Impact of Different Lipid Ligands on the Stability and IgE-Binding Capacity of the Lentil Allergen Len c 3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mass Spectrometry
2.3. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
2.4. Lipid Binding
2.5. In Vitro Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.6. Patients’ Sera and Immunoglobulin Binding Assay
3. Results
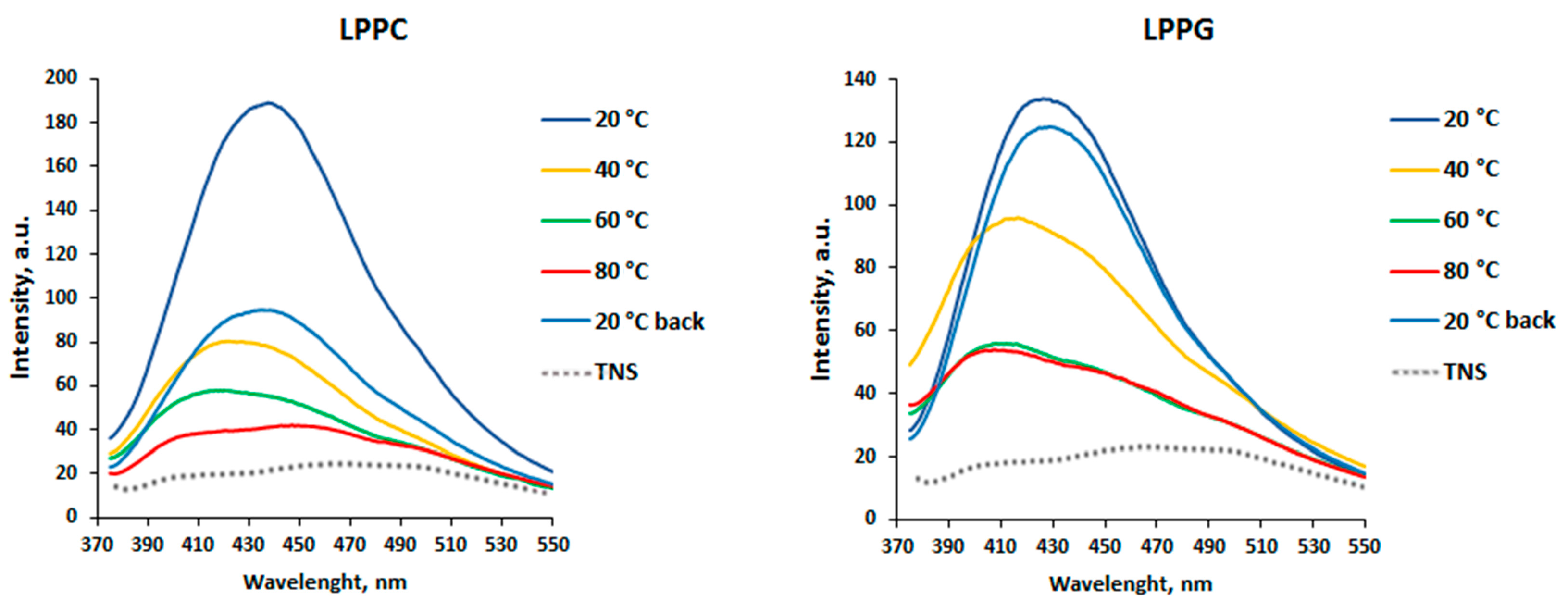
3.1. Effects of pH Change and Heating on Ligand Binding to rLen c 3
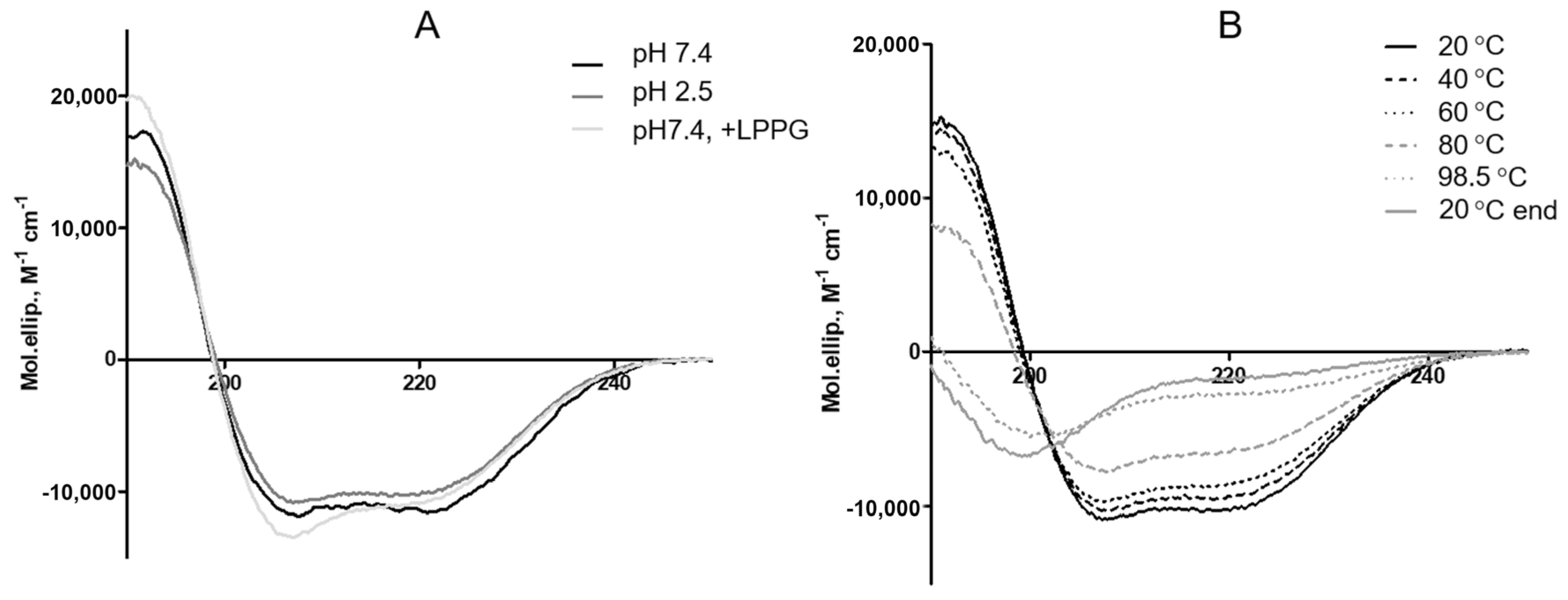
3.2. Effects of pH and Heating on the Secondary Structure of rLen c 3
3.3. Effects of Different Lipid Ligands on Thermostability of rLen c 3
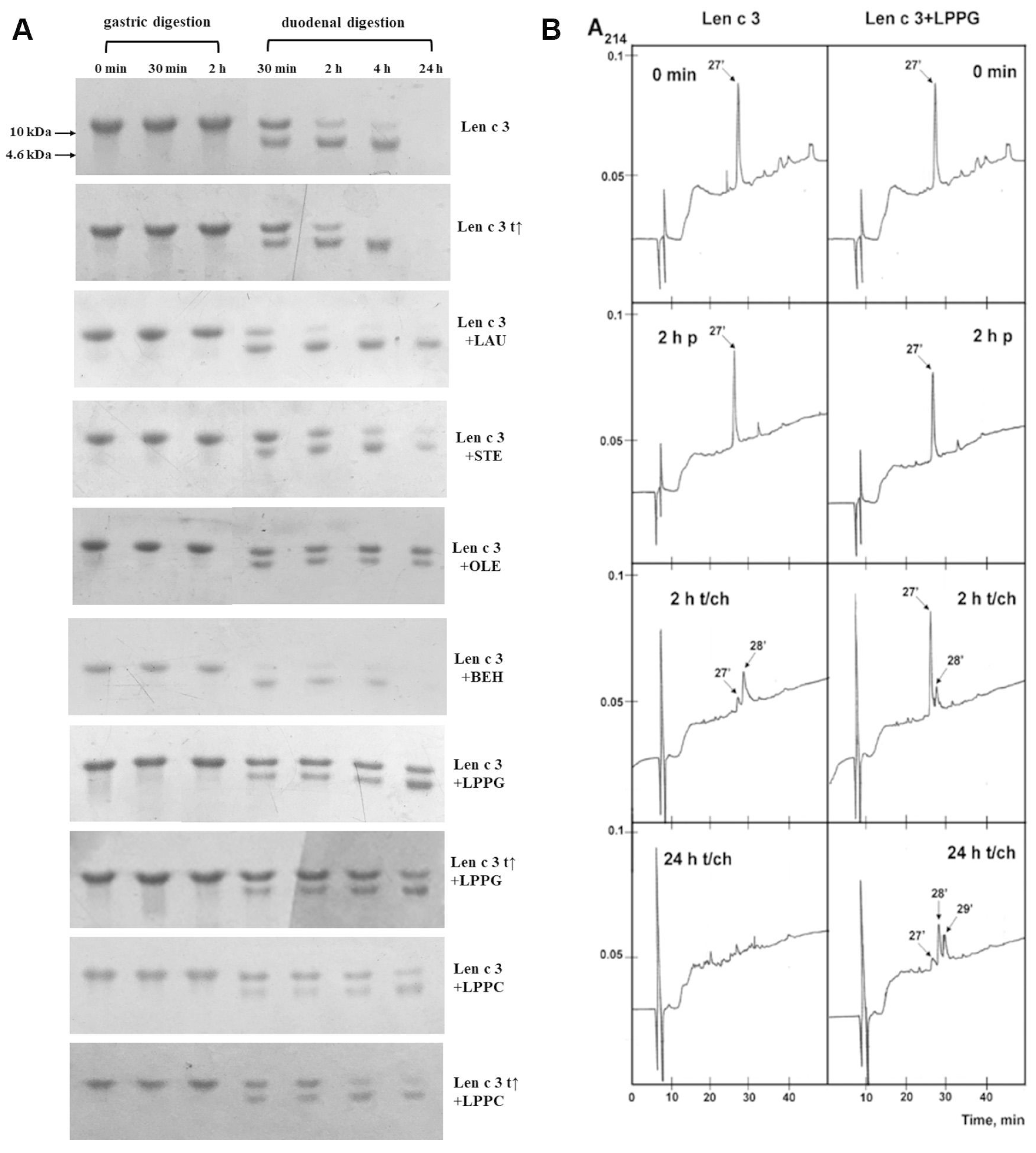
3.4. Effects of Different Lipid Ligands on Gastrointestinal Digestion of rLen c 3
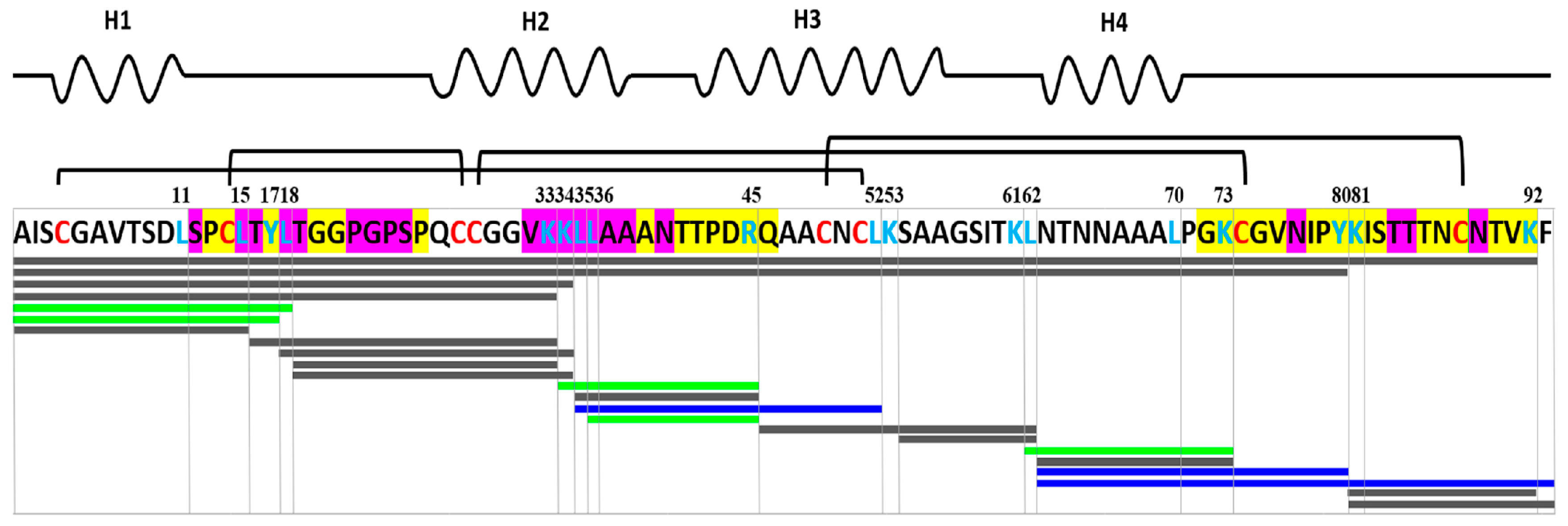
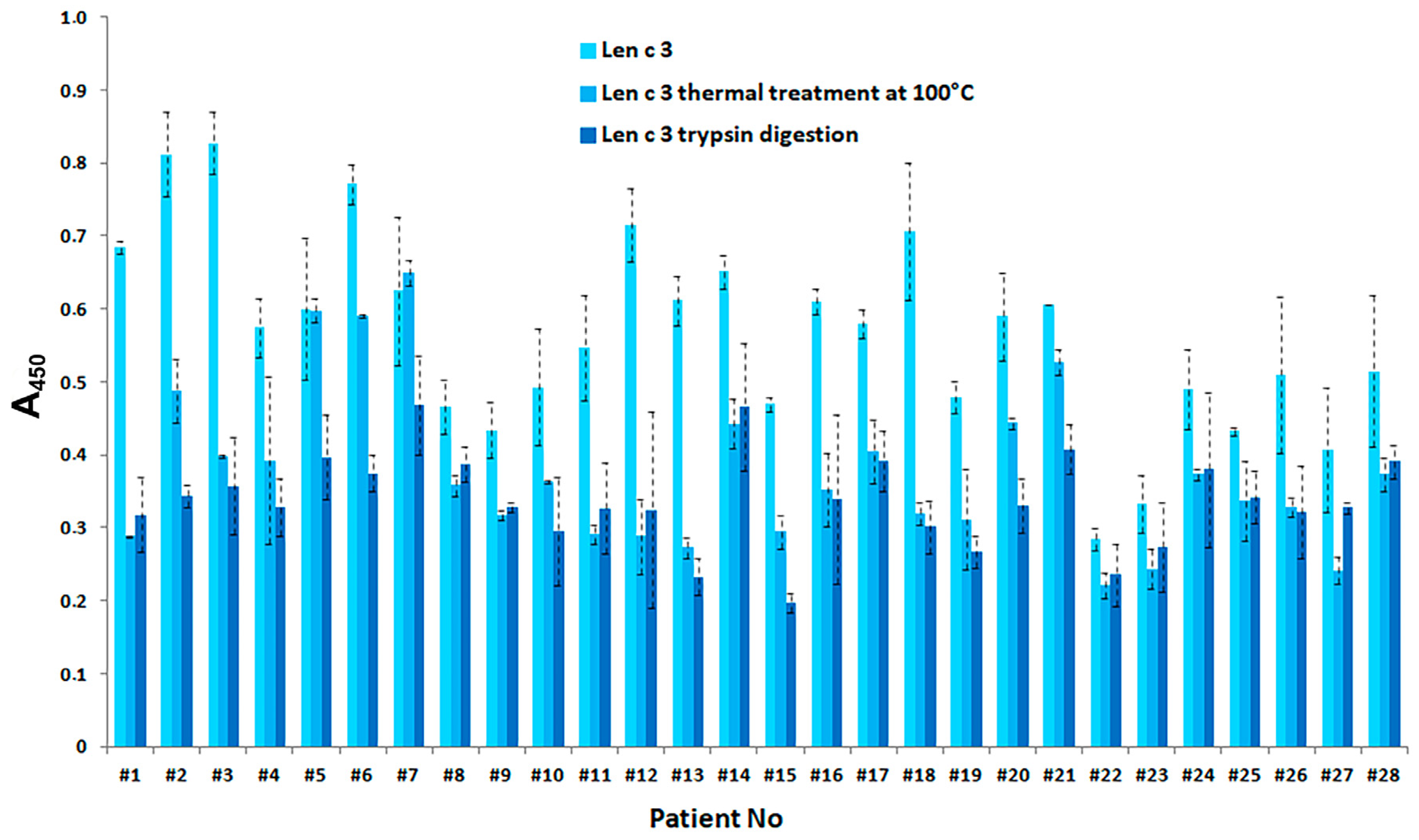
3.5. Effect of Gastric Conditions and Heat Treatment on IgE-Binding Capacity of rLen c 3
3.6. Effects of Different Lipid Ligands on IgE Binding Capacity of rLen c 3
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPPC | lyso-palmitoyl phosphatidylcholine |
| LPPG | lyso-palmitoyl phosphatidylglycerol |
| FA | fatty acid |
| LAU | lauric acid |
| STE | stearic acid |
| BEH | behenic (docosanoic) acid |
| OLE | oleic acid |
| TNS | 2-p-toluidinonaphthalene-6-sulphonate |
| LTP | lipid transfer protein |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
References
- Sackesen, C.; Erman, B.; Gimenez, G.; Grishina, G.; Yilmaz, O.; Yavuz, S.T.; Sahiner, U.M.; Buyuktiryaki, B.; Yilmaz, E.A.; Cavkaytar, O.; et al. IgE and IgG4 binding to lentil epitopes in children with red and green lentil allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 31, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pali-Schöll, I.; Untersmayr, E.; Klems, M.; Jensen-Jarolim, E. The effect of digestion and digestibility on allergenicity of food. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jappe, U.; Schwager, C.; Schromm, A.B.; González Roldán, N.; Stein, K.; Heine, H.; Duda, K.A. Lipophilic allergens, different modes of allergen-lipid interaction and their impact on asthma and allergy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Bavaro, S.L.; Benedé, S.; Diaz-Perales, A.; Bueno-Diaz, C.; Gelencser, E.; Klueber, J.; Larré, C.; Lozano-Ojalvo, D.; Lupi, R.; et al. Are Physicochemical Properties Shaping the Allergenic Potency of Plant Allergens? Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkina, E.I.; Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Plant pathogenesis-related proteins PR-10 and PR-14 as components of innate immunity system and ubiquitous allergens. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1772–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizatullina, A.K.; Finkina, E.I.; Mineev, K.S.; Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Telezhinskaya, I.N.; Balandin, S.V.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Arseniev, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Recombinant production and solution structure of lipid transfer protein from lentil Lens culinaris. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkina, E.I.; Akkerdaas, J.; Balandin, S.V.; Santos Magadon, S.; Knulst, A.; Fernandez-Rivas, M.; Asero, R.; van Ree, R.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Lentil (Lens culinaris) lipid transfer protein Len c 3, a novel legume allergen. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.N.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Finkina, E.I.; Sukhanov, S.V.; Boldyrev, I.A.; Gizatullina, A.K.; Mineev, K.S.; Arseniev, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Ligand binding properties of the lentil lipid transfer protein: Molecular insight into the possible mechanism of lipid uptake. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 1785–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelaa, E.R.; Günterb, K.D. Fatty acid composition and tocopherol content of some legume seeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Techn. 1995, 52, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; Galvin, K.; O’Connor, T.P.; Maguire, A.R.; O’Brien, N.M. Phytosterol, squalene, tocopherol content and fatty acid profile of selected seeds, grains, and legumes. Plant. Foods Hum. Nutr. 2007, 62, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R. A comparative study of the composition of lipids associated with starch granules from various botanical sources. Food Chem. 1992, 43, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.; Rahman, K. Lipid flow in bile formation. BBA 1992, 1125, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, I.V.; Finkina, E.I.; Balandin, S.V.; Melnikova, D.N.; Stukacheva, E.A.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Structural and functional characterization of recombinant isoforms of the lentil lipid transfer protein. Acta Nat. 2015, 7, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.M.; Mineev, K.S.; Finkina, E.I.; Arseniev, A.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. A novel lipid transfer protein from the dill Anethum graveolens L.: Isolation, structure, heterologous expression, and functional characteristics. J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejvar, E.; Himly, M.; Briza, P.; Eichhorn, S.; Ebner, C.; Hemmer, W.; Ferreira, F.; Gadermaier, G. Allergenic relevance of nonspecific lipid transfer proteins 2: Identification and characterization of Api g 6 from celery tuber as representative of a novel IgE-binding protein family. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 2061–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K.; Favre, M. Gel electrophoresis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 80, 573–599. [Google Scholar]
- Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Ovchinnikova, T.V.; Finkina, E.I. New insights into ligand binding by plant lipid transfer proteins: A case study of the lentil Lc-LTP2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 528, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Le, T.M.; Welsing, P.; Houben, G.; Knulst, A.; Verhoeckx, K. Legume protein consumption and the prevalence of legume sensitization. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, S.T.; Sahiner, U.M.; Buyuktiryaki, B.; Tuncer, A.; Yilmaz, E.A.; Cavkaytar, O.; Karabulut, E.; Sackesen, C. Role of specific IgE in predicting the clinical course of lentil allergy in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 24, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkina, E.I.; Balandin, S.V.; Serebryakova, M.V.; Potapenko, N.A.; Tagaev, A.A.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Purification and primary structure of novel lipid transfer proteins from germinated lentil (Lens culinaris) seeds. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaier, S.; Marsh, J.; Oberhuber, C.; Rigby, N.M.; Lovegrove, A.; Alessandri, S.; Briza, P.; Radauer, C.; Zuidmeer, L.; van Ree, R.; et al. Purification and structural stability of the peach allergens Pru p 1 and Pru p 3. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, S220–S229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheurer, S.; Lauer, I.; Foetisch, K.; San Miguel Moncin, M.; Retzek, M.; Hartz, C.; Enrique, E.; Lidholm, J.; Cistero-Bahima, A.; Vieths, S. Strong allergenicity of Pru av 3, the lipid transfer protein from cherry, is related to high stability against thermal processing and digestion. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, S.U.; Alexeev, Y.; Johnson, P.E.; Rigby, N.M.; Mackie, A.R.; Dhaliwal, B.; Mills, E.N.C. Ligand binding to an allergenic lipid transfer protein enhances conformational flexibility resulting in an increase in susceptibility to gastroduodenal proteolysis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilopoulou, E.; Rigby, N.; Moreno, F.J.; Zuidmeer, L.; Akkerdaas, J.; Tassios, I.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Saxoni-Papageorgiou, P.; van Ree, R.; Mills, C. Effect of in vitro gastric and duodenal digestion on the allergenicity of grape lipid transfer protein. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Casado, G.; Pacios, L.F.; Dıaz-Perales, A.; Sanchez-Monge, R.; Lombardero, M.; García-Selles, F.J.; Polo, F.; Barber, D.; Salcedo, G. Identification of IgE-binding epitopes of the major peach allergen Pru p 3. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadermaier, G.; Hauser, M.; Egger, M.; Ferrara, R.; Briza, P.; Santos, S.K.; Zennaro, D.; Girbl, T.; Zuidmeer-Jongejan, L.; Mari, A.; et al. Sensitization Prevalence, Antibody Cross-Reactivity and Immunogenic Peptide Profile of Api g 2, the Non-Specific Lipid Transfer Protein 1 of Celery. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekara, J.; Reta, D.; Untersmayra, E. Stability of allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiela, P.; Aina, R.; Polak, D.; Geiselhart, S.; Humeniuk, P.; Bohle, B.; Alessandri, S.; Del Conte, R.; Cantini, F.; Borowski, T.; et al. Enhanced Pru p 3 IgE-binding activity by selective free fatty acid interaction. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 1728–1731.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubiela, P.; Del Conte, R.; Cantini, F.; Borowski, T.; Aina, R.; Radauer, C.; Bublin, M.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Alessandri, S. Impact of lipid binding on the tertiary structure and allergenic potential of Jug r 3, the non-specific lipid transfer protein from walnut. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, R.; Dubiela, P.; Geiselhart, S.; Bublin, M.; Bruschi, M.; Radauer, C.; Nagl, C.; Humeniuk, P.; Asero, R.; Mortz, C.G.; et al. Distinct Lipid Transfer Proteins display different IgE-binding activities that are affected by fatty acid binding. Allergy 2019, 74, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeo-Santos, C.; López-Rodríguez, J.C.; García-Mouton, C.; San Segundo-Acosta, P.; Jurado, A.; Moreno-Aguilar, C.; García-Álvarez, B.; Pérez-Gil, J.; Villalba, M.; Barderas, R.; et al. Biophysical and biological impact on the structure and IgE-binding of the interaction of the olive pollen allergen Ole e 7 with lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Ligand | IC50 (μM) * | |
|---|---|---|
| 10 mM Phosphate Buffer, pH 7.4 | 150 mM Sodium Chloride, pH 2.5 | |
| LAU | 2.1 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.01 |
| STE | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 5.1 ± 0.1 |
| OLE | 2.4 ± 0.1 | 2.6 ± 0.1 |
| BEH | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 6.2 ± 0.1 |
| LPPC | 7.7 ± 0.02 | 7.3 ± 0.01 |
| LPPG | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 4.3 ± 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Finkina, E.I.; Melnikova, D.N.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Matveevskaya, N.S.; Ignatova, A.A.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Impact of Different Lipid Ligands on the Stability and IgE-Binding Capacity of the Lentil Allergen Len c 3. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121668
Finkina EI, Melnikova DN, Bogdanov IV, Matveevskaya NS, Ignatova AA, Toropygin IY, Ovchinnikova TV. Impact of Different Lipid Ligands on the Stability and IgE-Binding Capacity of the Lentil Allergen Len c 3. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(12):1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121668
Chicago/Turabian StyleFinkina, Ekaterina I., Daria N. Melnikova, Ivan V. Bogdanov, Natalia S. Matveevskaya, Anastasia A. Ignatova, Ilia Y. Toropygin, and Tatiana V. Ovchinnikova. 2020. "Impact of Different Lipid Ligands on the Stability and IgE-Binding Capacity of the Lentil Allergen Len c 3" Biomolecules 10, no. 12: 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121668
APA StyleFinkina, E. I., Melnikova, D. N., Bogdanov, I. V., Matveevskaya, N. S., Ignatova, A. A., Toropygin, I. Y., & Ovchinnikova, T. V. (2020). Impact of Different Lipid Ligands on the Stability and IgE-Binding Capacity of the Lentil Allergen Len c 3. Biomolecules, 10(12), 1668. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121668








