Proton Charge Radius from Electron Scattering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Electron Scattering
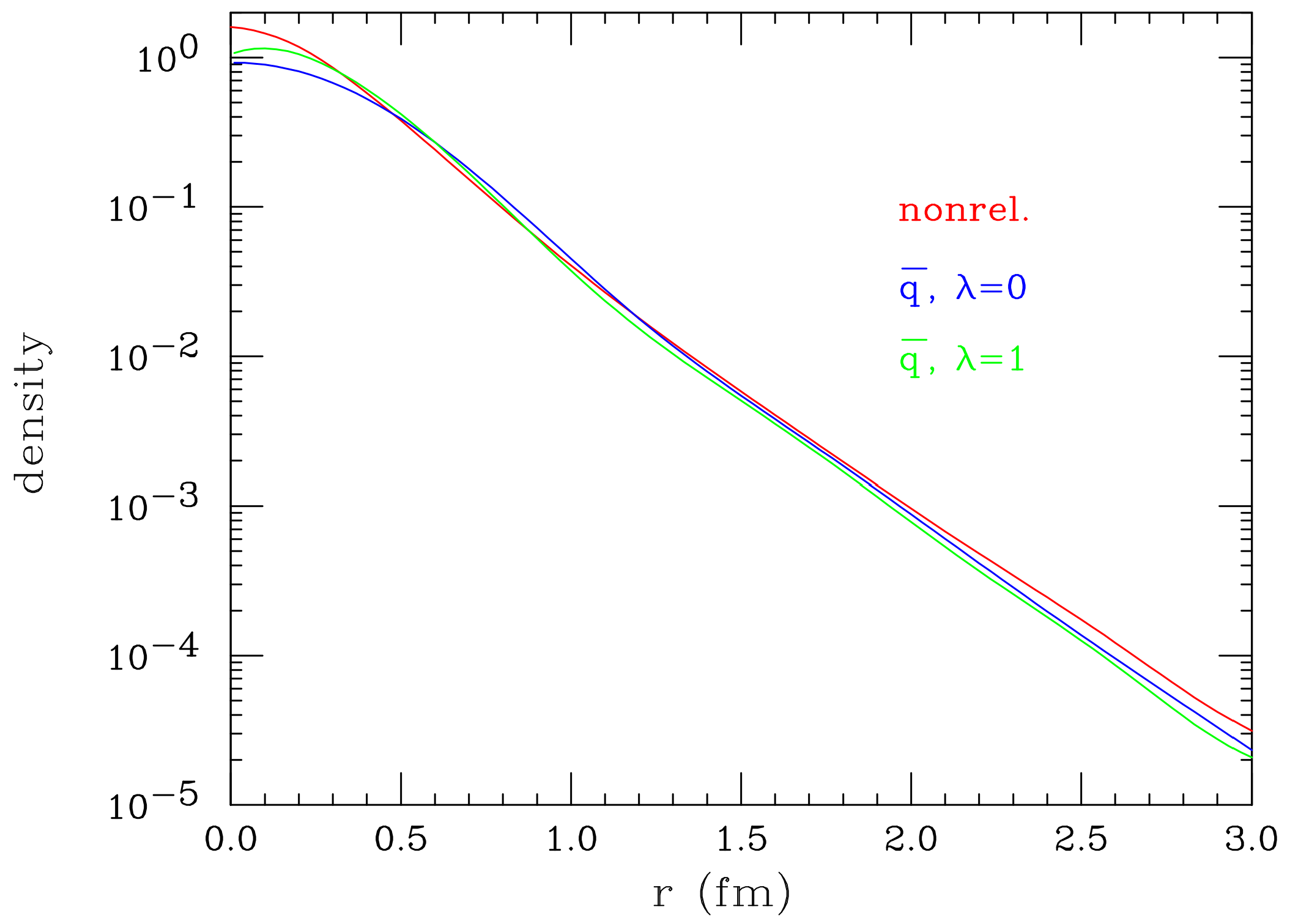
3. Charge Radius and Density
- a.
- b.
4. Data
5. Peculiarities and Difficulties
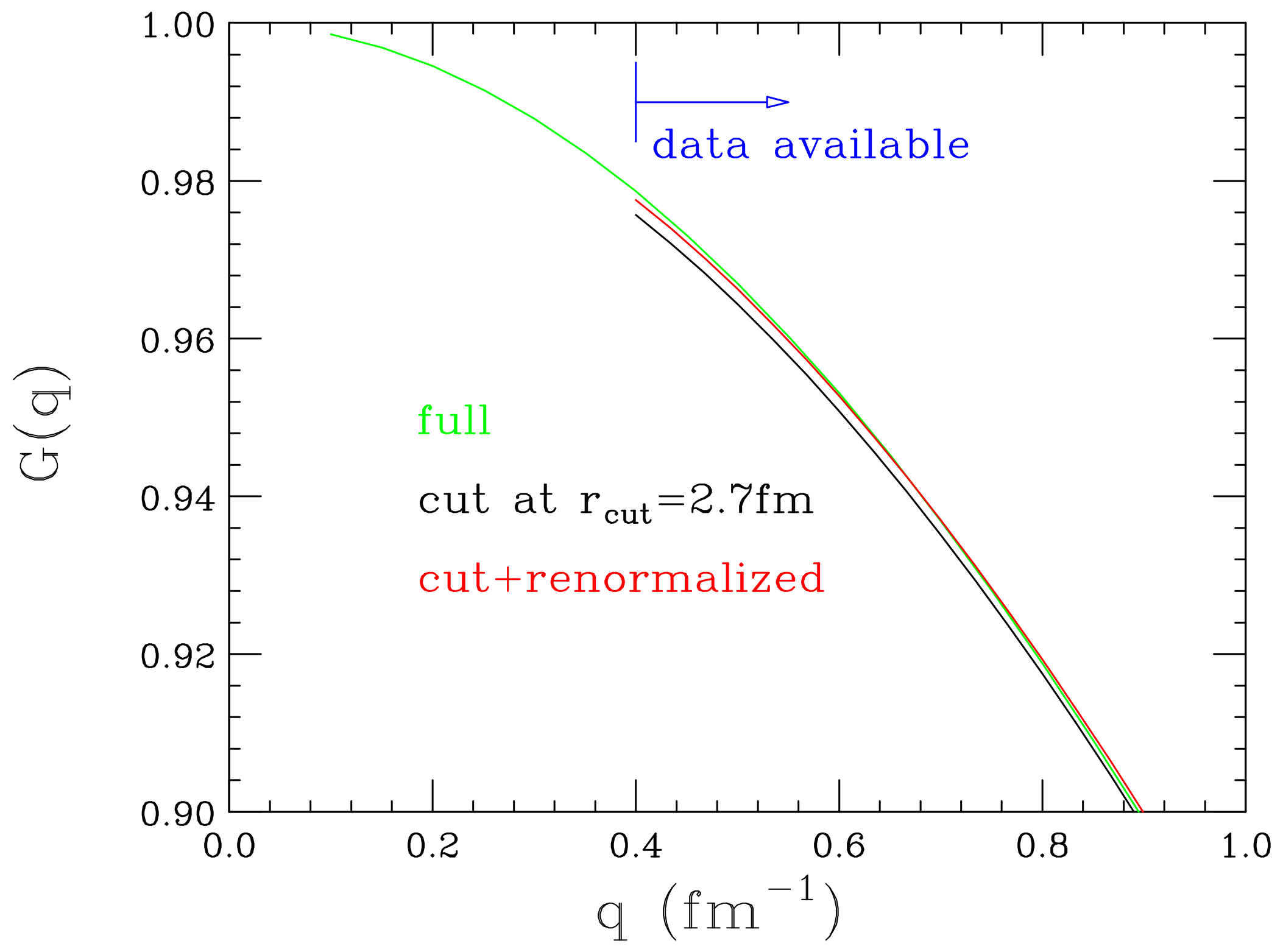
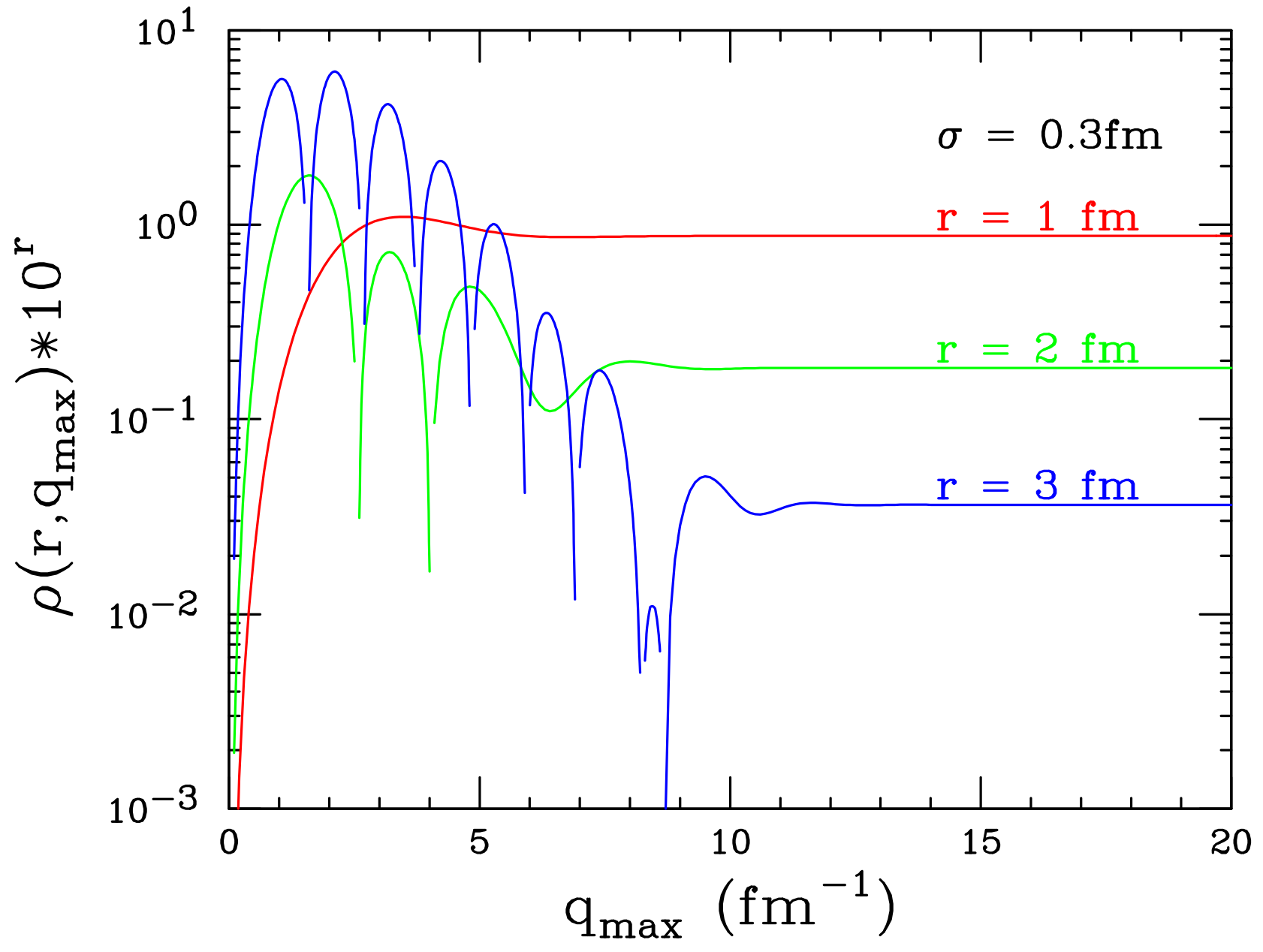
5.1. Importance of at Large r
- Dipole form factor (exponential density).
- Form factor corresponding to exponential density truncated at fm.
- Form factor corresponding to truncated density, renormalized to agree best with the Dipole form factor for momentum transfers above the minimum momentum transfer of the data; this renormalization corresponds to the standard renormalizations of data applied in most analyses.
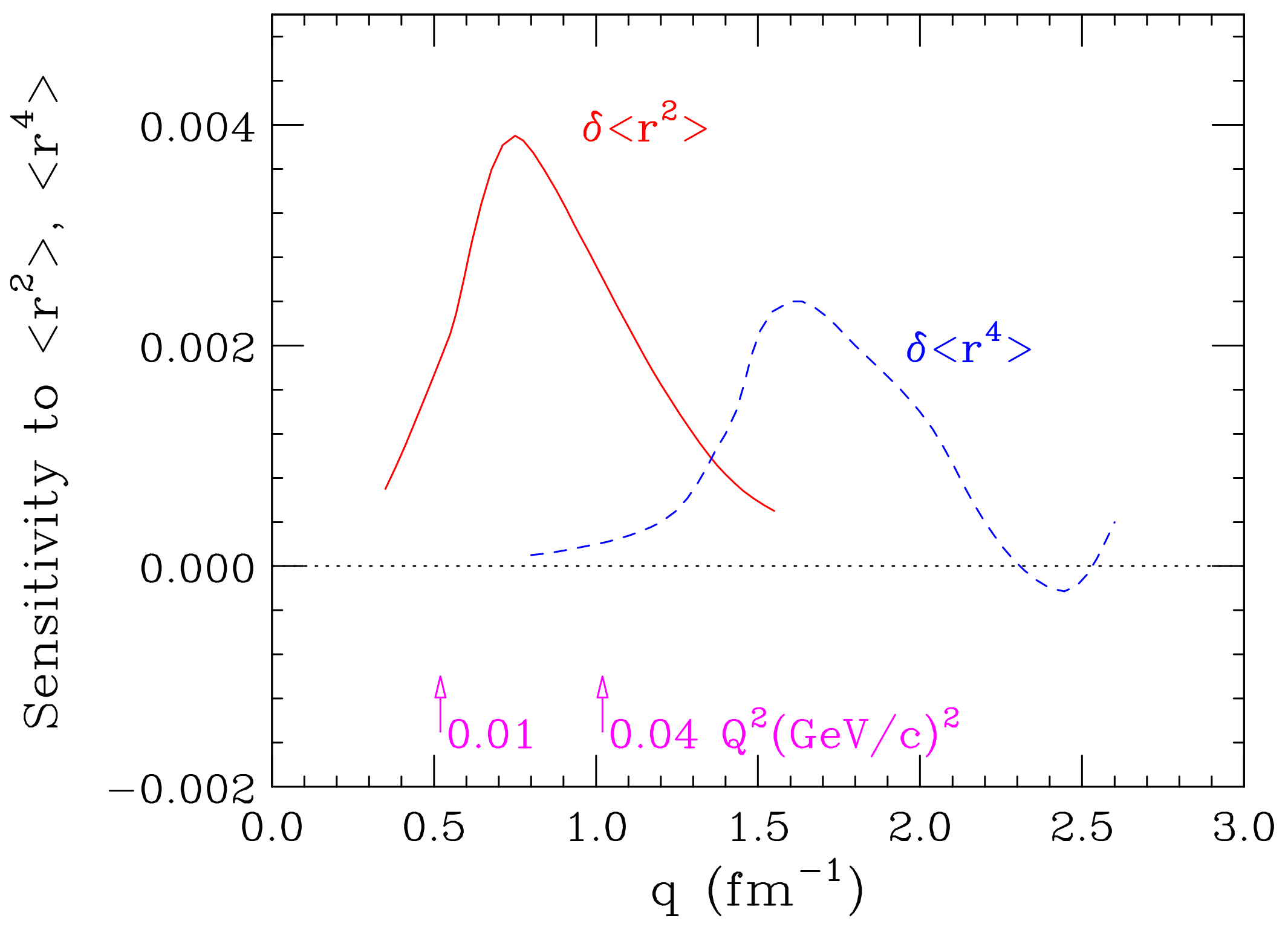
5.2. Smallness of Contribution of R to
5.3. Parameterizations in q-Space Only?
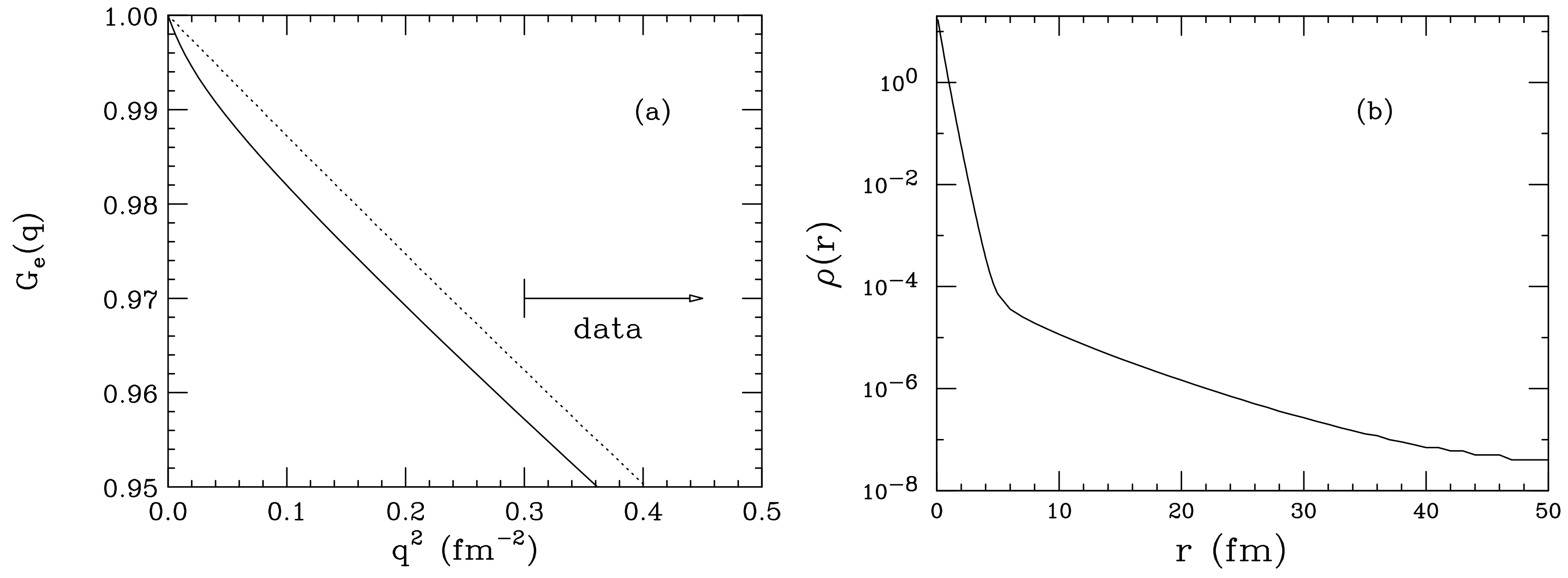
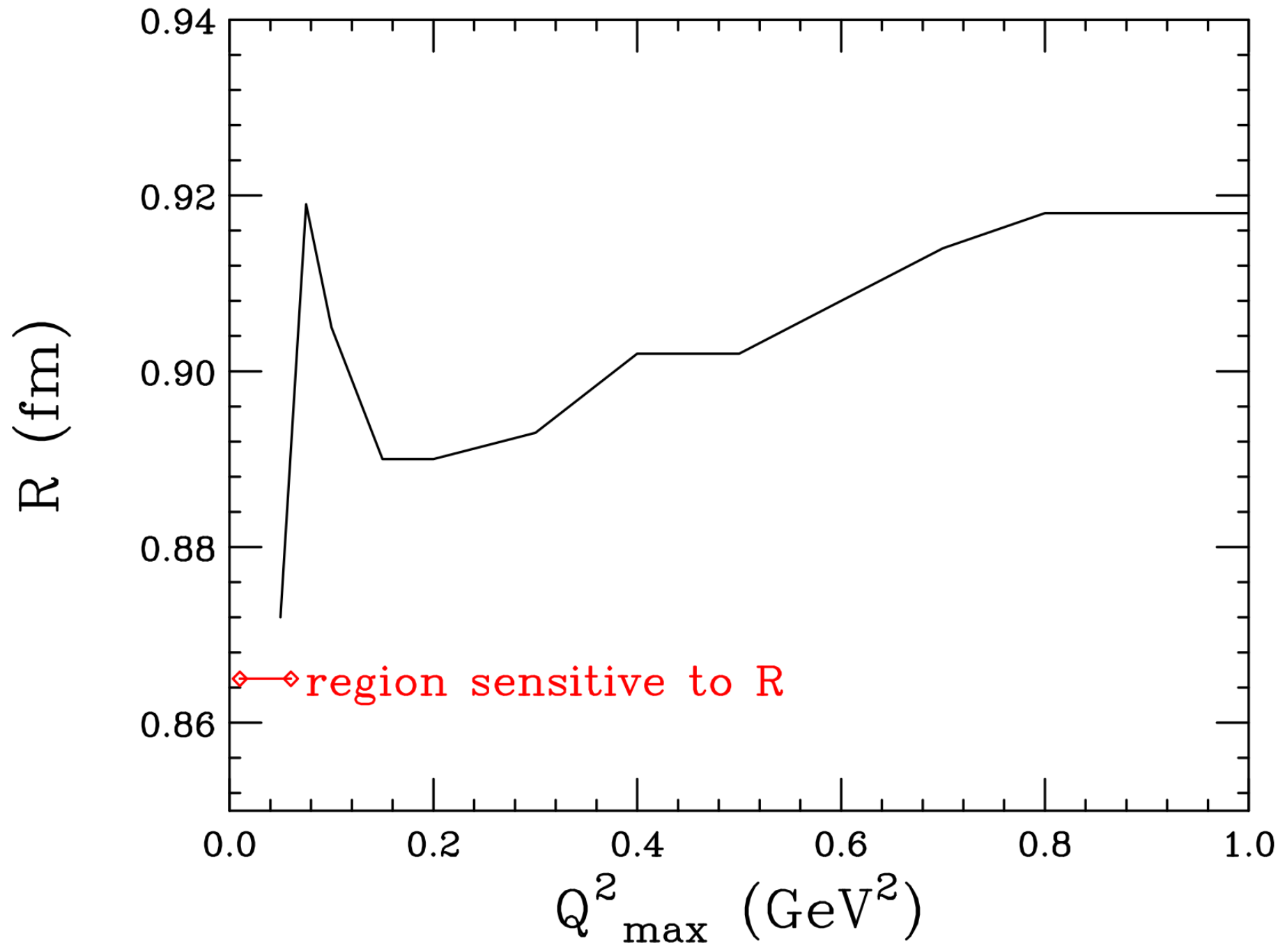
5.4. R from Very-Low-q Data?
- Due to the peculiar shape of the proton density, the moments are large and the -terms strongly coupled [15]. This is illustrated in Figure 7 [88], which shows the contributions (in %) of the higher moments to the finite size effect FSE . In order to make the contribution of smaller than, say, 1% in R (2% in FSE), one has to restrict to an extremely small value of ≤0.34 fm (0.004 GeV).
- At these low q’s, the term of interest becomes very small—0.015 at fm—but the experimental uncertainty of the measured quantity remains of order 0.01. A measurement of to, say, 2% (1% in R) then would require a measurement of G to 0.015·2% = 0.03%. Such an accuracy is not within reach for a very long time. Extracting an accurate slope directly from a measurement [89] without dealing with the higher moments (without extrapolations) is pretty hopeless.
5.5. A Counter-Intuitive Observation
6. Parameterizations and Fits
6.1. Types of Parameterizations Used
- For the interpretation of data at very low values of q, various traditional expressions, depending on one or two parameters, have been used: dipole, double dipole, Gaussian, Yukawa, etc.; see, e.g., [82,90]. Only those parameterizations are retained that give a close to the minimal one found. The obvious risk of this approach is that parametrizations with too few degrees of freedom yield too large and unreliable R [82,83,84]. Figure 7 can be used to estimate how many independent parameters (moments) are needed to achieve a given accuracy of R for a given .
- When fitting data up to large q, which requires many free parameters, a different approach is needed. Multi-parameter models such as the Padé form factors [15,91], polynomials or inverse polynomials of high order [90,91,92] or polynomials as a function of derived quantities [64,93,94] have been employed. Typically, the number of parameters is increased until the per degree of freedom reaches a plateau. Occasionally, the model dependence is estimated by generating and fitting pseudo-data and comparing the fit-results to the known input values [15,90,92,94].
- A somewhat more systematic approach employs an expansion of the form factors on an orthogonal basis [19,95,96]. This eases the determination of the parameters, but the selection of the appropriate cut-off in the order of the expansion (mostly based on the -plateau argument) is more delicate. The use of Gaussian bounds on the individual parameters, implemented by a “penalty” contribution to [64,93,97], is also quite efficient in limiting the values of the highest-order coefficients, which tend to be poorly constrained by the data.
- Safer approaches try to include known physics in the parameterization, hereby restricting the freedom of the fit. Examples are the Sum-Of-Gaussians (SOG) densities, which limit the fine structure in the density [98], or semi-phenomenological Vector Dominance Model (VDM)-based fits, which employ the analytical form of the VDM- and/or constrain the large-r fall-off; see [99,100,101,102,103] and Section 6.8 and Section 6.9.
- The strongest (and often too strong) input from theory is present in approaches such as the VDM fits, where constraints come from the assumption of vector dominance and the experimentally-known masses and couplings of the vector mesons (see Section 6.7).
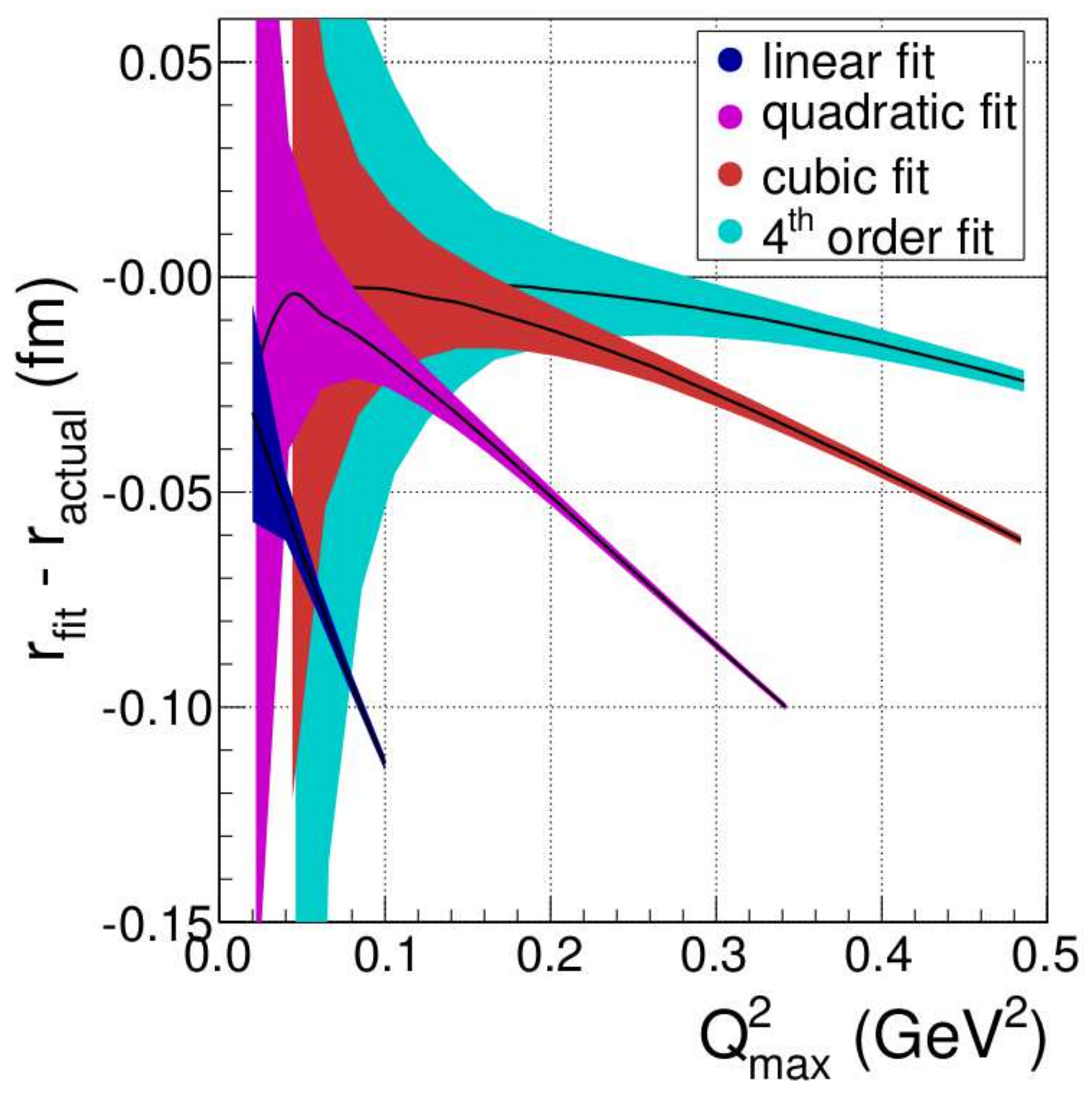
6.2. Polynomials in q
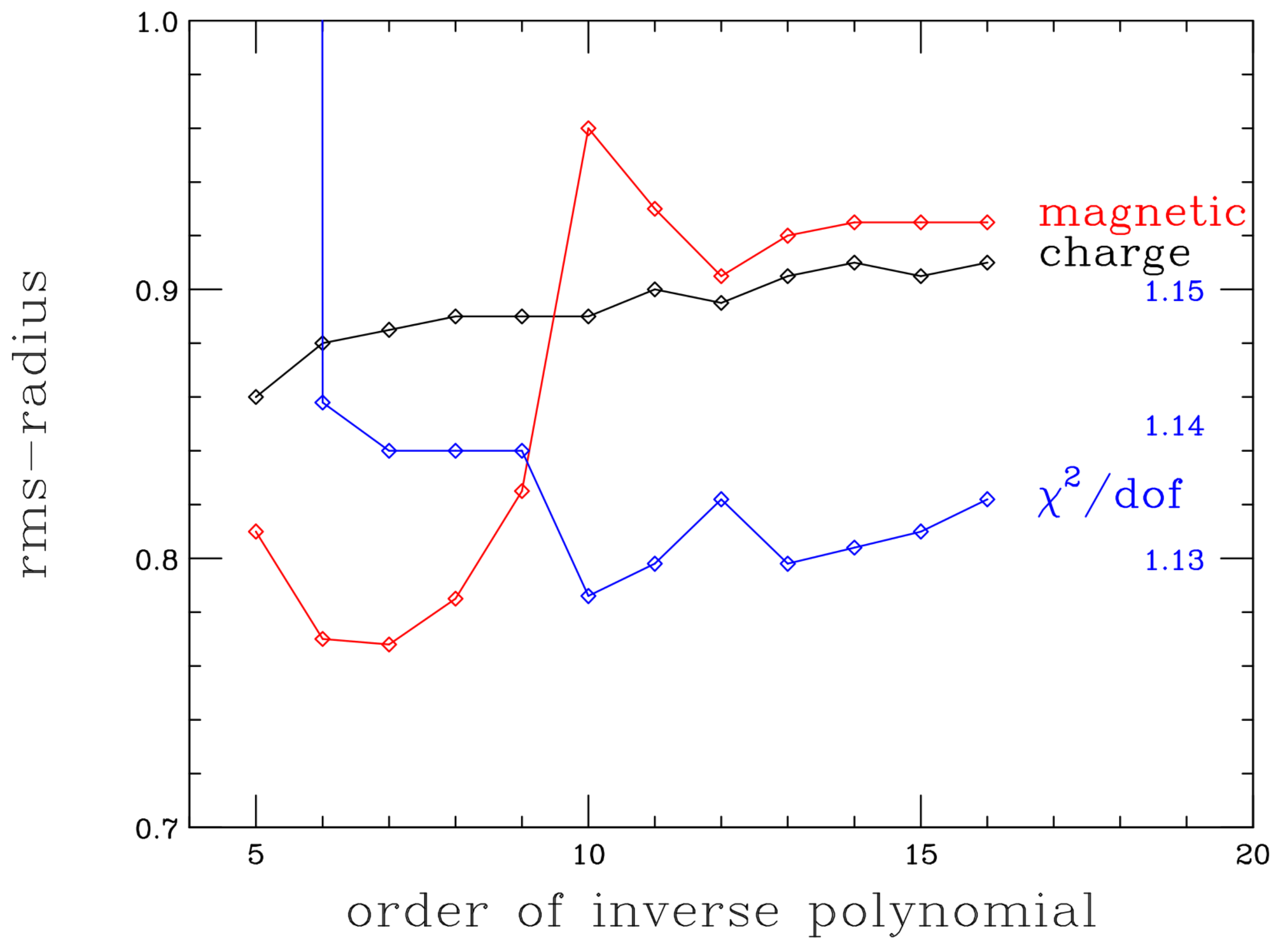
6.3. Inverse-Polynomial Type
6.4. Polynomials in z(q)
6.5. Polynomial in Times Dipole
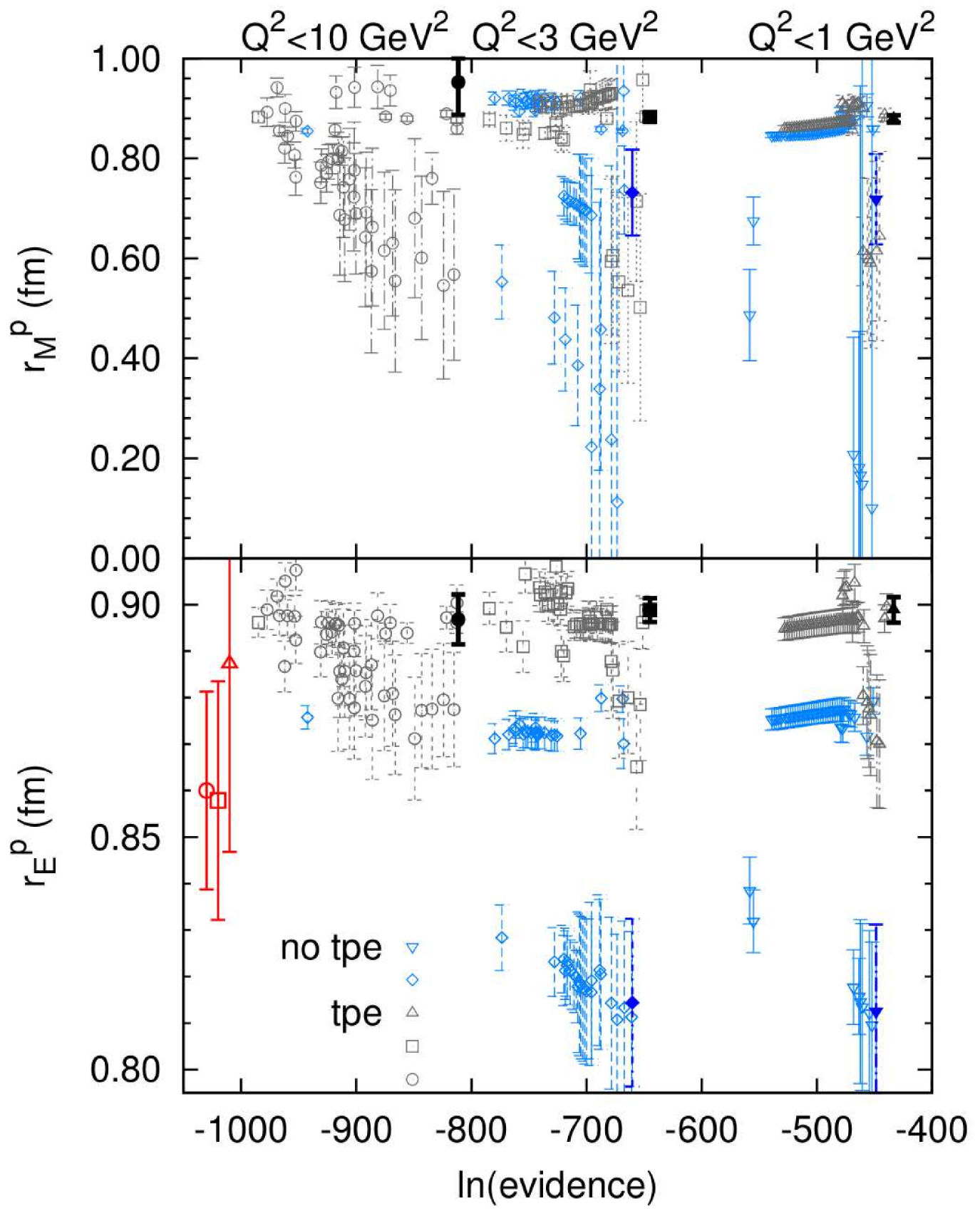
6.6. R from Bayesian Inference
6.7. Vector Dominance Model Fits
6.8. VDM-Motivated Parameterizations
6.9. Laguerre Polynomial Fits
6.10. Sum-Of-Gaussians with Tail Constraint
7. Summary
- –
- Use of a parameterized that is physical, i.e., does indeed correspond to a density. This is not the case for most parameterizations employed in the literature.
- –
- Fit of the data to the largest , in which case the data themselves fix to a fair degree the shape of including its behavior at large r, hereby constraining the shape of at low q.
- –
- Verification that at large r shows a physical behavior and, better, use of a physical constraint to enforce the correct behavior. The fall-off given by the pion tail provides a very general and helpful physics constraint.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohr, P.; Taylor, B.; Newell, D. CODATA Recommended Values of the Fundamental Physical Constants: 2010. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrington, J.; Sick, I. Evaluation of the Proton Charge Radius from Electron-Proton Scattering. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2015, 44, 031204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, R.; Antognini, A.; Nez, F.; Amaro, F.; Biraben, F.; Cardoso, J.M.R.; Covita, D.S.; Dax, A.; Dhawan, S.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; et al. The size of the proton. Nature 2010, 466, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohl, R.; Nez, F.; Fernandes, L.M.P.; Amaro, F.D.; Biraben, F.; Cardoso, J.M.R.; Covita, D.S.; Dax, A.; Dhawan, S.; Diepold, M.; et al. Laser spectroscopy of muonic deuterium. Science 2016, 353, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peset, C.; Pineda, A. The Lamb shift in muonic hydrogen and the proton radius from effective field theories. Eur. Phys. J. A 2015, 51, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, A.; Maisenbacher, L.; Matveev, A.; Pohl, R.; Khabarova, K.; Grinin, A.; Lamour, T.; Yost, D.C.; Hänsch, T.W.; Kolachevsky, N.; et al. The Rydberg constant and proton size from atomic hydrogen. Science 2017, 358, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleurbaey, H. Frequency metrology of the 1S-3S transition of hydrogen: contribution to the proton charge radius puzzle. Available online: https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-01633631 (accessed on 15 November 2017).
- Sick, I.; Trautmann, D. On the rms radius of the deuteron. Nucl. Phys. A 1998, 637, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfelder, R. Coulomb corrections to elastic electron-proton scattering and the proton charge radius. Phys. Lett. B 2000, 479, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunden, P.; Melnitchouk, W.; Tjon, J. Two-photon exchange in elastic electron-nucleon scattering. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 72, 034612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasev, A.; Blunden, P.; Hasell, D.; Raue, B. Two-photon exchange in elastic electron-proton scattering. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2017, 95, 245–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, D.; Adikaram, D.; Raue, B.A.; Weinstein, L.B.; Arrington, J.; Brooks, W.K.; Ungaro, M.; Adhikari, K.P.; Afanasev, A.V.; Akbar, Z.; et al. Measurement of two-photon exchange effect by comparing elastic e±p cross sections. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 065201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachek, I.A.; Arrington, J.; Dmitriev, V.F.; Gauzshtein, V.V.; Gerasimov, R.E.; Gramolin, A.V.; Holt, R.J.; Kaminskiy, V.V.; Lazarenko, B.A.; Mishnev, S.I.; et al. Measurement of the Two-Photon Exchange Contribution to the Elastic Scattering Cross Sections at the VEPP-3 Storage Ring. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 062005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, B.S.; Ice, L.D.; Khaneft, D.; O’Connor, C.; Russell, R.; Schmidt, A.; Bernauer, J.C.; Kohl, M.; Akopov, N.; Alarcon, R.; et al. Hard Two-Photon Contribution to Elastic Lepton-Proton Scattering Determined by the OLYMPUS Experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 092501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sick, I. On the rms-radius of the proton. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 576, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, A.; Pagnamenta, A. Wave Functions and Form Factors for Relativistic Composite Particles. I. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 2, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Kumari, I. Relativistic form factors for clusters with nonrelativistic wave functions. Phys. Rev. D 1977, 15, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X. A relativistic skyrmion and its form factors. Phys. Lett. B 1991, 254, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J. Nucleon charge and magnetization densities from Sachs form factors. Phys. Rev. C 2002, 66, 065203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J. Simple parametrization of nucleon form factors. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 068202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumiller, F.; Croissiaux, M.; Dally, E.; Hofstadter, R. Electromagnetic Form Factors of the Proton. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, T.; Hofstadter, R.; Hughes, E.; Yearian, M. Proton form factors from elastic electron-proton scattering. Phys. Rev. 1966, 142, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, F.; Peuser, P.; Simon, G.; Walther, V.; Wendling, R. Electromagnetic form factors of the proton at low four-momentum transfer. Nucl. Phys. A 1974, 222, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, F.; Simon, G.; Walther, V.; Wendling, R. Electromagnetic form factors of the peoton at low four-momentum transfer (II). Nucl. Phys. B 1975, 93, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.; Schmitt, C.; Borkowski, F.; Walther, V. Absolute electron-proton cross sections at low momentum transfer measured with a high pressure gas target system. Nucl. Phys. A 1980, 333, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.; Schmitt, C.; Walther, V. Elastic electric and magnetic e-d scattering at low momentum transfer. Nucl. Phys. A 1981, 364, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, W.; Behrend, H.; Brasse, F.; Flauger, W.; Hultschig, H.; Steffen, K.G. Elastic Electron-Proton Scattering at Momentum Transfers up to 245 F−2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 17, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, W.; Dudelzak, B.; Krehbiel, H.; McElroz, J.; Meyer-Berkhout, U.; Morrison, R.J.; Nguyen-Ngoc, H.; Schmidt, W.; Weber, G. Small-Angle Electron-Proton Elastic-Scattering Cross Sections for Squared Momentum Transfers Between 10 and 105 F−2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1966, 17, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerejacque, D.; Benaksas, D.; Drickey, D. Proton Form Factors from Observation of Recoil Protons. Phys. Rev. 1966, 141, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, W.; Behrend, H.-J.; Dorner, H.; Flauger, W.; Hultschig, H. Some Recent Measurements of Proton Form Factors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1967, 18, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, W.; Dudelzak, B.; Krehbiel, H.; McElroy, J.; Meyer-Berkhout, U.; Morrison, R.J.; Nguyen-Ngoc, H.; Schmidt, W.; Weber, G. The charge form factor of the proton at a momentum transfer of 75 F−2. Phys. Lett. B 1967, 25, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, W.; Buesser, F.; Dix, W.; Felst, R.; Harms, D.; Krehbiel, H.; Kuhlmann, P.E.; McElroy, j.; Meyer, J.; Weber, G. Measurement of proton and neutron electromagnetic form factors at squared four-momentum transfers up to 3 (GeV/c)2. Nucl. Phys. B 1973, 58, 429–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganichot, D.; Grossetête, B.; Isabelle, D. Backward electron-deuteron scattering below 280 MeV. Nucl. Phys. A 1972, 178, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.; Breidenbach, M.; Friedman, J.; Hartmann, G.; Kendall, H.; Buschhorn, G.; Coward, D.H.; DeStaebler, H.; Early, R.A.; Litt, J.; et al. Elastic Electron-Proton Scattering at Large Four-Momentum Transfer. Phys. Rev. D 1973, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Shin, Y.; Skopik, D. Proton form factor from 0.15 to 0.79 fm−2. Phys. Rev. C 1974, 9, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Burkert, V.; Knop, G.; Langenbeck, B.; Rith, K. Electromagnetic form factors of the proton at squared four-momentum transfers between 10 and 50 fm−2. Phys. Lett. B 1971, 35, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, W.; Buesser, F.W.; Dix, W.R.; Felst, R.; Harms, D.; Krehbiel, H.; Kuhlmann, P.E.; McElroy, J.; Weber, G. Electromagnetic proton form factors at squared four-momentum transfers between 1 and 3(GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 33, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowski, F.; Simon, G.; Walther, V.; Wendling, R. On the determination of the proton RMS-radius from electron scattering data. Z. Physik A 1975, 275, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, J.; Achenbach, P.; Gayoso, C.A.; Böhm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Debenjak, L.; Distler, M.O.; Doria, L.; Esser, A.; Fonvieille, H.; et al. High-Precision Determination of the Electric and Magnetic Form Factors of the Proton. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 242001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amroun, A. Mesure Des Facteurs De Forme Electromagnetiques Des Noyaux Helium-3 Et Tritium Par Diffusion D’electrons. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Bordeaux, Bordeaux, France, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Dudelzak, B.; Sauvage, G.; Lehmann, P. Measurements of the form factors of the proton at momentum transfers q22 fermi−2. Nuov. Cim. 1963, 28, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qattan, I.; Arrington, J.; Segel, R.; Zheng, X.; Aniol, K.; Baker, O.K.; Beams, R.; Brash, E.J.; Calarco, J.; Camsonne, A.; et al. Precision Rosenbluth Measurement of the Proton Elastic Form Factors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 142301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christy, M.E.; Ahmidouch, A.; Armstrong, C.S.; Arrington, J.; Asaturyan, R.; Avery, S.; Baker, O.; Beck, D.; Blok, H.P.; Bochna, C.W.; et al. Measurements of electron-proton elastic cross sections for 0.4 < Q2 < 5.5 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 70, 015206. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, D.; Van Westrum, D.; Abbott, D.; Ahmidouch, A.; Amatuoni, T.A.; Armstrong, C.; Arrington, J.; Assamagan, K.A.; Bailey, K.; Baker, O.K.; et al. Quasielastic (e,e′p) reaction on 12C, 56Fe, and 197Au. Phys. Rev. C 2003, 68, 064603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, I.; Armstrong, C.; Arrington, J.; Assamagan, K.; Baker, O.; Beck, D.H.; Bochna, C.W.; Carlini, R.D.; Cha, J.; Cothran, C.; et al. Evidence for valencelike quark-hadron duality. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, S.; Arnold, R.; Bosted, P.; Chertok, B.; Mecking, B.; Schmidt, I.; Szalata, Z.M.; York, R.C.; Zdarko, R. Measurement of elastic electron-neutron scattering and inelastic electron-deuteron scattering cross sections at high momentum transfer. Phys. Rev. D 1992, 46, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Atwood, W.; Bloom, E.; Cottrell, R.; DeStaebler, H.; Jordan, C.L.; Piel, H.G.; Prescott, C.Y.; Siemann, R.; Taylor, R.E.; et al. Electron scattering at 4∘ with energies of 4.5–20 GeV. Phys. Rev. D 1975, 12, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goitein, M.; Budnitz, R.; Carroll, L.; Chen, J.; Dunning, J.; Hanson, K.; Imrie, D.C.; Mistretta, C.; Wilson, R. Elastic Electron-Proton Scattering Cross Sections Measured by a Coincidence Technique. Phys. Rev. D 1970, 1, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosted, P.; Katramatou, A.; Arnold, R.; Benton, D.; Clogher, L.; DeChambrier, G.; Lambert, J.; Lung, A.; Petratos, G.G.; Rahbar, A.; et al. Measurements of the deuteron and proton magnetic form factors at large momentum transfers. Phys. Rev. C 1990, 42, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosted, P.E.; Andivahis, L.; Lung, A.; Stuart, L.M.; Alster, J.; Arnold, R.G.; Chang, C.C.; Dietrich, F.S.; Dodge, W.; Gearhart, R.; et al. Measurements of the electric and magnetic form factors of the proton from Q2 = 1.75 to 8.83 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 68, 3841–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sill, A. Jailbar optical studies of the SLAC 8-GeV/c spectrometer. Available online: http://inspirehep.net/record/243145/ (accessed on 10 November 2017).
- Price, L.E.; Dunning, J.R.; Goitein, M.; Hanson, K.; Kirk, T.; Wilson, R. Backward-angle electron-proton elastic scattering and proton electromagnetic form factors. Phys. Rev. D 1971, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litt, J.; Buschhorn, G.; Coward, D.; Destaebler, H.; Mo, L.; Taylor, R.E.; Barish, B.C.; Loken, S.C.; Pine, J.; Friedman, J.I.; et al. Measurement of the ratio of the proton form factors, GE/GM, at high momentum transfers and the question of scaling. Phys. Lett. B 1970, 31, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Filippone, B.; Jourdan, J.; Milner, R.; McKeown, R.; Potterveld, D.; Arnold, R.; Benton, D.; Bosted, P.; Clogher, L.; et al. Measurement of the proton elastic form factors for Q2 = 1–3 (Gev/c)2. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 224, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.; Filippone, B.; Jourdan, J.; Milner, R.; McKeown, R.; Potterveld, D.; Andivahis, L.; Arnold, R.; Benton, D.; Bosted, P.; et al. Measurements of the proton elastic form factors for 1 ≤ Q2 ≤ 3 (GeV/c)2 at SLAC. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 49, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andivahis, L.; Bosted, P.E.; Lung, A.; Stuart, L.M.; Alster, J.; Arnold, R.G.; Chang, C.C.; Dietrich, F.S.; Dodge, W.; Gearhart, R.; et al. Measurements of the electric and magnetic form factors of the proton from Q2 = 1.75 to 8.83 (GeVc)2. Phys. Rev. D 1994, 50, 5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drickey, D.; Hand, L. Precise Neutron and Proton Form Factors at Low Momentum Transfers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1962, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjabi, V.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Aniol, K.A.; Baker, F.T.; Berthot, J.; Bertin, P.Y.; Bertozzi, W.; Besson, A.; Bimbot, L.; Boeglin, W.U.; et al. Proton elastic form factor ratios to Q2 = 3.5 GeV2 by polarization transfer. Phys. Rev. C 2005, 71, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayou, O.; Wijesooriya, K.; Afanasev, A.; Amarian, M.; Aniol, K.; Becher, S.; Benslama, K.; Bimbot, L.; Bosted, P.; Brash, E.; et al. Measurements of the elastic electromagnetic form factor ratio μp GEp/GMp via polarization transfer. Phys. Rev. C 2001, 64, 038202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayou, O.; Aniol, K.A.; Averett, T.; Benmokhtar, F.; Bertozzi, W.; Bimbot, L.; Brash, E.J.; Calarco, J.R.; Cavata, C.; Chai, Z.; et al. Measurement of GEp/GMp in p → to Q2 = 5.6 GeV2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 092301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, X.; Allada, K.; Armstrong, D.; Arrington, J.; Bertozzi, W.; Boeglin, W.; Chen, J.P.; Chirapatpimol, K.; Choi, S.; Chudakov, E.; et al. High-precision measurement of the proton elastic form factor ratio μpGE/GM at low Q2. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 705, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botterill, D.; Braben, D.; Montgomery, H.; Norton, P.; Matone, G.; Del Guerra, A.; Giazotto, A.; Giorgi, M.A.; Orsitto, F.; Stefaninia, A. Elastic electron-proton scattering between 0.05 and 0.30 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Lett. B 1973, 46, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, J. Measurement of the elastic electron-proton cross section and separation of the electric and magnetic form factor in the Q2 range from 0.004 to 1 (GeV/c)2. Available online: http://wwwa1.kph.uni-mainz.de/A1/publications/doctor/bernauer.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2017).
- Lee, G.; Arrington, J.; Hill, R. Extraction of the proton radius from electron-proton scattering data. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 013013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I. Problems with proton radii. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2012, 67, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Tsai, Y. Radiative Corrections to Elastic and Inelastic ep and up Scattering. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1969, 41, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximon, L.; Tjon, J. Radiative corrections to electron-proton scattering. Phys. Rev. C 2000, 62, 054320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, S.; Dieterich, S.; Aniol, K.A.; Annand, J.R.M.; Baker, O.K.; Bertozzi, W.; Boswell, M.; Brash, E.J.; Chai, Z.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Polarization Transfer in the 4He (, e’)3H Reaction up to Q2 = 2.6 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milbrath, B.; McIntyre, J.; Armstrong, C.; Barkhuff, D.; Bertozzi, W.; Chen, J.P.; Dale, D.; Dodson, G.; Dow, K.A.; Epstein, M.B.; et al. Comparison of Polarization Observables in Electron Scattering from the Proton and Deuteron. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospischil, T.; Bartsch, P.; Baumann, D.; Bermuth, J.; Böhm, R.; Bohinc, K.; Derber, S.; Ding, M.; Distler, M.; Drechsel, D.; et al. Measurement of the Recoil Polarization in the p (, e’ ) π 0 Reaction at the Δ (1232) Resonance. Phys Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, C.B.; Sindile, A.; Akdogan, T.; Alarcon, R.; Bertozzi, W.; Booth, E.; Botto, T.; Calarco, J.; Clasie, B.; DeGrush, A.; et al. Measurement of the Proton’s Electric to Magnetic Form Factor Ratio from (,e’p). Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 052301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, G.; Glister, J.; Lee, B.; Allada, K.; Armstrong, W.; Arrington, J.; Beck, A.; Benmokhtar, F.; Berman, B.L.; Boeglin, W.; et al. Measurements of the Proton Elastic-Form-Factor Ratio mu pG p E/G p M at Low Momentum Transfer. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 202002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, G.; Aghalaryan, A.; Ahmidouch, A.; Anderson, B.D.; Asaturyan, R.; Baker, O.; Baldwin, A.R.; Barkhuff, D.; Breuer, H.; Carlini, R.; et al. The ratio of proton electromagnetic form factors via recoil polarimetry at Q2 = 1.13 (GeV/c)2. Nucl. Phys. A 2006, 764, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.K.; Aniol, K.A.; Baker, F.T.; Berthot, J.; Bertin, P.Y.; Bertozzi, W.; Besson, A.; Bimbot, L.; Boeglin, W.U.; Brash, E.J.; et al. GEp/GMp Ratio by Polarization Transfer in p→ . Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.K.; Aghalaryan, A.; Ahmidouch, A.; Asaturyan, R.; Bloch, F.; Boeglin, W.; Bosted, P.; Carasco, C.; Carlini, R.; Cha, J.; et al. Proton GE/GM from beam-target asymmetry. Phys. Rev. C 2006, 74, 035201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckett, A.J.R.; Brash, E.J.; Jones, M.K.; Luo, W.; Meziane, M.; Pentchev, L.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Wesselmann, F.R.; Abdellah, A.; et al. Recoil Polarization Measurements of the Proton Electromagnetic Form Factor Ratio to Q2 = 8.5 GeV2. Phy. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 242301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckett, A.J.R.; Brash, E.J.; Gayou, O.; Jones, M.K.; Pentchev, L.; Perdrisat, C.F.; Punjabi, V.; Aniol, K.A.; Averett, T.; Benmokhtar, F.; et al. Final analysis of proton form factor ratio data at Q2 = 4.0, 4.8, and 5.6 GeV2. Phys. Rev. C 2012, 85, 045203. [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich, S.; Bartsch, P.; Baumann, D.; Böhm, J.B.R.; Bohinc, K.; Böhm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Derber, S.; Ding, M.; Distler, M.; et al. Polarization transfer in the 4He (e→, e’p→)3 H reaction. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 500, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolone, M.; Malace, S.P.; Strauch, S.; Albayrak, I.; Arrington, J.; Berman, B.L.; Brash, E.J.; Briscoe, B.; Camsonne, A.; Chen, J.P.; et al. Polarization Transfer in the 4He(,e’)3H Reaction at Q2 = 0.8 and 1.3 (GeV/c)2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friar, J.; Sick, I. Zemach moments for hydrogen and deuterium. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 579, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friar, J.; Sick, I. Muonic hydrogen and the third Zemach moment. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbatsch, M.; Hessels, E. Evaluation of the strength of electron-proton scattering data for determining the proton charge radius. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 93, 015204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higinbotham, D.; Kabir, A.; Lin, V.; Meekins, D.; Norum, B.; Sawatzky, B. Proton radius from electron scattering data. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 93, 055207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, K.; Carlson, C.; Maddox, S. Consistency of electron scattering data with a small proton radius. Phys. Rev. C 2016, 93, 065207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, I.; Meissner, U.G. Reduction of the proton radius discrepancy by 3σ. Phys. Lett. B 2014, 737, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I.; Trautmann, D. Proton root-mean-square radii and electron scattering. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 89, 012201(R). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I. Importance of Tail of Proton Density. Few-Body Syst. 2014, 55, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I.; Trautmann, D. Reexamination of proton rms radii from low-q power expansions. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 012501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparian, A.; Pedroni, R.; Ahmed, A.; Khandaker, M.; Punjabi, V.; Salgado, v.; Akushevich, I.; Gao, H.; Huang, M.; Laskaris, G.; et al. High precision measurement of the proton charge radius. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/06d6/1cc255edb67eb9adccf3605dd313eaff5504.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2017).
- Bernauer, J.; Distler, M.; Friedrich, J.; Walcher, T.; Achenbach, P.; Ayerbe Gayoso, C.; Böhm, R.; Bosnar, D.; Debenjak, L.; Doria, L.; et al. Electric and magnetic form factors of the proton. Phys. Rev. C. 2014, 90, 015206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrington, J.; Melnitchouk, W.; Tjon, J. Global analysis of proton elastic form factor data with two-photon exchange corrections. Phys. Rev. C 2007, 76, 035205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, E.; Mesick, K.; White, A.; Gilman, R.; Strauch, S. Polynomial fits and the proton radius puzzle. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 90, 045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Paz, G. Model-independent extraction of the proton charge radius from electron scattering. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 82, 113005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisyuk, D. Proton charge and magnetic rms radii from the elastic ep scattering data. Nucl. Phys. A 2010, 843, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friar, J. Relativistic corrections to electron scattering by 2He, 3He, and 4He. Ann. Phys. 1973, 81, 332–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anni, R.; Có, G.; Pellegrino, P. Nuclear charge density distributions from elastic electron scattering data. Nucl. Phys. A 1995, 584, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, K.; Juszczak, C. Proton radius from Bayesian inference. Phys. Rev. C 2014, 90, 054334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I. Model-independent nuclear charge densities from elastic electron scattering. Nucl. Phys. A 1974, 218, 509–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iachello, F.; Jackson, A.; Lande, A. Semi-phenomenological fits to nucleon electromagnetic form factors. Phys. Lett. B 1973, 43, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatnik, S.; Zovko, N. Nucleon form factors in the extended VDM supplemented with asymptotic constraints. Acta Phys. Austriaca 1974, 39, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Gari, M.; Krümpelmann, W. The electric neutron form factor and the strange quark content of the nucleon. Phys. Lett. B 1992, 274, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomon, E. Extended Gari-Krümpelmann model fits to nucleon electromagnetic form factors. Phys. Rev. C 2001, 64, 035204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijker, R.; Iachello, F. Reanalysis of the nucleon spacelike and timelike electromagnetic form factors in a two-component model. Phys. Rev. C 2004, 69, 068201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernauer, J.; Distler, M. Avoiding common pitfalls and misconceptions in extractions of the proton radius. arXiv, 2016; arXiv:1606.02159. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, I.; Hammer, H.W.; Meissner, U.G. The size of the proton: Closing in on the radius puzzle. Eur. Phys. J. A 2012, 48, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, K.; Plonski, P.; Sulei, R. Neural network parameterizations of electromagnetic nucleon form-factors. arXiv, 2010; arXiv:1006.0342. [Google Scholar]
- Gari, M.; Krümpelmann, W. Semiphenomenological synthesis of meson and quark dynamics and the E.M. structure of the nucleon. Z. Phys. 1985, 322, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergell, P.; Meissner, U.G.; Drechsel, D. Dispersion-theoretical analysis of the nucleon electromagnetic form factors. Nucl. Phys. A 1996, 596, 367–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, H.W.; Drechsel, D.; Meissner, U.G. On the pion cloud of the nucleon. Phys. Lett. B 2004, 586, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, I.; Meissner, U.G.; Hammer, H.W.; Dong, Y. Theoretical constraints and systematic effects in the determination of the proton form factors. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 014023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhler, G.; Pietarinen, E.; Sabba-Stefanescu, I.; Borkowski, F.; Simon, G.; Walther, V.H.; Wendling, R.D. Analysis of electromagnetic nucleon form factors. Nucl. Phys. B 1976, 114, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhler, G.; Pietarinen, E. Electromagnetic radii of nucleon and pion. Phys. Lett. B 1975, 53, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhler, G. Landolt-Boernstein, Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1983; Volume 9.
- Adamuscin, C.; Dubnicka, S.; Dubnickova, A. New value of the proton charge root mean square radius. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2012, 67, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcon, J.; Weiss, C. Nucleon form factors in dispersively improved Chiral Effective Field Theory II: Electromagnetic form factors. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1710.06430v1. [Google Scholar]
- Horbatsch, M.; Hessels, E.; Pineda, A. Proton radius from electron-proton scattering and chiral perturbation theory. Phys. Rev. C 2017, 95, 035203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I. Precise root-mean-square radius of 4He. Phys. Rev. C 2008, 77, 041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sick, I. Precise nuclear radii from electron scattering. Phys. Lett. B 1982, 116, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, I. Private communication, 2012.
| 1. | The tail density is much higher than the 1- tail deduced initially in [109] (dashed). |



© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sick, I. Proton Charge Radius from Electron Scattering. Atoms 2018, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms6010002
Sick I. Proton Charge Radius from Electron Scattering. Atoms. 2018; 6(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms6010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleSick, Ingo. 2018. "Proton Charge Radius from Electron Scattering" Atoms 6, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms6010002
APA StyleSick, I. (2018). Proton Charge Radius from Electron Scattering. Atoms, 6(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms6010002



