Network Dynamics Caused by Genomic Alteration Determine the Therapeutic Response to FGFR Inhibitors for Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Input-Output Relationships of the Lung Cancer Network Model
2.2. Selection of Functional Genomic Alterations
2.3. Mapping Genomic Alterations to Network Model
2.4. Defining Cell Line-Specific Initial State Probability
2.5. Attractor Landscape and Perturbation Analysis Using the Boolean Network Model of Lung Cancer
2.6. FGFR Inhibitor Response Data
3. Results
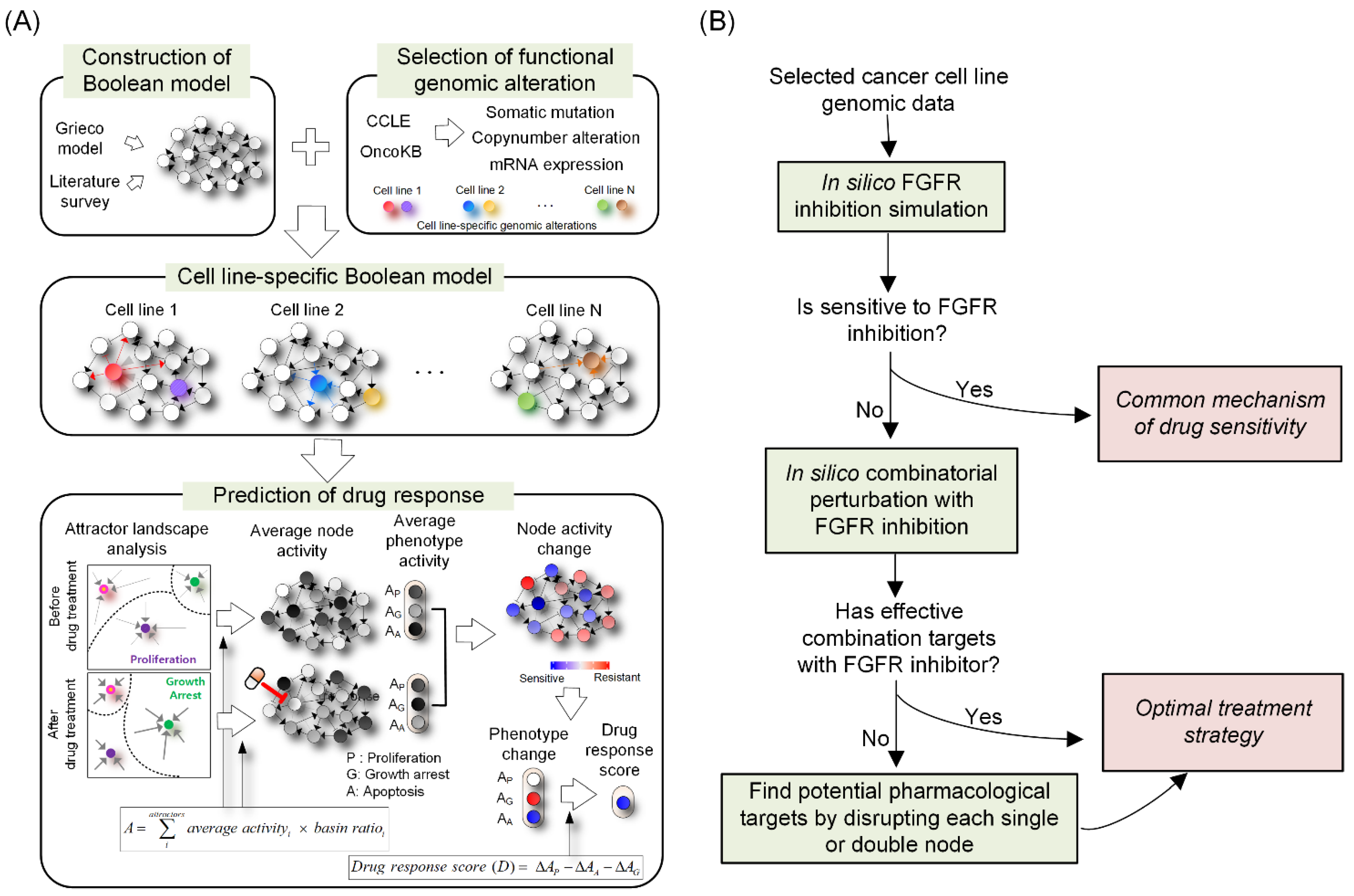
3.1. Network Dynamics-Based Drug Response Prediction
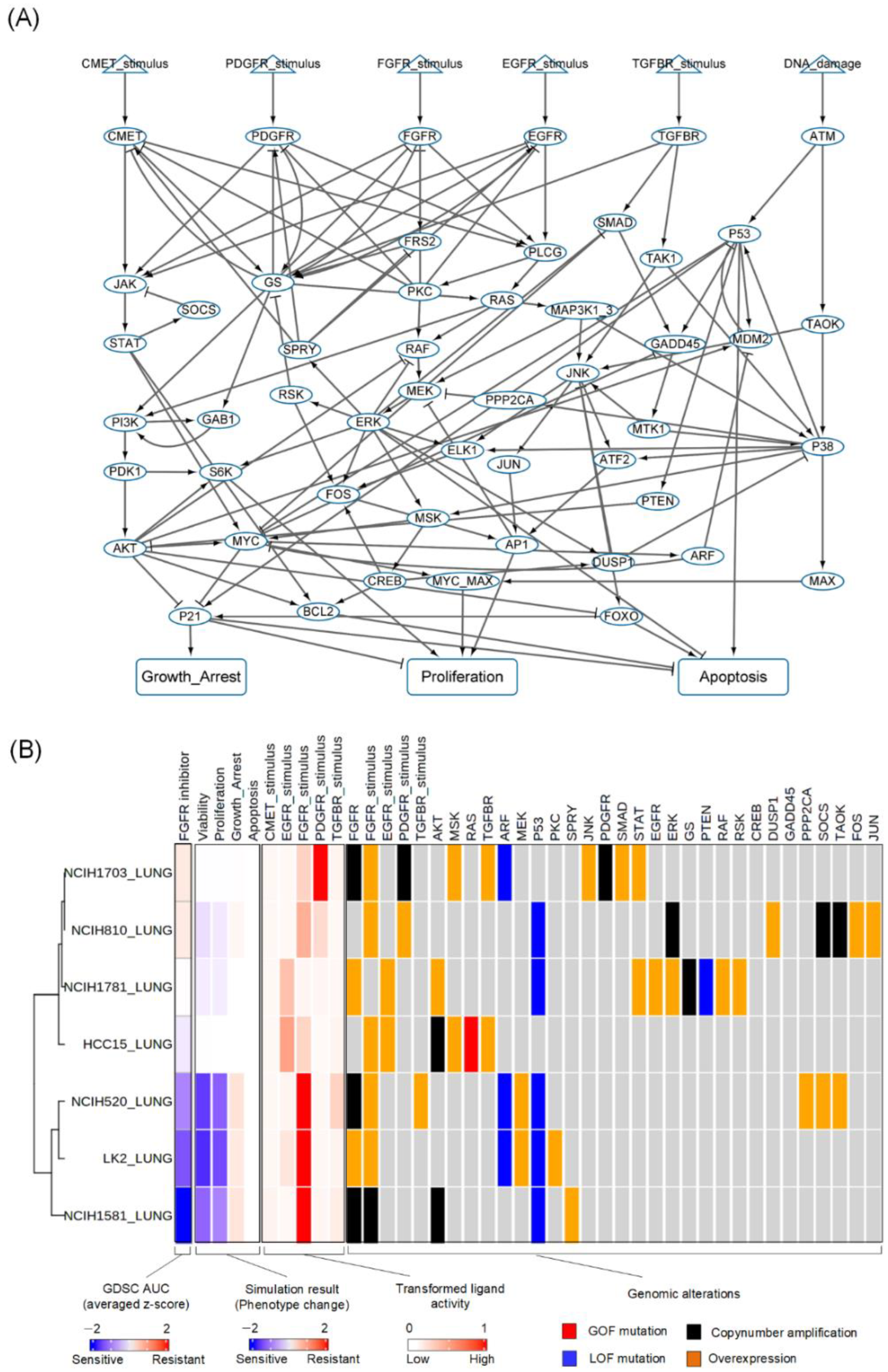
3.2. Construction of a Network Model of Lung Cancer
3.3. Reflecting Molecular Features of Lung Cancer Cell Lines to the Network Model
3.4. Prediction of Cell Line-Specific Drug Responses to FGFR Inhibitor
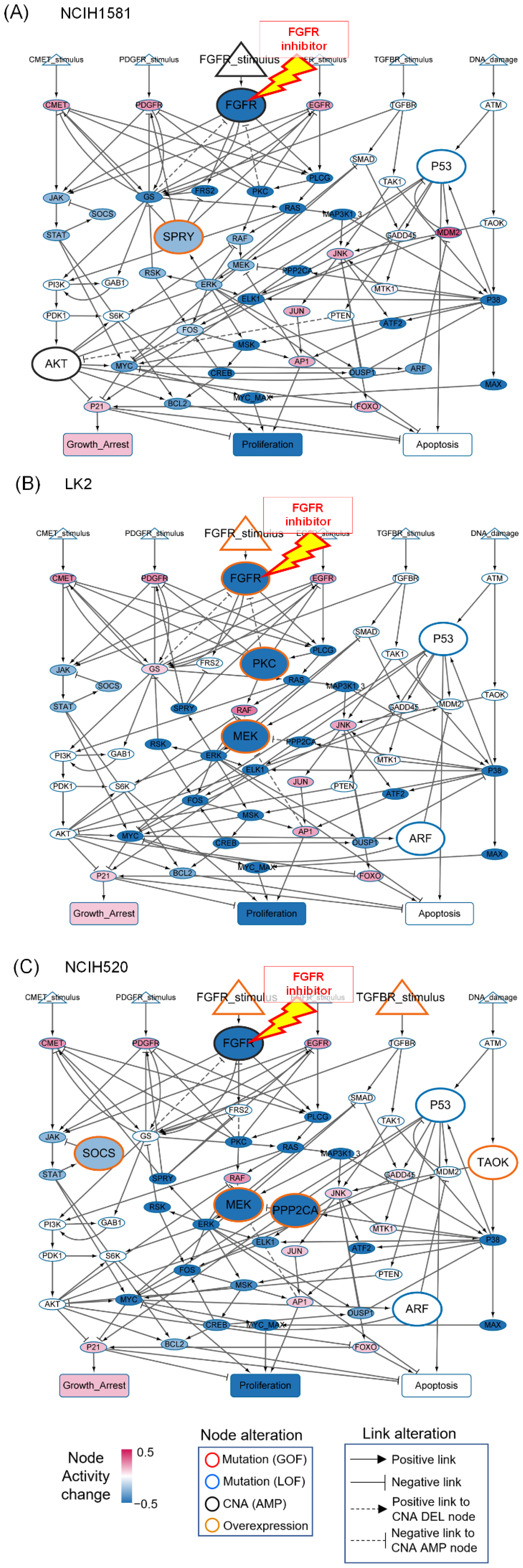
3.5. Resistant Responses to FGFR Inhibitor from the Representative Cell Line-Specific Network Models
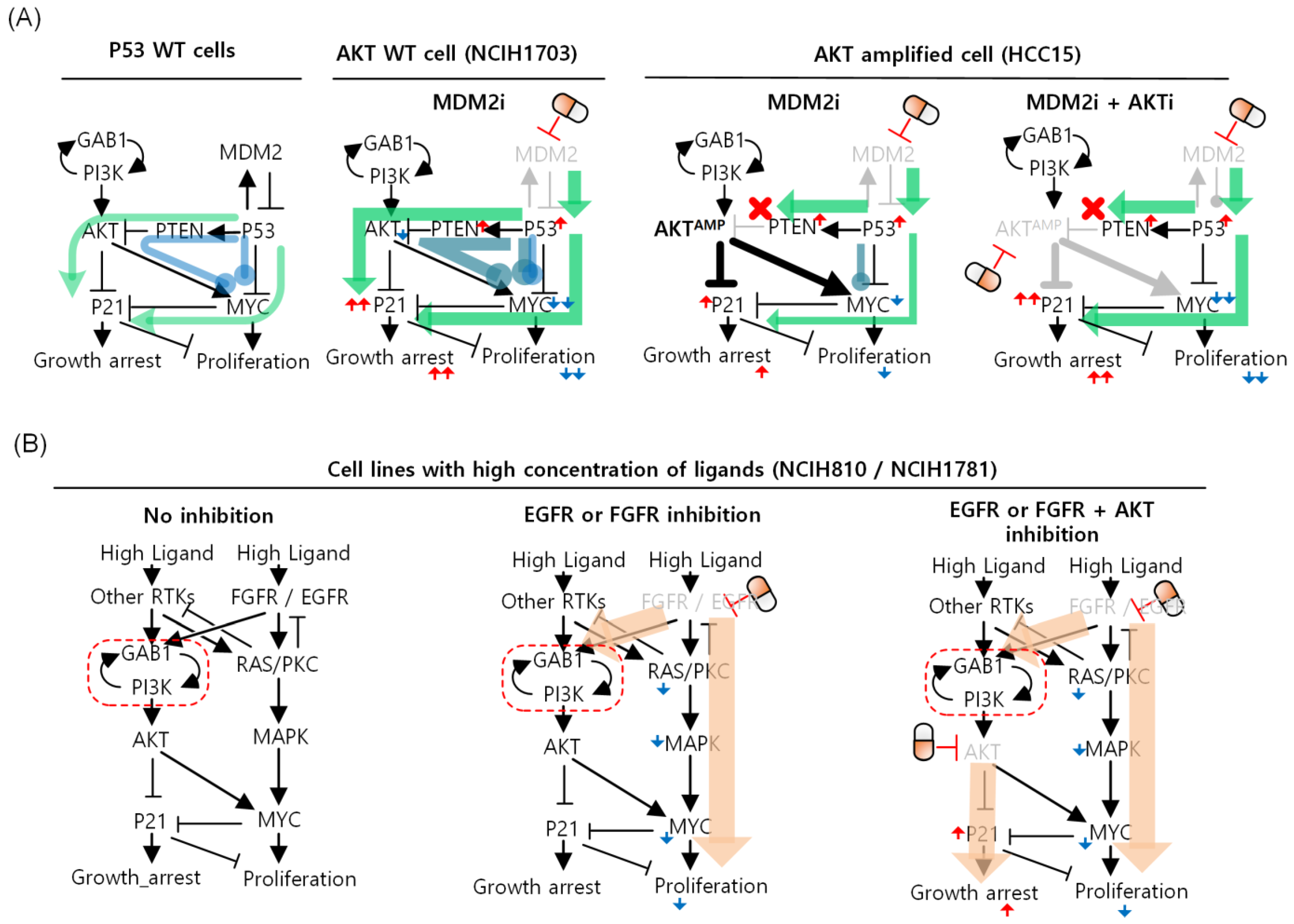
3.6. Differential Strategies and Mechanisms to Overcome FGFR Resistance
min(Drug response score of drug1, Drug response score of drug2)]
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jameson, J.L.; Longo, D.L. Precision medicine—Personalized, problematic, and promising. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Luo, X.; Jiang, C.; Zhao, H. Difficulties and challenges in the development of precision medicine. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, A.E.; Gould, C.R.; Grose, R.P. FGFR signalling in women’s cancers. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2832–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M.; Nakagama, H. FGF receptors: Cancer biology and therapeutics. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Parris, A.B.; Howard, E.W.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xing, Y.; Yang, X. FGFR inhibitor, AZD4547, impedes the stemness of mammary epithelial cells in the premalignant tissues of MMTV-ErbB2 transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumarola, C.; Cretella, D.; La Monica, S.; Bonelli, M.A.; Alfieri, R.; Caffarra, C.; Quaini, F.; Madeddu, D.; Falco, A.; Cavazzoni, A.; et al. Enhancement of the anti-tumor activity of FGFR1 inhibition in squamous cell lung cancer by targeting downstream signaling involved in glucose metabolism. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91841–91859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moes-Sosnowska, J.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1-4 Genetic Aberrations as Clinically Relevant Biomarkers in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 780650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Tao, W.; Wu, D.; Ma, F.; Li, N. Expression Atlas of FGF and FGFR Genes in Pancancer Uncovered Predictive Biomarkers for Clinical Trials of Selective FGFR Inhibitors. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5658904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, H.; Kitagawa, C.; Kogure, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Fujikawa, K.; Sagawa, T.; Iwasa, S.; Takahashi, N.; Fukao, T.; Tchinou, C.; et al. Safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of the fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor AZD4547 in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours: A Phase I study. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, P.; Massard, C.; Peltola, K.J.; Azaro, A.; Italiano, A.; Kristeleit, R.S.; Curigliano, G.; Lassen, U.; Arkenau, H.T.; Hakulinen, P.; et al. Phase I/IIa, open-label, multicentre study to evaluate the optimal dosing and safety of ODM-203 in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumours. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e001081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Xu, J.; Colvin, J.S.; McEwen, D.G.; MacArthur, C.A.; Coulier, F.; Gao, G.; Goldfarb, M. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 15292–15297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Iwata, T.; Leung, H.Y. Mechanisms of FGFR-mediated carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touat, M.; Ileana, E.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Andre, F.; Soria, J.C. Targeting FGFR Signaling in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.; Pearson, A.; Sharpe, R.; Lambros, M.; Geyer, F.; Lopez-Garcia, M.A.; Natrajan, R.; Marchio, C.; Iorns, E.; Mackay, A.; et al. FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.M.; Su, F.; Kalyana-Sundaram, S.; Khazanov, N.; Ateeq, B.; Cao, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Vats, P.; Wang, R.; Lin, S.F.; et al. Identification of targetable FGFR gene fusions in diverse cancers. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.K.; Cho, K.H. Boolean dynamics of biological networks with multiple coupled feedback loops. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fumia, H.F.; Martins, M.L. Boolean network model for cancer pathways: Predicting carcinogenesis and targeted therapy outcomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.Y.; Kim, T.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, D.H. The switching role of beta-adrenergic receptor signalling in cell survival or death decision of cardiomyocytes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, B.B.; Burke, J.M.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Sorger, P.K. Physicochemical modelling of cell signalling pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.M.; Cho, K.H. Discovery of a kernel for controlling biomolecular regulatory networks. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Rodriguez, J.; Alexopoulos, L.G.; Epperlein, J.; Samaga, R.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Klamt, S.; Sorger, P.K. Discrete logic modelling as a means to link protein signalling networks with functional analysis of mammalian signal transduction. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, S.A. Metabolic stability and epigenesis in randomly constructed genetic nets. J. Theor. Biol. 1969, 22, 437–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehar, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieco, L.; Calzone, L.; Bernard-Pierrot, I.; Radvanyi, F.; Kahn-Perles, B.; Thieffry, D. Integrative modelling of the influence of MAPK network on cancer cell fate decision. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H. Targeting the PDGF signaling pathway in tumor treatment. Cell Commun. Signal 2013, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: From bench to clinic. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2021, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeger, J.; Moser, C.; Hellerbrand, C.; Mycielska, M.E.; Glockzin, G.; Schlitt, H.J.; Geissler, E.K.; Stoeltzing, O.; Lang, S.A. Targeting FGFR/PDGFR/VEGFR impairs tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis by effects on tumor cells, endothelial cells, and pericytes in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flobak, A.; Baudot, A.; Remy, E.; Thommesen, L.; Thieffry, D.; Kuiper, M.; Laegreid, A. Discovery of Drug Synergies in Gastric Cancer Cells Predicted by Logical Modeling. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaux, J.P.; Le, X.; Vijayan, R.S.K.; Hicks, J.K.; Heeke, S.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Udagawa, H.; Skoulidis, F.; Tran, H.; et al. Structure-based classification predicts drug response in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. Nature 2021, 597, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. The Importance of Patient-Specific Factors for Hepatic Drug Response and Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshava, N.; Toh, T.S.; Yuan, H.; Yang, B.; Menden, M.P.; Wang, D. Defining subpopulations of differential drug response to reveal novel target populations. NPJ Syst. Biol. Appl. 2019, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzhauser, S.; Wild, N.; Zupancic, M.; Ursu, R.G.; Bersani, C.; Nasman, A.; Kostopoulou, O.N.; Dalianis, T. Targeted Therapy with PI3K and FGFR Inhibitors on Human Papillomavirus Positive and Negative Tonsillar and Base of Tongue Cancer Lines with and without Corresponding Mutations. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 640490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Choi, S.R.; Cho, K.-H. Network Dynamics Caused by Genomic Alteration Determine the Therapeutic Response to FGFR Inhibitors for Lung Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091197
Lee J, Choi SR, Cho K-H. Network Dynamics Caused by Genomic Alteration Determine the Therapeutic Response to FGFR Inhibitors for Lung Cancer. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(9):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091197
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jonghoon, Sea Rom Choi, and Kwang-Hyun Cho. 2022. "Network Dynamics Caused by Genomic Alteration Determine the Therapeutic Response to FGFR Inhibitors for Lung Cancer" Biomolecules 12, no. 9: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091197
APA StyleLee, J., Choi, S. R., & Cho, K.-H. (2022). Network Dynamics Caused by Genomic Alteration Determine the Therapeutic Response to FGFR Inhibitors for Lung Cancer. Biomolecules, 12(9), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12091197





