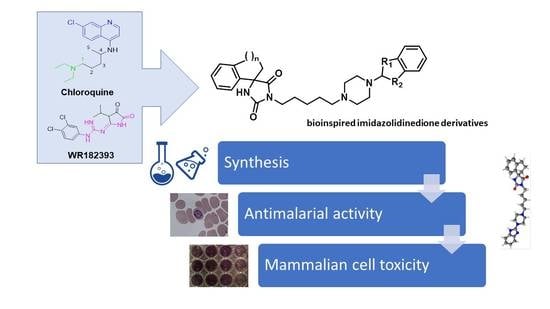
Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. General Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. General Procedure for Obtaining Spirohydantoin Derivatives (1, 2)
2.2.2. General Procedure for Alkylation of Spirohydantoin (3, 4)
- (R,S)-1-(5-bromopentyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (3)
- (R,S)-1-(5-bromopentyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (4)
2.2.3. General Procedure for Obtaining the Final Compound Series (5–8)
- (R,S)-1-(5-(4-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)pentyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (5)
- (R,S)-1-(5-(4-(1H-Benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)pentyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (6)
- (R,S)-1-(5-(4-(2,3-Dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)pentyl)-3′,4′-dihydro-2′H-spiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-naphthalene]-2,5-dione (7)
- (R,S)-1-(5-(4-(2,3-Dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)piperazin-1-yl)pentyl)-2′,3′-dihydrospiro[imidazolidine-4,1′-indene]-2,5-dione (8)
2.3. pKa and Log D Calculation
2.4. P. falciparum Cultures and Drug Susceptibility Assay
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Hemolysis Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Biological Activities
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Malaria Programme. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- Reyburn, H. New WHO guidelines for the treatment of malaria. BMJ 2010, 341, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, E.L.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Winzeler, E.A. Antimalarial drug discovery-approaches and progress towards new medicines. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- When Is Enough Enough? The Need for a Robust Pipeline of High-quality Antimalarials—Timothy N Wells—Discovery Medicine. Available online: https://www.discoverymedicine.com/Timothy-N-Wells/2010/05/01/when-is-enough-enough-the-need-for-a-robust-pipeline-of-high-quality-antimalarials/ (accessed on 3 November 2020).
- Guan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Montip, G.; Karle, J.M.; Ditusa, C.A.; Milhous, W.K.; Skillman, D.R.; Lin, A.J. Structure identification and prophylactic antimalarial efficacy of 2-guanidinoimidazolidinedione derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.J.; Bom, J.; Capela, R.; Casimiro, C.; Chambel, P.; Gomes, P.; Iley, J.; Lopes, F.; Morais, J.; Moreira, R.; et al. Imidazolidin-4-one Derivatives of Primaquine as Novel Transmission-Blocking Antimalarials. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 888–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mital, A.; Murugesan, D.; Kaiser, M.; Yeates, C.; Gilbert, I.H. Discovery and optimisation studies of antimalarial phenotypic hits. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 103, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
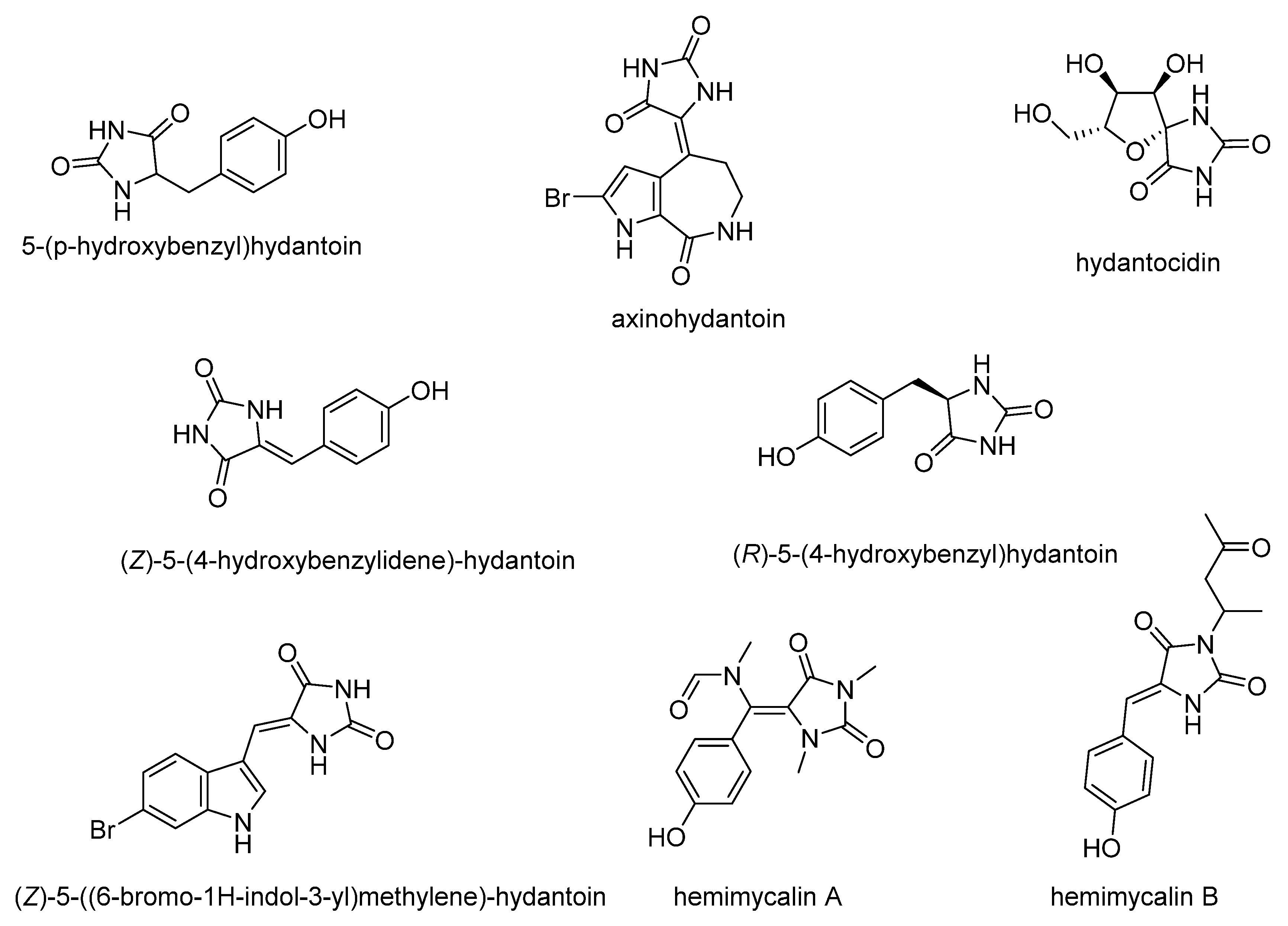
- Bialonska, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Aplysinopsins—Marine indole alkaloids: Chemistry, bioactivity and ecological significance. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passemar, C.; Saléry, M.; Soh, P.N.; Linas, M.D.; Ahond, A.; Poupat, C.; Benoit-Vical, F. Indole and aminoimidazole moieties appear as key structural units in antiplasmodial molecules. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzdalev, K.F.; Babakova, M.N. Synthesis of Analogues of Indole Alkaloids from Sea Sponges—Aplysinopsins by the Reaction of Amines with (4 Z)-4-[(1 H -indol-3-yl)-methylene]-1,3-oxazol-5(4 H)-ones. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2016, 53, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewellyn, K.; Zjawiony, J.K. Aplysinopsins as Promising Marine Natural Product Drug Leads: Recent Developments. In Grand Challenges in Marine Biotechnology; Rampelotto, P., Trincone, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 191–215. [Google Scholar]
- Konnert, L.; Frédé, F.; Lamaty, F.; Martinez, J.; Colacino, E. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Hydantoins: The State of the Art of a Valuable Scaffold. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 13757–13809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malawska, B. New Anticonvulsant Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czopek, A.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Bucki, A.; Byrtus, H.; Pawłowski, M.; Kazek, G.; Bojarski, A.J.; Piaskowska, A.; Kalinowska-Tłuścik, J.; Partyka, A.; et al. Novel spirohydantoin derivative as a potent multireceptor-active antipsychotic and antidepressant agent. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3436–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiallo, M.M.; Kozlowski, H.; Garnier-Suillerot, A. Mitomycin antitumor compounds. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriou, M.; Noble, M.E.; Watson, K.A.; Garman, E.F.; Krulle, T.M.; de la Fuente, C.; Fleet, G.W.; Oikonomakos, N.G.; Johnson, L.N. The structure of a glycogen phosphorylase glucopyranose spirohydantoin complex at 1.8 A resolution and 100 K: The role of the water structure and its contribution to binding. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.; Shaala, L.; Alshali, K. Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6609–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.D.; Freyer, A.J.; Killmer, L.; Hofmann, G.; Johnson, R.K. Z-axinohydantoin and debromo-z-axinohydantoin from the sponge Stylotella aurantium: Inhibitors of protein kinase C. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1997, 9, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, M.; Itoi, K.; Takamatsu, Y.; Kinoshita, T.; Okazaki, T.; Kawakubo, K.; Shindo, M.; Honma, T.; Tohjigamori, M.; Haneishi, T. Hydantocidin: A new compound with herbicidal activity from Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudit, M.; Khanfar, M.; Muralidharan, A.; Thomas, S.; Shah, G.V.; van Soest, R.W.M.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery, design, and synthesis of anti-metastatic lead phenylmethylene hydantoins inspired by marine natural products. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, M.J.; Anderson, E.J.; McNitt, S.A.; Krenning, T.M.; Singh, M.; Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Qin, L.; Xu, W.; Zhao, S.; et al. Evaluation of spiropiperidine hydantoins as a novel class of antimalarial agents. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5144–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneaux, C.A.; Krugliak, M.; Ginsburg, H.; Chibale, K. Arylpiperazines displaying preferential potency against chloroquine-resistant strains of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 71, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.; Pérez-Silanes, S.; Quiliano, M.; Pabón, A.; Galiano, S.; González, G.; Garavito, G.; Zimic, M.; Vaisberg, A.; Aldana, I.; et al. Aryl piperazine and pyrrolidine as antimalarial agents. Synthesis and investigation of structure-activity relationships. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 128, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Li, Z.F.; Hu, W.; Wu, X. Small molecules enhance functional O-mannosylation of Alpha-dystroglycan. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7661–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, A.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y. Nickel-Catalyzed Cyanation of Unactivated Alkyl Chlorides or Bromides with Zn(CN) 2. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7735–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trager, W.; Jensen, J.B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976, 193, 673–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makler, M.T.; Hinrichs, D.J. Measurement of the lactate dehydrogenase activity of Plasmodium falciparum as an assessment of parasitemia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 48, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaromin, A.; Korycińska, M.; Piȩtka-Ottlik, M.; Musiał, W.; Peczyńska-Czoch, W.; Kaczmarek, Ł.; Kozubek, A. Membrane perturbations induced by new analogs of neocryptolepine. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhal, S.K.; Kassam, K.; Peirson, I.G.; Pearl, G.M. The rule of five revisited: Applying log D in place of log P in drug-likeness filters. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guan, J.; Sacci, J.; Ager, A.; Ellis, W.; Milhous, W.; Kyle, D.; Lin, A.J. Unambiguous synthesis and prophylactic antimalarial activities of imidazolidinedione derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6472–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travassos, M.A.; Laufer, M.K. Resistance to antimalarial drugs: Molecular, pharmacologic, and clinical considerations. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 65 Pt 2, 64R–70R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaromin, A.; Parapini, S.; Basilico, N.; Zaremba-Czogalla, M.; Lewińska, A.; Zagórska, A.; Walczak, M.; Tyliszczak, B.; Grzeszczak, A.; Łukaszewicz, M.; et al. Azacarbazole n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids ethyl esters nanoemulsion with enhanced efficacy against Plasmodium falciparum. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, C.; Vaiana, N.; Casagrande, M.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D.; Romeo, S.; Sparatore, A. Synthesis and comparison of antiplasmodial activity of (+), (−) and racemic 7-chloro-4-(N-lupinyl)aminoquinoline. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5980–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, K.; Lötsch, F.; Kremsner, P.G.; Ramharter, M. Haemolysis associated with the treatment of malaria with artemisinin derivatives: A systematic review of current evidence. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 29, e268–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | Structure | MW | pKa | Log D pH 7.4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Q) Quinine | 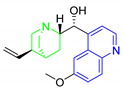 | 324.41 | 13.89 | 0.86 |
| 9.05 | ||||
| 4.02 | ||||
| (CQ) Chloroquine | 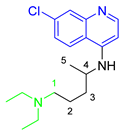 | 319.87 | 10.32 | 0.88 |
| 7.29 | ||||
| (PQ) Primaquine | 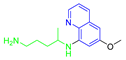 | 259.35 | 10.20 | −1.13 |
| 4.09 | ||||
| 0.60 | ||||
| (AQ) Amodiaquine | 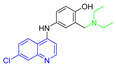 | 355.86 | 10.17 | 2.32 |
| 9.10 | ||||
| 6.46 | ||||
| (MQ) Mefloquine | 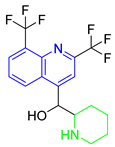 | 378.31 | 13.79 | 2.07 |
| 9.46 | ||||
| WR182393 | 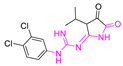 | 341.19 | 12.69 | 3.12 |
| 4.37 | ||||
| General structure of imidazolidin-4-ones | 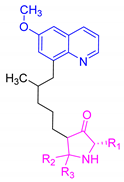 | - | - | - |
| TDR32750 | 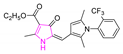 | 418.41 | No ionizable atoms found | 3.97 |
| Aplysinopsin | 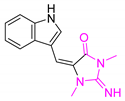 | 254.29 | 15.84 | 1.74 |
| 2.93 |
| Compound | Structure | pKa | Log D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.4 | pH 7.2 | pH 5.5 | |||
| (5) | 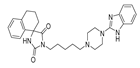 | 12.32 | 3.39 | 3.20 | 1.11 |
| 11.11 | |||||
| 8.41 | |||||
| 5.86 | |||||
| (6) | 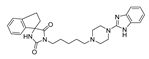 | 12.32 | 2.99 | 2.80 | 0.72 |
| 11.03 | |||||
| 8.41 | |||||
| 5.86 | |||||
| (7) | 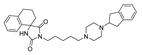 | 11.14 | 3.00 | 2.81 | 1.20 |
| 8.64 | |||||
| 2.86 | |||||
| (8) | 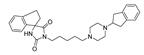 | 11.05 | 2.60 | 2.41 | 0.80 |
| 8.64 | |||||
| 2.86 | |||||
| CQ | - | 0.88 | 0.64 | −0.76 | |
| Compound | P. falciparum IC50 (ng/mL) | RI a | HaCaT IC50 (ng/mL) | SI b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 | W2 | D10 | W2 | |||
| (5) | 6202.00 ± 892.09 | 2424.15 ± 255.34 | 0.39 | 20,216.67 ± 1181.54 | 3.26 | 8.34 |
| 12.75 ± 0.02 c | 4.98 ± 0.52 c | 41.55 ± 2.43 c | ||||
| (6) | 8269.85 ± 736.88 | 4782.00 ± 97.44 | 0.58 | 27,406.67 ± 701.17 | 3.31 | 5.73 |
| 17.50 ± 1.55 c | 10.12 ± 0.20 c | 57.99 ± 1.48 c | ||||
| (7) | 9659.70 ± 140.86 | 4346.50 ± 659.31 | 0.45 | 30,536.67 ± 1033.89 | 3.16 | 7.02 |
| 19.85 ± 0.29 c | 8.93 ± 1.35 c | 62.75 ± 2.12 c | ||||
| (8) | >10,000 | 5648.07 ± 1946.84 | - | 22,723.33 ± 1175.00 | - | 4.02 |
| 11.95 ± 4.12 c | 48.08 ± 2.49 c | |||||
| CQ | 7.64 ± 1.70 | 102.67 ± 27.49 | 13.44 | nd | nd | nd |
| 0.01 ± 0.003 c | 0.20 ± 0.05 c | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaromin, A.; Czopek, A.; Parapini, S.; Basilico, N.; Misiak, E.; Gubernator, J.; Zagórska, A. Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010033
Jaromin A, Czopek A, Parapini S, Basilico N, Misiak E, Gubernator J, Zagórska A. Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaromin, Anna, Anna Czopek, Silvia Parapini, Nicoletta Basilico, Ernest Misiak, Jerzy Gubernator, and Agnieszka Zagórska. 2021. "Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives" Biomolecules 11, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010033
APA StyleJaromin, A., Czopek, A., Parapini, S., Basilico, N., Misiak, E., Gubernator, J., & Zagórska, A. (2021). Synthesis and Antiplasmodial Activity of Novel Bioinspired Imidazolidinedione Derivatives. Biomolecules, 11(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11010033