Understanding the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis
Abstract
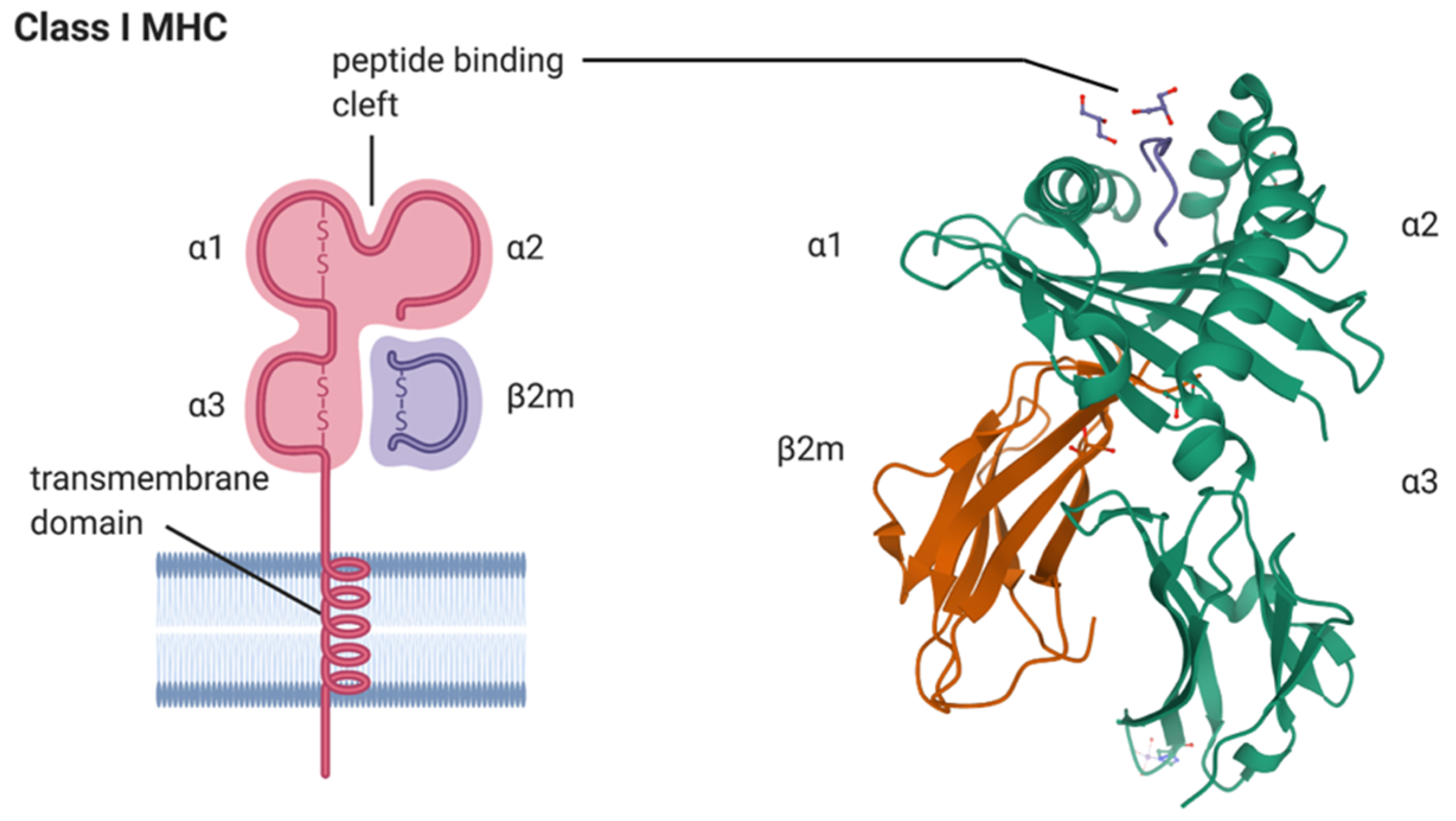
1. Introduction
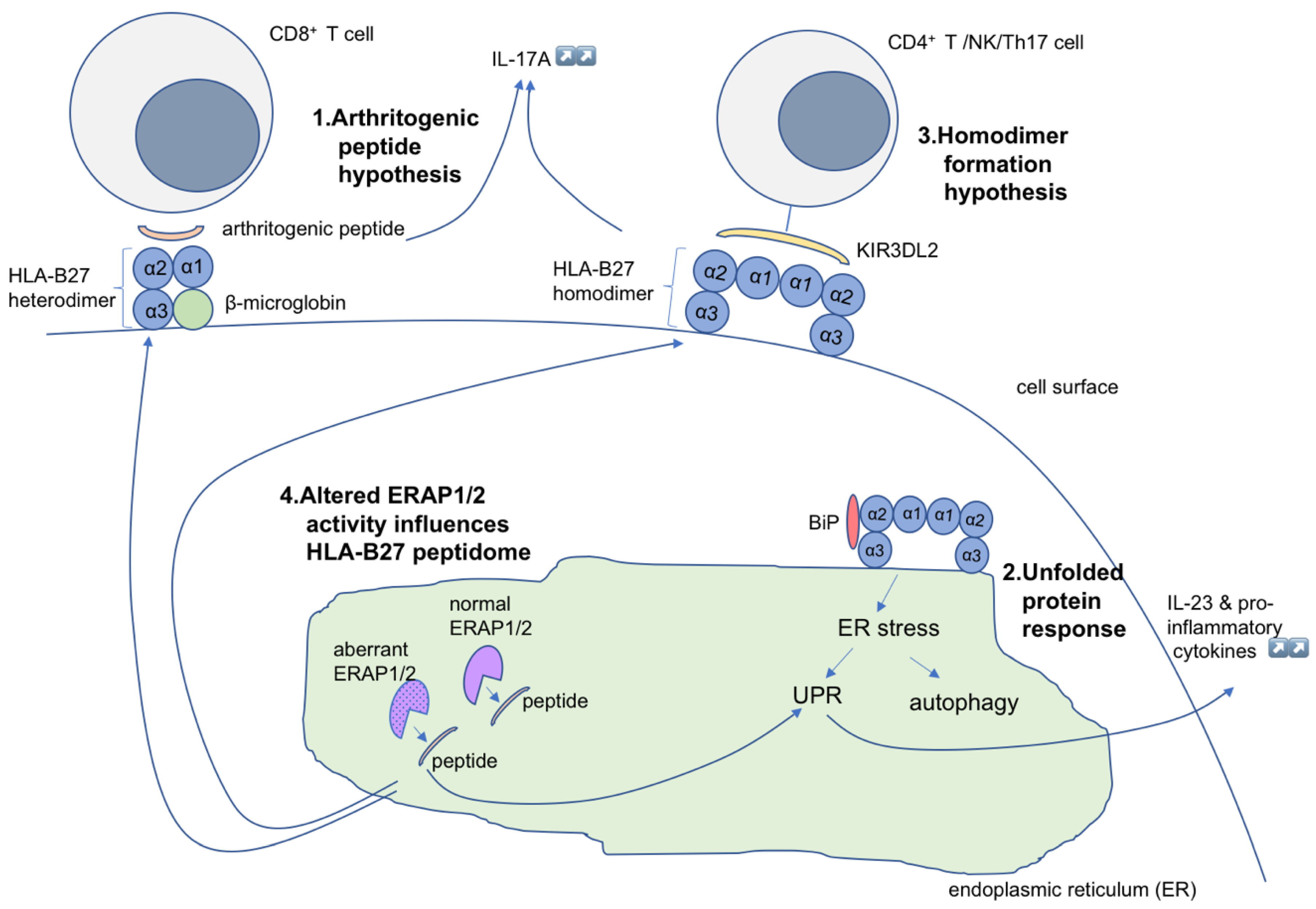
2. Models of SpA Pathogenesis: Hypotheses
2.1. Arthritogenic Peptide Hypothesis
2.2. The Unfolded Protein Response Hypothesis
2.3. HLA-B*27 Homodimer Formation Hypothesis
2.4. The ERAP Polymorphism Hypothesis
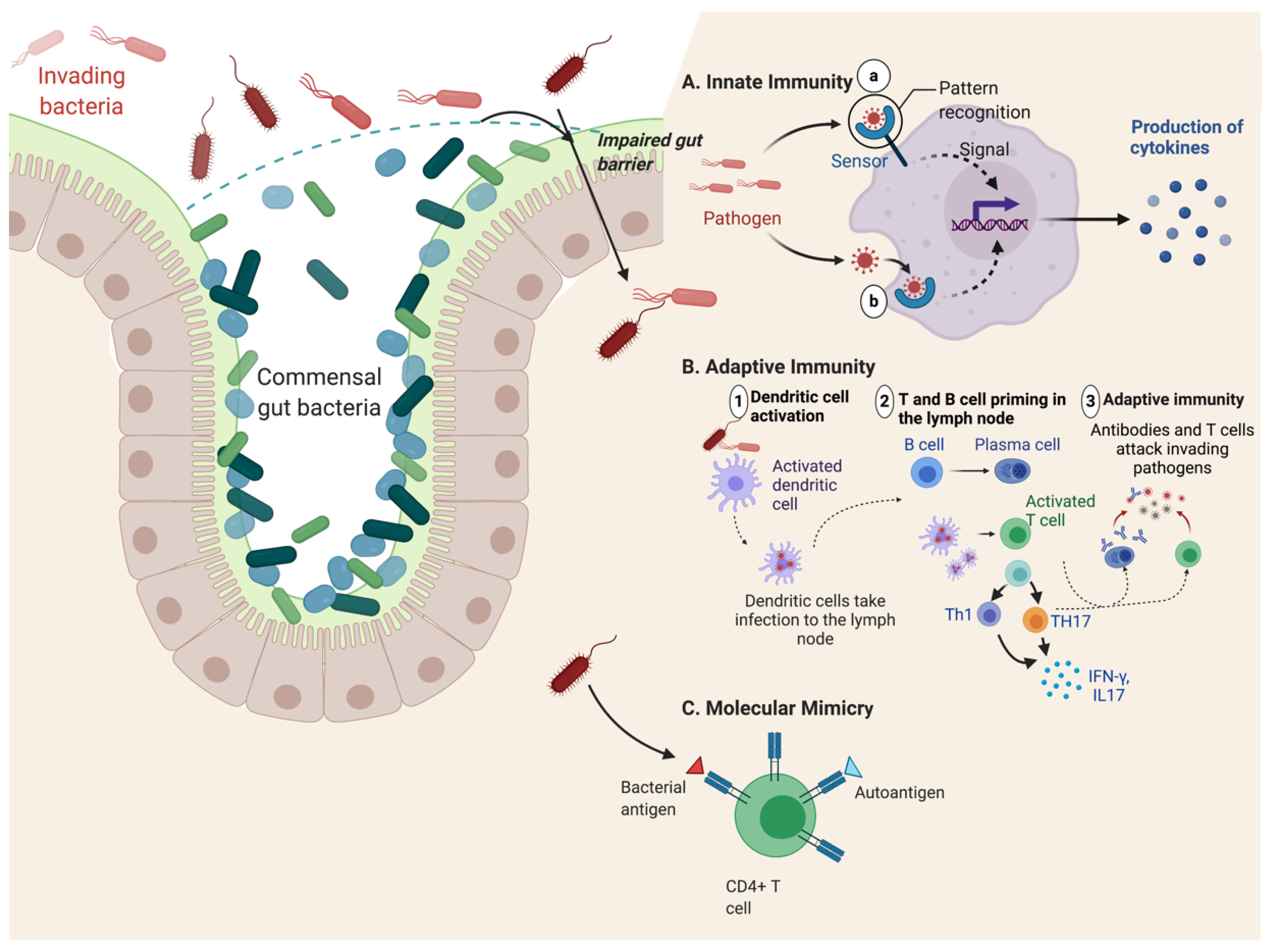
2.5. Gut Inflammation and Dysbiosis Hypothesis
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zochling, J.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J. The current concept of spondyloarthritis with special emphasis on undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A. Polymorphism of HLA-B27: 105 subtypes currently known. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolwijk, C.; Boonen, A.; van Tubergen, A.; Reveille, J.D. Epidemiology of spondyloarthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 38, 441–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakland, G.; Nossent, H.C. Epidemiology of Spondyloarthritis: A Review. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2013, 15, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, J.; Sieper, J. Ankylosing spondylitis. Lancet 2007, 369, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotch, F.; Rothbard, J.; Howland, K.; Townsend, A.; McMichael, A. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a fragment of influenza virus matrix protein in association with HLA-A2. Nature 1987, 326, 881–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, A.R.M.; Rothbard, J.; Gotch, F.M.; Bahadur, G.; Wraith, D.; McMichael, A.J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell 1986, 44, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, R.A.; Tran, T.M.; Layh-Schmitt, G. HLA-B27 misfolding and ankylosing spondylitis. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 57, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsmeyer, M.; Hillig, R.C.; Volz, A.; Ruhl, M.; Schroder, W.; Saenger, W.; Ziegler, A.; Uchanska-Ziegler, B. HLA-B27 subtypes differentially associated with disease exhibit subtle structural alterations. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 47844–47853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowsdale, J.; Knight, J.C. Major histocompatibility complex genomics and human disease. Ann. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2013, 14, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorkman, P.; Parham, P. Structure, Function, and Diversity of Class I Major Histocompatibility Complex Molecules. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 253–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crux, N.; Elahi, S. Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) and Immune Regulation: How Do Classical and Non-Classical HLA Alleles Modulate Immune Response to Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infections? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMichael, A.; Bowness, P. HLA-B27: Natural function and pathogenic role in spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl. 3), S153–S158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveille, J.D. 57-Spondyloarthritis. In Clinical Immunology, 5th ed.; Rich, R.R., Fleisher, T.A., Shearer, W.T., Schroeder, H.W., Frew, A.J., Weyand, C.M., Eds.; Content Repository Only: London, UK, 2019; pp. 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill Gaston, J.S.; Lillicrap, M.S. Arthritis associated with enteric infection. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2003, 17, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieper, J.; Braun, J.; Kingsley, G.H. Report on the Fourth International Workshop on Reactive Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granfors, K.; Jalkanen, S.; von Essen, R.; Lahesmaa-Rantala, R.; Isomäki, O.; Pekkola-Heino, K.; Merilahti-Palo, R.; Saario, R.; Isomäki, H.; Toivanen, A. Yersinia Antigens in Synovial-Fluid Cells from Patients with Reactive Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.L.; Bowness, P.; McMichael, A. The role of HLA-B27 in spondyloarthritis. Immunogenetics 1999, 50, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; He, X.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Qiu, G.; Cao, X.; Weng, X. Ankylosing spondylitis: Etiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Bone Res. 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldstone, M.B.A. Molecular Mimicry as a Mechanism for the Cause and as a Probe Uncovering Etiologic Agent(S) of Autoimmune-Disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 1989, 145, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Grandon, B.; Rincheval-Arnold, A.; Jah, N.; Corsi, J.M.; Araujo, L.M.; Glatigny, S.; Prevost, E.; Roche, D.; Chiocchia, G.; Guenal, I.; et al. HLA-B27 alters BMP/TGFbeta signalling in Drosophila, revealing putative pathogenic mechanism for spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, S.J.; Maksymowych, W.P. The Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Montoya, L.; Gul, H.; Emery, P. Recent advances in ankylosing spondylitis: Understanding the disease and management. F1000Res 2018, 7, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Esteban, A.; Sanz-Bravo, A.; Guasp, P.; Barnea, E.; Admon, A.; de Castro, J.A.L. Separate effects of the ankylosing spondylitis associated ERAP1 and ERAP2 aminopeptidases determine the influence of their combined phenotype on the HLA-B*27 peptidome. J. Autoimmun. 2017, 79, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaie, F.; Mohammadi, H.; Hemmatzadeh, M.; Ebrazeh, M.; Torkamandi, S.; Yousefi, M.; Hajaliloo, M.; Rezaiemanesh, A.; Salimi, S.; Salimi, R.; et al. Evaluation of ERAP1 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms in immunomodulation of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines profile in ankylosing spondylitis. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 217, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, M.L. Interactions of the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 322–330. [Google Scholar]
- Cusick, M.F.; Libbey, J.E.; Fujinami, R.S. Molecular Mimicry as a Mechanism of Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 42, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuon, W.; Holzhutter, H.G.; Appel, H.; Grolms, M.; Kollnberger, S.; Traeder, A.; Henklein, P.; Weiss, E.; Thiel, A.; Lauster, R.; et al. Identification of HLA-B27-restricted peptides from the Chlamydia trachomatis proteome with possible relevance to HLA-B27-associated diseases. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 4738–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, M.; Lopez de Castro, J.A. HLA-B27 and the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis. Tissue Antigens 2002, 60, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowness, P. Hla-B27. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, H.; Kuon, W.; Kuhne, M.; Wu, P.H.; Kuhlmann, S.; Kollnberger, S.; Thiel, A.; Bowness, P.; Sieper, J. Use of HLA-B27 tetramers to identify low-frequency antigen-specific T cells in Chlamydia-triggered reactive arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R521–R534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, E.; Yu, D.T.Y.; Zumbuschenfelde, K.H.M.; Fleischer, B. Hla-B27-Restricted Cd8 T-Cells Derived from Synovial-Fluids of Patients with Reactive Arthritis and Ankylosing-Spondylitis. Lancet 1993, 342, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugrinovic, S.; Mertz, A.; Wu, P.; Braun, J.; Sieper, J. A single nonamer from the Yersinia 60-kDa heat shock protein is the target of HLA-B27-restricted CTL response in Yersinia-induced reactive arthritis. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 5715–5723. [Google Scholar]
- Scofield, R.H.; Kurien, B.; Gross, T.; Warren, W.L.; Harley, J.B. HLA-B27 binding of peptide from its own sequence and similar peptides from bacteria: Implications for spondyloarthropathies. Lancet 1995, 345, 1542–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, C.; Ebringer, R.; Tribbick, G.; Geysen, H.M. Antibody activity in ankylosing spondylitis sera to two sites on HLA B27.1 at the MHC groove region (within sequence 65–85), and to a Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase reductase peptide (within sequence 181–199). J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Dror, L.; Barnea, E.; Beer, I.; Mann, M.; Admon, A. The HLA-B*2705 peptidome. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, M.T.; Maragno, M.; Butler, R.; Dupuis, M.L.; Sorrentino, R. CD8(+) T-cell autoreactivity to an HLA-B27-restricted self-epitope correlates with ankylosing spondylitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syrbe, U.; Sieper, J. Chapter 36-Spondyloarthritides. In The Autoimmune Diseases, 6th ed.; Rose, N.R., Mackay, I.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schittenhelm, R.B.; Sian, T.C.; Wilmann, P.G.; Dudek, N.L.; Purcell, A.W. Revisiting the arthritogenic peptide theory: Quantitative not qualitative changes in the peptide repertoire of HLA-B27 allotypes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaie, F.; Hasankhani, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Safarzadeh, E.; Rezaiemanesh, A.; Salimi, R.; Baradaran, B.; Babaloo, Z. The role of gut microbiota and IL-23/IL-17 pathway in ankylosing spondylitis immunopathogenesis: New insights and updates. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 196, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mear, J.P.; Schreiber, K.L.; Munz, C.; Zhu, X.M.; Stevanovic, S.; Rammensee, H.G.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Colbert, R.A. Misfolding of HLA-B27 as a result of its B pocket suggests a novel mechanism for its role in susceptibility to spondyloarthropathies. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6665–6670. [Google Scholar]
- Kenna, T.J.; Robinson, P.C.; Haroon, N. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambarus, C.A.; Yeremenko, N.; Baeten, D.L. Altered cytokine expression by macrophages from HLA-B27-positive spondyloarthritis patients without evidence of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2018, 2, rky014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A. Regulation of Cytokine Production by the Unfolded Protein Response; Implications for Infection and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busch, R.; Kollnberger, S.; Mellins, E.D. HLA associations in inflammatory arthritis: Emerging mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 364–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navid, F.; Layh-Schmitt, G.; Sikora, K.A.; Cougnoux, A.; Colbert, R.A. The Role of Autophagy in the Degradation of Misfolded HLA-B27 Heavy Chains. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebringer, A. The Cross-Tolerance Hypothesis, Hla-B27 and Ankylosing-Spondylitis. Rheumatology 1983, 22, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.J.; Delay, M.L.; Bai, S.; Klenk, E.; Colbert, R.A. HLA-B27 up-regulation causes accumulation of misfolded heavy chains and correlates with the magnitude of the unfolded protein response in transgenic rats: Implications for the pathogenesis of spondylarthritis-like disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delay, M.L.; Turner, M.J.; Klenk, E.I.; Smith, J.A.; Sowders, D.P.; Colbert, R.A. HLA-B27 Misfolding and the Unfolded Protein Response Augment Interleukin-23 Production and Are Associated with Th17 Activation in Transgenic Rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2633–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.N.; Ford, S.; Taurog, J.D.; Butcher, G.W.; Powis, S.J. Formation of HLA-B27 homodimers and their relationship to assembly kinetics. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 8895–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangoria, N.S.; DeLay, M.L.; Kingsbury, D.J.; Mear, J.P.; Uchanska-Ziegler, B.; Ziegler, A.; Colbert, R.A. HLA-B27 misfolding is associated with aberrant intermolecular disulfide bond formation (dimerization) in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23459–23468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.M.; Satumtira, N.; Dorris, M.L.; May, E.; Wang, A.; Furuta, E.; Taurog, J.D. HLA-B27 in transgenic rats forms disulfide-linked heavy chain oligomers and multimers that bind to the chaperone BiP. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 5110–5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, M.J.; Sowders, D.P.; DeLay, M.L.; Mohapatra, R.; Bai, S.; Smith, J.A.; Brandewie, J.R.; Taurog, J.D.; Colbert, R.A. HLA-B27 misfolding in transgenic rats is associated with activation of the unfolded protein response. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2438–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.M.; Dorris, M.L.; Satumtira, N.; Richardson, J.A.; Hammer, R.E.; Shang, J.; Taurog, J.D. Additional human beta(2)-microglobulin curbs HLA-B27 misfolding and promotes arthritis and spondylitis without colitis in male HLA-B27-transgenic rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, E.C.; Fettke, F.; Bhat, S.; Morley, K.D.; Powis, S.J. Expression of MHC class I dimers and ERAP1 in an ankylosing spondylitis patient cohort. Immunology 2011, 133, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccia, F.; Accardo-Palumbo, A.; Rizzo, A.; Guggino, G.; Raimondo, S.; Giardina, A.; Cannizzaro, A.; Colbert, R.A.; Alessandro, R.; Triolo, G. Evidence that autophagy, but not the unfolded protein response, regulates the expression of IL-23 in the gut of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and subclinical gut inflammation. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, A.N.; Lenart, I.; Kriston-Vizi, J.; Iwawaki, T.; Turmaine, M.; McHugh, K.; Ali, S.; Blake, N.; Bowness, P.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; et al. Salmonella exploits HLA-B27 and host unfolded protein responses to promote intracellular replication. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaiemanesh, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Amirzargar, A.A.; Vojdanian, M.; Jamshidi, A.R.; Nicknam, M.H. Ankylosing spondylitis M-CSF-derived macrophages are undergoing unfolded protein response (UPR) and express higher levels of interleukin-23. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurog, J.D.; Dorris, M.L.; Satumtira, N.; Tran, T.M.; Sharma, R.; Dressel, R.; van den Brandt, J.; Reichardt, H.M. Spondylarthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2-microglobulin-transgenic rats is not prevented by lack of CD8. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, L.H.; Hill Gaston, J.S. Breaking the rules: The unconventional recognition of HLA-B27 by CD4+ T lymphocytes as an insight into the pathogenesis of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowness, P.; Ridley, A.; Shaw, J.; Chan, A.T.; Wong-Baeza, I.; Fleming, M.; Cummings, F.; McMichael, A.; Kollnberger, S. Th17 cells expressing KIR3DL2+ and responsive to HLA-B27 homodimers are increased in ankylosing spondylitis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollnberger, S.; Bird, L.; Sun, M.-Y.; Retiere, C.; Braud, V.M.; McMichael, A.; Bowness, P. Cell-surface expression and immune receptor recognition of HLA–B27 homodimers. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2972–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ridley, A.; Hammitzsch, A.; Al-Mossawi, M.H.; Bunting, H.; Georgiadis, D.; Chan, A.; Kollnberger, S.; Bowness, P. Silencing or inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) suppresses free heavy chain expression and Th17 responses in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 75, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A. Solving the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 186, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, F.; Ebrazeh, M.; Hemmatzadeh, M.; Sadat Mohammadi, F.; Gowhari Shabgah, A.; Hajaliloo, M.; Ebrahimi, A.A.; Shirafkan, N.; Azizi, G.; Mohammadi, H.; et al. Association analysis of ERAP1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism in susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis in Iranian population. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 201, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.; Shaw, J.; Piper, C.; Wong-Baeza, I.; McHugh, K.; Ridley, A.; Li, D.; Lenart, I.; Antoniou, A.N.; DiGleria, K.; et al. HLA-B27 homodimers and free H chains are stronger ligands for leukocyte Ig-like receptor B2 than classical HLA class I. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 6184–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.T.; Kollnberger, S.D.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Bowness, P. Expansion and enhanced survival of natural killer cells expressing the killer immunoglobulin-like receptor KIR3DL2 in spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3586–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauli, A.; Shaw, J.; Giles, J.; Hatano, H.; Rysnik, O.; Payeli, S.; McHugh, K.; Dessole, G.; Porru, G.; Desogus, E.; et al. The arthritis-associated HLA-B*27:05 allele forms more cell surface B27 dimer and free heavy chain ligands for KIR3DL2 than HLA-B*27:09. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1952–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim Kam Sian, T.C.C.; Indumathy, S.; Halim, H.; Greule, A.; Cryle, M.J.; Bowness, P.; Rossjohn, J.; Gras, S.; Purcell, A.W.; Schittenhelm, R.B. Allelic association with ankylosing spondylitis fails to correlate with human leukocyte antigen B27 homodimer formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 20185–20195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.M.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Pointon, J.J.; Su, Z.; Harvey, D.; Kochan, G.; Opperman, U.; Dilthey, A.; Pirinen, M.; Stone, M.A.; et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Jamshidi, A.R.; Amirzargar, A.A.; Farhadi, E.; Nourijelyani, K.; Fallahi, S.; Oraei, M.; Noori, S.; Nicknam, M.H. Association between Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase-1 (ERAP-1) and Susceptibility to Ankylosing Spondylitis in Iran. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 11, 294–300. [Google Scholar]
- Dashti, N.; Mahmoudi, M.; Aslani, S.; Jamshidi, A. HLA-B*27 subtypes and their implications in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Gene 2018, 670, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, S.I.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wei, M.; Danoy, P.A.; Thomas, G.; Cai, Q.; Sun, L.; Duncan, E.; Wang, N.; et al. Association of ERAP1, but not IL23R, with ankylosing spondylitis in a Han Chinese population. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3263–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, P.; Clayton, D.; Cardon, L.; Craddock, N.; Duncanson, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.; McCarthy, M.; Ouwehand, W.; Samani, N.; Todd, J.; et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.A. Breakthroughs in genetic studies of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology 2007, 47, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, M.T.; Grant, E.P.; Gramm, C.; Goldberg, A.L.; Rock, K.L. A role for the ubiquitin-dependent proteolytic pathway in MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation. Nature 1993, 363, 552–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Gramm, C.; Rothstein, L.; Clark, K.; Stein, R.; Dick, L.; Hwang, D.; Goldberg, A.L. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell 1994, 78, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, K.L.; Reits, E.; Neefjes, J. Present Yourself! By MHC Class I and MHC Class II Molecules. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemali, M.; Radtke, K.; Desjardins, M.; English, L. Alternative pathways for MHC class I presentation: A new function for autophagy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kaer, L.; Parekh, V.V.; Postoak, J.L.; Wu, L. Role of autophagy in MHC class I-restricted antigen presentation. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 113, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgevin, A.; Saveanu, L.; Kim, Y.; Barilleau, E.; Kotturi, M.; Sette, A.; van Endert, P.; Peters, B. A detailed analysis of the murine TAP transporter substrate specificity. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Endert, P.M.; Riganelli, D.; Greco, G.; Fleischhauer, K.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Bach, J.F. The peptide-binding motif for the human transporter associated with antigen processing. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saric, T.; Chang, S.C.; Hattori, A.; York, I.A.; Markant, S.; Rock, K.L.; Tsujimoto, M.; Goldberg, A.L. An IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the ER, ERAP1, trims precursors to MHC class I-presented peptides. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de Castro, J.A. How ERAP1 and ERAP2 Shape the Peptidomes of Disease-Associated MHC-I Proteins eCollection 2018. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.L.; Hawari, F.; Alsaaty, S.; Lawrence, M.; Combs, C.A.; Geng, W.D.; Rouhani, F.N.; Miskinis, D.; Levine, S.J. Identification of ARTS-1 as a novel TNFR1-binding protein that promotes TNFR1 ectodomain shedding. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, N.; Tsui, F.; Chiu, B.; Tsui, H.; Inman, R. Serum Cytokine Receptors in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Relationship to Inflammatory Markers and Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase Polymorphisms. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1907–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reveille, J.D. Genetics of spondyloarthritis—Beyond the MHC. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, I.A.; Chang, S.C.; Saric, T.; Keys, J.A.; Favreau, J.M.; Goldberg, A.L.; Rock, K.L. The ER aminopeptidase ERAP1 enhances or limits antigen presentation by trimming epitopes to 8–9 residues. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, A.M.; Dennis, M.Y.; Kretzschmar, W.W.; Cannons, J.L.; Lee-Lin, S.Q.; Hurle, B.; Program, N.C.S.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Williamson, S.H.; Bustamante, C.D.; et al. Balancing selection maintains a form of ERAP2 that undergoes nonsense-mediated decay and affects antigen presentation. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Fiorillo, M.T.; Tedeschi, V.; Mattorre, B.; Sorrentino, R. The Multifaceted Nature of Aminopeptidases ERAP1, ERAP2, and LNPEP: From Evolution to Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Momburg, F.; Bhutani, N.; Goldberg, A.L. The ER aminopeptidase, ERAP1, trims precursors to lengths of MHC class I peptides by a “molecular ruler” mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 17107–17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidel, S.; Chen, L.; Pointon, J.; Wordsworth, P. ERAP1 and ankylosing spondylitis. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirino, Y.; Bertsias, G.; Ishigatsubo, Y.; Mizuki, N.; Tugal-Tutkun, I.; Seyahi, E.; Ozyazgan, Y.; Sacli, F.S.; Erer, B.; Inoko, H.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behcet’s disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium; the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2; Strange, A.; Capon, F.; Spencer, C.C.A.; Knight, J.; Weale, M.E.; Allen, M.H.; Barton, A.; Band, G.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Low, H.Q.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Ellinghaus, E.; Han, J.; Estivill, X.; Sun, L.; Zuo, X.; Shen, C.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies multiple novel associations and ethnic heterogeneity of psoriasis susceptibility. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Spain, S.L.; Knight, J.; Ellinghaus, E.; Stuart, P.E.; Capon, F.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Tejasvi, T.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; et al. Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.C.; Costello, M.E.; Leo, P.; Bradbury, L.A.; Hollis, K.; Cortes, A.; Lee, S.; Joo, K.B.; Shim, S.C.; Weisman, M.; et al. ERAP2 is associated with ankylosing spondylitis in HLA-B27-positive and HLA-B27-negative patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis Consortium (IGAS); Cortes, A.; Hadler, J.; Pointon, J.P.; Robinson, P.C.; Karaderi, T.; Leo, P.; Cremin, K.; Pryce, K.; Harris, J.; et al. Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seregin, S.S.; Rastall, D.P.; Evnouchidou, I.; Aylsworth, C.F.; Quiroga, D.; Kamal, R.P.; Godbehere-Roosa, S.; Blum, C.F.; York, I.A.; Stratikos, E.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 alleles associated with increased risk of ankylosing spondylitis reduce HLA-B27 mediated presentation of multiple antigens. Autoimmunity 2013, 46, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochan, G.; Krojer, T.; Harvey, D.; Fischer, R.; Chen, L.; Vollmar, M.; von Delft, F.; Kavanagh, K.L.; Brown, M.A.; Bowness, P.; et al. Crystal structures of the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 (ERAP1) reveal the molecular basis for N-terminal peptide trimming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7745–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, K.; Bowness, P. The link between HLA-B27 and SpA—New ideas on an old problem. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1529–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveanu, L.; van Endert, P. The role of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase in MHC class I antigen presentation. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Batliwala, M.; Bouvier, M. ERAP1 enzyme-mediated trimming and structural analyses of MHC I—Bound precursor peptides yield novel insights into antigen processing and presentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, jbc.RA119.010102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, H.; Zong, S.Y. Association of polymorphisms in ERAP1 and risk of ankylosing spondylitis in a Chinese population. Gene 2018, 646, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, A.; Kasprzyk, S.; Majorczyk, E.; Nowak, I.; Wilczynska, K.; Chlebicki, A.; Zon-Giebel, A.; Kusnierczyk, P. ERAP1-ERAP2 haplotypes are associated with ankylosing spondylitis in Polish patients. Hum. Immunol. 2019, 80, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Fiorillo, M.T.; Tedeschi, V.; D’Otolo, V.; Piga, M.; Cauli, A.; Mathieu, A.; Sorrentino, R. The rs75862629 minor allele in the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases intergenic region affects human leucocyte antigen B27 expression and protects from ankylosing spondylitis in Sardinia. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez de Castro, J.A.; Alvarez-Navarro, C.; Brito, A.; Guasp, P.; Martin-Esteban, A.; Sanz-Bravo, A. Molecular and pathogenic effects of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases ERAP1 and ERAP2 in MHC-I-associated inflammatory disorders: Towards a unifying view. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 77, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitulano, C.; Tedeschi, V.; Paladini, F.; Sorrentino, R.; Fiorillo, M.T. The interplay between HLA-B27 and ERAP1/ERAP2 aminopeptidases: From anti-viral protection to spondyloarthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 190, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, I.A.; Brehm, M.A.; Zendzian, S.; Towne, C.F.; Rock, K.L. Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) trims MHC class I-presented peptides in vivo and plays an important role in immunodominance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9202–9207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastall, D.P.; Aldhamen, Y.A.; Seregin, S.S.; Godbehere, S.; Amalfitano, A. ERAP1 functions override the intrinsic selection of specific antigens as immunodominant peptides, thereby altering the potency of antigen-specific cytolytic and effector memory T-cell responses. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, E.J.; Garboczi, D.N.; Wiley, D.C. Three-dimensional structure of a peptide extending from one end of a class I MHC binding site. Nature 1994, 371, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst-Kepper, M.; Hecht, H.J.; Herrmann, H.; Janke, V.; Ocklenburg, F.; Klempnauer, J.; van den Eynde, B.J.; Weiss, S. Conformational restraints and flexibility of 14-meric peptides in complex with HLA-B*3501. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 5610–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tynan, F.E.; Burrows, S.R.; Buckle, A.M.; Clements, C.S.; Borg, N.A.; Miles, J.J.; Beddoe, T.; Whisstock, J.C.; Wilce, M.C.; Silins, S.L.; et al. T cell receptor recognition of a ‘super-bulged’ major histocompatibility complex class I-bound peptide. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, P.C.; Lau, E.; Keith, P.; Lau, M.C.; Thomas, G.P.; Bradbury, L.A.; Brown, M.A.; Kenna, T.J. ERAP2 functional knockout in humans does not alter surface heavy chains or HLA-B27, inflammatory cytokines or endoplasmic reticulum stress markers. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 2092–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, E.; Fontela, M.G.; Barnea, E.; Martin-Galiano, A.J.; Mir, C.; Galocha, B.; Admon, A.; Lauzurica, P.; Lopez, D. Modulation of Natural HLA-B*27:05 Ligandome by Ankylosing Spondylitis-associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Aminopeptidase 2 (ERAP2). Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2020, 19, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, E.; Redondo-Anton, J.; Martin-Esteban, A.; Guasp, P.; Barnea, E.; Lauzurica, P.; Admon, A.; Lopez de Castro, J.A. Substantial Influence of ERAP2 on the HLA-B*40:02 Peptidome: Implications for HLA-B*27-Negative Ankylosing Spondylitis. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2019, 18, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Li, D.; Xu, W. Association of ankylosing spondylitis with HLA-B27 and ERAP1: Pathogenic role of antigenic peptide. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 80, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, G.E.; Gonzalez, F.; Champsaur, M.; Cado, D.; Shastri, N. The aminopeptidase ERAAP shapes the peptide repertoire displayed by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastall, D.P.W.; Alyaquob, F.S.; O’Connell, P.; Pepelyayeva, Y.; Peters, D.; Godbehere-Roosa, S.; Pereira-Hicks, C.; Aldhamen, Y.A.; Amalfitano, A. Mice expressing human ERAP1 variants associated with ankylosing spondylitis have altered T-cell repertoires and NK cell functions, as well as increased in utero and perinatal mortality. Int. Immunol. 2017, 29, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garboczi, D.N.; Ghosh, P.; Utz, U.; Fan, Q.R.; Biddison, W.E.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the complex between human T-cell receptor, viral peptide and HLA-A2. Nature 1996, 384, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardetzky, T. Not just another Fab: The crystal structure of a TcR-MHC-peptide complex. Structure 1997, 5, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.G.; Boyington, J.C.; Sun, P.D. Natural killer cell recognition of HLA class I molecules. Rev. Immunogenet. 2000, 2, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gill, T.; Asquith, M.; Brooks, S.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Colbert, R.A. Effects of HLA-B27 on Gut Microbiota in Experimental Spondyloarthritis Implicate an Ecological Model of Dysbiosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for Intestinal Bacteria, Viruses, and Fungi in Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339.e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Ferrante, A.; Guggino, G.; Ciccia, F. Gut inflammation in spondyloarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 31, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Younes, J.A.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Gloor, G.B.; Knight, R.; Busscher, H.J. Microbiota restoration: Natural and supplemented recovery of human microbial communities. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielants, H.; Veys, E.M.; De Vos, M.; Cuvelier, C. Increased intestinal permeability in ankylosing spondylitis. Gut 1992, 33, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van Praet, L.; Jacques, P.; Van den Bosch, F.; Elewaut, D. The transition of acute to chronic bowel inflammation in spondyloarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cypers, H.; Van Praet, L.; Varkas, G.; Elewaut, D. Relevance of the gut/joint axis for the management of spondyloarthritis in daily clinical practice. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.; Asquith, M.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Colbert, R.A. The intestinal microbiome in spondyloarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombrello, M.J.; Remmers, E.F.; Tachmazidou, I.; Grom, A.; Foell, D.; Haas, J.P.; Martini, A.; Gattorno, M.; Ozen, S.; Prahalad, S.; et al. HLA-DRB1*11 and variants of the MHC class II locus are strong risk factors for systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15970–15975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurog, J.D.; Chhabra, A.; Colbert, R.A. Ankylosing Spondylitis and Axial Spondyloarthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Bach, M.; Asquith, M.; Lee, A.Y.; Akileswaran, L.; Stauffer, P.; Davin, S.; Pan, Y.; Cambronne, E.D.; Dorris, M.; et al. HLA-B27 and human beta2-microglobulin affect the gut microbiota of transgenic rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, H.C.; Herfarth, H.H.; Ikeda, J.S.; Grenther, W.B.; Hamm, T.E., Jr.; Balish, E.; Taurog, J.D.; Hammer, R.E.; Wilson, K.H.; Sartor, R.B. Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, M.J.; Stauffer, P.; Davin, S.; Mitchell, C.; Lin, P.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Perturbed Mucosal Immunity and Dysbiosis Accompany Clinical Disease in a Rat Model of Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansalone, C.; Utriainen, L.; Milling, S.; Goodyear, C.S. Role of Gut Inflammation in Altering the Monocyte Compartment and Its Osteoclastogenic Potential in HLA-B27-Transgenic Rats. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Zheng, Z.; Shao, T.; Liu, L.; Xie, Z.; Le Chatelier, E.; He, Z.; Zhong, W.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Quantitative metagenomics reveals unique gut microbiome biomarkers in ankylosing spondylitis. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, M.E.; Ciccia, F.; Willner, D.; Warrington, N.; Robinson, P.C.; Gardiner, B.; Marshall, M.; Kenna, T.J.; Triolo, G.; Brown, M.A. Brief Report: Intestinal Dysbiosis in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Li, M. The correlation between intestinal dysbiosis and the development of ankylosing spondylitis. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.; Brooks, S.; Rosenbaum, J.; Asquith, M.; Colbert, R. Novel Inter-omic Analysis Reveals Relationships Between Diverse Gut Microbiota and Host Immune Dysregulation in HLA-B27-Induced Experimental Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breban, M.; Tap, J.; Leboime, A.; Said-Nahal, R.; Langella, P.; Chiocchia, G.; Furet, J.P.; Sokol, H. Faecal microbiota study reveals specific dysbiosis in spondyloarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouz, D.; Omarbekova, A.; Heguy, A.; Schwudke, D.; Gisch, N.; Rovin, B.H.; Caricchio, R.; Buyon, J.P.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Silverman, G.J. Lupus nephritis is linked to disease-activity associated expansions and immunity to a gut commensal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, M.T.; Kenny, D.J.; Cassilly, C.D.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Clardy, J. Ruminococcus gnavus, a member of the human gut microbiome associated with Crohn’s disease, produces an inflammatory polysaccharide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12672–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, J.S.; Burakoff, R. Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 7, 235–241. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Sternes, P.R.; Wang, M.; Song, J.; Morrison, M.; Li, T.; Zhou, L.; Wu, X.; He, F.; Zhu, J.; et al. Shotgun metagenomics reveals an enrichment of potentially cross-reactive bacterial epitopes in ankylosing spondylitis patients, as well as the effects of TNFi therapy upon microbiome composition. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharip, A.; Kunz, J. Understanding the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101461
Sharip A, Kunz J. Understanding the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(10):1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101461
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharip, Aigul, and Jeannette Kunz. 2020. "Understanding the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis" Biomolecules 10, no. 10: 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101461
APA StyleSharip, A., & Kunz, J. (2020). Understanding the Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis. Biomolecules, 10(10), 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10101461




