, S.; Dilger, M.; Diabaté, S.; Schlager, C.; Krebs, T.; Zimmermann, R.; Buters, J.; Oeder, S.; Wäscher, T.; Weiss, C.; et al. Toxicity testing of combustion aerosols at the air–liquid interface with a self-contained and easy-to-use exposure system. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 96, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.T.T.; Hinwood, A.L.; Callan, A.C.; Zosky, G.; Stock, W.D. In vitro assessment of the toxicity of bushfire emissions: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 603, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aske, K.C.; Waugh, C.A. Expanding the 3R principles. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 1490–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strech, D.; Dirnagl, U. 3Rs missing: Animal research without scientific value is unethical. BMJ Open Sci. 2019, 3, e000048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Coyle, J.P.; Xiong, R.; Wang, Y.; Heflich, R.H.; Ren, B.; Gwinn, W.M.; Hayden, P.; Rojanasakul, L. Invited review: Human air-liquid-interface organotypic airway tissue models derived from primary tracheobronchial epithelial cells—Overview and perspectives. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2021, 57, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, G.; Koch, W.; Ritter, D.; Gutleb, A.C.; Larsen, S.T.; Loret, T.; Zanetti, F.; Constant, S.; Chortarea, S.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; et al. Air–Liquid Interface In Vitro Models for Respiratory Toxicology Research: Consensus Workshop and Recommendations. Appl. Vitr. Toxicol. 2018, 4, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkel, J.M. Visiting “Noncodarnia”. BioTechniques 2013, 54, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, F.; Valadkhan, S. Computational analysis of functional long noncoding RNAs reveals lack of peptide-coding capacity and parallels with 3’ UTRs. RNA 2012, 18, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, K.; Henderson, L.; Bonetti, A.; Carninci, P. Discovery and functional analysis of lncRNAs: Methodologies to investigate an uncharacterized transcriptome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1859, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Feng, D.; Li, M.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Hao, B.; Li, D.; Ding, K. Transcriptomic Analysis of mRNA-lncRNA-miRNA Interactions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16012–16096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, H.; Jin, C.; Cheng, M.; Xu, D. Long Non-coding RNA HIX003209 Promotes Inflammation by Sponging miR-6089 via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.N.; Antonangeli, F. LncRNAs: New Players in Apoptosis Control. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 2014, 473857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.; Luettich, K.; Heguy, A.; Hackett, N.R.; Harvey, B.-G.; Crystal, R.G. Monoallelic Up-Regulation of the Imprinted H19 Gene in Airway Epithelium of Phenotypically Normal Cigarette Smokers. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.M.; Perez, D.S.; Pritchett, J.R.; Halling, M.L.; Tang, H.; Smith, D.I. Identification of Long stress-induced non-coding transcripts that have altered expression in cancer. Genomics 2010, 95, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beane, J.; Vick, J.; Schembri, F.; Anderlind, C.; Gower, A.; Campbell, J.; Luo, L.; Zhang, X.H.; Xiao, J.; Alekseyev, Y.O.; et al. Characterizing the Impact of Smoking and Lung Cancer on the Airway Transcriptome Using RNA-Seq. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Tian, L.; Zhou, C.; He, M.Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhou, F.; Shi, S.; Feng, X.; et al. LncRNA profile study reveals a three-lncRNA signature associated with the survival of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut 2014, 63, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinzl, M.; Marberger, M.; Horvath, S.; Chypre, C. DD3PCA3 RNA analysis in urine--a new perspective for detecting prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2004, 46, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gál, Z.; Gézsi, A.; Semsei, Á.F.; Nagy, A.; Sultész, M.; Csoma, Z.; Tamási, L.; Gálffy, G.; Szalai, C. Investigation of circulating lncRNAs as potential biomarkers in chronic respiratory diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segeritz, C.-P.; Vallier, L. Cell Culture Growing Cells as Model Systems In Vitro. In Basic Science Methods for Clinical Researchers; Jalali, M., Saldanha, F.Y.L., Jalali, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 151–172. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC, version 0.11.9; Babraham Bioinformatics: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, B.; Rood, J.; Singer, E. BBMerge–Accurate paired shotgun read merging via overlap. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Ferreira, A.-M.; Johnson, R.; Jungreis, I.; Loveland, J.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.; Armstrong, J.; et al. GENCODE reference annotation for the human and mouse genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D766–D773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. feature Counts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; Version 4.0.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Su, Y.; Zhang, X. A Robust 6-lncRNA Prognostic Signature for Predicting the Prognosis of Patients With Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.E.; Brauer, M.; Johnston, F.H.; Jerrett, M.; Balmes, J.R.; Elliott, C.T. Critical Review of Health Impacts of Wildfire Smoke Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.M.; Garcia-Menendez, F. Uncertainty in Health Impact Assessments of Smoke From a Wildfire Event. GeoHealth 2022, 6, e2021GH000526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ao, L.; Yang, J. Long non-coding RNAs in diseases related to inflammation and immunity. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, P.K.; Son, Y.; Petereit, J.; Khlystov, A.; Panella, R. Modeling Human Lung Cells Exposure to Wildfire Uncovers Aberrant lncRNAs Signature. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010155
Nguyen PK, Son Y, Petereit J, Khlystov A, Panella R. Modeling Human Lung Cells Exposure to Wildfire Uncovers Aberrant lncRNAs Signature. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(1):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010155
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Piercen K., Yeongkwon Son, Juli Petereit, Andrey Khlystov, and Riccardo Panella. 2023. "Modeling Human Lung Cells Exposure to Wildfire Uncovers Aberrant lncRNAs Signature" Biomolecules 13, no. 1: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010155
APA StyleNguyen, P. K., Son, Y., Petereit, J., Khlystov, A., & Panella, R. (2023). Modeling Human Lung Cells Exposure to Wildfire Uncovers Aberrant lncRNAs Signature. Biomolecules, 13(1), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13010155









