TCMacro: A Simple and Robust ImageJ-Based Method for Automated Measurement of Tail Coiling Activity in Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.2. Chemical Preparation and Exposure
2.3. Agarose Wells Preparation
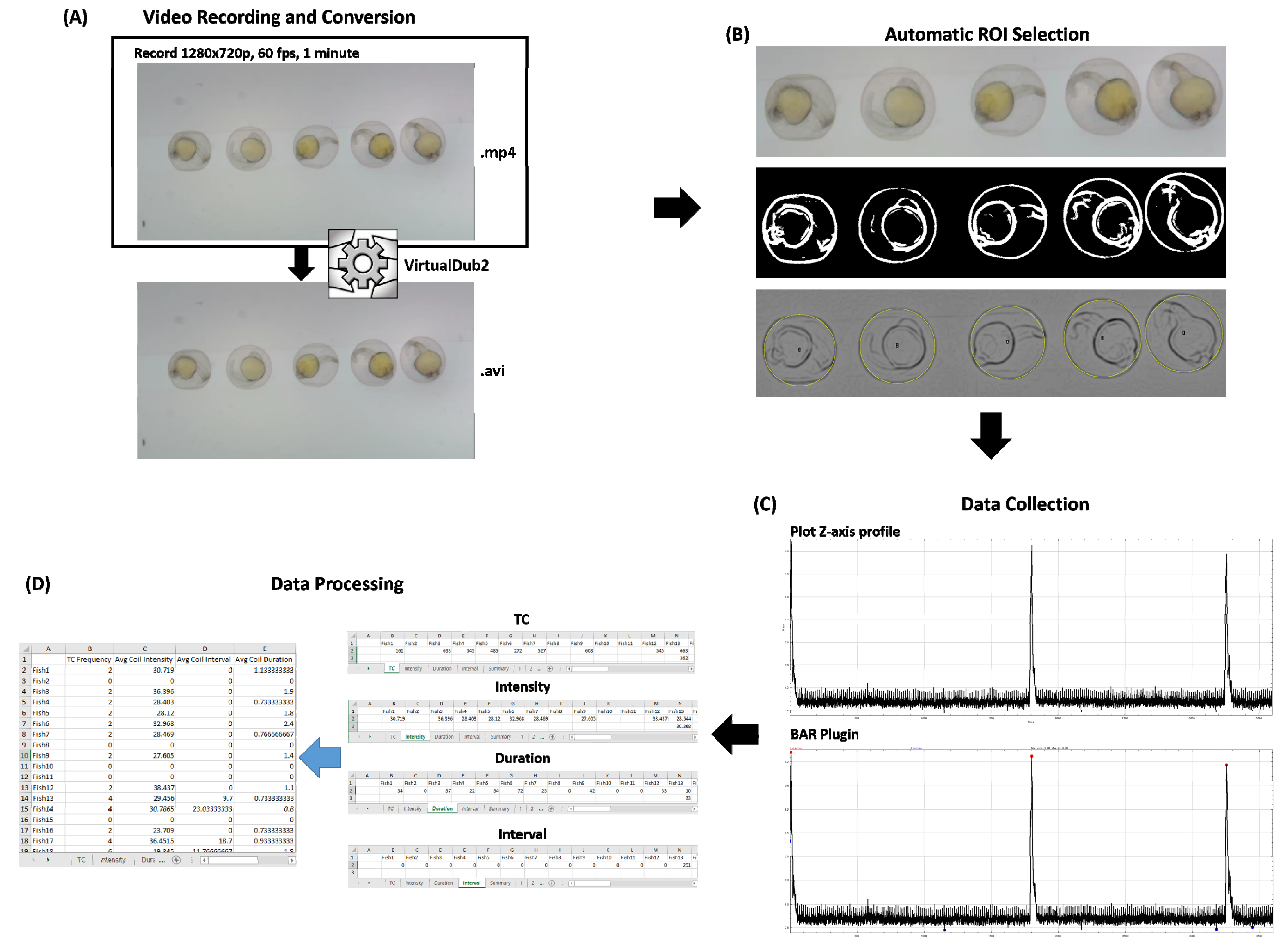
2.4. Video Recording and Conversion
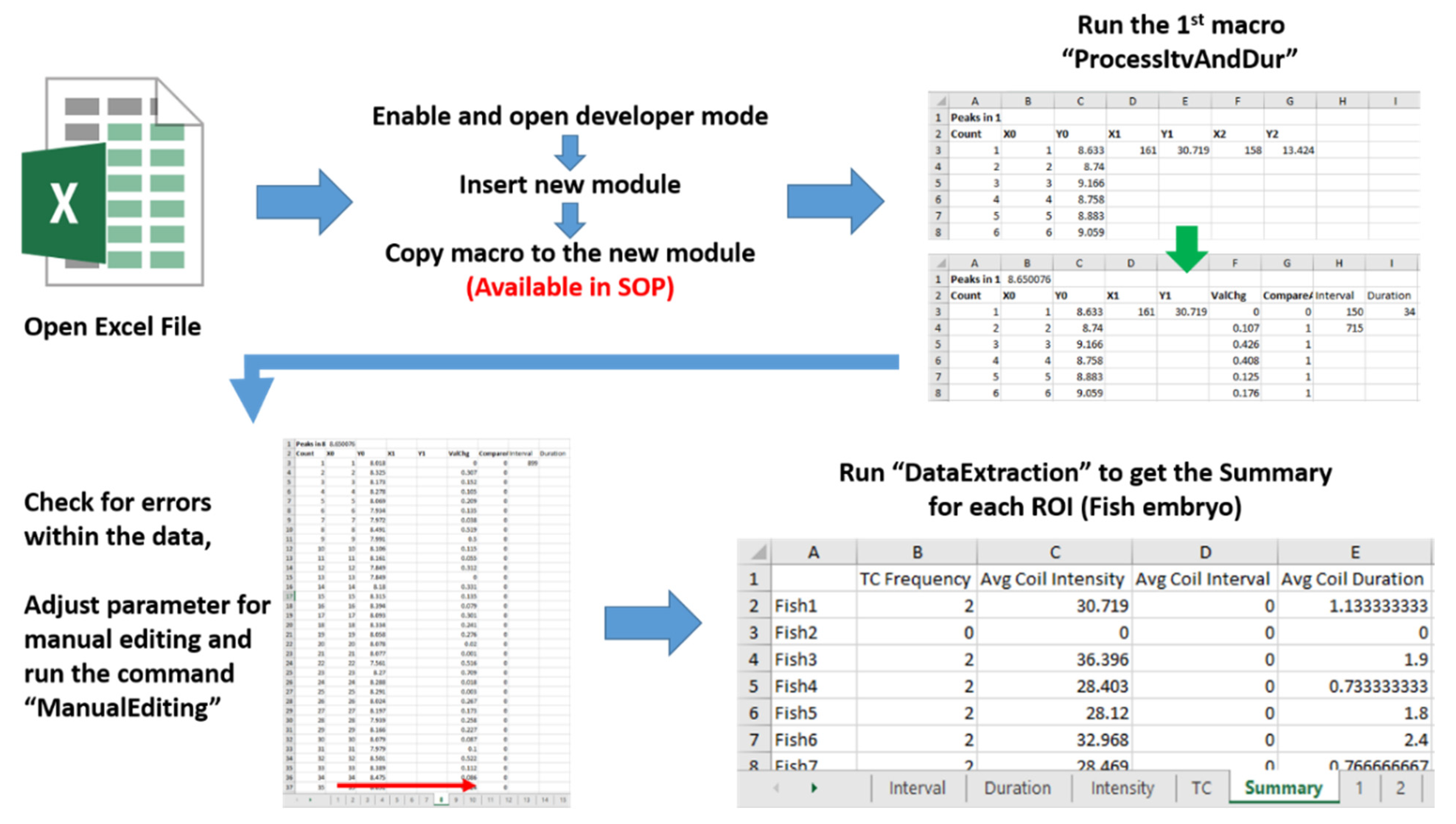
2.5. Data Collection Using ImageJ and Microsoft Excel 2016
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
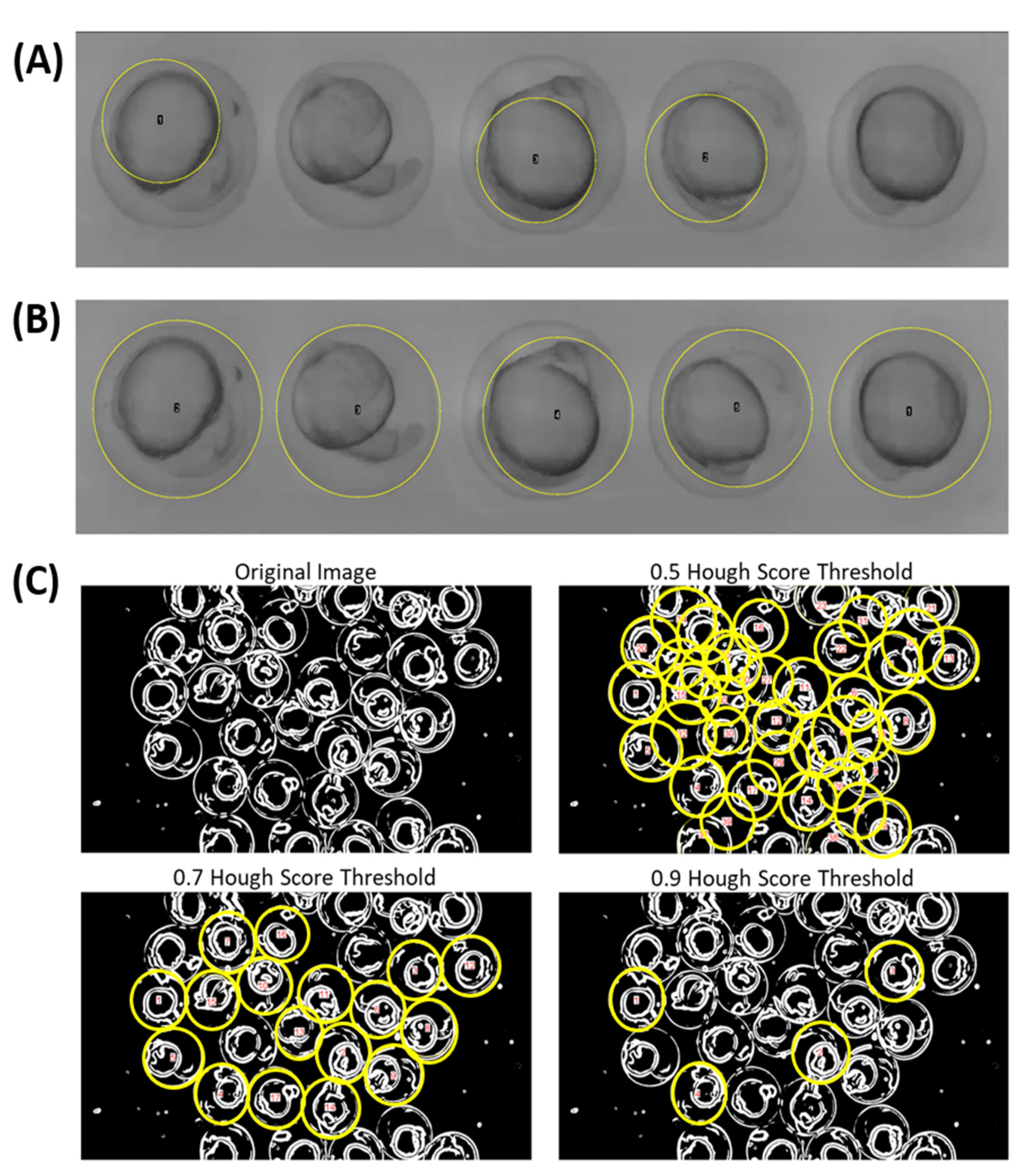
3.1. Automatic Region of Interest (ROI) Selection Using Hough Circle Transform Plugin in Bright-Field Microscope Recording
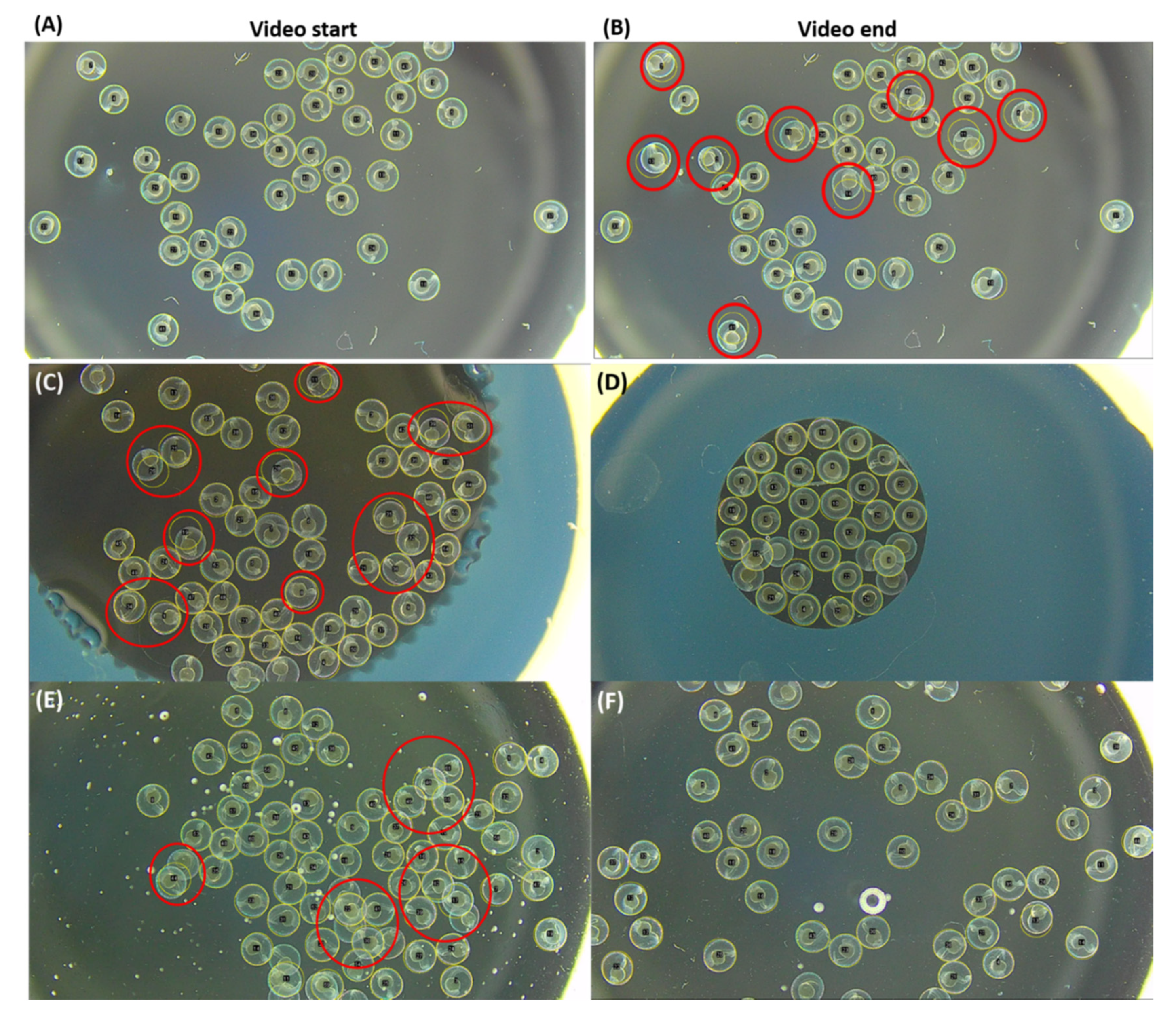
3.2. Automatic ROI Selection Using Hough Circle Transform Plugin in Using Dark-Field Microscopy Method
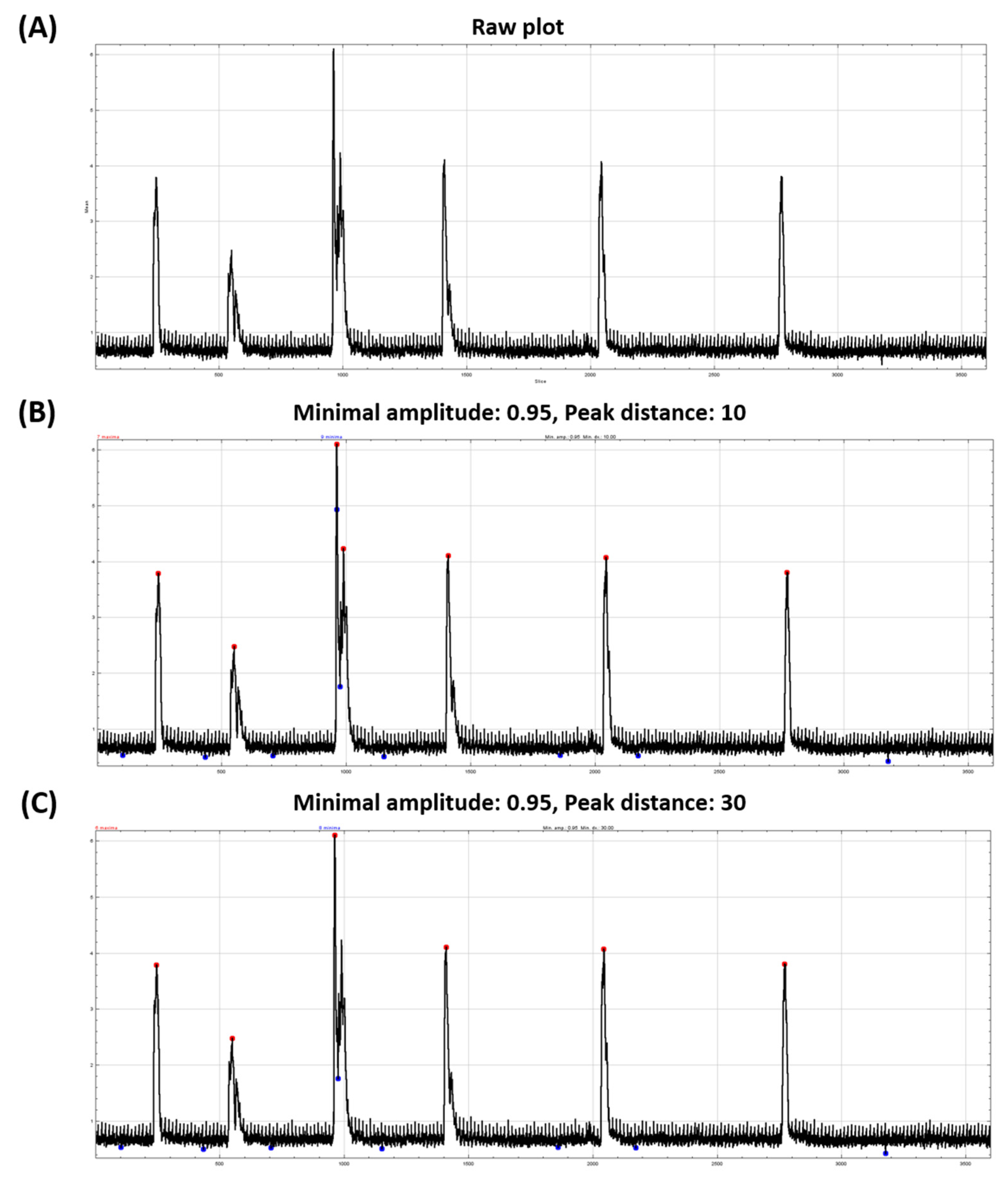
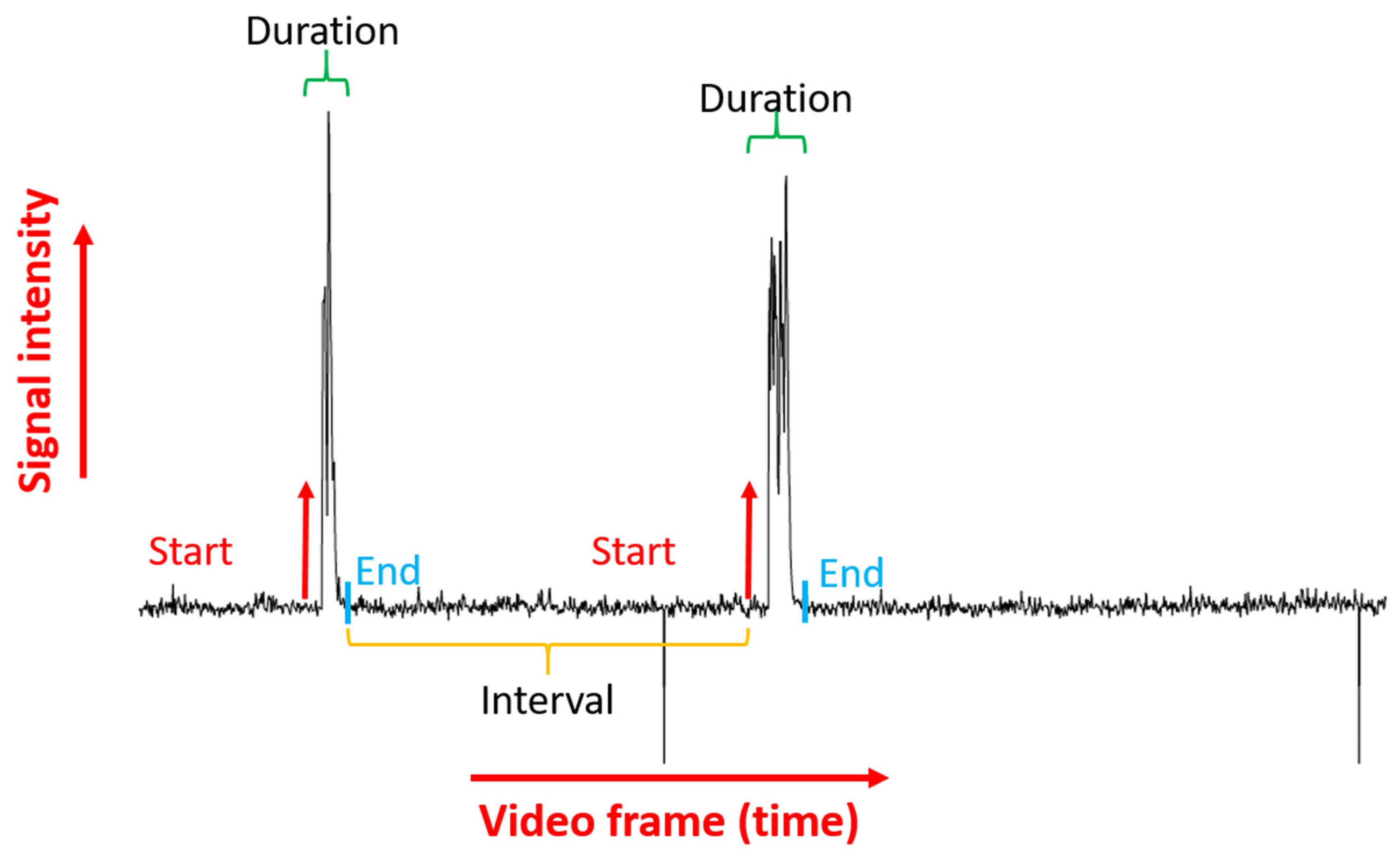
3.3. Tail Coiling Activity Data Processing in ImageJ
3.4. Tail Coiling Data Processing Using Microsoft Excel Visual Basic for Application (Excel VBA)
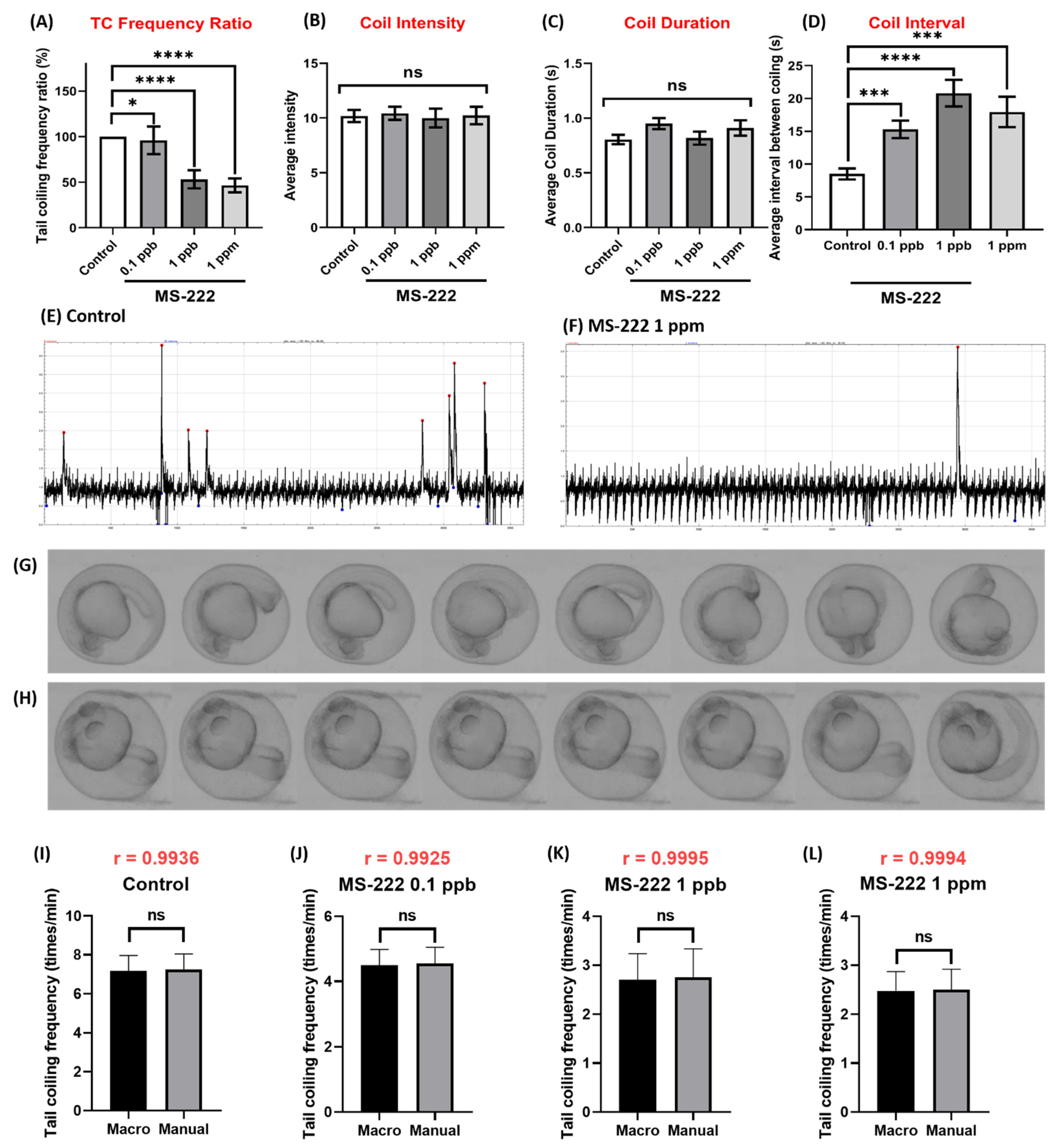
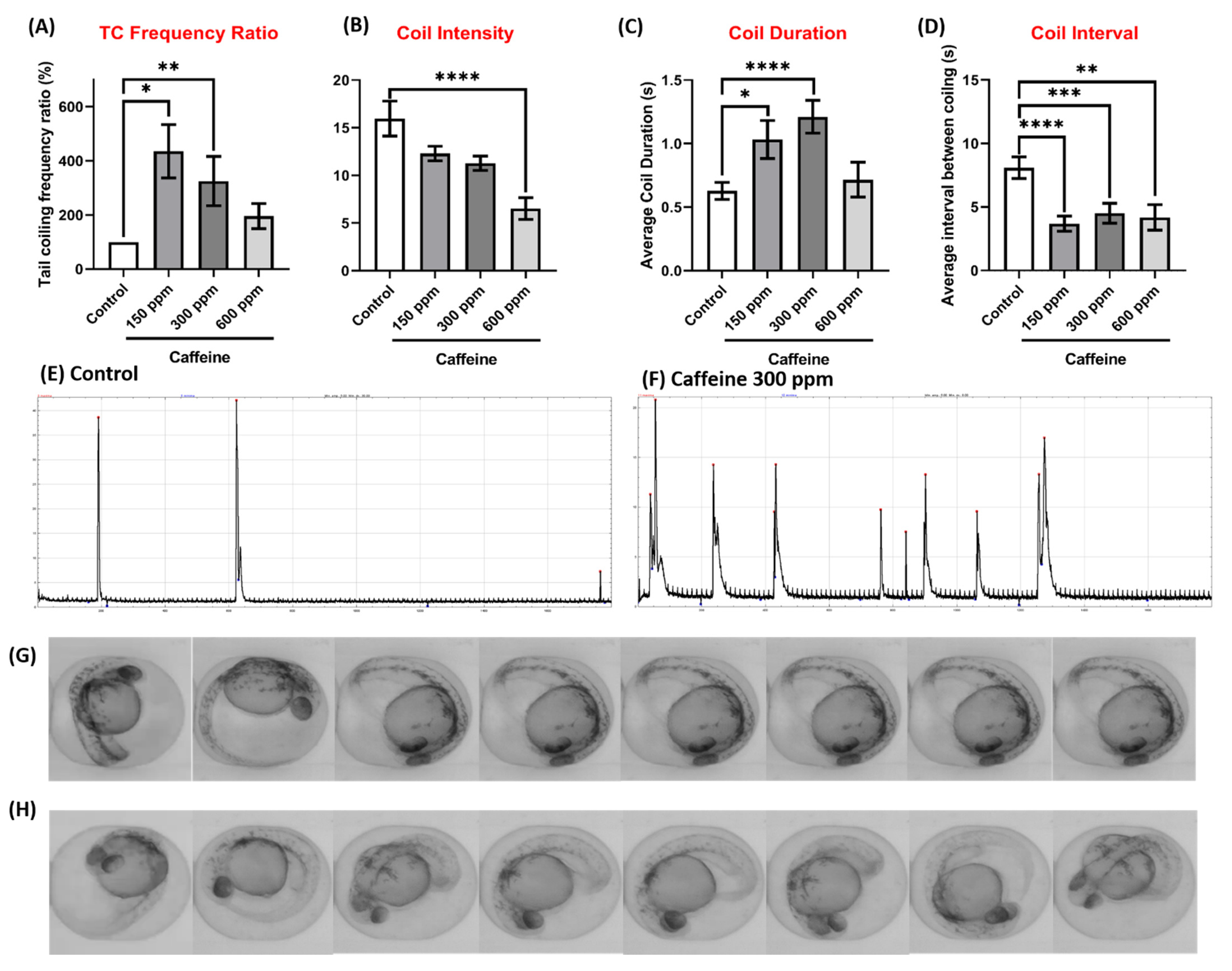
3.5. Method Validation Using MS-222 and Caffeine
4. Discussion
- The incident when the duration counting does not stop which is caused due to inadequate end threshold value.
- The incident where duration counting stop before TC stops. This incident is caused due to end threshold value set at excessive value.
- The incident when duration counting did not start, which is happened due to the start threshold value is set too high.
- The incident when there is a lot of duration with small values. This problem is caused due to start threshold being set too low. This incident will result in a lot of “false durations”.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Saint-Amant, L.; Drapeau, P. Time course of the development of motor behaviors in the zebrafish embryo. J. Neurobiol. 1998, 37, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, P. Zebrafish as a pharmacological tool: The how, why and when. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2004, 4, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.J.; Jia, Y.F.; Chen, N.; Bian, W.P.; Li, Q.K.; Ma, Y.B.; Chen, Y.L.; Pei, D.S. Zebrafish as a model system to study toxicology. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanguay, R.L. The rise of zebrafish as a model for toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogungbemi, A.O.; Teixido, E.; Massei, R.; Scholz, S.; Küster, E. Optimization of the spontaneous tail coiling test for fast assessment of neurotoxic effects in the zebrafish embryo using an automated workflow in KNIME®. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2020, 81, 106918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, F.; Beedgen, F.; Braunbeck, T. Time-course of coiling activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos exposed to ethanol as an endpoint for developmental neurotoxicity (DNT)–Hidden potential and underestimated challenges. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindler, F.; Beedgen, F.; Brandt, D.; Steiner, M.; Stengel, D.; Baumann, L.; Braunbeck, T. Analysis of tail coiling activity of zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos allows for the differentiation of neurotoxicants with different modes of action. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 186, 109754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selderslaghs, I.W.; Hooyberghs, J.; Blust, R.; Witters, H.E. Assessment of the developmental neurotoxicity of compounds by measuring locomotor activity in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2013, 37, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, J.; Barnett, J.A.; Hancock, L.; Saszik, S. Ethanol exposure alters zebrafish development: A novel model of fetal alcohol syndrome. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakar, N.A.; Sata, N.S.A.M.; Ramlan, N.F.; Ibrahim, W.N.W.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Ahmad, S.; Amal, M.N.A. Evaluation of the neurotoxic effects of chronic embryonic exposure with inorganic mercury on motor and anxiety-like responses in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2017, 59, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Bai, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Li, R.; Zhu, J.-H.; Huang, C. Developmental lead acetate exposure induces embryonic toxicity and memory deficit in adult zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Cao, Z.; Liao, X.; Ye, R.; Lu, H. Effects of acetochlor on neurogenesis and behaviour in zebrafish at early developmental stages. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, L.; Meng, Z.; Su, M.; Zhang, S.; Huang, P.; Jiang, F.; Liao, X.; Cao, Z.; Lu, H. Clethodim exposure induced development toxicity and behaviour alteration in early stages of zebrafish life. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Fraga, J.; Dipp-Alvarez, V.; Bardullas, U. Quantification of spontaneous tail movement in zebrafish embryos using a novel open-source MATLAB application. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.A.; Brigante, T.A.; Oliveira, D.P. Tail Coiling Assay in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Embryos: Stage of Development, Promising Positive Control Candidates, and Selection of an Appropriate Organic Solvent for Screening of Developmental Neurotoxicity (DNT). Water 2021, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Liang, J.; Brun, N.R.; Zhao, Y.; Werdich, A.A. Rapid Zebrafish Behavioral Profiling Assay Accelerates the Identification of Environmental Neurodevelopmental Toxicants. Env. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogungbemi, A.O.; Teixido, E.; Massei, R.; Scholz, S.; Küster, E. Automated measurement of the spontaneous tail coiling of zebrafish embryos as a sensitive behavior endpoint using a workflow in KNIME. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.; Varga, Z.M. Anesthesia and euthanasia in zebrafish. ILAR J. 2012, 53, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rueden, C.T.; Schindelin, J.; Hiner, M.C.; DeZonia, B.E.; Walter, A.E.; Arena, E.T.; Eliceiri, K.W. ImageJ2: ImageJ for the next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B. Hough Circle Transform. Available online: https://imagej.net/Hough_Circle_Transform (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Schmid, M. Highpass Filter. Available online: https://imagejdocu.tudor.lu/plugin/filter/highpass_filter/start (accessed on 21 April 2021).
- Ferreira, T.; Miura, K.; Chef, B.; Eglinger, J. BAR. Available online: https://imagej.net/BAR (accessed on 20 April 2021).
- Sinandinos, A.; Kromhout, B. Read and Write Excel. Available online: https://imagej.net/Read_and_Write_Excel (accessed on 29 April 2021).
- Frazier, D.T.; Narahashi, T. Tricaine (MS-222): Effects on ionic conductances of squid axon membranes. Eur. J. Pharm. 1975, 33, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, S.; Daria, P.; Sani, G.; Aromatario, M. Caffeine: Cognitive and physical performance enhancer or psychoactive drug? Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2015, 13, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, S.; Fulcher, N.; Nowicki, M.; Desai, P.; Tsang, B.; Facciol, A.; Chow, H.; Gerlai, R. Time-dependent interacting effects of caffeine, diazepam, and ethanol on zebrafish behaviour. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 75, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virus, R.; Ticho, S.; Pilditch, M.; Radulovacki, M. A comparison of the effects of caffeine, 8-cyclopentyltheophylline, and alloxazine on sleep in rats. Possible roles of central nervous system adenosine receptors. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 1990, 3, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, R.S.; Haugen, R.; Rueber, A.; Huang, C.-C. Reversible neuronal and muscular toxicity of caffeine in developing vertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 163, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Paper | Platform | Free Accessible? | Feature | Processing Speed | Endpoints | Internet Connection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Our method | TCMacro, ImageJ and Microsoft Excel 2016 | Yes | Automatic ROI selection, detection via pixel changes | 2–3 min for 1 min, 1280 × 720 p, 60 fps video | Tail coiling activity, coil duration, interval and coiling intensity | No, only for software update |
| Bakar et al., 2017 [10] | Manual | Yes | Manual detection | Not available | Tail coiling activity | No |
| Chen et al., 2012 [11] | Manual | Yes | Manual detection | Not available | Tail coiling activity | No |
| Wang et al., 2019 [12,13] | Manual | Yes | Manual detection | Not available | Tail coiling activity | No |
| Zindler et al., 2019 [6,7] | DanioScope | No | Automatic ROI selection, detection via pixel changes | Not available | Tail coiling activity and coil duration | No |
| González-Fraga et al., 2019 [14] | ZebraSTM, MATLAB® | Yes | Detection via pixel changes | Not available | Tail coiling activity | No |
| de Oliveira et al., 2021 [15] | DanioScope | No | Automatic ROI selection, detection via pixel changes | Not available | Tail coiling activity and coil duration | No |
| Zhang et al., 2021 [16] | EMAnalysis, ImageJ and Website | Yes | Automatic ROI selection, detection via pixel changes | 30 s for 20 s, 30 fps video | Tail coiling activity, coil duration, interval, coiling intensity and differentiation between live and dead zebrafish eggs | Yes, for data processing |
| Ogungbemi et al., 2021 [17] | KNIME | No | Automatic ROI selection, detection via pixel changes | Not available | Tail coiling activity | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurnia, K.A.; Santoso, F.; Sampurna, B.P.; Audira, G.; Huang, J.-C.; Chen, K.H.-C.; Hsiao, C.-D. TCMacro: A Simple and Robust ImageJ-Based Method for Automated Measurement of Tail Coiling Activity in Zebrafish. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081133
Kurnia KA, Santoso F, Sampurna BP, Audira G, Huang J-C, Chen KH-C, Hsiao C-D. TCMacro: A Simple and Robust ImageJ-Based Method for Automated Measurement of Tail Coiling Activity in Zebrafish. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081133
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurnia, Kevin Adi, Fiorency Santoso, Bonifasius Putera Sampurna, Gilbert Audira, Jong-Chin Huang, Kelvin H.-C. Chen, and Chung-Der Hsiao. 2021. "TCMacro: A Simple and Robust ImageJ-Based Method for Automated Measurement of Tail Coiling Activity in Zebrafish" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081133
APA StyleKurnia, K. A., Santoso, F., Sampurna, B. P., Audira, G., Huang, J.-C., Chen, K. H.-C., & Hsiao, C.-D. (2021). TCMacro: A Simple and Robust ImageJ-Based Method for Automated Measurement of Tail Coiling Activity in Zebrafish. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081133









