The Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α N-Terminal C2 Domain Binds and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Positive Curvature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Protein Purification
2.3. Cloning and Mutagenesis
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Confocal Microscopy
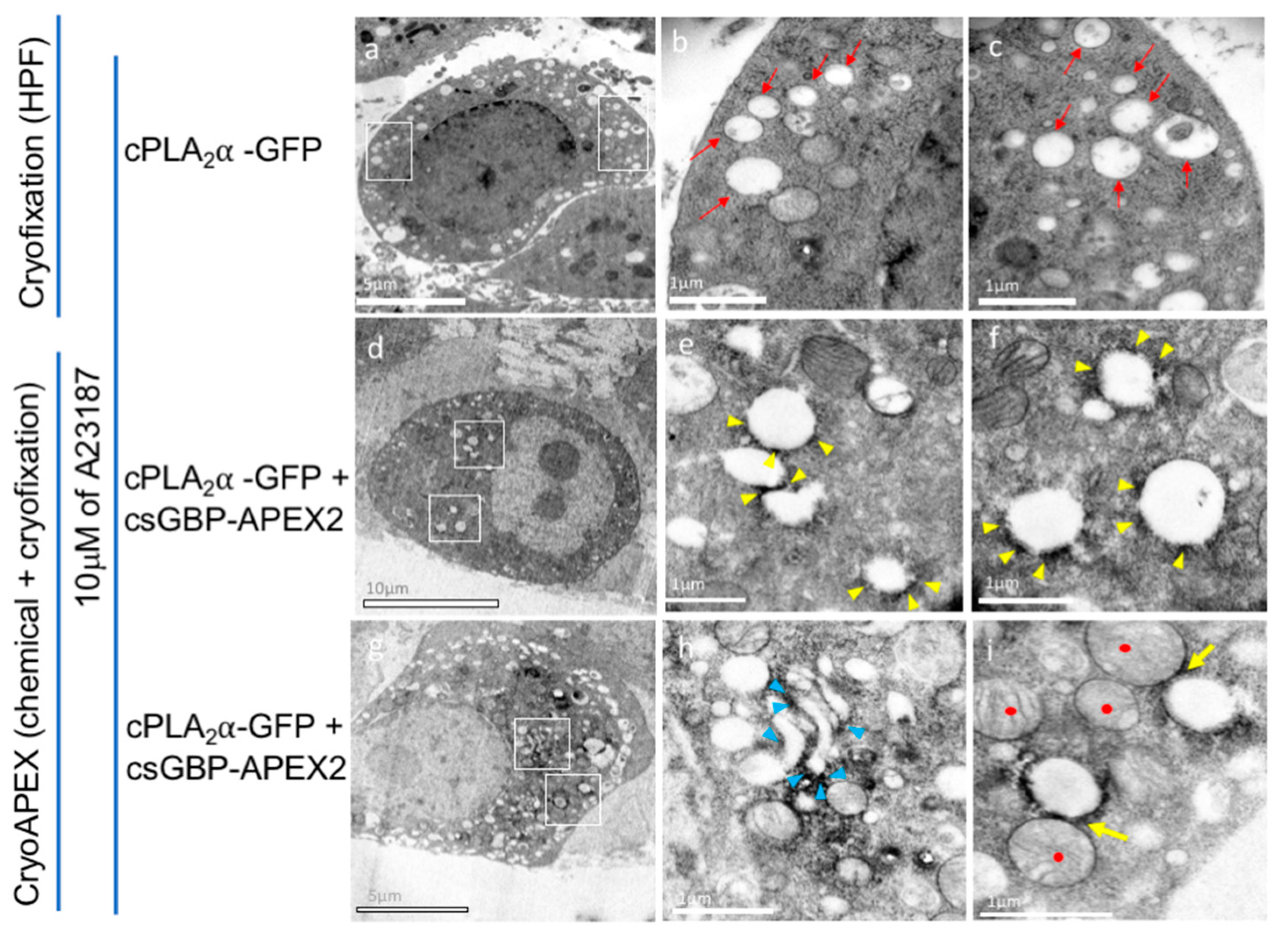
2.6. CryoAPEX Method for Localization of cPLA2α and Visualization of Morphological Changes of the Golgi Apparatus
2.7. Cross-Linking Assay
2.8. Giant Unilamellar Vesicle Experiments
2.9. Number and Brightness Analysis
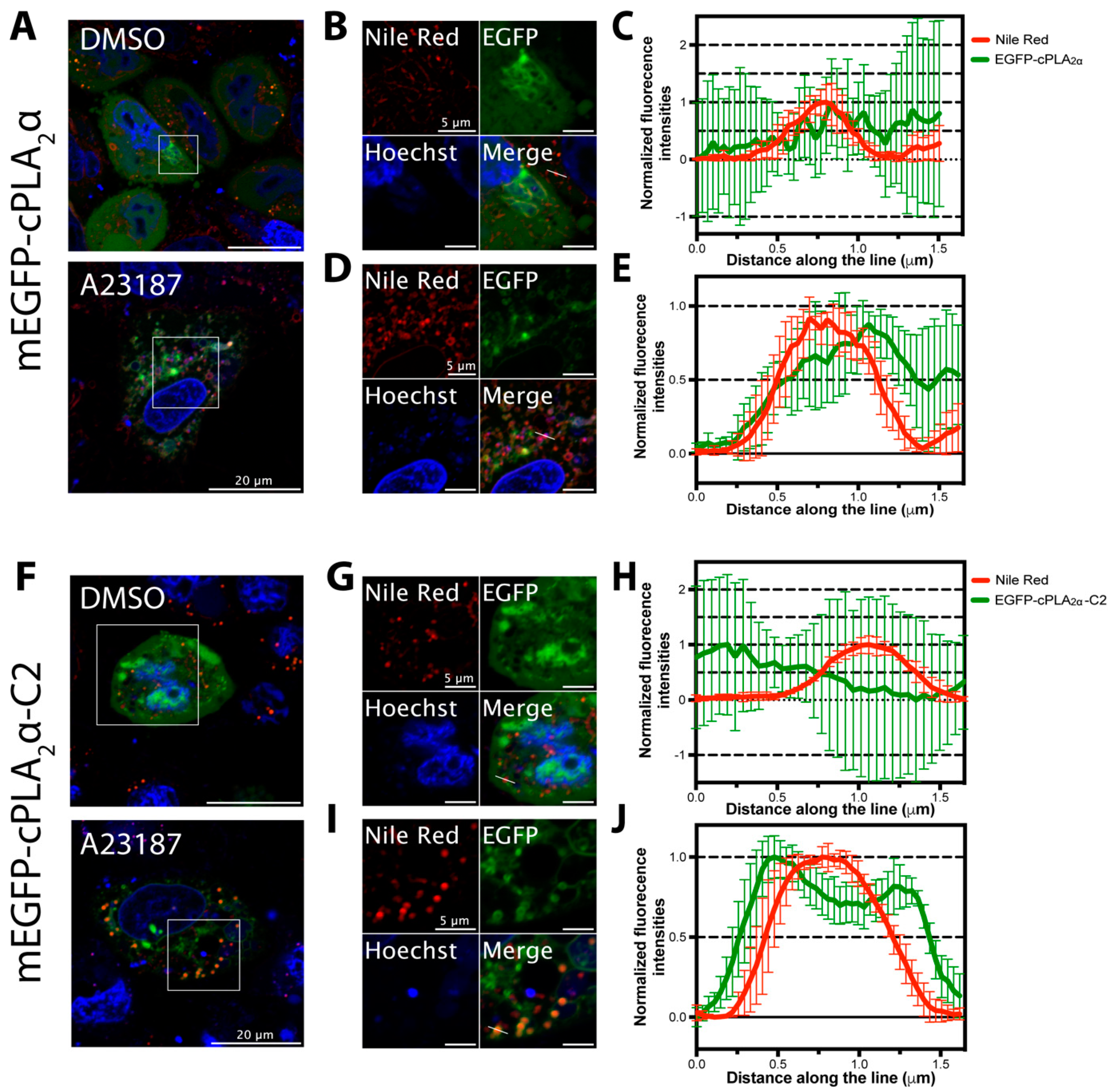
2.10. Lipid Droplet Staining and Imaging
3. Results
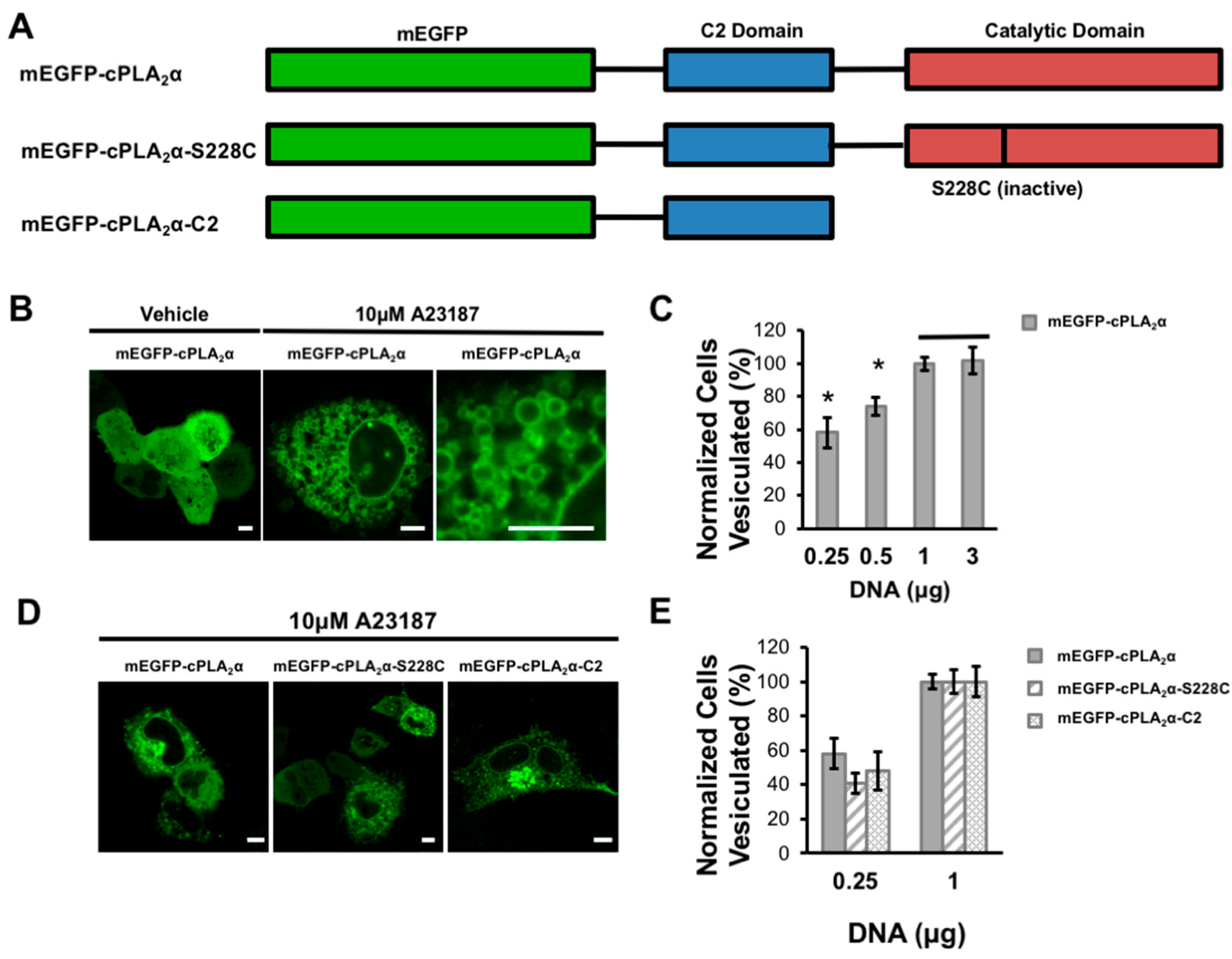
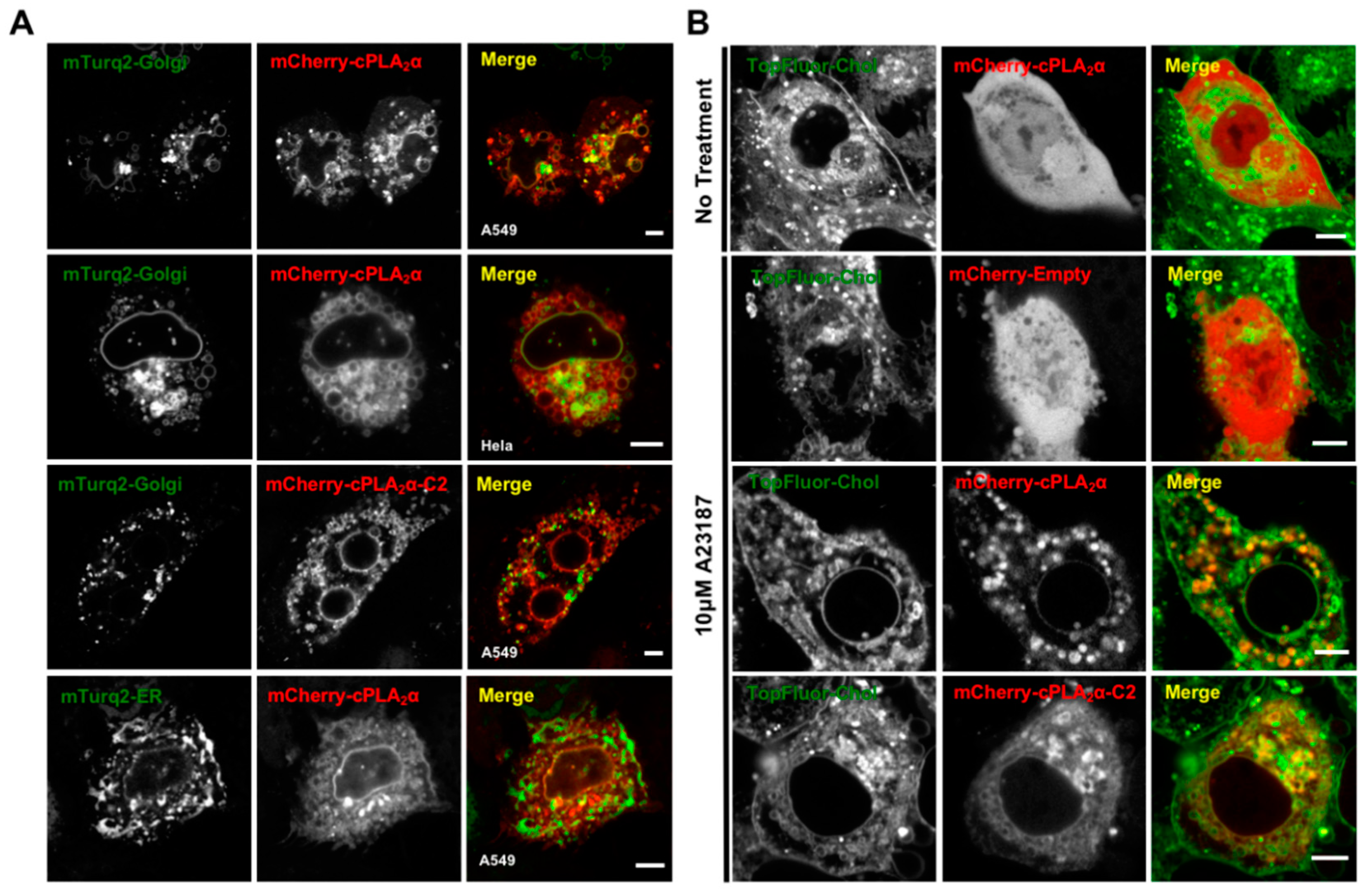
3.1. cPLA2α Induces Cellular Vesiculation via its C2 Domain
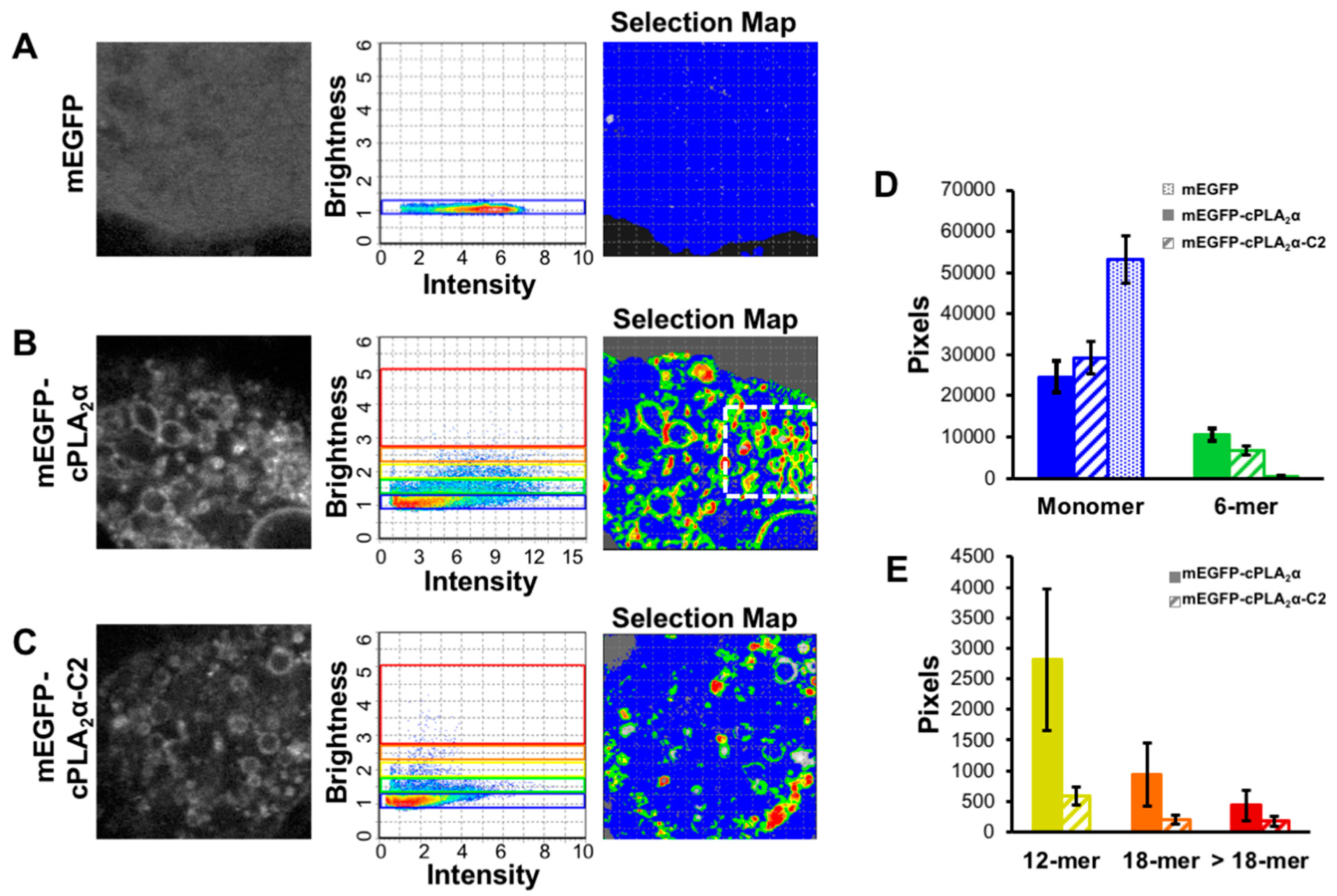
3.2. cPLA2α Oligomerizes on Membranes in A549 Cells
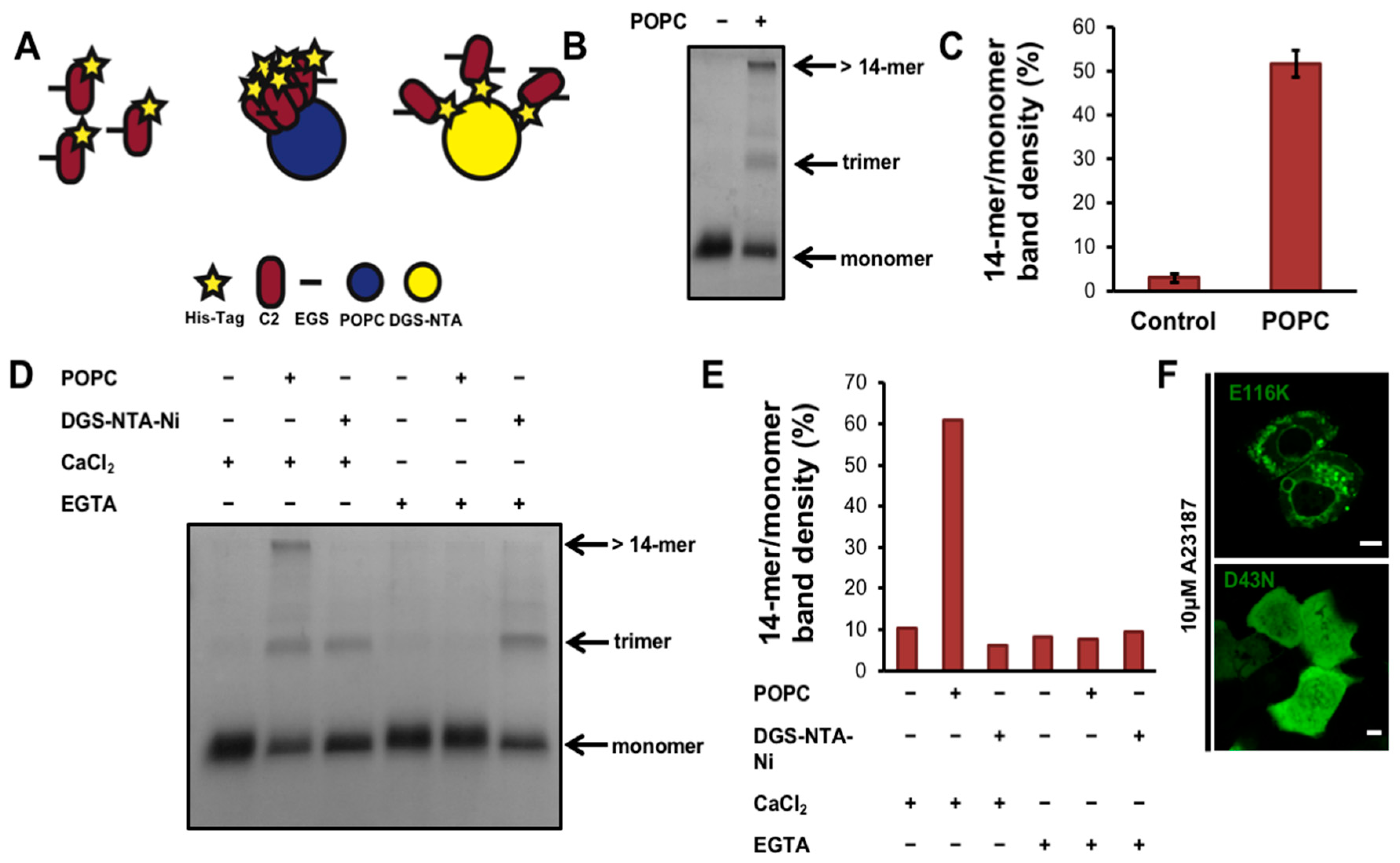
3.3. cPLA2α-C2 Oligomerizes on Lipid Vesicles
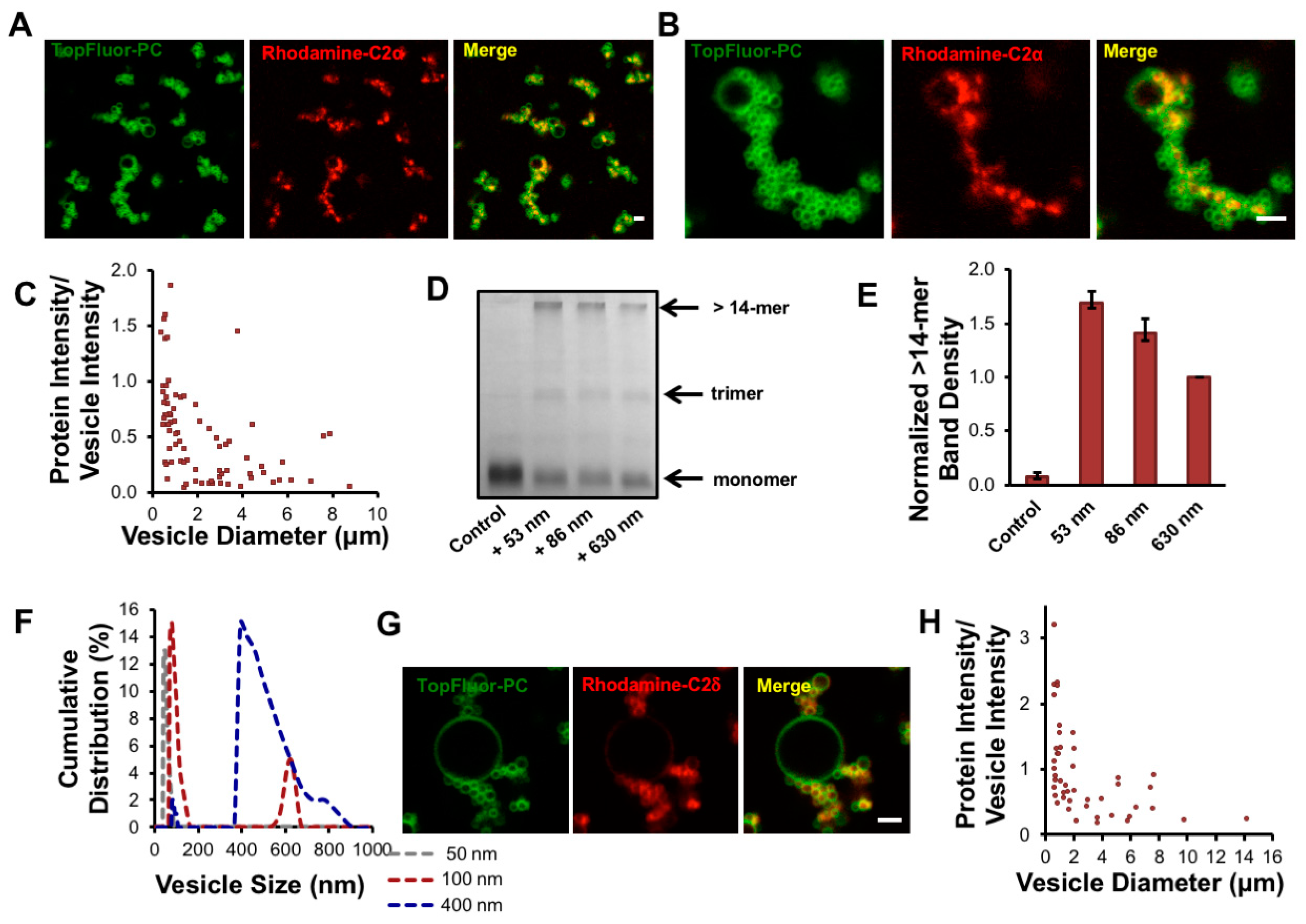
3.4. cPLA2 Selectively Binds to and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Increasing Positive Curvature
3.5. cPLA2α Induces Vesiculation from the Golgi in Cholesterol-Rich Vesicles
3.6. CryoAPEX Method for Transmission Electron Microscopy Visualization of cPLA2α Localization
3.7. CryoAPEX Method for Transmission Electron Microscopy Visualization of cPLA2α Localization
3.8. Lipid Droplet Imaging for cPLA2α and cPLA2α-C2 Localization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, C.C.; Channon, J.Y. Anionic phospholipids stimulate an arachidonoyl-hydrolyzing phospholipase A2 from macrophages and reduce the calcium requirement for activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1045, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Huang, Z.; Taheri, M.R.; O’Leary, E.; Li, E.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Sapirstein, A. Reduced fertility and postischaemic brain injury in mice deficient in cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nature 1997, 390, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uozumi, N.; Kume, K.; Nagase, T.; Nakatani, N.; Ishii, S.; Tashiro, F.; Komagata, Y.; Maki, K.; Ikuta, K.; Ouchi, Y.; et al. Role of cytosolic phospholipase A2 in allergic response and parturition. Nature 1997, 390, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.D.; Milona, N.; Knopf, J.L. Purification of a 110-kilodalton cytosolic phospholipase A2 from the human monocytic cell line U937. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7708–7712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Rafter, J.D.; Das, S.; Cho, W. The molecular basis of differential subcellular localization of C2 domains of protein kinase C-alpha and group IVa cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12452–12460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittova, L.; Sumandea, M.; Cho, W. A structure-function study of the C2 domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2. Identification of essential calcium ligands and hydrophobic membrane binding residues. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9665–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisic, O.; Paterson, H.F.; Mosedale, G.; Lara-Gonzalez, S.; Williams, R.L. Mapping the phospholipid-binding surface and translocation determinants of the C2 domain from cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 14979–14987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.A.; Wisner, M.A.; Malmberg, N.J.; Victor, K.G.; Fanucci, G.E.; Nalefski, E.A.; Falke, J.J.; Cafiso, D.S. Membrane orientation and position of the C2 domain from cPLA2 by site-directed spin labeling. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6282–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Subramanian, P.; Vora, M.; Cho, W.; Chalfant, C.E. Ceramide-1-phosphate binds group IVA cytosolic phospholipase a2 via a novel site in the C2 domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20467–20474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.E.; Bhardwaj, N.; Vora, M.; Chalfant, C.E.; Lu, H.; Stahelin, R.V. The molecular basis of ceramide-1-phosphate recognition by C2 domains. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamour, N.F.; Subramanian, P.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Stahelin, R.V.; Bonventre, J.V.; Chalfant, C.E. Ceramide 1-phosphate is required for the translocation of group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 and prostaglandin synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26897–26907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zizza, P.; Iurisci, C.; Bonazzi, M.; Cossart, P.; Leslie, C.C.; Corda, D.; Mariggio, S. Phospholipase A2IValpha regulates phagocytosis independent of its enzymatic activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16849–16859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, B.; Caplan, S.; Naslavsky, N. cPLA2alpha and EHD1 interact and regulate the vesiculation of cholesterol-rich, GPI-anchored, protein-containing endosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 1874–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Pietro, E.; Capestrano, M.; Polishchuk, E.V.; DiPentima, A.; Trucco, A.; Zizza, P.; Mariggio, S.; Pulvirenti, T.; Sallese, M.; Tete, S.; et al. Group IV phospholipase A(2)alpha controls the formation of inter-cisternal continuities involved in intra-Golgi transport. PLoS Biol. 2009, 7, e1000194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Valente, C.; Polishchuk, R.S.; Turacchio, G.; Layre, E.; Moody, D.B.; Leslie, C.C.; Gelb, M.H.; Brown, W.J.; Corda, D.; et al. COPI acts in both vesicular and tubular transport. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, Y.; Hu, J.; Kozlov, M.M.; Rapoport, T.A. Mechanisms shaping the membranes of cellular organelles. Ann. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009, 25, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucrot, E.; Pick, A.; Camdere, G.; Liska, N.; Evergren, E.; McMahon, H.T.; Kozlov, M.M. Membrane fission is promoted by insertion of amphipathic helices and is restricted by crescent BAR domains. Cell 2012, 149, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunovic, M.; Voth, G.A.; Callan-Jones, A.; Bassereau, P. When physics takes over: BAR proteins and membrane curvature. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M.G.; Mills, I.G.; Peter, B.J.; Vallis, Y.; Praefcke, G.J.; Evans, P.R.; McMahon, H.T. Curvature of clathrin-coated pits driven by epsin. Nature 2002, 419, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Koshiba, S.; Kigawa, T.; Kikuchi, A.; Yokoyama, S.; Takenawa, T. Role of the ENTH domain in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding and endocytosis. Science 2001, 291, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahelin, R.V.; Long, F.; Peter, B.J.; Murray, D.; de Camilli, P.; McMahon, H.T.; Cho, W. Contrasting membrane interaction mechanisms of AP180 N-terminal homology (ANTH) and epsin N-terminal homology (ENTH) domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28993–28999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Tong, J.; Lee, P.J.; Albanese, A.; Bhardwaj, N.; Kallberg, M.; Digman, M.A.; Lu, H.; Gratton, E.; Shin, Y.K.; et al. Molecular basis of the potent membrane-remodeling activity of the epsin 1 N-terminal homology domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.L.; Jao, C.C.; Lyman, E.; Gallop, J.L.; Peter, B.J.; McMahon, H.T.; Langen, R.; Voth, G.A. Membrane binding and self association of the epsin N-terminal homology domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 423, 800–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.; Johnson, C.P.; Yao, J.; Dunning, F.M.; Chapman, E.R. Synaptotagmin-mediated bending of the target membrane is a critical step in Ca(2+)-regulated fusion. Cell 2009, 138, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, K.E.; Ropa, J.P.; Adu-Gyamfi, E.; Stahelin, R.V. C2 domain membrane penetration by group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A(2) induces membrane curvature changes. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sot, B.; Behrmann, E.; Raunser, S.; Wittinghofer, A. Ras GTPase activating (RasGAP) activity of the dual specificity GAP protein Rasal requires colocalization and C2 domain binding to lipid membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Rathore, S.S.; Davis, E.M.; Ouyang, Y.; Shen, J. Doc2b promotes GLUT4 exocytosis by activating the SNARE-mediated fusion reaction in a calcium-and membrane bending-dependent manner. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedhart, J.; von Stetten, D.; Noirclerc-Savoye, M.; Lelimousin, M.; Joosen, L.; Hink, M.A.; van Weeren, L.; Gadella, T.W., Jr.; Royant, A. Structure-guided evolution of cyan fluorescent proteins towards a quantum yield of 93%. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maxfield, F.R.; Wustner, D. Analysis of cholesterol trafficking with fluorescent probes. Methods Cell Biol. 2012, 108, 367–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariotti, N.; Hall, T.E.; Rae, J.; Ferguson, C.; McMahon, K.A.; Martel, N.; Webb, R.E.; Webb, R.I.; Teasdale, R.D.; Parton, R.G. Molecular detection of GFP-labeled proteins for rapid screening by electron microscopy in cells and organisms. Dev. Cell 2015, 35, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, R.; Poderycki, M.; Mattoo, S. CryoAPEX—An electron tomography tool for subcellular localization of membrane proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2019, 132, jcs222315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihelc, E.M.; Angel, S.; Stahelin, R.V.; Mattoo, S. The CryoAPEX method for electron miroscopy analysis of membrane protein localization with ultrastructurally-preserved cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 156, e60677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, M.J.; Sasaki, J.M.; Digman, M.A.; Gratton, E. Raster image correlation spectroscopy in live cells. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1761–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, D.H.; Shin, Y.K.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.B.; Seo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S. Membrane topology of helix 0 of the Epsin N-terminal homology domain. Mol. Cells 2006, 21, 428–435. [Google Scholar]
- Dannhauser, P.N.; Ungewickell, E.J. Reconstitution of clathrin-coated bud and vesicle formation with minimal components. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowiak, J.C.; Schmid, E.M.; Ryan, C.J.; Ann, H.S.; Sasaki, D.Y.; Sherman, M.B.; Geissler, P.L.; Fletcher, D.A.; Hayden, C.C. Membrane bending by protein-protein crowding. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu-Gyamfi, A.; Digman, M.A.; Gratton, E.; Stahelin, R.V. Investigation of Ebola VP40 assembly and oligomerization in live cells using number and brightness analysis. Biophys. J. 2012, 102, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmins, J.; Schoehn, G.; Kohlhaas, C.; Klenk, H.D.; Ruigrok, R.W.; Weissenhorn, W. Oligomerization and polymerization of the filovirus matrix protein VP40. Virology 2003, 312, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.S.; Schmitz, K.R.; Bessman, N.J.; Setty, T.G.; Ferguson, K.M.; Burd, C.G. PtdIns4P recognition by Vps74/GOLPH3 links PtdIns 4-kinase signaling to retrograde Golgi trafficking. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtta-Vuori, M.; Uronen, R.L.; Repakova, J.; Salonen, E.; Vattulainen, I.; Panula, P.; Li, Z.; Bittman, R.; Ikonen, E. BODIPY-cholesterol: A new tool to visualize sterol trafficking in living cells and organisms. Traffic 2008, 9, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariotti, N.; Rae, J.; Giles, N.; Martel, N.; Sierecki, E.; Gambin, Y.; Hall, T.E.; Parton, R.G. Ultrastructural localisation of protein interactions using conditionally stable nanobodies. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e20005473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martell, J.D.; Deernick, T.J.; Lam, S.S.; Ellisman, M.H.; Ting, A.Y. Electron microscopy using the genetically encoded APEX2 tag in cultured mammalian cells. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 1792–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.H.; Gerber, S.H.; Murray, D.; Leslie, C.C. The calcium binding loops of the cytosolic phospholipase A2 C2 domain specify targeting to Golgi and ER in live cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jollivet, F.; Raposo, G.; Dimitrov, A.; Sougrat, R.; Goud, B.; Perez, F. Analysis of de novo Golgi complex formation after enzyme-based inactivation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 4637–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wooten, R.E.; Willingham, M.C.; Daniel, L.W.; Leslie, C.C.; Rogers, L.; Sergeant, S.; O’Flaherty, J.T. Novel translocation responses of cytosolic phospholipase A2a fluorescent proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2008, 1783, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, L.S.; Piva, B.; Gentile, L.B.; Mesquita-Santos, F.P.; D’Avila, H.; Maya-Monteiro, C.M.; Bozza, P.T.; Bandeira-Melo, C.; Diaz, B.L. Cytosolic phospholipase A2-driven PGE2 synthesis within unsaturated fatty acids-induced lipid bodies of epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2009, 1791, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijas, C.; Perez-Chacon, G.; Astudillo, A.M.; Rubio, J.M.; Gil-de-Gomez, L.; Balboa, M.A.; Balsinde, J. Simultaneous activation of p38 and JNK by arachidonic acid stimulates the cytosolic phospholipase A2-dependent synthesis of lipid droplets in human monocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2343–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijman, E.E.; Chupin, V.; Fuller, N.L.; Kozlov, M.M.; de Kruijff, B.; Burger, K.N.; Rand, P.R. Spontaneous curvature of phosphatidic acid and lysophosphatidic acid. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchlis, V.D.; Chen, Y.; McCammon, J.A.; Dennis, E.A. Membrane allostery and unique hydrophobic sites promote enzyme substrate specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3285–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Gao, Y.G.; Stephenson, D.J.; Vu, N.T.; Malinina, L.; Simanshu, D.K.; Chalfant, C.E.; Patel, D.J.; Brown, R.E. Structural basis of phosphatidylcholine recognition by the C2-domain of cytosolic phospholipase A2a. Elife 2019, 8, e44760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessen, A.; Tang, J.; Schmidt, H.; Stahl, M.; Clark, J.D.; Seehra, J.; Somers, W.S. Crystal structure of the human cytosolic phospholipase A2 reveals novel a novel topology and catalytic mechanism. Cell 1999, 97, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mim, C.; Cui, H.; Gawronski-Salerno, J.A.; Frost, A.; Lyman, E.; Voth, G.A.; Unger, V.M. Structural basis of membrane bending by the N-BAR protein endophilin. Cell 2012, 149, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capestrano, M.; Mariggio, S.; Perinetti, G.; Egorova, A.V.; Iacobacci, S.; Santoro, M.; di Pentima, A.; Iurisci, C.; Egorov, M.V.; di Tullio, G.; et al. Cytosolic phospholipase A2{varepsilon} drives recycling in the clathrin-independent endocytic route. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ward, K.E.; Sengupta, R.; Ropa, J.P.; Amiar, S.; Stahelin, R.V. The Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α N-Terminal C2 Domain Binds and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Positive Curvature. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040647
Ward KE, Sengupta R, Ropa JP, Amiar S, Stahelin RV. The Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α N-Terminal C2 Domain Binds and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Positive Curvature. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040647
Chicago/Turabian StyleWard, Katherine E., Ranjan Sengupta, James P. Ropa, Souad Amiar, and Robert V. Stahelin. 2020. "The Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α N-Terminal C2 Domain Binds and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Positive Curvature" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040647
APA StyleWard, K. E., Sengupta, R., Ropa, J. P., Amiar, S., & Stahelin, R. V. (2020). The Cytosolic Phospholipase A2α N-Terminal C2 Domain Binds and Oligomerizes on Membranes with Positive Curvature. Biomolecules, 10(4), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040647






