Sorbaria kirilowii Ethanol Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting Src/Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals, Cell Culture, and Compound Preparation
2.3. Peritoneal Macrophages Preparation
2.4. NO Production Assay
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
2.6. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.7. mRNA Expression Analysis by Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.8. Plasmid Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. Total and Nuclear Cell Lysate Preparation
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Cellular Thermal-Shift Assay
2.12. HCl/EtOH-Induced Acute Gastritis in ICR Mice
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
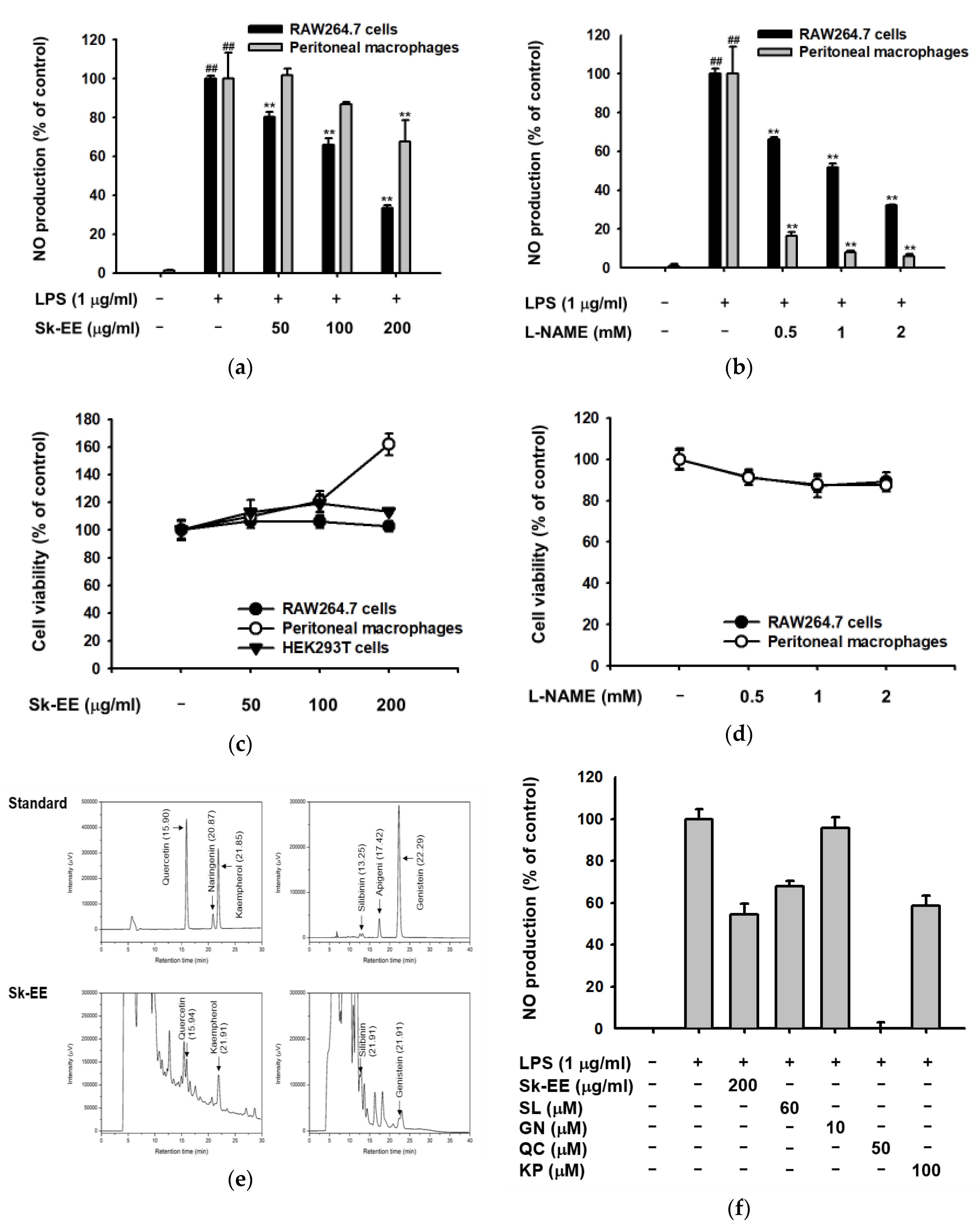
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sk-EE In Vitro and Ex Vivo
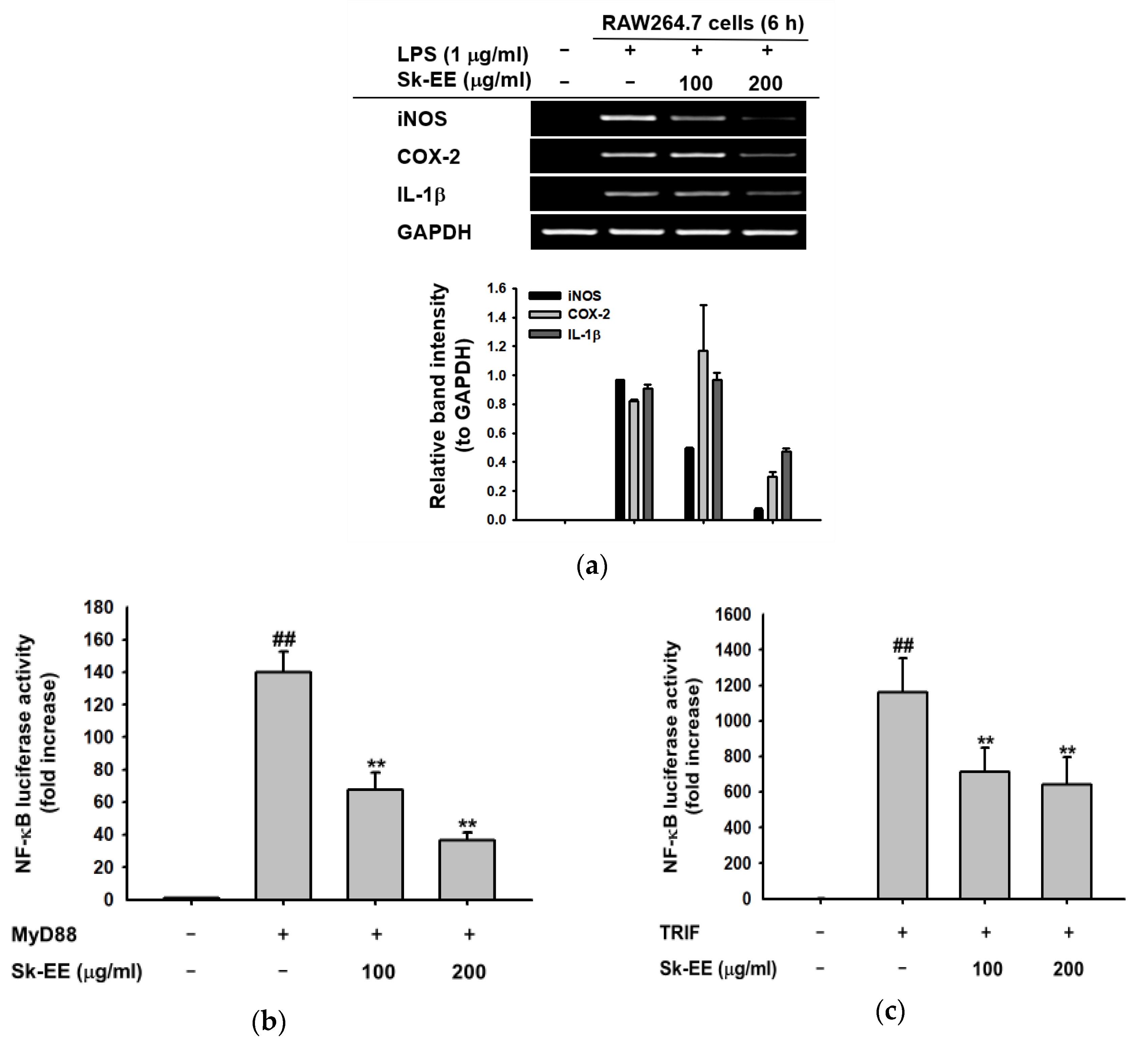
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sk-EE at the Transcriptional Level
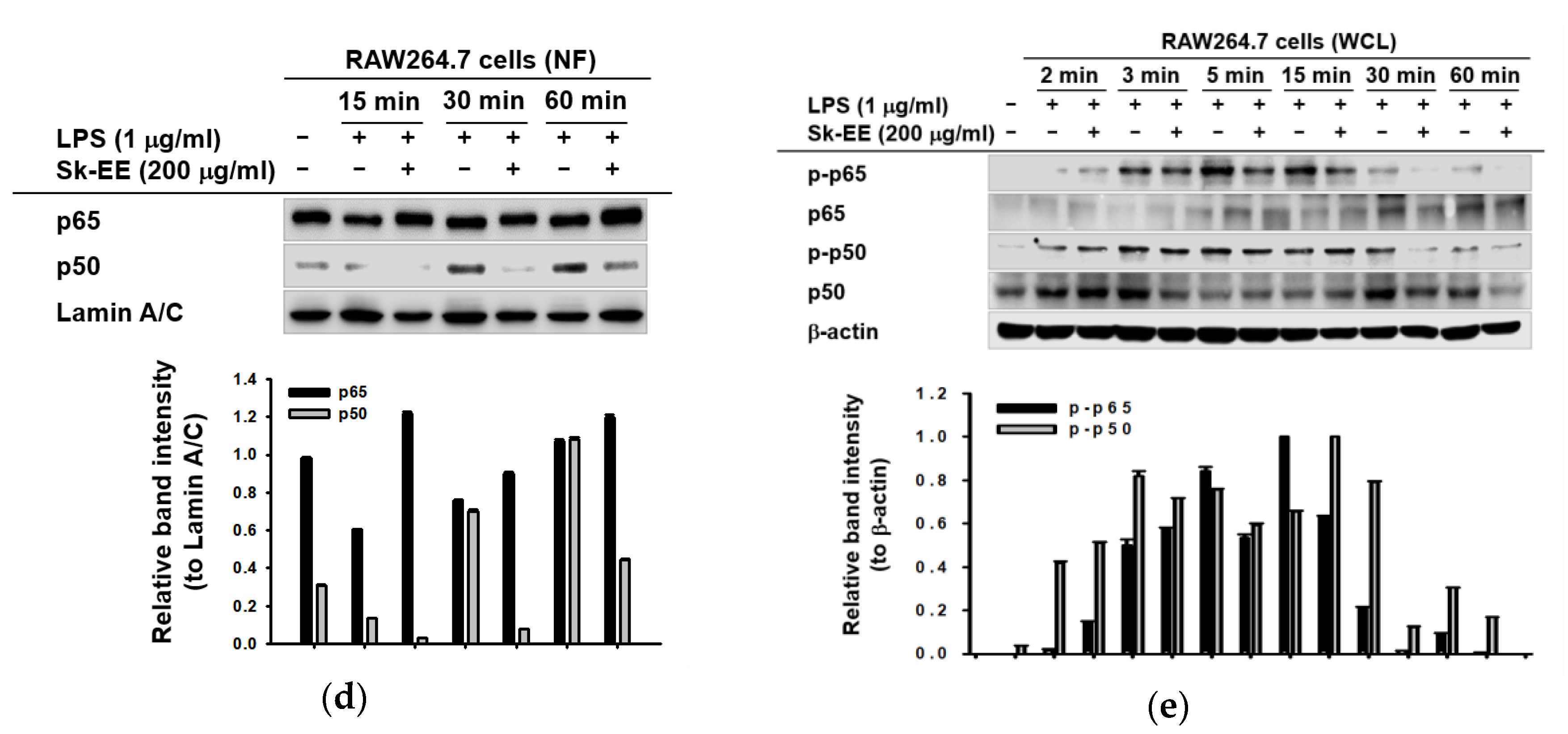
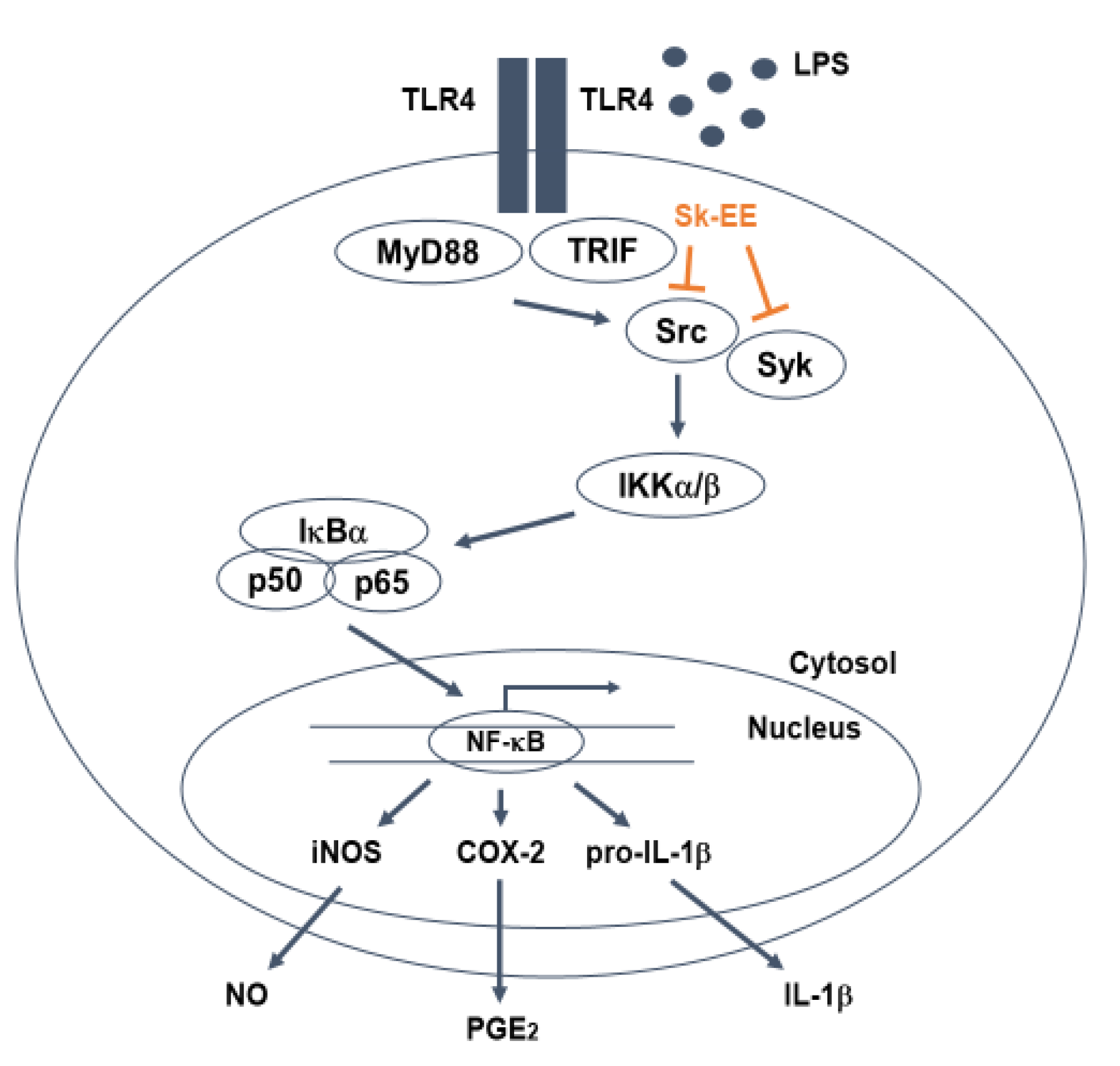
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sk-EE on the NF-κB Signaling Pathway
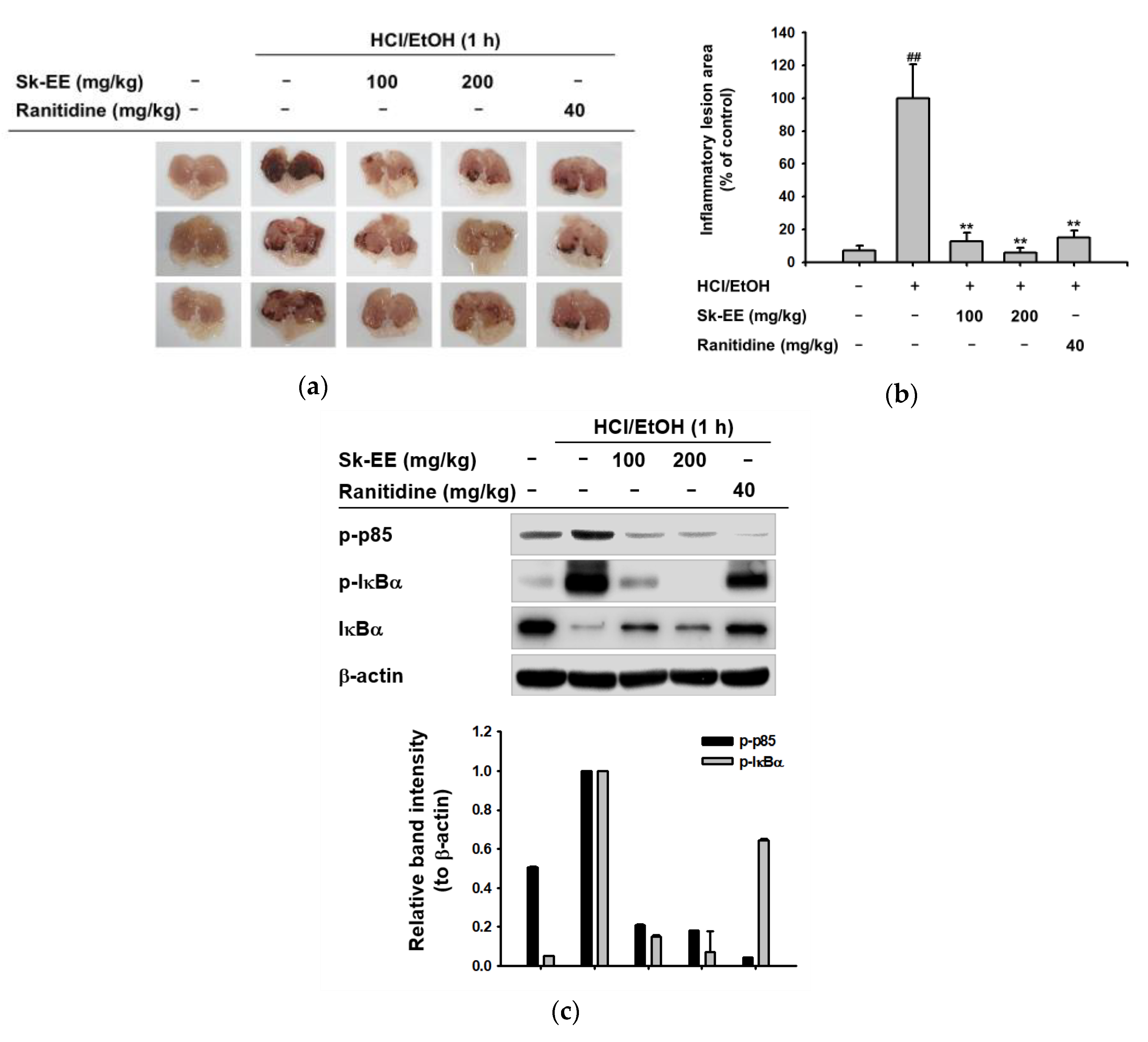
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sk-EE In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Kobayashi, K. Macrophages in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Huang, J.; Gong, W.; Iribarren, P.; Dunlop, N.M.; Wang, J.M. Toll-like receptors in inflammation, infection and cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1271–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas, A.; van der Poll, T.; de Vos, A.F. Role of CD14 in lung inflammation and infection. Critical Care 2010, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, G.M.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 2003, 300, 1524–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmi, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Kawai, T.; Kaisho, T.; Sato, S.; Sanjo, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Hoshino, K.; Wagner, H.; Takeda, K. A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 2000, 408, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptor function and signaling. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G. Pathways of intracellular signal transduction. Cell 2004, 558–571. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, K.; Dixit, V.M. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a006049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. NF-κB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rowe, D.C.; Barnes, B.J.; Caffrey, D.R.; Visintin, A.; Latz, E.; Monks, B.; Pitha, P.M.; Golenbock, D.T. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-κB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Finotto, S. IL-6 signaling in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, M.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Perkins, D.J.; Medvedev, A.E.; Piao, W.; Fenton, M.J.; Vogel, S.N. TLR4/MyD88/PI3K interactions regulate TLR4 signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2009, 85, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, C.A. Src-family and Syk kinases in activating and inhibitory pathways in innate immune cells: Signaling cross talk. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a002352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.-C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S. Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2007, 15, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, R.; Al-Omran, A.; Parvathy, S. Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, S.F. Cytokine mediators of immunity and inflammation. Arch. Surgery 1993, 128, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghetti, L. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in inflammatory and degenerative brain diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Pinho, V.; Perretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of Inflammation: What Controls Its Onset? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, K. A survey of the genus Sorbaria (Rosaceae). Nord. J. Bot. 1989, 8, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Guan, L.; Quan, Y. Experimental study on Sorbaria sorbifolia extract against chronic liver damage in rats. Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2004, 27, 751–753. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, C.; Chen, L. Inhibition of Sorbaria sorbifolia on proliferarion of hepatoma HepG-2 cell line. Zhong Yao Cai = Zhongyaocai = J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2007, 30, 681–684. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Quan, J.; Shen, M.; Jin, H. Inhibitory effect of sorbaria sorbifolia on DEN-induced precancerous hepatic foci and its antioxidativee activities in rats. China J. Cancer Prev. Treat. 2003, 10, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.G.; Kang, W.S.; Park, K.T.; Park, D.J.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Anticancer effect of joboksansam, Korean wild ginseng germinated from bird feces. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.J.; Kim, M.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. AP-1-targeted inhibition of macrophage function and lipopolysaccharide/D-galactosamine-induced hepatitis by Phyllanthus acidus methanolic extract. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, B.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Anti-inflammatory effects of water chestnut extract on cytokine responses via nuclear factor-κB-signaling pathway. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Syk and Src-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of aripiprazole, an atypical antipsychotic. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Kim, D.; Yi, Y.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, H.Y.; Hwang, K.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. AKT-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of the methanol extract of Chrysanthemum indicum var. albescens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 201, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qomaladewi, N.P.; Aziz, N.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Piper cubeba L. Methanol Extract Has Anti-Inflammatory Activity Targeting Src/Syk via NF- κ B Inhibition. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kang, Y.-G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, T.R.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Cho, J.Y. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of 8-Hydroxydaidzein (8-HD) in Activated Macrophage-Like RAW264.7 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Lorz, L.R.; Yi, D.-K.; Noh, J.K.; Yi, Y.-S.; Cho, J.Y. Viburnum pichinchense methanol extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects via targeting the NF-κB and caspase-11 non-canonical inflammasome pathways in macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 245, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.J.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, D.; Sung, N.Y.; Yang, S.; Baek, K.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, D.H.; et al. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of Phyllanthus acidus methanolic extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, W.S.; Yu, T.; Yi, Y.-S.; Park, J.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.S.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Novel anti-inflammatory function of NSC95397 by the suppression of multiple kinases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory activities of Canarium subulatum Guillaumin methanol extract operate by targeting Src and Syk in the NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 238, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Yang, W.S.; Hong, Y.H.; Kweon, D.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory functions of the CDC25 phosphatase inhibitor BN82002 via targeting AKT2. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 164, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.G.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Alisma canaliculatum ethanol extract suppresses inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated macrophages, HCl/EtOH-induced gastritis, and DSS-triggered colitis by targeting Src/Syk and TAK1 activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 219, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orucevic, A.; Lala, P.K. NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis, ameliorates interleukin 2-induced capillary leakage and reduces tumour growth in adenocarcinoma-bearing mice. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 73, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Strum, W.B. Ranitidine. JAMA 1983, 250, 1894–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Korbut, R.; Adamek-Guzik, T. Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2003, 54, 469–487. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, P.; Tripathi, P.; Kashyap, L.; Singh, V. The role of nitric oxide in inflammatory reactions. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.B.; Lovewell, R.R.; Olive, A.J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Eugenin, E.; Smith, C.M.; Phuah, J.Y.; Long, J.E.; Dubuke, M.L. Nitric oxide prevents a pathogen-permissive granulocytic inflammation during tuberculosis. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, M.; Peluso, I.; Raguzzini, A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2010, 69, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, C.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Di Benedetto, R.; Filesi, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, intracellular signalling and inflammation. Annali-Istituto Superiore di Sanita 2007, 43, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Opal, S.M.; DePalo, V.A. Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 117, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, E.; FitzGerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willoughby, D.A.; Moore, A.R.; Colville-Nash, P.R. COX-1, COX-2, and COX-3 and the future treatment of chronic inflammatory disease. Lancet 2000, 355, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Molgora, M.; Garlanda, C. Interleukin-1 and Related Cytokines in the Regulation of Inflammation and Immunity. Immunity 2019, 50, 778–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Roux, B. Src kinase conformational activation: Thermodynamics, pathways, and mechanisms. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Palomo, E.; Recuero-Checa, M.A.; Bustelo, X.R.; Llorca, O. Conformational rearrangements upon Syk auto-phosphorylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1794, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihály, E.; Micsik, T.; Juhász, M.; Herszényi, L.; Tulassay, Z. Gastritis and gastropathy. Orv Hetil 2014, 155, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Croley, C.R.; Pandey, A.K.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Kumar Patra, J.; Das, G.; Kerry, R.G.; Annunziata, G.; et al. Targeting Inflammation by Flavonoids: Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Chen, C.; Kai, S.; Fu, X.; Man, W.; Ding, B.; Wang, C.; Xu, R. Eupatilin attenuates the inflammatory response induced by intracerebral hemorrhage through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 76, 105837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Hao, J.; Wu, C.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H. Eupatilin Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 8289–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checker, R.; Sandur, S.K.; Sharma, D.; Patwardhan, R.S.; Jayakumar, S.; Kohli, V.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Sainis, K.B. Potent anti-inflammatory activity of ursolic acid, a triterpenoid antioxidant, is mediated through suppression of NF-κB, AP-1 and NF-AT. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossen, M.J.; Baek, K.-S.; Kim, E.; Yang, W.S.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Kweon, D.-H.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, T.W.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of Persicaria chinensis methanolic extract targeting Src/Syk/NF-κB. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 159, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Park, J.G.; Lee, J.; Yang, W.S.; Park, G.W.; Kim, H.G.; Yi, Y.-S.; Baek, K.-S.; Sung, N.Y.; Hossen, M.J. The dietary flavonoid Kaempferol mediates anti-inflammatory responses via the Src, Syk, IRAK1, and IRAK4 molecular targets. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankhong, S.; Iawsipo, P.; Srisook, E.; Srisook, K.J.P. 4-methoxycinnamyl p-coumarate isolated from Etlingera pavieana rhizomes inhibits inflammatory response via suppression of NF-κB, Akt and AP-1 signaling in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Host | Dilution | Exposure (Time/Temperature) |
|---|---|---|---|
| p65 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p-p65 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p50 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p-p50 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| Lamin A/C | Mouse | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p85 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| IKKα | Rabbit | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| p-IKKα/β | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| IκBα | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p-IκBα | Mouse | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| Syk | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p-Syk | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| Src | Rabbit | 1:2500 | Overnight/4 °C |
| p-Src | Rabbit | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| p85 | Rabbit | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| β-actin | Rabbit | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| HA | Mouse | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| Myc | Mouse | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| Rabbit IgG | Goat | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| Mouse IgG | Horse | 1:2500 | 2 h/RT |
| Instrument | Condition A | Condition B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column | CAPCELL PAK C18 MG, 4.6 mm I.D. × 250 mm | |||||
| Detector | UV-Vis Detector | |||||
| Wavelength | 254 nm | 350 nm | ||||
| Analyzed period | 30 min | 40 min | ||||
| Solvent | Solvent A | 2% acetic acid in water | Solvent A | 0.1% formin acid in MeOH:water = 10:90 | ||
| Solvent B | 0.5% acetic acid in water:ACN = 50:50 | Solvent B | 0.1% formin acid in MeOH:water = 90:10 | |||
| Flow rate | 1 mL/min | 0.4 mL/min | ||||
| Volume | 10 µL | 10 µL | ||||
| Gradient | Time (min) | Composition (%) | Time (min) | Composition (%) | ||
| A | B | A | B | |||
| 0 | 28 | 72 | 0 | 40 | 60 | |
| 20 | 0 | 100 | 20 | 40 | 60 | |
| 30 | 0 | 100 | 25 | 70 | 30 | |
| - | - | - | 40 | 70 | 30 | |
| Targets | Direction | Sequences (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| iNOS | Forward | GGAGCCTTTAGACCTCAACAGA |
| Reverse | TGAACGAGGAGGGTGGTG | |
| COX-2 | Forward | CACTACATCCTGACCCACTT |
| Reverse | ATGCTCCTGCTTGAGTATGT | |
| IL-1β | Forward | CAACCAACAAGTGATATTCTCCATG |
| Reverse | GATCCACACACTCCAGCTGCA | |
| GAPDH | Forward | CAATGAATACGGCTACAGCAAC |
| Reverse | AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, J.; Lee, J.S.; Jang, Y.-J.; Choung, E.S.; Li, W.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. Sorbaria kirilowii Ethanol Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting Src/Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050741
Jang J, Lee JS, Jang Y-J, Choung ES, Li WY, Lee SW, Kim E, Kim J-H, Cho JY. Sorbaria kirilowii Ethanol Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting Src/Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050741
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Jiwon, Jong Sub Lee, Young-Jin Jang, Eui Su Choung, Wan Yi Li, Sang Woo Lee, Eunji Kim, Jong-Hoon Kim, and Jae Youl Cho. 2020. "Sorbaria kirilowii Ethanol Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting Src/Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050741
APA StyleJang, J., Lee, J. S., Jang, Y.-J., Choung, E. S., Li, W. Y., Lee, S. W., Kim, E., Kim, J.-H., & Cho, J. Y. (2020). Sorbaria kirilowii Ethanol Extract Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects In Vitro and In Vivo by Targeting Src/Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB. Biomolecules, 10(5), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050741






