Structural Changes of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Induced by Rutin Arachidonate: A Molecular Dynamics Study
Abstract
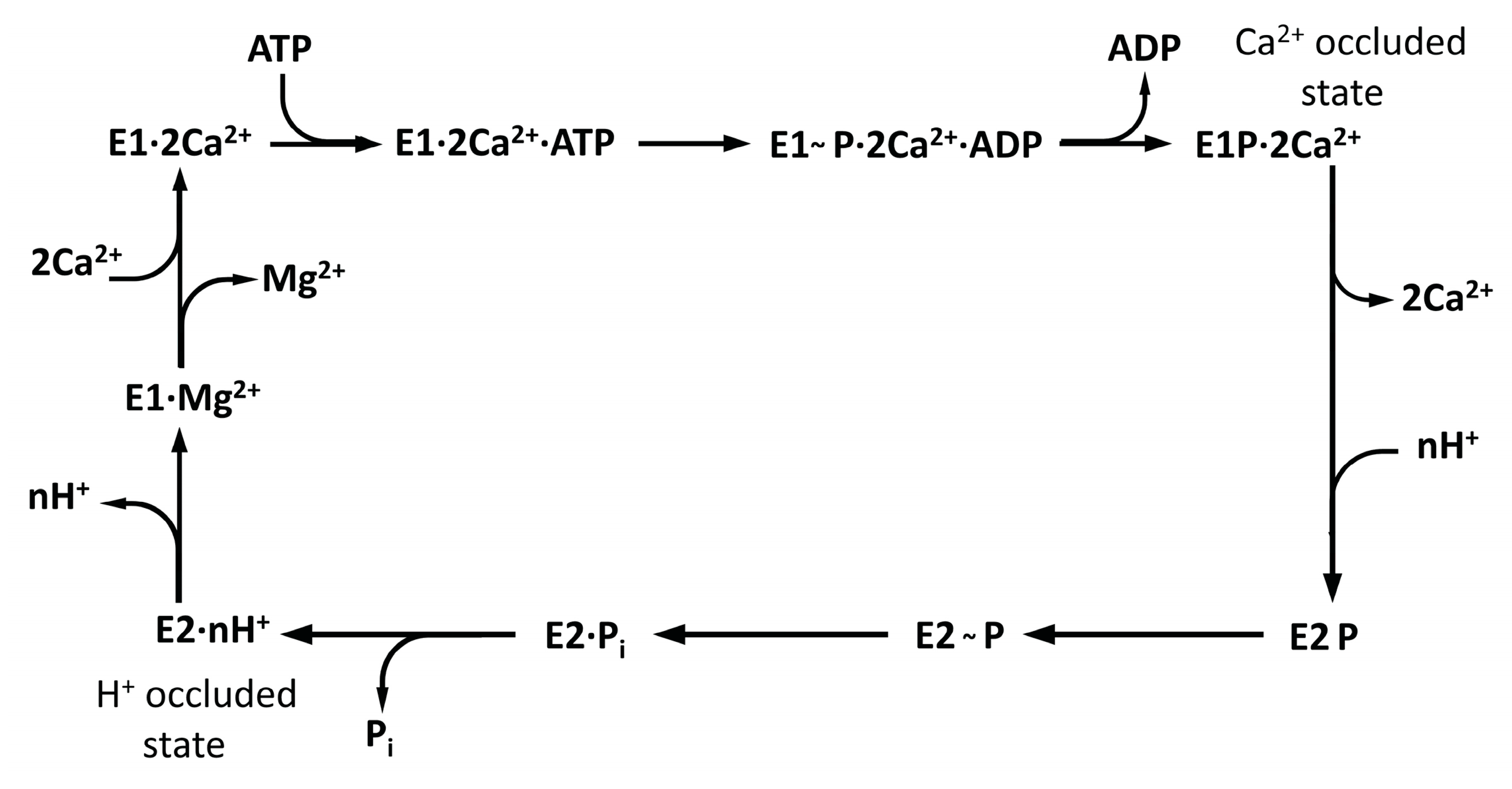
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bilayer Setup
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Protocol
2.3. Parameterization of Rutin Arachidonate
3. Results and Discussion
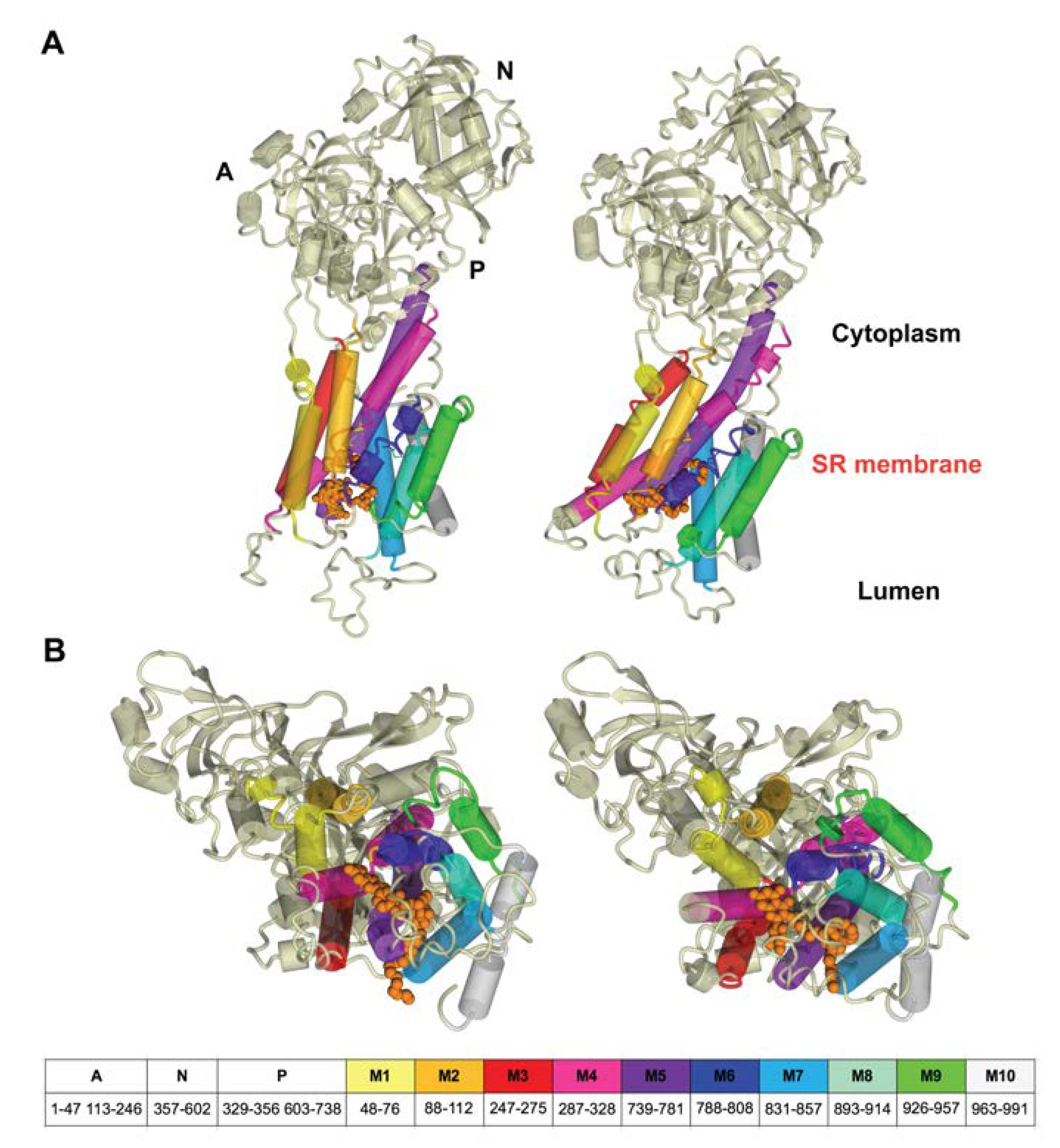
3.1. Starting Structure of SERCA1a-RA Complex
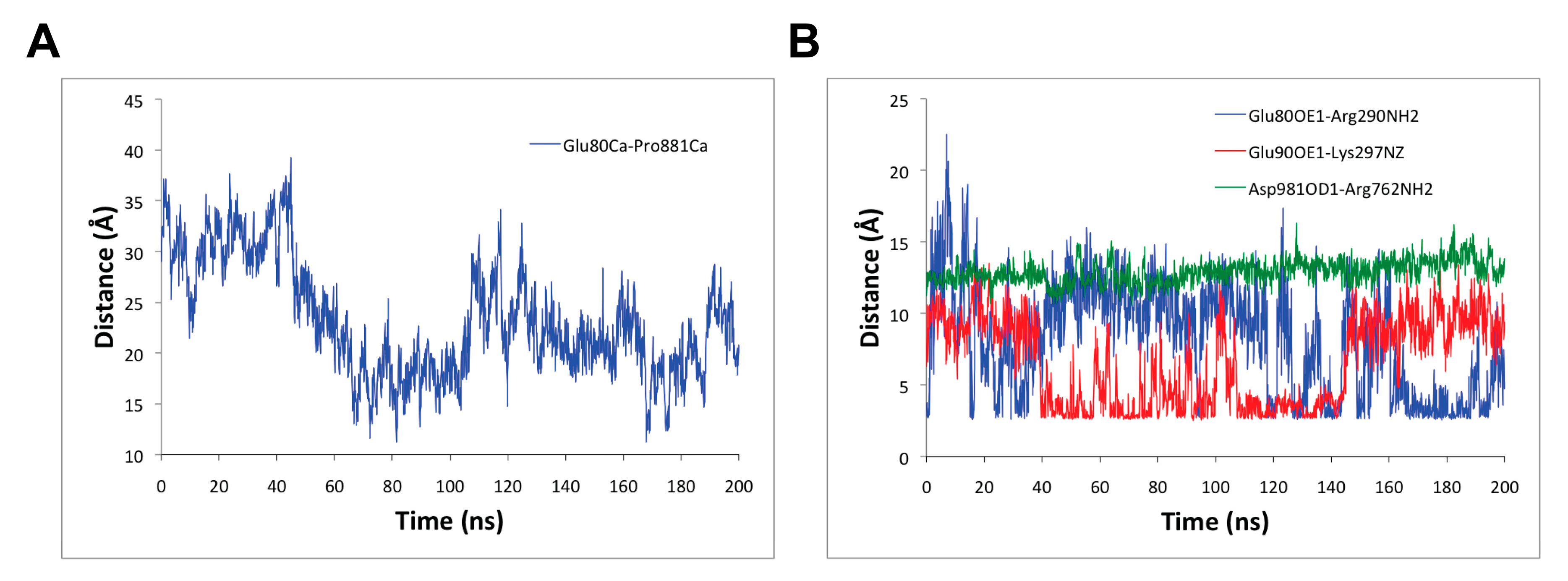
3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of SERCA1a-RA-POPC System
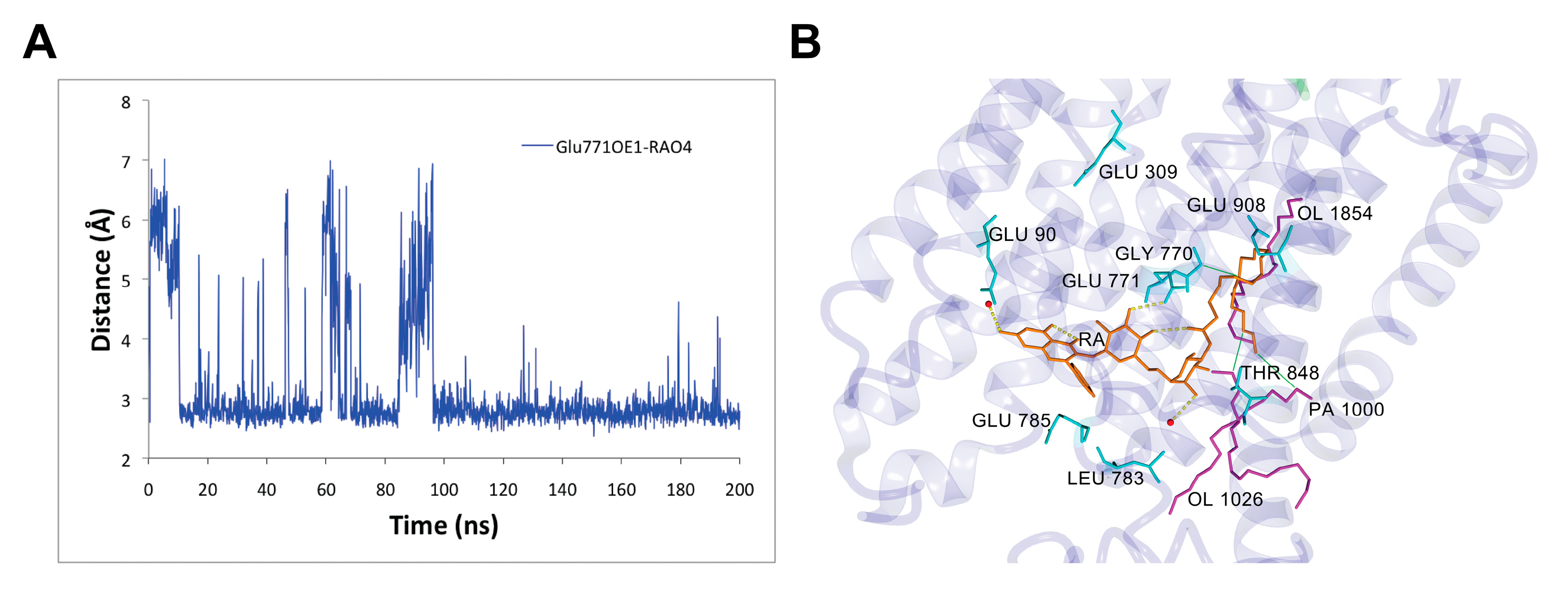
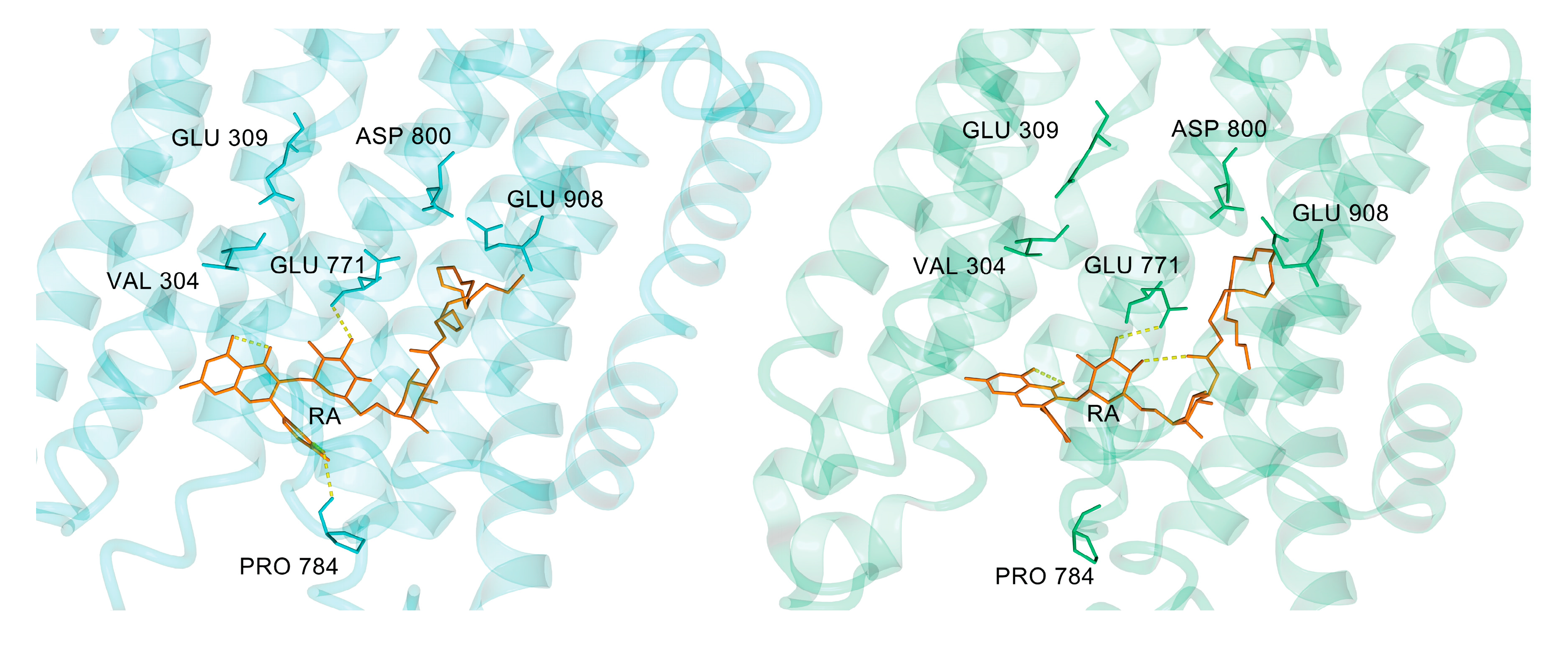
3.3. Rutin Arachidonate Binding Site
3.4. Changes in SERCA1a
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berridge, M.J.; Lipp, P.; Bootman, M.D. The versatility and universality of calcium signaling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, L.; Oakes, S.A.; Opferman, J.T.; Cheng, E.H.; Sorcinelli, M.D.; Pozzan, T.; Korsmeyer, S.J. BAX and BAK regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: A control point for apoptosis. Science 2003, 300, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapham, D.E. Calcium Signaling. Cell 2007, 131, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Regulation of Insulin Synthesis and Secretion and Pancreatic Beta-Cell Dysfunction in Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 25–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y. Modification of sarco-endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+)-ATPase in the failing cardiomyocyte. Clin. Calcium 2013, 23, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Brini, M.; Calì, T.; Ottolini, D.; Carafoli, E. The plasma membrane calcium pump in health and disease. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 5385–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezprozvanny, I.B. Calcium signaling and neurodegeneration. Acta Naturae 2010, 2, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marambaud, P.; Dreses-Werringloer, U.; Vingtdeux, V. Calcium signaling in neurodegeneration. Mol Neurodegener. 2009, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Yonekura, S.I.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Mitsuhashi, S.; Nishino, I.; Toyoshima, C.; Ishiura, S. Functional analysis of SERCA1b, a highly expressed SERCA1 variant in myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle. Biochim. Bioph. Acta 2015, 1852, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, A.K.; Kwan, C.Y.; Samson, S.E. Effects of peroxynitrite on sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump isoforms SERCA2b and SERCA3a. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2003, 285, C1537–C1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, M.; Kalyanasundaram, A. SERCA pump isoforms: Their role in calcium transport and disease. Muscle Nerve 2007, 35, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, C.; Iwasawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Hirata, A.; Tsueda, J.; Inesi, G. Crystal structures of the calcium pump and sarcolipin in the Mg2+-bound E1 state. Nature 2013, 495, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, C.; Flemming, C. New crystal structures of PII-type ATPases: Excitement continues. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.H.; Asahi, M.; Tupling, A.R. The regulation of SERCA-type pumps by phospholamban and sarcolipin. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 986, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardo, V.A.; Bombardier, E.; Vigna, C.; Devji, T.; Bloemberg, D.; Gamu, D.; Gramolini, A.O.; Quadrilatero, J.; Tupling, A.R. Co-expression of SERCA isoforms, phospholamban and sarcolipin in human skeletal muscle fibers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelangeli, F.; East, J.M. A diversity of SERCA Ca2+ pump inhibitors. Bioch. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elam, C.; Lape, M.; Deye, J.; Zultowsky, J.; Stanton, D.T.; Paula, S. Discovery of novel SERCA inhibitors by virtual screening of a large compound library. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thastrup, O.; Cullen, P.J.; Drøbak, B.K.; Hanley, M.R.; Dawson, A.P. Thapsigargin, a tumor promoter, discharges intracellular Ca2+ stores by specific inhibition of the endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 2466–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytton, J.; Westlin, M.; Hanley, M.R. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17067–17071. [Google Scholar]
- Goeger, D.E.; Riley, R.T.; Dorner, J.W.; Cole, R.J. Cyclopiazonic acid inhibition of the Ca2+-transport ATPase in rat skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilmen, J.G.; Khan, S.Z.; Javed, M.H.; Michelangeli, F. Inhibition of the SERCA Ca2+ pumps by curcumin: Curcumin putatively stabilizes the interaction between the nucleotide-binding and phosphorylation domains in the absence of ATP. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 6318–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunbayo, O.A.; Harris, R.M.; Waring, R.H.; Kirk, C.J.; Michelangeli, F. Inhibition of the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase by flavonoids: A quantitative structure–activity relationship study. IUBMB Life 2008, 60, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolommei, G.; Tadini-Buoninsegni, F.; Hua, S.; Moncelli, M.R.; Inesi, G.; Guidelli, R. Clotrimazole inhibits the Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) by interfering with Ca2+ binding and favoring the E2 conformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 9547–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunbayo, O.A.; Michelangeli, F. The widely utilized brominated flame retardant tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) is a potent inhibitor of the SERCA Ca2+ pump. Biochem. J. 2007, 408, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mousa, F.; Michelangeli, F. The sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) is the likely molecular target for the acute toxicity of the brominated flame retardant hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD). Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 207, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, L.L.; Michelangeli, F. The effects of the phenylalanine 256 to valine mutation on the sensitivity of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase (SERCA) Ca2+ pump isoforms 1, 2, and 3 to thapsigargin and other inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6970–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.F.; Longland, C.L.; Michelangeli, F. The effects of phenothiazines and other calmodulin antagonists on the sarcoplasmic and endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pumps. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskupicova, J.; Danihelova, M.; Ondrejovic, M.; Liptaj, T.; Sturdik, E. Lipophilic rutin derivatives for antioxidant protection of oil-based foods. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskupicova, J.; Danihelova, M.; Majekova, M.; Liptaj, T.; Sturdik, E. Polyphenol fatty acid esters as serine protease inhibitors: A quantum-chemical QSAR analysis. J. Enzyme Inhibit. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, L.; Humeau, C.; Falcimaigne, A.; Engasser, J.M.; Ghoul, M. Enzymatic acylation of flavonoids. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskupicova, J.; Ondrejovic, M.; Sturdik, E. The potential and practical applications of acylated flavonoids. Pharmazie 2009, 64, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viskupicova, J.; Maliar, T. Rutin fatty acid esters: From synthesis to biological health effects and application. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2017, 56, 232–243. [Google Scholar]
- Viskupicova, J.; Majekova, M.; Horakova, L. Inhibition of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA1) by rutin derivatives. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2015, 36, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonntag, Y.; Musgaard, M.; Olesen, C.; Schiøtt, B.; Møller, J.V.; Nissen, P.; Thøgersen, L. Mutual adaptation of a membrane protein and its lipid bilayer during conformational changes. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M. Probing the effects of nonannular lipid binding on the stability of the calcium pump SERCA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-de Gortari, E.; Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M. Structural basis for relief of phospholamban-mediated inhibition of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase at saturating Ca2+ conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 12405–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaves, J.P.; Primeau, J.O.; Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M.; Lemieux, M.J.; Young, H.S. The Phospholamban Pentamer Alters Function of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Pump SERCA. Biophys. J. 2019, 116, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autry, J.M.; Thomas, D.D.; Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M. Sarcolipin Promotes Uncoupling of the SERCA Ca2+ Pump by Inducing a Structural Rearrangement in the Energy-Transduction Domain. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6083–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, H.; Das, A.; Nakamoto, R.; Roux, B. Proton Countertransport and Coupled Gating in the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Calcium Pump. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 5050–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M.; Ramirez-Salinas, G.L. Microsecond Molecular Simulations Reveal a Transient Proton Pathway in the Calcium Pump. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7055–7058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Salinas, G.L.; Espinoza-Fonseca, L.M. Atomistic Characterization of the First Step of Calcium Pump Activation Associated with Proton Countertransport. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5235–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, E.; Vriend, G. YASARA View—Molecular graphics for all devices—From smartphones to workstations. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2981–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Lim, J.B.; Klauda, J.B.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI Membrane Builder for Mixed Bilayers and Its Application to Yeast Membranes. Biophys. J. 2009, 97, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, D.; Babin, V.; Berryman, J.; Betz, R.; Cai, Q.; Cerutti, D.; Cheatham, T., III; Darden, T.; Duke, R.; Gohlke, H.; et al. Amber 14; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.A.; Cheatham, T.E., 3rd; Darden, T.; Gohlke, H.; Luo, R.; Merz, K.M., Jr.; Onufriev, A.; Simmerling, C.; Wang, B.; Woods, R.J. The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1668–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, C.J.; Madej, B.D.; Skjevik, Å.A.; Betz, R.M.; Teigen, K.; Gould, I.R.; Walker, R.C. Lipid14: The Amber Lipid Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, R.; Brooks, B.; Szabo, A. An analysis of the accuracy of Langevin and molecular dynamics algorithms. Mol. Phys. 1988, 65, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical-Integration of Cartesian Equations of Motion of a System with Constraints—Molecular-Dynamics of N-Alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezei, M. Simulaid: A simulation facilitator and analysis program. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2658–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A. Antechamber: An accessory software package for molecular mechanical calculations. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 222, U403. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and Testing of a General Amber Force Field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bublitz, M.; Nass, K.; Drachmann, N.D.; Markvardsen, A.J.; Gutmann, M.J.; Barends, T.R.M.; Mattle, D.; Shoeman, R.L.; Doak, R.B.; Boutet, S.; et al. Structural studies of P-type ATPase–ligand complexes using an X-ray free-electron laser. IUCrJ 2015, 2, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchetto, R.; Bertipaglia, I.; Giannetti, S.; Cendron, L.; Mascarello, F.; Damiani, E.; Carafoli, E.; Zanotti, G. Crystal structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) from bovine muscle. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 178, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Mahaney, J.E.; Uljana Mayer, M.; Bigelow, D.J.; Squier, T.C. Concerted but Noncooperative Activation of Nucleotide and Actuator Domains of the Ca-ATPase Upon Calcium Binding. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 12448–12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, J.D.; Andersen, J.P. Glutamate 90 at the Luminal Ion Gate of Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Is Critical for Ca2+ Binding on Both Sides of the Membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 20780–20792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, C.R.; Olsson, M.H.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. Improved Treatment of Ligands and Coupling Effects in Empirical Calculation and Rationalization of pKa Values. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2284–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.H.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: Consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical pKa predictions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoshima, C.; Nomura, H. Structural changes in the calcium pump accompanying the dissociation of calcium. Nature 2002, 418, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
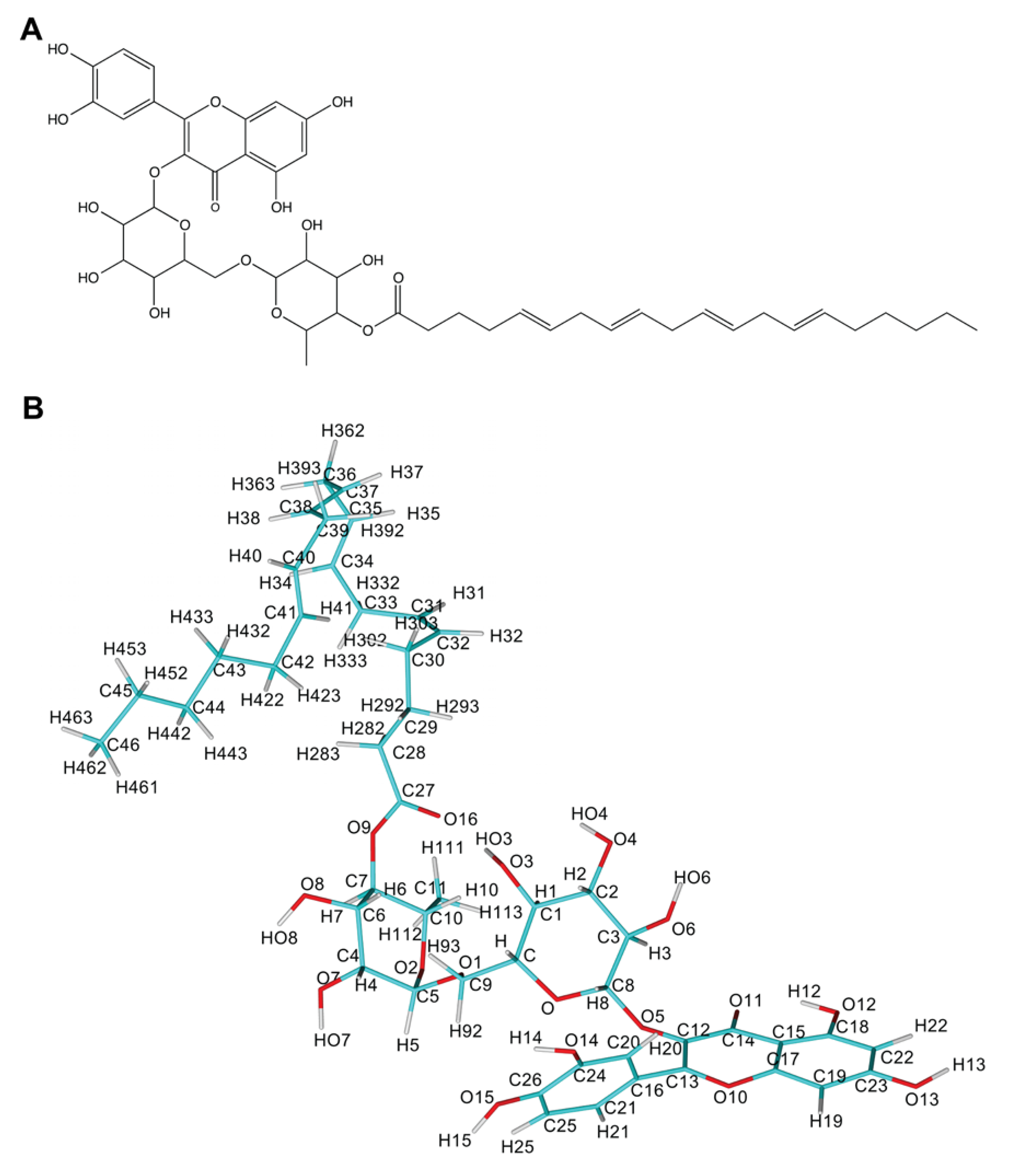
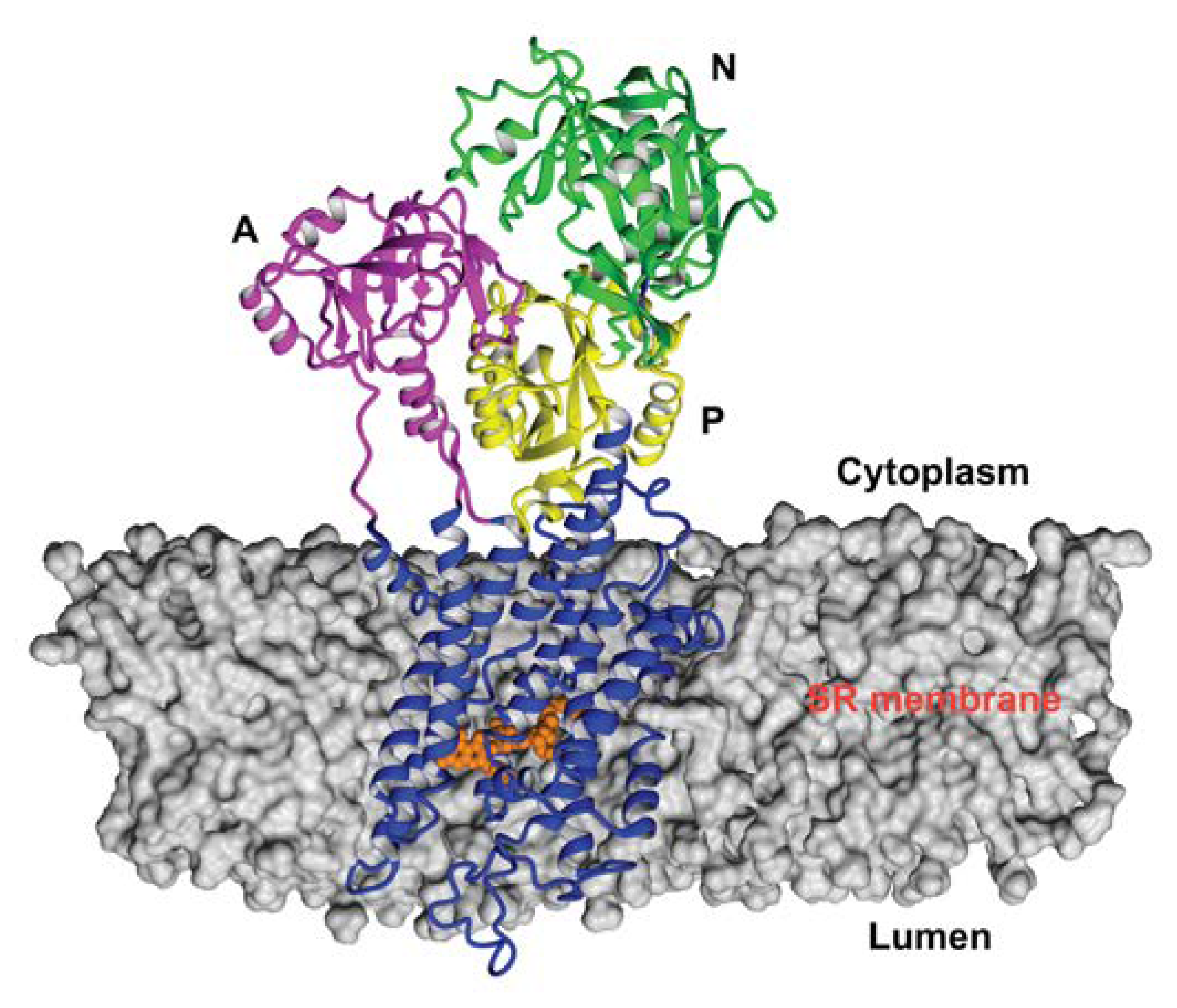
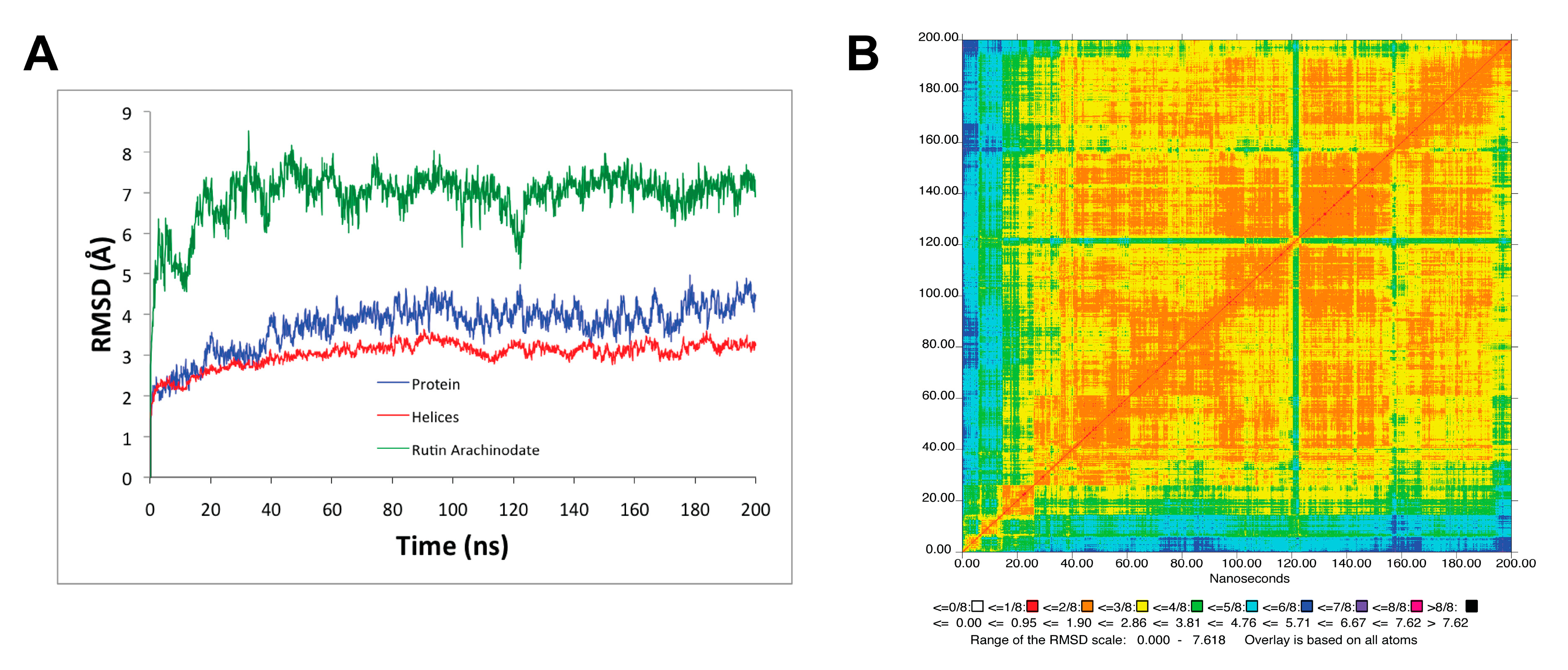
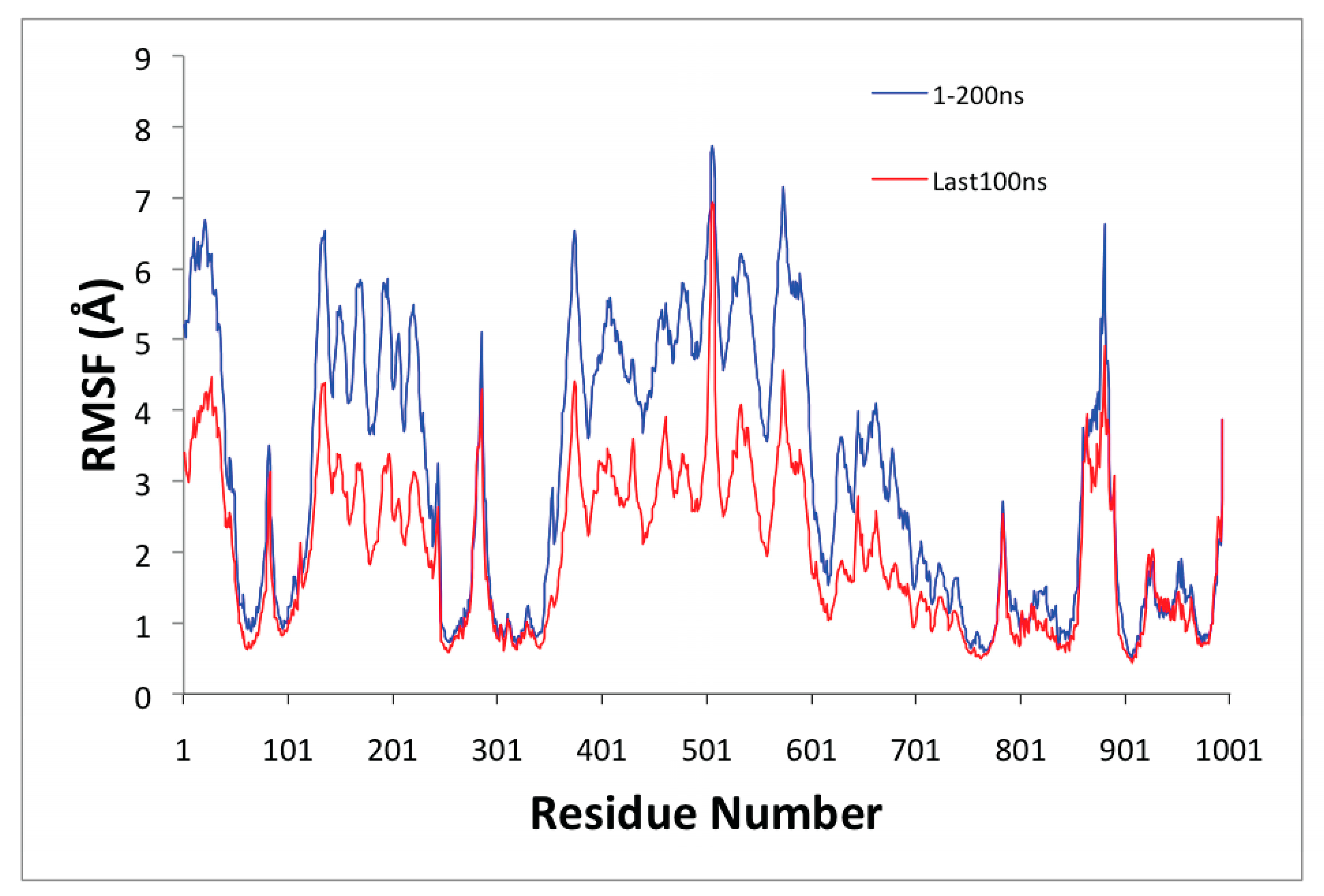
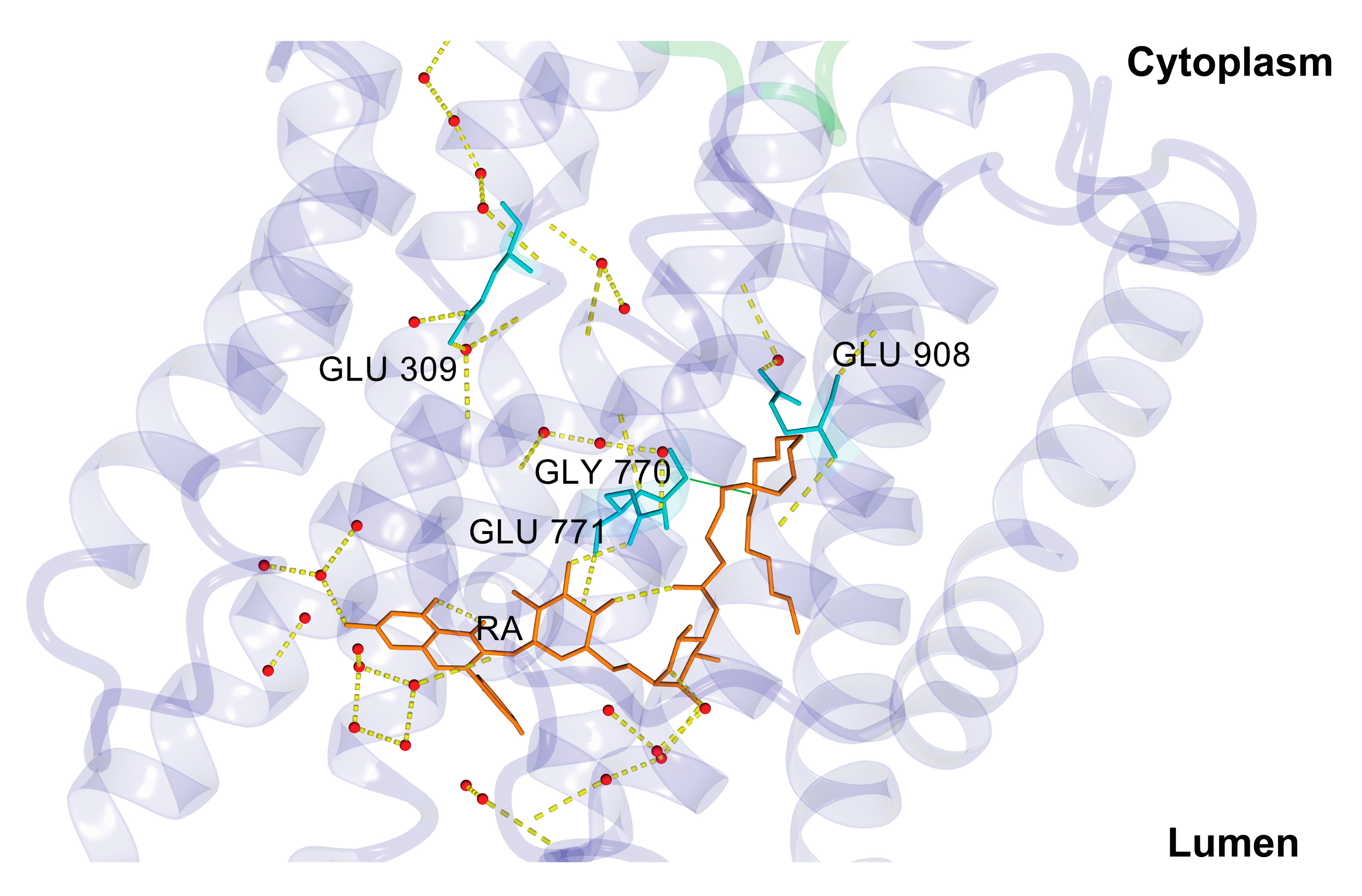
| Acceptor | DonorH | Donor | Fraction Occupied | Distance (Å) | Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLU771@OE1 | RA995@HO4 | RA995@O4 | 0.880 | 2.740 | 157.68 |
| LEU783@O | RA995@H15 | RA995@O15 | 0.472 | 2.739 | 161.95 |
| GLU90@OE1 | RA995@H13 | RA995@O13 | 0.316 | 2.635 | 161.03 |
| GLU90@OE2 | RA995@H13 | RA995@O13 | 0.255 | 2.638 | 160.98 |
| THR848@OG1 | RA995@HO8 | RA995@O8 | 0.267 | 2.846 | 156.79 |
| GLU785@OE1 | RA995@H14 | RA995@O14 | 0.216 | 2.625 | 165.96 |
| GLU785@OE2 | RA995@H14 | RA995@O14 | 0.067 | 2.609 | 166.30 |
| LEU783@O | RA995@H14 | RA995@O14 | 0.109 | 2.681 | 159.78 |
| GLU771@OE1 | RA995@HO3 | RA995@O3 | 0.061 | 2.814 | 150.23 |
| PRO784@O | RA995@HO7 | RA995@O7 | 0.013 | 2.812 | 157.84 |
| Simulation Time | Predicted pKa | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Glu309 | Glu771 | Glu908 | |
| 1–200 ns | 7.85 ± 0.77 | 8.65 ± 0.51 | 10.59 ± 1.76 |
| 100–200 ns | 7.50 ± 0.34 | 8.41 ± 0.22 | 10.70 ± 1.87 |
| Interaction | Parameter | Simulation Time | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 ns | 200 ns | ||
| Hbond * (SERCA1a) | E * (kJ/mol) | 69 | 23 |
| Residues | Glu771, Pro784, Leu787, Thr848 | Glu771 | |
| Hbond (Water) | E (kJ/mol) | 49 | 88 |
| Number of Water Molecules | 3 | 4 | |
| Hydrophobic | Strength * | 51 | 61 |
| Number of Residues | 27 | 29 | |
| π-π | Strength | 0 | 1 |
| Number of Residues | 0 | 3 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, Y.; Májeková, M. Structural Changes of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Induced by Rutin Arachidonate: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020214
Rodríguez Y, Májeková M. Structural Changes of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Induced by Rutin Arachidonate: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020214
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Yoel, and Magdaléna Májeková. 2020. "Structural Changes of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Induced by Rutin Arachidonate: A Molecular Dynamics Study" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020214
APA StyleRodríguez, Y., & Májeková, M. (2020). Structural Changes of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Induced by Rutin Arachidonate: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Biomolecules, 10(2), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020214





