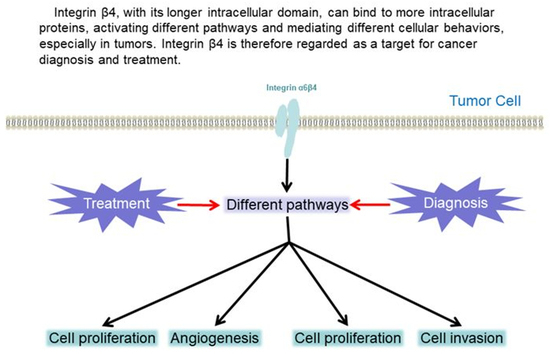
Integrin β4 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tumor Marker
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Integrin β4
2.1. Structure of Integrin β4
2.2. Function of Integrin β4
3. Differential Expression of Integrin β4 in Tumors
3.1. Lung Cancer
3.2. Breast Cancer
3.3. Prostate Cancer
3.4. Colon Cancer
4. Integrin-β4-Mediated Cancer Progression
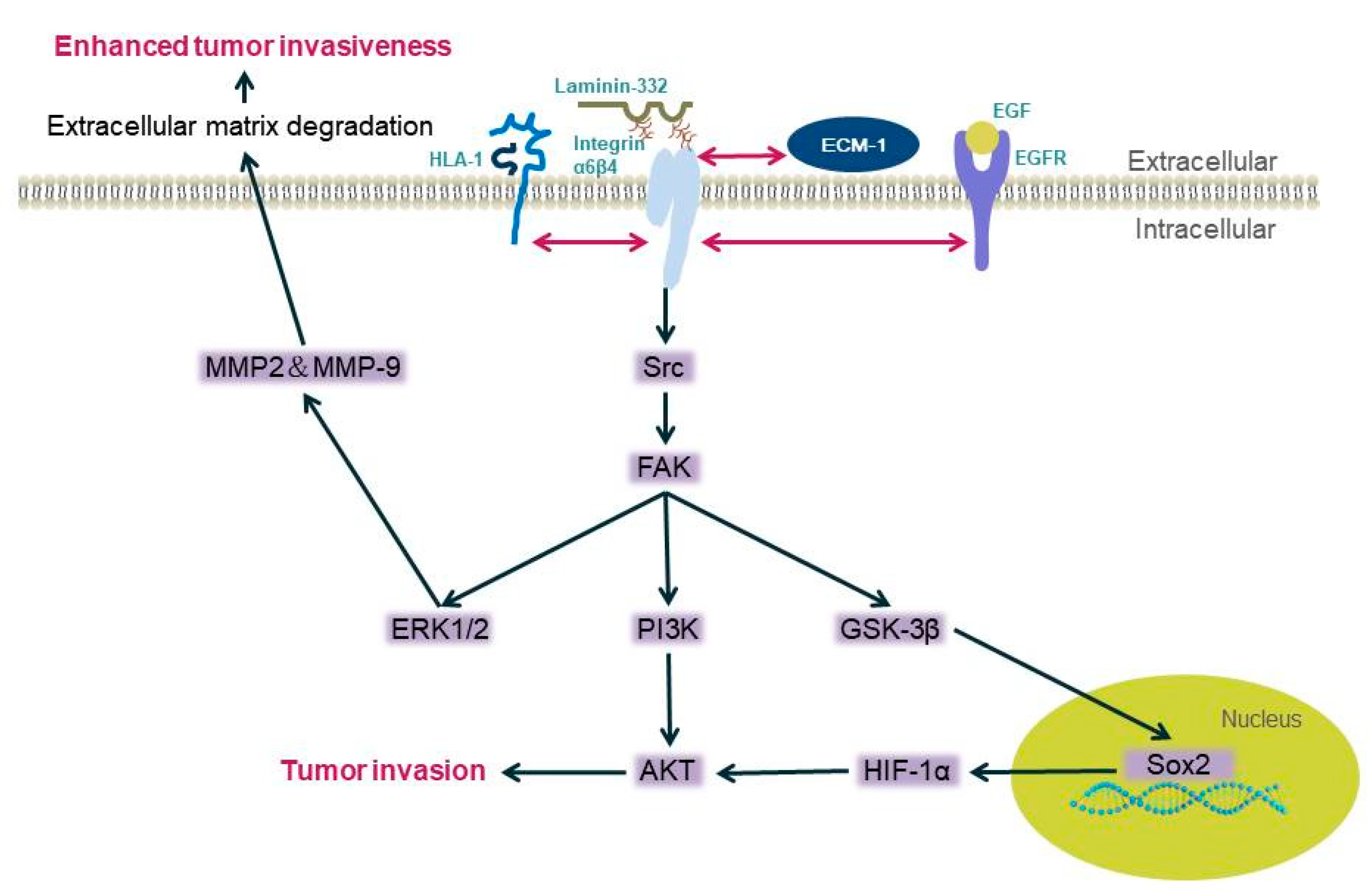
4.1. Integrin β4 Is Associated with Tumor Invasion and Migration
4.2. Integrin β4 Is Associated with Tumor Cell Proliferation
4.3. Integrin β4 Is Related to Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
4.4. Integrin β4 Is Associated with Angiogenesis
5. Potential Clinical Applications of Integrin β4
5.1. Diagnosis
5.2. Treatment Targeting Integrin β4
5.2.1. Potential Targets for Integrin β4 Pathway Therapy
5.2.2. Drug Intervention of the Integrin β4 Pathway
5.2.3. Physical Intervention in the Integrin β4 Pathway
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Current Cancer Epidemiology. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2019, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, R.; Baade, P.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A.; Yu, X.Q.; He, J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.L.; O’Connor, K.L. Clinical significance of the integrin alpha6beta4 in human malignancies. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsen, K.; Litjens, S.H.; Sonnenberg, A. Multiple functions of the integrin alpha6beta4 in epidermal homeostasis and tu-morigenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.H.; Li, S.T.; Cheng, N.C.; Ji, Y.R.; Wang, J.H.; Young, T.H. Label-free platform on pH-responsive chitosan: Adhesive heterogeneity for cancer stem-like cell isolation from A549 cells via integrin beta4. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Simin, K.; Khan, A.; Mercurio, A.M. Analysis of integrin beta4 expression in human breast cancer: Association with basal-like tumors and prognostic significance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Cai, Y.; Joshi, S.B.; Tovar, E.; Tucker, S.C.; Maddipati, K.R.; Crissman, J.D.; Repaskey, W.T.; Honn, K.V. Convergence of eicosanoid and integrin biology: 12-lipoxygenase seeks a partner. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basora, N.; Herring-Gillam, F.E.; Boudreau, F.; Perreault, N.; Pageot, L.P.; Simoneau, M.; Bouatrouss, Y.; Beaulieu, J.F. Expression of functionally distinct variants of the beta(4)A integrin subunit in relation to the differentiation state in human intestinal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29819–29825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.X.; Xiang, Y.; Qin, X.Q. The research progress of integrin beta4. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2018, 70, 504–510. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Gu, J. Roles of Integrin alpha6beta4 Glycosylation in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K. Laminin-5 (laminin-332): Unique biological activity and role in tumor growth and invasion. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margadant, C.; Frijns, E.; Wilhelmsen, K.; Sonnenberg, A. Regulation of hemidesmosome disassembly by growth factor receptors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Oyama, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Gu, J.; Kariya, Y. beta4-Integrin/PI3K Signaling Promotes Tumor Progression through the Galectin-3-N-Glycan Complex. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Rubin, B.K.; Voynow, J.A. Mucins, Mucus, and Goblet Cells. Chest 2018, 154, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmanan, I.; Rachagani, S.; Hauke, R.; Krishn, S.R.; Paknikar, S.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Karmakar, S.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Kaushik, G.; Johansson, S.L.; et al. MUC5AC interactions with integrin beta4 enhances the migration of lung cancer cells through FAK signaling. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4112–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.L.; West, D.; Wang, C.; Weiss, H.L.; Gal, T.; Durbin, E.B.; O’Connor, W.; Chen, M.; O’Connor, K.L. Elevated integrin alpha6beta4 expression is associated with venous invasion and decreased overall survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 54, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soung, Y.H.; Ford, S.; Yan, C.; Chung, J. The Role of Arrestin Domain-Containing 3 in Regulating Endocytic Recycling and Extracellular Vesicle Sorting of Integrin beta4 in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, H.; Feltri, M.L.; Mercurio, A.M. Integrin beta4 regulation of PTHrP underlies its contribution to mammary gland development. Dev. Biol. 2015, 407, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.-L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierie, B.; Pierce, S.E.; Kroeger, C.; Stover, D.G.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Thiru, P.; Donaher, J.L.; Reinhardt, F.; Chaffer, C.L.; Keckesova, Z.; et al. Integrin-beta4 identifies cancer stem cell-enriched populations of partially mesenchymal carcinoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2337–E2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, J.S.; Kang, C.W.; Kang, S.; Jang, Y.; Chae, Y.C.; Gil Kim, B.; Cho, N.H. ITGB4-mediated metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Oncogene 2020, 39, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.T.; Soung, Y.H.; Surh, Y.J.; Cardelli, J.A.; Chung, J. Curcumin Prevents Palmitoylation of Integrin beta4 in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Chang, F.W.; Huang, F.S.; Liu, J.M.; Liu, Y.P.; Chen, S.P.; Liu, Y.L.; Cheng, K.C.; Yu, C.P.; Hsu, R.J. Estrogen Enhances the Cell Viability and Motility of Breast Cancer Cells through the ERalpha-DeltaNp63-Integrin beta4 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148301. [Google Scholar]
- Siddharth, S.; Nayak, A.; Das, S.; Nayak, D.; Panda, J.; Wyatt, M.D.; Kundu, C.N. The soluble nectin-4 ecto-domain promotes breast cancer induced angiogenesis via endothelial Integrin-beta4. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 102, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, T.; Otero, J.; Chen, Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Koutcher, J.A.; Satagopan, J.; Reuter, V.; Carver, B.; De Stanchina, E.; Enomoto, K.; et al. beta4 Integrin signaling induces expansion of prostate tumor progenitors. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 682–699. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, E.J.; Woodworth, A.M.; Parker, M.; Phillips, J.L.; Malley, R.C.; Dickinson, J.L.; Holloway, A.F. Epigenetic regulation of the ITGB4 gene in prostate cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 392, 112055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, K.; Fujita, Y.; Kato, T.; Mizutani, K.; Kameyama, K.; Tsumoto, H.; Miura, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Ito, M. Integrin beta4 and vinculin contained in exosomes are potential markers for progression of prostate cancer asso-ciated with taxane-resistance. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Dydensborg, A.B.; Herring, F.E.; Basora, N.; Gagné, D.; Vachon, P.H.; Beaulieu, J.-F. Upregulation of a functional form of the beta4 integrin subunit in colorectal cancers correlates with c-Myc expression. Oncogene 2005, 24, 6820–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Ohno, Y.; Nobuhisa, T.; Takaoka, M.; Sirmali, M.; Nakajima, M.; Gunduz, M.; Shirakawa, Y.; Okawa, T.; Naomoto, Y.; et al. Localization of FAK is related with colorectal carcinogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lü, Y.; Han, B.; Yu, H.; Cui, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Berberine regulates the microRNA-21-ITGBeta4-PDCD4 axis and inhibits colon cancer viability. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5971–5976. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, T.; Shiozaki, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Miyazaki, S.; Satomi, S.; Kato, K.; Sakuraba, H.; Miyagi, T. Contribution of sialidase NEU1 to suppression of metastasis of human colon cancer cells through desialylation of integrin beta4. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Chiu, H.; Hopkins, B.D.; Bagrodia, S.; Cantley, L.C.; Abraham, R.T. The PI3K Pathway in Human Disease. Cell 2017, 170, 605–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draheim, K.M.; Chen, H.B.; Tao, Q.; Moore, N.; Roche, M.; Lyle, S. ARRDC3 suppresses breast cancer progression by negatively regulating integrin beta4. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5032–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elaimy, A.L.; Wang, M.; Sheel, A.; Brown, C.W.; Walker, M.R.; Amante, J.J.; Xue, W.; Chan, A.; Baer, C.E.; Goel, H.L.; et al. Real-time imaging of integrin beta4 dynamics using a reporter cell line generated by Crispr/Cas9 genome editing. J. Cell. Sci. 2019, 132, jcs231241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, M.M.; Nusrat, A.; Madara, J.L.; Ezzell, R.; Wewer, U.M.; Mercurio, A.M. Intestinal epithelial restitution. Involvement of specific laminin isoforms and integrin laminin receptors in wound closure of a transformed model epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 150, 747–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, K.L.; Nguyen, B.K.; Mercurio, A.M. RhoA function in lamellae formation and migration is regulated by the alpha6beta4 integrin and cAMP metabolism. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 148, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitz, I.; Mercurio, A.M. The integrin alpha6beta4 functions in carcinoma cell migration on laminin-1 by mediating the formation and stabilization of actin-containing motility structures. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitz, I.; Toker, A.; Mercurio, A.M. Protein kinase C-dependent mobilization of the alpha6beta4 integrin from hemidesmo-somes and its association with actin-rich cell protrusions drive the chemotactic migration of carcinoma cells. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 146, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; Rabinovitz, I.; Wang, H.H.; Toker, A.; Mercurio, A.M. Activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase by the alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma invasion. Cell 1997, 91, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, K.; Chen, M. Dynamic functions of RhoA in tumor cell migration and invasion. Small GTPases 2013, 4, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, E.A.; Mercurio, A.M. Mobilization and activation of a signaling competent alpha6beta4integrin underlies its contribution to carcinoma progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005, 24, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, S.N.; Blaikie, P.; Yoshioka, T.; Guo, W.; Puri, C.; Tacchetti, C.; Giancotti, F.G. Targeted deletion of the integrin beta4 signaling domain suppresses laminin-5-dependent nuclear entry of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-kappaB, causing defects in epidermal growth and migration. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 6090–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.O.; Shin, S.; Lipscomb, E.A. A novel mechanism for integrin-mediated ras activation in breast carcinoma cells: The al-pha6beta4 integrin regulates ErbB2 translation and transactivates epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB2 signaling. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Luo, M.; Ou, H.; Liu, X.; Kang, X.; Yin, W. Integrin beta4 promotes invasion and anoikis resistance of papillary thyroid carcinoma and is consistently overexpressed in lymphovascular tumor thrombus. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6635–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Rozengurt, E.; Reed, E.F. HLA class I molecules partner with integrin beta4 to stimulate endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Sci. Signal 2010, 3, ra85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Meng, J.; Xu, M.; Liu, M.; Qi, Y.; Tan, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Weng, W.; Sheng, W.; et al. Extracellular matrix protein 1 promotes cell metastasis and glucose metabolism by inducing integrin be-ta4/FAK/SOX2/HIF-1alpha signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Chen, W.-X.; Luo, H.-P.; Song, J.; Dong, W.; Zhu, X.-R.; Chen, X.-P.; Liang, H.-F.; Zhang, B.-X. An integrin beta4-EGFR unit promotes hepatocellular carcinoma lung metastases by enhancing anchorage independence through activation of FAK–AKT pathway. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.L.; Chu, P.Y.; Lai, I.R.; Wang, M.Y.; Tseng, H.Y.; Guan, J.L.; Liou, J.Y.; Shen, T.L. An EGFR/Src-dependent beta4 integrin/FAK complex contributes to malignancy of breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.-N.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.-M.; Ding, X.; Li, H.-Q.; Geng, M.; Xie, Z.-Q.; Wu, H.-M. Monocarboxylate Transporter 4 Facilitates Cell Proliferation and Migration and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, V.; Juarez, J.; Patel, P.; Hutter-Lobo, D. Density-dependent ERK MAPK expression regulates MMP-9 and influences growth. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 456, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.H.; Suh, H.N.; Kim, M.O.; Han, H.J. Glucosamine-induced reduction of integrin beta4 and plectin complex stimulates migration and proliferation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem. Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, K.D.; Shearstone, J.R.; Maddula, V.K.; Seligmann, B.E.; Mercurio, A.M. Integrin beta4 regulates SPARC protein to promote invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9835–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Molder, L.; Sonnenberg, A. PKD2 and RSK1 Regulate Integrin beta4 Phosphorylation at Threonine 1736. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sammani, S.; Mitra, S.; Ma, S.F.; Garcia, J.G.; Jacobson, J.R. Critical role for integrin-beta4 in the attenuation of murine acute lung injury by simvastatin. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2012, 303, L279–L285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, V.; Yebra, M. Netrins: Beyond the brain. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ylivinkka, I.; Chen, P.; Li, L.; Hautaniemi, S.; Nyman, T.A.; Keski-Oja, J.; Hyytiäinen, M. Netrin-4 promotes glioblastoma cell proliferation through integrin beta4 signaling. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Yang, X.; Pursell, B.; Mercurio, A.M. Id2 complexes with the SNAG domain of Snai1 inhibiting Snai1-mediated repression of integrin beta4. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 3795–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugo, H.; Ackland, L.; Blick, T.; Lawrence, M.G.; Clements, J.; Williams, E.D.; Thompson, E.W. Epithelial—mesenchymal and mesenchymal—epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, E.; Patra, H.K.; Jangamreddy, J.R.; Rashedi, I.; Kawalec, M.; Pariti, R.K.R.; Batakis, P.; Wiechec, E. Cell adhesion molecules and their relation to (cancer) cell stemness. Carcinog. 2014, 35, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, H.B.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, W.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, M.C.; Su, J.M.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human lung cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk1/2 signaling pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 3549–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Liang, W.; Xiong, Z.; Xiong, Z. Integrin beta4 in EMT: An implication of renal diseases. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 6967–6976. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Radisky, D.C.; Yang, D.; Xu, R.; Radisky, E.S.; Bissell, M.J.; Bishop, J.M. MYC suppresses cancer metastasis by direct transcriptional silencing of alphav and beta3 integrin subunits. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2012, 14, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannelli, G.; Villa, E.; Lahn, M. Targeting transforming growth factor (TGF)-betaRI inhibits activation of beta1 integrin and blocks vascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 839–850. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, Y.Y.; Chiao, C.C.; Kuo, W.Y.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y. TGF-beta1 increases motility and alphavbeta3 integrin up-regulation via PI3K, Akt and NF-kappaB-dependent pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Tian, Z.L.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhao, X.X.; Yao, L. Activation of integrin beta1-focal adhesion kinase-RasGTP pathway plays a critical role in TGF beta1-induced po-docyte injury. Cell Signal. 2013, 25, 2769–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, A.S.; Yamada, T.; Gotoh, M.; Kanai, Y.; Imai, K.; Hirohashi, S. Cloning and characterization of the human beta4-integrin gene promoter and enhancers. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33848–33855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Pursell, B.; Lu, S.; Chang, T.K.; Mercurio, A.M. Regulation of beta 4-integrin expression by epigenetic modifications in the mammary gland and during the epitheli-al-to-mesenchymal transition. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2473–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hao, N.; Han, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Yang, N. ZKSCAN3 drives tumor metastasis via integrin beta4/FAK/AKT mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepato-cellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. Int. 2020, 20, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Angiogenesis and apoptosis are cellular parameters of neoplastic progression in transgenic mouse models of tumorigenesis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 995–1002. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, B.; Khwaja, F.W.; Severson, E.A.; Matheny, S.L.; Brat, D.J.; Van Meir, E.G. Hypoxia and the hypoxia-inducible-factor pathway in glioma growth and angiogenesis. Neuro-Oncology 2005, 7, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, S.N.; Blaikie, P.; Yoshioka, T.; Guo, W.; Giancotti, F.G. Integrin beta4 signaling promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ephstein, Y.; Singleton, P.A.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Salgia, R.; Kanteti, P.; Dudek, S.M.; Garcia, J.G.; Jacobson, J.R. Critical role of S1PR1 and integrin beta4 in HGF/c-Met-mediated increases in vascular integrity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Tan, W.; Li, P.; Chen, G.; Peng, Q.; Yin, W. Integrin beta4 Is an Effective and Efficient Marker in Synchronously Highlighting Lymphatic and Blood Vascular Invasion, and Perineural Aggression in Malignancy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassan, M.; Pizzi, M.; Giacomelli, L.; Mescoli, C.; Ludwig, K.; Pucciarelli, S.; Rugge, M. PDCD4 nuclear loss inversely correlates with miR-21 levels in colon carcinogenesis. Virchows Archiv 2011, 458, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asangani, I.; Rasheed, S.A.K.; Nikolova, D.A.; Leupold, J.H.; Colburn, N.H.; Post, S.; Allgayer, H. MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2007, 27, 2128–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraro, A.; Kontos, C.K.; Boni, T.; Bantounas, I.; Siakouli, D.; Kosmidou, V.; Vlassi, M.; Spyridakis, Y.; Tsipras, I.; Zografos, G.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of miR-21 in colorectal cancer: ITGB4 as a novel miR-21 target and a three-gene network (miR-21-ITGBeta4-PDCD4) as predictor of metastatic tumor potential. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Pylayeva, Y.; Pepe, A.; Yoshioka, T.; Muller, W.J.; Inghirami, G.; Giancotti, F.G. Beta 4 integrin amplifies ErbB2 signaling to promote mammary tumorigenesis. Cell 2006, 126, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Chen, W.K.; Wang, C.J.; Lin, W.L.; Tseng, T.H. Apigenin inhibits HGF-promoted invasive growth and metastasis involving blocking PI3K/Akt pathway and beta 4 integrin function in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 226, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masugi, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Emoto, K.; Effendi, K.; Tsujikawa, H.; Kitago, M.; Itano, O.; Kitagawa, Y.; Sakamoto, M. Upregulation of integrin beta4 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and is a novel prognostic marker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Lab. Investg. 2015, 95, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendle, A.; Lei, H.; Brandt, A.; Johansson, R.; Enquist, K.; Henriksson, R.; Hemminki, K.; Lenner, P.; Försti, A. Polymorphisms in predicted microRNA binding sites in integrin genes and breast cancer- ITGB4 as prognostic marker. Eur. J. Cancer Suppl. 2008, 6, 42–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, X.; Wang, G.; Zhai, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhao, Z. ITGB4 is a novel prognostic factor in colon cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 5223–5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Liu, L.; Li, D.D.; He, Y.P.; Guo, L.H.; Sun, L.P.; Liu, L.N.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, X.P. Integrin beta4 promotes cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the modulation of Slug expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelens, M.C.; Berg, A.V.D.; Vogelzang, I.; Wesseling, J.; Postma, D.S.; Timens, W.; Groen, H.J. Differential expression and distribution of epithelial adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer and normal bronchus. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guan, J.L. Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, G.W.; Carragher, N.; Avizienyte, E.; Evans, J.; Brunton, V.G.; Frame, M. The role of focal-adhesion kinase in cancer—a new therapeutic opportunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aponte, M.; Jiang, W.; Lakkis, M.; Li, M.-J.; Edwards, D.; Albitar, L.; Vitonis, A.F.; Mok, S.C.; Cramer, D.W.; Ye, B. Activation of Platelet-Activating Factor Receptor and Pleiotropic Effects on Tyrosine Phospho-EGFR/Src/FAK/Paxillin in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5839–5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlou, H.; Sanguin-Gendreau, V.; Zuo, D.; Cardiff, R.D.; McLean, G.W.; Frame, M.; Muller, W.J. Mammary epithelial-specific disruption of the focal adhesion kinase blocks mammary tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20302–20307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Physiological Roles of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Qu, Y.; Wei, M.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Z.G.; Liu, B.Y.; Chen, G.Q.; Wu, Y.L.; Gu, Q.L. Metallopanstimulin-1 regulates invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells partially through integrin beta4. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2851–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, M.M.; Morrison, D.K. Integrating signals from RTKs to ERK/MAPK. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.W. The regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in mammalian cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2707–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Yu, B.; Han, J.; Jin, H.; Tan, X. Integrin beta 4 (ITGB4) and its tyrosine-1510 phosphorylation promote pancreatic tumorigenesis and regulate the MEK1-ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 20, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ge, D.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, S.; Miao, J.; Zhao, B. A small molecule induces integrin beta4 nuclear translocation and apoptosis selectively in cancer cells with high ex-pression of integrin beta4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16282–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Vikhreva, P.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; Amelio, I.; Barlev, N.; Knight, R.A.; Melino, G. Integrin-beta4 is a novel transcriptional target of TAp73. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, A.-M.; Bretz, A.C.; Mack, E.; Stiewe, T. Targeting p73 in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, W.H.; Logette, E.; Corcos, L.; Sabapathy, K. TAp73beta and DNp73beta activate the expression of the pro-survival caspase-2S. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4498–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giancotti, F.G. Targeting integrin beta4 for cancer and anti-angiogenic therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huafeng, J.; Deqing, Z.; Yong, D.; Yulian, Z.; Ailing, H. A cross-talk between integrin beta4 and epidermal growth factor receptor induces gefitinib chemoresistance to gastric cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.L.; Liu, N.; Han, X.Y.; Liu, Q.C.; Deng, W.J.; Liao, C.X. Induction of Apoptosis by Berberine in Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells via Downregulation of NF-kappaB. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Metabolic characterization and pathway analysis of berberine protects against prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 65022–65041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, N.; Li, H.-X.; Tian, L.; Ba, Y.-F.; Hao, B. Berberine induces apoptosis and DNA damage in MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im Kim, H.; Huang, H.; Cheepala, S.; Huang, S.; Chung, J. Curcumin inhibition of integrin (alpha6beta4)-dependent breast cancer cell motility and invasion. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnoux-Palacios, L.; Dans, M.; van’t Hof, W.; Mariotti, A.; Pepe, A.; Meneguzzi, G.; Resh, M.D.; Giancotti, F.G. Compartmentalization of integrin alpha6beta4 signaling in lipid rafts. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, R.K.; Singh, A.K.; Gaddipati, J.; Srimal, R.C. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short review. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, M.; Park, H.A.; Lee, H.C.; Kang, D.; Hwang, H.J.; Park, C.; Yu, D.M.; Jung, Y.R.; Hong, M.N. Integrin alpha6beta4-Src-AKT signaling induces cellular senescence by counteracting apoptosis in irradiated tumor cells and tissues. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lung Cancer | Breast Cancer | Prostate Cancer | Colon Cancer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expression Level | ① Abundantly present ② Strongly overexpressed | ① Occurs in transitional breast cancer cells ② Not in non-invasive breast cancer cells | Overexpressed (has a large CpG island) | ① Wild-type form is increased ② Integrin β4A(ctd-) is predominantly absent |
| Function | ① Initiates phosphorylation, invasion, and migration ② Occurs with gene mutation | ① Induces invasive status ② Enhances cell viability and motility ③ Promotes angiogenesis | ① Induces tumorigenesis ② Induces cell migration and invasion ③ Does not affect cell proliferation | ① Induces abnormal cell proliferation ② Affects the cell viability ③ Induces metastasis |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiang, Y. Integrin β4 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tumor Marker. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081197
Yang H, Xu Z, Peng Y, Wang J, Xiang Y. Integrin β4 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tumor Marker. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081197
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Haoyu, Zixuan Xu, Yuqian Peng, Jiali Wang, and Yang Xiang. 2021. "Integrin β4 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tumor Marker" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081197
APA StyleYang, H., Xu, Z., Peng, Y., Wang, J., & Xiang, Y. (2021). Integrin β4 as a Potential Diagnostic and Therapeutic Tumor Marker. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1197. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081197