Gold-Based Metal Drugs as Inhibitors of Coronavirus Proteins: The Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Auranofin and Its Analogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources of Compounds and Chemicals
2.2. Enzymatic Activity Assay
3. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Experimental Conditions
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Instrumental Parameters
3.3. Crystallization, Data Collection and Structure Solution
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Chemical Features of the Study Compounds
4.2. Enzyme Inhibition by the Study Compounds
4.3. Metallodrug-Enzyme Interactions Probed by ESI MS
4.4. Crystallographic Results
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Mullen, L.; Potter, C.; Gostin, L.O.; Cicero, A.; Nuzzo, J.B. An analysis of International Health Regulations Emergency Committees and Public Health Emergency of International Concern Designations. BMJ Glob. Health 2020, 5, e002502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheudjeu, A. The SARS-CoV-2 Entry Inhibition Mechanisms of Serine Protease Inhibitors, OM-85, Heparin and Soluble HS Might Be Linked to HS Attachment Sites. Molecules 2022, 27, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, R.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Huo, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Hao, Q.; Ying, T.; Gao, Y.; et al. Recent advances in developing small-molecule inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1591–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.H.; Stone, E.A.; Deshmukh, M.; Ippolito, J.A.; Ghahremanpour, M.M.; Tirado-Rives, J.; Spasov, K.A.; Zhang, S.; Takeo, Y.; Kudalkar, S.N.; et al. Potent Noncovalent Inhibitors of the Main Protease of SARS-CoV-2 from Molecular Sculpting of the Drug Perampanel Guided by Free Energy Perturbation Calculations. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothan, H.A.; Stone, S.; Natekar, J.; Kumari, P.; Arora, K.; Kumar, M. The FDA-approved gold drug auranofin inhibits novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) replication and attenuates inflammation in human cells. Virology 2020, 547, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonzogni-Desautels, K.; Ndao, M. Will Auranofin Become a Golden New Treatment Against COVID-19? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, G.H.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Huang, P.; Ge, G.B. The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)): Structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19. MedComm 2022, 3, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.L.; Cheng, S.C.; Shi, L.; Wang, T.Y.; Ho, K.I.; Chou, C.Y. Critical Assessment of the Important Residues Involved in the Dimerization and Catalysis of MERS Coronavirus Main Protease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunova, E.; Khan, M.B.; Fischer, C.; Lu, J.; Lamer, T.; Vuong, W.; van Belkum, M.J.; McKay, R.T.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Vederas, J.C.; et al. N-Terminal Finger Stabilizes the S1 Pocket for the Reversible Feline Drug GC376 in the SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) Dimer. J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 167003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziebuhr, J.; Snijder, E.J.; Gorbalenya, A.E. Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in the Nidovirales. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 853–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, B.; Urakova, N.; Snijder, E.J.; Campbell, E.A. Structures and functions of coronavirus replication-transcription complexes and their relevance for SARS-CoV-2 drug design. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, S.; Nitsche, C. The SARS-CoV-2 main protease as drug target. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Yang, Q.; Gribenko, A.; Perrin, B.S., Jr.; Zhu, Y.; Cardin, R.; Liberator, P.A.; Anderson, A.S.; Hao, L. Genetic Surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) Reveals High Sequence and Structural Conservation Prior to the Introduction of Protease Inhibitor Paxlovid. mBio 2022, 13, e0086922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, H.M.; Dilnessa, T.; Jin, T. Structural Basis of Potential Inhibitors Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 622898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xie, W.; Xue, X.; Yang, K.; Ma, J.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Pei, D.; Ziebuhr, J.; et al. Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grifagni, D.; Calderone, V.; Giuntini, S.; Cantini, F.; Fragai, M.; Banci, L. SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibition by a zinc ion: Structural features and hints for drug design. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 7910–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchariya, L.; Khan, W.A.; Kuila, S.; Sonkar, K.; Sahoo, S.; Ghoshal, A.; Kumar, A.; Verma, D.K.; Hasan, A.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Zinc(2+) ion inhibits SARS-CoV-2 main protease and viral replication in vitro. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 10083–10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Lu, K.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, P.H.; Pan, J.A.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication by zinc gluconate in combination with hinokitiol. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2022, 231, 111777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, I.; Goyal, A.; Bhatnagar, M.; Manhas, S.; Goel, P.; Pal, A.; Prasad, R. Potential molecular mechanisms of zinc- and copper-mediated antiviral activity on COVID-19. Nutr. Res. 2021, 92, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Moles, M.; Basu, U.; Büssing, R.; Hoffmeister, H.; Türck, S.; Varchmin, A.; Ott, I. Gold Metallodrugs to Target Coronavirus Proteins: Inhibitory Effects on the Spike-ACE2 Interaction and on PLpro Protease Activity by Auranofin and Gold Organometallics. Chemistry 2020, 26, 15140–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, C.; Carnamucio, F.; Giuffre, O.; Foti, C. Metal-Based Compounds in Antiviral Therapy. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Ye, F.; Zhang, C.; Fan, J.; Du, Z.; Zhao, W.; Yuan, Q.; Niu, W.; Gao, F.; He, B.; et al. A comparison of Remdesivir versus gold cluster in COVID-19 animal model: A better therapeutic outcome of gold cluster. Nano Today 2022, 44, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karges, J.; Cohen, S.M. Metal Complexes as Antiviral Agents for SARS-CoV-2. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 2600–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Pollini, S.; Prato, M.; Fallani, S.; Cassetta, M.I.; Novelli, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; Messori, L. Auranofin and its Analogues Show Potent Antimicrobial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens: Structure-Activity Relationships. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2448–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massai, L.; Messori, L.; Carpentieri, A.; Amoresano, A.; Melchiorre, C.; Fiaschi, T.; Modesti, A.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F. The effects of two gold-N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) complexes in ovarian cancer cells: A redox proteomic study. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2022, 89, 809–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massai, L.; Cirri, D.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. Auranofin and its analogs as prospective agents for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messori, L.; Marchetti, L.; Massai, L.; Scaletti, F.; Guerri, A.; Landini, I.; Nobili, S.; Perrone, G.; Mini, E.; Leoni, P.; et al. Chemistry and biology of two novel gold(I) carbene complexes as prospective anticancer agents. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Gabbiani, C.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Pratesi, A.; Guerri, A.; Biver, T.; Binacchi, F.; Stefanini, M.; et al. Auranofin, Et(3)PAuCl, and Et(3)PAuI Are Highly Cytotoxic on Colorectal Cancer Cells: A Chemical and Biological Study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagin, A.A.; Teplyakov, A. An approach to multi-copy search in molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2000, 56, 1622–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkòczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.-W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.B.; Arendall, W.B., III; Headd, J.J.; Keedy, D.A.; Immormino, R.M.; Kapral, G.J.; Murray, L.W.; Richardson, J.S.; Richardson, D.C. MolProbity: All-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegria-Arcos, M.; Barbosa, T.; Sepulveda, F.; Combariza, G.; Gonzalez, J.; Gil, C.; Martinez, A.; Ramirez, D. Network pharmacology reveals multitarget mechanism of action of drugs to be repurposed for COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 952192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberi, T.; Chiappetta, G.; Fiaschi, T.; Modesti, A.; Sorbi, F.; Magherini, F. Upgrade of an old drug: Auranofin in innovative cancer therapies to overcome drug resistance and to increase drug effectiveness. Med. Res. Rev. 2022, 42, 1111–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. Repurposing of the gold drug auranofin and a review of its derivatives as antibacterial therapeutics. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, S.F.Z.; Ur-Rahman, M.S.; Hussain, M.A.; Etheshaam uz Zaman, U.S.M.; Koneru, A. Drug Information of Auranofin and Its Effectiveness in COVID-19. IOSR J. Pharm. 2021, 11, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Laplantine, E.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Oudin, A.; Swain, J.; Soria, A.; Merida, P.; Gourdelier, M.; Mestiri, S.; Besseghe, I.; Bremaud, E.; et al. The FDA-approved drug Auranofin has a dual inhibitory effect on SARS-CoV-2 entry and NF-kappaB signaling. iScience 2022, 25, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirri, D.; Schirmeister, T.; Seo, E.J.; Efferth, T.; Massai, L.; Messori, L.; Micale, N. Antiproliferative Properties of a Few Auranofin-Related Gold(I) and Silver(I) Complexes in Leukemia Cells and their Interferences with the Ubiquitin Proteasome System. Molecules 2020, 25, 4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tialiou, A.; Chin, J.; Keppler, B.K.; Reithofer, M.R. Current Developments of N-Heterocyclic Carbene Au(I)/Au(III) Complexes toward Cancer Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, M.; Casini, A. Mass spectrometry as a powerful tool to study therapeutic metallodrugs speciation mechanisms: Current frontiers and perspectives. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 352, 432–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, C.; Massai, L.; Cirri, D.; Gabbiani, C.; Pratesi, A.; Messori, L. Protein metalation by two structurally related gold(I) carbene complexes: An ESI MS study. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 520, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppi, C.; Messori, L.; Pratesi, A. ESI MS studies highlight the selective interaction of Auranofin with protein free thiols. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 5906–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugone, V.; Sanna, D.; Sciortino, G.; Crans, D.C.; Garribba, E. ESI-MS Study of the Interaction of Potential Oxidovanadium(IV) Drugs and Amavadin with Model Proteins. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 9739–9755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, A.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L. Protein Metalation by Anticancer Metallodrugs: A Joint ESI MS and XRD Investigative Strategy. Chemistry 2017, 23, 6942–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartinger, C.G.; Tsybin, Y.O.; Fuchser, J.; Dyson, P.J. Characterization of platinum anticancer drug protein-binding sites using a top-down mass spectrometric approach. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
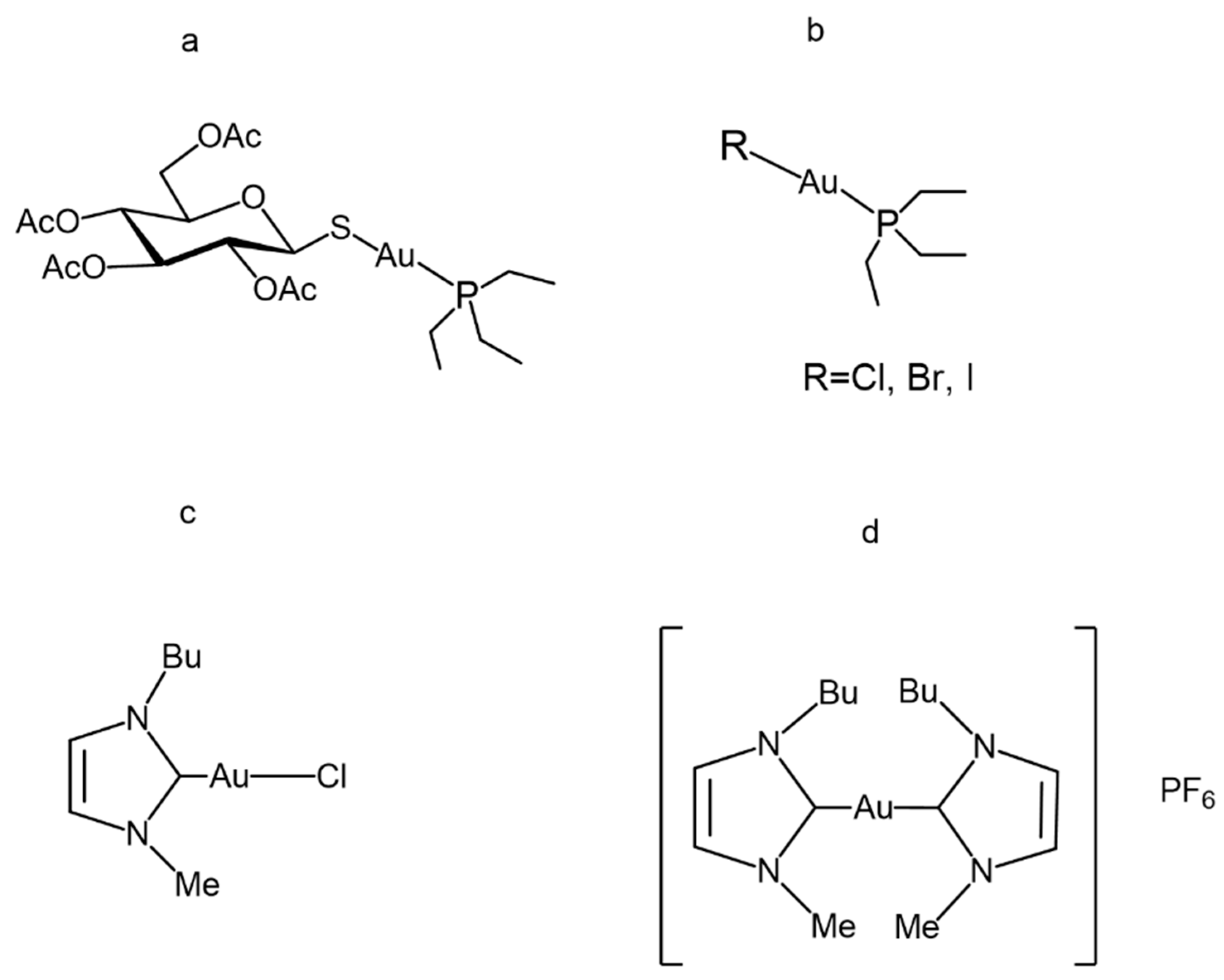
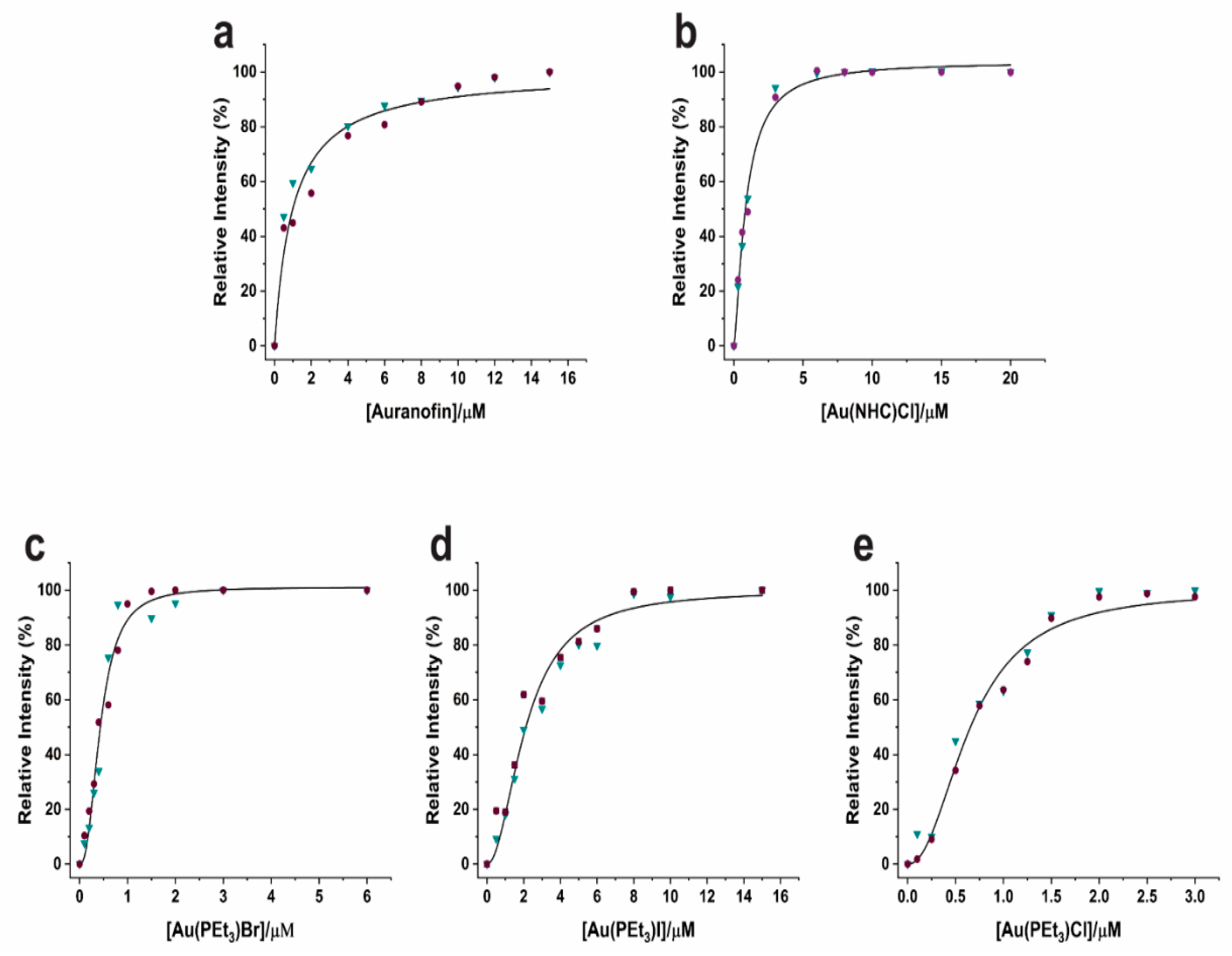
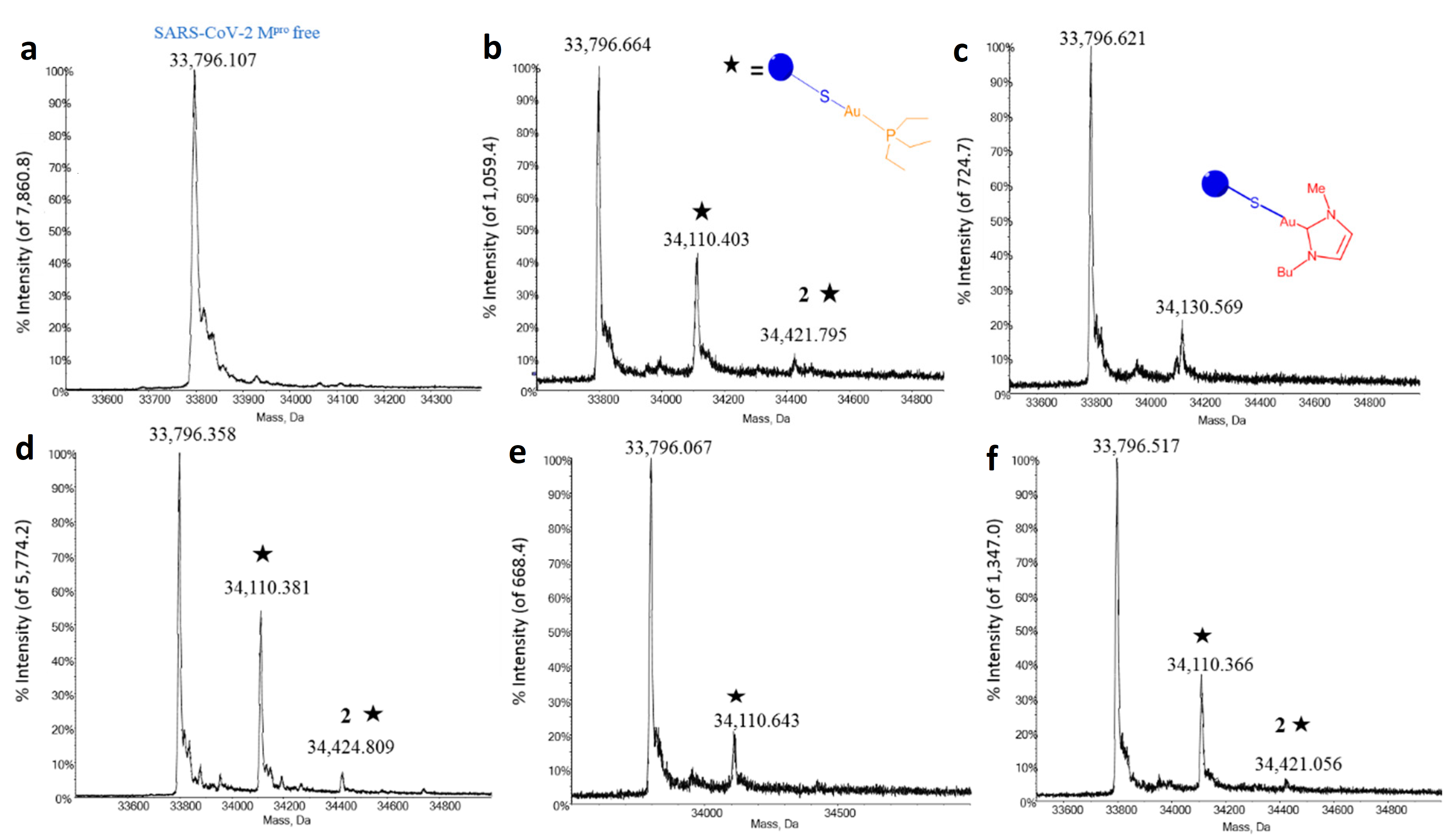
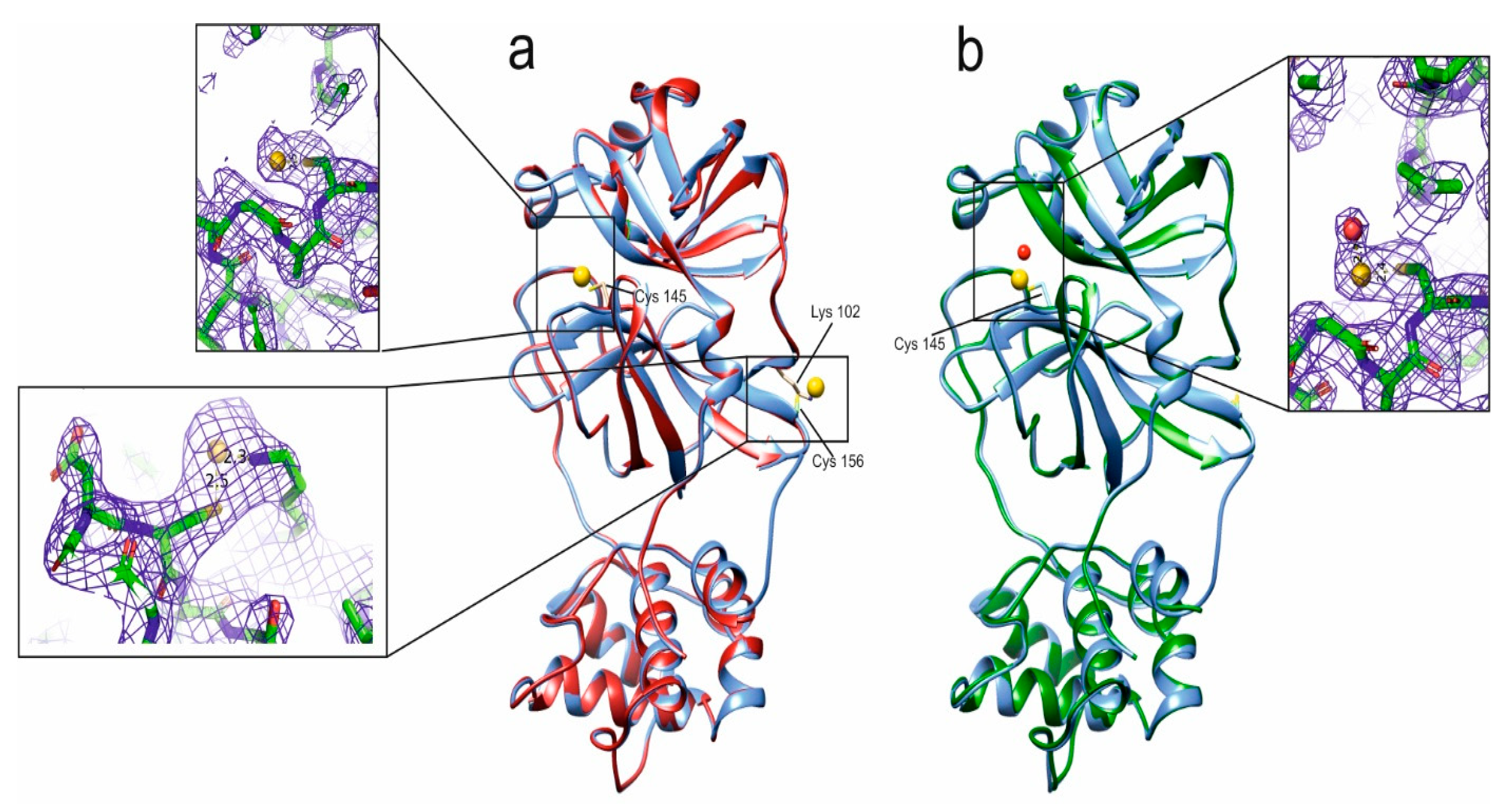
| Compound | Ki |
|---|---|
| Auranofin | 0.99 ± 0.107 µM |
| Au(NHC)Cl | 0.87 ± 0.04 µM |
| Au(PEt3)Br | 0.44 ± 0.022 µM |
| Au(PEt3)I | 2.12 ± 0.096 µM |
| Au(PEt3)Cl | 0.66 ± 0.026 µM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massai, L.; Grifagni, D.; De Santis, A.; Geri, A.; Cantini, F.; Calderone, V.; Banci, L.; Messori, L. Gold-Based Metal Drugs as Inhibitors of Coronavirus Proteins: The Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Auranofin and Its Analogs. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111675
Massai L, Grifagni D, De Santis A, Geri A, Cantini F, Calderone V, Banci L, Messori L. Gold-Based Metal Drugs as Inhibitors of Coronavirus Proteins: The Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Auranofin and Its Analogs. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111675
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassai, Lara, Deborah Grifagni, Alessia De Santis, Andrea Geri, Francesca Cantini, Vito Calderone, Lucia Banci, and Luigi Messori. 2022. "Gold-Based Metal Drugs as Inhibitors of Coronavirus Proteins: The Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Auranofin and Its Analogs" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111675
APA StyleMassai, L., Grifagni, D., De Santis, A., Geri, A., Cantini, F., Calderone, V., Banci, L., & Messori, L. (2022). Gold-Based Metal Drugs as Inhibitors of Coronavirus Proteins: The Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease by Auranofin and Its Analogs. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1675. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111675








