Identification and Computational Analysis of Novel Pathogenic Variants in Pakistani Families with Diverse Epidermolysis Bullosa Phenotypes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing and Segregation Analyses
2.3. Protein Modeling and Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Family 1: JEB Laryngo-Onycho-Cutaneous Syndrome
3.2. Family 2: JEB without Pylori Atresia
3.3. Family 3: EBS-Ogna Type
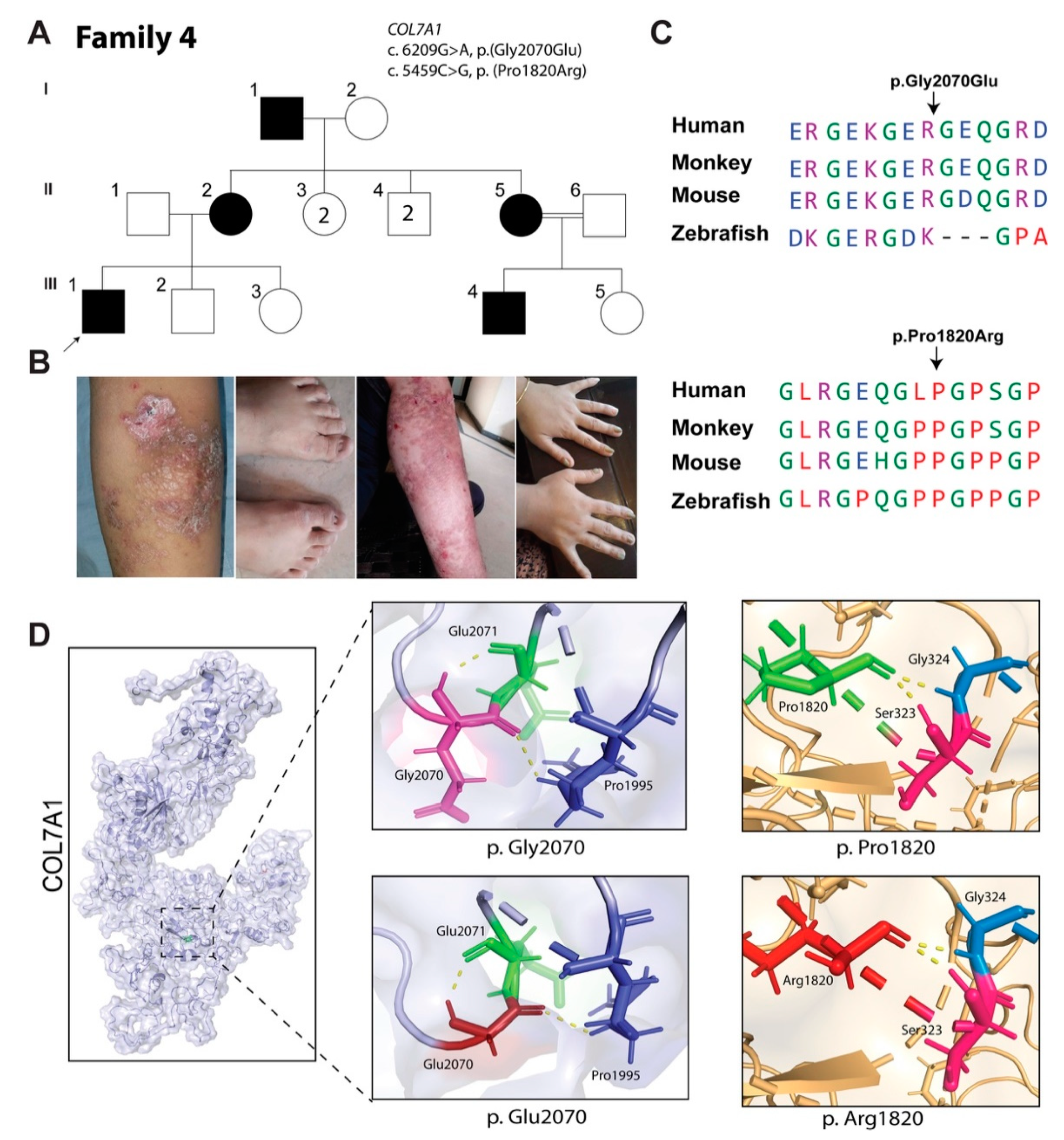
3.4. Family 4: Dominant EB Dystrophica, Pruriginosa Type
3.5. Family 5: Kindler Syndrome
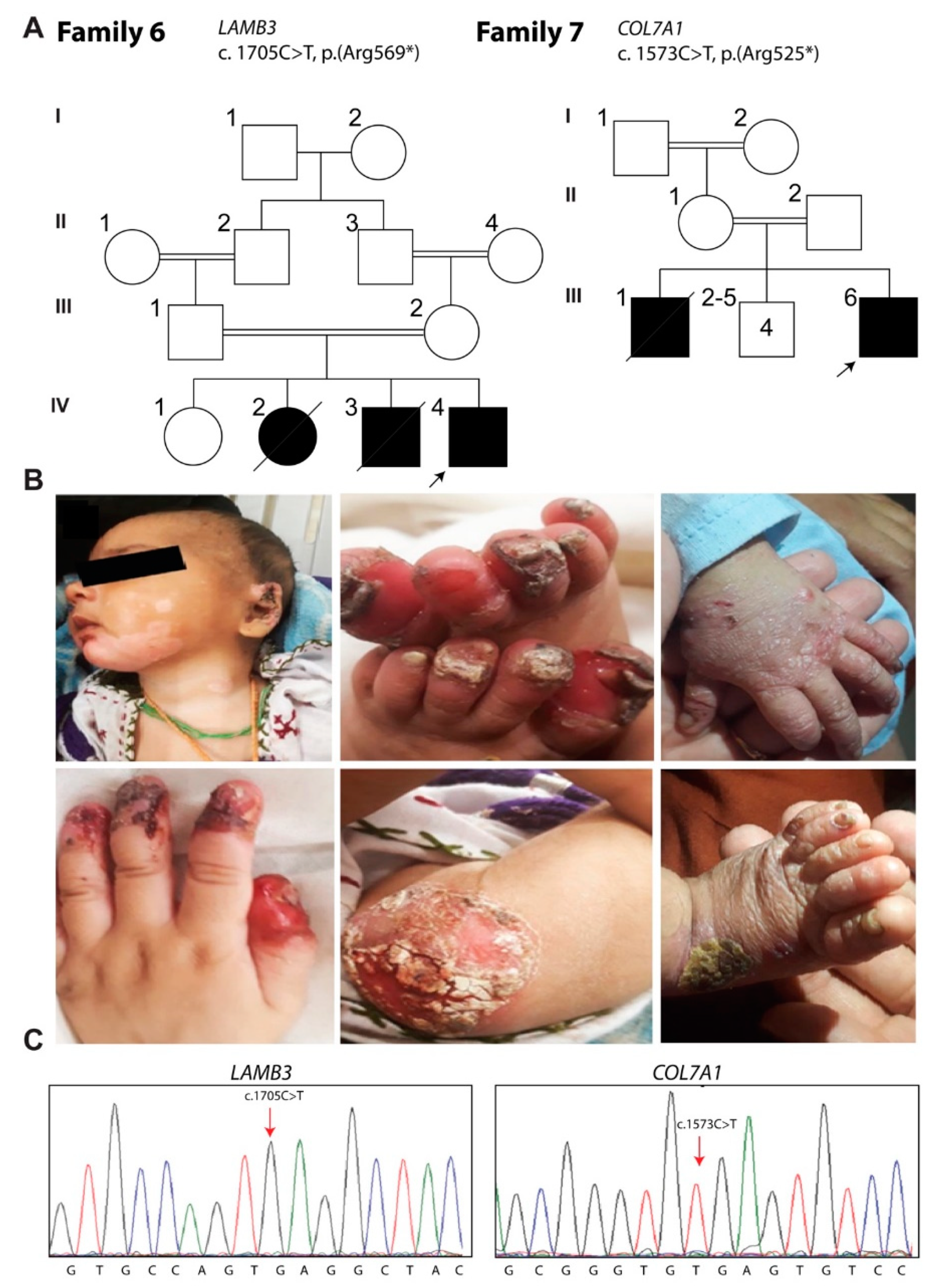
3.6. Family 6: Herlitz JEB
3.7. Family 7: EB Dystrophica
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fine, J.D.; Eady, R.A.; Bauer, E.A.; Bauer, J.W.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Heagerty, A.; Hintner, H.; Hovnanian, A.; Jonkman, M.F.; Leigh, I.; et al. The classification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa (EB): Report of the Third International Consensus Meeting on Diagnosis and Classification of EB. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 931–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.D. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.D.; Bauer, E.A.; McGuire, J.; Moshell, A. Epidermolysis Bullosa: Clinical, Epidemiological and Laboratory Advances and the Findings of the National Epidermolysis Bullosa Registry; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, J. Diagnosis, treatment and management of epidermolysis bullosa. Br. J. Nurs. 2016, 25, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Has, C.; Vahidnezhad, H.; Youssefian, L.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L. Molecular pathology of the basement membrane zone in heritable blistering diseases: The paradigm of epidermolysis bullosa. Matrix Biol. 2017, 57–58, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudva, P.; Jain, R. Periodontal manifestation of epidermolysis bullosa: Looking through the lens. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2016, 20, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uitto, J.; Tuderman, L.B.; Christiano, A.M.; McGrath, J.A.; Has, C.; South, A.P.; Kopelan, B.; Robinson, E.C. Progress Towards Treatment and Cure of Epidermolysis Bullosa: Summary of the DEBRA International Research Symposium EB2015. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Nyström, A.; Saeidian, A.H.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Uitto, J. Epidermolysis bullosa: Molecular pathology of connective tissue components in the cutaneous basement membrane zone. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71–72, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.D.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Eady, R.A.; Bauer, E.A.; Bauer, J.W.; Has, C.; Heagerty, A.; Hintner, H.; Hovnanian, A.; Jonkman, M.F.; et al. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: Updated recommendations on diagnosis and classification. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 70, 1103–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, R.; Vellarikkal, S.K.; Handa, S.; Verma, A.; Jayarajan, R.; Kumar, A.; De, D.; Kaur, J.; Panigrahi, I.; Vineeth, V.S.; et al. Utility of whole exome sequencing in detecting novel compound heterozygous mutations in COL7A1 among families with severe recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa in India—implications on diagnosis, prognosis and prenatal testing. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenedini, E.; Artuso, L.; Bernardis, I.; Artusi, V.; Percesepe, A.; De Rosa, L.; Contin, R.; Manfredini, R.; Pellacani, G.; Giannetti, A.; et al. Amplicon-based next-generation sequencing: An effective approach for the molecular diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucky, A.W.; Dagaonkar, N.; Lammers, K.; Husami, A.; Kissell, D.; Zhang, K. A comprehensive next-generation sequencing assay for the diagnosis of epidermolysis bullosa. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2018, 35, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybert, V.P. Genetic counseling in epidermolysis bullosa. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, A.; Simpson, M.A.; Stone, K.L.; Takeichi, T.; Nanda, A.; Akiyama, M.; McGrath, J.A. Next generation diagnostics of heritable connective tissue disorders. Matrix Biol. 2013, 33C, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, L.H.; Lucky, A.W.; Ballard, E.; Stanley, J.R.; Stolar, E.; Tabas, M.; Bauer, E.A.; Paller, A.S. Severe infantile epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Dowling-Meara type. Arch. Dermatol. 1986, 122, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfendner, E.G.; Bruckner, A.; Conget, P.; Mellerio, J.; Palisson, F.; Lucky, A.W. Basic science of epidermolysis bullosa and diagnostic and molecular characterization: Proceedings of the 2nd international symposium on epidermolysis bullosa, Santiago, Chile, 2005. Int. J. Dermatol. 2007, 46, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, W.H.I.; Irvine, A.D.; Hamill, K.J.; Whittock, N.V.; Coleman-Campbell, C.M.; Mellerio, J.E.; Ashton, G.S.; Dopping-Hepenstal, P.J.H.; Eady, R.A.J.; Jamil, T.; et al. An unusual N-terminal deletion of the laminin α3a isoform leads to the chronic granulation tissue disorder laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome. Hum. Mol. Gen. 2003, 12, 2395–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, H.I.; Murrell, D.F. Laryngo-onycho-cutaneous syndrome. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.; Klingberg, S.; Rubin, A.I.; Edwards, M.; Borelli, S.; Relic, J.; Marr, P.; Tran, K.; Turner, A.; Smith, N.; et al. Differential expression of pyloric atresia in junctional epidermolysis bullosa with ITGB4 mutations suggests that pyloric atresia is due to factors other than the mutations and not predictive of a poor outcome: Three novel mutations and a review of the literature. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2008, 88, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schumann, H.; Kiritsi, D.; Pigors, M.; Hausser, I.; Kohlhase, J.; Peters, J.; Ott, H.; Hyla-Klekot, L.; Gacka, E.; Sieron, A.L.; et al. Phenotypic spectrum of epidermolysis bullosa associated with alpha6beta4 integrin mutations. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Tamai, K.; Shimizu, H.; Owaribe, K.; Nakama, T.; Hashimoto, T.; McGrath, J.A. A homozygous missense mutation in the cytoplasmic tail of beta4 integrin, G931D, that disrupts hemidesmosome assembly and underlies Non-Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa without pyloric atresia? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 114, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, W.; Sinke, R.; Jonkman, M. ITGB4-associated junctional epidermolysis bullosa, type non-Herlitz: Report of two new cases carrying two novel ITGB4 mutations. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 432–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuga, K.; Nishie, W.; Akiyama, M.; Nakamura, H.; Shinkuma, S.; McMillan, J.R.; Nagasaki, A.; Has, C.; Ouchi, T.; Ishiko, A.; et al. Plectin expression patterns determine two distinct subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa simplex. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, A.; Chiaverini, C.; Chevrant-Breton, J.; DelRio, M.; Diociaiuti, A.; Dupuis, R.P.; El Hachem, M.; Le Fiblec, B.; Sankari-Ho, A.M.; Valhquist, A.; et al. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with PLEC mutations: New phenotypes and new mutations. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 168, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsuga, K. Plectin-related skin diseases. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 77, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koss-Harnes, D.; Hoyheim, B.; Anton-Lamprecht, I.; Gjesti, A.; Jørgensen, R.S.; Jahnsen, F.L.; Olaisen, B.; Wiche, G.; Gedde-Dahl, T., Jr. A site-specific plectin mutation causes dominant epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna: Two identical de novo mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiritsi, D.; Pigors, M.; Tantcheva-Poor, I.; Wessel, C.; Arin, M.; Kohlhase, J.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Has, C. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex Ogna revisited. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolling, M.C.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; Boven, L.G.; Diercks, G.F.H.; Smith, F.J.D.; Irwin McLean, W.H.; Jonkman, M.F. Plectin Mutations Underlie Epidermolysis Bullosa Simplex in 8% of Patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, J.; Van-Wilpe, S.; Kuikman, I.; Litjens, S.; Sonnenberg, A. Role of binding of plectin to the integrin β4 subunit in the assembly of hemidesmosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2004, 15, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koster, J.; Geerts, D.; Favre, B.; Borradori, L.; Sonnenberg, A. Analysis of the interactions between BP180, BP230, plectin and the integrin α6β4 important for hemidesmosome assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, J.A.; Schofield, O.M.V.; Eady, R.A.J. Epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa: Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa with distinctive clinicopathological features. Br. J. Dermatol. 1994, 130, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Lu, Y.; Farhi, A.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Kashgarian, M.; Glusac, E.J.; Lifton, R.P.; Antaya, R.J.; Choate, K.A. An incompletely penetrant novel mutation in COL7A1 causes epidermolysis bullosa pruriginosa and dominant dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa phenotypes in an extended kindred. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2012, 29, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Has, C.; Castiglia, D.; del Rio, M.; Diez, M.G.; Piccinni, E.; Kiritsi, D.; Kohlhase, J.; Itin, P.; Martin, L.; Fischer, J.; et al. Kindler syndrome: Extension of FERMT1 mutational spectrum and natural history. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, D.H.; Ashton, G.H.; Penagos, H.G.; Lee, J.V.; Feiler, H.S.; Wilhelmsen, K.C.; South, A.P.; Smith, F.J.; Prescott, A.R.; Wessagowit, V.; et al. Loss of Kindling-1, a human homolog of the Caenorhabditis elegans actin-extracellular-matrix linker protein UNC112, causes Kindler syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.H.; McLean, W.H.; South, A.P.; Oyama, N.; Smith, F.J.; Al-Suwaid, R.; Al-Ismaily, A.; Atherton, D.J.; Harwood, C.A.; Leigh, I.M.; et al. Recurrent mutations in Kindlin-1, a novel keratinocyte focal adhesion protein, in the autosomal recessive skin fragility and photosensitivity disorder, Kindler Syndrome. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2004, 127, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, M.A.; Ashton, G.H.S.; McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Moss, C. Retrospective diagnosis of Kindler syndrome in a 37-year-old man. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 31, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaiq, P.A.; Klausegger, A.; Muzaffar, F.; Bauer, J.W.; Khan, M.I.; Khanum, A.; Qamar, R.; Raja, G.K. Founder mutation c.676insC in three unrelated Kindler syndrome families belonging to a particular clan from Pakistan. J. Dermatol. 2012, 39, 640–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivirikko, S.; McGrath, J.A.; Pulkkinen, L.; Uitto, J.; Christiano, A.M. Mutational hotspots in the LAMB3 gene in the lethal (Herlitz) type of junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkkinen, L.; Kurtz, K.; Xu, Y.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Uitto, J. Genomic organization of the integrin beta 4 gene (ITGB4): A homozygous splice-site mutation in a patient with junctional epidermolysis bullosa associated with pyloric atresia. Lab. Invest. 1997, 76, 823–833. [Google Scholar]
- Laimer, M.; Lanschuetzer, C.M.; Diem, A.; Bauer, J.W. Herlitz junctional epidermolysis bullosa. Dermatol. Clin. 2010, 28, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittock, N.V.; Ashton, G.H.; Mohammedi, R.; Mellerio, J.E.; Mathew, C.G.; Abbs, S.J. Comparative mutation detection screening of the type VII collagen gene (COL7A1) using the protein truncation test, fluorescent chemical cleavage of mismatch, and conformation sensitive gel electrophoresis. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Vogel, A.; Rüegger, S.; Odermatt, B.; Tönz, O.; Schnyder, U.W. Epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 21, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intong, L.R.; Murrell, D.F. Inherited epidermolysis bullosa: New diagnostic criteria and classification. Clin. Dermatol. 2012, 30, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| EB Type | Genes |
|---|---|
| Epidermolysis bullosa simplex | KRT5, KRT14, JUP, DSP, DST, EXPH5, PLEC, PKP1, TGM5, ITGA6, ITGB4, KLHL24 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa junctional | LAMA3, LAMB3, LAMC2, ITGA6, ITGB4, ITGA3, COL 17A1, CD151 |
| Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica | COL7A1 |
| Kindler syndrome | FERMT1 |
| Gene | cDNA Change | Protein Change | CADD | GnomAD | Polyphen2 | SIFT | ACMG Classification (Criteria Used) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITGB4 | c.1285G>T | p.(Asp429Tyr) | 32 | 0 | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP3, PP5) |
| c.3373G>G | p.(Gly1125Ser) | 21.4 | 0.000127 | Probably damaging | Damaging | Likely pathogenic (PP2, PP3) | |
| PLEC | c.1828C>G | p.(Arg610Gly) | 25.4 | 0 | Possibly damaging | Damaging | Likely pathogenic (PS3, PP2, PP3) |
| COL7A1 | c.6209G>A | p.(Gly2070Glu) | 28.7 | 0 | Damaging | Damaging | Pathogenic (PVS1, PM2, PP3, PP5) |
| c.5459C>G | p.(Pro1820Arg) | 17.8 | 0.000256 | Damaging | Tolerated | Likely pathogenic (PP2, PP3) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, F.F.; Khan, N.; Rehman, S.; Ejaz, A.; Ali, U.; Erfan, M.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Naeem, M. Identification and Computational Analysis of Novel Pathogenic Variants in Pakistani Families with Diverse Epidermolysis Bullosa Phenotypes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050620
Khan FF, Khan N, Rehman S, Ejaz A, Ali U, Erfan M, Ahmed ZM, Naeem M. Identification and Computational Analysis of Novel Pathogenic Variants in Pakistani Families with Diverse Epidermolysis Bullosa Phenotypes. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(5):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050620
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Fehmida F., Naima Khan, Sakina Rehman, Amir Ejaz, Uzma Ali, Muhammad Erfan, Zubair M. Ahmed, and Muhammad Naeem. 2021. "Identification and Computational Analysis of Novel Pathogenic Variants in Pakistani Families with Diverse Epidermolysis Bullosa Phenotypes" Biomolecules 11, no. 5: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050620
APA StyleKhan, F. F., Khan, N., Rehman, S., Ejaz, A., Ali, U., Erfan, M., Ahmed, Z. M., & Naeem, M. (2021). Identification and Computational Analysis of Novel Pathogenic Variants in Pakistani Families with Diverse Epidermolysis Bullosa Phenotypes. Biomolecules, 11(5), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11050620






