Characterization of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Changes in the Skin after Chronic Fluocinolone Acetonide Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
2.2. Histological Analysis and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. RNA Extraction
2.4. Transcriptomic Ananlysis
2.5. Real-Time qPCR
2.6. Protein Extraction
2.7. Proteomic Analysis
2.8. Western Blotting
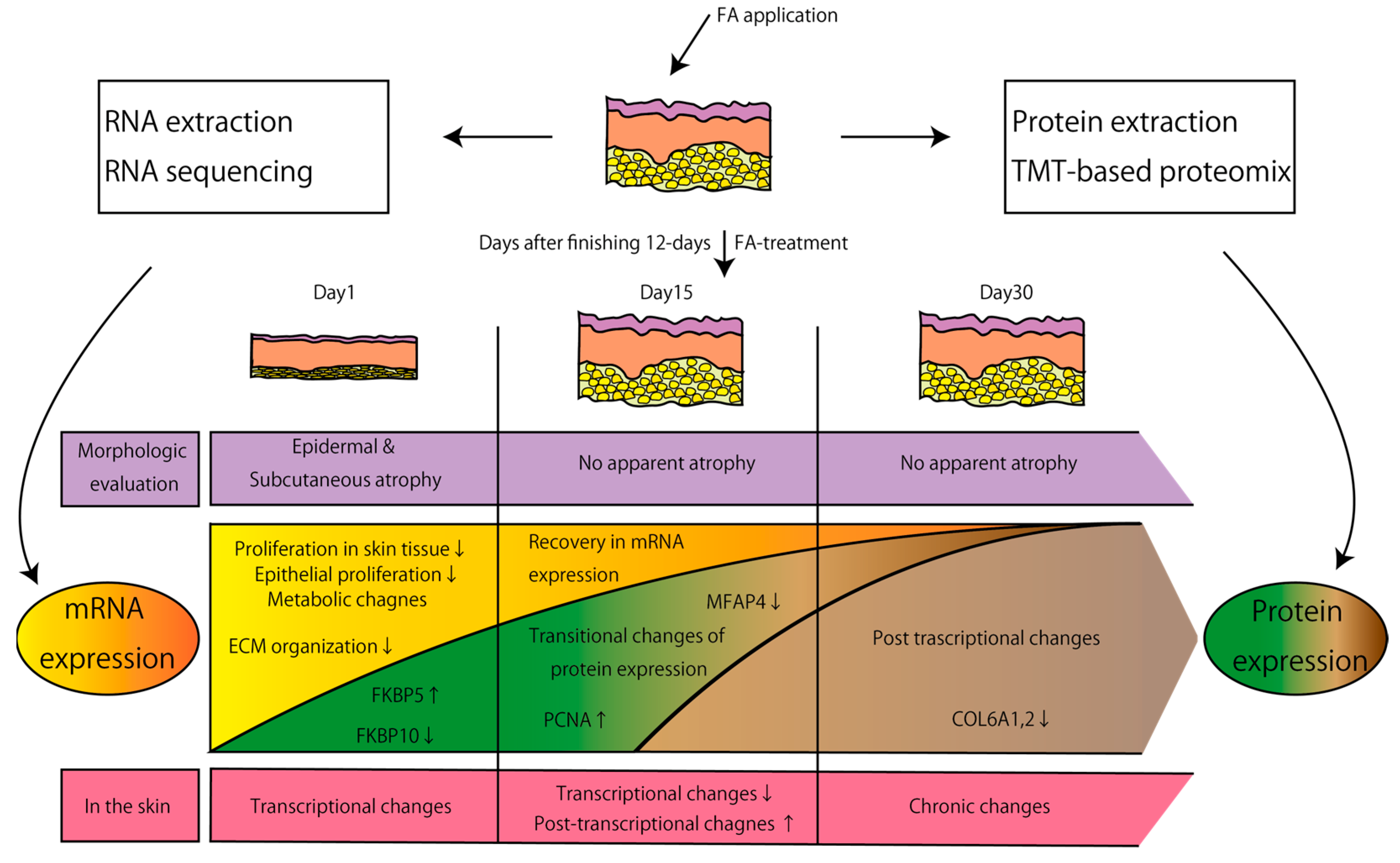
3. Results
3.1. Trancriptomic Effects of FA Treatment on the Skin
3.2. Proteomic Effects of FA Treatment on the Skin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Niculet, E.; Bobeica, C.; Tatu, A.L. Glucocorticoid-Induced Skin Atrophy: The Old and the New. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 13, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coondoo, A.; Phiske, M.; Verma, S.; Lahiri, K. Side-effects of topical steroids: A long overdue revisit. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-López, F.; Marghoob, A.A. Dermoscopic assessment of long-term topical therapies with potent steroids in chronic psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2004, 51, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheary, B. Steroid Withdrawal Effects Following Long-term Topical Corticosteroid Use. Dermatitis 2018, 29, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, A.J.; Griffiths, C.E.; Talwar, H.S.; Finkel, L.J.; Rafal, E.S.; Hamilton, T.A.; Voorhees, J.J. Concurrent application of tretinoin (retinoic acid) partially protects against corticosteroid-induced epidermal atrophy. Br. J. Dermatol. 1996, 135, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Queille-Roussel, C.; Paul, C.; Duteil, L.; Lefebvre, M.C.; Rapatz, G.; Zagula, M.; Ortonne, J.P. The new topical ascomycin derivative SDZ ASM 981 does not induce skin atrophy when applied to normal skin for 4 weeks: A randomized, double-blind controlled study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 144, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.K.; Bak, H.N.; Park, B.D.; Kim, Y.H.; Youm, J.K.; Choi, E.H.; Hong, S.P.; Lee, S.H. Effects of a multilamellar emulsion on glucocorticoid-induced epidermal atrophy and barrier impairment. J. Dermatol. 2006, 33, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, G.; Tran, C.; Sorg, O.; Hotz, R.; Grand, D.; Carraux, P.; Didierjean, L.; Stamenkovic, I.; Saurat, J.H. Hyaluronate fragments reverse skin atrophy by a CD44-dependent mechanism. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbellay, B.; Barnes, L.; Boehncke, W.H.; Saurat, J.H.; Kaya, G. Reversal of murine epidermal atrophy by topical modulation of calcium signaling. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baida, G.; Bhalla, P.; Kirsanov, K.; Lesovaya, E.; Yakubovskaya, M.; Yuen, K.; Guo, S.; Lavker, R.M.; Readhead, B.; Dudley, J.T.; et al. REDD1 functions at the crossroads between the therapeutic and adverse effects of topical glucocorticoids. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baida, G.; Bhalla, P.; Yemelyanov, A.; Stechschulte, L.A.; Shou, W.; Readhead, B.; Dudley, J.T.; Sánchez, E.R.; Budunova, I. Deletion of the glucocorticoid receptor chaperone FKBP51 prevents glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34772–34783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Mirzoeva, S.; Readhead, B.; Dudley, J.T.; Budunova, I. PI3K inhibitors protect against glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy. eBioMedicine 2019, 41, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LoCoco, P.M.; Boyd, J.T.; Espitia Olaya, C.M.; Furr, A.R.; Garcia, D.K.; Weldon, K.S.; Zou, Y.; Locke, E.; Tobon, A.; Lai, Z.; et al. Reliable approaches to extract high-integrity RNA from skin and other pertinent tissues used in pain research. Pain Rep. 2020, 5, e818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Supek, F.; Bošnjak, M.; Škunca, N.; Šmuc, T. REVIGO summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, T.; Tomita, M.; Ishihama, Y. Phase transfer surfactant-aided trypsin digestion for membrane proteome analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.S.; Moggridge, S.; Müller, T.; Sorensen, P.H.; Morin, G.B.; Krijgsveld, J. Single-pot, solid-phase-enhanced sample preparation for proteomics experiments. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, H.; Okada, K.; Araki, M.; Adachi, J.; Takemoto, A.; Kutkowska, J.; Maruyama, K.; Yanagitani, N.; Oh-Hara, T.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Gilteritinib overcomes lorlatinib resistance in ALK-rearranged cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiganescu, A.; Tahrani, A.A.; Morgan, S.A.; Otranto, M.; Desmoulière, A.; Abrahams, L.; Hassan-Smith, Z.; Walker, E.A.; Rabbitt, E.H.; Cooper, M.S.; et al. 11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase blockade prevents age-induced skin structure and function defects. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3051–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Belyaeva, O.V.; Adams, M.K.; Klyuyeva, A.V.; Lee, S.A.; Goggans, K.R.; Kesterson, R.A.; Popov, K.M.; Kedishvili, N.Y. Mice lacking the epidermal retinol dehydrogenases SDR16C5 and SDR16C6 display accelerated hair growth and enlarged meibomian glands. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17060–17074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasamatsu, S.; Hachiya, A.; Fujimura, T.; Sriwiriyanont, P.; Haketa, K.; Visscher, M.O.; Kitzmiller, W.J.; Bello, A.; Kitahara, T.; Kobinger, G.P.; et al. Essential role of microfibrillar-associated protein 4 in human cutaneous homeostasis and in its photoprotection. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lili, L.N.; Klopot, A.; Readhead, B.; Baida, G.; Dudley, J.T.; Budunova, I. Transcriptomic network interactions in the human skin treated with topical glucocorticoid clobetasol propionate. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 11, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knüppel, L.; Heinzelmann, K.; Lindner, M.; Hatz, R.; Behr, J.; Eickelberg, O.; Staab-Weijnitz, C.A. FK506-binding protein 10 (FKBP10) regulates lung fibroblast migration via collagen VI synthesis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theocharidis, G.; Drymoussi, Z.; Kao, A.P.; Barber, A.H.; Lee, D.A.; Braun, K.M.; Connelly, J.T. Type VI Collagen Regulates Dermal Matrix Assembly and Fibroblast Motility. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.; Takasugi, M.; Takemura, K.; Yoshida, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Adachi, J.; Tsuruta, D.; Ohtani, N. Characterization of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Changes in the Skin after Chronic Fluocinolone Acetonide Treatment. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121822
Choi Y, Takasugi M, Takemura K, Yoshida Y, Kamiya T, Adachi J, Tsuruta D, Ohtani N. Characterization of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Changes in the Skin after Chronic Fluocinolone Acetonide Treatment. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121822
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yongsu, Masaki Takasugi, Kazuaki Takemura, Yuya Yoshida, Tomonori Kamiya, Jun Adachi, Daisuke Tsuruta, and Naoko Ohtani. 2022. "Characterization of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Changes in the Skin after Chronic Fluocinolone Acetonide Treatment" Biomolecules 12, no. 12: 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121822
APA StyleChoi, Y., Takasugi, M., Takemura, K., Yoshida, Y., Kamiya, T., Adachi, J., Tsuruta, D., & Ohtani, N. (2022). Characterization of Transcriptomic and Proteomic Changes in the Skin after Chronic Fluocinolone Acetonide Treatment. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121822





