Calculation of Electron Impact Single Ionization TDCS of Tungsten Atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
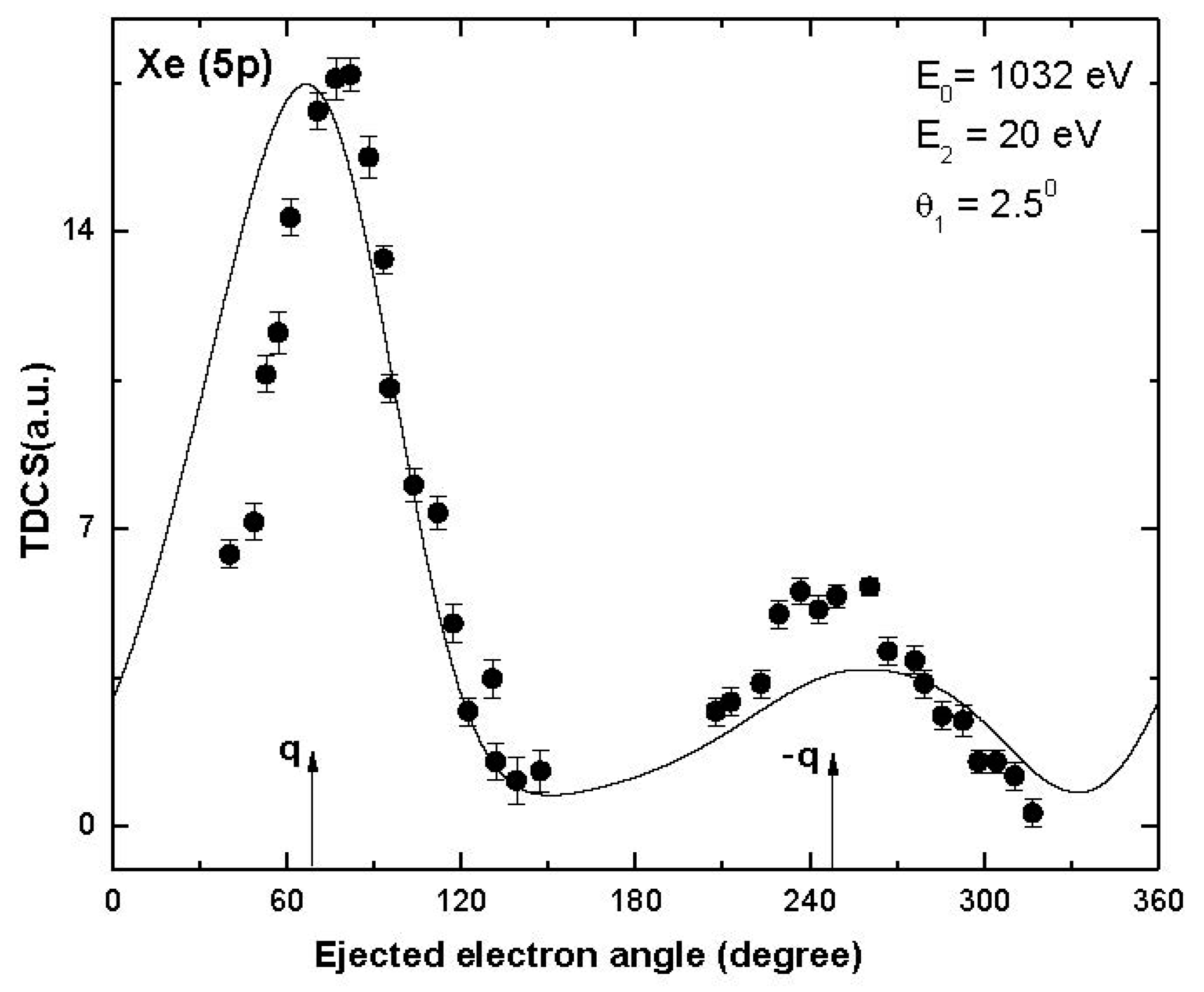
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehrhardt, H.; Hesselbacher, K.H.; Jung, K.; Willmann, K. Collisional Ionization of Helium by Slow Electrons. J. Phys. B 1972, 5, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.H. Full Second-Order Distorted Wave Calculation Without Approximations for Atomic Excitation by Electron Impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmam-Bennani, A. Recent developments and New Trends in (e, 2e) and (e, 3e) Studies. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1991, 24, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, T.N.; Baertschy, M.W.; Isaacs, A.; McCurdy, C.W. Collisional Breakup in a Quantum System of Three Charged Particles. Science 1999, 286, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakel, W.; Whelan, C.T. Relativistic (e, 2e) Processes. Phys. Rep. 1999, 315, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, I.; Fursa, D.V.; Kheifets, A.S.; Stelbovics, A.T. Electtrons and Photons Colliding With Atoms: Development and Application of the Convergent Close-Coupling Method. J. Phys. B 2002, 35, R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartschat, K.; Vorov, O. Channel-coupling, Target-structure and Second-order Effects in Electron-impact Ionization of Ar (3p) and Ar (3s). Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 022728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K. Triple Differential Cross Section of Potassium for Doubly Symmetric Ionization. Phys. Lett. A. 2010, 374, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Singh, P.; Patidar, V.; Azuma, Y.; Sud, K.K. Effect of Target Polarization and Post Collision Interaction on the Electron Impact Single Ionization of Ne (2p), Ar (3p) and Na (3s) atoms. Phys. Rev. A. 2012, 85, 022714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.H.; Al-Hagan, O. The Distorted-Wave Born Approach for Calculating Electron-Impact Ionization of Molecules. J. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 2010, 367180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Calculation for Electron Impact Ionization of Be atoms and its charged states Be+ and Be+2. J. Phys. B At. Mol.Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 135201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Projectile Charge Effects on the Differential Cross Sections for the Ionization of Molecular Nitrogen by Positrons and Electrons. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 135202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mars, C.M.; Ward, S.J.; Colgan, J.; Amami, S.; Madison, D.H. Deep Minima in the Triply Differential Cross Section for Ionization of Atomic Hydrogen by Electron and Positron Impact. Atoms 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, R.A.; Carpentier, S.; Escourbiac, F.; Hirai, T.; Komarov, V.; Kukushkin, A.S.; Lisgo, S.; Loarte, A.; Merola, M.; Mitteau, R.; et al. Physics Basis and Design of the ITER Plasma-Facing Components. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, G. Plasma Wall Interactions in ITER. Phys. Scr. 2006, T124, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, R.; Bobkov, V.; Dux, R.; Kallenbach, A.; Pütterich, T.; Greuner, H.; Gruber, O.; Herrmann, A.; Hopf, C.; Krieger, K.; et al. Final Steps to an All Tungsten Divertor Tokamak. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 52, 363–365. [Google Scholar]
- Balance, C.P.; Loch, S.D.; Pinzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C. Electron Impact Excitation and Ionization of W3+ for the determination of tungsten influx in a fusion plasma. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 46, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruck, K.; Becker, A.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Gharaibeh, M.F.; Rausch, J.; Schippers, S.; Muller, A. Electron-Impact Ionization of Multiply Charged Tungsten Ions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 488, 062026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A. Fusion-Related Ionization and Recombination Data for Tungsten Ions in Low to Moderately High Charge States. Atoms 2015, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C. Electron-Impact Ionization of the Tungsten Atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, H.; Hilpert, K.; Becker, K.; Probst, M.; Märk, T.D. Calculated Absolute Electron-Impact Ionization Cross Sections for AlO, Al2O, and WOx (x = 1-3). J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwon, D.H.; Rhee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K. Ionization of W and W+ by Electron Impact. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 252, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainshtein, L.; Beigman, I.; Mertens, P.; Brezinse, S.; Pospieszczykand, A.; Borodin, D. Ionization of W atoms and W+ ions by Electrons. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2011, 44, 125201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Naghma, R.; Antony, B. Calculation of Electron Impact Total Ionization Cross sections for tungsten, uranium and their oxide radicals. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 372, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Loch and, S.D.; Foster, A.R. Electron Impact Single and Double Ionization of W. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2017, 50, 095201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Ferreira da Silva, F.; Limão-Vieiraand, P.; García, G. Electron Scattering Cross Section Data for Tungsten and Beryllium atoms from 0.1 to 5000 eV. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2017, 26, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D.; Murakami, I. Electron Impact Ionization Cross Sections of Tungsten Atoms and Tungsten Ions. Plasma Fusion Res. 2018, 13, 3401026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D.; Murakami, I.; Gupta, S.; Sinha, P. Calculation of Electron Induced Ionization Cross Sections of Fusion Plasma Relevant Material: W atoms. Eur. Phys. J. D. 2021, 75, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G. Electron Impact Single Ionization Differential Cross Sections of W(6s), W(5d), W(5p) and W(4f). J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2021, 54, 065203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Dependence of Electron Impact Differential Cross Sections on the Ionic Charge to Mass Ratio for the A/3+(2p) and Be2+(1s) ions. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 084307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, V.; Surendra, M. A Monte Carlo Collision Model for the Particle-in-Cell Method: Applications to Argon and Oxygen Discharges. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 87, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, A.D.; Mclean, R.S. Roothaan-Hartree-Fock Atomic Wave Functions Slater Basis-Set Expansions for Z = 55-92. At. Data Nucl. Data Tab. 1981, 26, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; McCarthy, I.E. Semiphenomenological Optical Model for Electron Scattering on Atoms. J. Phys. B. 1973, 6, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.E.; Truhlar, D.G. Approximations for the Exchange Potential in Electron Scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 63, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.E. Distorted-Wave Born and Impulse Approximations for Electron-Atom Ionisation. Aust. J. Phys. 1995, 48, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, J.; Zitnik, M.; Avaldi, L.; Colm, T.; Whelan, G.; Stefani, R.; Camilloni, R.; Allan, J.; Walters, H.R.J. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of the Triple-Differential Cross Sections for Electron-Impact Ionization of Kr(4p) and Xe(5p) at 1-keV Impact Energy. Phys. Rev. A. 1997, 56, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Singh, P.; Patidar, V. Fully Differential Cross Sections for Low to Intermediate Energy Perpendicular Plane Ionization of Xenon Atoms. J. Elec. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 2014, 197, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K. Importance of Polarization Effects in Electron Impact Single Ionization of Argon Atom. J. Elec. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 2009, 175, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
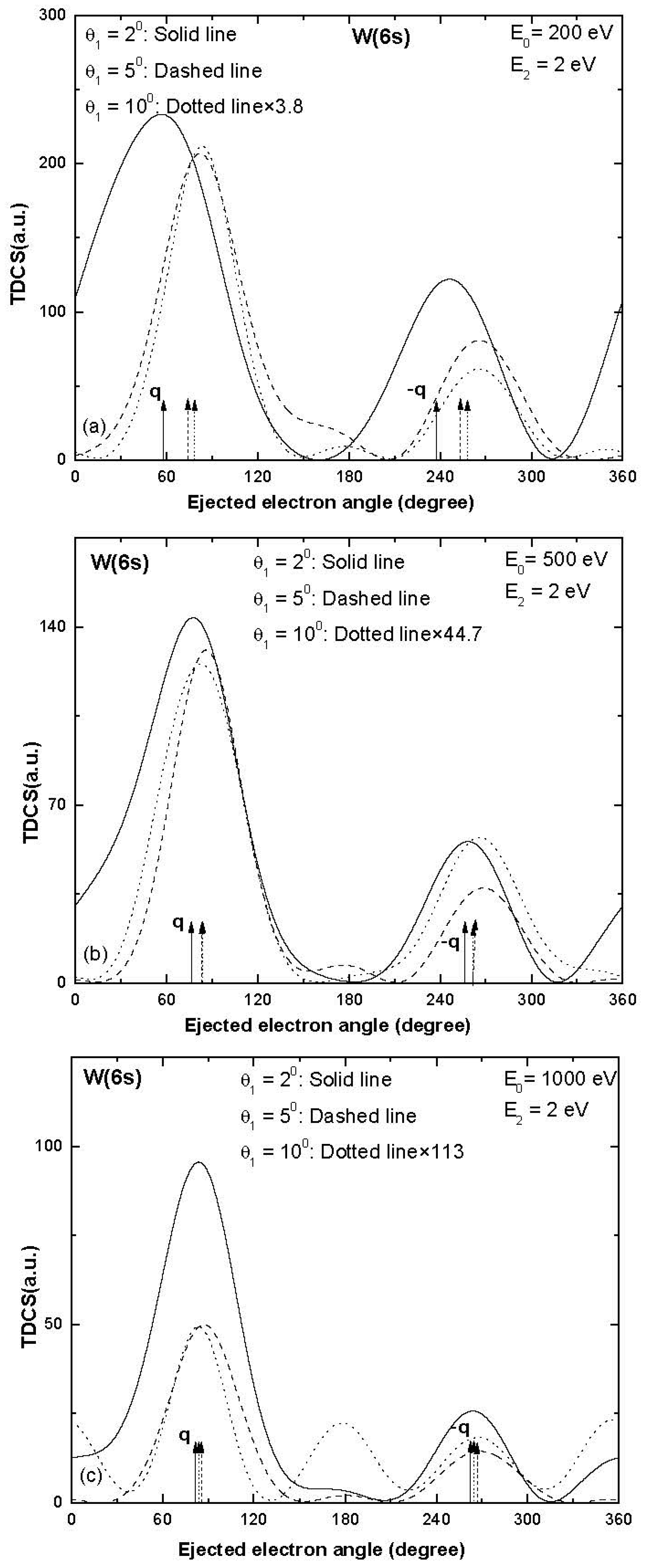

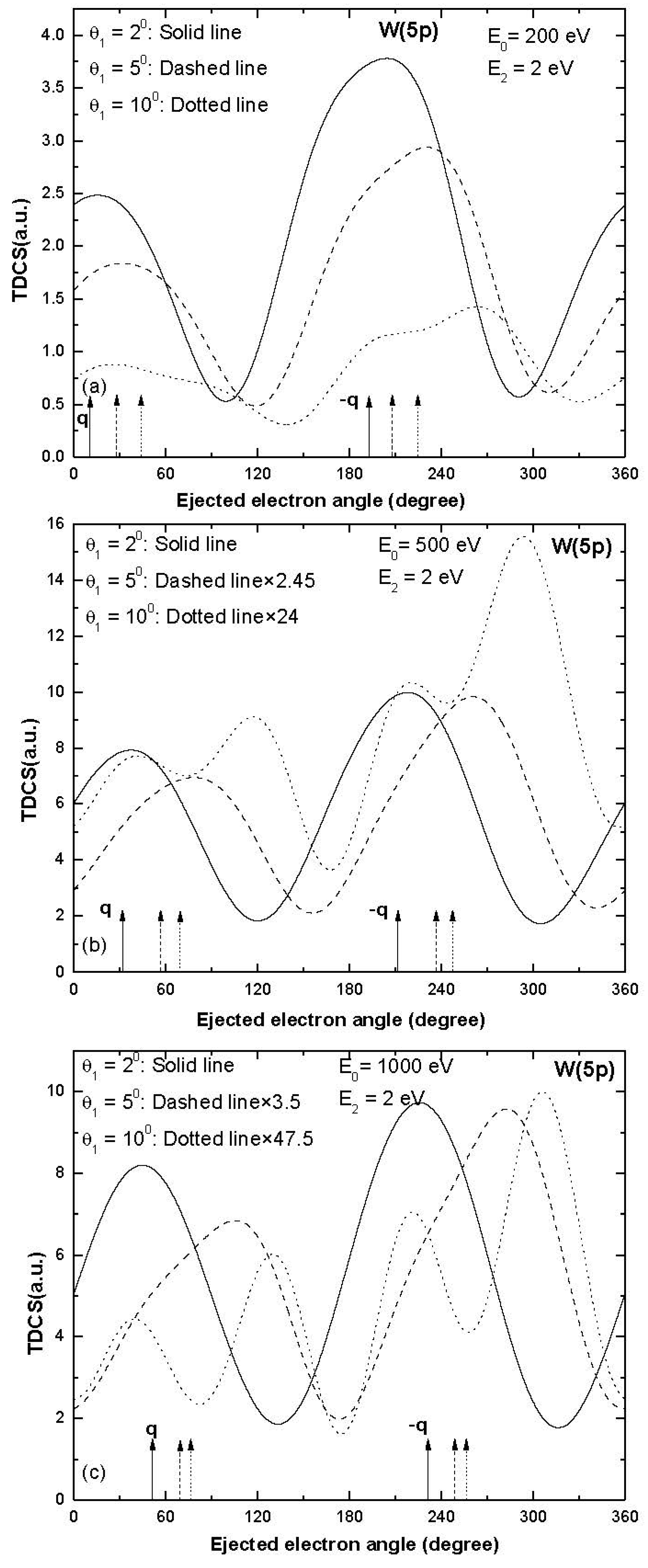


| Sub-Shell | Incident Electron Energy (eV), Ejected Electron Energy (eV) | Scattered Electron Angle (Degree) | Momentum Transfer Value (a.u.) | Momentum Transfer Direction (Degree) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W(6s) | 200, 2 | 2° | 0.15 | 59 |
| 5° | 0.34 | 74 | ||
| 10° | 0.67 | 78 | ||
| 500, 2 | 2° | 0.22 | 76 | |
| 5° | 0.53 | 82 | ||
| 10° | 1.1 | 82 | ||
| 1000, 2 | 2° | 0.3 | 82 | |
| 5° | 0.75 | 85 | ||
| 10° | 1.5 | 84 | ||
| W(5d) | 200, 2 | 2° | 0.19 | 44 |
| 5° | 0.35 | 65 | ||
| 10° | 0.67 | 74 | ||
| 500, 2 | 2° | 0.23 | 67 | |
| 5° | 0.53 | 79 | ||
| 10° | 1.1 | 81 | ||
| 1000, 2 | 2° | 0.30 | 78 | |
| 5° | 0.75 | 83 | ||
| 10° | 1.5 | 83 | ||
| W(5p) | 200, 2 | 2° | 0.54 | 12 |
| 5° | 0.61 | 28 | ||
| 10° | 0.81 | 45 | ||
| 500, 2 | 2° | 0.38 | 32 | |
| 5° | 0.60 | 56 | ||
| 10° | 1.07 | 68 | ||
| 1000, 2 | 2° | 0.37 | 52 | |
| 5° | 0.77 | 71 | ||
| 10° | 1.5 | 77 | ||
| W(4f) | 200, 2 | 2° | 0.62 | 11 |
| 5° | 0.68 | 25 | ||
| 10° | 0.86 | 41 | ||
| 500, 2 | 2° | 0.42 | 29 | |
| 5° | 0.63 | 52 | ||
| 10° | 1.1 | 66 | ||
| 1000, 2 | 2° | 0.39 | 48 | |
| 5° | 0.78 | 69 | ||
| 10° | 1.5 | 73 | ||
| W(5d) | 200, 10 | 2° | 0.25 | 30 |
| 5° | 0.39 | 54 | ||
| 10° | 0.68 | 67 | ||
| 500, 10 | 2° | 0.25 | 57 | |
| 5° | 0.54 | 73 | ||
| 10° | 1.05 | 77 | ||
| 1000, 10 | 2° | 0.31 | 72 | |
| 5° | 0.75 | 80 | ||
| 10° | 1.5 | 81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purohit, G. Calculation of Electron Impact Single Ionization TDCS of Tungsten Atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV. Atoms 2021, 9, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9020031
Purohit G. Calculation of Electron Impact Single Ionization TDCS of Tungsten Atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV. Atoms. 2021; 9(2):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9020031
Chicago/Turabian StylePurohit, Ghanshyam. 2021. "Calculation of Electron Impact Single Ionization TDCS of Tungsten Atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV" Atoms 9, no. 2: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9020031
APA StylePurohit, G. (2021). Calculation of Electron Impact Single Ionization TDCS of Tungsten Atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV. Atoms, 9(2), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9020031





