Concomitant Administration of Red Ginseng Extract with Lactic Acid Bacteria Increases the Plasma Concentration of Deglycosylated Ginsenosides in Healthy Human Subjects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In Vitro RGE Fermentation Study with LAB
2.3. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.4. The Transport of Ginsenosides in Caco-2 and LLC-PK1-P-gp Cells
2.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ginsenosides
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
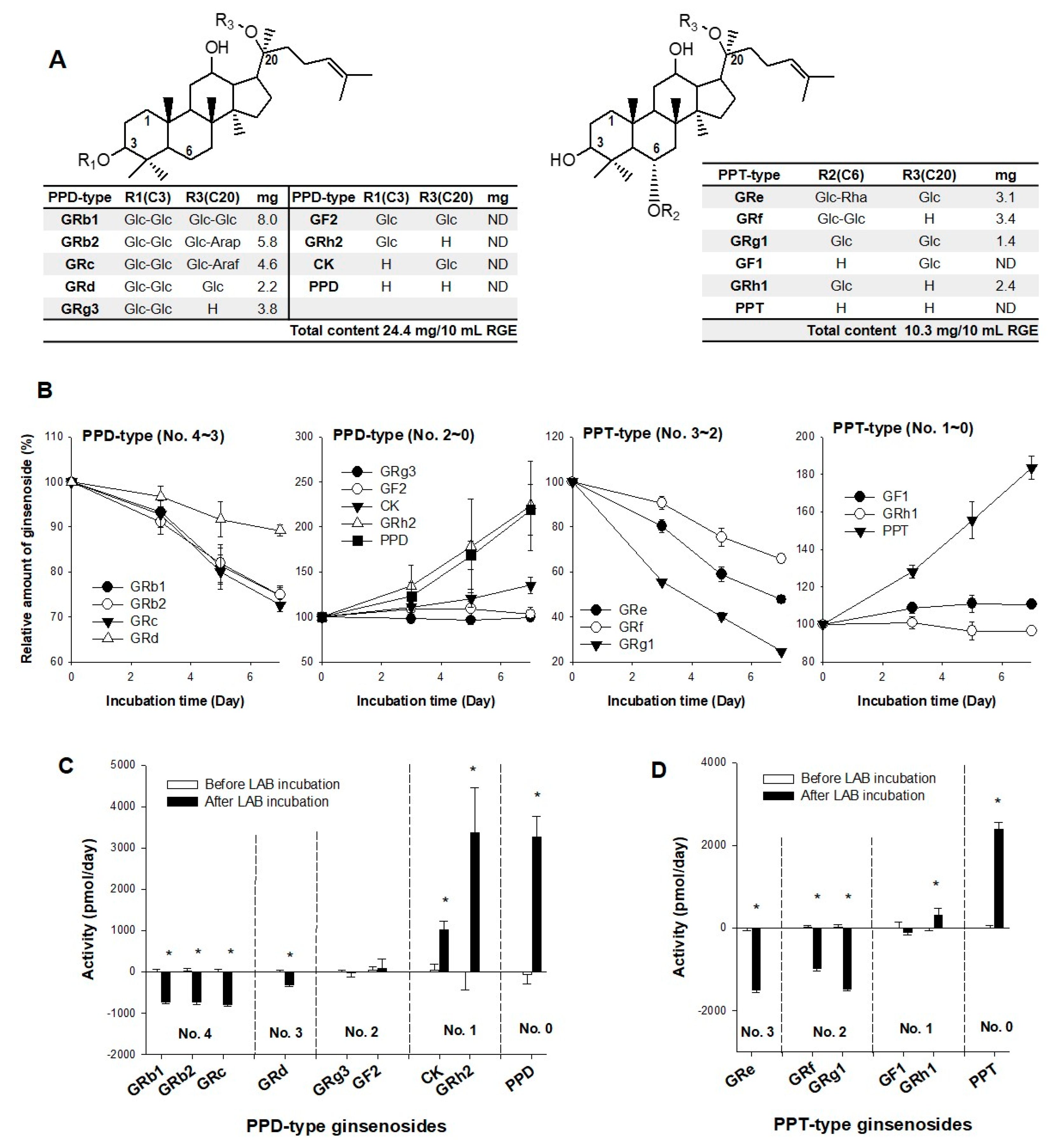
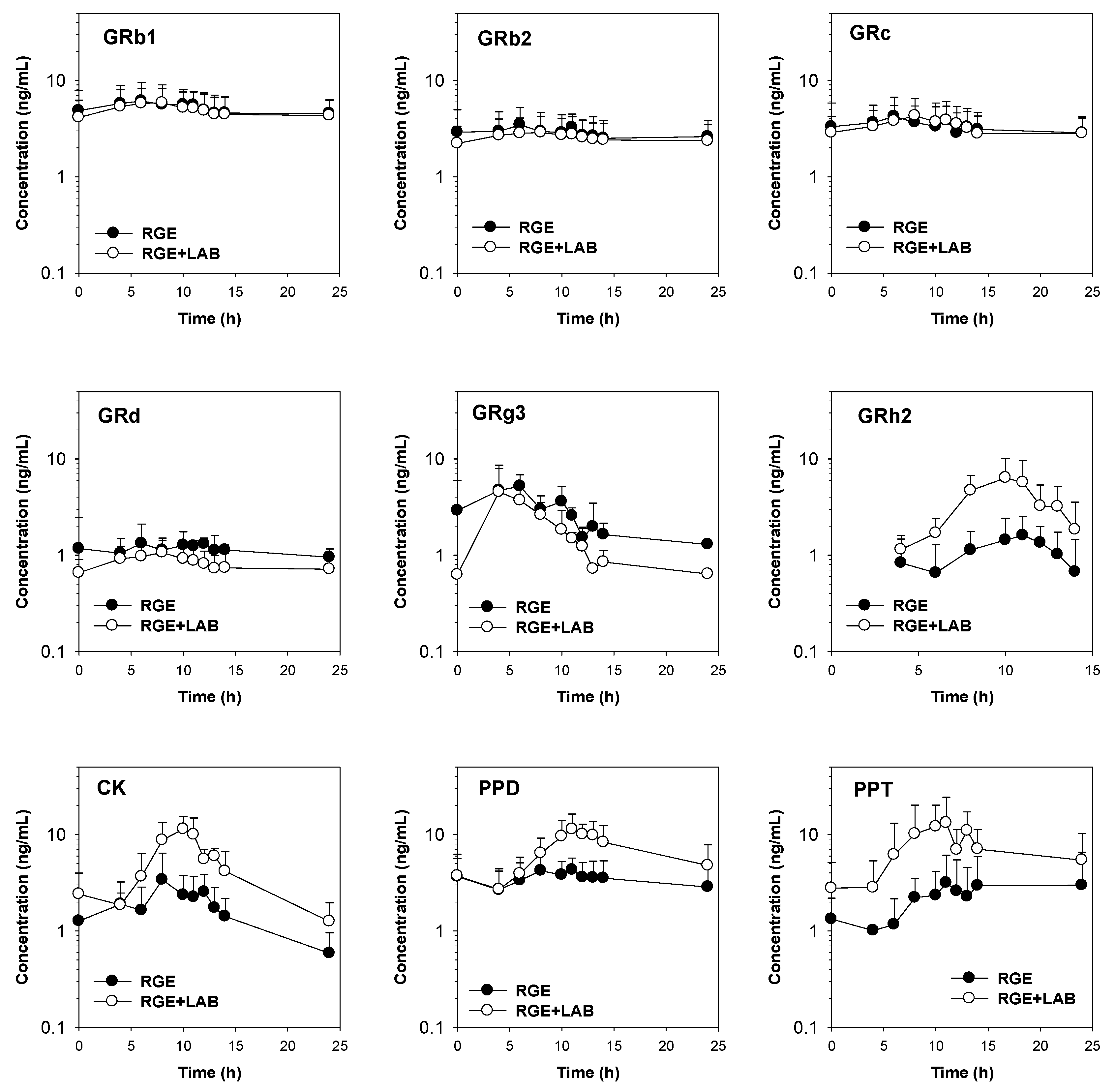
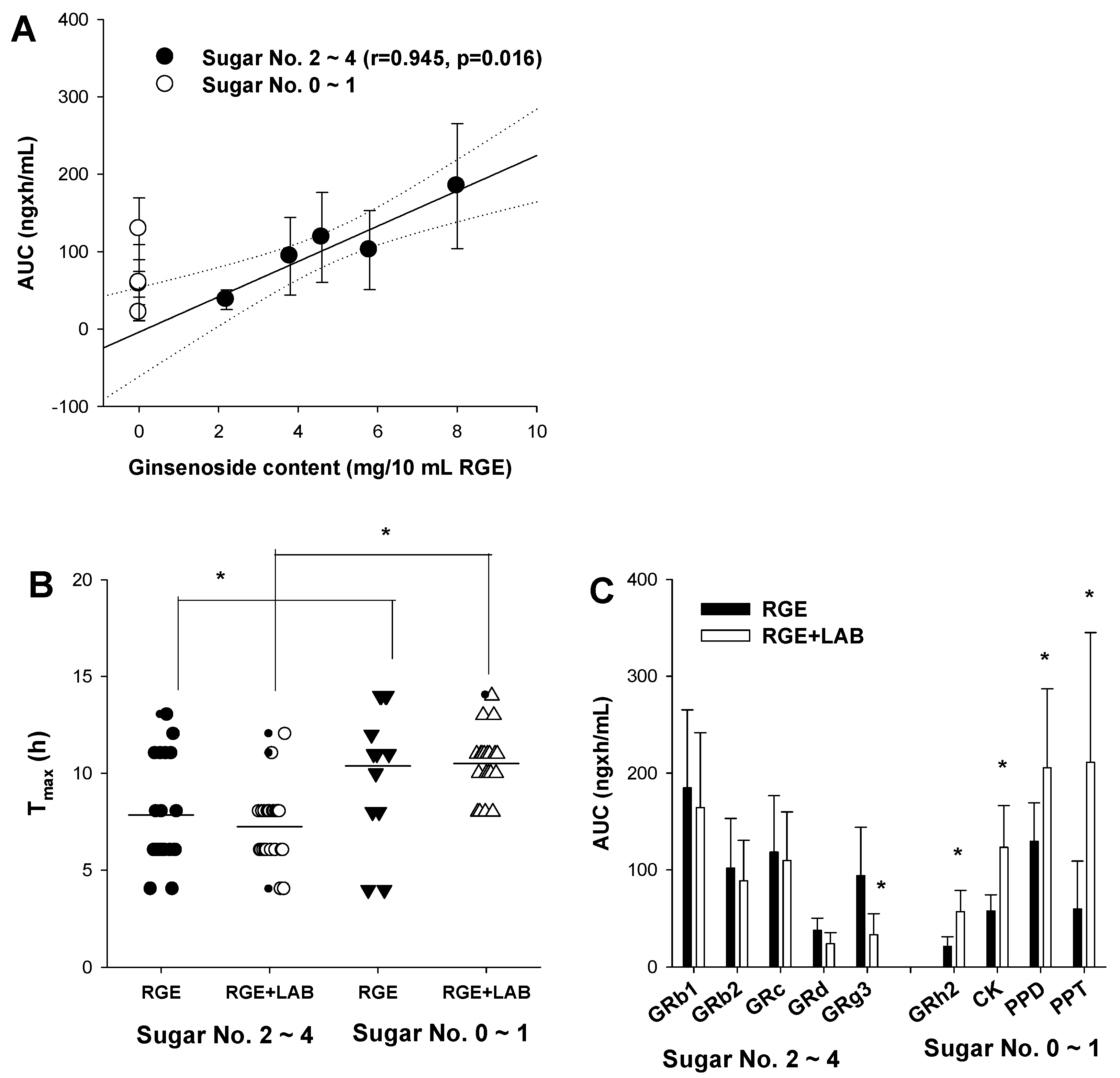
3.1. Effect of LAB Supplementation on the In Vitro Ginsenoside Metabolism and In Vivo Pharmacokinetics of Ginsenosides in Human Subjects
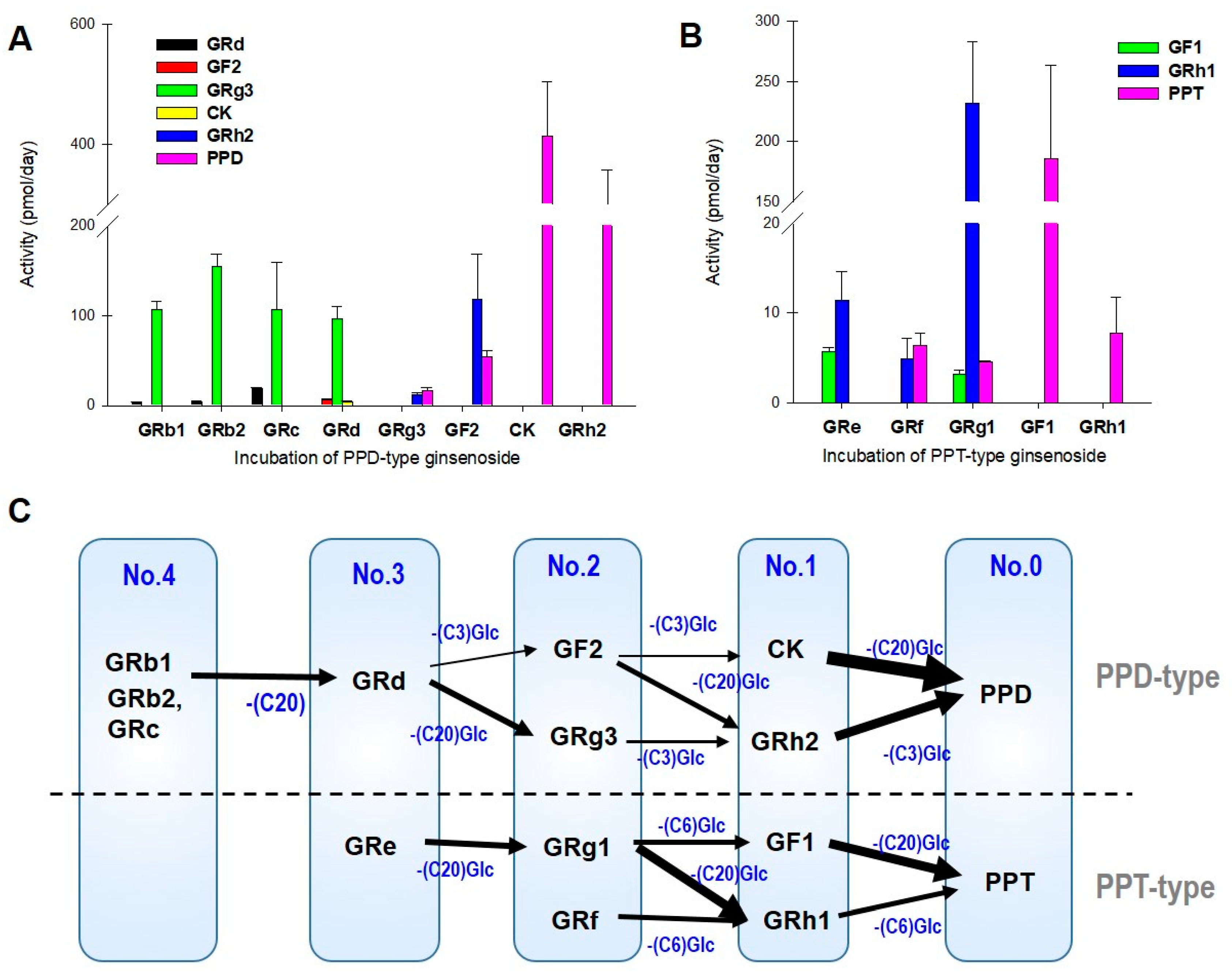
3.2. LAB-Mediated Ginsenosides Metabolic Pathway
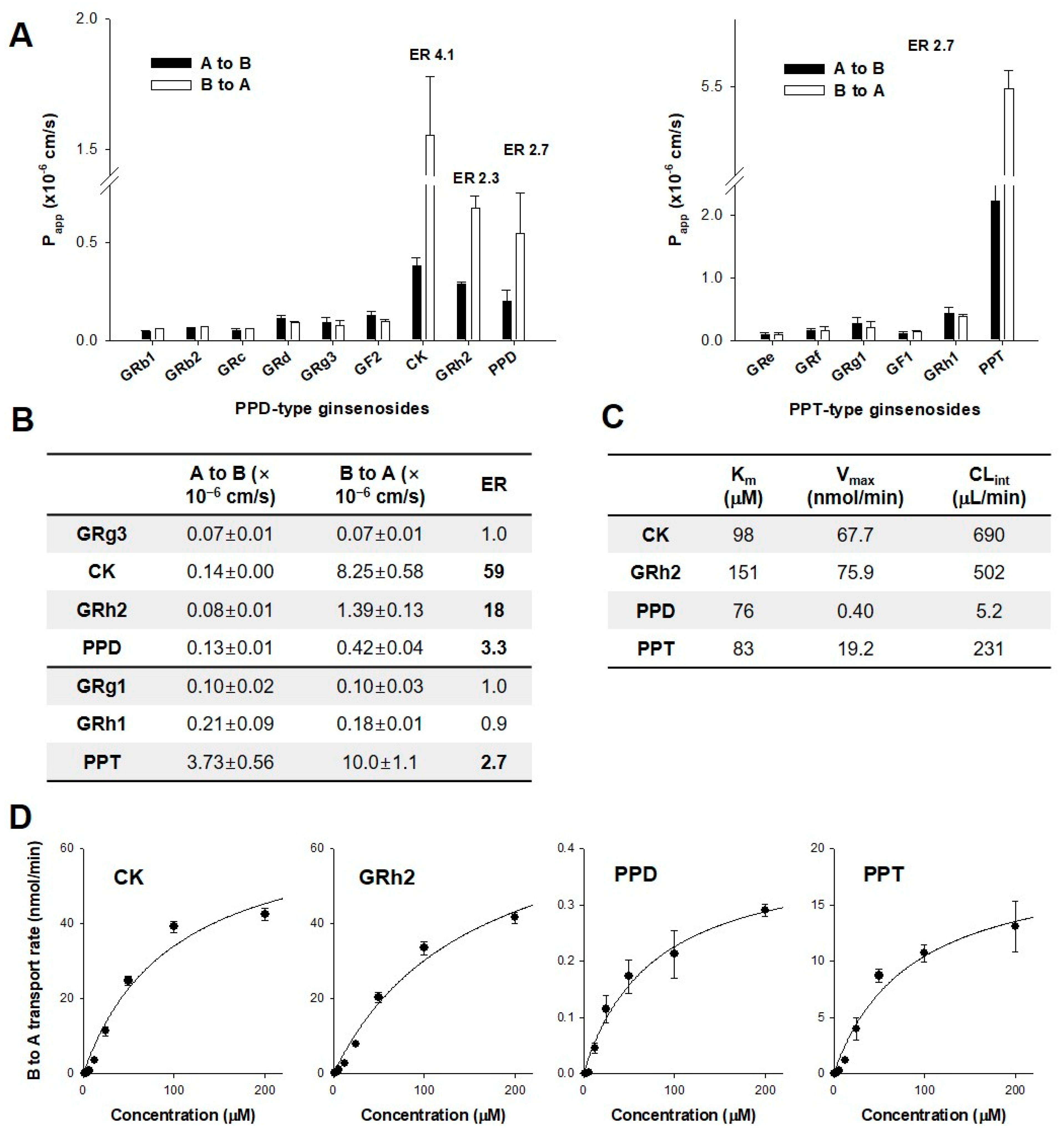
3.3. Permeability of Ginsenosides in CaCo-2 and LLC-PK1-P-gp Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leung, K.W.; Wong, A.S. Pharmacology of ginsenosides: A literature review. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Q.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Xu, K.Y.; Yang, Y.M. The efficacy of ginseng-related therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Interactions of ginseng with therapeutic drugs. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2019, 42, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.F.; Chiou, W.F.; Zhang, J.T. Comparison of the pharmacological effects of Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolium. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Han, Y.H.; Song, I.S. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, and compound K after single or multiple administration of red ginseng extract in human beings. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Detection of 13 ginsenosides (Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg3, Rh2, F1, Compound K, 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol, and 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol) in human plasma and application of the analytical method to human pharmacokinetic studies following two week-repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Pan, J.H.; Cho, H.T.; Kim, Y.J. Black Ginseng Extract Counteracts Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Park, B.I.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.H.; Shim, W.S.; Seo, Y.K.; Kang, K.; Lee, K.T.; Yim, S.V.; et al. Ginsenoside Absorption Rate and Extent Enhancement of Black Ginseng (CJ EnerG) over Red Ginseng in Healthy Adults. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Correlation between the content and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides from four different preparation of panax ginseng CA Meyer in rats. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2021, 12, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, M.S.; Jeung, W.; Ra, J.; Yoo, H.H.; Kim, D.H. Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy volunteers treated orally with red ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.; Park, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on the pharmacokinetics and metabolism of ginsenosides in mice. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H. Gut microbiota-mediated pharmacokinetics of ginseng saponins. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Jung, I.H.; Park, S.H.; Ahn, Y.T.; Huh, C.S.; Kim, D.H. Comparative analysis of the gut microbiota in people with different levels of ginsenoside Rb1 degradation to compound K. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.J.; Kim, H.I.; Park, T.; Kim, H.; Jo, K.; Jeon, H.; Ha, S.J.; Hyun, J.M.; Jeong, A.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Non-clinical pharmacokinetic behavior of ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.D.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, M.H.; Shim, J.J.; Ahn, Y.T.; Sim, J.H.; Huh, C.S.; Shim, W.S.; Yim, S.V.; et al. Enhanced absorption study of ginsenoside Compound K (20-O-beta-(D-Glucopyranosyl)-20(S)-protopanaxadiol) after oral administration of fermented red ginseng extract (HYFRG) in healthy Korean volunteers and rats. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 3908142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukami, H.; Ueda, T.; Matsuoka, N. Pharmacokinetic study of compound K in Japanese subjects after ingestion of Panax ginseng fermented by Lactobacillus paracasei A221 reveals significant increase of absorption into blood. J. Med. Food 2019, 22, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Xue, B.; Yang, C.; Miao, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; He, H.; et al. Biopharmaceutical characters and bioavailability improving strategies of ginsenosides. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.-T.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, B.-X.; Liao, Y.-H.; He, X.-X.; Ye, L.-H.; Liu, X.-M.; Chang, Q. Different pharmacokinetics of the two structurally similar dammarane sapogenins, protopanaxatriol and protopanaxadiol, in rats. Fitoterapia 2013, 86, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hou, J.; Jin, X.; Ke, Z.C.; Liu, D.; Du, M.; Jia, X.B.; Lv, H.X. Targeted delivery of ginsenoside compound K using TPGS/PEG-PCL mixed micelles for effective treatment of lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7653–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.R.; Niu, T.; Gao, S.; Yin, T.J.; You, M.; Jiang, Z.H.; Hu, M. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein leads to improved oral bioavailability of compound K, an anticancer metabolite of red ginseng extract produced by gut microflora. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.S.; Jeong, H.U.; Choi, M.K.; Kwon, M.; Shin, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S. Interactions between cyazofamid and human drug transporters. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.J.; Lee, T.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Characterization of preclinical in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic properties of KPLA-012, a benzopyranyl 1,2,3-triazole compound, with anti-angiogenetic and anti-tumor progressive effects. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2018, 9, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Enhanced intestinal absorption and pharmacokinetic modulation of berberine and its metabolites through the inhibition of P-glycoprotein and intestinal metabolism in rats using a berberine mixed micelle formulation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S.J.; Song, I.S.; Choi, M.K. Improved hygroscopicity and bioavailability of solid dispersion of red ginseng extract with silicon dioxide. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides following repeated oral administration of red ginseng extract significantly differ between species of experimental animals. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2020, 43, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.U.; Kwon, M.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Shin, D.H.; Song, I.S.; Lee, H.S. Organic anion transporter 3- and organic anion transporting polypeptides 1B1- and 1B3-mediated transport of catalposide. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.-S.; Choi, Y.A.; Choi, M.-K. Comparison of gastrointestinal permeability of caffeine, propranolol, atenolol, ofloxacin, and quinidine measured using Ussing chamber system and Caco-2 cell monolayer. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2017, 8, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, M.G. Effect of red ginseng on cytochrome P450 and P-glycoprotein activities in healthy volunteers. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, D.S. Effect of fermented red ginseng on cytochrome P450 and P-glycoprotein activity in healthy subjects, as evaluated using the cocktail approach. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malati, C.Y.; Robertson, S.M.; Hunt, J.D.; Chairez, C.; Alfaro, R.M.; Kovacs, J.A.; Penzak, S.R. Influence of Panax ginseng on cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) activity in healthy participants. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, H.; Kwak, J.H.; Ahn, H.Y.; Shin, D.Y.; Lee, J.H. Korean red ginseng improves glucose control in subjects with impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Woo, J.-Y.; Han, C.-K.; Chang, I.-M. Safety analysis of Panax ginseng in randomized clinical trials: A systematic review. Medicines 2015, 2, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Lee, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Enhanced intestinal permeability and plasma concentration of metformin in rats by the repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.E.; Na, C.S.; Yoo, S.A.; Seo, S.H.; Son, H.S. Biotransformation of major ginsenosides in ginsenoside model culture by lactic acid bacteria. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.D.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ouyang, D.S.; Yang, G.P. A review of biotransformation and pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Fitoterapia 2015, 100, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doh, E.-S.; Chang, J.-P.; Lee, K.-H.; Seong, N.-S. Ginsenoside change and antioxidation activity of fermented ginseng. Kor. J. Med. Crop Sci. 2010, 18, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.-H.; Lee, K.-J.; Hur, S.-S.; Lee, D.-S.; Lee, S.-H.; Shin, K.-S.; Lee, J.-M. Ginsenoside derivatives and quality characteristics of fermented ginseng using lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Preserv. 2013, 20, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Du, F.; Gao, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Xu, F.; Niu, W.; Wang, F.; Mao, Y. Absorption and disposition of ginsenosides after oral administration of Panax notoginseng extract to rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2290–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, L.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Li, G.H.; Choi, K.-T.; Yang, D.-C. Microbial transformation of ginsenoside rb1 to compound k by lacto-Bacillus paralimentarius. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Kim, D.-H.; Ji, G.-E. Transformation of ginsenosides Rb2 and Rc from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Lee, B.-H.; You, H.-J.; Park, M.-S.; Ji, G.-E. Differential transformation of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng by lactic acid bacteria. J. Microbiol. Biotech. 2006, 16, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, E.-A.; Shin, J.-e.; Kim, D.-H. Metabolism of ginsenoside Re by human intestinal microflora and its estrogenic effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.-A.; Choo, M.-K.; Park, E.-K.; Park, S.-Y.; Shin, H.-Y.; Kim, D.-H. Metabolism of ginsenoside Rc by human intestinal bacteria and its related antiallergic activity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.-A.; Park, S.-Y.; KIM, D.-H. Constitutive β-gluccosidases hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 from human intestinal bacteria. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-H. Metabolism of ginsenosides to bioactive compounds by intestinal microflora and its industrial application. J. Ginseng Res. 2009, 33, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, E.-A.; Han, M.J.; Choo, M.-K.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-H. Metabolism of 20 (S)-and 20 (R)-ginsenoside Rg3 by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to in vitro biological activities. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.-M.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, Y.G.; Baek, S.; Kim, M.R. Enhanced production of compound K in fermented ginseng extracts by Lactobacillus brevis. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-K.; Paik, H.-D. Bioconversion using lactic acid bacteria: Ginsenosides, GABA, and phenolic compounds. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renchinkhand, G.; Park, Y.W.; Song, G.Y.; Cho, S.H.; Urgamal, M.; Bae, H.C.; Choi, J.W.; Nam, M.S. Identification of β-glucosidase activity of enterococcus faecalis CRNB-A3 in A irag and its potential to convert ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax Ginseng. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.; Ensom, M.H. Post hoc power analysis: An idea whose time has passed? Pharmacotherapy 2001, 21, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.W.; Song, I.S.; Shin, H.J.; Yeo, C.W.; Cho, D.Y.; Shon, J.H.; Shin, J.G. The effect of SLCO1B1*15 on the disposition of pravastatin and pitavastatin is substrate dependent: The contribution of transporting activity changes by SLCO1B1*15. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2008, 18, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ginsenosides | RGE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (ng/mL·h) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | MRT (h) | |
| GRb1 | 184.6 ± 80.6 | 7.1 ± 3.2 | 5.3 ± 4.6 | 18.3 ± 1.1 |
| GRb2 | 102.0 ± 51.0 | 3.9 ± 1.8 | 6.2 ± 4.0 | 18.5 ± 1.4 |
| GRc | 118.4 ± 58.2 | 5.1 ± 2.4 | 6.2 ± 4.0 | 18.0 ± 1.2 |
| GRd | 37.9 ± 12.6 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 7.5 ± 5.8 | 18.2 ± 1.4 |
| GRg3 | 94.1 ± 50.0 | 7.2 ± 4.8 | 7.2 ± 3.0 | 7.6 ± 2.8 |
| GRh2 | 21.3 ± 10.1 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 10.7 ± 0.6 | 17.0 ± 9.3 |
| CK | 57.9 ± 16.6 | 5.1 ± 2.2 | 8.0 ± 4.0 | 17.2 ± 4.5 |
| PPD | 129.5 ± 39.9 | 7.6 ± 1.7 | 16.0 ± 18.5 | 18.6 ± 5.0 |
| PPT | 59.9 ± 49.2 | 9.5 ± 4.8 | 17.4 ± 17.4 | 19.4 ± 10.5 |
| Ginsenosides | RGE + LAB | |||
| AUC (ng/mL·h) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | MRT (h) | |
| GRb1 | 164.4 ± 77.3 | 6.2 ± 2.9 | 6.8 ± 1.1 | 16.9 ± 0.5 |
| GRb2 | 88.6 ± 42.0 | 3.0 ± 1.4 | 7.2 ± 1.1 | 17.4 ± 0.1 |
| GRc | 109.6 ± 50.3 | 4.6 ± 2.3 | 8.2 ± 1.8 | 16.8 ± 0.3 |
| GRd | 24.1 ± 11.3 * | 0.9 ± 0.4 * | 7.6 ± 0.9 | 16.4 ± 0.8 |
| GRg3 | 33.3 ± 21.7 * | 4.8 ± 3.1 | 6.4 ± 3.3 | 6.7 ± 0.7 |
| GRh2 | 57.1 ± 22.0 * | 13.9 ± 12.8 | 10.6 ± 1.8 | 10.2 ± 1.6 |
| CK | 123.3 ± 43.1 * | 12.6 ± 3.7 * | 9.6 ± 1.5 | 13.1 ± 2.6 |
| PPD | 205.4 ± 81.7 * | 12.5 ± 4.1 * | 11.2 ± 1.6 | 16.6 ± 2.7 |
| PPT | 211.2 ± 134.0 * | 18.0 ± 7.3 * | 10.6 ± 1.8 | 13.1 ± 4.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Pang, M.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Concomitant Administration of Red Ginseng Extract with Lactic Acid Bacteria Increases the Plasma Concentration of Deglycosylated Ginsenosides in Healthy Human Subjects. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121896
Jeon J-H, Park J-H, Jeon SY, Pang M, Choi M-K, Song I-S. Concomitant Administration of Red Ginseng Extract with Lactic Acid Bacteria Increases the Plasma Concentration of Deglycosylated Ginsenosides in Healthy Human Subjects. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121896
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Ji-Hyeon, Jin-Hyang Park, So Yeon Jeon, Minyeong Pang, Min-Koo Choi, and Im-Sook Song. 2022. "Concomitant Administration of Red Ginseng Extract with Lactic Acid Bacteria Increases the Plasma Concentration of Deglycosylated Ginsenosides in Healthy Human Subjects" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121896
APA StyleJeon, J.-H., Park, J.-H., Jeon, S. Y., Pang, M., Choi, M.-K., & Song, I.-S. (2022). Concomitant Administration of Red Ginseng Extract with Lactic Acid Bacteria Increases the Plasma Concentration of Deglycosylated Ginsenosides in Healthy Human Subjects. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1896. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121896








