Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives from Different Starting Materials
Abstract
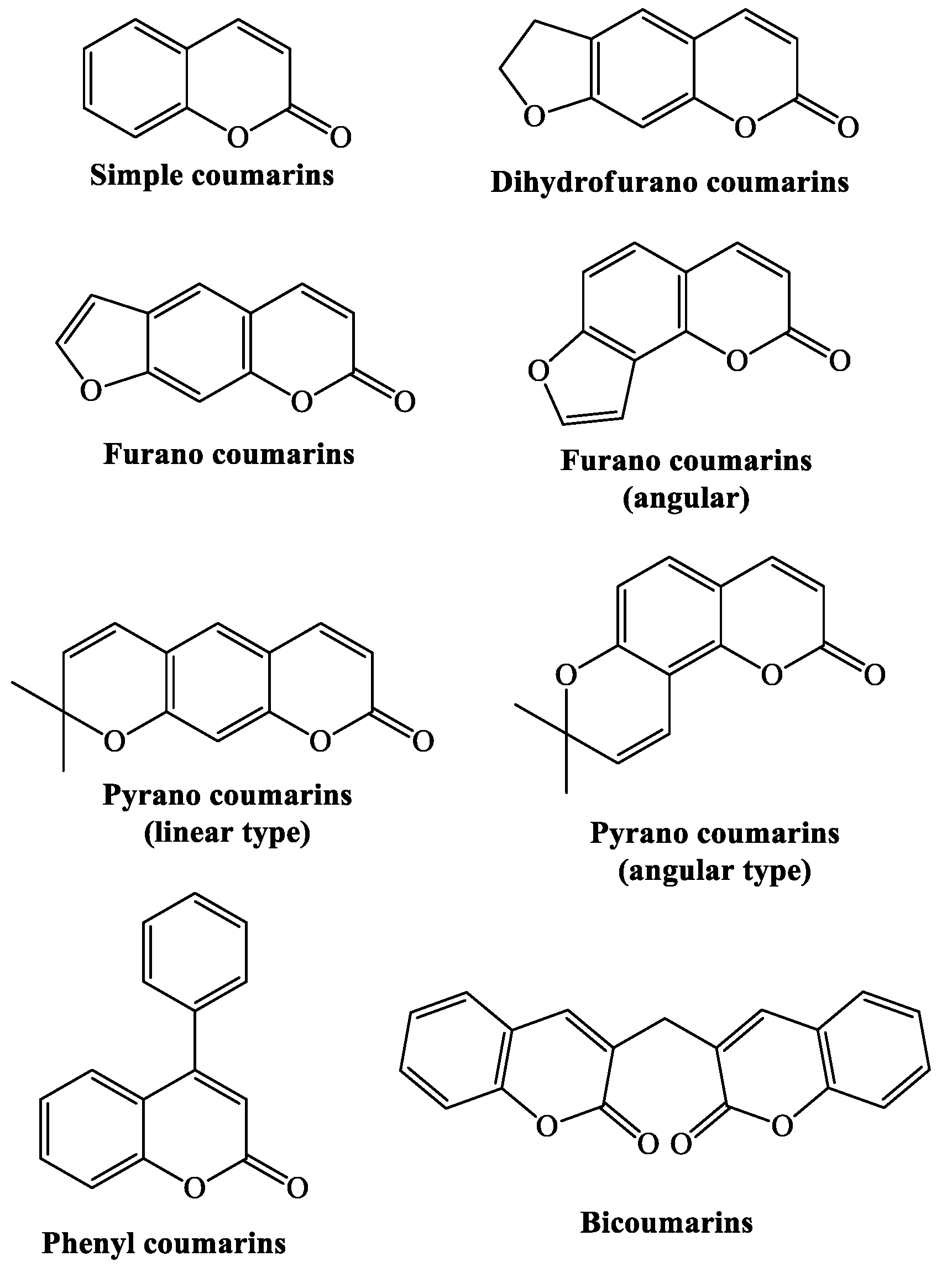
1. Introduction
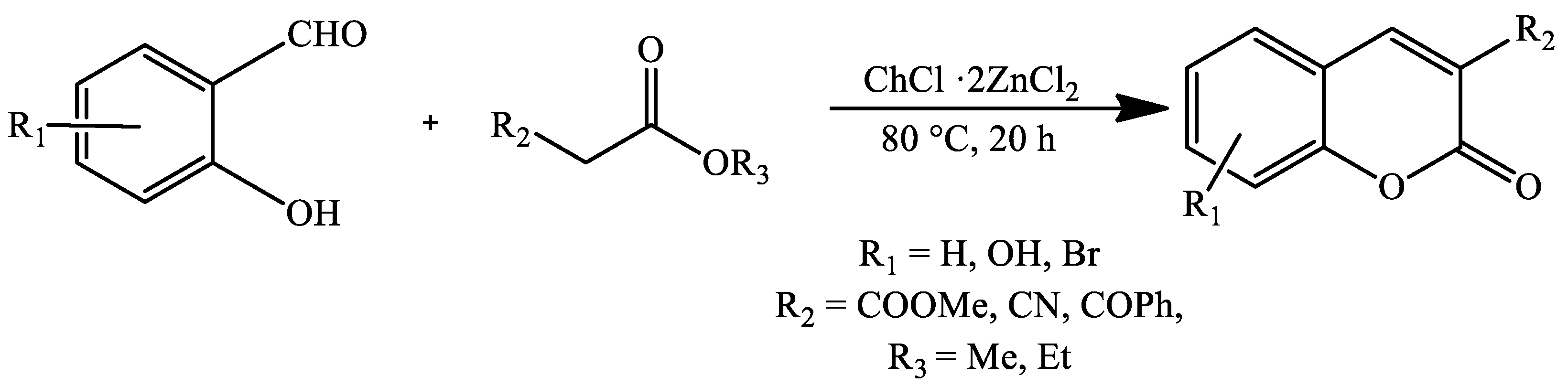
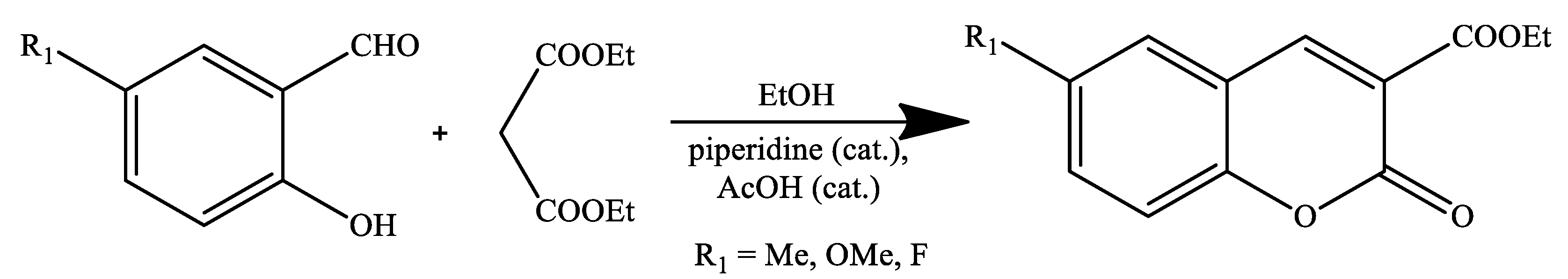
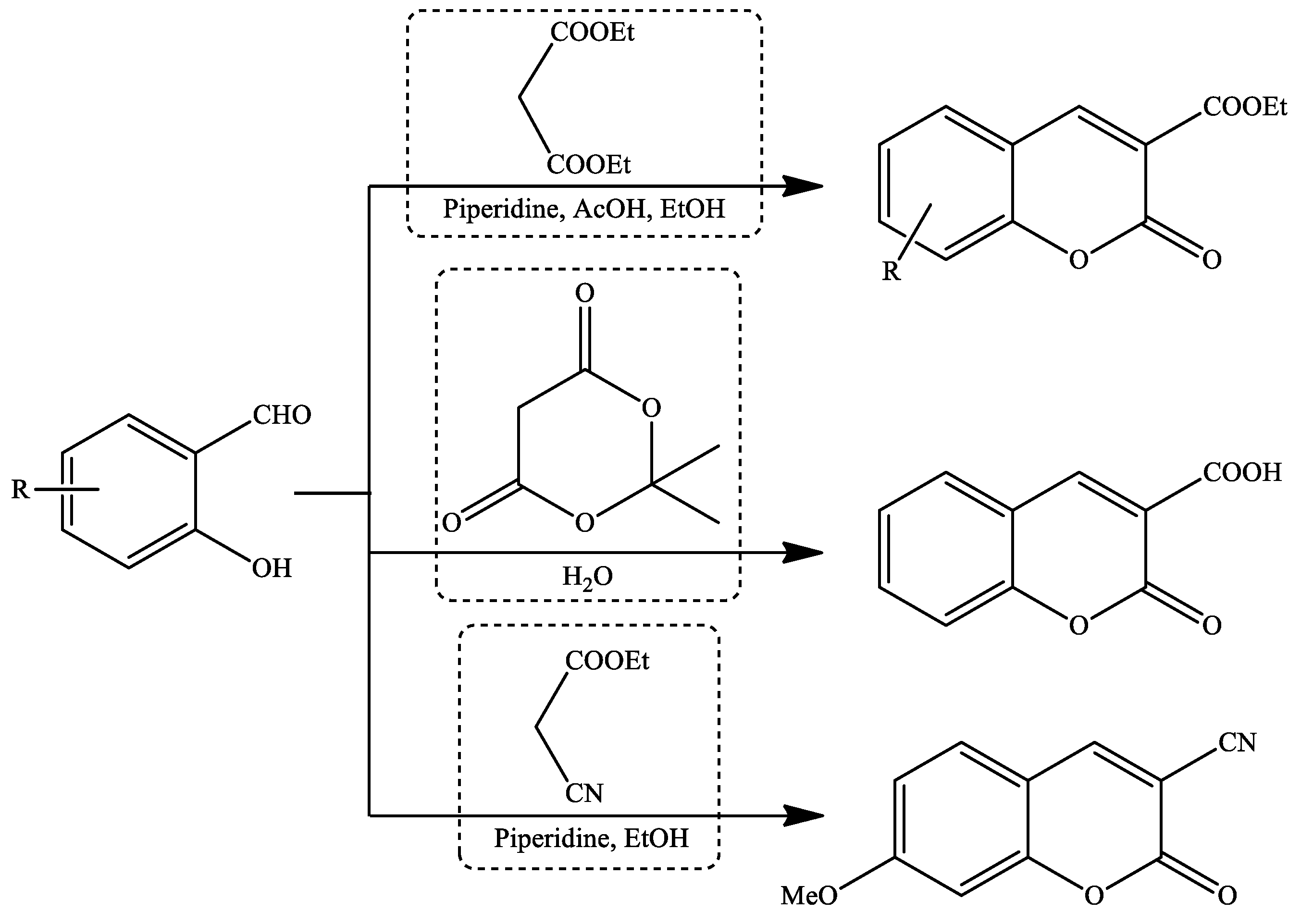
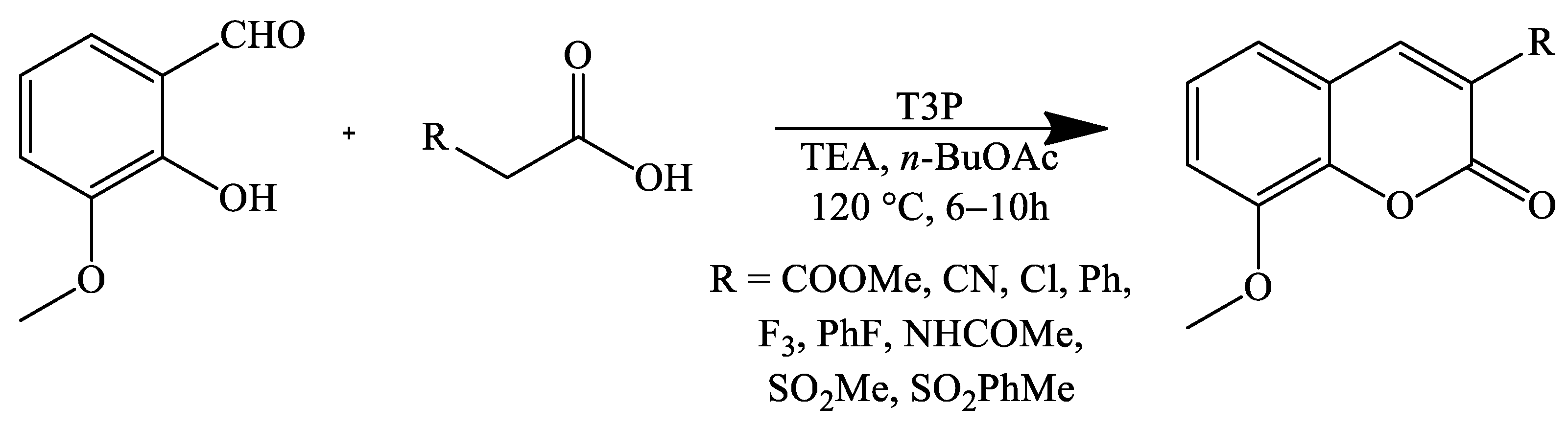
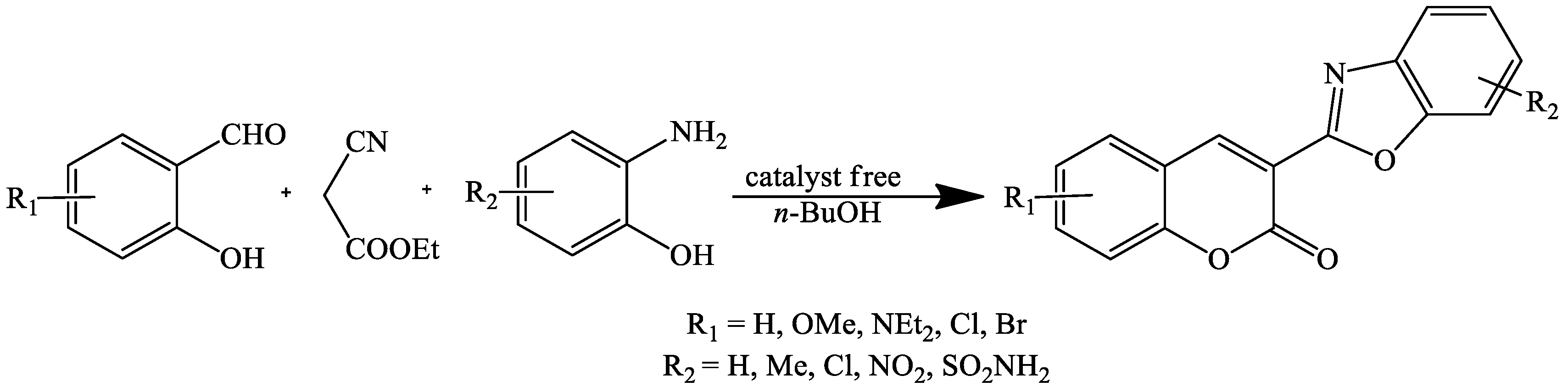
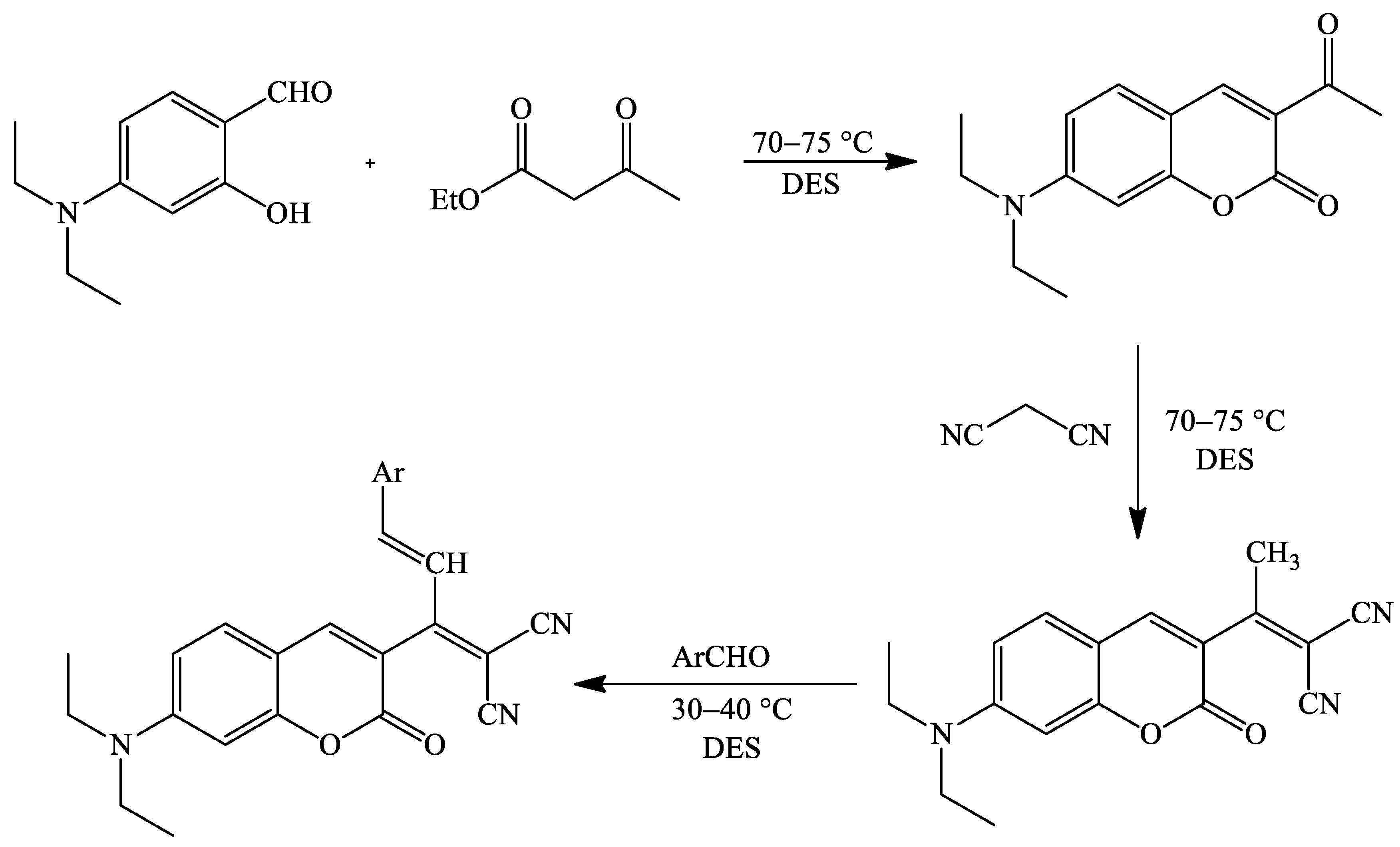
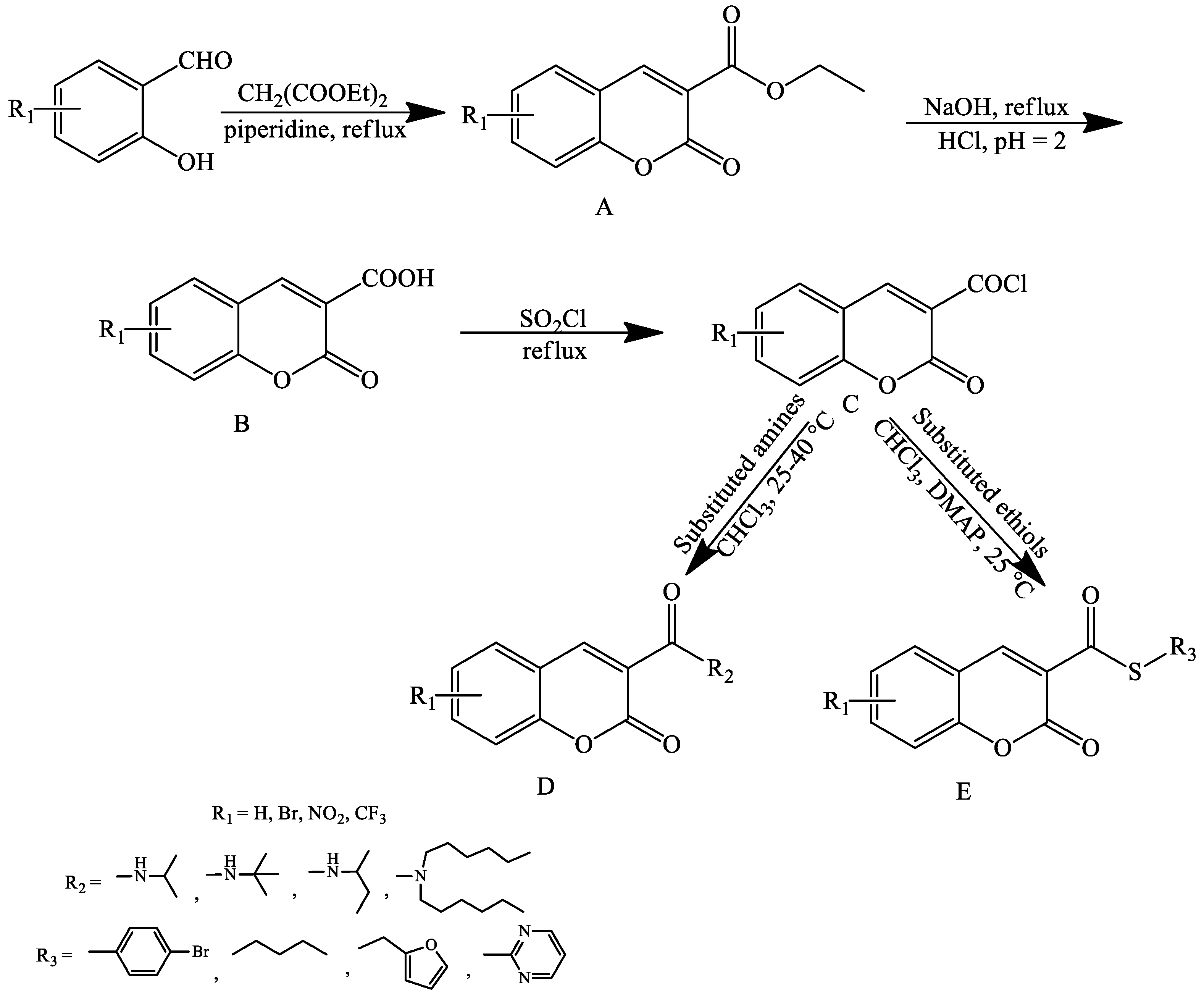
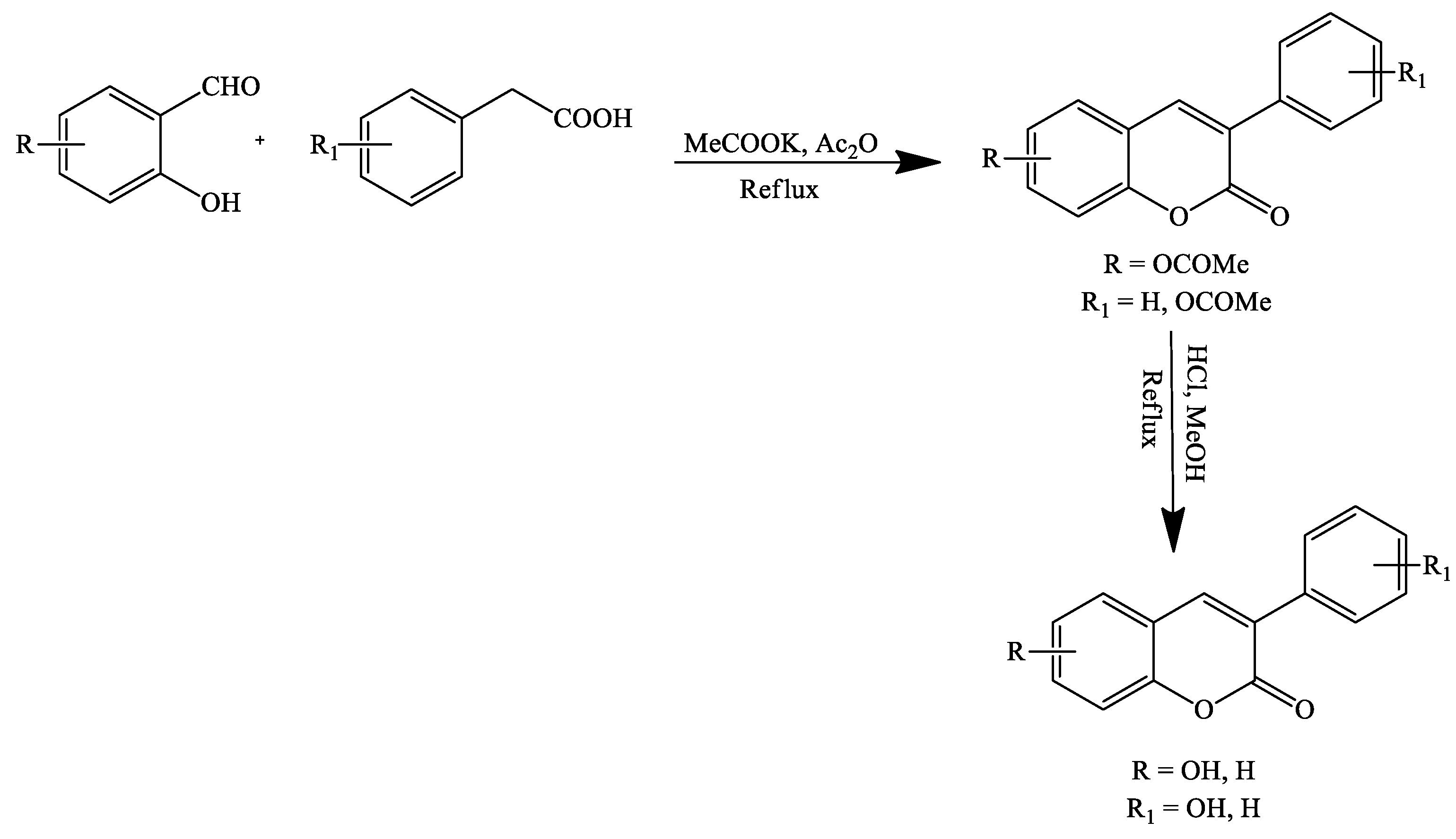
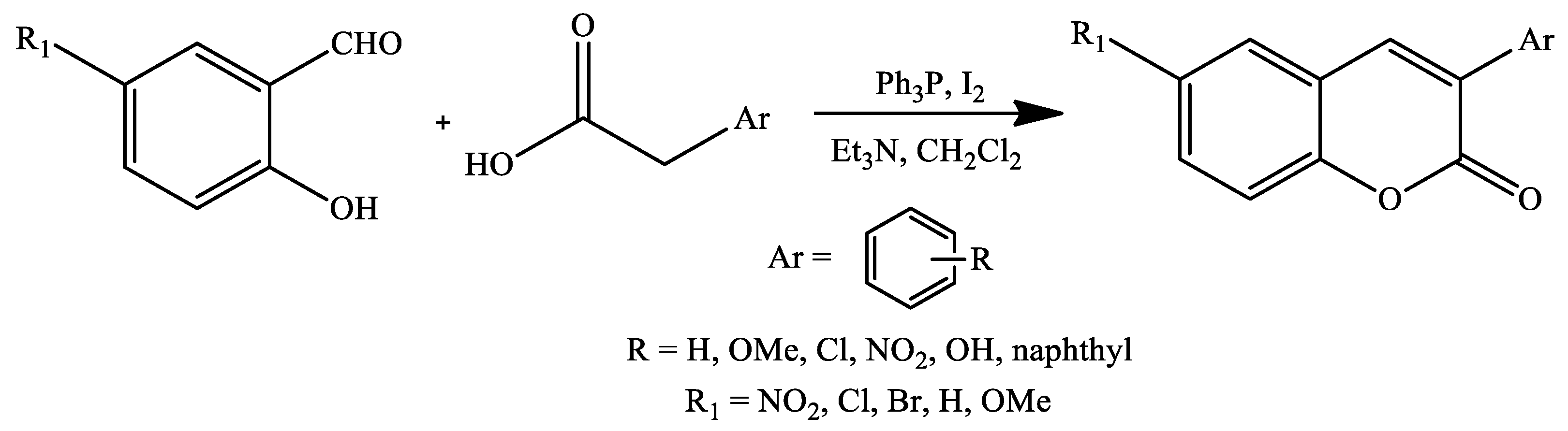
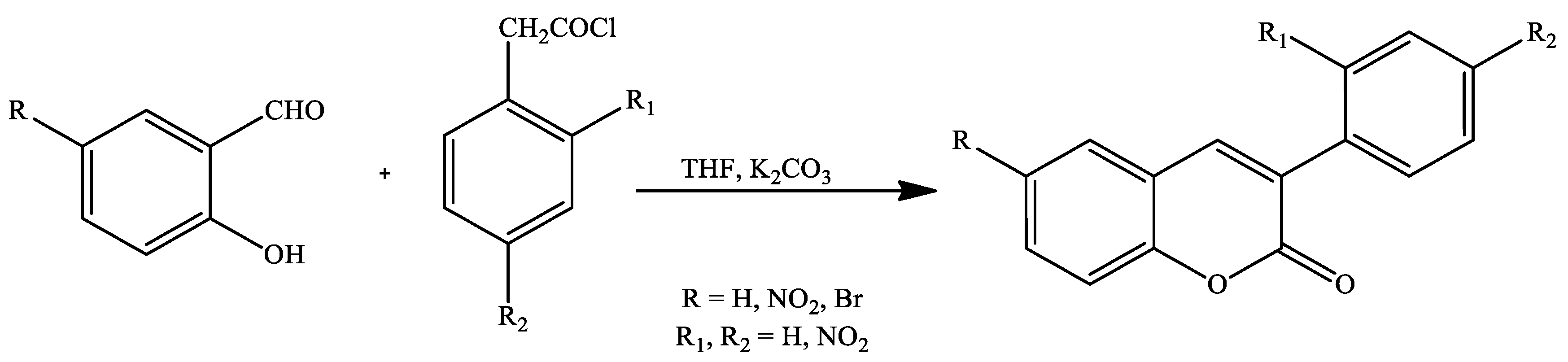
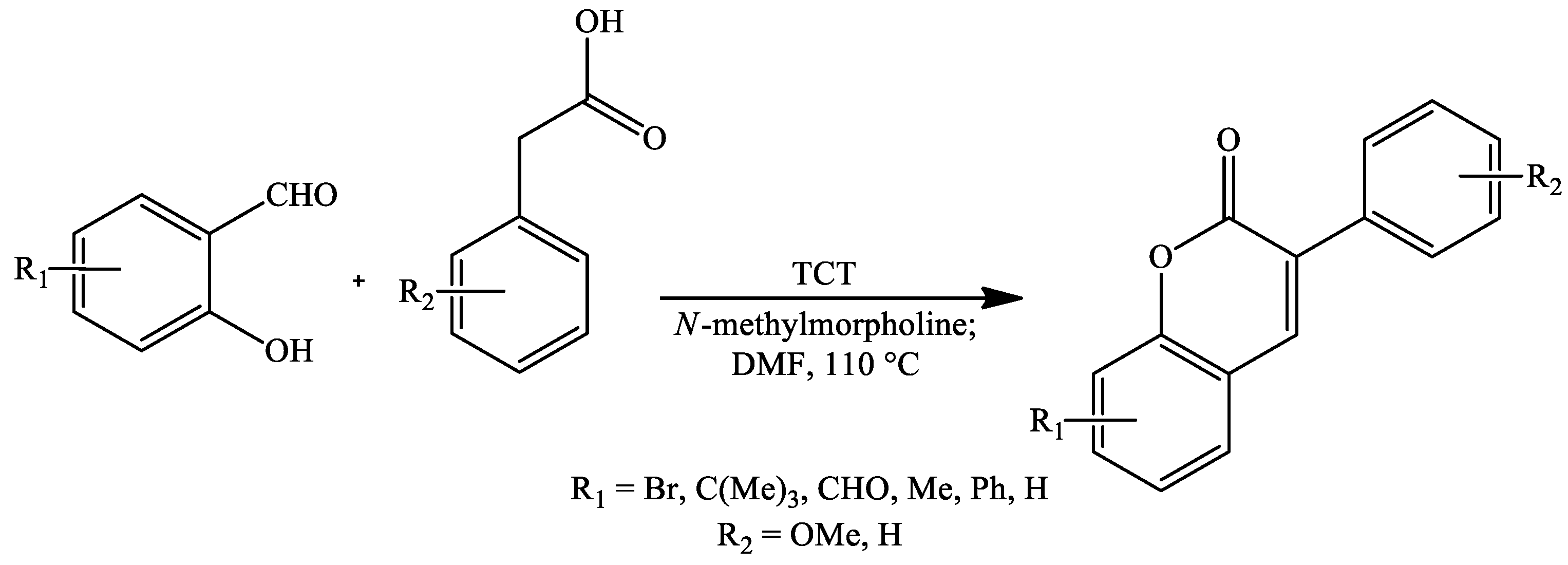
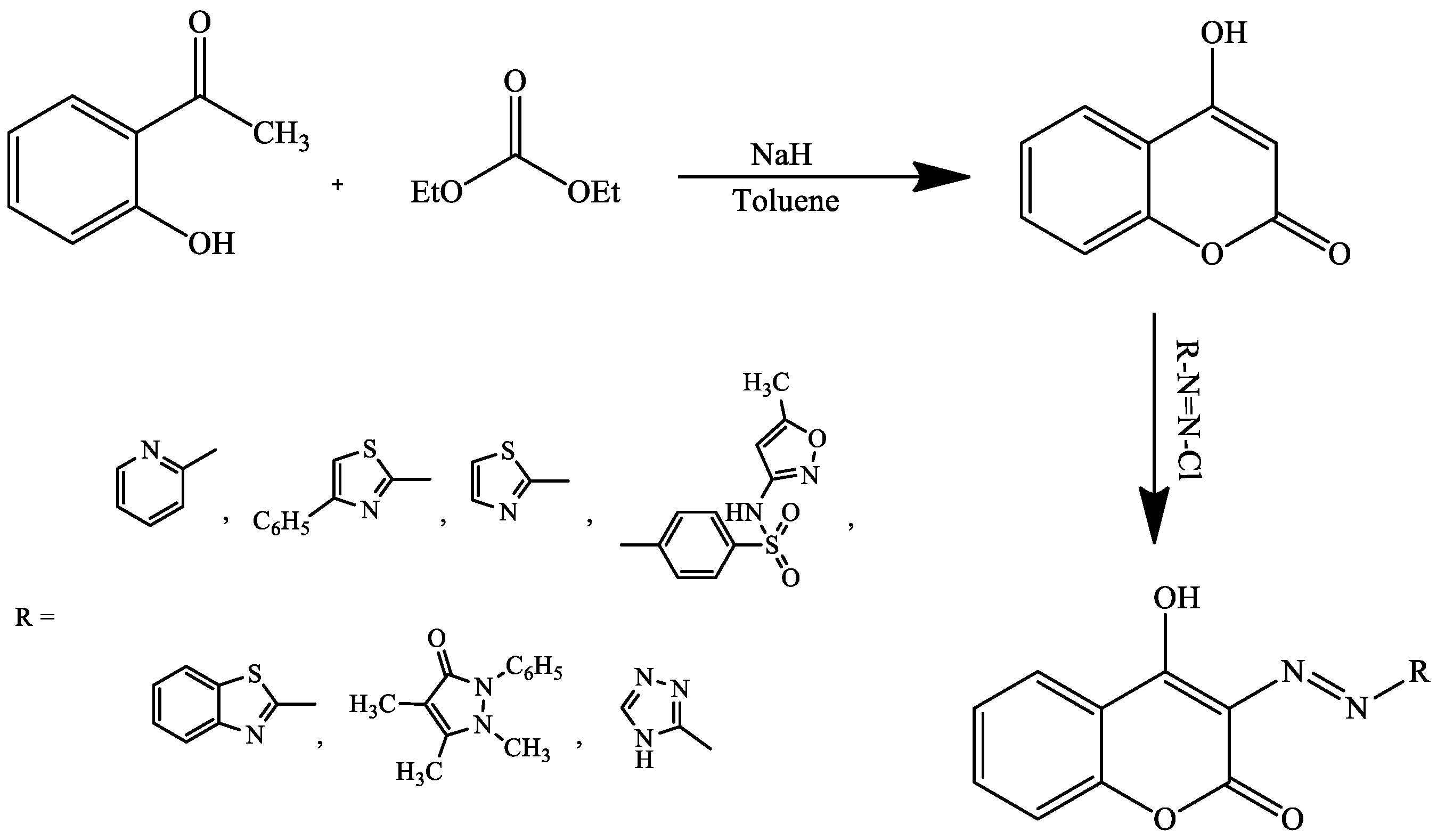
2. Coumarin Derivatives Synthesized from Aldehydes
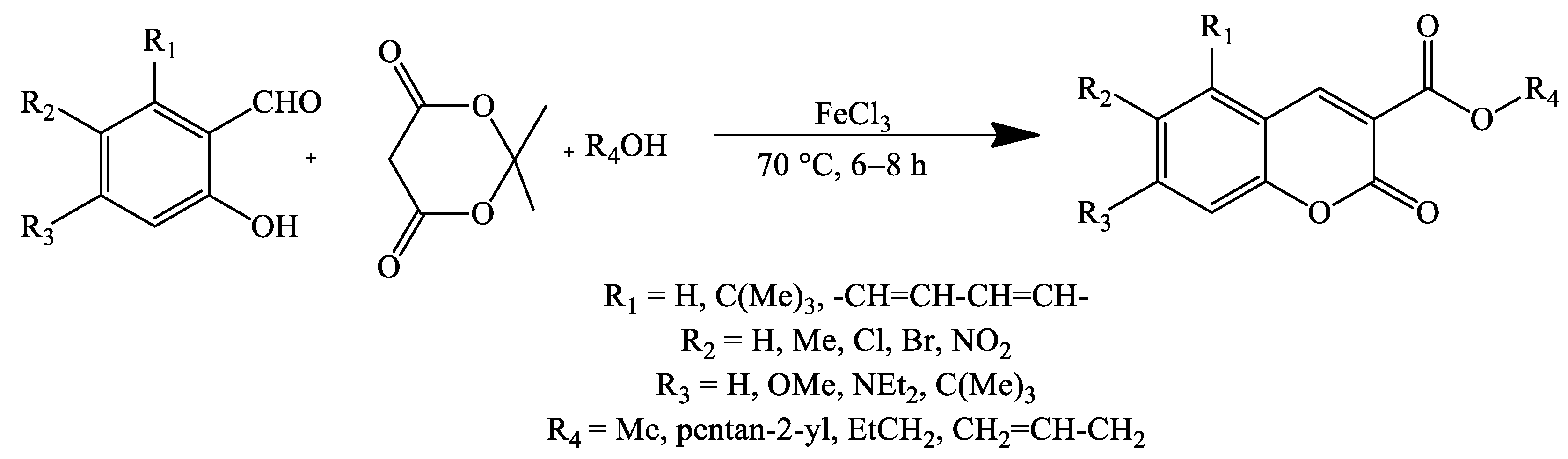
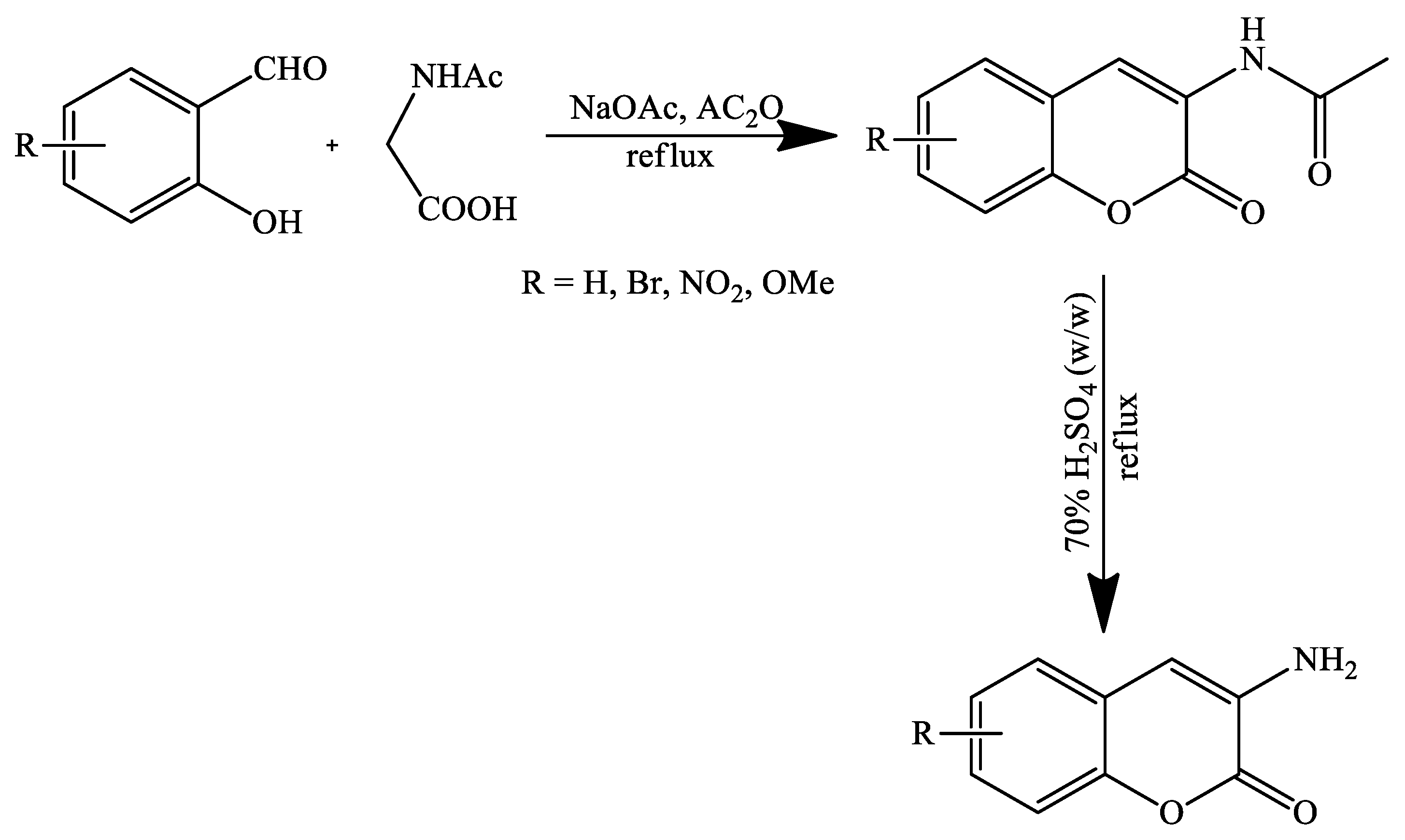
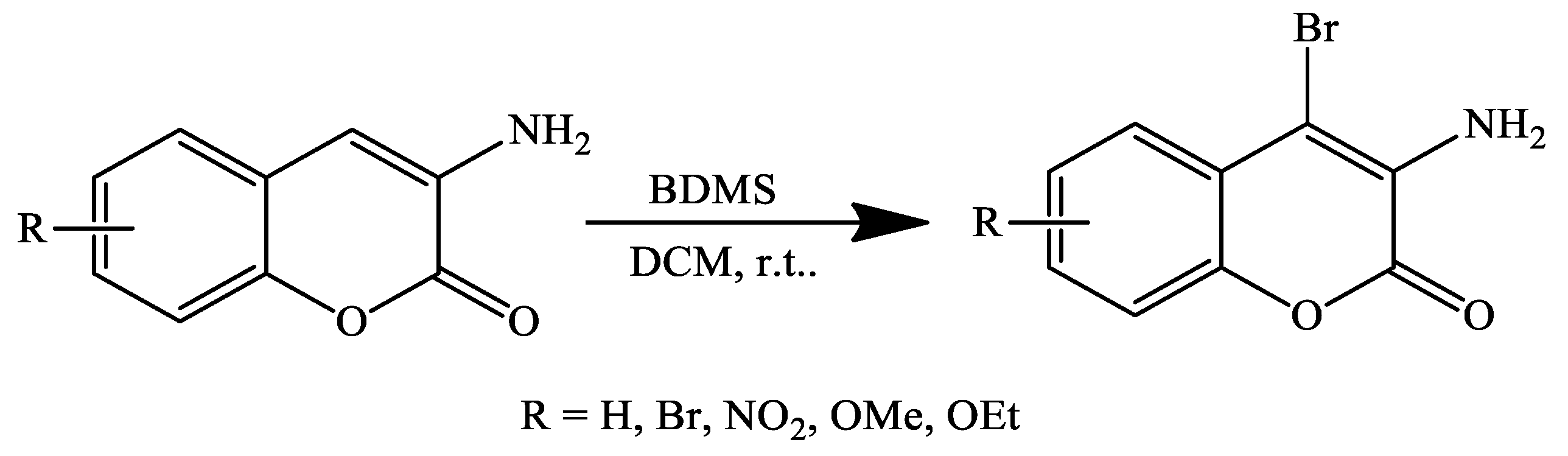
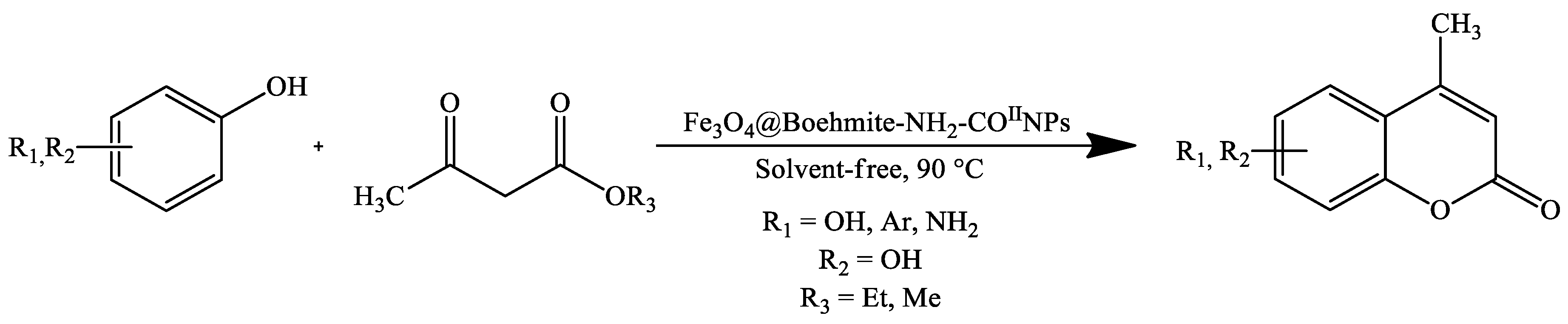
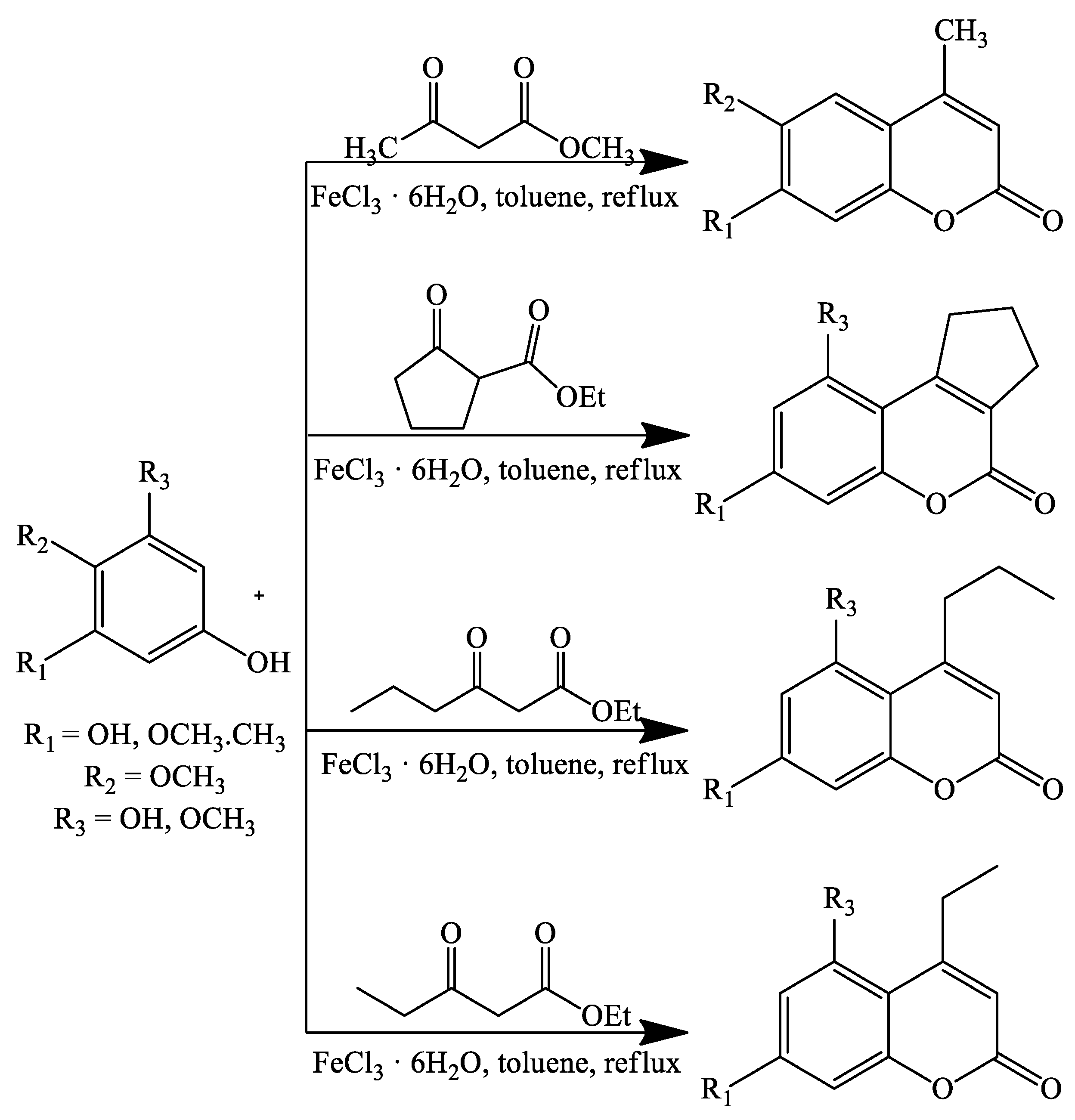
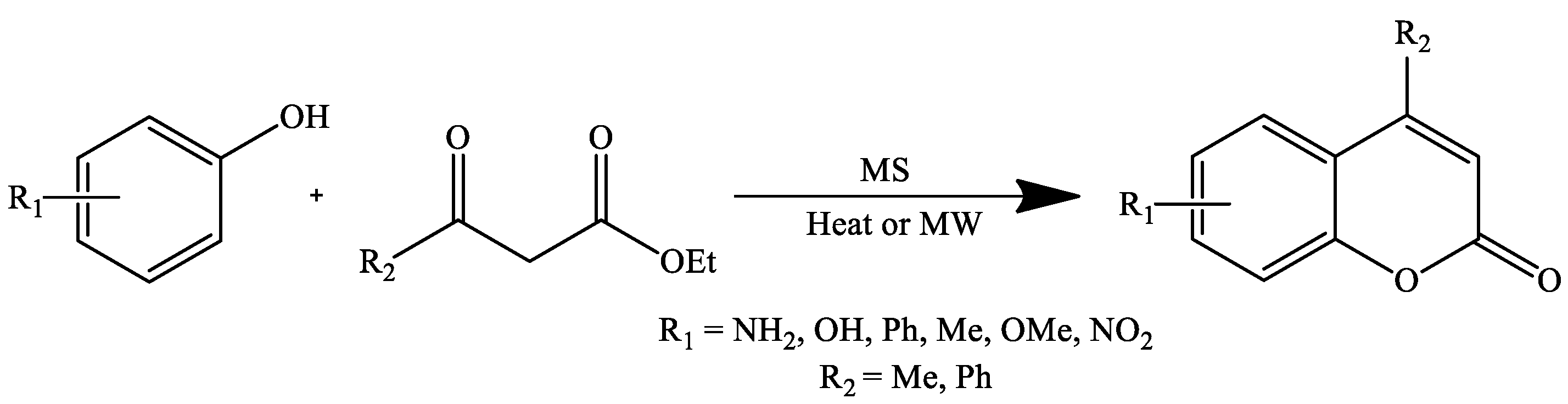
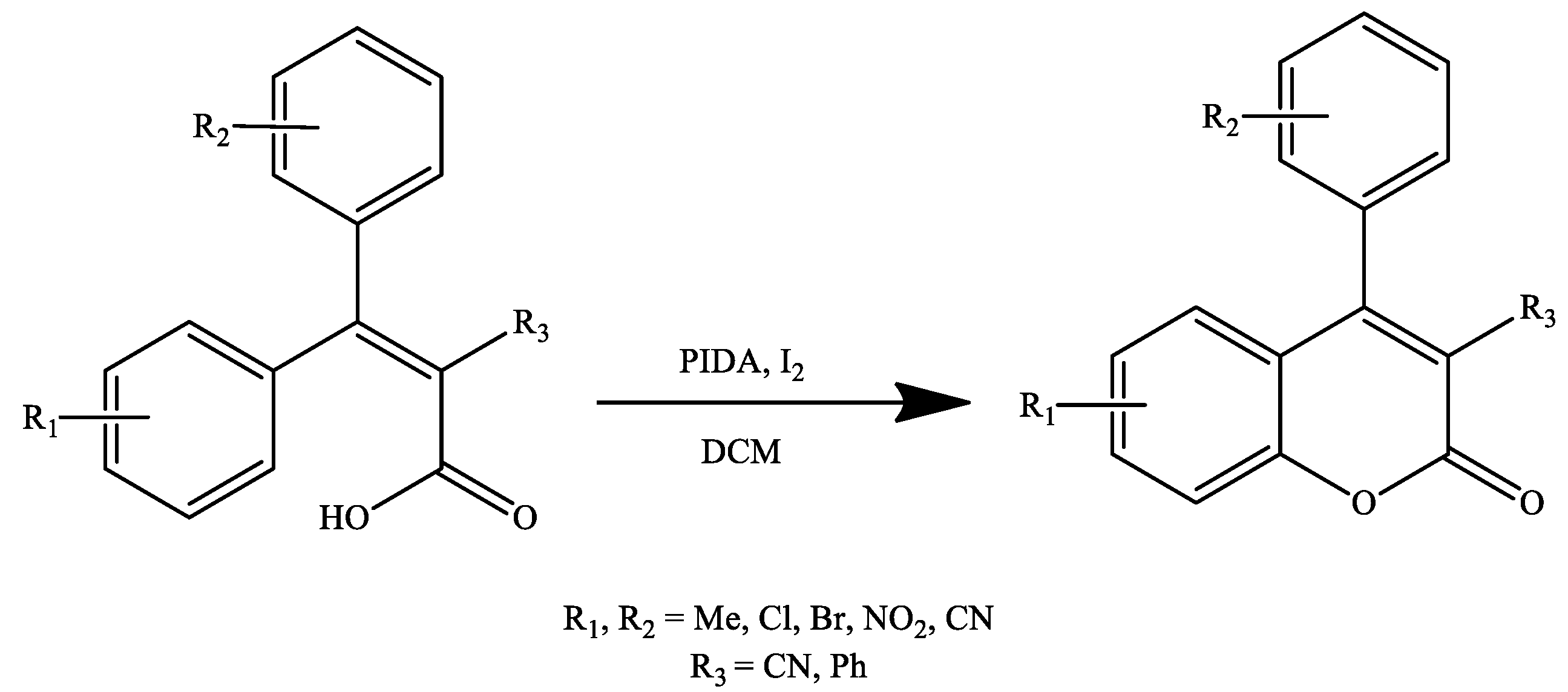
3. Coumarin Derivatives Synthesized from Phenols
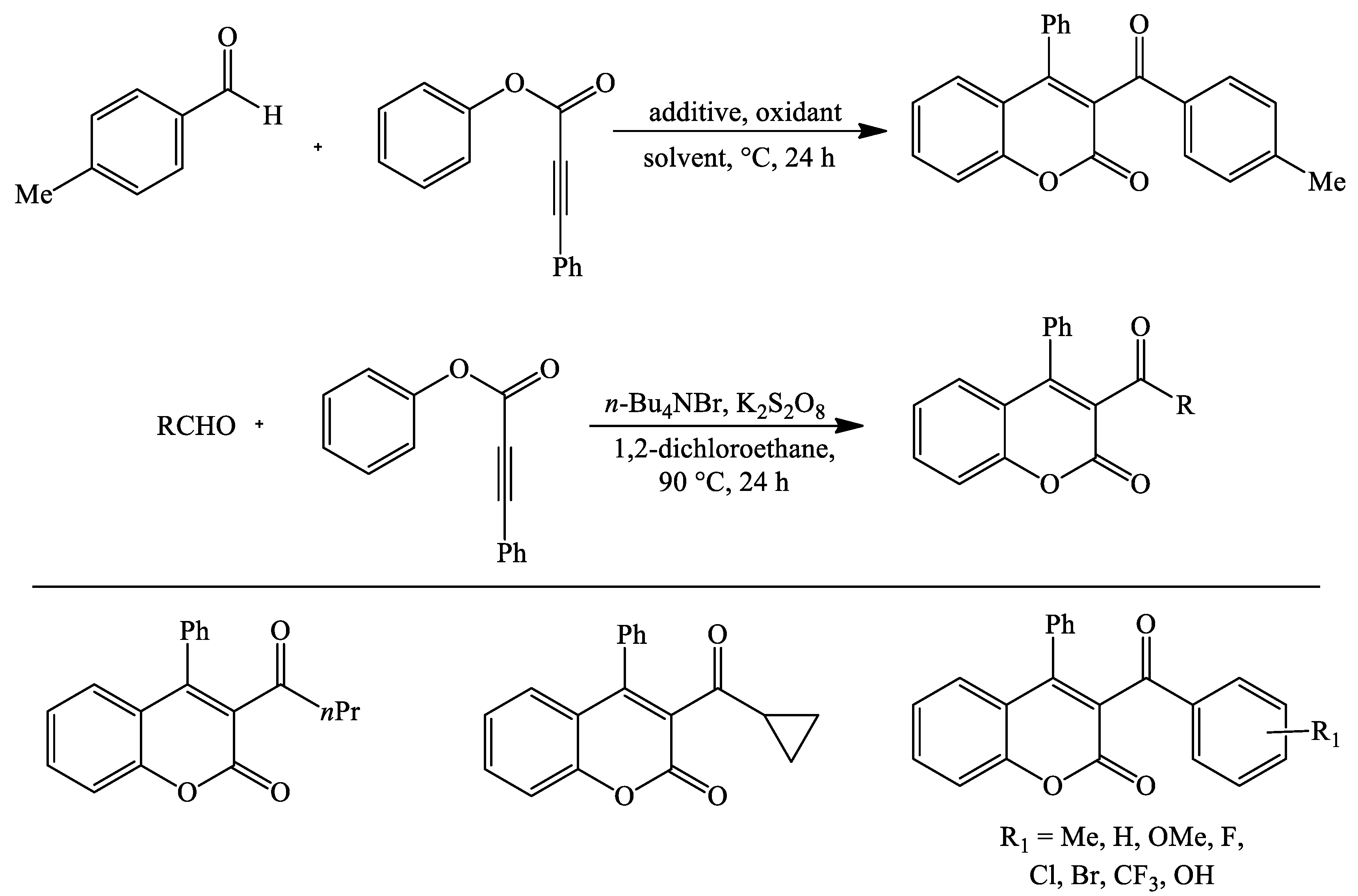
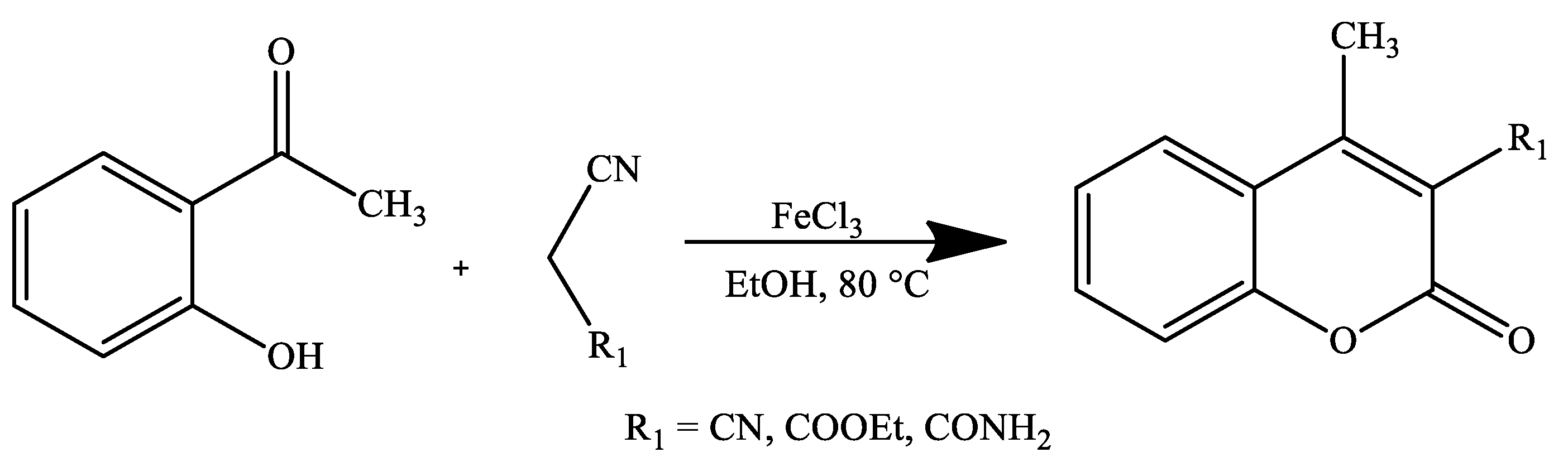
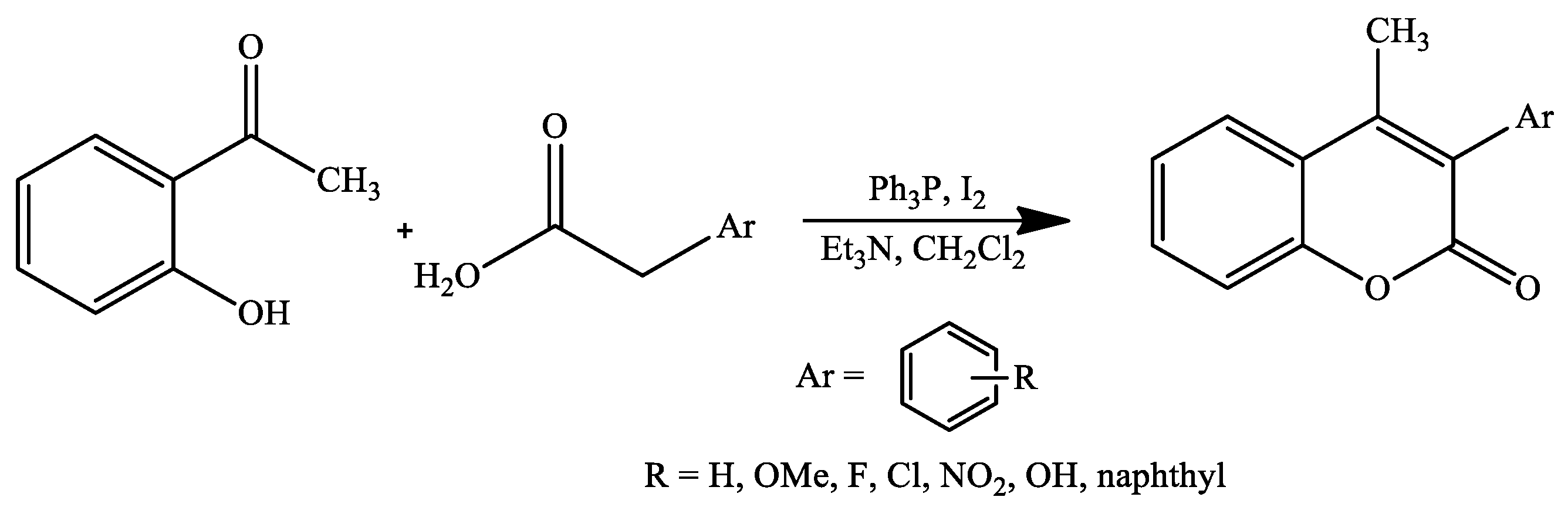
4. Coumarin Derivatives Synthesized from Ketones
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nikhil, B.; Shikha, B.; Anil, P.; Prakash, N.B. Diverse pharmacological activities of 3-substituted coumarins: A review. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2012, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kontogiorgis, C.; Detsi, A.; Hadjipavlou-Litina, D. Coumarin-based drugs: A patent review (2008–present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Rashmi, V.; Odhav, B. Review on Natural Coumarin Lead Compounds for Their Pharmacological Activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prahadeesh, N.; Sithambaresan, M.; Mathiventhan, U. A Study on Hydrogen Peroxide Scavenging Activity and Ferric Reducing Ability of Simple Coumarins. Emerg. Sci. J. 2018, 2, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, M.V.; Kulkarni, G.M.; Lin, C.-H.; Sun, C.-M. Recent advances in coumarins and 1-azacoumarins as versatile biodynamic agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2795–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bairagi, S.H.; Salaskar, P.P.; Loke, S.D.; Surve, N.N.; Tandel, D.V.; Dusara, M.D. Medicinal significance of coumarins: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, A.; Singla, R.; Jaitak, V. Coumarins as anticancer agents: A review on synthetic strategies, mechanism of action and SAR studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 476–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, W.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Han, S.-I.; Ra, J.-E.; Seo, K.H.; Jang, K.C.; Lee, J.H. Identification and characterisation of coumarins from the roots of Angelica dahurica and their inhibitory effects against cholinesterase. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, D.; Zhou, T.; Qin, N.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Hua, H. Coumarins from the roots of Angelica dahurica with antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranshahi, M.; Kalategi, F.; Sahebkar, A.; Sardashti, A.; Schneider, B. New sesquiterpene coumarins from the roots of Ferula flabelliloba. Pharm. Boil. 2010, 48, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.-W.; Zheng, Y.-Q.; Chen, Y.-S.; Zhao, S.-M.; Ji, C.-J.; Tan, N.-H. Coumarins from roots of Clausena excavata. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, M.; Monsef-Esfehani, H.; Saeidnia, S.; Dastan, D.; Gohari, A. Antioxidative Coumarins from the Roots of Ferulago subvelutina. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 1875–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.R.; Devkota, H.P.; Yahara, S. Chemical Analysis of Flowers of Bombax ceiba from Nepal. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 583–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Kiruba, S.; Mahesh, M.; Nisha, S.; Miller, P.Z.; Ben, C.; Jeeva, S. Phytochemical constituents and antibacterial efficacy of the flowers of Peltophorum pterocarpum (DC.) Baker ex Heyne. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2011, 4, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicel, A.; Wolbis, M. Coumarins from the flowers of Trifolium repens. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2012, 48, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joselin, J.; Brintha, T.S.S.; Florence, A.R.; Jeeva, S. Screening of select ornamental flowers of the family Apocynaceae for phytochemical constituents. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2012, 2, S260–S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tang, F.; Yue, Y.; Yao, X.; Wei, Q.; Yu, J. Simultaneous Determination of 12 Coumarins in Bamboo Leaves by HPLC. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.-H.; Zhao, B.T.; Kim, O.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, J.S.; Min, B.S.; Woo, M.H. Anti-inflammatory terpenylated coumarins from the leaves of Zanthoxylum schinifolium with α-glucosidase inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chang, T.-H.; Lim, Y.-P.; Sung, P.-J.; Lee, T.-H.; Chen, J.-J. New coumarins and anti-inflammatory constituents from Zanthoxylum avicennae. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakunpak, A.; Matsunami, K.; Otsuka, H.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Isolation of new monoterpene coumarins from Micromelum minutum leaves and their cytotoxic activity against Leishmania major and cancer cells. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 458–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruľová-Poracká, V.; Repcak, M.; Vilkova, M.; Imrich, J. Coumarins of Matricaria chamomilla L.: Aglycones and glycosides. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.S.S.A.; Sukari, M.A.; Rahmani, M.; Kitajima, M.; Aimi, N.; Ahpandi, N.J. Coumarins from Murraya paniculata (Rutaceae). Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2010, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Yue, Y.-D.; Tang, F.; Guo, X.-F. Coumarins from the leaves of Bambusa pervariabilis McClure. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-L.; Li, Y.; Qin, N.-B.; Li, D.-H.; Liu, Z.-G.; Liu, Q.; Hua, H.-M. Four new coumarins from the leaves of Calophyllum inophyllum. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.M.; Imanzadeh, G.; Davari, M. Coumarins from Zosima absinthifolia seeds, with allelopatic effects. Eur. Asian J. Biosci. 2010, 4, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Si, J. Sesquiterpene coumarins from seeds of Ferula sinkiangensis. Fitoterapia 2015, 103, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Cao, L.; Lv, N.; Chen, G.; Zhu, J.; Si, J. Two new sesquiterpene coumarins from the seeds of Ferula sinkiangensis. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 13, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dien, P.H.; Nhan, N.T.; Le Thuy, H.T.; Quang, D.N. Main constituents from the seeds of Vietnamese Cnidium monnieri and cytotoxic activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 2107–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Dugrand, A.; Olry, A.; Duval, T.; Hehn, A.; Froelicher, Y.; Bourgaud, F.; Dugrand-Judek, A. Coumarin and Furanocoumarin Quantitation in Citrus Peel via Ultraperformance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10677–10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanavade, M.J.; Jalkute, C.B.; Ghosh, J.S.; Sonawane, K.D. Study antimicrobial activity of lemon (Citrus lemon L.) peel extract. Br. J. Pharm. Toxicol. 2011, 2, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, Y.; Hiramitsu, M. Isolation and extraction of antimicrobial substances against oral bacteria from lemon peel. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, S.; Chen, Y.; Saravanan, D.; Sundram, K.M.; Latha, L.Y. Extraction, isolation and characterization of bioactive compounds from plants’ extracts. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekariya, R.H.; Patel, H.D. Recent advances in the synthesis of coumarin derivatives via Knoevenagel condensation: A review. Synth. Commun. 2014, 44, 2756–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, Z.; Hu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Jiang, C.; Jin, L.; Shang, Y. FeCl 3-Catalyzed Cascade Reaction: An Efficient Approach to Functionalized Coumarin Derivatives. Synth. Commun. 2014, 44, 1507–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, M. Pharmacologically potentials of different substituted coumarin derivatives. Chem. Int. 2015, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Barot, K.P.; Jain, S.V.; Kremer, L.; Singh, S.; Ghate, M.D. Recent advances and therapeutic journey of coumarins: Current status and perspectives. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 2771–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, N.S.; Pattan, S.R.; Dengale, S.S.; Musmade, D.S.; Shelar, M.; Tambe, V.; Hole, M.B. Synthetic and pharmacological profiles of coumarins: A review. Sch. Res. Libr. 2010, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
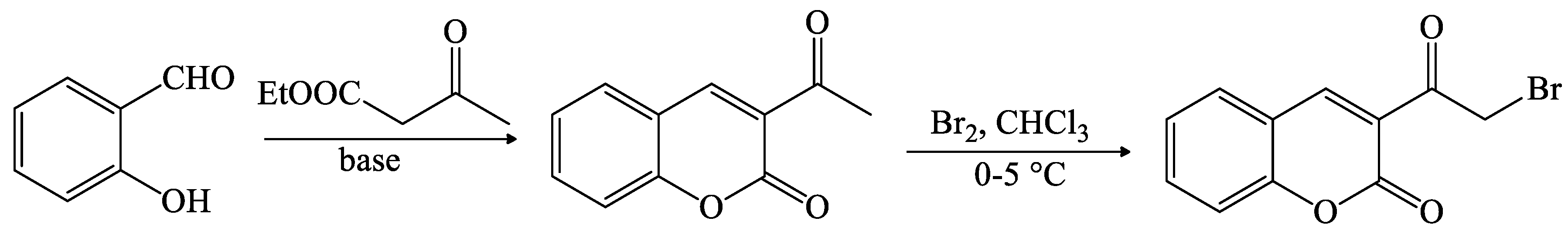
- Abdou, M.M. 3-Acetyl-4-hydroxycoumarin: Synthesis, reactions and applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3664–S3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ayed, A.S. Synthesis, Spectroscopy and Electrochemistry of New 3-(5-Aryl-4,5-Dihydro-1H-Pyrazol-3-yl)-4-Hydroxy-2H-Chromene-2-One 4, 5 as a Novel Class of Potential Antibacterial and Antioxidant Derivatives. Int. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 1, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majedy, Y.K.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Mohamad, A.B. Coumarins: The Antimicrobial agents. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2017, 8, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, K.K.; Khosa, M.K.; Jahan, N.; Nosheen, S. Short communication: Synthesis and applications of Coumarin. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 23, 449–454. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ren, Z.-L.; Wang, W.; Gong, J.-X.; Chu, M.-J.; Ma, Q.-W.; Wang, J.-C.; Lv, X.-H. Novel coumarin-pyrazole carboxamide derivatives as potential topoisomerase II inhibitors: Design, synthesis and antibacterial activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, J.; Kumar, P.S.; Mekap, S.K. Synthesis, spectral characterization of some new 3-heteroaryl azo 4-hydroxy coumarin derivatives and their antimicrobial evaluation. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2015, 9, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekariya, R.H.; Patel, K.D.; Rajani, D.P.; Rajani, S.D.; Patel, H.D. A one pot, three component synthesis of coumarin hybrid thiosemicarbazone derivatives and their antimicrobial evolution. J. Assoc. Arab. Univ. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 23, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basanagouda, M.; Shivashankar, K.; Kulkarni, M.V.; Rasal, V.P.; Patel, H.; Mutha, S.S.; Mohite, A.A. Synthesis and antimicrobial studies on novel sulfonamides containing 4-azidomethyl coumarin. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, J.N.; Soman, S.S. Reactions of coumarin-3-carboxylate, its crystallographic study and antimicrobial activity. Pharma Chem. 2014, 6, 396–403. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, K.B.; Nimavat, K.S.; Jani, G.R.; Hathi, M.V. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of coumarin derivatives metal complexes: An in vitro evaluation. Orbital Electron. J. Chem. 2009, 1, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Li, S.Q.; Hao, S.H. New angular oxazole-fused coumarin derivatives: Synthesis and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiery, A.A.; Al-Majedy, Y.K.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B. Novel macromolecules derived from coumarin: Synthesis and antioxidant activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.J.; Mura, F.; Vazquez-Rodriguez, S.; Borges, F.; Santana, L.; Uriarte, E.; Olea-Azar, C. Study of Coumarin-Resveratrol Hybrids as Potent Antioxidant Compounds. Molecules 2015, 20, 3290–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cruz, K.; Moncada-Basualto, M.; Morales-Valenzuela, J.; Barriga-González, G.; Navarrete-Encina, P.; Núñez-Vergara, L.; Squella, J.; Olea-Azar, C.; Barriga, G. Synthesis and antioxidant study of new polyphenolic hybrid-coumarins. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamallu, R.; Srinivasan, B.; Ningappa, M.B.; Kariyappa, A.K. Synthesis of novel coumarin appended bis(formylpyrazole) derivatives: Studies on their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.A.I.; Marzouk, M.I.; El-Kazak, A.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Some New Coumarins with in Vitro Antitumor and Antioxidant Activity and High Protective Effects against DNA Damage. Molecules 2016, 21, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B.; Singh, N. A review on coumarins as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, S.M.; Khoobi, M.; Nadri, H.; Moradi, A.; Emami, S.; Jalili-Baleh, L.; Jafarpour, F.; Moghadam, F.H.; Foroumadi, A.; Shafiee, A. Synthesis and Anticholinergic Activity of 4-hydroxycoumarin Derivatives Containing Substituted Benzyl-1,2,3-triazole Moiety. Chem. Boil. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.F.; Khoobi, M.; Nadri, H.; Sakhteman, A.; Moradi, A.; Emami, S.; Foroumadi, A.; Shafiee, A. Synthesis and evaluation of 4-substituted coumarins as novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 64, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Z.; Sun, W.W.; Bo, L.; Wang, J.Q.; Xiu, C.; Tang, W.J.; Shi, J.B.; Zhou, H.P.; Liu, X.H. New arylpyrazoline-coumarins: Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. 3-Arylcoumarins: Synthesis and potent anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5432–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo, D.; Sancho, R.; Bedoya, L.M.; López-Pérez, J.L.; Del Olmo, E.; Muñoz, E.; Alcami, J.; Gupta, M.P.; Feliciano, A.S. 3-Phenylcoumarins as Inhibitors of HIV-1 Replication. Molecules 2012, 17, 9245–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, S.; Dadashpour, S. Current developments of coumarin-based anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 102, 611–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keri, R.S.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Nagaraja, B.M.; Santos, M.A. Recent progress in the drug development of coumarin derivatives as potent antituberculosis agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 100, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoudad, S.; Darweesh, S.K.; Leening, M.J.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Hofman, A.; Van Der Lugt, A.; Stricker, B.H.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W. Use of Coumarin Anticoagulants and Cerebral Microbleeds in the General Population. Stroke 2014, 45, 3436–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.Z.; Osman, H.; Ali, M.A.; Ahsan, M.J.; Ahsan, M.J. Therapeutic potential of coumarins as antiviral agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 236–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijayabandara, M.D.J.; Choudhary, M.I.; Adhikari, A. Characterization of an anti-hyperglycemic coumarin from the fruits of Averrhoa. P. Ann. Sci. Sess. Fac. Med. Sci. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzipour, F.; Tavakol, H. The synthesis of coumarin derivatives using choline chloride/zinc chloride as a deep eutectic solvent. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2016, 13, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadtare, S.B.; Shankarling, G.S. Greener coumarin synthesis by Knoevenagel condensation using biodegradable choline chloride. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2012, 10, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, Y. Preparation of 3-Acyl-4-arylcoumarins via Metal-Free Tandem Oxidative Acylation/Cyclization between Alkynoates with Aldehydes. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 80, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suljić, S.; Pietruszka, J. Synthesis of 3-Arylated 3,4-Dihydrocoumarins: Combining Continuous Flow Hydrogenation with Laccase-Catalysed Oxidation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmachari, G. Room Temperature One-Pot Green Synthesis of Coumarin-3-carboxylic Acids in Water: A Practical Method for the Large-Scale Synthesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2350–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
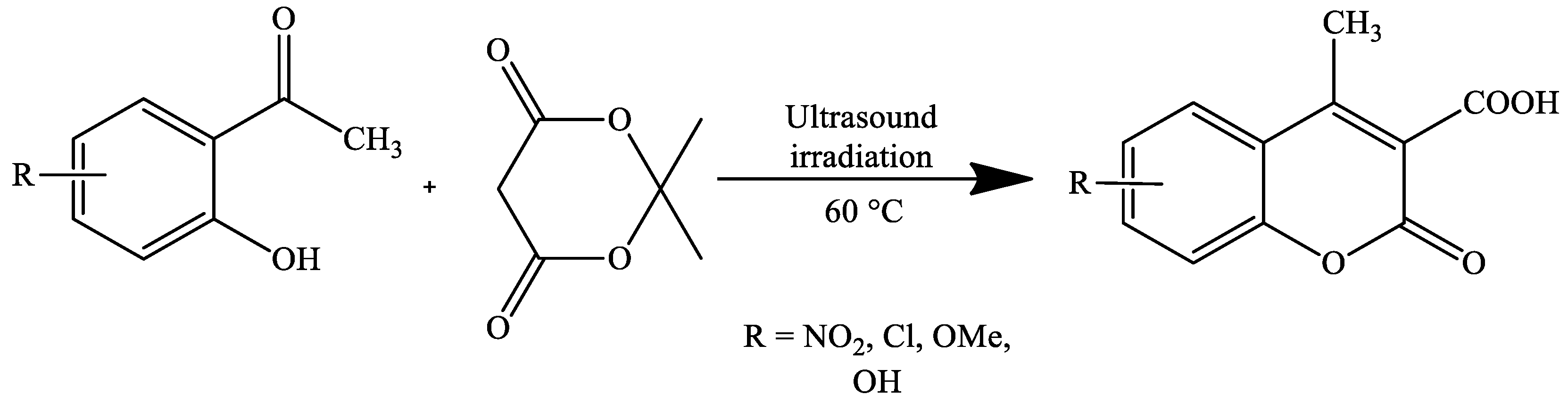
- Pinto, L.D.S.; De Souza, M.V.N. Sonochemistry as a General Procedure for the Synthesis of Coumarins, Including Multigram Synthesis. Synthesis 2017, 49, 2677–2682. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, D.; Mukhtar, S.; Alsharif, M.A.; Alahmdi, M.I.; Ahmed, N. PhI(OAc) 2 mediated an efficient Knoevenagel reaction and their synthetic application for coumarin derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 3183–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, S.; Taddeo, V.A.; Genovese, S.; Epifano, F. A green chemical synthesis of coumarin-3-carboxylic and cinnamic acids using crop-derived products and waste waters as solvents. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 4795–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomi, J.S.; Akbarzadeh, Z. Ultrasonic accelerated Knoevenagel condensation by magnetically recoverable MgFe2O4 nanocatalyst: A rapid and green synthesis of coumarins under solvent-free conditions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sairam, M.; Saidachary, G.; Raju, B.C. Condensation of salicylaldehydes with ethyl 4, 4, 4-trichloro-3-oxobutanoate: A facile approach for the synthesis of substituted 2H-chromene-3-carboxylates. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, J.K.; Bombrun, A.; Ramappa, B.; Boodappa, C. An efficient one-pot synthesis of coumarins mediated by propylphosphonic anhydride (T3P) via the Perkin condensation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4422–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Shang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Han, G.; Jin, W.; Chen, J. Synthesis of coumarin-3-carboxylic esters via FeCl3-catalyzed multicomponent reaction of salicylaldehydes, Meldrum’s acid and alcohols. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Gao, J.; Han, L. One-pot catalyst-free synthesis of 3-heterocyclic coumarins. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2016, 42, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.H. Meglumine catalyzed one-pot, three-component combinatorial synthesis of pyrazoles bearing a coumarin unit. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 25625–25633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.E.A.A. Bismuth triflate: A highly efficient catalyst for the synthesis of bio-active coumarin compounds via one-pot multi-component reaction. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Murugavel, G.; Punniyamurthy, T. Microwave-assisted copper-catalyzed four-component tandem synthesis of 3-N-sulfonylamidine coumarins. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 6291–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, H.; Arshad, A.; Lam, C.K.; Bagley, M.C. Microwave-assisted synthesis and antioxidant properties of hydrazinyl thiazolyl coumarin derivatives. Chem. Central J. 2012, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
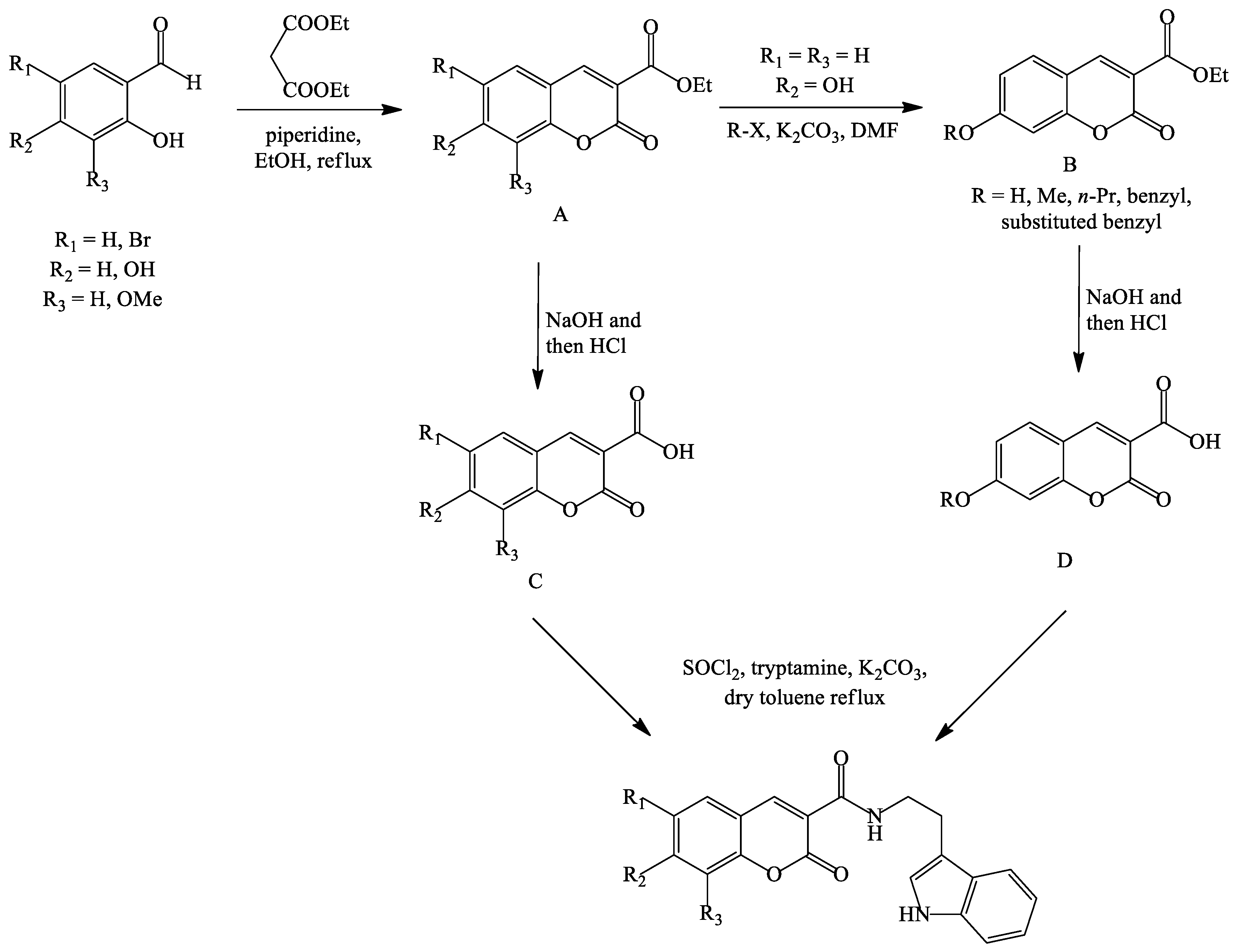
- Ghanei-Nasab, S.; Khoobi, M.; Hadizadeh, F.; Marjani, A.; Moradi, A.; Nadri, H.; Emami, S.; Foroumadi, A.; Shafiee, A. Synthesis and anticholinesterase activity of coumarin-3-carboxamides bearing tryptamine moiety. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabahi, A.; Makhloufi-Chebli, M.; Hamdi, S.M.; Silva, A.M.; Kheffache, D.; Boutemeur-Kheddis, B.; Hamdi, M. Synthesis and optical properties of coumarins and iminocoumarins: Estimation of ground- and excited-state dipole moments from a solvatochromic shift and theoretical methods. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 195, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadtare, S.B.; Jarag, K.J.; Shankarling, G.S. Greener protocol for one pot synthesis of coumarin styryl dyes. Dye. Pigment. 2013, 97, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.K.; Sarkar, S.; Khan, M.; Belal, M.; Khan, A.T. A mild and efficient method for large scale synthesis of 3-aminocoumarins and its further application for the preparation of 4-bromo-3-aminocoumarins. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 4869–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Shi, J.-B.; Tang, W.-J.; Pan, Z.-X.; Dong, Z.-Q.; Song, B.-A.; Li, J.; Liu, X.-H. New coumarin derivatives: Design, synthesis and use as inhibitors of hMAO. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3732–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phakhodee, W.; Duangkamol, C.; Yamano, D.; Pattarawarapan, M. Ph3P/I2-Mediated Synthesis of 3-Aryl-Substituted and 3,4-Disubstituted Coumarins. Synlett 2017, 28, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathi, S.K.; Logeeswari, K. Synthesis of 3-Aryl Coumarin Derivatives Using Ultrasound. Int. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 3, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhara, K.; Palnati, G.; Avula, S.; Kumar, A. Efficient and General Synthesis of 3-Aryl Coumarins Using Cyanuric Chloride. Synlett 2012, 23, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Nezhad, S.; Khosravani, L.; Saeedi, M.; Divsalar, K.; Firoozpour, L.; Pourshojaei, Y.; Sarrafi, Y.; Nadri, H.; Moradi, A.; Mahdavi, M.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Coumarin–Resveratrol Hybrids as 15-Lipoxygenaze Inhibitors. Synth. Commun. 2015, 45, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Kumar, H.V. ChemInform Abstract: An Expeditious Coumarin Synthesis via a “Pseudocycloaddition” Between Salicylaldehydes and Ketene. Synth. Commun. 2015, 46, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
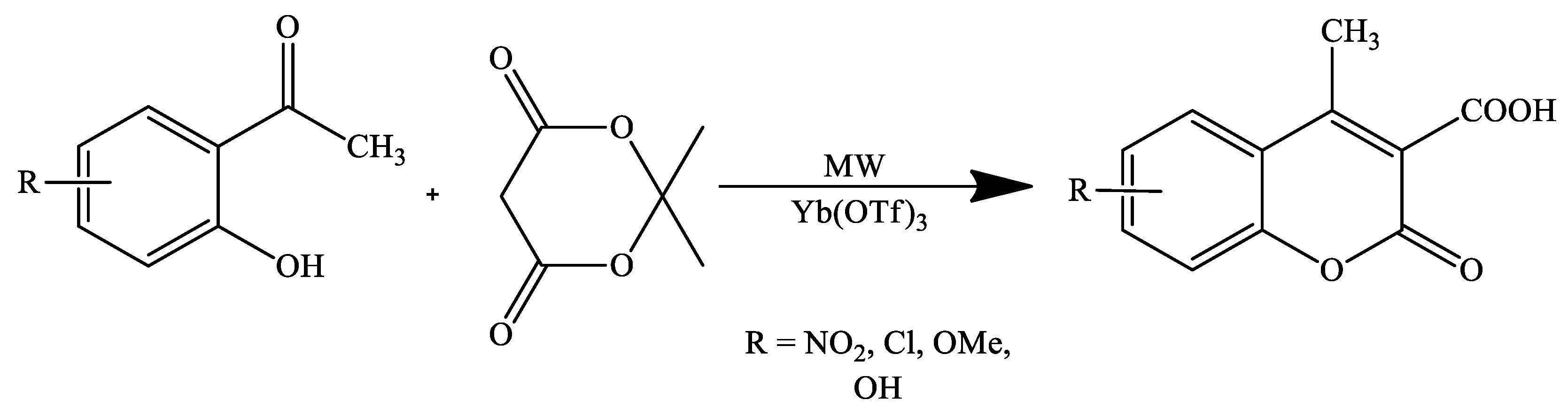
- Fiorito, S.; Genovese, S.; Taddeo, V.A.; Epifano, F. Microwave-assisted synthesis of coumarin-3-carboxylic acids under ytterbium triflate catalysis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 2434–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyani, H.; Daroonkala, M.D. A cost-effective and green aqueous synthesis of 3-substituted coumarins catalyzed by potassium phthalimide. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2015, 29, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieu, T.N.; Nguyen, K.D.; Le, D.T.; Truong, T.; Phan, N.T.S. Application of iron-based metal–organic frameworks in catalysis: Oxidant-promoted formation of coumarins using Fe 3 O(BPDC) 3 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 5916–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
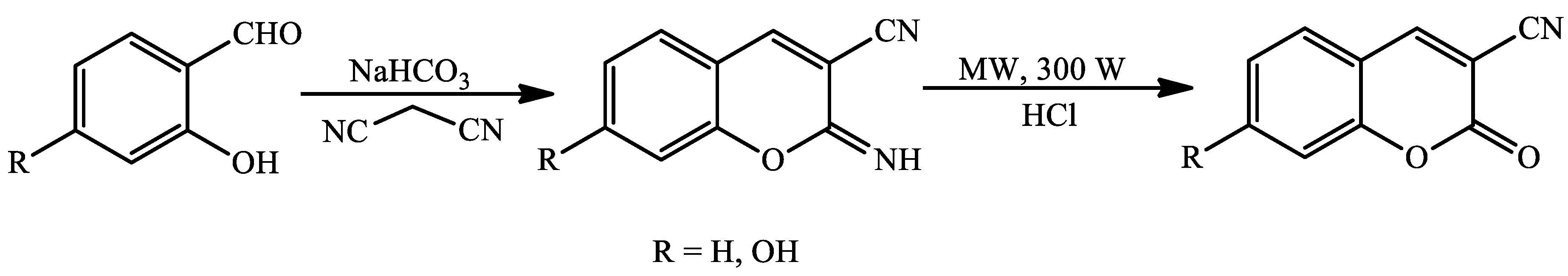
- Sharma, D.; Makrandi, J.K. Iodine-mediated one-pot synthesis of 3-cyanocoumarins and 3-cyano-4-methylcoumarins. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2014, 79, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Farjam, M.H.; Farasat, M. Coumarin synthesis via Pechmann condensation utilizing starch sulfuric acid as a green and efficient catalyst under solvent-free conditions. Org. Chem. Indian J. 2014, 10, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Pornsatitworakul, S.; Boekfa, B.; Maihom, T.; Treesukol, P.; Namuangruk, S.; Jarussophon, S.; Limtrakul, J. The coumarin synthesis: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2017, 148, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouasla, S.; Amaro-Gahete, J.; Esquivel, D.; López, M.I.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Teguiche, M.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. Coumarin Derivatives Solvent-Free Synthesis under Microwave Irradiation over Heterogeneous Solid Catalysts. Molecules 2017, 22, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirosanloo, A.; Zareyee, D.; Khalilzadeh, M.A. Recyclable cellulose nanocrystal supported Palladium nanoparticles as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of coumarin derivatives via von Pechmann condensation. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, S.; Akhlaghinia, B.; Mohammadinezhad, A. Fe3O4@Boehmite-NH2-CoII NPs: An Environment Friendly Nanocatalyst for Solvent Free Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives Through Pechmann Condensation Reaction. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prateeptongkum, S.; Duangdee, N.; Thongyoo, P. Facile iron (III) Chloride Hexahydrate Catalyzed Synthesis of Coumarins; Michigan Publishing, University of Michigan Library: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2015; pp. 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhtary, M.; Najafizadeh, F. Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone-bound boron trifluoride (PVPP-BF3); a mild and efficient catalyst for synthesis of 4-metyl coumarins via the Pechmann reaction. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2012, 15, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, L.; Rabiei, K.; Belali, F. ChemInform Abstract: Meglumine Sulfate Catalyzed Solvent-Free One-Pot Synthesis of Coumarins under Microwave and Thermal Conditions. Synth.Commun. 2016, 47, 1283–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozadeh, A.; Ahmadzadeh, M.; Kolvari, E. Easy access to coumarin derivatives using alumina sulfuric acid as an efficient and reusable catalyst under solvent-free conditions. J. Chem. 2012, 2013, 767825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi-Jaberi, Z.; Masoudi, B.; Rahmani, A.; Alborzi, K. Triethylammonium Hydrogen Sulfate [Et 3 NH][HSO 4] as an Efficient Ionic Liquid Catalyst for the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojati, S.F.; Hadadnia, Z. A New Highly Efficient Approach to the Synthesis of Coumarin and Its Derivatives. Jordan J. Chem. 2016, 146, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Prousis, K.C.; Avlonitis, N.; Heropoulos, G.A.; Calogeropoulou, T. FeCl3-catalysed ultrasonic-assisted, solvent-free synthesis of 4-substituted coumarins. A useful complement to the Pechmann reaction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeruddin, G.; Pandharpatte, M.; Mulani, K. PEG-SO3H: A mild and efficient recyclable catalyst for the synthesis of coumarin derivatives. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2012, 15, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgogary, S.R.; Hashem, N.M.; Khodeir, M.N. Synthesis and Photooxygenation of Linear and Angular Furocoumarin Derivatives as a Hydroxyl Radical Source: Psoralen, Pseudopsoralen, Isopseudopsoralen, and Allopsoralen. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2015, 52, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
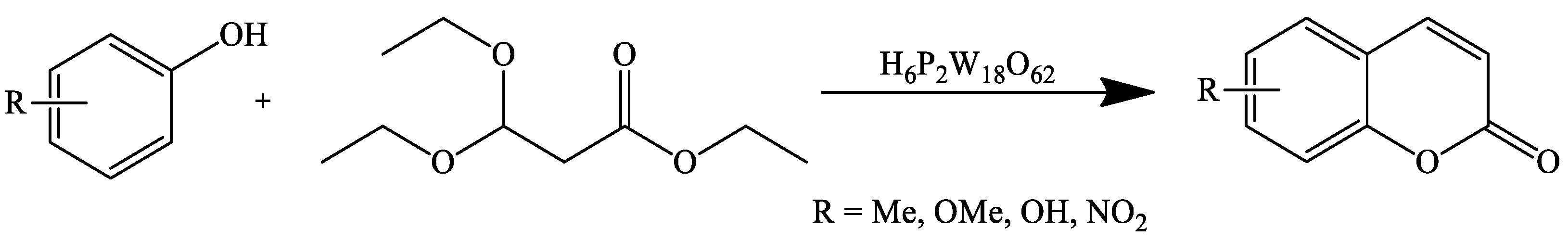
- Sun, Y.-F.; Liu, J.-M.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.-T.; Lu, J.; Li, M.-M.; Jin, N.; Dai, X.-F.; Fan, B. One-Pot Synthesis of Coumarins Unsubstituted on the Pyranic Nucleus Catalysed by a Wells–Dawson Heteropolyacid (H6P2W18O62). Preprints 2018, 2018090349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
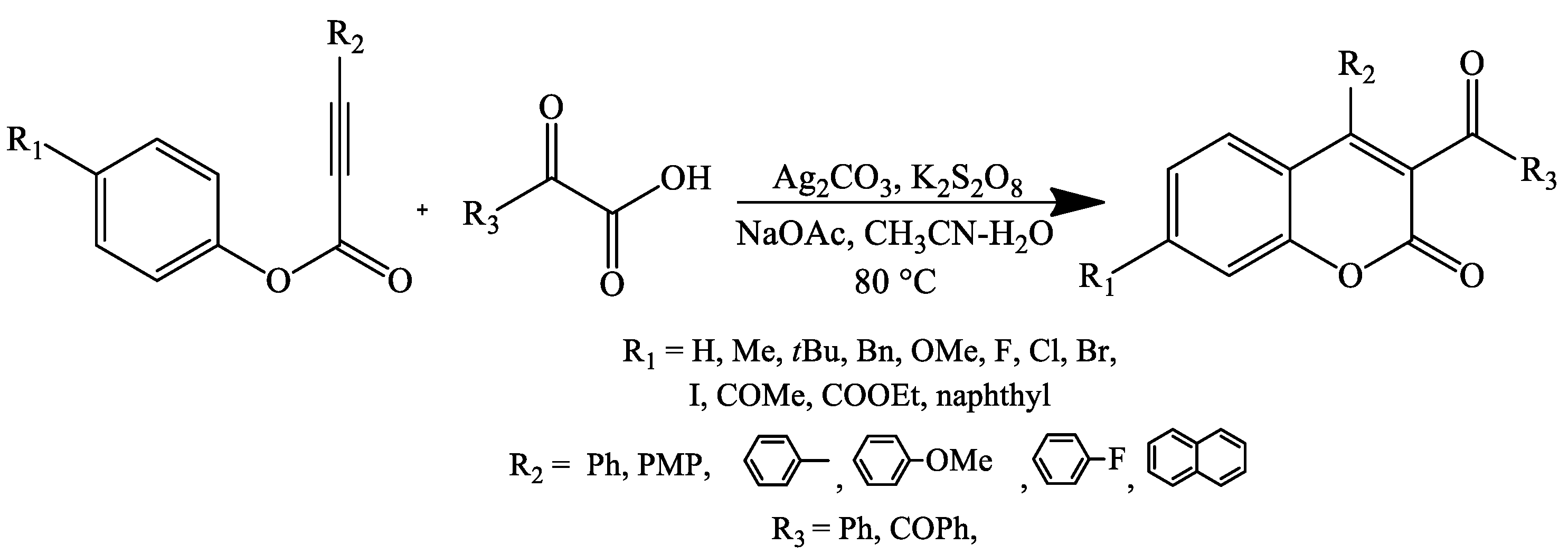
- Zhu, F.; Wu, X.-F. Selectivity Controlled Palladium-Catalyzed Carbonylative Synthesis of Propiolates and Chromenones from Phenols and Alkynes. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3422–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang-Negrerie, D.; Du, Y.; Zhao, K. Synthesis of coumarins via PIDA/I2-mediated oxidative cyclization of substituted phenylacrylic acids. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Yang, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, F.; Shuai, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Silver-Mediated Radical Cyclization of Alkynoates and α-Keto Acids Leading to Coumarins via Cascade Double C–C Bond Formation. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Ding, Q.; Zong, Q.; Qiu, G. Radical 5-exo cyclization of alkynoates with 2-oxoacetic acids for synthesis of 3-acylcoumarins. Org. Chem. Front. 2015, 2, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
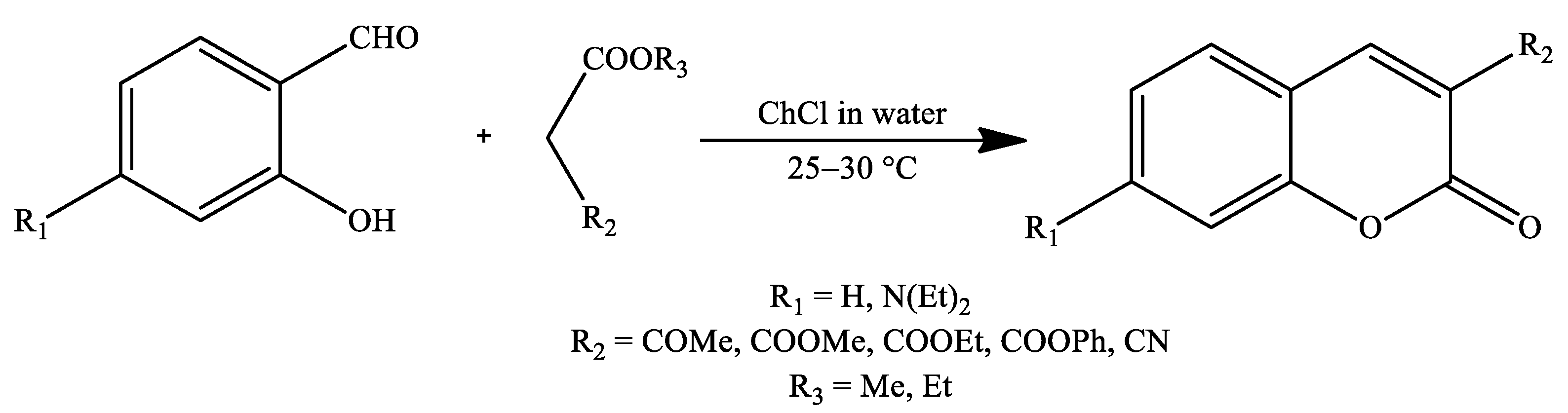
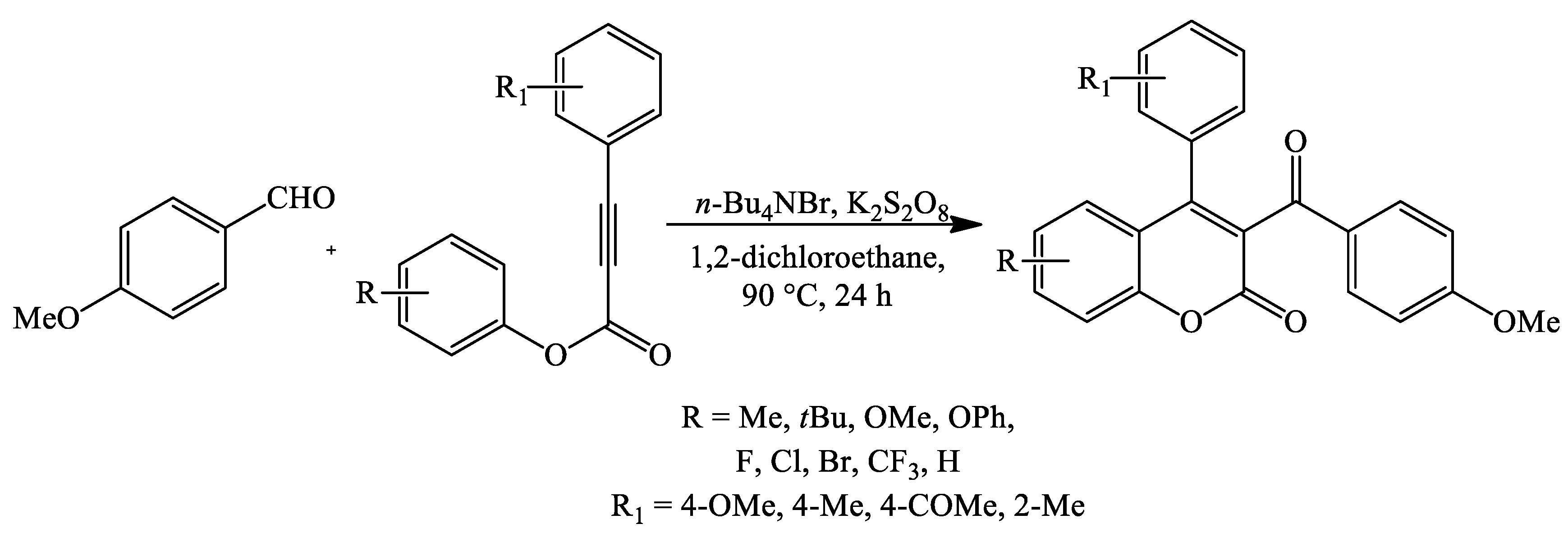
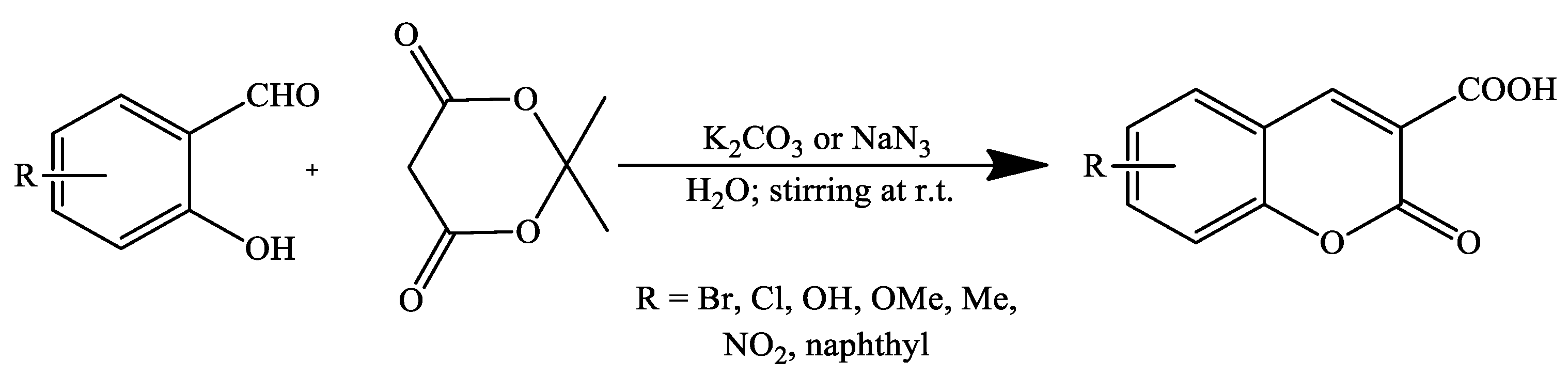
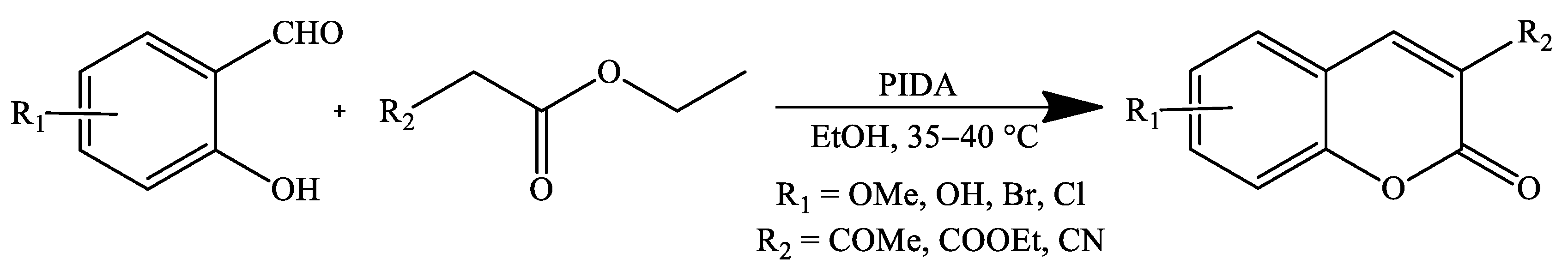
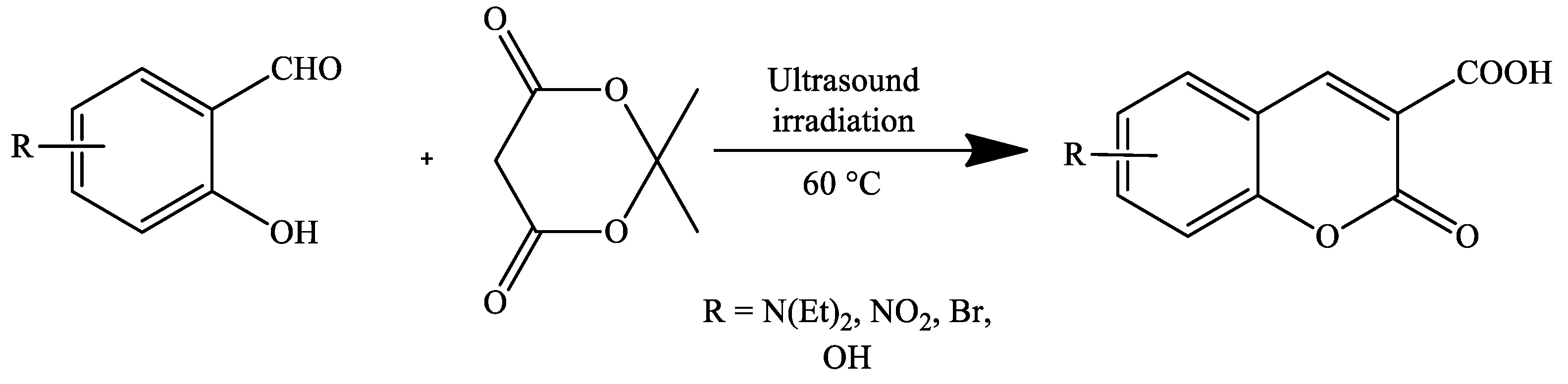
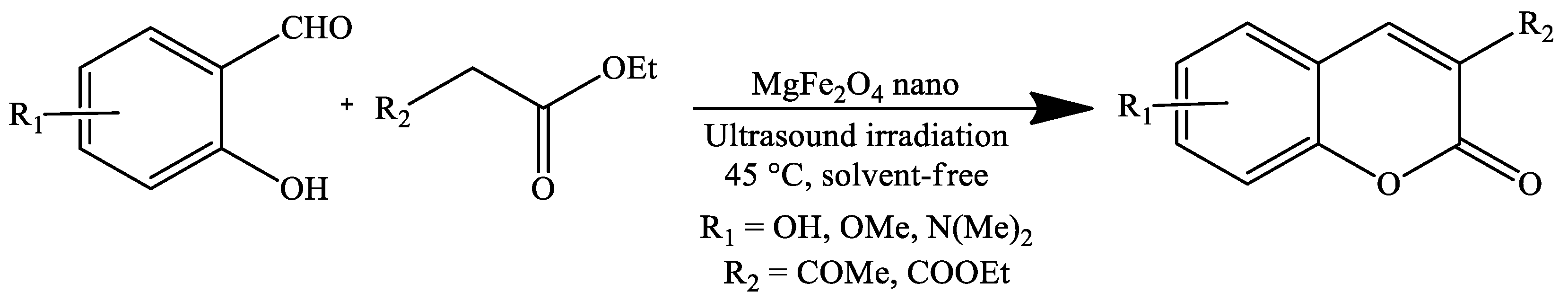
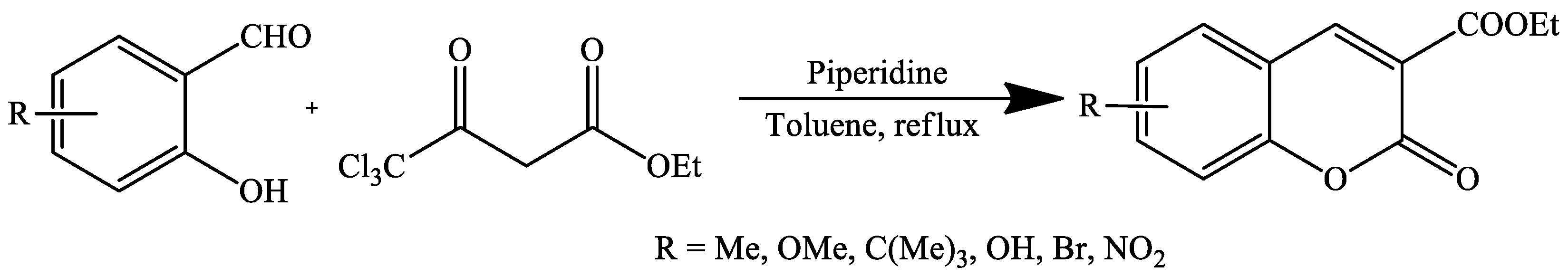



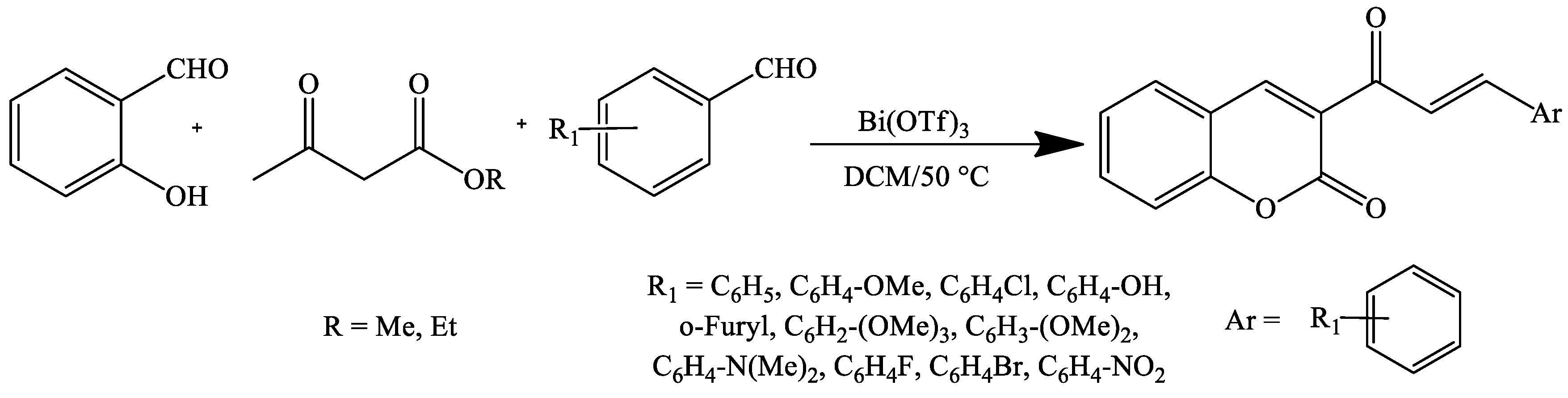
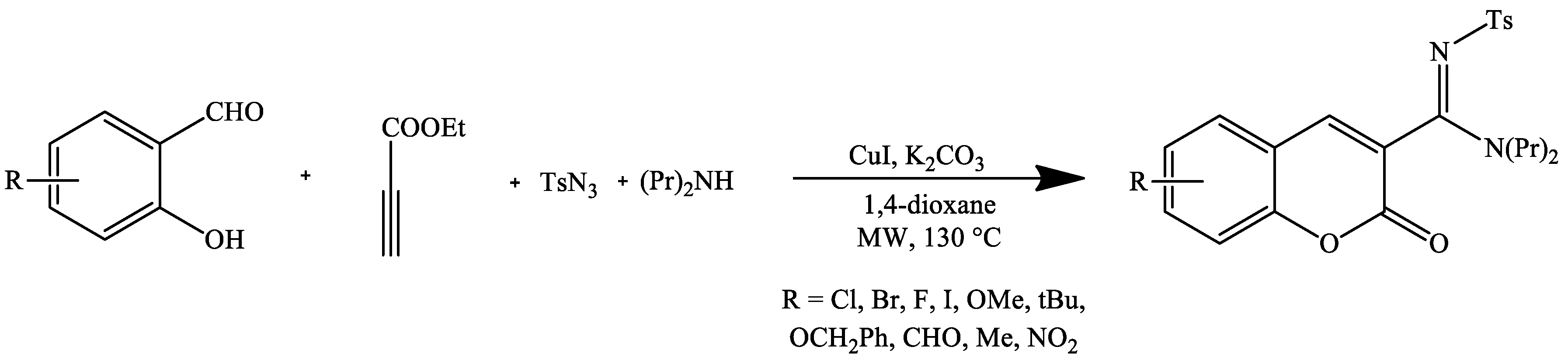

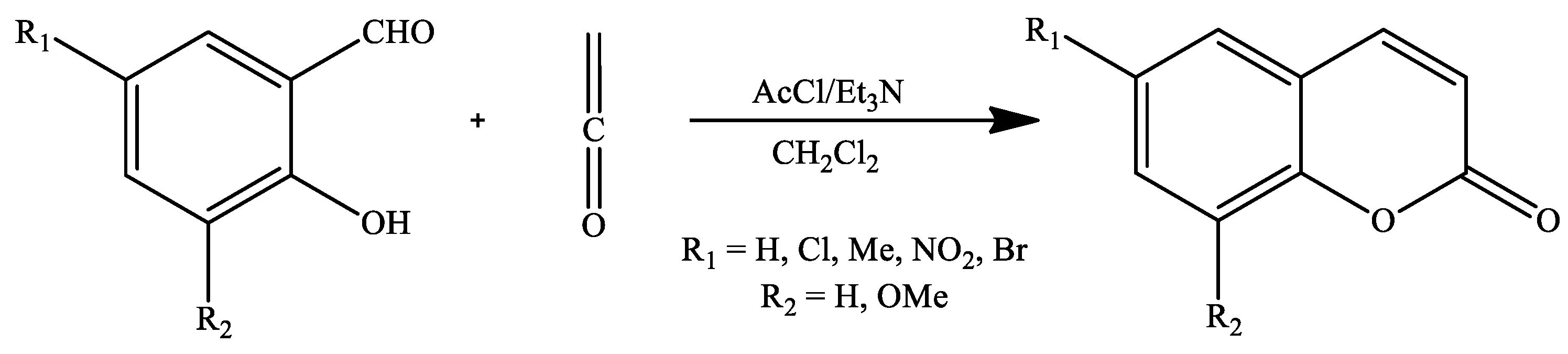
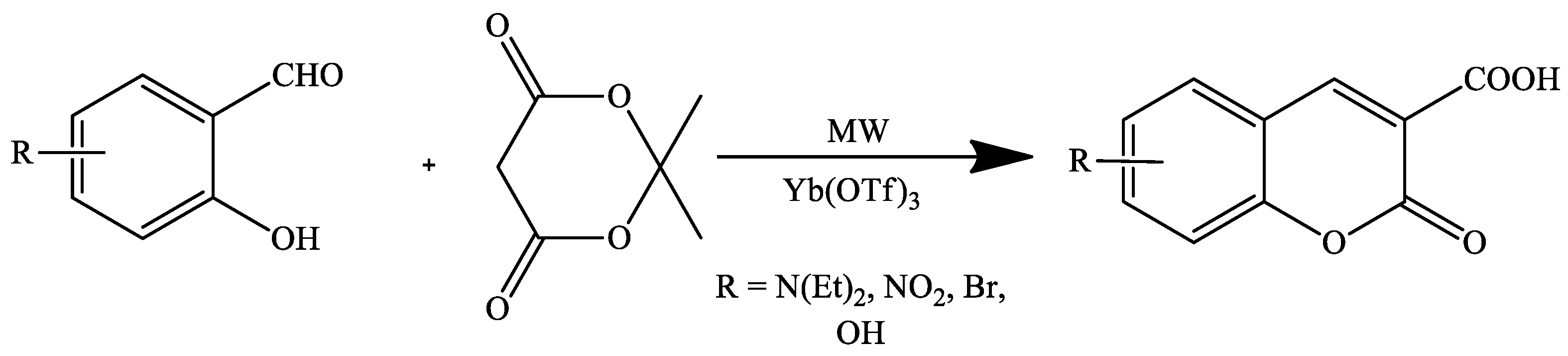

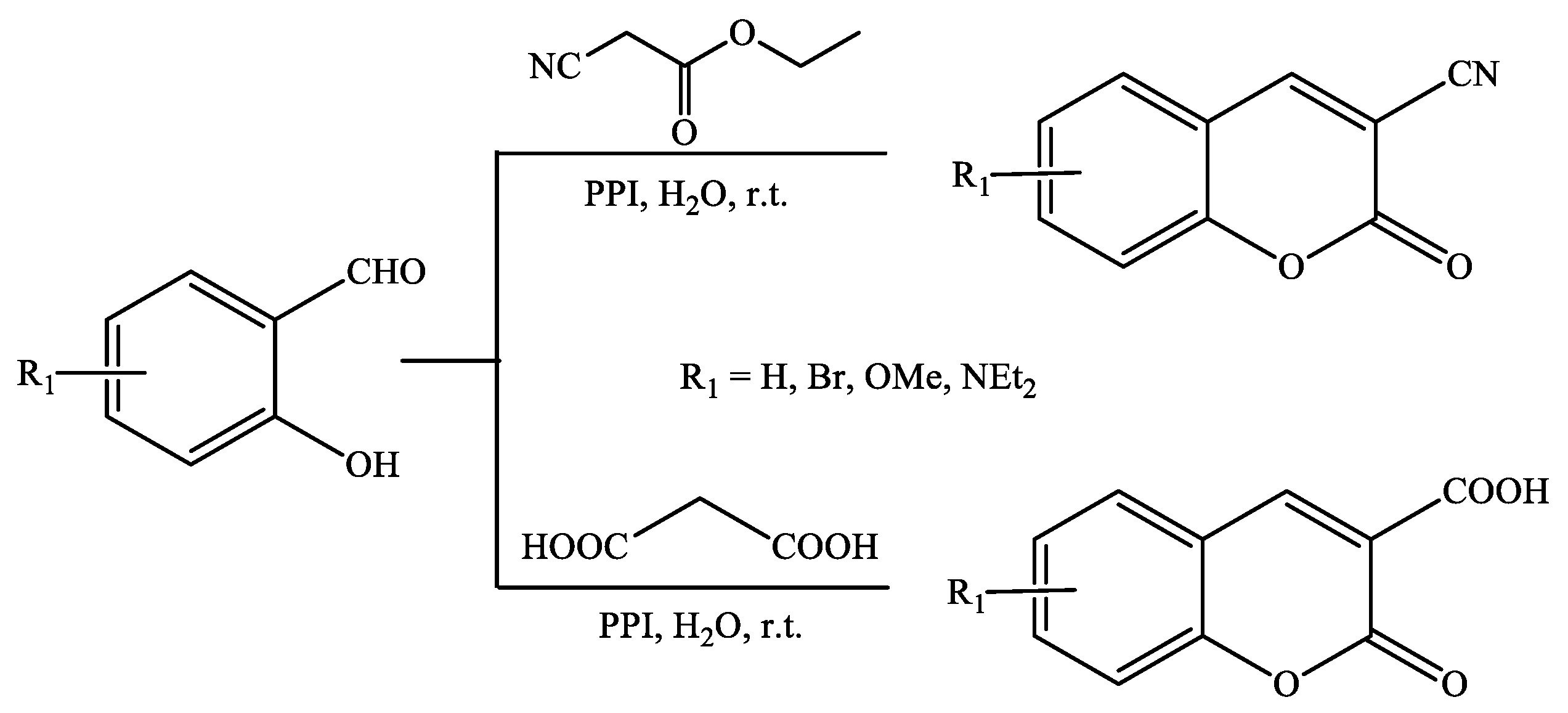
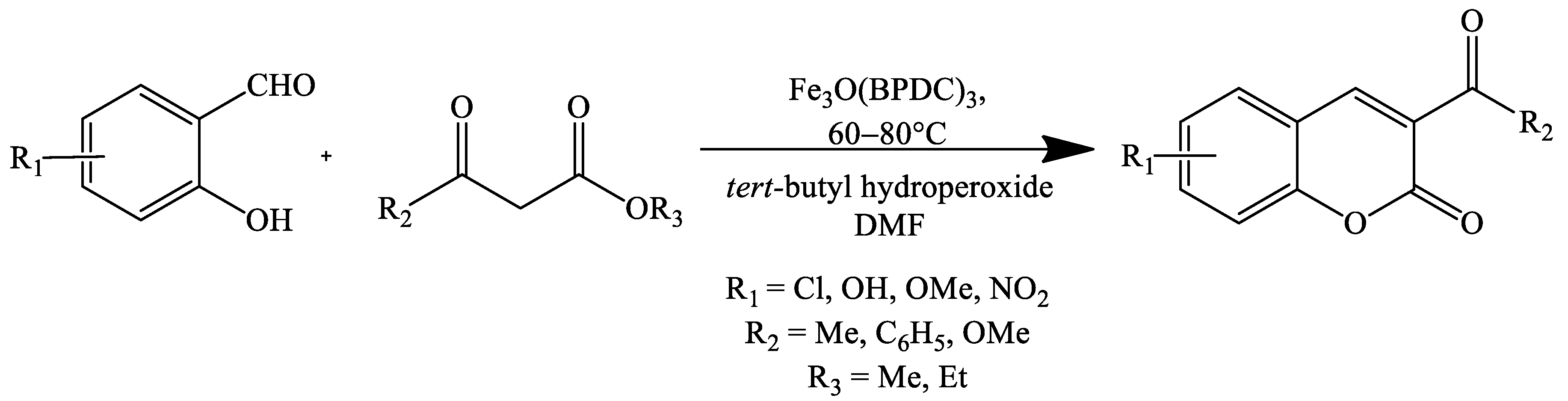
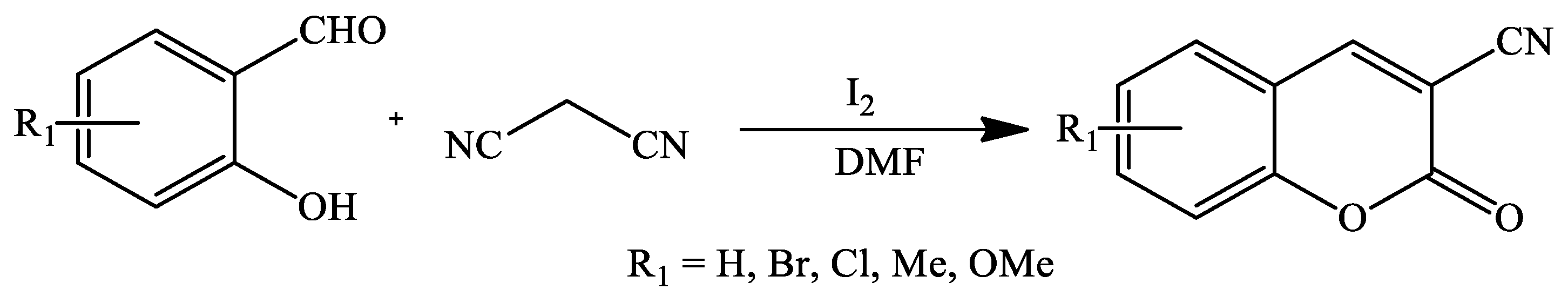
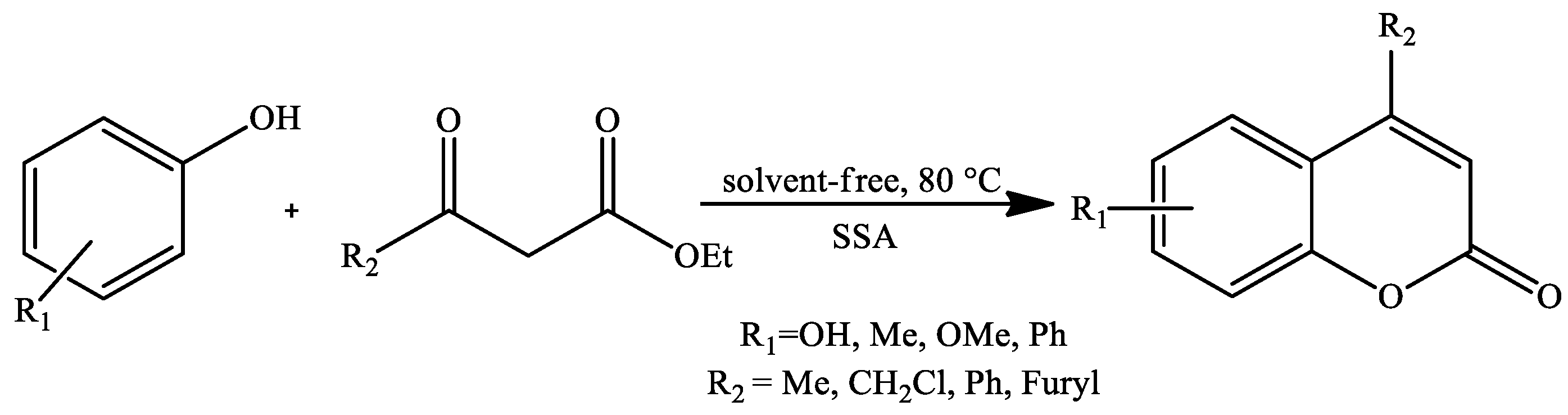
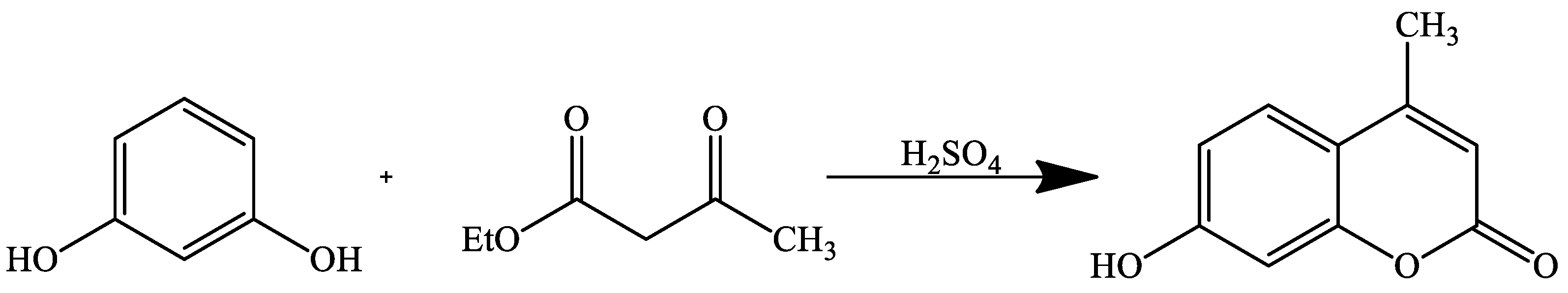

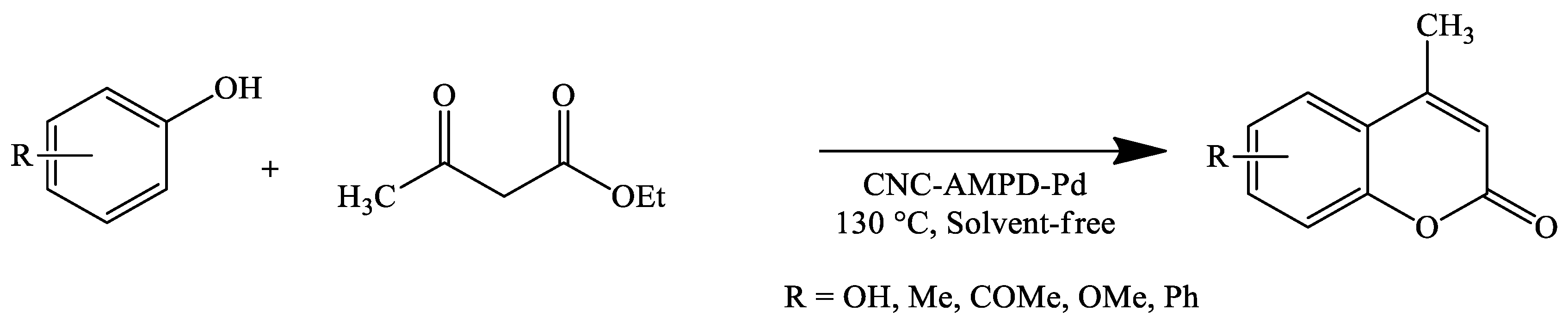


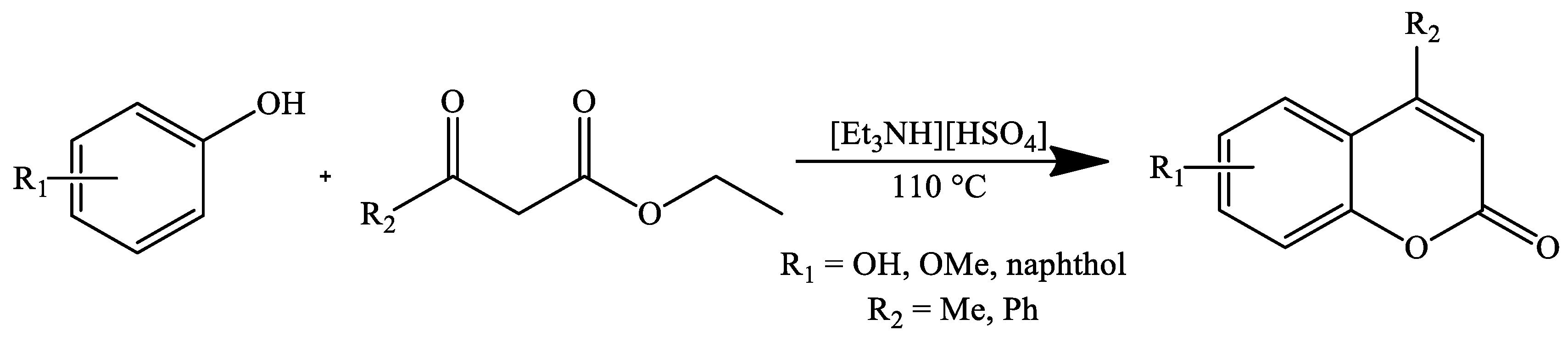
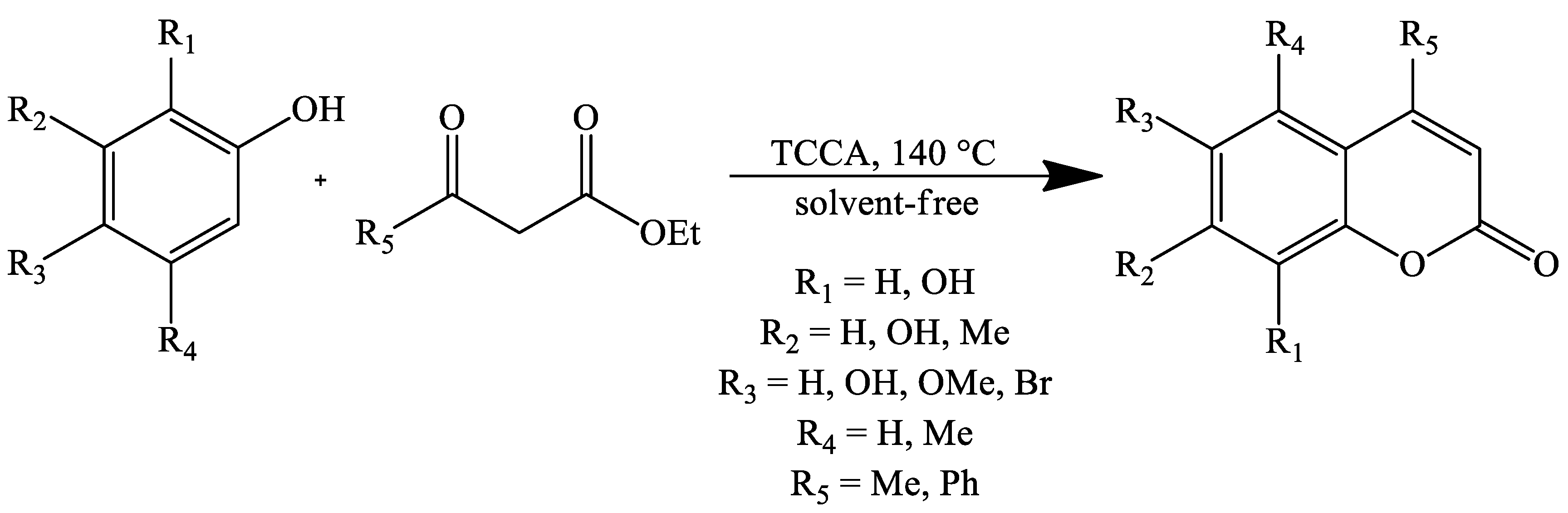
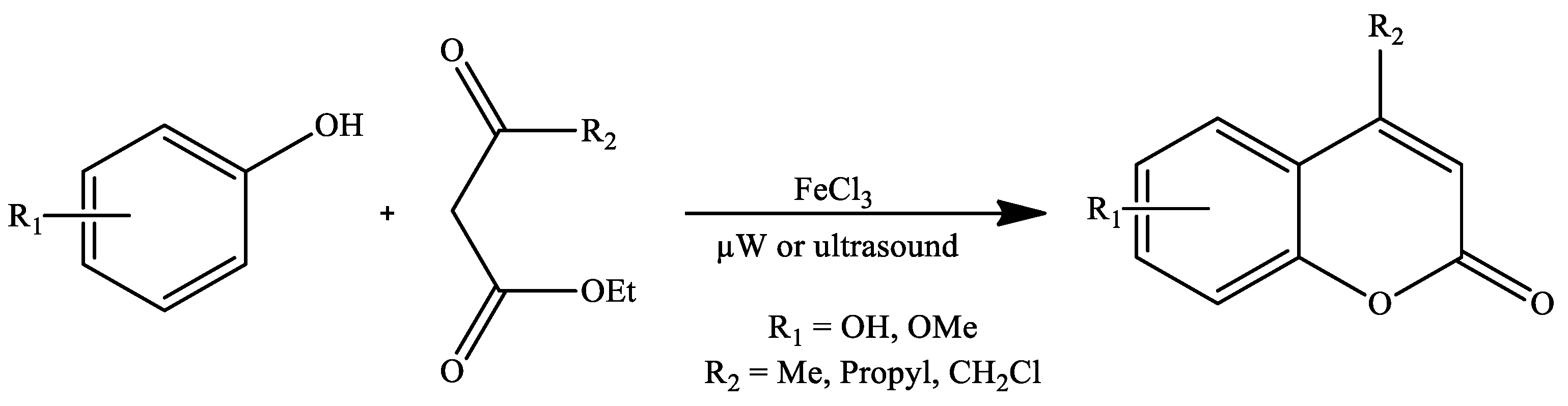

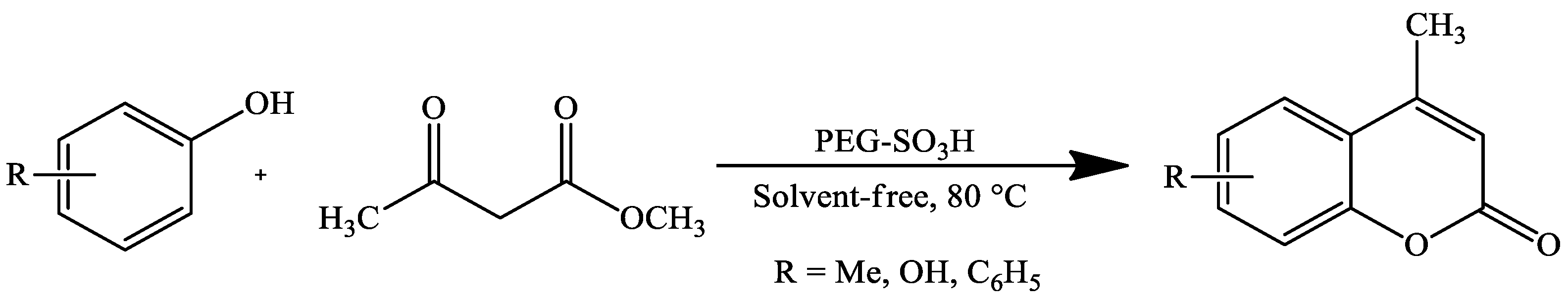
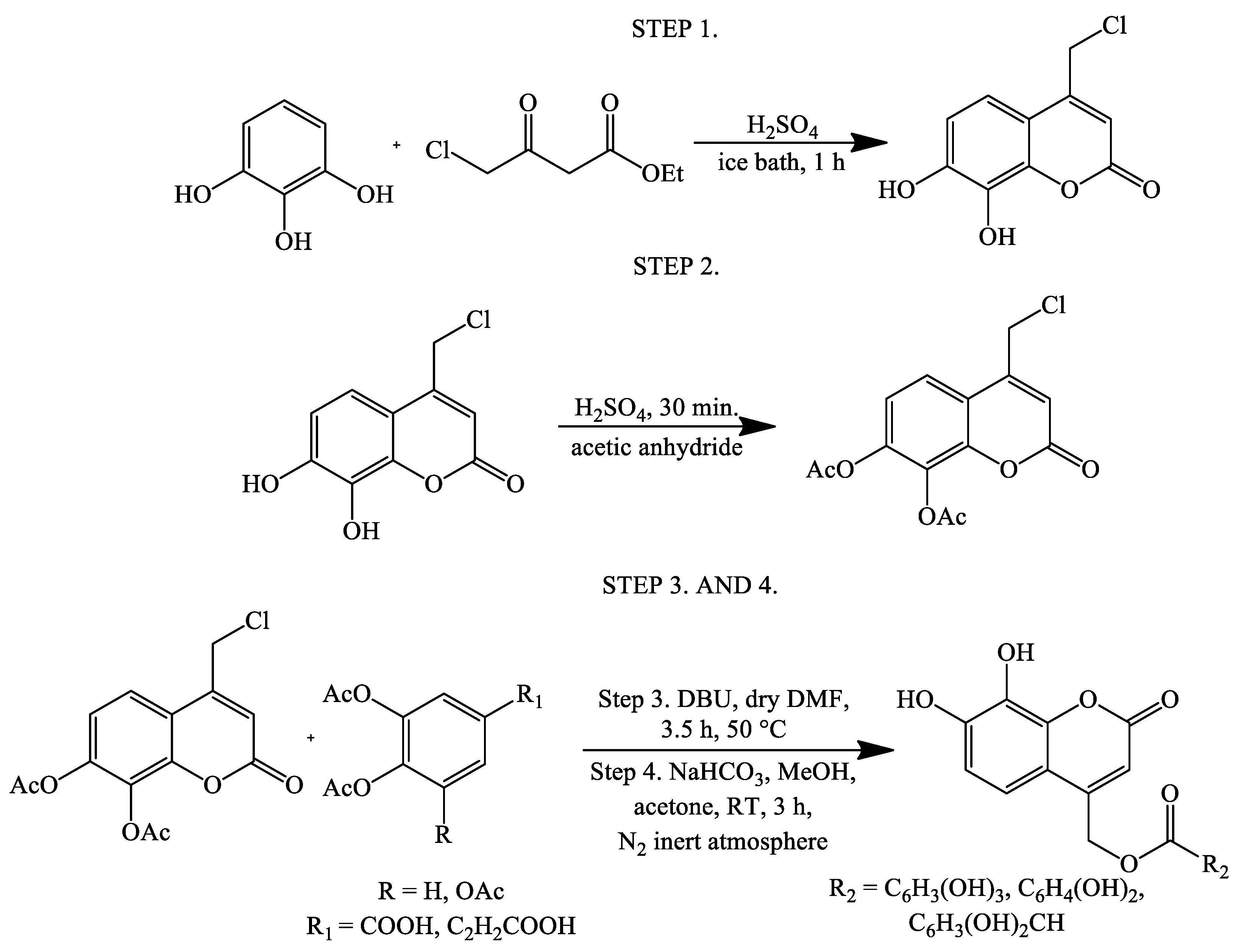
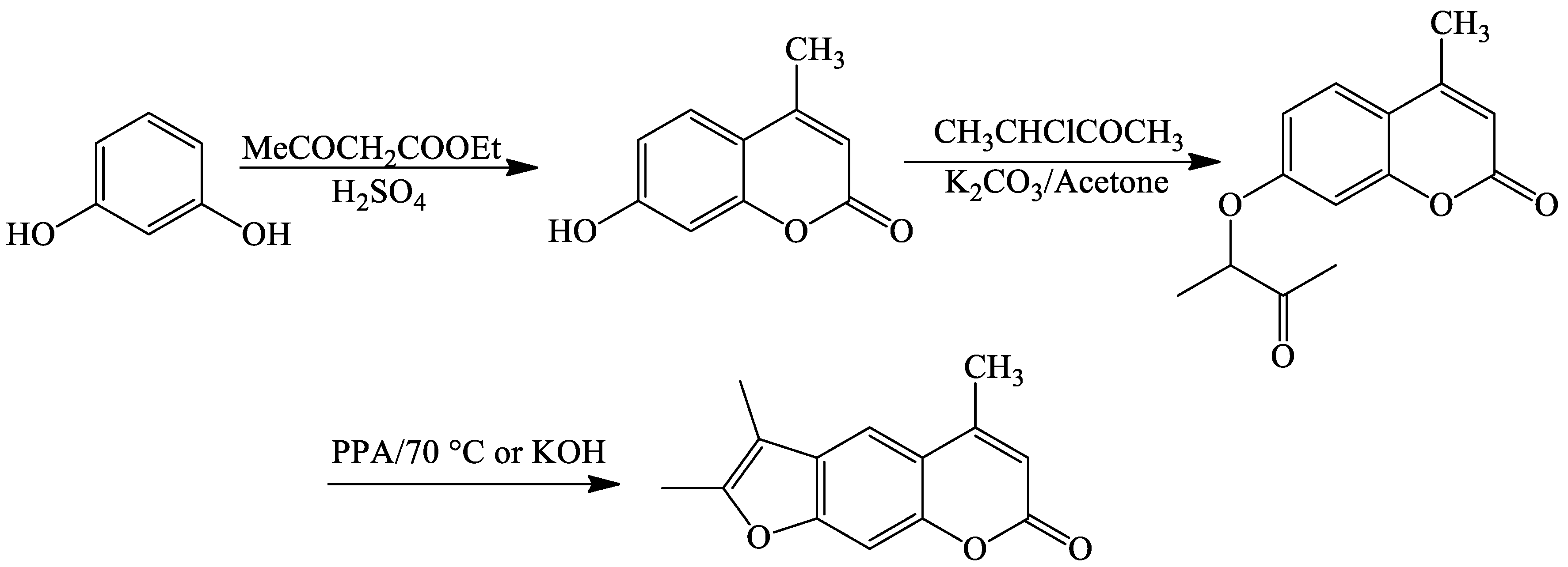


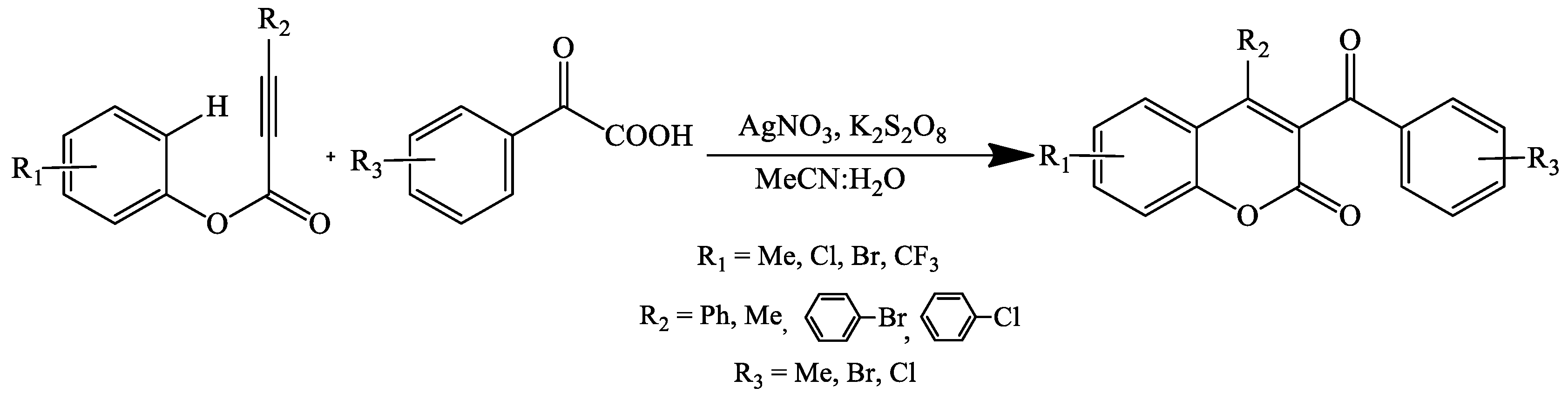
| Reaction Conditions | Solvent | Catalyst | Yields (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Substituted 2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-carboxylic acids | ||||
| Microwave irradiation | Solvent-free | Yb(OTf)3 | 93–98 | [92] |
| Stirring, RT | Water | Potassium phtalamide (PPI) | 87–90 | [93] |
| Stirring, RT | Water | K2CO3 | 73–93 | [69] |
| NaN3 | 78–99 | |||
| Ultrasound irradiation | Water | No-catalyst | 80 | [70] |
| Reflux | 95 | |||
| Stirring, RT | Lemon, pomegranate, grapefruit, carrot, tomato, kiwi and limoncello juice, vinegar, olive mil and buttermilk waste water | No-catalyst | 91–99 | [72] |
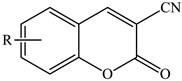 Substituted 2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-carbonitriles | ||||
| Stirring, 25–30 °C | Water | Choline chloride | 79–87 | [66] |
| Stirring, RT | Water | Potassium phtalamide (PPI) | 89–93 | [93] |
| Ultrasound irradiation | Ethanol | Piperidine | 49 | [70] |
| Reflux | 50 | |||
| Stirring, 35–40 °C | Ethanol | PhI(OAc)2 | 80–92 | [71] |
| Stirring, 80 °C | Ethanol | FeCl3 | 72–93 * | [34] |
| Stirring, 80 °C | Deep eutectic solvent | Deep eutectic solvent | 73–92 | [65] |
| Reflux | Dimethylformamide | I2 | 80–92 | [95] |
| Microwave irradiation | 85–95 | |||
| Stirring, 120 °C | Butyl acetate | Propylphosphonic anhydride (T3P), trimethylamine (TEA) | 85–98 | [75] |
 Substituted 3-acetyl-2H-chromen-2-ones | ||||
| Ultrasound irradiation, 45 °C | Solvent-free | MgFe2O4 nanoparticles | 92–96 | [73] |
| Stirring, 25–30 °C | Water | Choline chloride | 90 | [66] |
| Stirring, 35–40 °C | Ethanol | PhI(OAc)2 | 82–92 | [71] |
| Stirring, 60–80 °C, tert-butyl hydroperoxide | Dimethylformamide | Fe3O(BPDC)3 | 65–96 | [94] |
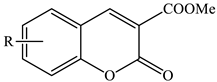 Substituted methyl 2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-carboxylates | ||||
| Stirring, 2–30 °C | Water | Choline chloride | 87–96 | [66] |
| Stirring, 120 °C | Butyl acetate | Propylphosphonic anhydride (T3P), trimethylamine (TEA) | 94 | [75] |
| Stirring, 60–80 °C, tert-butyl hydroperoxide | Dimethylformamide | Fe3O(BPDC)3 | 28 | [94] |
 Substituted ethyl 2-oxo-2H-chromene-3-carboxylates | ||||
| Ultrasound irradiation, 45 °C | Solvent-free | MgFe2O4 nanoparticles | 88–93 | [73] |
| Stirring, 25–30 °C | Water | Choline chloride | 91–92 | [66] |
| Stirring, RT | Ethanol | Piperidine, AcOH | 67–83 | [68] |
| Stirring, 35–40 °C | Ethanol | PhI(OAc)2 | 84–92 | [71] |
| Ultrasound irradiation | Ethanol | Piperidine, AcOH | 60–88 | [70] |
| Reflux | 48–85 | |||
| Stirring, 80 °C | Ethanol | FeCl3 | 70–95 | [34] |
| Reflux | Toluene | Piperidine | 25–82 | [74] |
| Reaction Conditions | Solvent | Catalyst | Yields (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Substituted 4-methyl-2H-chromen-2-ones | ||||
| Stirring, 80 °C | Solvent-free | Starch sulfuric acid (SSA) | 75–95 | [96] |
| Ultrasound irradiation | Solvent-free | H2SO4 | 87 | [70] |
| Stirring | Solvent-free | H2SO4 | 86 | [97] |
| Microwave irradiation, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Amberlyst-15 | 43–97 | [98] |
| Stirring, 130 °C | Solvent-free | Cellulose nanocrystal supported palladium nanoparticles (CNC-AMPD-Pd) | 45–97 | [99] |
| Stirring, 90 °C | Solvent-free | Magnetic-core-shell-like Fe3O4@Boehmite-NH2-CoII NPs | 60–95 * | [100] |
| Stirring, 80 °C | Solvent-free | PEG-SO3H | 78–91 | [108] |
| Stirring, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Meglumine sulfate (MS) | 88–92 | [103] |
| Microwave irradiation | 88–93 | |||
| Stirring, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Alumina sulfuric acid (ASA) | 25–99 * | [104] |
| Stirring, 110 °C | Solvent-free | Triethylammonium hydrogen sulfate | 79–94 | [105] |
| Stirring, 140 °C | Solvent-free | TCCA (1,3,5-trichloroisocyanuric acid) | 53–98 | [106] |
| Stirring, 70 °C | Solvent-free | FeCl3 | 36–99 | [107] |
| Microwave irradiation, 100 °C | 39–99 | |||
| Ultrasound irradiation | 55–99 | |||
| Reflux | Ethanol | Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone-bound boron trifluoride (PVPP-BF3) | 72–96 | [102] |
| Reflux | Toluene | FeCl3·6H2O | 44–92 | [101] |
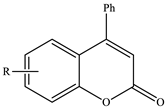 Substituted 4-phenyl-2H-chromen-2-ones | ||||
| Stirring, 80 °C | Solvent-free | Starch sulfuric acid (SSA) | 78 | [96] |
| Stirring, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Alumina sulfuric acid (ASA) | 91 | [104] |
| Heating, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Meglumine sulfate (MS) | 88–90 | [103] |
| Microwave irradiation | 88–92 | |||
| Stirring, 110 °C | Solvent-free | Triethylammonium hydrogen sulfate | 85–88 | [105] |
| Stirring, 140 °C | Solvent-free | TCCA (1,3,5-trichloroisocyanuric acid) | 50–98 | [106] |
 Substituted 4-(chloromethyl)-2H-chromen-2-ones | ||||
| Stirring, 80 °C | Solvent-free | Starch sulfuric acid (SSA) | 85 | [96] |
| Stirring, 100 °C | Solvent-free | Alumina sulfuric acid (ASA) | 88–96 | [104] |
| Stirring, 70 °C | Solvent-free | FeCl3 | 95 * | [107] |
| Microwave irradiation, 100 °C | 68 * | |||
| Ultrasound irradiation | 75–96 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lončarić, M.; Gašo-Sokač, D.; Jokić, S.; Molnar, M. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives from Different Starting Materials. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010151
Lončarić M, Gašo-Sokač D, Jokić S, Molnar M. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives from Different Starting Materials. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010151
Chicago/Turabian StyleLončarić, Melita, Dajana Gašo-Sokač, Stela Jokić, and Maja Molnar. 2020. "Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives from Different Starting Materials" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010151
APA StyleLončarić, M., Gašo-Sokač, D., Jokić, S., & Molnar, M. (2020). Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Coumarin Derivatives from Different Starting Materials. Biomolecules, 10(1), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010151







