The Effect of a Fast-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor on Vascularization of Subcutaneous Scaffolds in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Scaffold Preparation
2.3. Animals
2.4. Implantations and NaHS Injections
2.5. Histology
2.6. RT-PCR
2.7. Blood Vessel Functionality Tests
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
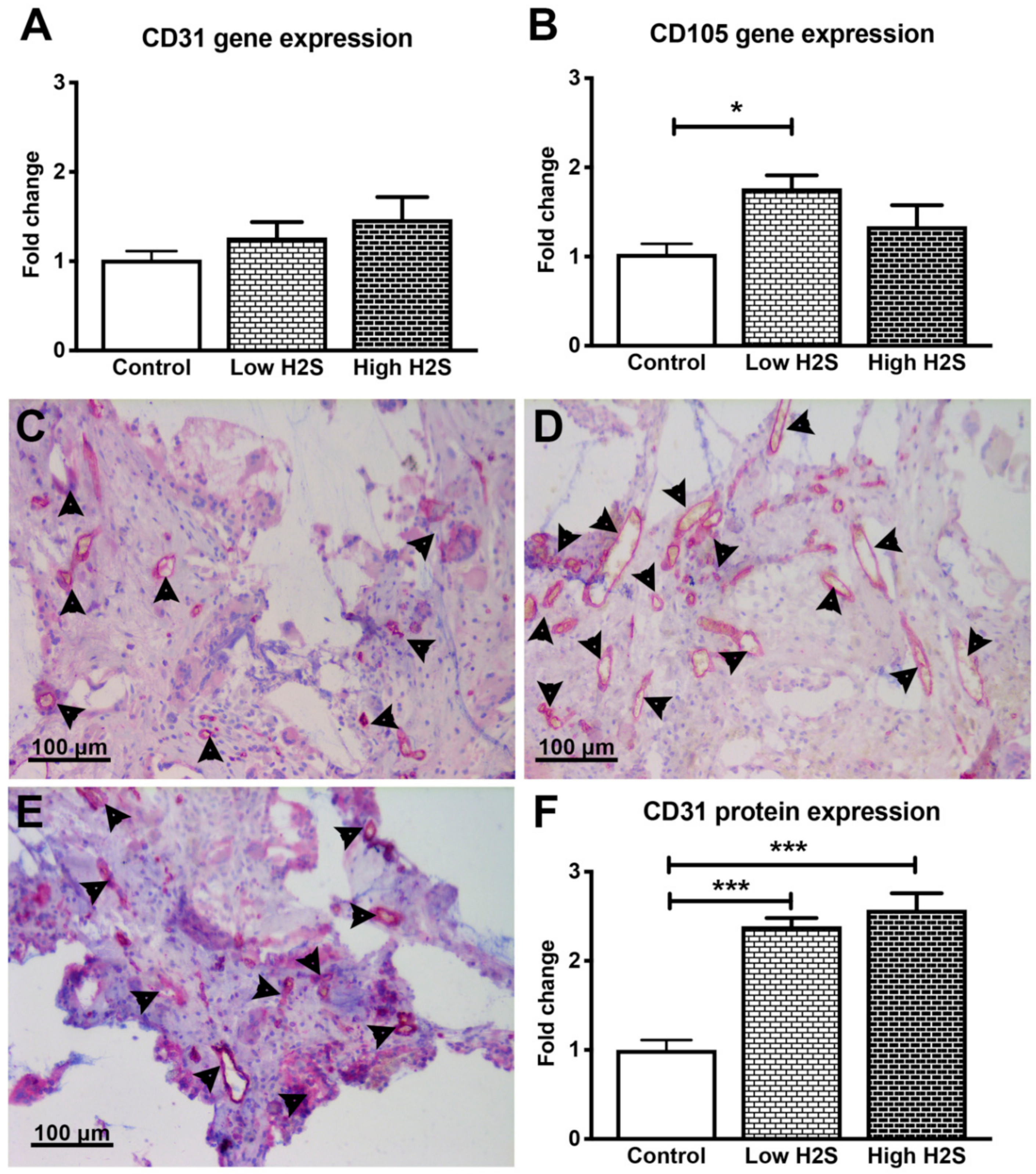
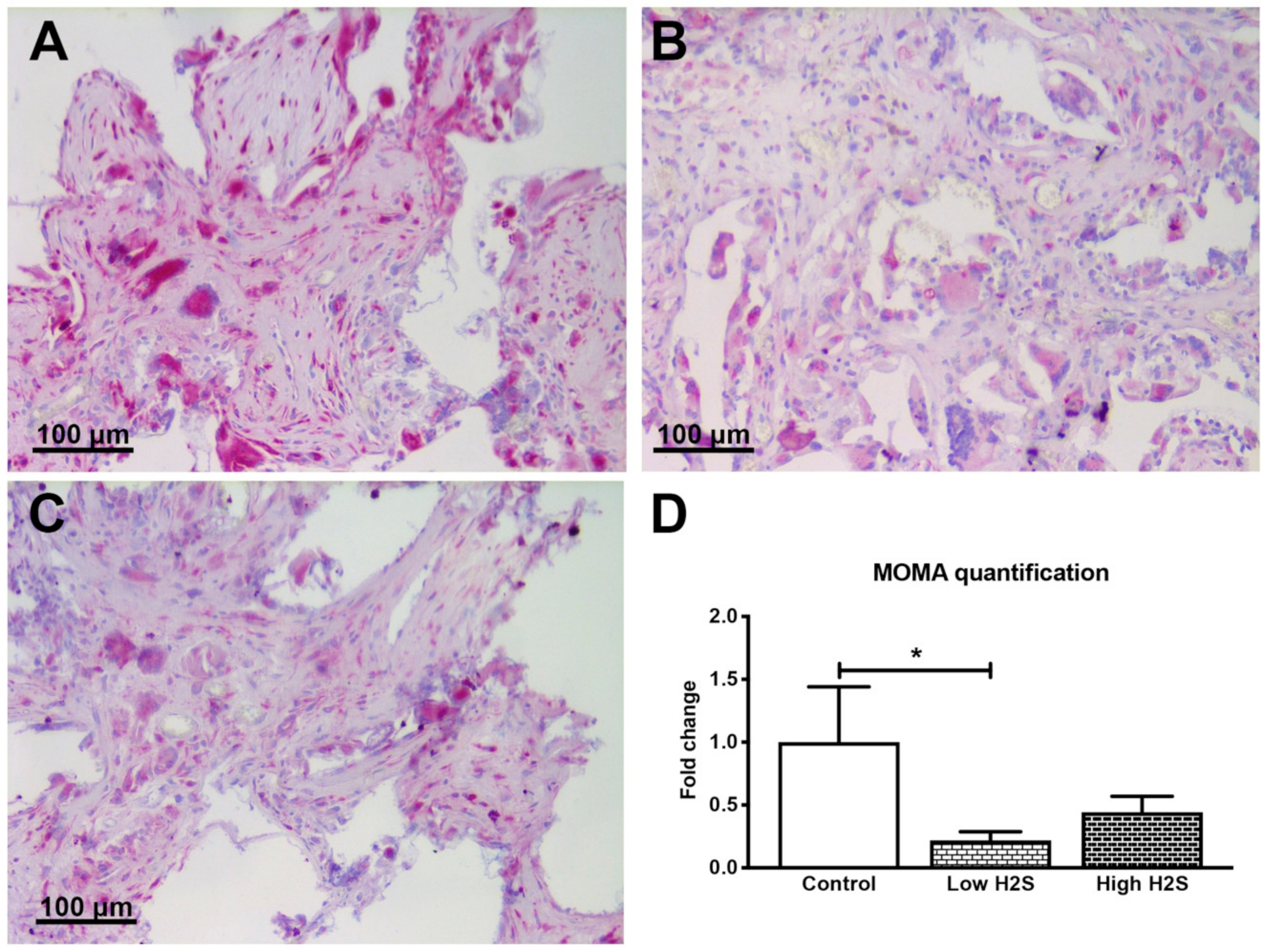
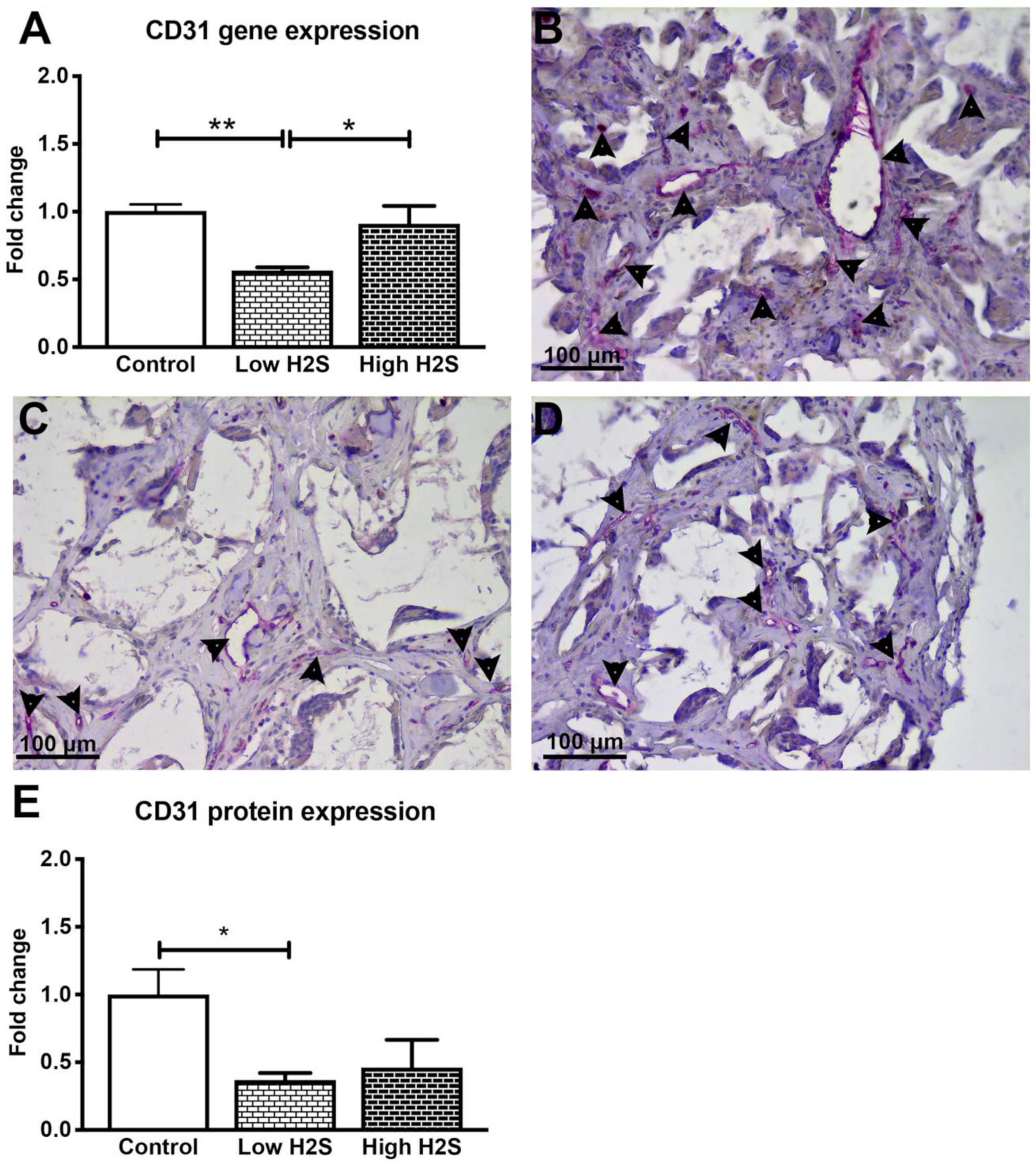
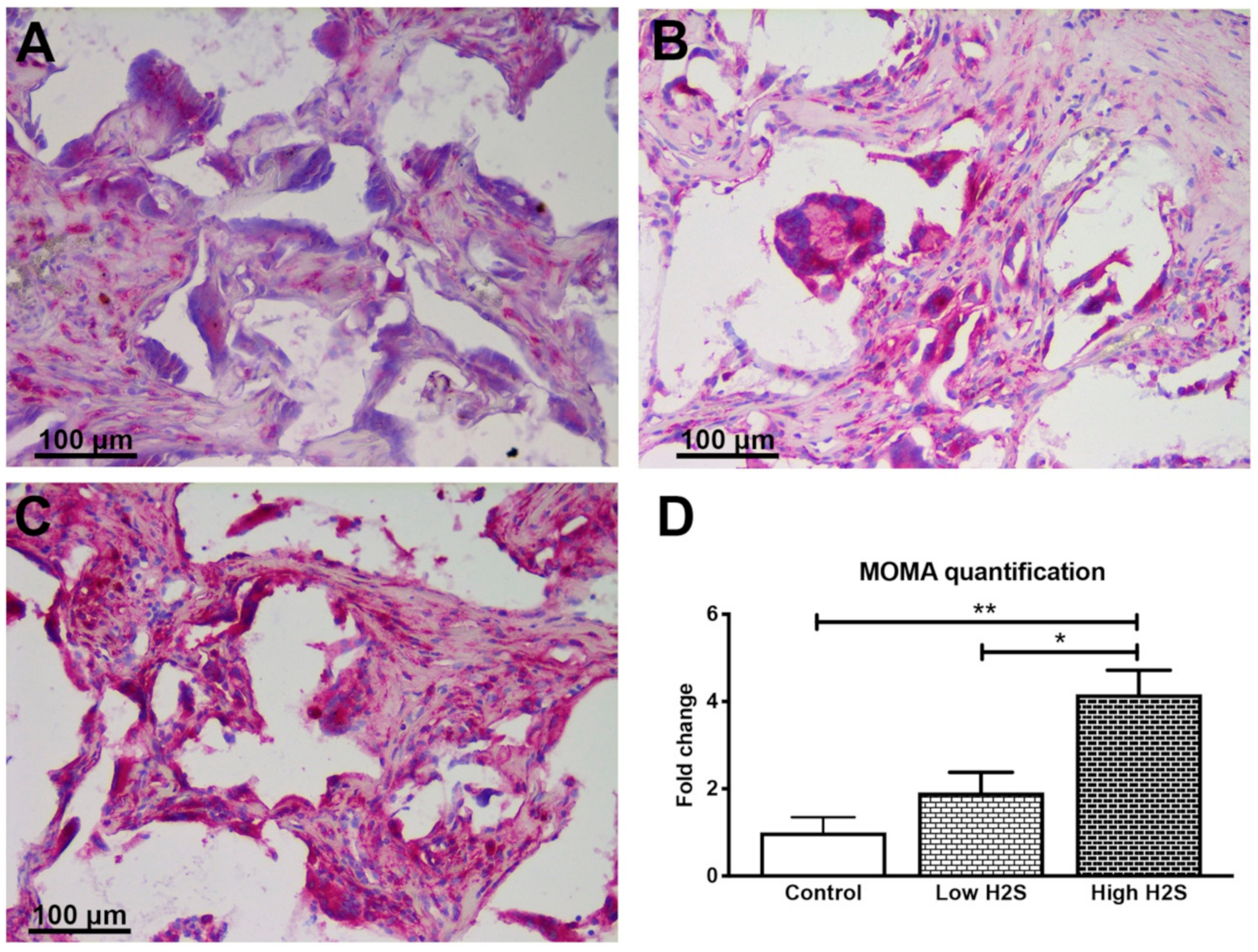
3.1. Vascularization of the Scaffolds in C57BL/6 Mice not Affected by H2S
3.2. Vascularization of the Scaffolds in Nude Mice Impaired by H2S
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shapiro, A.M.J.; Pokrywczynska, M.; Ricordi, C. Clinical pancreatic islet transplantation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 13, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaune, V.; Berney, T.; Lacotte, S.; Toso, C. Intraportal islet transplantation: The impact of the liver microenvironment. Transpl. Int. 2017, 30, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smink, A.M.; Faas, M.M.; De Vos, P. Toward Engineering a Novel Transplantation Site for Human Pancreatic Islets. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, S.; Piemonti, L.; Sordi, V. Pluripotent stem cell replacement approaches to treat type 1 diabetes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 43, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smink, A.M.; Li, S.; Hertsig, D.T.; de Haan, B.J.; Schwab, L.; van Apeldoorn, A.A.; de Koning, E.; Faas, M.M.; Lakey, J.R.; de Vos, P. The Efficacy of a Prevascularized, Retrievable Poly(D,L,-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) Subcutaneous Scaffold as Transplantation Site for Pancreatic Islets. Transplantation 2017, 101, e112–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smink, A.M.; Hertsig, D.T.; Schwab, L.; Van Apeldoorn, A.A.; De Koning, E.; Faas, M.M.; De Haan, B.J.; De Vos, P. A Retrievable, Efficacious Polymeric Scaffold for Subcutaneous Transplantation of Rat Pancreatic Islets. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, L.; Barbu, A.; Bodin, B.; Drott, C.J.; Espes, D.; Gao, X.; Grapensparr, L.; Källskog, Ö.; Lau, J.; Liljebäck, H.; et al. Pancreatic islet blood flow and its measurement. Upsala J. Med Sci. 2016, 121, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallard, V.; Armanet, M.; Parnaud, G.; Meyer, J.; Barbieux, C.; Montanari, E.; Meier, R.; Morel, P.; Berney, T.; Bosco, D. Cell rearrangement in transplanted human islets. FASEB J. 2015, 30, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Shen, X.; Kevil, C.G. Beyond a Gasotransmitter: Hydrogen Sulfide and Polysulfide in Cardiovascular Health and Immune Response. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 634–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Moore, P.K.; Wang, M.-J.; Jin, H.-M.; Yao, T.; Zhu, Y.-C. The novel proangiogenic effect of hydrogen sulfide is dependent on Akt phosphorylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 76, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapetropoulos, A.; Pyriochou, A.; Altaany, Z.; Yang, G.; Marazioti, A.; Zhou, Z.; Jeschke, M.G.; Branski, L.K.; Herndon, D.N.; Wang, R.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous stimulator of angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21972–21977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Image J. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 21 January 2020).
- Weaver, J.D.; Headen, D.M.; Hunckler, M.D.; Coronel, M.; Stabler, C.L.; García, A.J. Design of a vascularized synthetic poly(ethylene glycol) macroencapsulation device for islet transplantation. Biomaterials 2018, 172, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prism—GraphPad. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/ (accessed on 14 February 2018).
- Kasoju, N.; Kubies, D.; Fábryová, E.; Kříž, J.; Kumorek, M.M.; Sticová, E.; Rypáček, F. In Vivo Vascularization of Anisotropic Channeled Porous Polylactide-Based Capsules for Islet Transplantation: The Effects of Scaffold Architecture and Implantation Site. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64 Suppl. 1, S75–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, J.; Shigehiro, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Satoh, A.; Mizutani, A.; Umemura, C.; Saito, S.; Kijihira, M.; Takayama, E.; Seno, A.; et al. Cytokine Expression and Macrophage Localization in Xenograft and Allograft Tumor Models Stimulated with Lipopolysaccharide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Qu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Konkel, J.E.; Shi, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide Promotes Tet1- and Tet2-Mediated Foxp3 Demethylation to Drive Regulatory T Cell Differentiation and Maintain Immune Homeostasis. Immunity 2015, 43, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.M.; Rodriguez, A.; Chang, D.T. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2007, 20, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Moochhala, S.M.; Bhatia, M. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates inflammatory response by activating the ERK pathway in polymicrobial sepsis. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4320–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, L.; Ang, A.D.; Zhang, H.; Moore, P.K.; Bhatia, M. Hydrogen sulfide induces the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in human monocyte cell line U937 via the ERK-NF-kappaB pathway. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufton, N.; Natividad, J.; Verdu, E.F.; Wallace, J.L. Hydrogen sulfide and resolution of acute inflammation: A comparative study utilizing a novel fluorescent probe. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, M.E.; E Segar, C.; Sridhar, S.; Botchwey, E.A. Monocytes and macrophages in tissue repair: Implications for immunoregenerative biomaterial design. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Liu, F.; Cui, S.; Jiang, N.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kou, X. Mechanical load-induced H2S production by periodontal ligament stem cells activates M1 macrophages to promote bone remodeling and tooth movement via STAT1. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarczyk, R.B.; Tuli, N.Y.; Hanly, E.K.; Ben Rahoma, G.; Maniyar, R.; Mittelman, A.; Geliebter, J.; Tiwari, R.K. Macrophage inflammatory factors promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 24272–24282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bir, S.C.; Kolluru, G.; McCarthy, P.; Shen, X.; Pardue, S.; Pattillo, C.B.; Kevil, C.G. Hydrogen Sulfide Stimulates Ischemic Vascular Remodeling Through Nitric Oxide Synthase and Nitrite Reduction Activity Regulating Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor–Dependent Angiogenesis. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushing, A.M.; Donnarumma, E.; Polhemus, D.J.; Au, K.R.; Victoria, S.E.; Schumacher, J.D.; Li, Z.; Jenkins, J.S.; Lefer, D.J.; Goodchild, T.T. Effects of a novel hydrogen sulfide prodrug in a porcine model of acute limb ischemia. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polhemus, D.J.; Kondo, K.; Bhushan, S.; Bir, S.C.; Kevil, C.G.; Murohara, T.; Lefer, D.J.; Calvert, J.W. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates cardiac dysfunction after heart failure via induction of angiogenesis. Circ. Hear. Fail. 2013, 6, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Mikami, Y.; Osumi, K.; Tsugane, M.; Oka, J.-I.; Kimura, H. Polysulfides are possible H 2 S-derived signaling molecules in rat brain. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Cheng, Z.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-Z. Hydrogen sulfide and translational medicine. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene | Assay ID |
|---|---|
| CD31 (PECAM1) | Mm01242576_m1 |
| VEGFa | Mm00437306_m1 |
| VE-Cadherin (CDH5) | Mm00486938_m1 |
| Angiopoietin 1 | Mm00456503_m1 |
| Angiopoietin 2 | Mm00545822_m1 |
| CD105 (Endoglin) | Mm00468252_m1 |
| GAPDH | Mm99999915_g1 |
| Gene | Control | Low H2S | High H2S |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFa | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.01 |
| VE-Cadherin (CDH5) | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 1.0 |
| Angiopoietin 1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.6 |
| Angiopoietin 2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.5 |
| Gene | Control | Low H2S | High H2S |
|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFa | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.04 |
| VE-Cadherin (CDH5) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Angiopoietin 1 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 |
| Angiopoietin 2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.03 | 1.0 ± 0.2 |
| CD105 (Endoglin) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smink, A.M.; Najdahmadi, A.; Alexander, M.; Li, S.; Rodriquez, S.; van Goor, H.; Hillebrands, J.-L.; Botvinick, E.; Lakey, J.R.T.; de Vos, P. The Effect of a Fast-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor on Vascularization of Subcutaneous Scaffolds in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050722
Smink AM, Najdahmadi A, Alexander M, Li S, Rodriquez S, van Goor H, Hillebrands J-L, Botvinick E, Lakey JRT, de Vos P. The Effect of a Fast-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor on Vascularization of Subcutaneous Scaffolds in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(5):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050722
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmink, Alexandra M., Avid Najdahmadi, Michael Alexander, Shiri Li, Samuel Rodriquez, Harry van Goor, Jan-Luuk Hillebrands, Elliot Botvinick, Jonathan R. T. Lakey, and Paul de Vos. 2020. "The Effect of a Fast-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor on Vascularization of Subcutaneous Scaffolds in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice" Biomolecules 10, no. 5: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050722
APA StyleSmink, A. M., Najdahmadi, A., Alexander, M., Li, S., Rodriquez, S., van Goor, H., Hillebrands, J.-L., Botvinick, E., Lakey, J. R. T., & de Vos, P. (2020). The Effect of a Fast-Releasing Hydrogen Sulfide Donor on Vascularization of Subcutaneous Scaffolds in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice. Biomolecules, 10(5), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10050722








