Comparison of Different Rydberg Atom-Based Microwave Electrometry Techniques
Abstract
1. Introduction
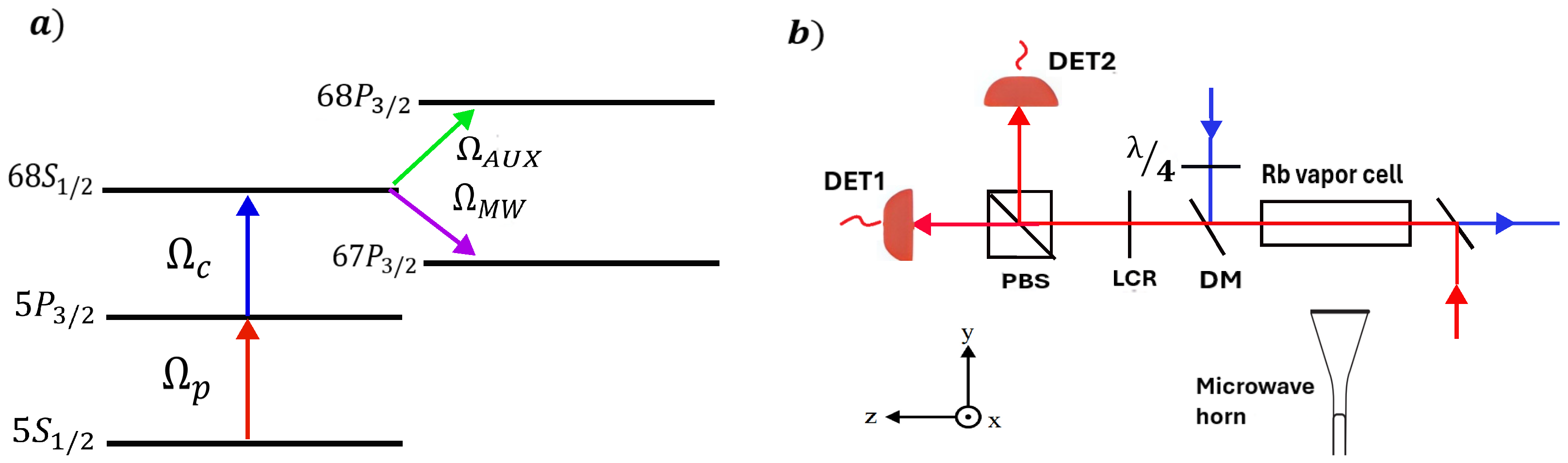
2. Materials and Methods
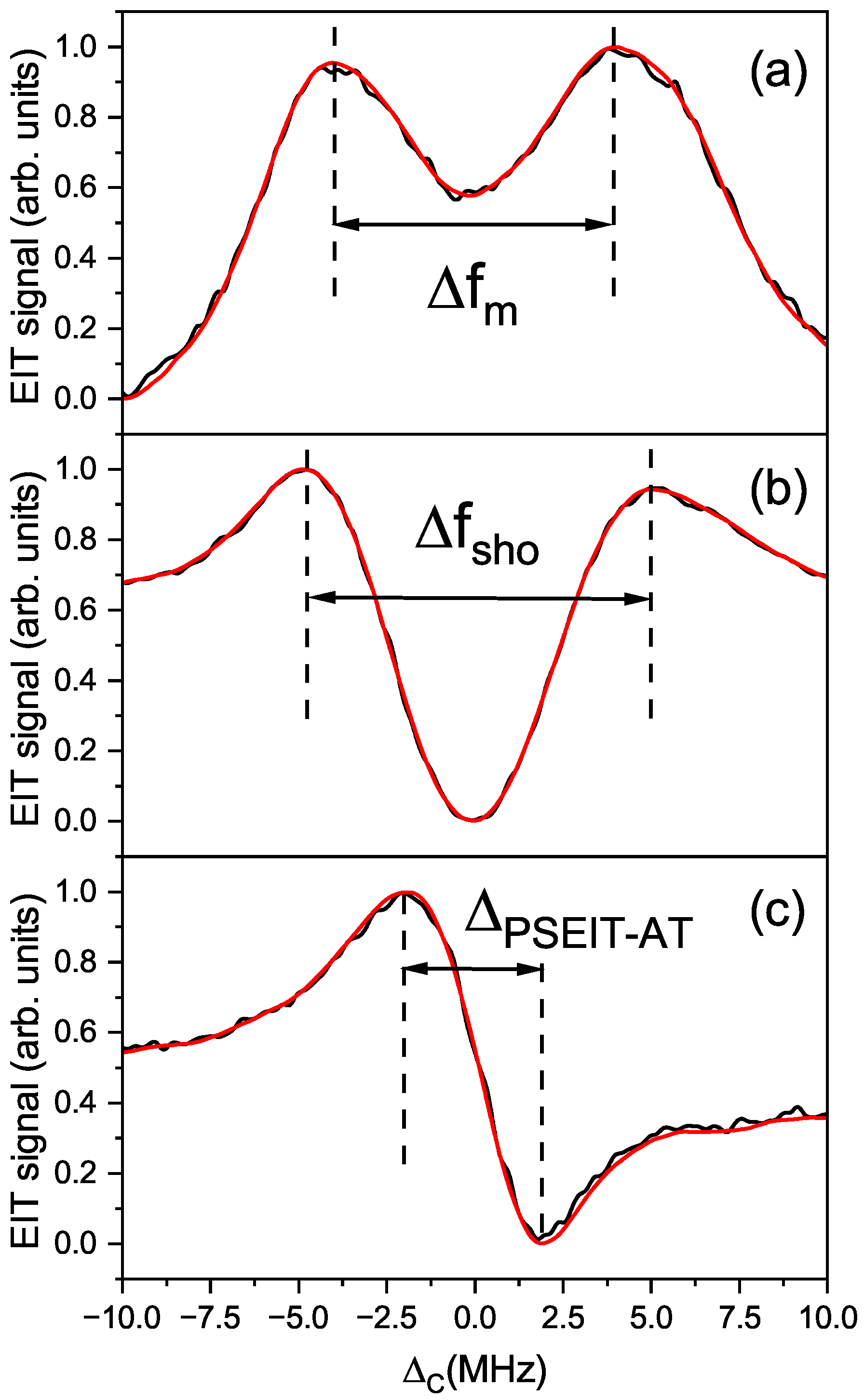
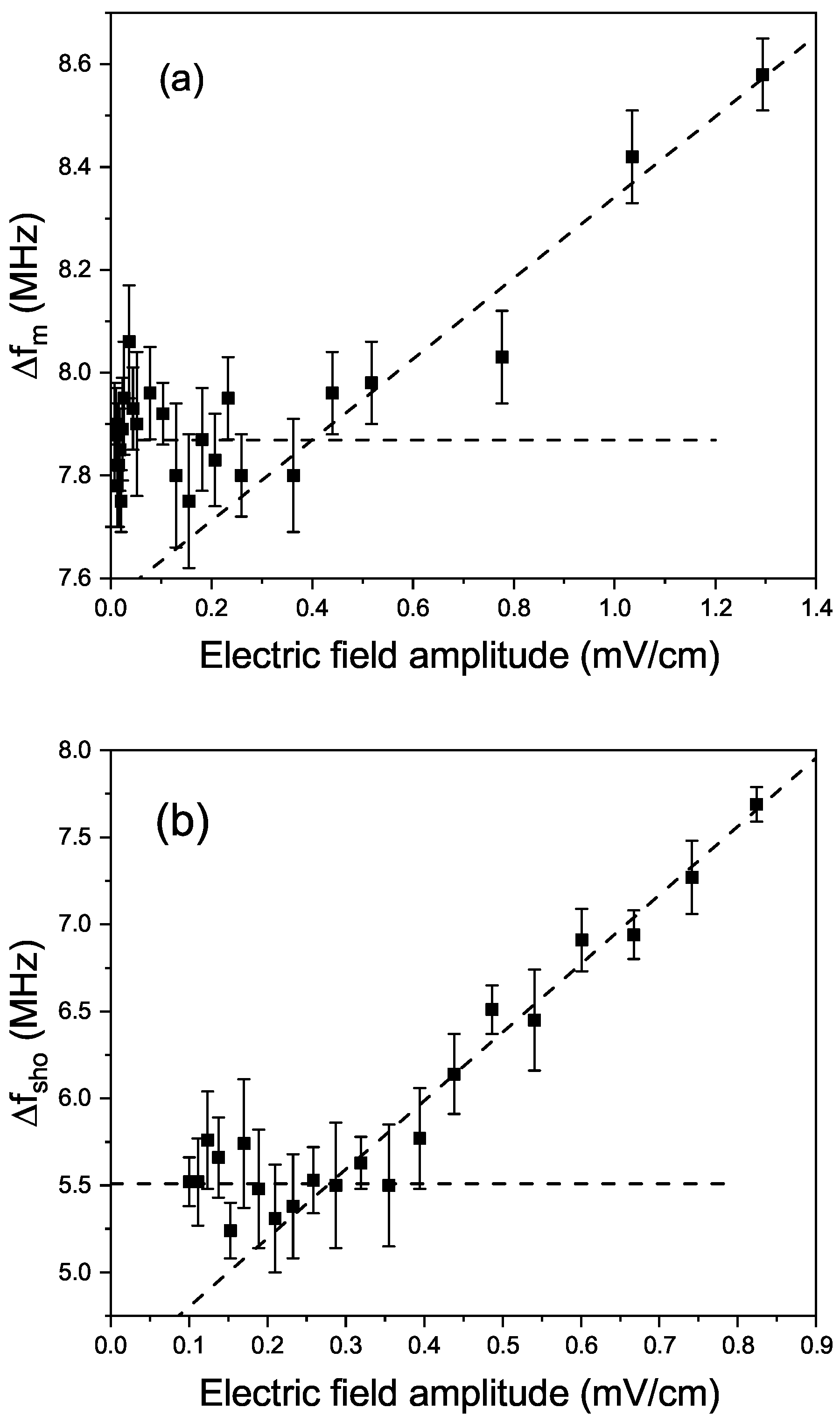
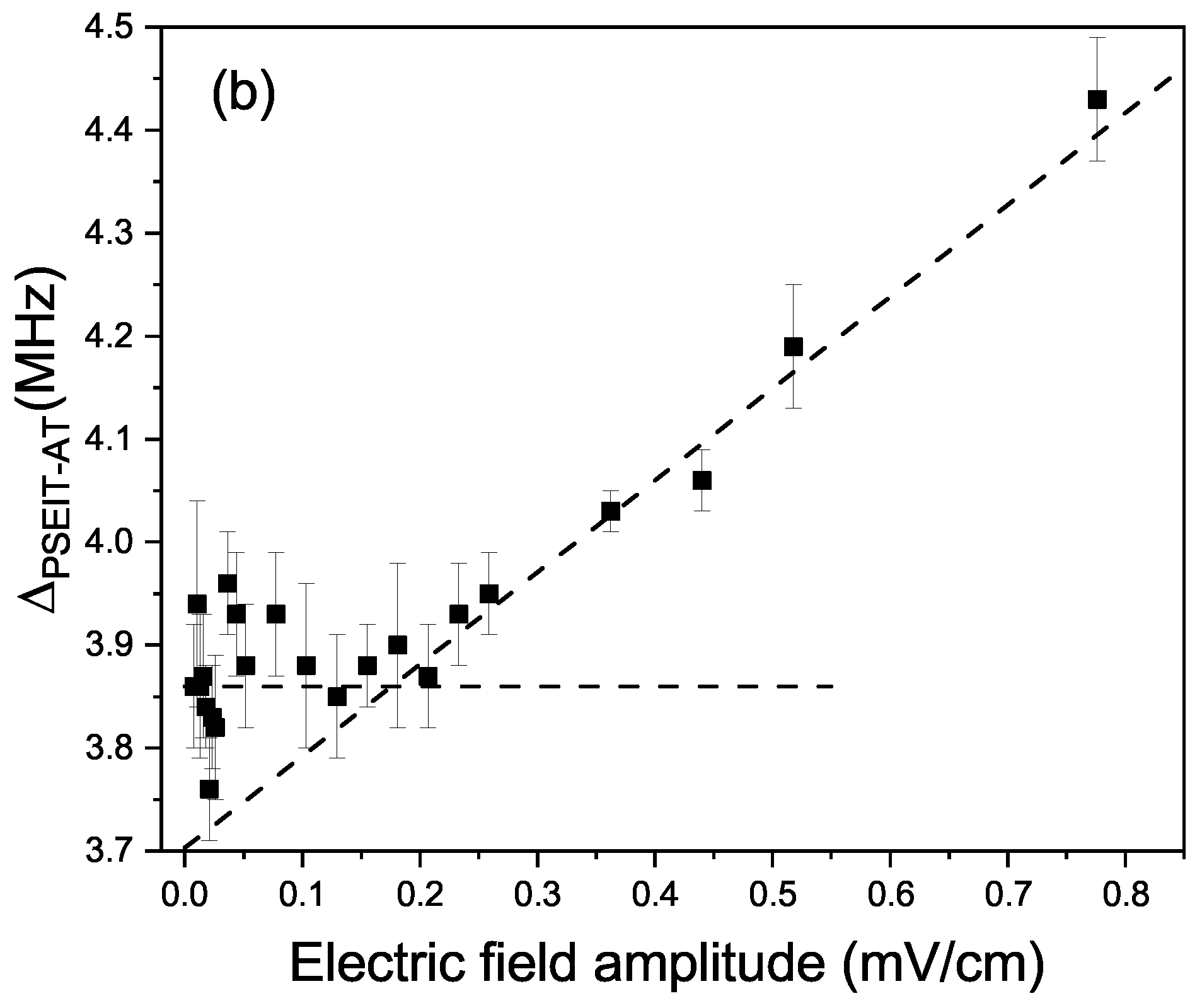
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gallagher, T. Rydberg Atoms; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Šibalić, N.; Adams, C.S. Rydberg Physics; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; pp. 2399–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischhauer, M.; Imamoglu, A.; Marangos, J.P. Electromagnetically induced transparency: Optics in coherent media. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 77, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangos, J.P. Electromagnetically induced transparency. J. Mod. Opt. 1998, 45, 471–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, A.K.; Jackson, T.R.; Adams, C.S. Coherent Optical Detection of Highly Excited Rydberg States Using Electromagnetically Induced Transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, C.S.; Pritchard, J.D.; Shaffer, J.P. Rydberg atom quantum technologies. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2019, 53, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, C.; Tanasittikosol, M.; Sargsyan, A.; Sarkisyan, D.; Adams, C.S.; Weatherill, K.J. Three-photon electromagnetically induced transparency using Rydberg states. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 3858–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosyan, D.; Otterbach, J.; Fleischhauer, M. Electromagnetically Induced Transparency with Rydberg Atoms. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 213601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlacek, J.A.; Schwettmann, A.; Kübler, H.; Löw, R.; Pfau, T.; Shaffer, J.P. Microwave electrometry with Rydberg atoms in a vapour cell using bright atomic resonances. Nat. Phys. 2012, 8, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.L.; Simons, M.T.; Gordon, J.A.; Dienstfrey, A.; Anderson, D.A.; Raithel, G. Electric field metrology for SI traceability: Systematic measurement uncertainties in electromagnetically induced transparency in atomic vapor. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 233106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.L.; Gordon, J.A.; Jefferts, S.; Schwarzkopf, A.; Anderson, D.A.; Miller, S.A.; Thaicharoen, N.; Raithel, G. Broadband Rydberg atom-based electric-field probe for SI-traceable, self-calibrated measurements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2014, 62, 6169–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.L.; Gordon, J.A.; Schwarzkopf, A.; Anderson, D.A.; Miller, S.A.; Thaicharoen, N.; Raithel, G. Sub-wavelength imaging and field mapping via electromagnetically induced transparency and Autler-Townes splitting in Rydberg atoms. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 244102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, J.A.; Schwettmann, A.; Kübler, H.; Shaffer, J.P. Atom-Based Vector Microwave Electrometry Using Rubidium Rydberg Atoms in a Vapor Cell. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanasittikosol, M.; Pritchard, J.; Maxwell, D.; Gauguet, A.; Weatherill, K.; Potvliege, R.; Adams, C. Microwave dressing of Rydberg dark states. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2011, 44, 184020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Kumar, S.; Sedlacek, J.; Kübler, H.; Karimkashi, S.; Shaffer, J.P. Atom based RF electric field sensing. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2015, 48, 202001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.A.; Miller, S.A.; Raithel, G.; Gordon, J.A.; Butler, M.L.; Holloway, C.L. Optical Measurements of Strong Microwave Fields with Rydberg Atoms in a Vapor Cell. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2016, 5, 034003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.A.; Schwarzkopf, A.; Miller, S.A.; Thaicharoen, N.; Raithel, G.; Gordon, J.A.; Holloway, C.L. Two-photon microwave transitions and strong-field effects in a room-temperature Rydberg-atom gas. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 043419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.T.; Gordon, J.A.; Holloway, C.L. Simultaneous use of Cs and Rb Rydberg atoms for dipole moment assessment and RF electric field measurements via electromagnetically induced transparency. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 120, 123103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, C.L.; Simons, M.T.; Kautz, M.D.; Haddab, A.H.; Gordon, J.A.; Crowley, T.P. A quantum-based power standard: Using Rydberg atoms for a SI-traceable radio-frequency power measurement technique in rectangular waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 094101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, M.T.; Kautz, M.D.; Holloway, C.L.; Anderson, D.A.; Raithel, G.; Stack, D.; St. John, M.C.; Su, W. Electromagnetically Induced Transparency (EIT) and Autler-Townes (AT) splitting in the presence of band-limited white Gaussian noise. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 203105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.H.; Cox, K.C.; Fatemi, F.K.; Kunz, P.D. Digital communication with Rydberg atoms and amplitude-modulated microwave fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 211108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Q.; Kumar, S.; Daschner, R.; Kübler, H.; Shaffer, J.P. Subwavelength microwave electric-field imaging using Rydberg atoms inside atomic vapor cells. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 3030–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Tannoudji, C.N. The autler-townes effect revisited. In Amazing Light; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov, P.M.; Dowling, J.P.; Sanders, B.C. Objectively discerning Autler-Townes splitting from electromagnetically induced transparency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 163604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Salloum, T.Y. Electromagnetically induced transparency and Autler-Townes splitting: Two similar but distinct phenomena in two categories of three-level atomic systems. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 053836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Hu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L.; Jia, S. Atomic superheterodyne receiver based on microwave-dressed Rydberg spectroscopy. Nat. Phys. 2020, 16, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.D.; Liu, X.B.; Mei, J.; Yu, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lin, Z.Q.; Dong, H.Y.; Zhang, J.; Xie, F.; Zhong, Z.P. Span shift and extension of quantum microwave electrometry with Rydberg atoms dressed by an auxiliary microwave field. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 103, 063113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jia, F.; Zhang, H.; Mei, J.; Yu, Y.; Liang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xie, F.; Zhong, Z. Using amplitude modulation of the microwave field to improve the sensitivity of Rydberg-atom based microwave electrometry. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 085127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Gomes, N.; Marrara Pepino, V.; Viana Borges, B.H.; Varela Magalhães, D.; de Jesus Napolitano, R.; Alejandro Lefrán Torres, M.; Douglas Massayuki Kondo, J.; Gustavo Marcassa, L. Rydberg atom-based microwave electrometry using polarization spectroscopy. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2024, 57, 235502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Gomes, N.; da Fonseca Magnani, B.; Massayuki Kondo, J.D.; Marcassa, L.G. Polarization Spectroscopy Applied to Electromagnetically Induced Transparency in Hot Rydberg Atoms Using a Laguerre–Gaussian Beam. Atoms 2022, 10, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Fernandez, D.; Lefran Torres, M.A.; Cardoso, M.R.; Kondo, J.D.M.; Saffman, M.; Marcassa, L.G. Affordable medium-finesse optical cavity for diode laser stabilization. Appl. Phys. B 2024, 130, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.H.; Jia, F.D.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhou, F.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, F.; Bai, J.H.; You, J.Q.; et al. Microwave electrometry with Rydberg atoms in a vapor cell using microwave amplitude modulation. Chin. Phys. B 2024, 33, 050702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopinaud, A.; Pritchard, J. Optimal State Choice for Rydberg-Atom Microwave Sensors. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 16, 024008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutman, M.; Chilcott, M.; Elliott, A.; Otto, J.S.; Deb, A.B.; Kjærgaard, N. Polarization-insensitive microwave electrometry using Rydberg atoms. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2024, 21, 044025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves Junior, E.L.; Lefrán Torres, M.A.; Kondo, J.D.M.; Marcassa, L.G. Comparison of Different Rydberg Atom-Based Microwave Electrometry Techniques. Atoms 2025, 13, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070059
Alves Junior EL, Lefrán Torres MA, Kondo JDM, Marcassa LG. Comparison of Different Rydberg Atom-Based Microwave Electrometry Techniques. Atoms. 2025; 13(7):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070059
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves Junior, Eliel Leandro, Manuel Alejandro Lefrán Torres, Jorge Douglas Massayuki Kondo, and Luis Gustavo Marcassa. 2025. "Comparison of Different Rydberg Atom-Based Microwave Electrometry Techniques" Atoms 13, no. 7: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070059
APA StyleAlves Junior, E. L., Lefrán Torres, M. A., Kondo, J. D. M., & Marcassa, L. G. (2025). Comparison of Different Rydberg Atom-Based Microwave Electrometry Techniques. Atoms, 13(7), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms13070059





