Darling: A Web Application for Detecting Disease-Related Biomedical Entity Associations with Literature Mining
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
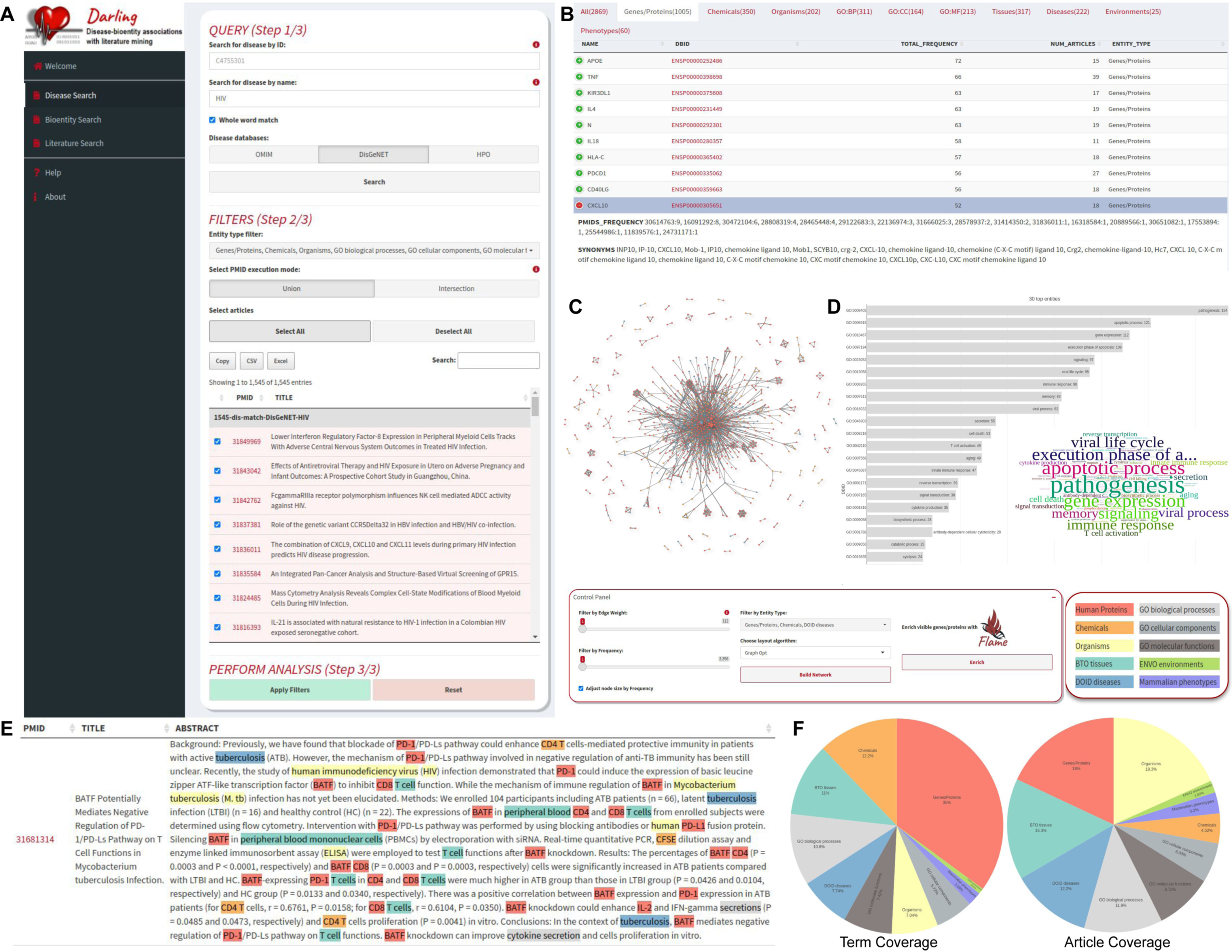
2.2. Darling Application and Analysis
2.3. Implementation
3. Results
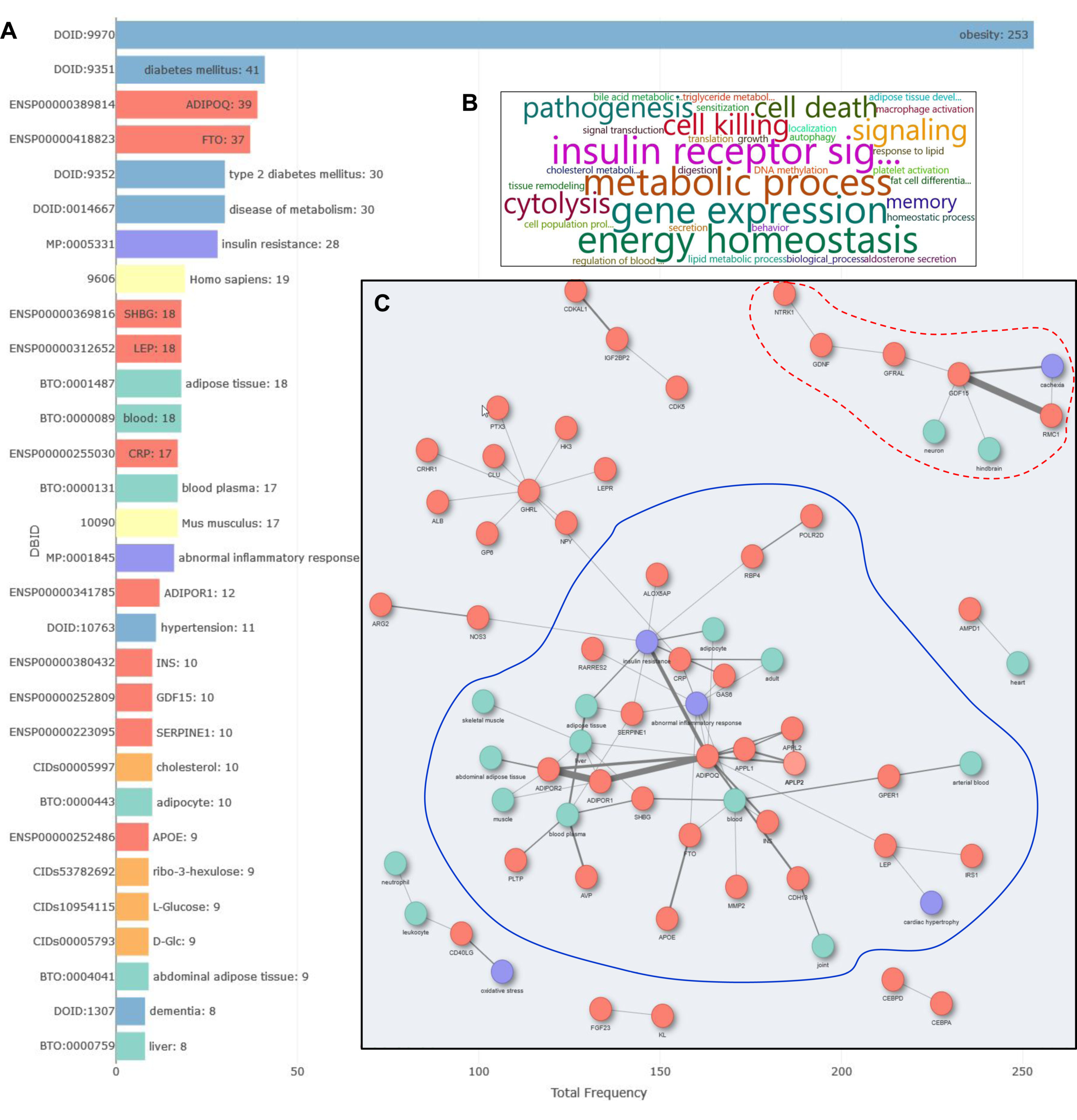
3.1. Investigating the Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Diseases
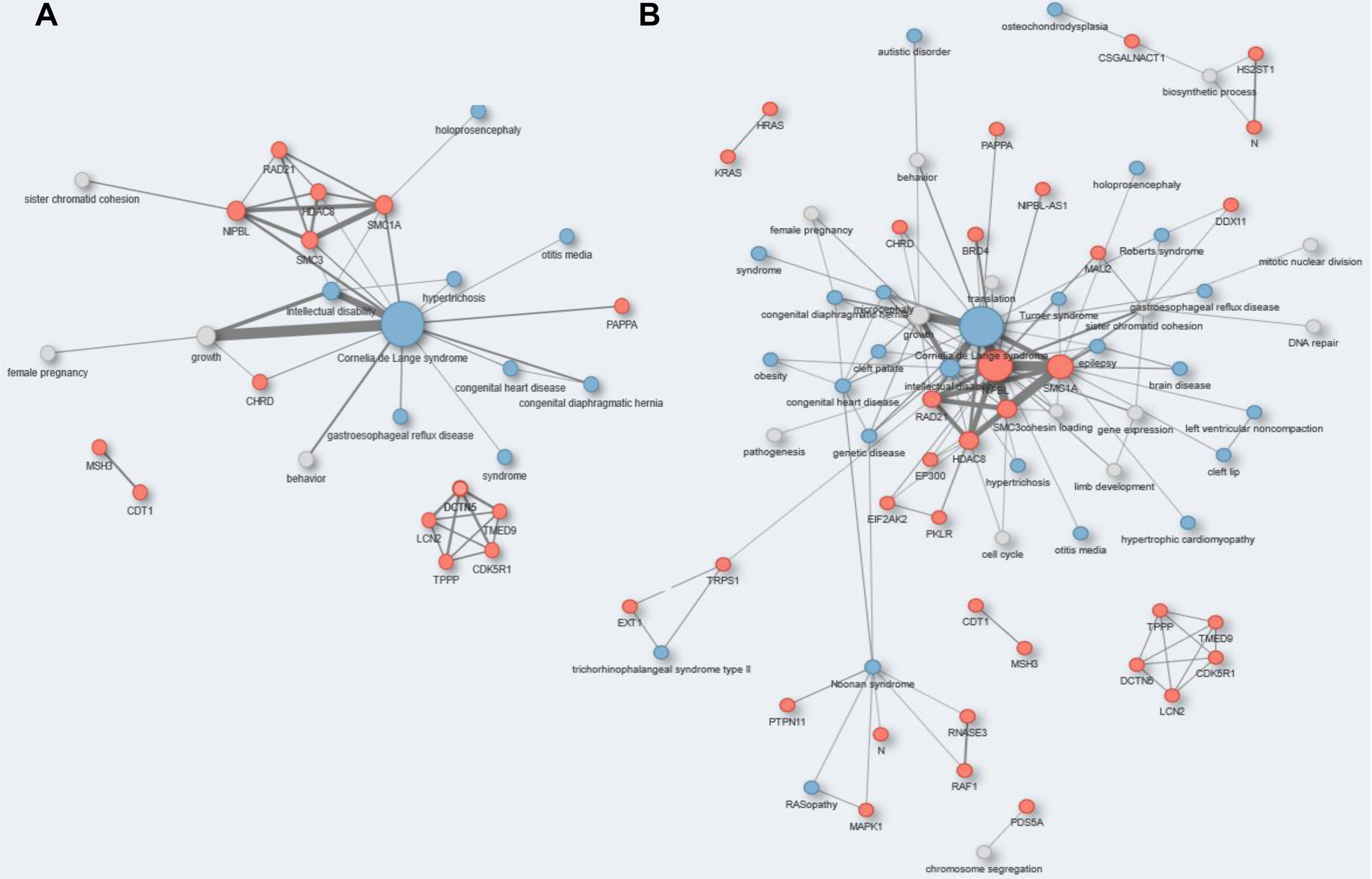
3.2. Querying Multiple Disease Databases Simultaneously with Darling
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, R.J. PubMed Central: The GenBank of the published literature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 381–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lightbody, G.; Haberland, V.; Browne, F.; Taggart, L.; Zheng, H.; Parkes, E.; Blayney, J.K. Review of applications of high-throughput sequencing in personalized medicine: Barriers and facilitators of future progress in research and clinical application. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1795–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheerkoot-Jalim, S.; Khedo, K.K. A systematic review of text mining approaches applied to various application areas in the biomedical domain. J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 25, 642–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybyła, P.; Shardlow, M.; Aubin, S.; Bossy, R.; Eckart de Castilho, R.; Piperidis, S.; McNaught, J.; Ananiadou, S. Text mining resources for the life sciences. Database 2016, 2016, baw145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebholz-Schuhmann, D.; Oellrich, A.; Hoehndorf, R. Text-mining solutions for biomedical research: Enabling integrative biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Lo, K. Text mining approaches for dealing with the rapidly expanding literature on COVID-19. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, N.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Theodosiou, T.; Iliopoulos, I. Protein-protein interaction predictions using text mining methods. Methods S. Diego Calif. 2015, 74, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, N.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Pafilis, E.; Theodosiou, T.; Schneider, R.; Satagopam, V.P.; Ouzounis, C.A.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Promponas, V.J.; Iliopoulos, I. BioTextQuest(+): A knowledge integration platform for literature mining and concept discovery. Bioinforma. Oxf. Engl. 2014, 30, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papanikolaou, N.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Theodosiou, T.; Vizirianakis, I.S.; Iliopoulos, I. DrugQuest—A text mining workflow for drug association discovery. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletscher-Frankild, S.; Pallejà, A.; Tsafou, K.; Binder, J.X.; Jensen, L.J. DISEASES: Text mining and data integration of disease-gene associations. Methods S. Diego Calif. 2015, 74, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, H.; Paragkamian, S.; Ninidakis, S.; Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Jensen, L.J.; Pafilis, E. PREGO: A Literature and Data-Mining Resource to Associate Microorganisms, Biological Processes, and Environment Types. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pafilis, E.; O′Donoghue, S.I.; Jensen, L.J.; Horn, H.; Kuhn, M.; Brown, N.P.; Schneider, R. Reflect: Augmented browsing for the life scientist. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 508–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pafilis, E.; Buttigieg, P.L.; Ferrell, B.; Pereira, E.; Schnetzer, J.; Arvanitidis, C.; Jensen, L.J. EXTRACT: Interactive extraction of environment metadata and term suggestion for metagenomic sample annotation. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2016, 2016, baw005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuruoka, Y.; Tsujii, J.; Ananiadou, S. FACTA: A text search engine for finding associated biomedical concepts. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2559–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltoumas, F.A.; Zafeiropoulou, S.; Karatzas, E.; Paragkamian, S.; Thanati, F.; Iliopoulos, I.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Schneider, R.; Jensen, L.J.; Pafilis, E.; et al. OnTheFly2.0: A text-mining web application for automated biomedical entity recognition, document annotation, network and functional enrichment analysis. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2021, 3, lqab090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleuren, W.W.M.; Verhoeven, S.; Frijters, R.; Heupers, B.; Polman, J.; van Schaik, R.; de Vlieg, J.; Alkema, W. CoPub update: CoPub 5.0 a text mining system to answer biological questions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W450–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolino, A.; Di Maria, A.; Rapicavoli, R.V.; Alaimo, S.; Bellomo, L.; Billeci, F.; Borzì, S.; Ferragina, P.; Ferro, A.; Pulvirenti, A. NETME: On-the-fly knowledge network construction from biomedical literature. Appl. Netw. Sci. 2022, 7, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-D.; Wang, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Okuda, S.; Callahan, T.J.; Cohen, K.B. Open Agile text mining for bioinformatics: The PubAnnotation ecosystem. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-H.; Kao, H.-Y.; Lu, Z. PubTator: A web-based text mining tool for assisting biocuration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W518–W522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, A.R.; Lang, F.-M. An overview of MetaMap: Historical perspective and recent advances. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2010, 17, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fontaine, J.-F.; Barbosa-Silva, A.; Schaefer, M.; Huska, M.R.; Muro, E.M.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. MedlineRanker: Flexible ranking of biomedical literature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W141–W146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- More, P.; Bindila, L.; Wild, P.; Andrade-Navarro, M.; Fontaine, J.-F. LipiDisease: Associate lipids to diseases using literature mining. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3981–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa-Silva, A.; Fontaine, J.-F.; Donnard, E.R.; Stussi, F.; Ortega, J.M.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A. PESCADOR, a web-based tool to assist text-mining of biointeractions extracted from PubMed queries. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baltoumas, F.A.; Zafeiropoulou, S.; Karatzas, E.; Koutrouli, M.; Thanati, F.; Voutsadaki, K.; Gkonta, M.; Hotova, J.; Kasionis, I.; Hatzis, P.; et al. Biomolecule and Bioentity Interaction Databases in Systems Biology: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Schiettecatte, F.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, S.; Gargano, M.; Matentzoglu, N.; Carmody, L.C.; Lewis-Smith, D.; Vasilevsky, N.A.; Danis, D.; Balagura, G.; Baynam, G.; Brower, A.M.; et al. The Human Phenotype Ontology in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1207–D1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, J.; Ramírez-Anguita, J.M.; Saüch-Pitarch, J.; Ronzano, F.; Centeno, E.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, gkz1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koutrouli, M.; Karatzas, E.; Paez-Espino, D.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. A Guide to Conquer the Biological Network Era Using Graph Theory. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Secrier, M.; Moschopoulos, C.N.; Soldatos, T.G.; Kossida, S.; Aerts, J.; Schneider, R.; Bagos, P.G. Using graph theory to analyze biological networks. BioData Min. 2011, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kans, J. Entrez Direct: E-Utilities on the Unix Command Line; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Rockville, MD, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pafilis, E.; Jensen, L.J. Real-time tagging of biomedical entities. BioRxiv 2016, 078469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D258–D261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, A.; Schomburg, I.; Placzek, S.; Jeske, L.; Ulbrich, M.; Xiao, M.; Sensen, C.W.; Schomburg, D. BRENDA in 2015: Exciting developments in its 25th year of existence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D439–D446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schriml, L.M.; Mitraka, E.; Munro, J.; Tauber, B.; Schor, M.; Nickle, L.; Felix, V.; Jeng, L.; Bearer, C.; Lichenstein, R.; et al. Human Disease Ontology 2018 update: Classification, content and workflow expansion. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D955–D962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nastou, K.C.; Nasi, G.I.; Tsiolaki, P.L.; Litou, Z.I.; Iconomidou, V.A. AmyCo: The amyloidoses collection. Amyloid 2019, 26, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Ciufo, S.; Domrachev, M.; Hotton, C.L.; Kannan, S.; Khovanskaya, R.; Leipe, D.; Mcveigh, R.; O′Neill, K.; Robbertse, B.; et al. NCBI Taxonomy: A comprehensive update on curation, resources and tools. Database 2020, 2020, baaa062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttigieg, P.L.; Morrison, N.; Smith, B.; Mungall, C.J.; Lewis, S.E. ENVO Consortium The environment ontology: Contextualising biological and biomedical entities. J. Biomed. Semant. 2013, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.L.; Eppig, J.T. The mammalian phenotype ontology: Enabling robust annotation and comparative analysis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romano, P.; Manniello, A.; Aresu, O.; Armento, M.; Cesaro, M.; Parodi, B. Cell Line Data Base: Structure and recent improvements towards molecular authentication of human cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D925–D932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Paez-Espino, D.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Iliopoulos, I. Empirical Comparison of Visualization Tools for Larger-Scale Network Analysis. Adv. Bioinform. 2017, 2017, 1278932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fruchterman, T.M.J.; Reingold, E.M. Graph drawing by force-directed placement. Softw. Pract. Exp. 1991, 21, 1129–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Kawai, S. An algorithm for drawing general undirected graphs. Inf. Process. Lett. 1989, 31, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosiou, T.; Efstathiou, G.; Papanikolaou, N.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Bagos, P.G.; Iliopoulos, I.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. NAP: The Network Analysis Profiler, a web tool for easier topological analysis and comparison of medium-scale biological networks. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koutrouli, M.; Theodosiou, T.; Iliopoulos, I.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. The Network Analysis Profiler (NAP v2.0): A web tool for visual topological comparison between multiple networks. EMBnet. J. 2021, 26, e943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramírez, F.; Schelhorn, S.-E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing topological parameters of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehlenborg, N.; O′Donoghue, S.I.; Baliga, N.S.; Goesmann, A.; Hibbs, M.A.; Kitano, H.; Kohlbacher, O.; Neuweger, H.; Schneider, R.; Tenenbaum, D.; et al. Visualization of omics data for systems biology. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, S56–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Wegener, A.-L.; Schneider, R. A survey of visualization tools for biological network analysis. BioData Min. 2008, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlopoulos, G.A.; Malliarakis, D.; Papanikolaou, N.; Theodosiou, T.; Enright, A.J.; Iliopoulos, I. Visualizing genome and systems biology: Technologies, tools, implementation techniques and trends, past, present and future. GigaScience 2015, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2009, 3, 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- Koutrouli, M.; Karatzas, E.; Papanikolopoulou, K.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. NORMA: The Network Makeup Artist—A Web Tool for Network Annotation Visualization. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, S1672022921001303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzas, E.; Baltoumas, F.A.; Panayiotou, N.A.; Schneider, R.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. Arena3Dweb: Interactive 3D visualization of multilayered networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W36–W45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanati, F.; Karatzas, E.; Baltoumas, F.A.; Stravopodis, D.J.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. FLAME: A Web Tool for Functional and Literature Enrichment Analysis of Multiple Gene Lists. Biology 2021, 10, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, S.; Yamada, T.; Hamajima, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Bork, P.; Goto, S.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG Atlas mapping for global analysis of metabolic pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W423–W426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabregat, A.; Jupe, S.; Matthews, L.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Gillespie, M.; Garapati, P.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Korninger, F.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D649–D655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutrouli, M.; Hatzis, P.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. Exploring Networks in the STRING and Reactome Database. In Systems Medicine; Wolkenhauer, O., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 507–520. ISBN 978-0-12-816078-7. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, M.; Ammar, A.; Riutta, A.; Waagmeester, A.; Slenter, D.N.; Hanspers, K.; A Miller, R.; Digles, D.; Lopes, E.N.; Ehrhart, F.; et al. WikiPathways: Connecting communities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D613–D621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g: Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schölz, C.; Lyon, D.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Jensen, L.J.; Choudhary, C.; Weinert, B.T. Avoiding abundance bias in the functional annotation of post-translationally modified proteins. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 1003–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The igraph software package for complex network research. InterJ. Complex Syst. 2006, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sievert, C. Interactive Web-Based Data Visualization with R, Plotly, and Shiny; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-138-33149-5. [Google Scholar]
- Laurance, S.; Lemarié, C.A.; Blostein, M.D. Growth Arrest-Specific Gene 6 (gas6) and Vascular Hemostasis. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gkouskou, K.; Vlastos, I.; Karkalousos, P.; Chaniotis, D.; Sanoudou, D.; Eliopoulos, A.G. The “Virtual Digital Twins” Concept in Precision Nutrition. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkouskou, K.; Vasilogiannakopoulou, T.; Andreakos, E.; Davanos, N.; Gazouli, M.; Sanoudou, D.; Eliopoulos, A.G. COVID-19 enters the expanding network of apolipoprotein E4-related pathologies. Redox Biol. 2021, 41, 101938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Yang, M.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Gao, G.; Tai, H.; Huang, N.; Xiao, H. Fat mass and obesity-associated protein attenuates lipid accumulation in macrophage foam cells and alleviates atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breit, S.N.; Brown, D.A.; Tsai, V.W.-W. The GDF15-GFRAL Pathway in Health and Metabolic Disease: Friend or Foe? Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, E.; Held, C.; Stewart, R.A.H.; Aylward, P.E.; Budaj, A.; Cannon, C.P.; Koenig, W.; Krug-Gourley, S.; Mohler, E.R., III; Steg, P.G.; et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 15 Predicts All-Cause Morbidity and Mortality in Stable Coronary Heart Disease. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, F.E.; Bennet, A.M.; Magnusson, P.K.E.; Eriksson, U.K.; Lindmark, F.; Wu, L.; Yaghoutyfam, N.; Marquis, C.P.; Stattin, P.; Pedersen, N.L.; et al. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1/GDF15): A new marker of all-cause mortality. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Noren Hooten, N.; Evans, M.K. CRP Stimulates GDF15 Expression in Endothelial Cells through p53. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, e8278039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olley, G.; Ansari, M.; Bengani, H.; Grimes, G.R.; Rhodes, J.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Blatnik, A.; Stewart, F.J.; Wakeling, E.; Carroll, N.; et al. BRD4 interacts with NIPBL and BRD4 is mutated in a Cornelia de Lange-like syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parenti, I.; Diab, F.; Gil, S.R.; Mulugeta, E.; Casa, V.; Berutti, R.; Brouwer, R.W.W.; Dupé, V.; Eckhold, J.; Graf, E.; et al. MAU2 and NIPBL Variants Impair the Heterodimerization of the Cohesin Loader Subunits and Cause Cornelia de Lange Syndrome. Cell Rep. 2020, 31, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, G.; Kreidl, E.; Peters, J.-M.; Eichele, G. The non-redundant function of cohesin acetyltransferase Esco2: Some answers and new questions. Nucl. Austin Tex 2012, 3, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harakalova, M.; van den Boogaard, M.-J.; Sinke, R.; van Lieshout, S.; van Tuil, M.C.; Duran, K.; Renkens, I.; Terhal, P.A.; de Kovel, C.; Nijman, I.J.; et al. X-exome sequencing identifies a HDAC8 variant in a large pedigree with X-linked intellectual disability, truncal obesity, gynaecomastia, hypogonadism and unusual face. J. Med. Genet. 2012, 49, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH Preprint Pilot. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/about/nihpreprints/ (accessed on 10 February 2022).
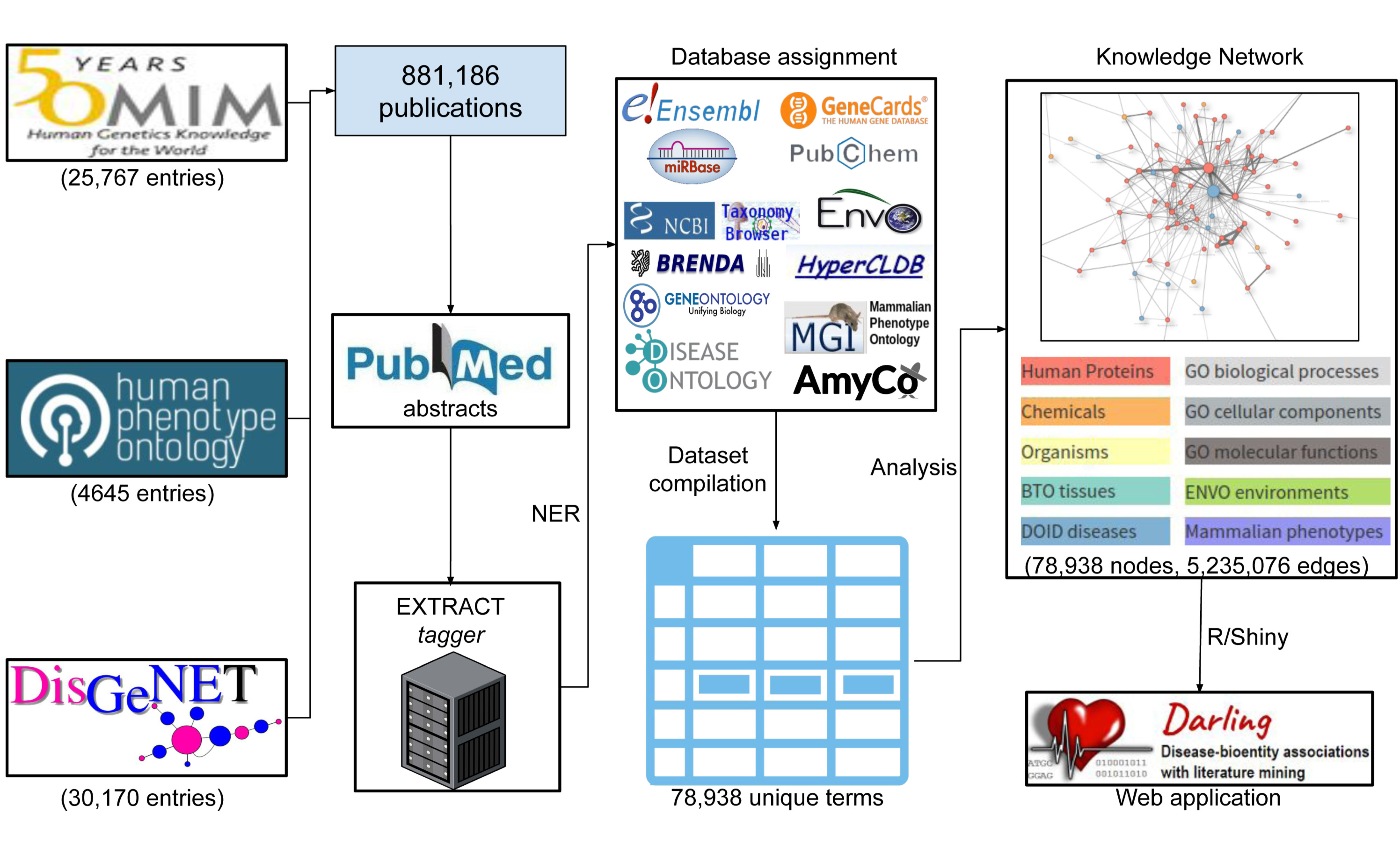
| Entity Type | Resource | #Terms |
|---|---|---|
| Chemicals | PubChem [33] | 23,593 |
| Genes/Proteins | ENSEMBL [34], miRBase [35], Gene Cards [36] | 19,731 |
| GO—Biological Process | Gene Ontology [37] | 6002 |
| GO—Molecular Function | Gene Ontology [37] | 3176 |
| GO—Cellular Component | Gene Ontology [37] | 1842 |
| Tissues | BRENDA Tissue Ontology (BTO) [38] | 4229 |
| Diseases | Disease Ontology [39], AmyCo [40] | 6172 |
| Organisms | NCBI Taxonomy [41] | 11,212 |
| Environments | Environmental Ontology (ENVO) [42] | 363 |
| Phenotypes | Mammalian Phenotype Ontology [43], Cell Line Data Base (CLDB) [44] | 2618 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karatzas, E.; Baltoumas, F.A.; Kasionis, I.; Sanoudou, D.; Eliopoulos, A.G.; Theodosiou, T.; Iliopoulos, I.; Pavlopoulos, G.A. Darling: A Web Application for Detecting Disease-Related Biomedical Entity Associations with Literature Mining. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040520
Karatzas E, Baltoumas FA, Kasionis I, Sanoudou D, Eliopoulos AG, Theodosiou T, Iliopoulos I, Pavlopoulos GA. Darling: A Web Application for Detecting Disease-Related Biomedical Entity Associations with Literature Mining. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(4):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040520
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaratzas, Evangelos, Fotis A. Baltoumas, Ioannis Kasionis, Despina Sanoudou, Aristides G. Eliopoulos, Theodosios Theodosiou, Ioannis Iliopoulos, and Georgios A. Pavlopoulos. 2022. "Darling: A Web Application for Detecting Disease-Related Biomedical Entity Associations with Literature Mining" Biomolecules 12, no. 4: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040520
APA StyleKaratzas, E., Baltoumas, F. A., Kasionis, I., Sanoudou, D., Eliopoulos, A. G., Theodosiou, T., Iliopoulos, I., & Pavlopoulos, G. A. (2022). Darling: A Web Application for Detecting Disease-Related Biomedical Entity Associations with Literature Mining. Biomolecules, 12(4), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12040520








