Regulation of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in IRF3-Mediated Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Compound Preparation
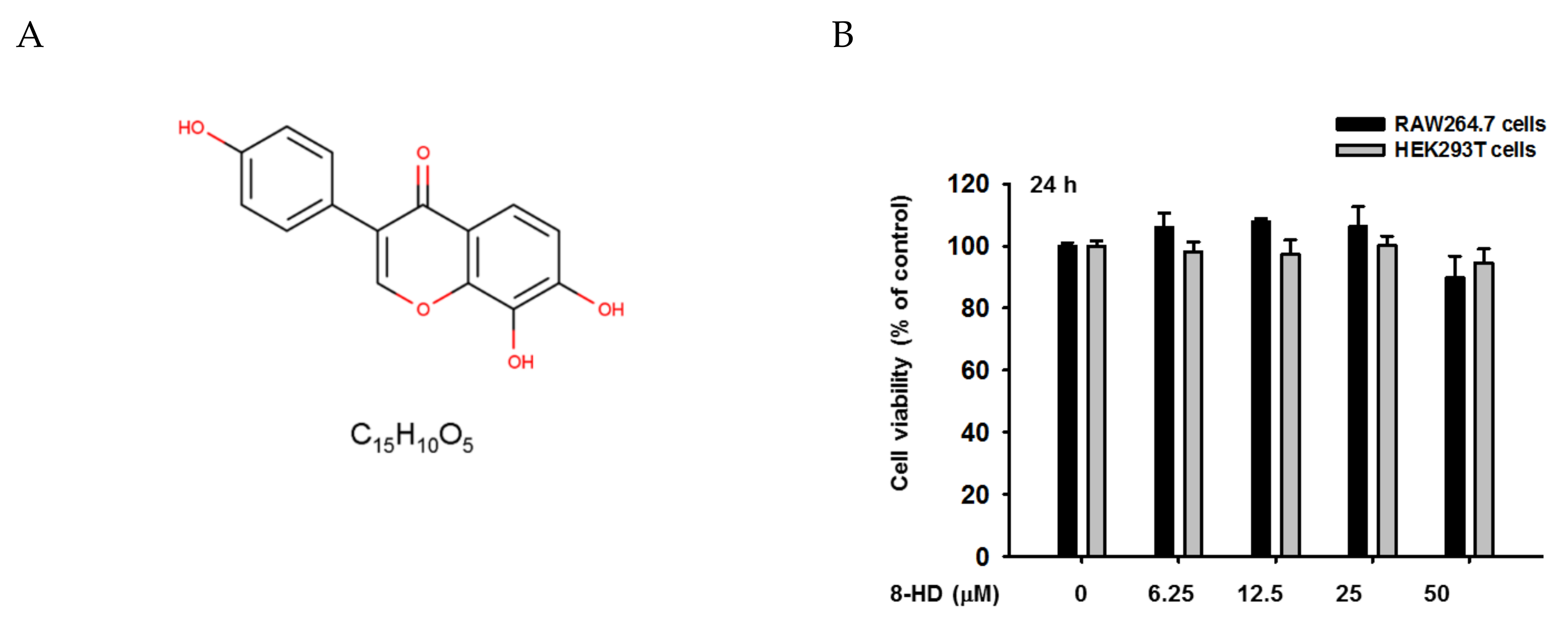
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. mRNA Expression Analysis by Semiquantitative Reverse Transcriptase (RT)-Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.5. siRNA Transfection
2.6. Preparation of Whole-Cell Lysates, Nuclear Fraction, and Immunoblotting
2.7. Immunoprecipitation-Kinase Assay
2.8. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
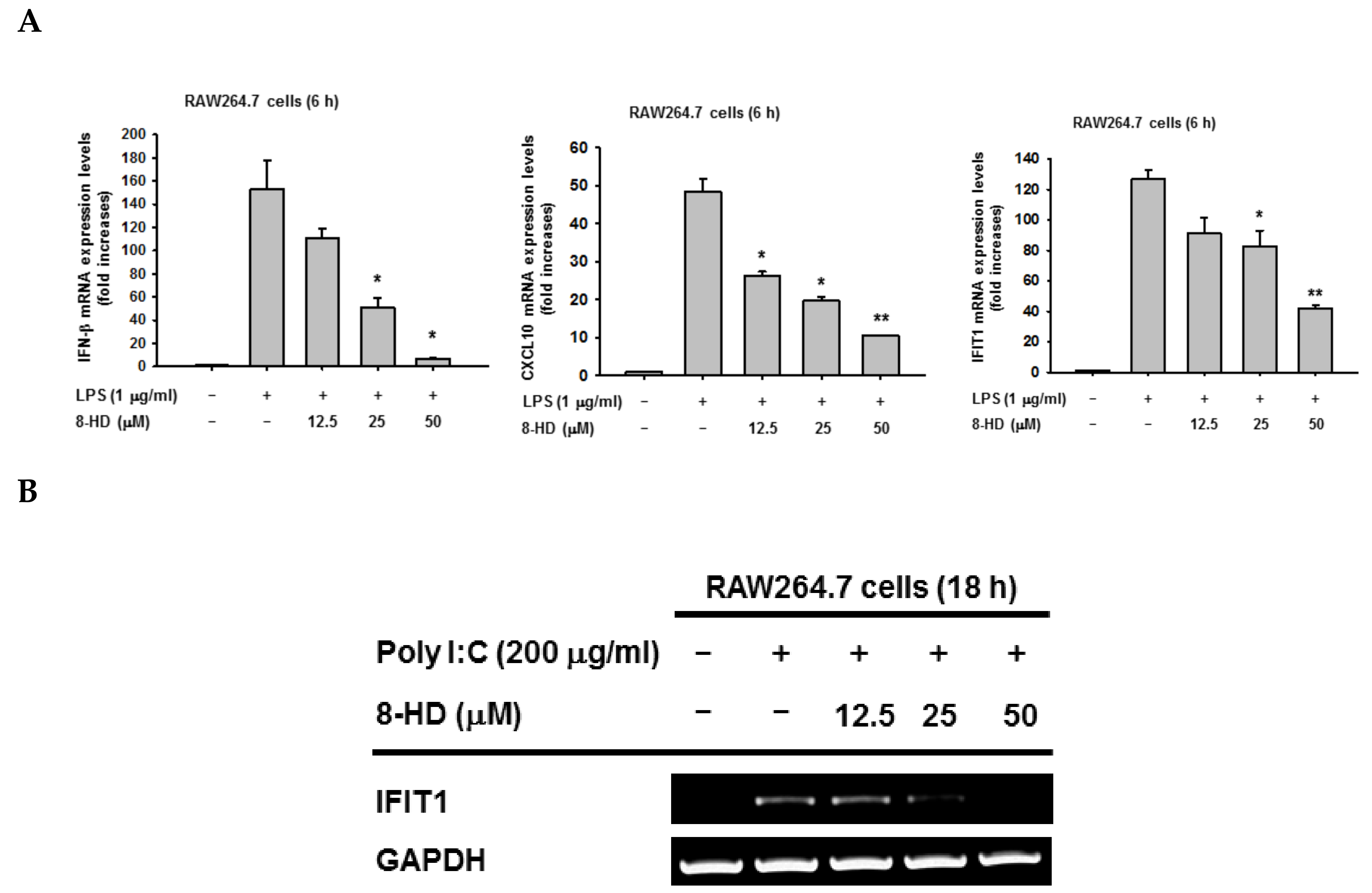
3.1. 8-HD Downregulates IRF-3-Dependent Genes in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
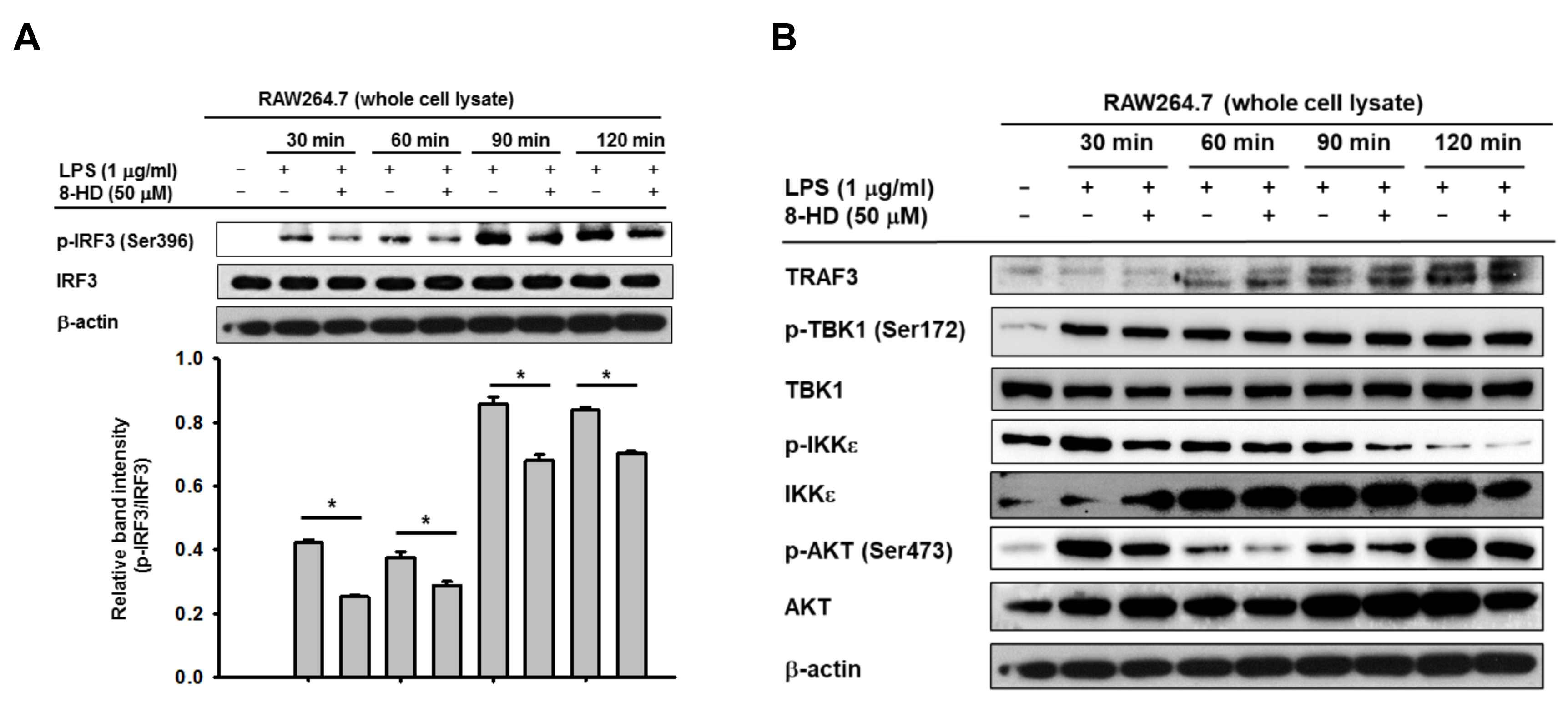
3.2. 8-HD Inhibits Phosphorylation IRF-3 and Nuclear Translocation of IRF-3
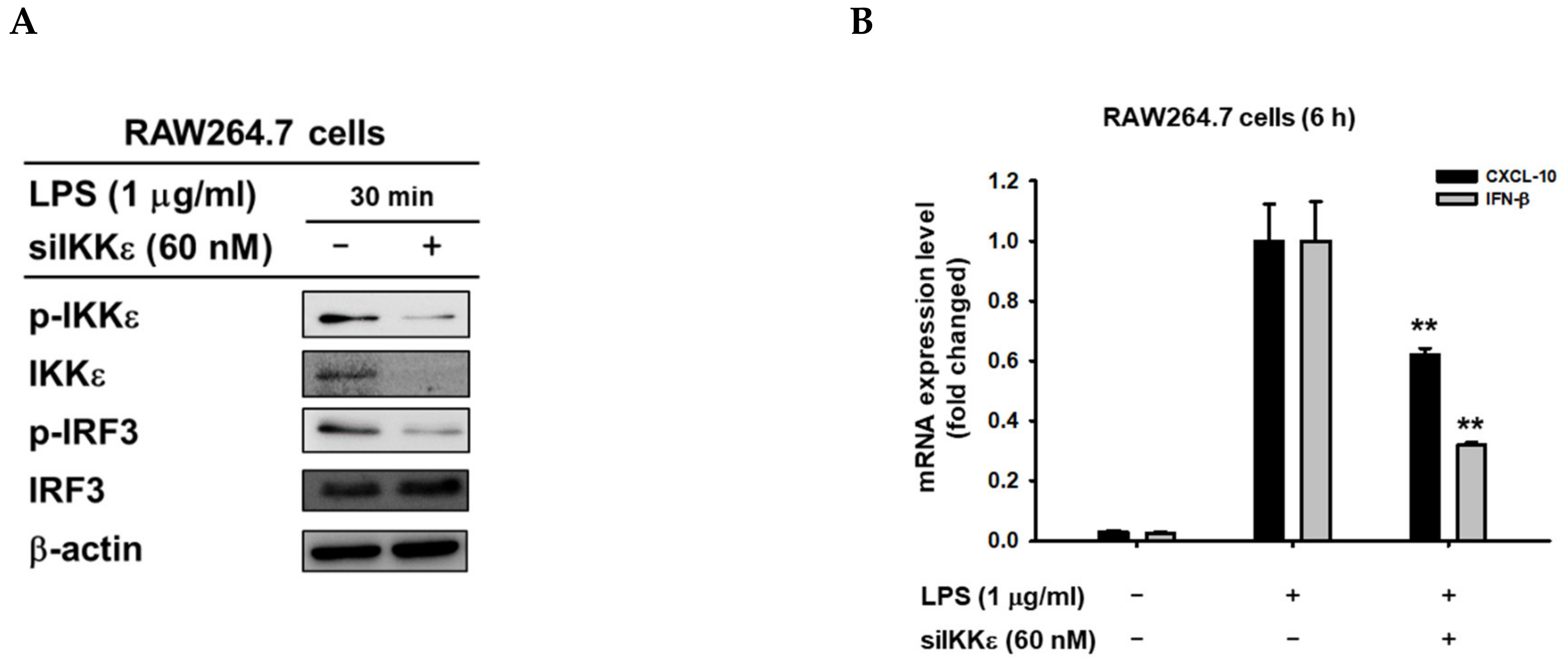
3.3. 8-HD Alters Upstream Signaling Enzymes of the IRF-3 Signaling Pathway
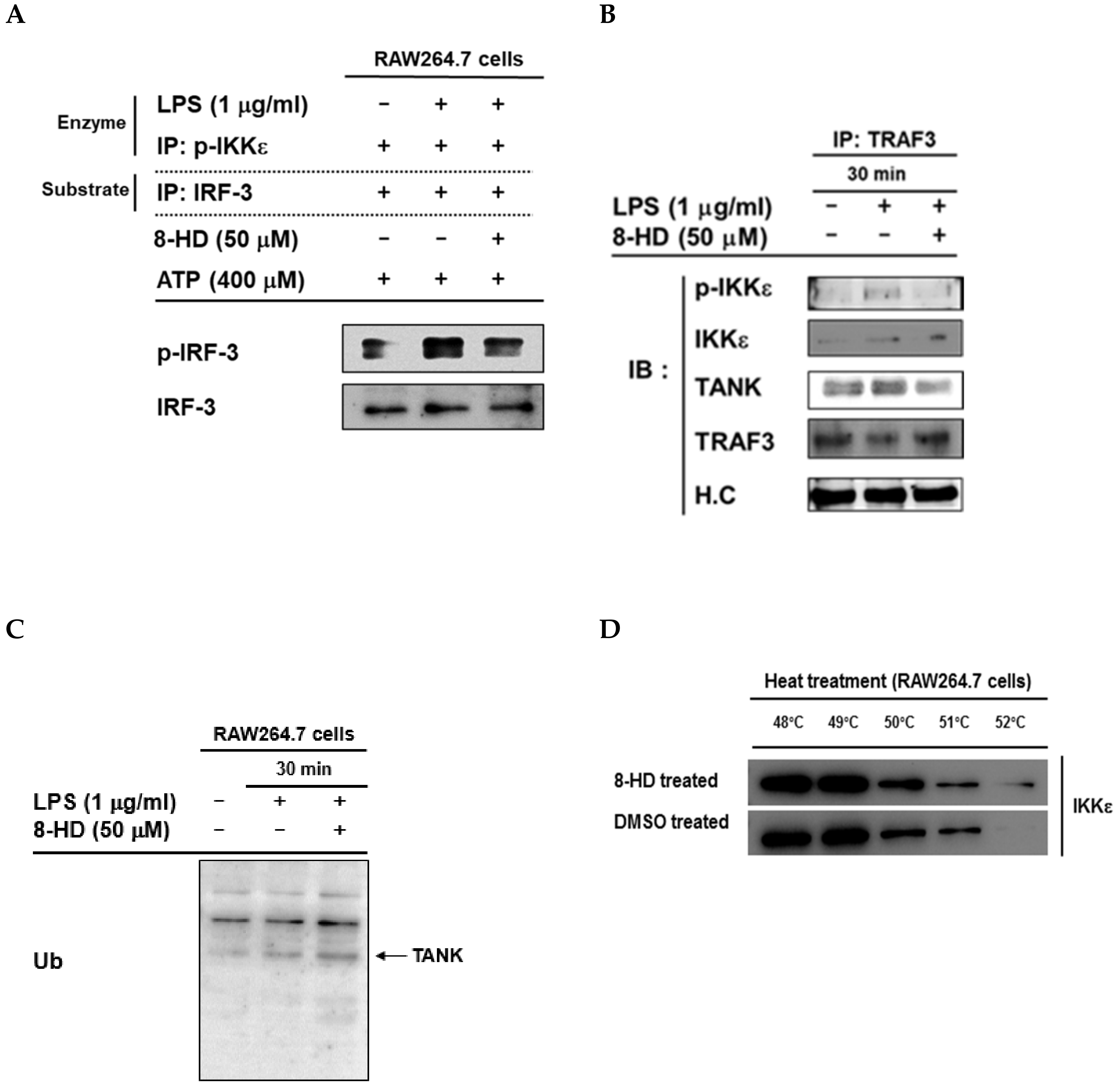
3.4. 8-HD Inhibits the Kinase Activity of IKKε to Phosphorylates IRF-3
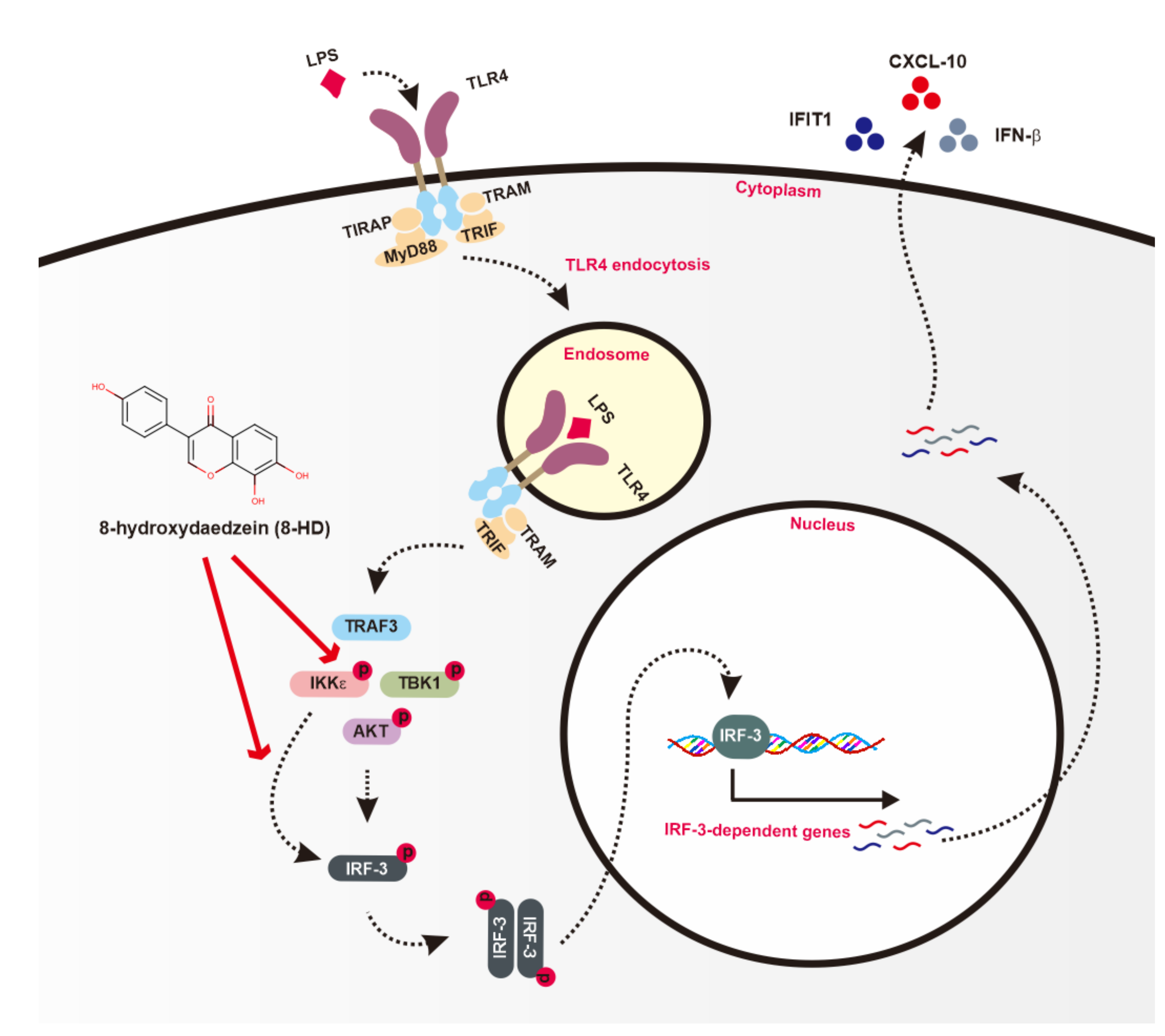
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-HD | 8-hydroxydaidzein |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| AP-1 | activator protein-1 |
| IRF-3 | interferon regulatory factor -3 |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| TRAF3 | TNF receptor associated factor 3 |
| IFN-β | Interferon-β |
| CXCL10 | (C-X-C motif) chemokine 10 |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PRRs | pattern recognition receptors |
| TLRs | Toll-like receptors |
| RLRs | RIG-I-like receptors |
| cGAS | cyclic GMP-AMP synthase |
| STING | stimulators of interferon genes |
| CCL5 | (C-C motif) ligand 5 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| TAK1 | Transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| IKKε | inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit epsilon |
| TBK1 | TANK binding kinase 1 |
| ATP | Adenosine 5′-triphosphate |
| TRIF | TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β |
| TRAM | TRIF–related adaptor molecule |
| MyD88 | Myeloid differentiation primary response 88 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase |
References
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, N.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: A review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Dixit, V.M. Signaling in innate immunity and inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a006049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.-N.; Jiang, D.-S.; Li, H. Interferon regulatory factors: At the crossroads of immunity, metabolism, and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Chiba, S.; Hangai, S.; Kometani, K.; Inoue, A.; Kimura, Y.; Abe, T.; Kiyonari, H.; Nishio, J.; Taguchi-Atarashi, N.; et al. Revisiting the role of IRF3 in inflammation and immunity by conditional and specifically targeted gene ablation in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5253–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, J.; Peng, D.; Ma, F.; Cheng, G.; Qin, F.X.-F. Complex Regulation Pattern of IRF3 Activation Revealed by a Novel Dimerization Reporter System. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4322–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarassishin, L.; Suh, H.-S.; Lee, S.C. Interferon regulatory factor 3 plays an anti-inflammatory role in microglia by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Neuroinflammation 2011, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahuja, A.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Cho, J.Y. Functional role of ginseng-derived compounds in cancer. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, P. The inflammation theory of disease. The growing realization that chronic inflammation is crucial in many diseases opens new avenues for treatment. Embo Rep. 2012, 13, 968–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.J.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, D.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Thymoquinone: An IRAK1 inhibitor with in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Bi, X.; Yu, B.; Chen, D. Isoflavones: Anti-Inflammatory Benefit and Possible Caveats. Nutrients 2016, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-S. Isolation, Bioactivity, and Production of ortho-Hydroxydaidzein and ortho-Hydroxygenistein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, M.-H.; Kim, B.-N.; Kim, K.-R.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, C.-H.; Oh, D.-K. Production of 8-Hydroxydaidzein from Soybean Extract by Aspergillus oryzae KACC 40247. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.-S.; Ding, H.-Y.; Yen, J.-H.; Chen, S.-F.; Lee, K.-H.; Wu, M.-J. Anti-inflammatory Activity of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in LPS-Stimulated BV2 Microglial Cells via Activation of Nrf2-Antioxidant and Attenuation of Akt/NF-κB-Inflammatory Signaling Pathways, as Well As Inhibition of COX-2 Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5790–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kang, Y.-G.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Cho, J. The Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of 8-Hydroxydaidzein (8-HD) in Activated Macrophage-Like RAW264.7 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, A.F.; Plummer, E.M.; Vizcarra, E.A.; Sheets, N.; Joo, Y.; Tang, W.; Day, J.; Greenbaum, J.; Glass, C.K.; Diamond, M.S.; et al. An IRF-3-, IRF-5-, and IRF-7-Independent Pathway of Dengue Viral Resistance Utilizes IRF-1 to Stimulate Type I and II Interferon Responses. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1600–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, W.S.; Yu, T.; Yi, Y.-S.; Park, J.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.H.; Oh, J.S.; Yoon, K.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Novel anti-inflammatory function of NSC95397 by the suppression of multiple kinases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 88, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, H.G.; Han, S.Y.; Jeong, D.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, J.-I.; Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.-S.; Cho, J.Y. Hydroquinone suppresses IFN-β expression by targeting AKT/IRF3 pathway. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 21, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; McWhirter, S.M.; Faia, K.L.; Rowe, D.C.; Latz, E.; Golenbock, D.T.; Coyle, A.J.; Liao, S.M.; Maniatis, T. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Yi, Y.S.; Son, Y.J.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Nam, G.; Hossain, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.; Cho, J.Y. BIOGF1K, a compound K-rich fraction of ginseng, plays an antiinflammatory role by targeting an activator protein-1 signaling pathway in RAW264.7 macrophage-like cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.; Son, Y.-J.; Cho, J. Thymoquinone Suppresses IRF-3-Mediated Expression of Type I Interferons via Suppression of TBK1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, E.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, D.B.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, S.S.; Cho, J.Y. AKT-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of Panax ginseng calyx ethanolic extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.G.; Son, Y.-J.; Yoo, B.C.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. Syk Plays a Critical Role in the Expression and Activation of IRAK1 in LPS-Treated Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, S.E.; Lee, Y.G.; Kim, B.H.; Shen, T.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.C.; Rhee, M.H.; Cho, J.Y. Surfactin blocks NO production in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 18, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.O.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, H.G.; Jeong, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.; Seo, D.B.; et al. Antimelanogenesis and skin-protective activities of Panax ginseng calyx ethanol extract. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Syk and Src-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of aripiprazole, an atypical antipsychotic. Biochem. Pharm. 2018, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, B.; Lu, M.-K.; You, M.; Condorelli, G.; Wang, C.-Y.; Guan, K.-L.; Dixon, J.E. IκB kinase ε and TANK-binding kinase 1 activate AKT by direct phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6474–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, S.M.; Park, Z.-Y.; Rani, S.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S.; Lee, J.Y. Akt Contributes to Activation of the TRIF-Dependent Signaling Pathways of TLRs by Interacting with TANK-Binding Kinase 1. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, A.; Bürckstümmer, T.; Dixit, E.; Scheicher, R.; Górna, M.; Karayel, E.; Sugar, C.; Stukalov, A.; Berg, T.; Kralovics, R.; et al. Functional Dissection of the TBK1 Molecular Network. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Molina, D.; Jafari, R.; Ignatushchenko, M.; Seki, T.; Larsson, E.A.; Dan, C.; Sreekumar, L.; Cao, Y.; Nordlund, P. Monitoring drug target engagement in cells and tissues using the cellular thermal shift assay. Science 2013, 341, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rowe, D.C.; Barnes, B.J.; Caffrey, D.R.; Visintin, A.; Latz, E.; Monks, B.; Pitha, P.M.; Golenbock, D.T. LPS-TLR4 signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-kappaB involves the toll adapters TRAM and TRIF. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häcker, H.; Tseng, P.-H.; Karin, M. Expanding TRAF function: TRAF3 as a tri-faced immune regulator. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.-Y.; Lee, K.-G.; Chin, C.-S.; Ng, S.-K.; Pereira, N.A.; Xu, S.; Lam, K.-P. DOK3 Is Required for IFN-β Production by Enabling TRAF3/TBK1 Complex Formation and IRF3 Activation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W. Negative regulation of TBK1-mediated antiviral immunity. Febs Lett. 2013, 587, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, I.M. Chapter 13 - Activation of the Innate Immune System: The Toll-Like Receptor-4 and Signaling through Ubiquitinylation. In Signal Transduction (Third Edition); Kramer, I.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 741–775. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, J.; Zhang, Q.; Baldwin, A. Roles for the IKK-Related Kinases TBK1 and IKKε in Cancer. Cells 2018, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrilenas, K.K.; Ramlall, V.; Kurland, J.; Leung, B.; Harbaugh, A.G.; Siggers, T. DNA-binding landscape of IRF3, IRF5 and IRF7 dimers: Implications for dimer-specific gene regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, H.; Xu, T.; Kong, Y.; Huang, M.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Xia, H.; Wu, Y.; et al. HECTD3 mediates TRAF3 polyubiquitination and type I interferon induction during bacterial infection. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 4148–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PCR Type | Genes Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semiquantitative RT-PCR | IFN-β | Forward | TCCAAGAAAGGACGAACATT |
| Reverse | TGAGGACATCTCCCACGTCA | ||
| IFIT1 | Forward | ATGCAGTCGTAGCCTATCGC | |
| Reverse | CCTGCAAGGCCCTGTTTAGA | ||
| GAPDH | Forward | ACCACAGTCCATGCCATCAC | |
| Reverse | CCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAG | ||
| qPCR | IFN-β | Forward | AAGAGTTACACTGCCTTTGCTATC |
| Reverse | CACTGTCTGCTGGTGGAGTTCATC | ||
| IKKε | Forward | CCACTTGGAGTGCAGGAAGA | |
| Reverse | CCGGAT TTCTTGTTTCGGGC | ||
| CXCL10 | Forward | ATCATCCCTGCGAGCCTATCC | |
| Reverse | CGGATTCAGACATCTCTGCTCATC | ||
| IFIT1 | Forward | ATGCAGTCGTAGCCTATCGC | |
| Reverse | CCTGCAAGGCCCTGTTTAGA | ||
| GAPDH | Forward | CAATGAATACGGCTACAGCA | |
| Reverse | AGGGAGATGCTCAGTGTTGG | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, N.; Kang, Y.-G.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, W.-S.; Jeong, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Cho, J.Y. Regulation of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in IRF3-Mediated Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020238
Aziz N, Kang Y-G, Kim Y-J, Park W-S, Jeong D, Lee J, Kim D, Cho JY. Regulation of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in IRF3-Mediated Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020238
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Nur, Young-Gyu Kang, Yong-Jin Kim, Won-Seok Park, Deok Jeong, Jongsung Lee, Donghyun Kim, and Jae Youl Cho. 2020. "Regulation of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in IRF3-Mediated Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020238
APA StyleAziz, N., Kang, Y.-G., Kim, Y.-J., Park, W.-S., Jeong, D., Lee, J., Kim, D., & Cho, J. Y. (2020). Regulation of 8-Hydroxydaidzein in IRF3-Mediated Gene Expression in LPS-Stimulated Murine Macrophages. Biomolecules, 10(2), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020238







