The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch
Abstract
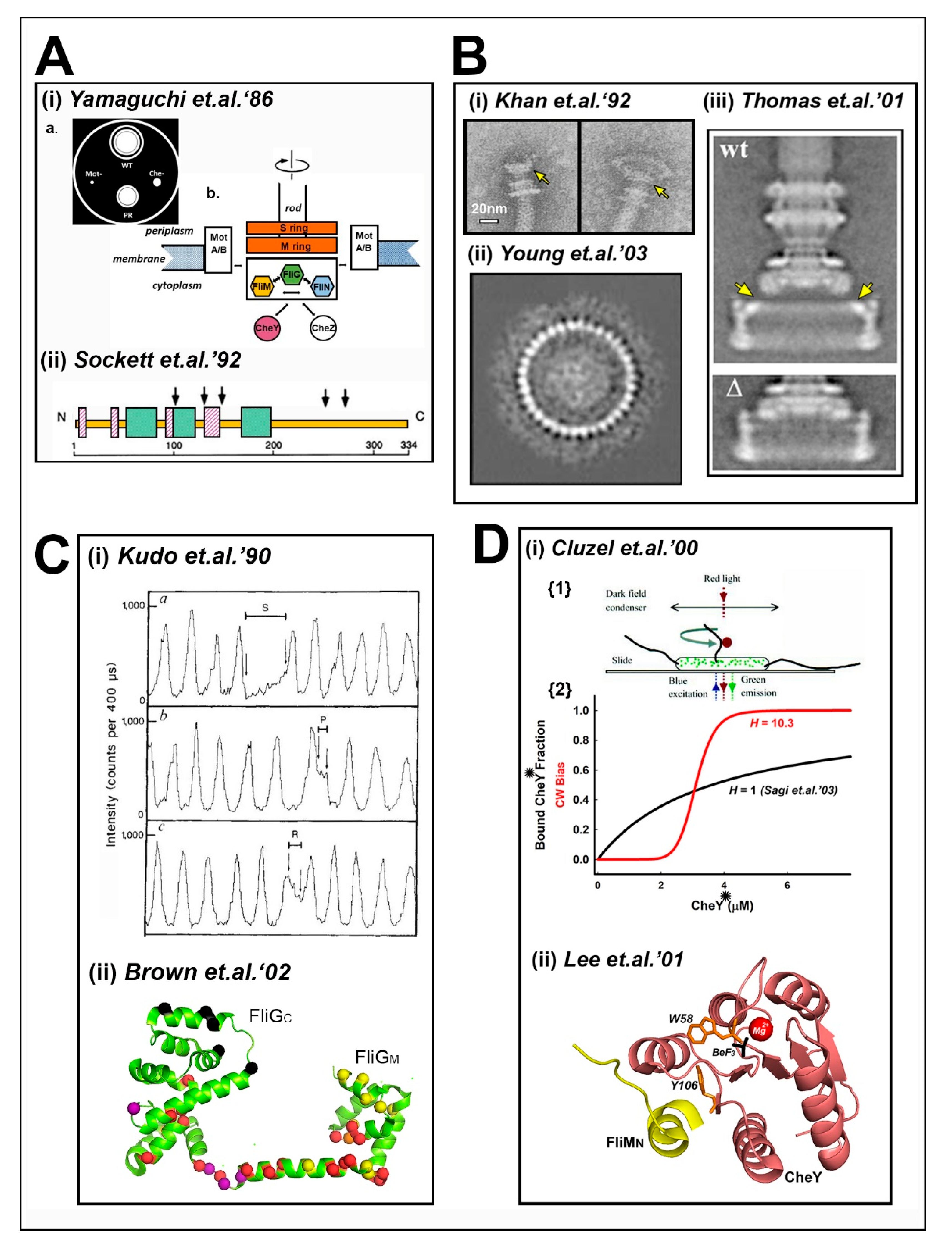
1. The Problem Framed—Historical Background (1973–2003)
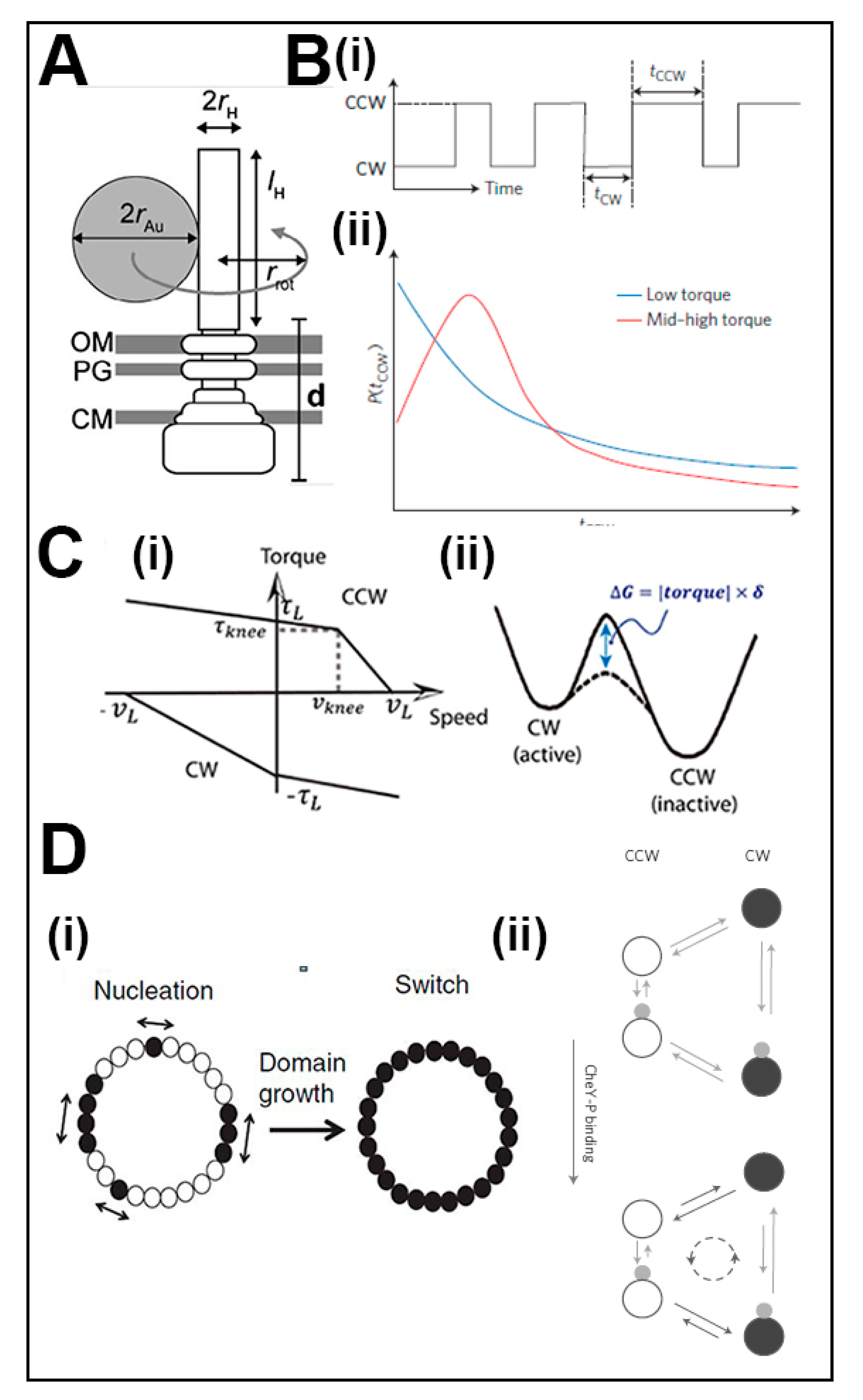
2. Switch Physiology and Mathematical Models
3. Architecture and Molecular Mechanism
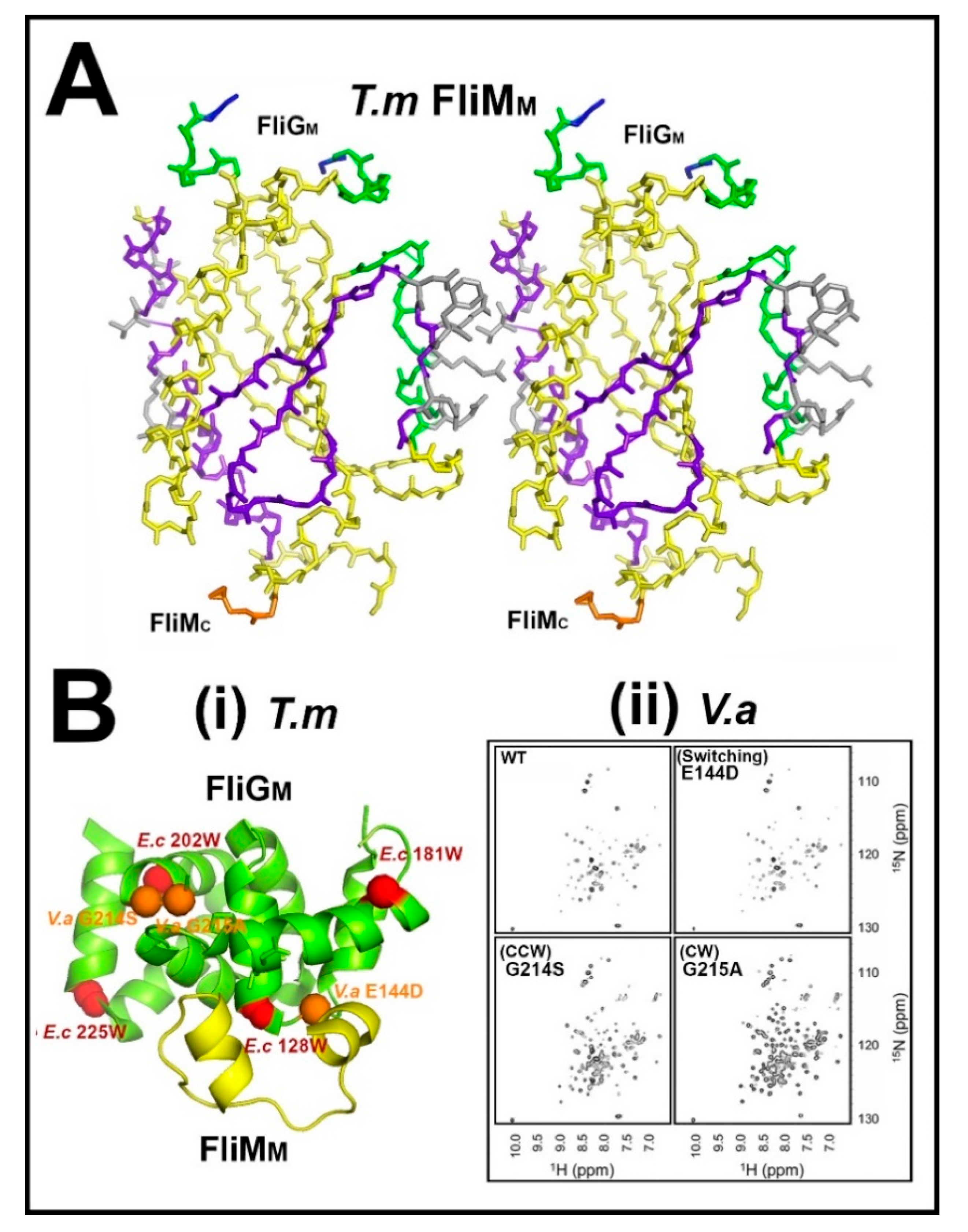
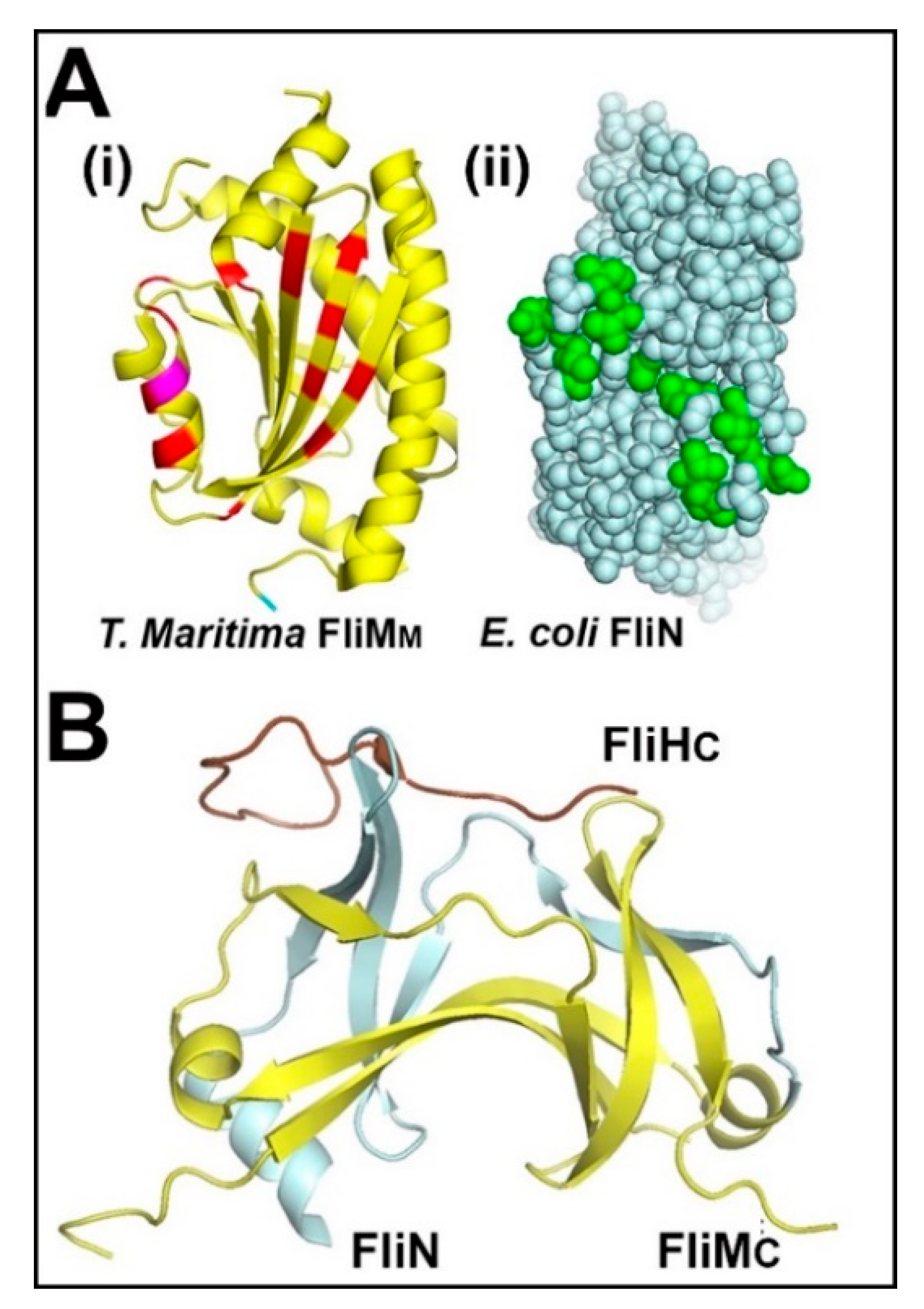
3.1. The Central Processing Unit—The FliMM.FliGM Complex
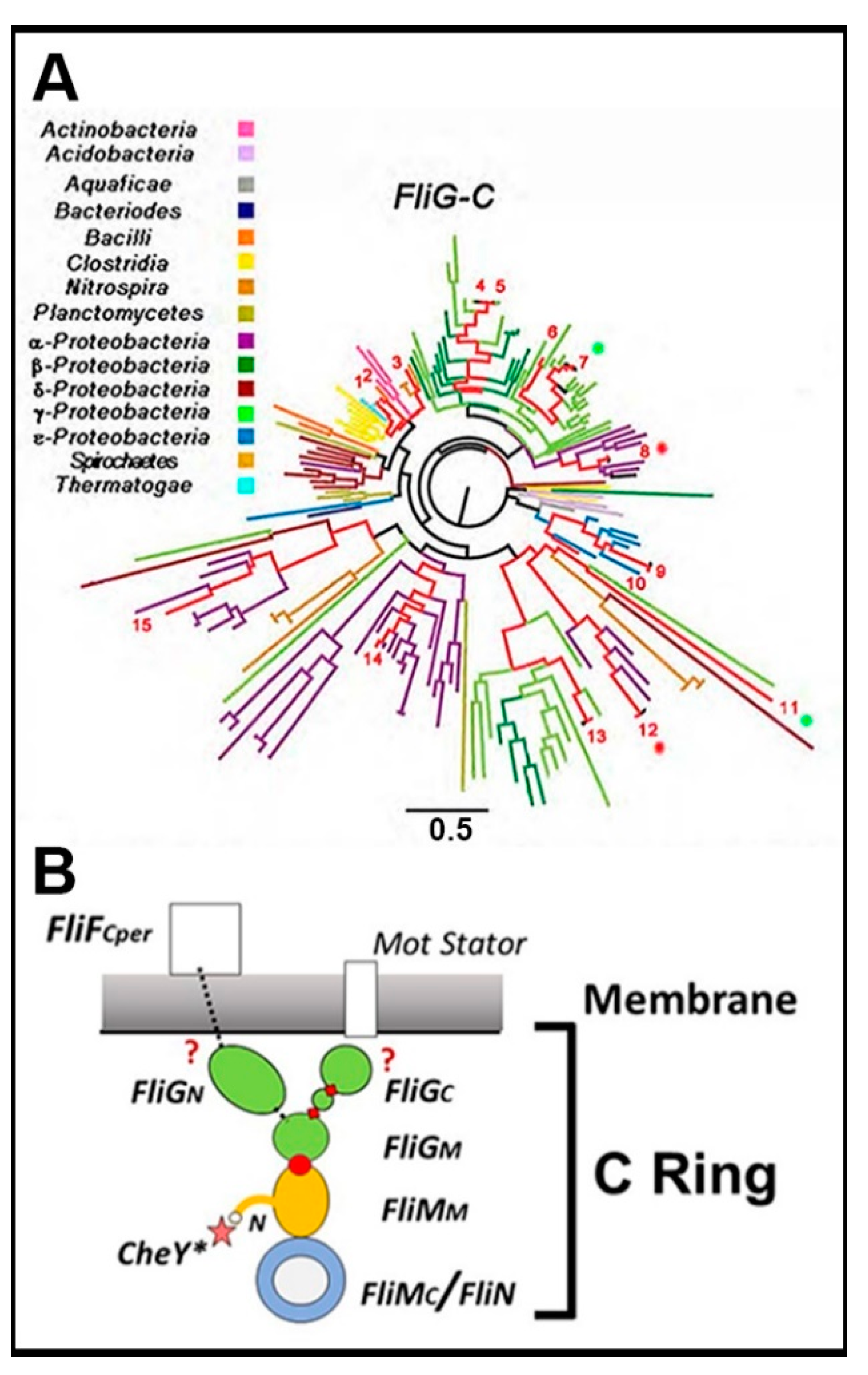
3.2. The Trigger Machinery—CheY and the Basal C Ring
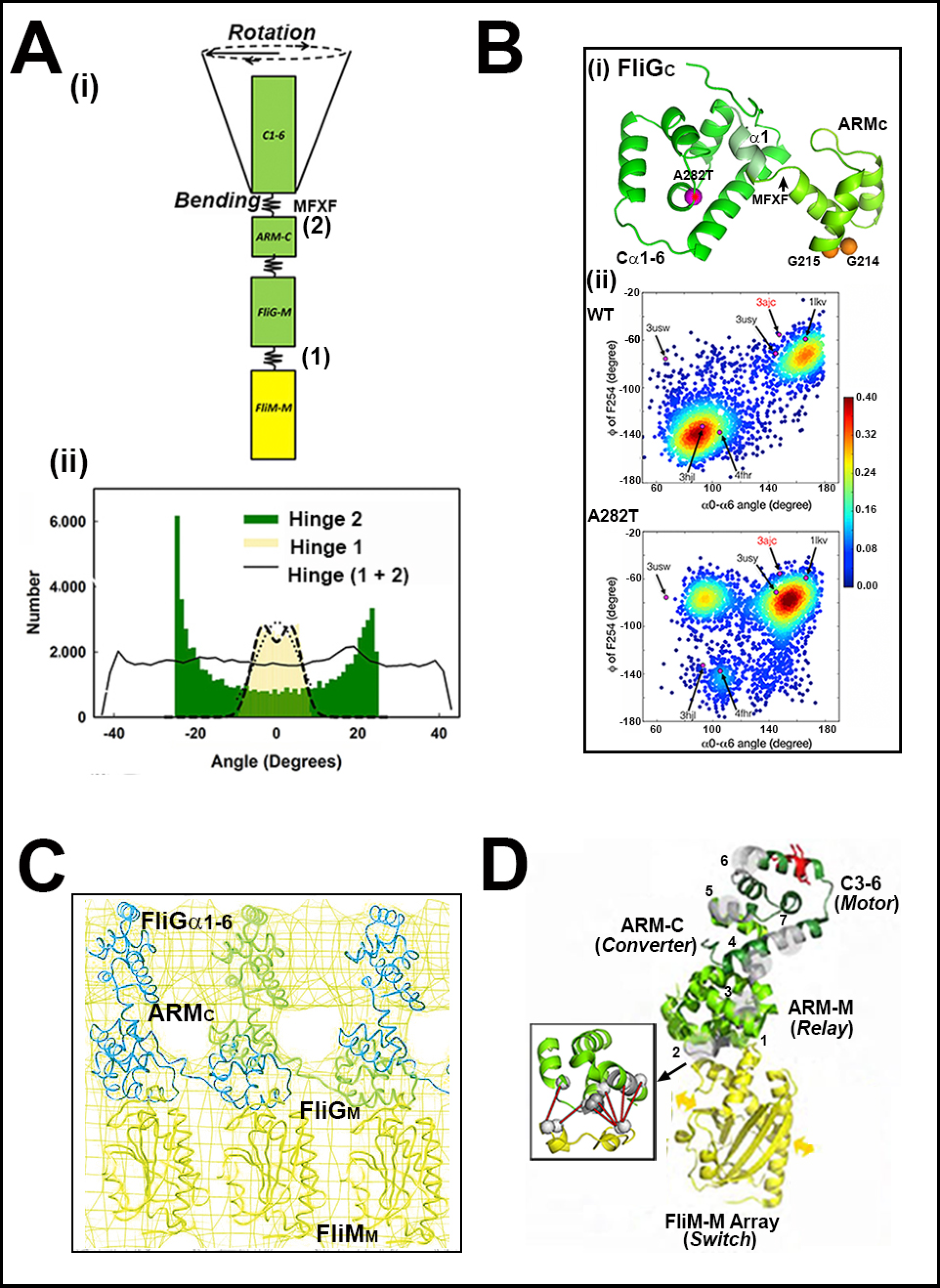
3.3. Bidirectional Torque Generation—FliGM–FliGC Interactions
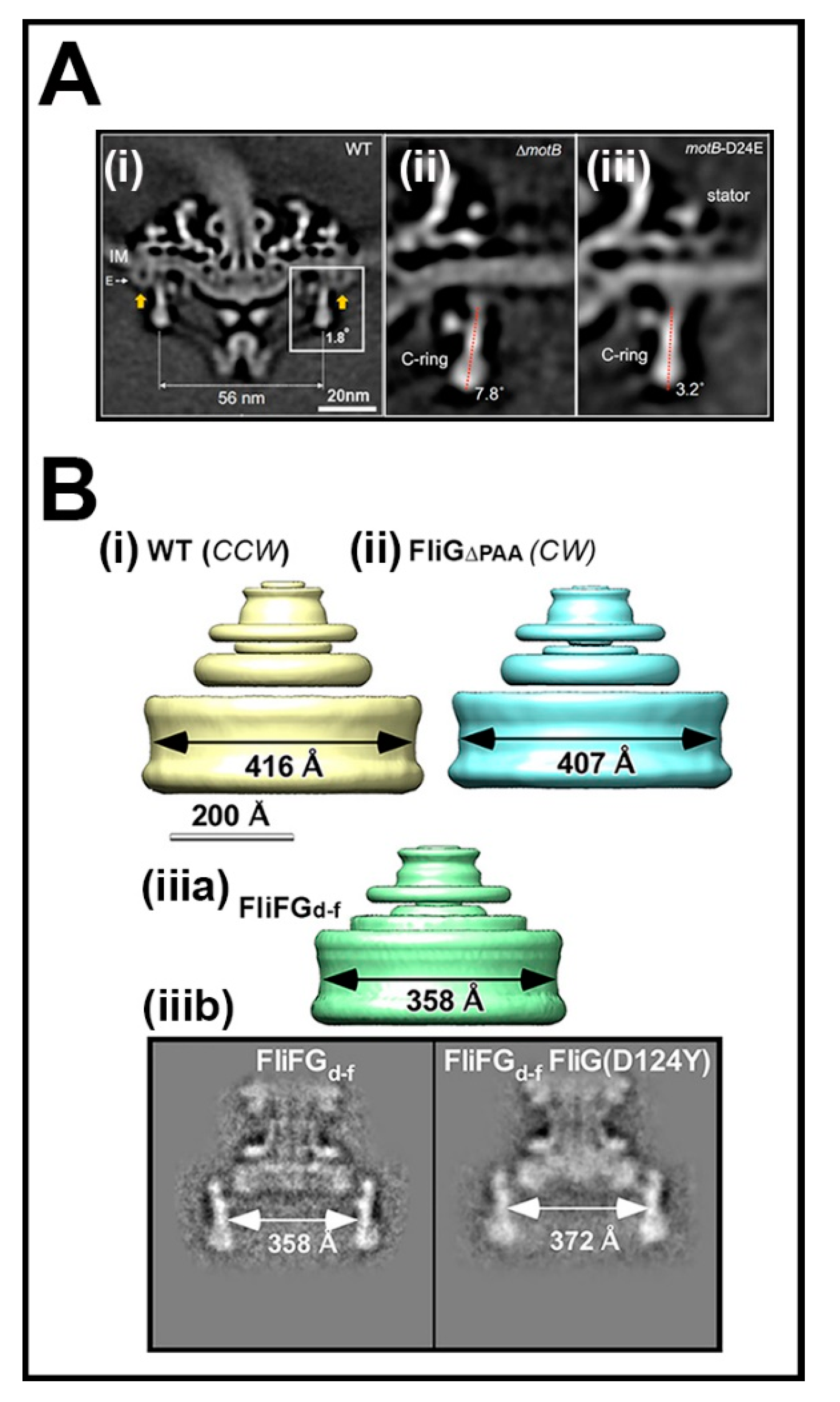
3.4. The Association of the Switch with the Mot Stators and the FliFC Scaffold
4. Current Challenges
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, N. The unseen world: Reflections on Leeuwenhoek (1677) ‘Concerning little animals’. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C.; Anderson, R.A. Bacteria swim by rotating their flagellar filaments. Nature 1973, 245, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, H.C. The rotary motor of bacterial flagella. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003, 72, 19–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Scholey, J.M. Assembly, Functions and Evolution of Archaella, Flagella and Cilia. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R278–R292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, J.S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J. Bacteriol. 1976, 126, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S.; Aizawa, S.; Kihara, M.; Isomura, M.; Jones, C.J.; Macnab, R.M. Genetic evidence for a switching and energy-transducing complex in the flagellar motor of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 168, 1172–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Kihara, M.; Homma, M.; Kutsukake, K.; Macnab, R.M. Flagellar switch of Salmonella typhimurium: Gene sequences and deduced protein sequences. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 3247–3257. [Google Scholar]
- Sockett, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kihara, M.; Irikura, V.M.; Macnab, R.M. Molecular analysis of the flagellar switch protein FliM of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irikura, V.M.; Kihara, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Sockett, H.; Macnab, R.M. Salmonella typhimurium fliG and fliN mutations causing defects in assembly, rotation, and switching of the flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Lloyd, S.A.; Blair, D.F. Electrostatic interactions between rotor and stator in the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6436–6441. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, S.A.; Blair, D.F. Charged residues of the rotor protein FliG essential for torque generation in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 266, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, D.F.; Berg, H.C. Restoration of torque in defective flagellar motors. Science 1988, 242, 1678–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sharp, L.L.; Tang, H.L.; Lloyd, S.A.; Billings, S.; Braun, T.F.; Blair, D.F. Function of protonatable residues in the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli: A critical role for Asp 32 of MotB. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 2729–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.H.; Reese, T.S.; Khan, S. The cytoplasmic component of the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5956–5960. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Francis, N.R.; Sosinsky, G.E.; Thomas, D.; DeRosier, D.J. Isolation, characterization and structure of bacterial flagellar motors containing the switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 235, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Pathak, N.; Jaffe, H.; Reese, T.S.; Khan, S. FliN is a major structural protein of the C-ring in the Salmonella typhimurium flagellar basal body. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Braun, T.F.; Blair, D.F. Motility protein complexes in the bacterial flagellar motor. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 261, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, R.; Kar, N.; Khan, S. Overproduced Salmonella typhimurium flagellar motor switch complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 298, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.A.; Glaeser, R.M. Retrospective on the early development of cryoelectron microscopy of macromolecules and a prospective on opportunities for the future. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 163, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, T.R.; Gao, H.; Baxter, W.T.; Asturias, F.J.; Boisset, N.; Leith, A.; Frank, J. SPIDER image processing for single-particle reconstruction of biological macromolecules from electron micrographs. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1941–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Morgan, D.G.; DeRosier, D.J. Rotational symmetry of the C ring and a mechanism for the flagellar rotary motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10134–10139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.; Morgan, D.G.; DeRosier, D.J. Structures of bacterial flagellar motors from two FliF-FliG gene fusion mutants. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6404–6412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, H.S.; Dang, H.; Lai, Y.; DeRosier, D.J.; Khan, S. Variable symmetry in Salmonella typhimurium flagellar motors. Biophys. J. 2003, 84, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubori, T.; Shimamoto, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Namba, K.; Aizawa, S. Morphological pathway of flagellar assembly in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 226, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Oosawa, K.; Aizawa, S. M ring, S ring and proximal rod of the flagellar basal body of Salmonella typhimurium are composed of subunits of a single protein, FliF. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 227, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Berg, H.C. The stall torque of the bacterial flagellar motor. Biophys. J. 1987, 52, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Berg, H.C. Torque-speed relationship of the flagellar rotary motor of Escherichia coli. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, Y.; Hotta, H.; Homma, M.; Ishijima, A. Torque-speed relationship of the Na+-driven flagellar motor of Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 327, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.M.; Berg, H.C. Absence of a barrier to backwards rotation of the bacterial flagellar motor demonstrated with optical tweezers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14433–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.M.; Berg, H.C. Torque generated by the flagellar motor of Escherichia coli while driven backward. Biophys. J. 1999, 76, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrner, K.A.; Ryu, W.S.; Berg, H.C. Biomechanics: Bacterial flagellar switching under load. Nature 2003, 423, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, S.; Magariyama, Y.; Aizawa, S. Abrupt changes in flagellar rotation observed by laser dark-field microscopy. Nature 1990, 346, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, S.A.; Whitby, F.G.; Blair, D.F.; Hill, C.P. Structure of the C-terminal domain of FliG, a component of the rotor in the bacterial flagellar motor. Nature 1999, 400, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.N.; Hill, C.P.; Blair, D.F. Crystal structure of the middle and C-terminal domains of the flagellar rotor protein FliG. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, A.G.; Biran, R.; Wohlschlegel, J.A.; Manson, M.D. Mutations in motB suppressible by changes in stator or rotor components of the bacterial flagellar motor. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 258, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.M.; Mottonen, J.M.; Stock, J.B.; Schutt, C.E. Three-dimensional structure of CheY, the response regulator of bacterial chemotaxis. Nature 1989, 337, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silversmith, R.E.; Bourret, R.B. Throwing the switch in bacterial chemotaxis. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Cho, H.S.; Hastings, C.A.; Igo, M.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Pelton, J.G.; Stewart, V.; Wemmer, D.E.; Kustu, S. Beryllofluoride mimics phosphorylation of NtrC and other bacterial response regulators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 14789–14794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, M.; Oosawa, K.; Aizawa, S.; Eisenbach, M. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a signal molecule to the flagellar switch of bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8787–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbach, M.; Caplan, S.R. Bacterial chemotaxis: Unsolved mystery of the flagellar switch. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, R444–R446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cho, H.S.; Pelton, J.G.; Yan, D.; Henderson, R.K.; King, D.S.; Huang, L.; Kustu, S.; Berry, E.A.; Wemmer, D.E. Crystal structure of an activated response regulator bound to its target. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, M.M.; Bren, A.; Eisenbach, M.; Dahlquist, F.W. Identification of the binding interfaces on CheY for two of its targets, the phosphatase CheZ and the flagellar switch protein fliM. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 289, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Pierce, D.; Vale, R.D. Interactions of the chemotaxis signal protein CheY with bacterial flagellar motors visualized by evanescent wave microscopy. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, B.E.; Fahrner, K.A.; Turner, L.; Berg, H.C. Control of direction of flagellar rotation in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cluzel, P.; Surette, M.; Leibler, S. An ultrasensitive bacterial motor revealed by monitoring signaling proteins in single cells. Science 2000, 287, 1652–1655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sagi, Y.; Khan, S.; Eisenbach, M. Binding of the chemotaxis response regulator CheY to the isolated, intact switch complex of the bacterial flagellar motor: Lack of cooperativity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 25867–25871. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Macnab, R.M. The steady-state counterclockwise/clockwise ratio of bacterial flagellar motors is regulated by protonmotive force. J. Mol. Biol. 1980, 138, 563–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, T.A.; Le Novere, N.; Bray, D. Conformational spread in a ring of proteins: A stochastic approach to allostery. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 308, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervushin, K.; Riek, R.; Wider, G.; Wuthrich, K. Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole-dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12366–12371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R.; Francis, N.R.; Xu, C.; DeRosier, D.J. The three-dimensional structure of the flagellar rotor from a clockwise-locked mutant of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7039–7048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalfie, M.; Tu, Y.; Euskirchen, G.; Ward, W.W.; Prasher, D.C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 1994, 263, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirody, J.A.; Sun, Y.-R.; Lo, C.-J. The biophysicist’s guide to the bacterial flagellar motor. Adv. Phys. 2017, 2, 324–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Branch, R.W.; Nicolau, D.V., Jr.; Pilizota, T.; Steel, B.C.; Maini, P.K.; Berry, R.M. Conformational spread as a mechanism for cooperativity in the bacterial flagellar switch. Science 2010, 327, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Hanaizumi, Y.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Inoue, Y.; Erhardt, M.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Direct observation of speed fluctuations of flagellar motor rotation at extremely low load close to zero. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, Y.; Rowe, A.D.; Leake, M.C.; Yakushi, T.; Homma, M.; Ishijima, A.; Berry, R.M. Direct observation of steps in rotation of the bacterial flagellar motor. Nature 2005, 437, 916–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Kami-ike, N.; Yokota, J.P.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K. Evidence for symmetry in the elementary process of bidirectional torque generation by the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17616–17620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilizota, T.; Brown, M.T.; Leake, M.C.; Branch, R.W.; Berry, R.M.; Armitage, J.P. A molecular brake, not a clutch, stops the Rhodobacter sphaeroides flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11582–11587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, T.; Yu, H.; Sowa, Y.; Wingreen, N.S. Steps in the bacterial flagellar motor. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkova, E.A.; Emonet, T.; Park, H.; Cluzel, P. Hidden stochastic nature of a single bacterial motor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 058105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Berg, H.C. Switching dynamics of the bacterial flagellar motor near zero load. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15752–15755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.; Ryu, W.S.; Berg, H.C. Real-time imaging of fluorescent flagellar filaments. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Fahrner, K.A.; Berg, H.C. Switching of the bacterial flagellar motor near zero load. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Fahrner, K.A.; Turner, L.; Berg, H.C. Asymmetry in the clockwise and counterclockwise rotation of the bacterial flagellar motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12846–12849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Shi, H.; He, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, J. Non-equilibrium effects in the allosteric regulation of the bacterial flagellar switch. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Che, Y.S.; Kami-ike, N.; Ma, Q.; Minamino, T.; Sowa, Y.; Namba, K. Populational heterogeneity vs. temporal fluctuation in Escherichia coli flagellar motor switching. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, T.; Bai, F.; Che, Y.S.; Minamino, T.; Namba, K.; Wingreen, N.S. Non-genetic individuality in Escherichia coli motor switching. Phys. Biol. 2011, 8, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, H.; Sagawa, T.; Inoue, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ishijima, A. Direct imaging of intracellular signaling components that regulate bacterial chemotaxis. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, H.; Inoue, Y.; Terasawa, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ishijima, A. Exchange of rotor components in functioning bacterial flagellar motor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 394, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalez, N.J.; Berry, R.M.; Armitage, J.P. Stoichiometry and turnover of the bacterial flagellar switch protein FliN. mBio 2014, 5, e01216-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Berg, H.C. Ultrasensitivity of an adaptive bacterial motor. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The nonequilibrium mechanism for ultrasensitivity in a biological switch: Sensing by Maxwell’s demons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11737–11741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, F.; Minamino, T.; Wu, Z.; Namba, K.; Xing, J. Coupling between switching regulation and torque generation in bacterial flagellar motor. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 178105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Nicolau, D.V., Jr.; Maini, P.K.; Berry, R.M.; Bai, F. Conformational spread in the flagellar motor switch: A model study. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Sowa, Y.; Baker, M.A.; Bai, F. Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch in Response to CheY-P Regulation and Motor Structural Alterations. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tu, Y. Driven to peak. Nat. Phys. 2017, 13, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lowder, B.; Bilwes, A.M.; Blair, D.F.; Crane, B.R. Structure of FliM provides insight into assembly of the switch complex in the bacterial flagella motor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11886–11891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowder, B.J.; Duyvesteyn, M.D.; Blair, D.F. FliG subunit arrangement in the flagellar rotor probed by targeted cross-linking. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5640–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vartanian, A.S.; Paz, A.; Fortgang, E.A.; Abramson, J.; Dahlquist, F.W. Structure of flagellar motor proteins in complex allows for insights into motor structure and switching. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35779–35783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.; Gonzalez-Bonet, G.; Bilwes, A.M.; Crane, B.R.; Blair, D. Architecture of the flagellar rotor. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Lam, W.W.; Wong, J.Y.; Chan, L.C.; Kotaka, M.; Ling, T.K.; Jin, D.Y.; Ottemann, K.M.; Au, S.W. Structural basis of FliG-FliM interaction in Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 88, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, A.; Morcos, F.; Khan, S. The Gearbox of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch. Structure 2016, 24, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brown, P.N.; Terrazas, M.; Paul, K.; Blair, D.F. Mutational analysis of the flagellar protein FliG: Sites of interaction with FliM and implications for organization of the switch complex. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikino, T.; Hijikata, A.; Miyanoiri, Y.; Onoue, Y.; Kojima, S.; Shirai, T.; Homma, M. Rotational direction of flagellar motor from the conformation of FliG middle domain in marine Vibrio. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lam, K.H.; Lam, W.W.L.; Wong, S.Y.Y.; Chan, V.S.F.; Au, S.W.N. A putative spermidine synthase interacts with flagellar switch protein FliM and regulates motility in Helicobacter pylori. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 106, 690–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, C.M.; Quillin, M.L.; Campos, A.; Lu, J.; McEvoy, M.M.; Hausrath, A.C.; Westbrook, E.M.; Matsumura, P.; Matthews, B.W.; Dahlquist, F.W. Structure of the constitutively active double mutant CheYD13K Y106W alone and in complex with a FliM peptide. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyer, C.M.; Dahlquist, F.W. Switched or not?: The structure of unphosphorylated CheY bound to the N terminus of FliM. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7354–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, A.; Fornili, A.; Fraternali, F.; Kleinjung, J. Detection of allosteric signal transmission by information-theoretic analysis of protein dynamics. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 26, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiberg, M.; Afanzar, O.; Cassidy, C.K.; Gabashvili, A.; Schulten, K.; Levin, Y.; Eisenbach, M. CheY’s acetylation sites responsible for generating clockwise flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 95, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, P.; Gupta, S.; Chen, Y.; Petzold, C.J.; Ralston, C.R.; Blair, D.F.; Khan, S. Allosteric priming of E. coli CheY by the flagellar motor protein FliM. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, C.M.; Vartanian, A.S.; Zhou, H.; Dahlquist, F.W. A molecular mechanism of bacterial flagellar motor switching. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 388, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.K.; Paul, K.; Blair, D. Chemotaxis signaling protein CheY binds to the rotor protein FliN to control the direction of flagellar rotation in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9370–9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.N.; Mathews, M.A.; Joss, L.A.; Hill, C.P.; Blair, D.F. Crystal structure of the flagellar rotor protein FliN from Thermotoga maritima. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2890–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.K.; Paul, K.; Blair, D.F. Subunit organization and reversal-associated movements in the flagellar switch of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notti, R.Q.; Bhattacharya, S.; Lilic, M.; Stebbins, C.E. A common assembly module in injectisome and flagellar type III secretion sorting platforms. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, M.A.; Marcoux, J.; McVicker, G.; Johnson, S.; Fong, Y.H.; Stevens, R.; Bowman, L.A.; Degiacomi, M.T.; Yan, J.; Wise, A.; et al. Characterisation of Shigella Spa33 and Thermotoga FliM/N reveals a new model for C-ring assembly in T3SS. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Pedrajo, B.; Minamino, T.; Kihara, M.; Namba, K. Interactions between C ring proteins and export apparatus components: A possible mechanism for facilitating type III protein export. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrusci, P.; Vergara-Irigaray, M.; Johnson, S.; Beeby, M.D.; Hendrixson, D.R.; Roversi, P.; Friede, M.E.; Deane, J.E.; Jensen, G.J.; Tang, C.M.; et al. Architecture of the major component of the type III secretion system export apparatus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sircar, R.; Greenswag, A.R.; Bilwes, A.M.; Gonzalez-Bonet, G.; Crane, B.R. Structure and activity of the flagellar rotor protein FliY: A member of the CheC phosphatase family. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13493–13502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, D.S.; Ordal, G.W. Identification and characterization of FliY, a novel component of the Bacillus subtilis flagellar switch complex. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szurmant, H.; Ordal, G.W. Diversity in chemotaxis mechanisms among the bacteria and archaea. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2004, 68, 301–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Kim, E.A.; Panushka, J.; Botelho, T.; Meyer, T.; Kearns, D.B.; Ordal, G.; Blair, D.F. Organization of the Flagellar Switch Complex of Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.H.; Ip, W.S.; Lam, Y.W.; Chan, S.O.; Ling, T.K.; Au, S.W. Multiple conformations of the FliG C-terminal domain provide insight into flagellar motor switching. Structure 2012, 20, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kinoshita, M.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. Effect of a clockwise-locked deletion in FliG on the FliG ring structure of the bacterial flagellar motor. Genes Cells 2018, 23, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Way, S.M.; Millas, S.G.; Lee, A.H.; Manson, M.D. Rusty, jammed, and well-oiled hinges: Mutations affecting the interdomain region of FliG, a rotor element of the Escherichia coli flagellar motor. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.K.; Ginsburg, M.A.; Crovace, C.; Donohoe, M.; Stock, D. Structure of the torque ring of the flagellar motor and the molecular basis for rotational switching. Nature 2010, 466, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhulin, I.B. By Staying Together, Two Genes Keep the Motor Running. Structure 2017, 25, 214–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Minamino, T.; Imada, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Nakamura, S.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Namba, K. Structural insight into the rotational switching mechanism of the bacterial flagellar motor. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1000616. [Google Scholar]
- Sircar, R.; Borbat, P.P.; Lynch, M.J.; Bhatnagar, J.; Beyersdorf, M.S.; Halkides, C.J.; Freed, J.H.; Crane, B.R. Assembly states of FliM and FliG within the flagellar switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 867–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Hynson, R.M.; Ganuelas, L.A.; Mohammadi, N.S.; Liew, C.W.; Rey, A.A.; Duff, A.P.; Whitten, A.E.; Jeffries, C.M.; Delalez, N.J.; et al. Domain-swap polymerization drives the self-assembly of the bacterial flagellar motor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, A.; Kleinjung, J.; Rasool, S.; Khan, S. Coevolved Mutations Reveal Distinct Architectures for Two Core Proteins in the Bacterial Flagellar Motor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.N.; Khan, S.; Morcos, F. Characterization of C-ring component assembly in flagellar motors from amino acid coevolution. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Guo, T.W.; Misra, S. A coevolution-guided model for the rotor of the bacterial flagellar motor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanoiri, Y.; Hijikata, A.; Nishino, Y.; Gohara, M.; Onoue, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kojima, C.; Shirai, T.; Kainosho, M.; Homma, M. Structural and Functional Analysis of the C-Terminal Region of FliG, an Essential Motor Component of Vibrio Na(+)-Driven Flagella. Structure 2017, 25, 1540–1548.e1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakushi, T.; Yang, J.; Fukuoka, H.; Homma, M.; Blair, D.F. Roles of charged residues of rotor and stator in flagellar rotation: Comparative study using H+-driven and Na+-driven motors in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoue, Y.; Takekawa, N.; Nishikino, T.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M. The role of conserved charged residues in the bidirectional rotation of the bacterial flagellar motor. Microbiologyopen 2018, 7, e00587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takekawa, N.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M. Contribution of many charged residues at the stator-rotor interface of the Na+-driven flagellar motor to torque generation in Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Nonoyama, N.; Takekawa, N.; Fukuoka, H.; Homma, M. Mutations targeting the C-terminal domain of FliG can disrupt motor assembly in the Na(+)-driven flagella of Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 414, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.V.; Nakamura, S.; Hiraoka, K.D.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. Distinct roles of highly conserved charged residues at the MotA-FliG interface in bacterial flagellar motor rotation. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Moon, K.H.; Zhao, X.; Norris, S.J.; Motaleb, M.A.; Liu, J. Structural insights into flagellar stator-rotor interactions. eLife 2019, 8, e48979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilcott, G.S.; Hughes, K.T. Coupling of flagellar gene expression to flagellar assembly in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. MMBR 2000, 64, 694–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.A.; Panushka, J.; Meyer, T.; Carlisle, R.; Baker, S.; Ide, N.; Lynch, M.; Crane, B.R.; Blair, D.F. Architecture of the Flagellar Switch Complex of Escherichia coli: Conformational Plasticity of FliG and Implications for Adaptive Remodeling. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Miyata, T.; Terahara, N.; Mori, K.; Inoue, Y.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Kato, T.; Namba, K.; Minamino, T. Novel Insights into Conformational Rearrangements of the Bacterial Flagellar Switch Complex. mBio 2019, 10, e00079-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenson, R.; Zhou, H.; Dahlquist, F.W. Structural insights into the interaction between the bacterial flagellar motor proteins FliF and FliG. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 5052–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, R.; Abe-Yoshizumi, R.; Kishi, T.; Homma, M.; Kojima, S. Interaction of the C-Terminal Tail of FliF with FliG from the Na+-Driven Flagellar Motor of Vibrio alginolyticus. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.J.; Levenson, R.; Kim, E.A.; Sircar, R.; Blair, D.F.; Dahlquist, F.W.; Crane, B.R. Co-Folding of a FliF-FliG Split Domain Forms the Basis of the MS:C Ring Interface within the Bacterial Flagellar Motor. Structure 2017, 25, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Lam, K.H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, K.; Lee, S.H.; Chen, X.; Au, S.W.N. Crystal structure of the FliF-FliG complex from Helicobacter pylori yields insight into the assembly of the motor MS-C ring in the bacterial flagellum. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Fong, Y.H.; Deme, J.C.; Furlong, E.J.; Kuhlen, L.; Lea, S.M. Symmetry mismatch in the MS-ring of the bacterial flagellar rotor explains the structural coordination of secretion and rotation. Nat. Microbiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takekawa, N.; Nishiyama, M.; Kaneseki, T.; Kanai, T.; Atomi, H.; Kojima, S.; Homma, M. Sodium-driven energy conversion for flagellar rotation of the earliest divergent hyperthermophilic bacterium. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Norris, S.J.; Liu, J. Molecular architecture of the bacterial flagellar motor in cells. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 4323–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, H.; Kawamoto, A.; Morimoto, Y.V.; Imada, K.; Minamino, T. Structural differences in the bacterial flagellar motor among bacterial species. Biophys. Phys. 2017, 14, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.E.; Leadbetter, J.R.; Jensen, G.J. In situ structure of the complete Treponema primitia flagellar motor. Nature 2006, 442, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Lin, T.; Botkin, D.J.; McCrum, E.; Winkler, H.; Norris, S.J. Intact flagellar motor of Borrelia burgdorferi revealed by cryo-electron tomography: Evidence for stator ring curvature and rotor/C-ring assembly flexion. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 5026–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, L.D.; Matthews-Palmer, T.R.S.; Gulbronson, C.J.; Ribardo, D.A.; Beeby, M.; Hendrixson, D.R. Diversification of Campylobacter jejuni Flagellar C-Ring Composition Impacts Its Structure and Function in Motility, Flagellar Assembly, and Cellular Processes. mBio 2020, 11, e02286-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeby, M.; Ribardo, D.A.; Brennan, C.A.; Ruby, E.G.; Jensen, G.J.; Hendrixson, D.R. Diverse high-torque bacterial flagellar motors assemble wider stator rings using a conserved protein scaffold. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1917–E1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- wwPDB Consortium. Protein Data Bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D520–D528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeliger, D.; Haas, J.; de Groot, B.L. Geometry-based sampling of conformational transitions in proteins. Structure 2007, 15, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, R.; Bouillet, S.; Stock, A.M. Structural Basis of Response Regulator Function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyakutake, A.; Homma, M.; Austin, M.J.; Boin, M.A.; Hase, C.C.; Kawagishi, I. Only one of the five CheY homologs in Vibrio cholerae directly switches flagellar rotation. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8403–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diepold, A.; Armitage, J.P. Type III secretion systems: The bacterial flagellum and the injectisome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallen, M.J.; Gophna, U. Bacterial flagella and Type III secretion: Case studies in the evolution of complexity. Genome Dyn. 2007, 3, 30–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Schuster, S.C.; Khan, S. Structural effects of mutations in Salmonella typhimurium flagellar switch complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 251, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, S. The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060833
Khan S. The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060833
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Shahid. 2020. "The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060833
APA StyleKhan, S. (2020). The Architectural Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Switch. Biomolecules, 10(6), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060833



