Molecular Structure and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Plastomes of Eight Sorbus Sensu Stricto Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and DNA Extraction
2.2. Cp Genome Assembly, Annotation, and Comparative Analysis
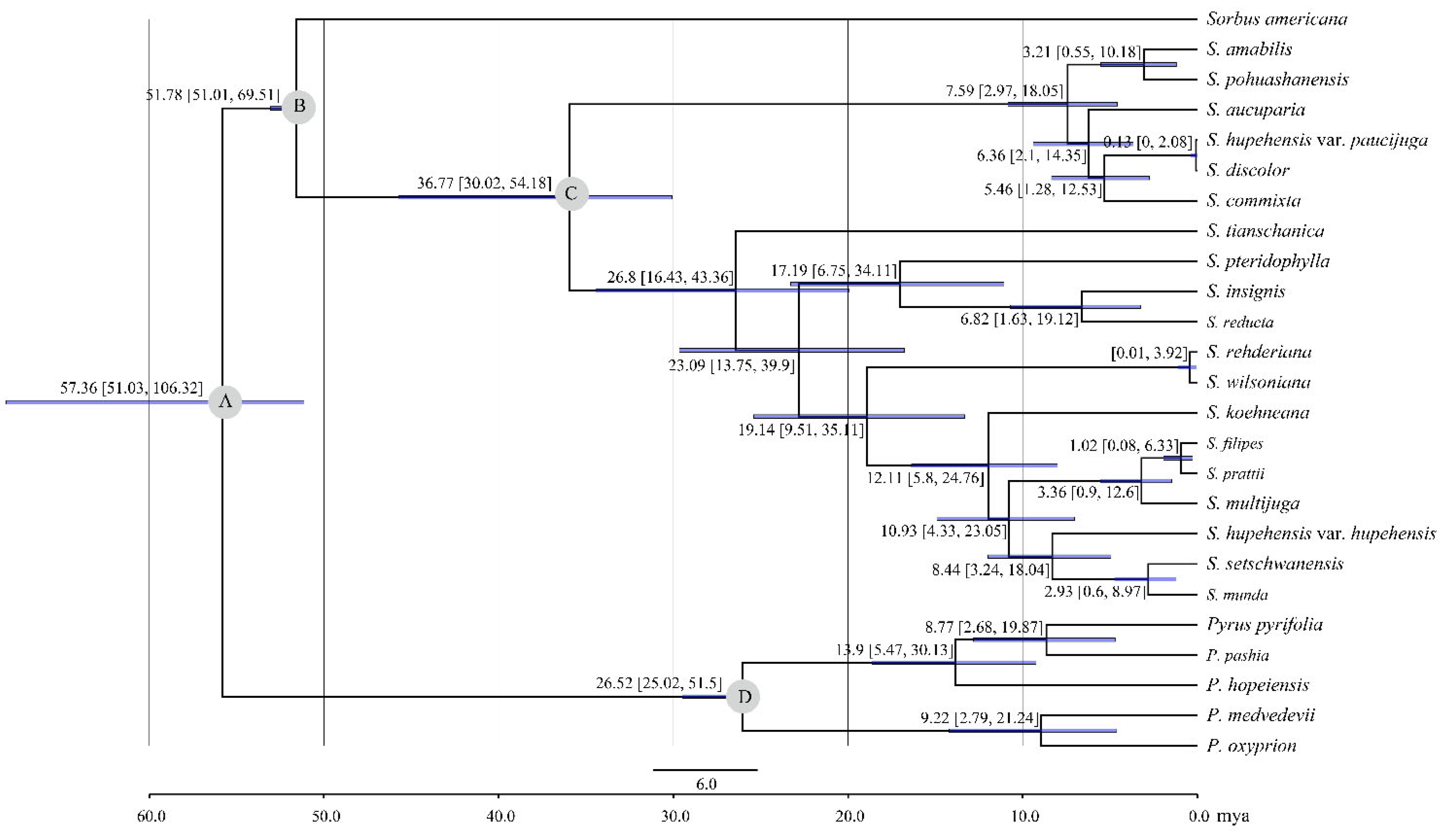
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Divergence Time Estimation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparative Analysis of the Features and Structure of Cp Genomes in Sorbus
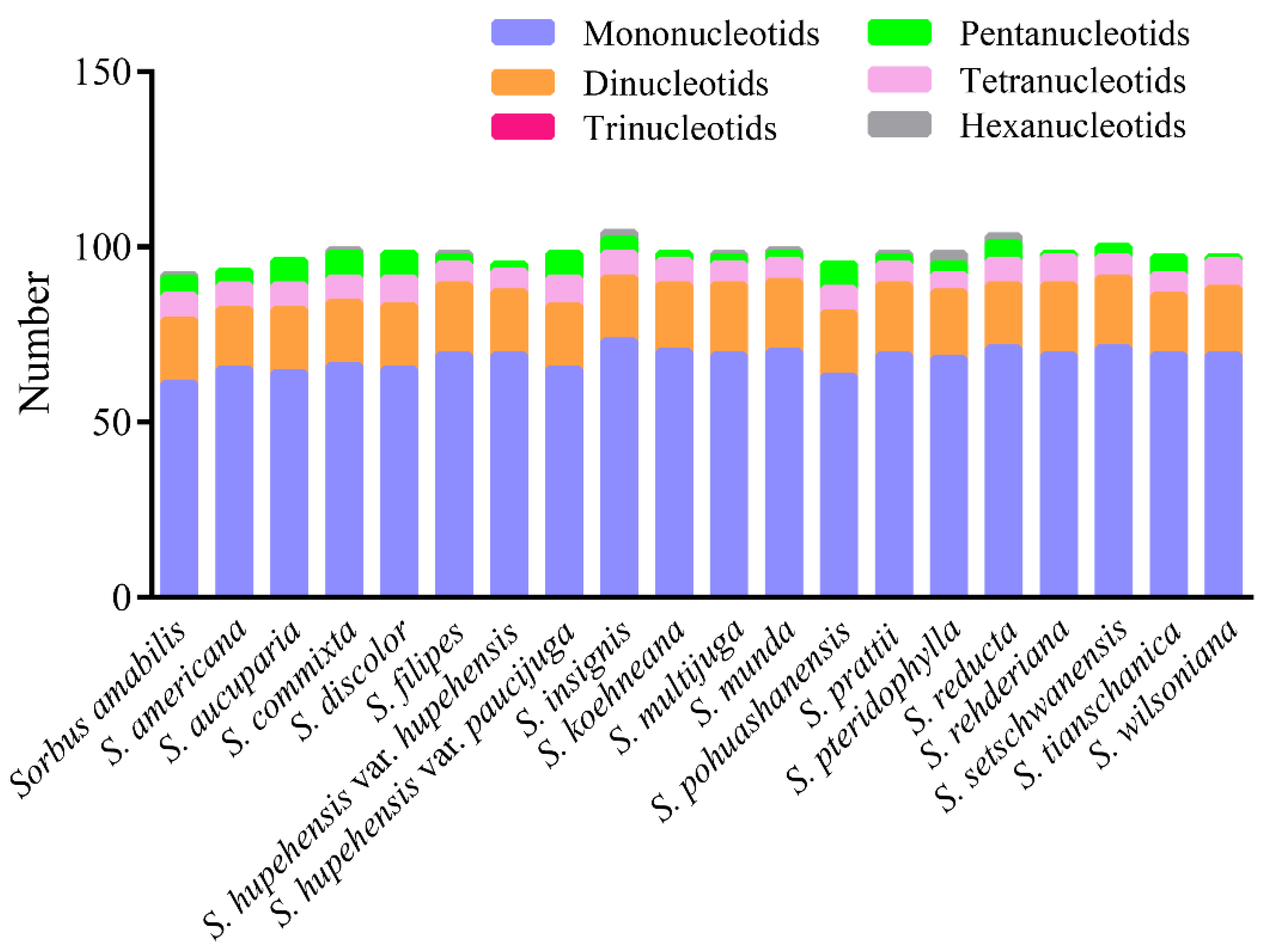
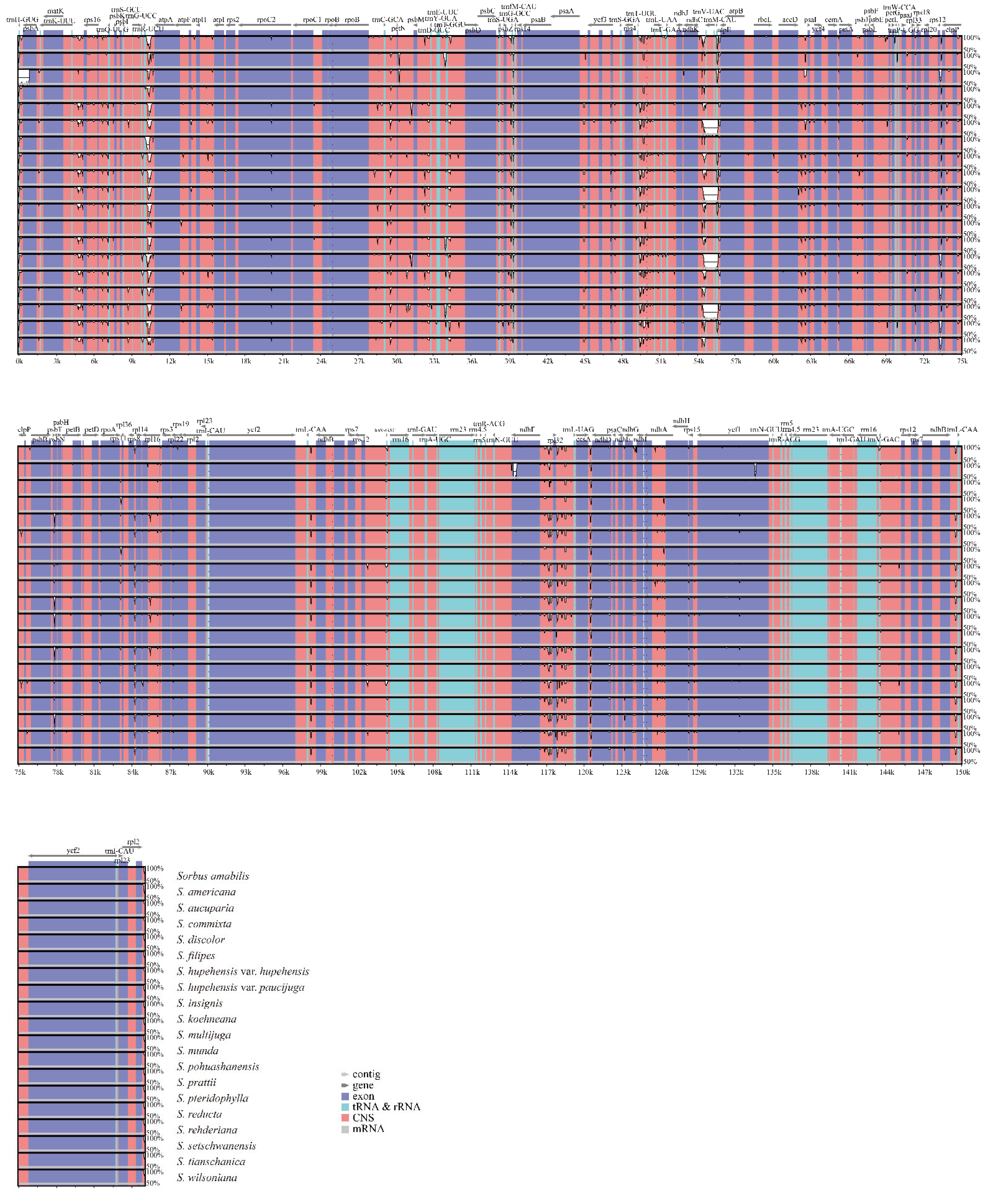
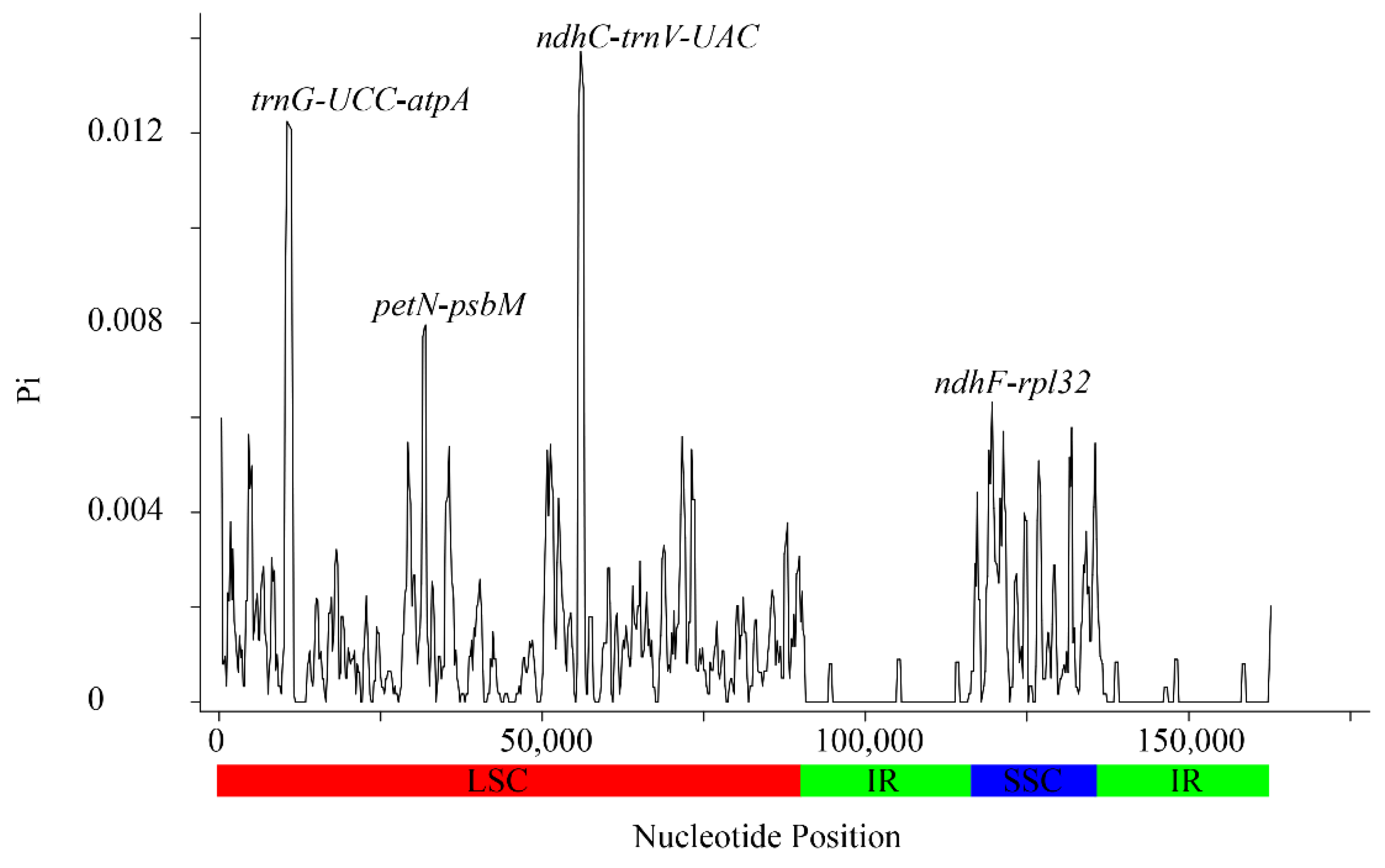
3.2. Sequence Polymorphism Variation and Divergence Analysis in Sorbus
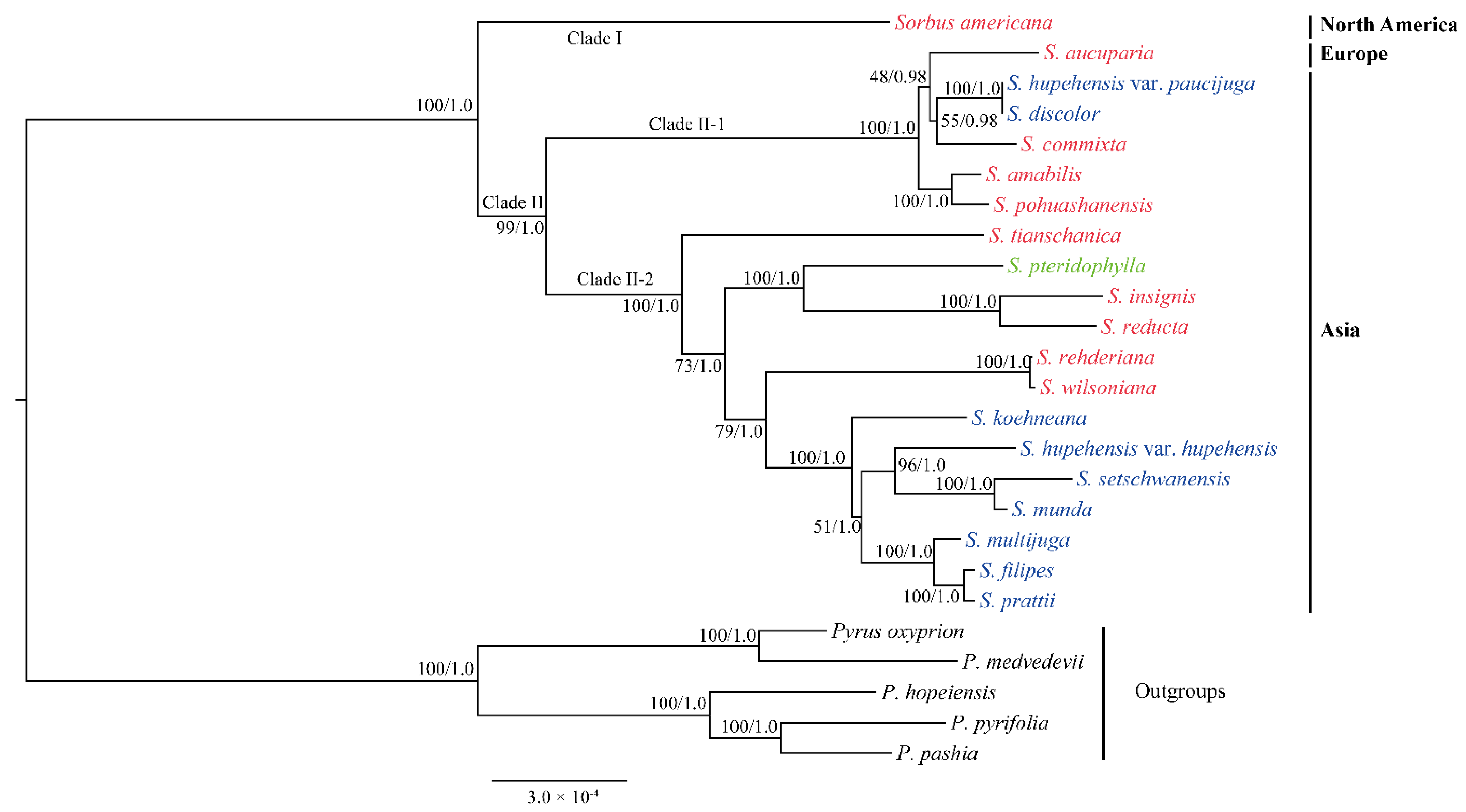
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of Sorbus
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldasoro, J.J.; Aedo, C.; Navarro, C.; Munoz Garmendia, F. The genus Sorbus (Maloideae, Rosaceae) in Europe and in North Africa: Morphological analysis and systematics. Syst. Bot. 1998, 23, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, J.B.; Robertson, K.R.; Rohrer, J.R.; Smith, P.G. Origins and evolution of subfam. Maloideae (Rosaceae). Syst. Bot. 1991, 16, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phipps, J.B.; Robertson, K.R.; Smith, P.G.; Rohrer, J.R. A checklist of the subfamily Maloideae (Rosaceae). Can. J. Bot. 1990, 68, 2209–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yü, D.; Lu, L. Sorbus L. In Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1974; Volume 36, pp. 283–344. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Li, J.-X.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Guo, L.-P. Research advances in Sorbus plants. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2019, 25, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sołtys, A.; Galanty, A.; Podolak, I. Ethnopharmacologically important but underestimated genus Sorbus: A comprehensive review. Phytochem. Rev. 2020, 19, 491–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Jin, J.J.; Chen, S.Y.; Chase, M.W.; Soltis, D.E.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Yi, T. Diversification of Rosaceae since the Late Cretaceous based on plastid phylogenomics. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.; Eriksson, T.; Evans, R.C.; Oh, S.; Smedmark, J.E.E.; Morgan, D.R.; Kerr, M.; Robertson, K.R.; Arsenault, M.; Dickinson, T.A.; et al. Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant Syst. Evol. 2007, 266, 5–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, E.Y.; Donoghue, M.J. Expanded phylogenetic and dating analyses of the apples and their relatives (Pyreae, Rosaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 63, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.-M.; Zhang, M.-L. A cladistic and phenetic analysis of the infrageneric relationships of Sorbus s. l. (Maloideae, Rosaceae) based on the morphological characters. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2007, 34, 723–728. [Google Scholar]
- Mcallister, H. Genus Sorbus: Mountain Ash and Other Rowans; The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew: London, UK, 2005; ISBN 9781842460887. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ohi-Toma, T.; Gao, Y.-D.; Xu, B.; Zhu, Z.-M.; Ju, W.-B.; Gao, X.-F. Molecular phylogenetics and historical biogeography of Sorbus sensu stricto (Rosaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 111, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Robert, K.J. Chloroplast genomes of plants. In Plant Diversity and Evolution. Genotypic and Phenotypic Variation in Higher Plants; Henry, R.J., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2005; Volume 42, pp. 45–68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.B.; Li, D.Z.; Li, H.T. Highly effective sequencing whole chloroplast genomes of angiosperms by nine novel universal primer pairs. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 14, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes De Novo Assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2020, 70, e102–e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.J.; Moore, M.J.; Li, D.Z.; Yi, T.S. PGA: A software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Plant Methods 2019, 15, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, G.; Pascal, L.; Ralph, B. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, S.-H.; Steven, C.; Matthew, S. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 228, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Lior, P.; Alexander, P.; Rubin, E.M.; Inna, D. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, B.; Thomas, T.; Thomas, M.; Uwe, S.; Martin, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Lee, C. Can RNA selection pressure distort the measurement of Ka/Ks? Gene 2006, 370, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikulin, S.V.; Bystriakova, N.; Schneider, H.; Jolley, D. Plant macrofossils from Boltysh crater provide a window into early Cenozoic vegetation. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 2014, 505, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, B.Y.; Jun-Rong, T.A.; Xie, G.P. Early Tertiary fossil plants and paleoclimate of Lanzhou Basin. J. Syst. Evol. 2001, 39, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Korotkova, N.; Parolly, G.; Khachatryan, A.; Ghulikyan, L.; Sargsyan, H.; Akopian, J.; Borsch, T.; Gruenstaeudl, M. Towards resolving the evolutionary history of Caucasian pears (Pyrus, Rosaceae)—Phylogenetic relationships, divergence times and leaf trait evolution. J. Syst. Evol. 2018, 56, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teske, D.; Peters, A.; Moellers, A.; Fischer, M. Genomic Profiling: The strengths and limitations of chloroplast genome-based plant variety authentication. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14323–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S.Q.; Xie, H.H.; Liu, J.Q.; Gao, X.F. Comparative plastid genome analyses of Rosa: Insights into the phylogeny and gene divergence. Tree Genet. Genomes 2022, 18, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Chapter 2—Plastid Chromosomes: Structure and Evolution. In The Molecular Biology of Plastids; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 5–53. ISBN 9780127150079. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, J.D.; Osorio, B.; Aldrich, J.; Thompson, W.F. Chloroplast DNA evolution among legumes: Loss of a large inverted repeat occurred prior to other sequence rearrangements. Curr. Genet. 1987, 11, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavin, M.; Doyle, J.J.; Palmer, J.D. Evolutionary significance of the loss of the chloroplast-DNA inverted repeat in the leguminosae subfamily papilionoideae. Evol. Int. J. Org. Evol. 1990, 44, 390–402. [Google Scholar]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Jansen, R.K. A rare chloroplast-DNA structural mutation is shared by all conifers. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1992, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Chloroplast evolution: Secondary symbiogenesis and multiple losses. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R62–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.S.; Cheon, K.S.; Hong, S.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Im, J.S.; Mekapogu, M.; Yu, Y.S.; Park, T.H. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Solanum commersonii and its application to chloroplast genotype in somatic hybrids with Solanum tuberosum. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.V.; Miller, J.T.; Small, I.; Nevill, P.G.; Boykin, L.M. Integration of complete chloroplast genome sequences with small amplicon datasets improves phylogenetic resolution in Acacia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, W.; Mcdevitt, R.; Vendramin, G.G.; Rafalski, J.A.; Morgante, M. Polymorphic simple sequence repeat regions in chloroplast genomes—Applications to the population genetics of pines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7759–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.P.; Bi, Y.; Yang, F.P.; Zhang, M.F.; Chen, X.Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X.H. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Lilium: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogenetic analyses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, A.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, A.R.; Muhammad, W.; Kang, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Seok-Min, L.; In-Jung, L. Complete chloroplast genome of Nicotiana otophora and its comparison with related species. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 843–854. [Google Scholar]
- Vamosi, J.C.; Dickinson, T.A. Polyploidy and diversification: A phylogenetic investigation in Rosaceae. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2006, 167, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, M.B.; Cushman, K.R.; Doucette, E.T.; Frye, C.T.; Campbell, C.S. Understanding diploid diversity: A first step in unraveling polyploid, apomictic complexity in Amelanchier. Am. J. Bot. 2015, 102, 2041–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVore, M.; Pigg, K. Biotic processes in the Okanagan Highlands floras: Possible evidence of hybridization in plants adapting to a temperate forest. Can. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 53, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
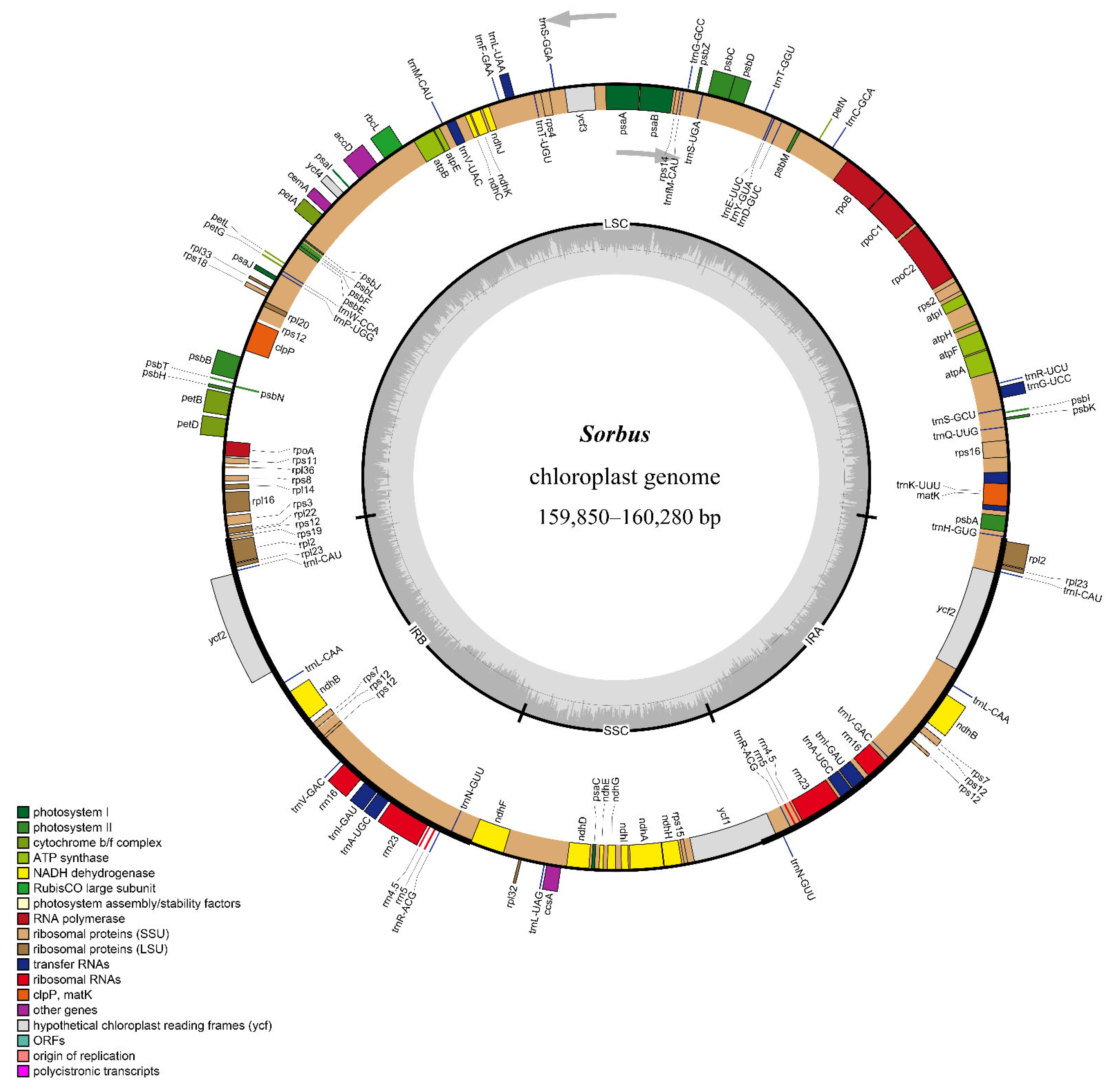
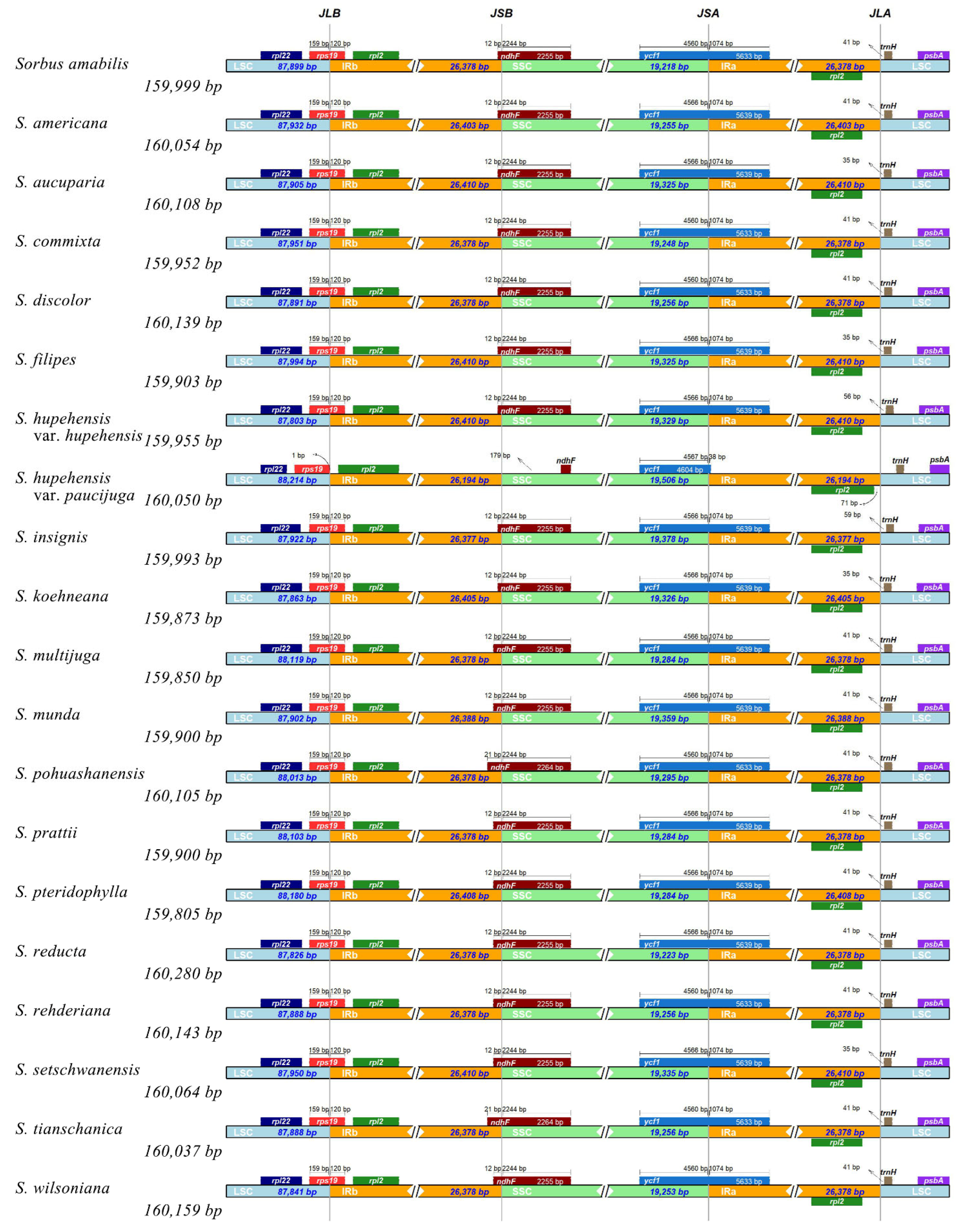
| Species | PCG | tRNA | rRNA | Total Number | Length of Plastome (bp) | Length of LSC (bp) | Length of IR (bp) | Length of SSC (bp) | GC Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sorbus amabilis * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,999 | 87,863 | 26,405 | 19,326 | 36.55 |
| S. discolor * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,139 | 87,994 | 26,410 | 19,325 | 36.53 |
| S. filipes * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,903 | 87,891 | 26,378 | 19,256 | 36.58 |
| S. hupehensis var. hupehensis * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,955 | 87,951 | 26,378 | 19,248 | 36.56 |
| S. multijuga * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,850 | 87,841 | 26,378 | 19,253 | 36.58 |
| S. pohuashanensis * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,105 | 87,950 | 26,410 | 19,335 | 36.54 |
| S. reducta * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,280 | 88,180 | 26,408 | 19,284 | 36.55 |
| S. wilsoniana * | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,159 | 88,119 | 26,378 | 19,284 | 36.54 |
| S. americana ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,054 | 87,922 | 26,377 | 19,378 | 36.55 |
| S. aucuparia ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,108 | 87,974 | 26,314 | 19,506 | 36.54 |
| S. commixta ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,952 | 87,803 | 26,410 | 19,329 | 36.55 |
| S. hupehensis var. paucijuga ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,050 | 87,905 | 26,410 | 19,325 | 36.55 |
| S. insignis ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,993 | 87,932 | 26,403 | 19,255 | 36.56 |
| S. koehneana ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,873 | 87,899 | 26,378 | 19,218 | 36.58 |
| S. munda ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,900 | 87,888 | 26,378 | 19,256 | 36.57 |
| S. prattii ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,900 | 87,888 | 26,378 | 19,256 | 36.58 |
| S. pteridophylla ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 159,805 | 87,826 | 26,378 | 19,223 | 36.59 |
| S. rehderiana ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,143 | 88,103 | 26,378 | 19,284 | 36.54 |
| S. setschwanensis ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,064 | 88,013 | 26,378 | 19,295 | 36.54 |
| S. tianschanica ** | 84 | 37 | 8 | 129 | 160,037 | 87,902 | 26,388 | 19,359 | 36.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.-D.; Ling, L.-Z. Molecular Structure and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Plastomes of Eight Sorbus Sensu Stricto Species. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111648
Zhang S-D, Ling L-Z. Molecular Structure and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Plastomes of Eight Sorbus Sensu Stricto Species. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111648
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shu-Dong, and Li-Zhen Ling. 2022. "Molecular Structure and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Plastomes of Eight Sorbus Sensu Stricto Species" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111648
APA StyleZhang, S.-D., & Ling, L.-Z. (2022). Molecular Structure and Phylogenetic Analyses of the Plastomes of Eight Sorbus Sensu Stricto Species. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111648





