Indigenisation of the Quantum Clock: An Indispensable Tool for Modern Technologies
Abstract
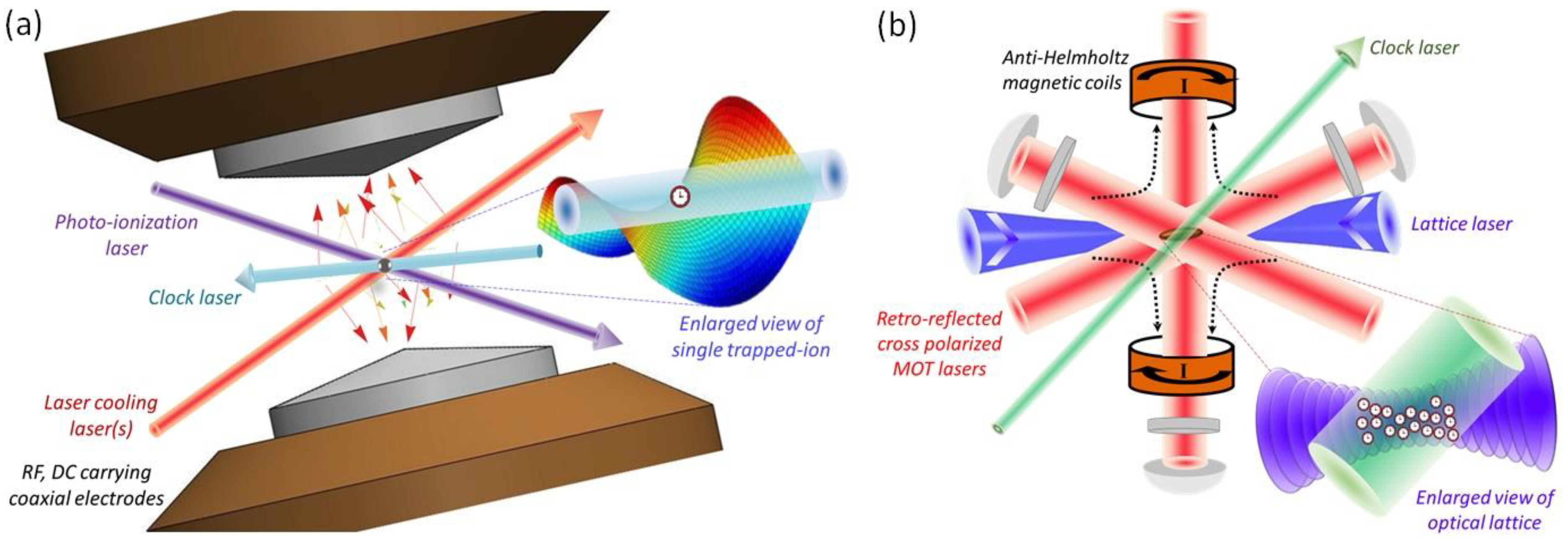
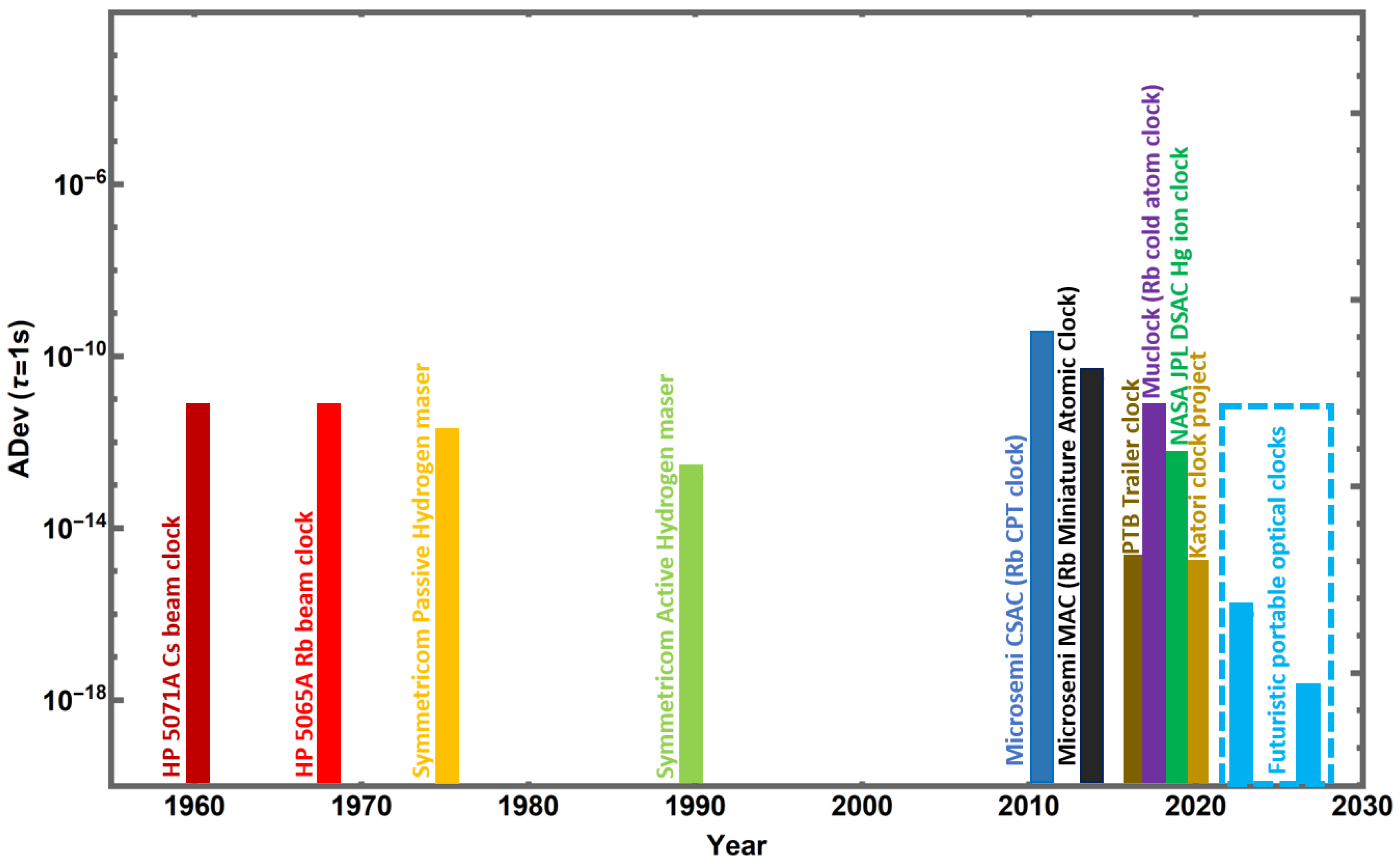
1. Introduction
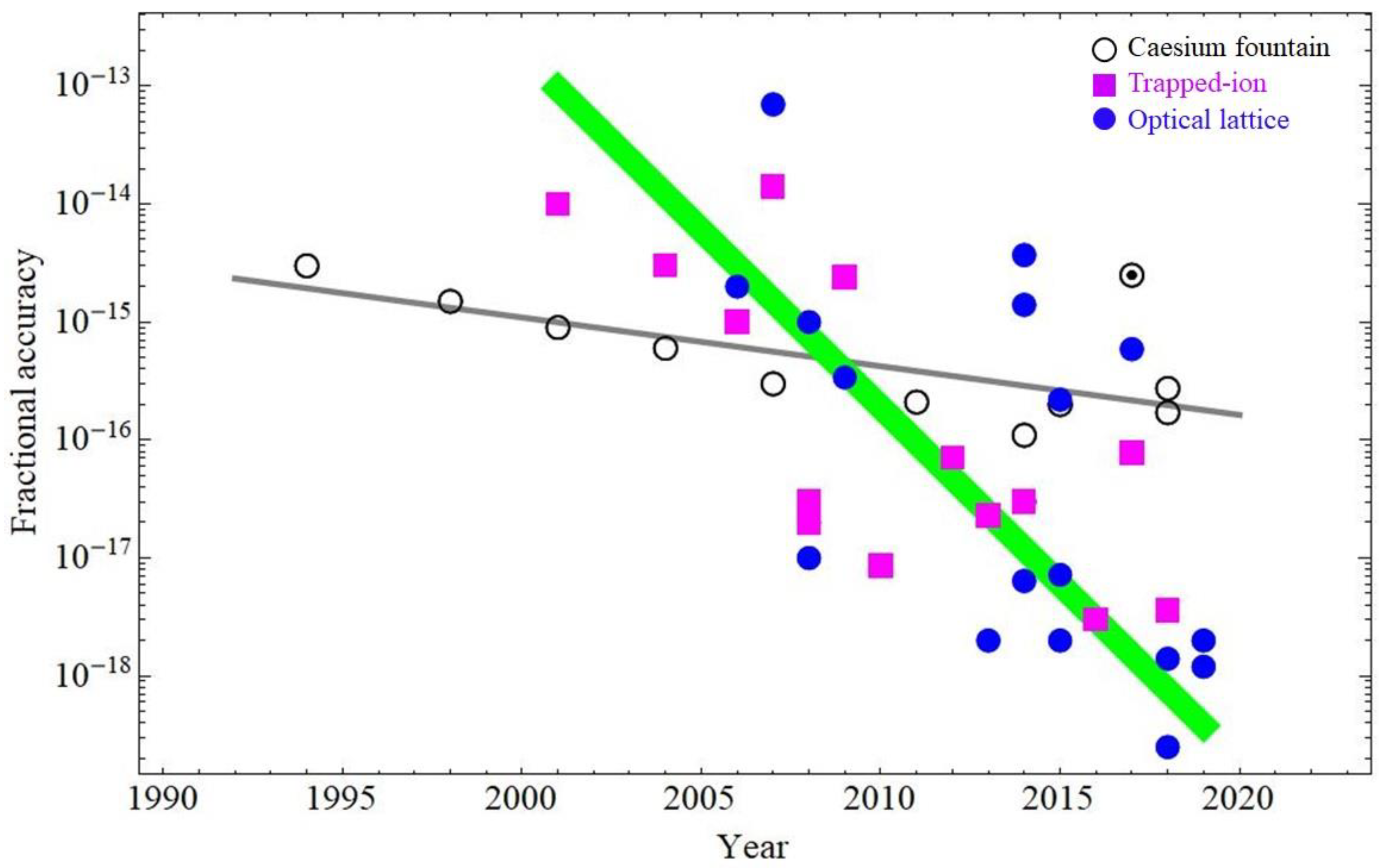
2. International Status
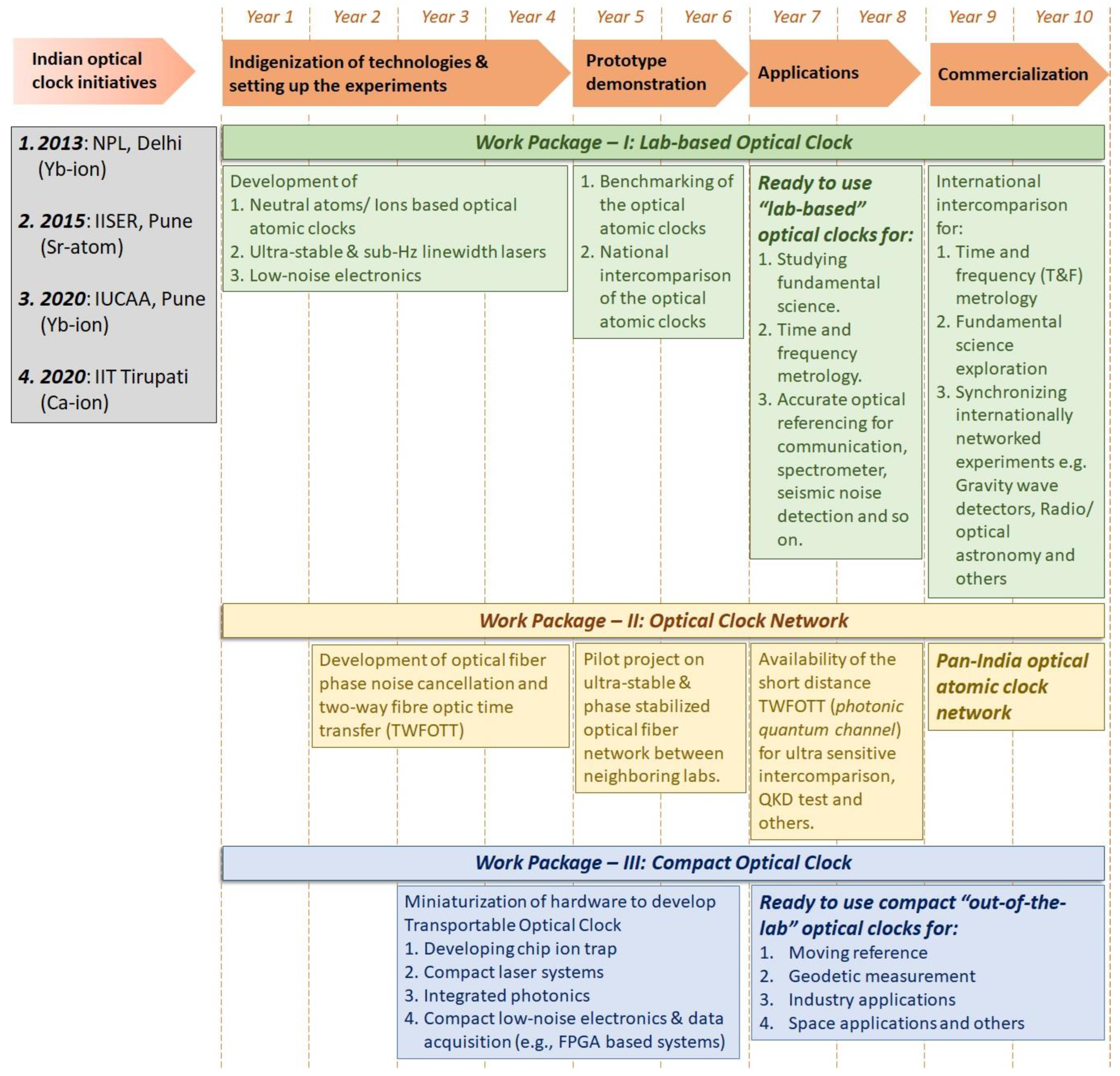
3. National Scenario and Scope
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Essen, L.; Parry, J.V.L. An Atomic Standard of Frequency and Time Interval: A Cæsium Resonator. Nature 1955, 176, 280–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoubrey, A.O. A survey of atomic frequency standards. Proc. IEEE 1966, 54, 116–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, B.L.S.; Scherer, D.R. A Review of Commercial and Emerging Atomic Frequency Standards. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2021, 68, 2007–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, B.K. Relativistic Calculations of Atomic Clock. In Handbook of Relativistic Quantum Chemistry; Liu, W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 611–655. [Google Scholar]
- Vanier, J.; Tomescu, C. The Quantum Physics of Atomic Frequency Standards: Recent Developments; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis Group: Abingdon, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey, N.F. A New Molecular Beam Resonance Method. Phys. Rev. 1949, 76, 996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, N.F. A Molecular Beam Resonance Method with Separated Oscillating Fields. Phys. Rev. 1950, 78, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, D.W.; Daams, H. Picosecond Time Difference Measurement System. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Symposium on Frequency Control, Atlantic City, NJ, USA, 28–30 May 1975; pp. 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P. Frequency standards and metrology. In Proceedings of the 6th Symposium on Frequency Standards and Metrology, University of St Andrews, Fife, Scotland, 9–14 September 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Takamoto, M.; Hong, F.; Higashi, R.; Katori, H. An optical lattice clock. Nature 2005, 435, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, F.; Physique, C.R. Towards a redefinition of the second based on optical atomic clocks. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2015, 16, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, F.; Gill, P.; Arias, F.; Robertsson, L. The CIPM list of recommended frequency standard values: Guidelines and procedures. Metrologia 2018, 55, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrew, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Leopardi, H.; Fasano, R.J.; Nicolodi, D.; Beloy, K.; Yao, J.; Sherman, J.A.; Schäffer, S.A.; Savory, J.; et al. Towards the optical second: Verifying optical clocks at the SI limit. Optica 2019, 6, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Davila-Rodriguez, J.; Leopardi, H.; Sherman, J.A.; Fortier, T.M.; Xie, X.; Campbell, J.C.; McGrew, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Hassan, Y.S.; et al. Coherent optical clock down-conversion for microwave frequencies with 10−18 instability. Science 2020, 368, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzwarth, R.; Udem, T.; Hänsch, T.W.; Knight, J.; Wadsworth, W.; Russell, P. Optical Frequency Synthesizer for Precision Spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2264–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.L. Nobel Lecture: Defining and measuring optical frequencies. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 1279–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänsch, T.W. Nobel Lecture: Passion for precision. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2006, 78, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolodi, D.; Argence, B.; Zhang, W.; Targat, R.; Santarelli, G.; LeCoq, Y. Spectral purity transfer between optical wavelengths at the 10−18 level Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picqué, N.; Hänsch, T.W. Frequency comb spectroscopy. Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, T.; Baumann, E. 20 years of developments in optical frequency comb technology and applications. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diddams, S.A.; Vahala, K.; Udem, T. Optical frequency combs: Coherently uniting the electromagnetic spectrum. Science 2020, 369, eaay3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoehr, H.; Mensing, F.; Helmcke, J.; Sterr, U. Diode laser with 1 Hz linewidth. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 736–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlow, A.D.; Huang, X.; Notcutt, M.; Zanon-Willette, T.; Foreman, S.M.; Boyd, M.M.; Blatt, S.; Ye, J. Compact, thermal-noise-limited optical cavity for diode laser stabilization at 1 × 10−15. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, T.; Hagemann, C.; Grebing, C.; Legero, T.; Sterr, U.; Riehle, F.; Martin, M.; Chen, L.; Ye, J. A sub-40-mHz-linewidth laser based on a silicon single-crystal optical cavity. Nat. Photonics 2012, 6, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, C.; Qi, W.; Yu, H.; Bi, Z.; Ma, L. 0.26-Hz-linewidth ultrastable lasers at 1557 nm. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matei, D.G.; Legero, T.; Häfner, S.; Grebing, C.; Weyrich, R.; Zhang, W.; Sonderhouse, L.; Robinson, J.M.; Ye, J.; Riehle, F.; et al. 1.5 μm Lasers with Sub-10 mHz Linewidth. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 263202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yue, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ding, M.; Zhai, Y. Far Off-Resonance Laser Frequency Stabilization Technology. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heavner, T.P.; A Donley, E.; Levi, F.; Costanzo, G.A.; E Parker, T.; Shirley, J.H.; Ashby, N.; Barlow, S.; Jefferts, S.R. First accuracy evaluation of NIST-F2. Metrologia 2014, 51, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, S.M.; Chen, J.-S.; Hankin, A.M.; Clements, E.R.; Chou, C.W.; Wineland, D.J.; Hume, D.B.; Leibrandt, D.R. Al+ 27 Quantum-Logic Clock with a Systematic Uncertainty below 10−18. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrew, W.F.; Zhang, X.; Fasano, R.J.; Schäffer, S.A.; Beloy, K.; Nicolodi, D.; Brown, R.C.; Hinkley, N.; Milani, G.; Schioppo, M.; et al. Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level. Nat. Phys. 2018, 564, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, W. Electromagnetic traps for charged and neutral particles. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1990, 62, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, B.G. An Ion Clock Reaches the Accuracy of the Best Atomic Fountain. Phys. Today 1998, 51, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, H.S. Trapped ion optical clocks. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2009, 172, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hafiz, M.; Ablewski, P.; Al-Masoudi, A.; Mart’inez, H.; Balling, P.; Barwood, G.P.; Benkler, E.; Bober, M.; Borkowski, M.; Bowden, W.; et al. Guidelines for developing optical clocks with 10−18 fractional frequency uncertainty, OC18 consortium. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.11495. [Google Scholar]
- Katori, H.; Takamoto, M.; Pal’Chikov, V.G.; Ovsiannikov, V.D. Ultrastable Optical Clock with Neutral Atoms in an Engineered Light Shift Trap. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 173005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Kimble, H.J.; Katori, H. Quantum State Engineering and Precision Metrology Using State-Insensitive Light Traps. Science 2008, 320, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katori, H.; Hashiguchi, K.; Il’Inova, E.Y.; Ovsiannikov, V.D. Magic Wavelength to Make Optical Lattice Clocks Insensitive to Atomic Motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 103, 153004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barredo, D.; de Léséleuc, S.; Lienhard, V.; Lahaye, T.; Browaeys, A. An atom-by-atom assembler of defect-free arbitrary two-dimensional atomic arrays. Science 2016, 354, 1021–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endres, M.; Bernien, H.; Keesling, A.; Levine, H.; Anschuetz, E.R.; Krajenbrink, A.; Senko, C.; Vuletic, V.; Greiner, M.; Lukin, M.D. Atom-by-atom assembly of defect-free one-dimensional cold atom arrays. Science 2016, 354, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madjarov, I.S.; Cooper, A.; Shaw, A.L.; Covey, J.P.; Schkolnik, V.; Yoon, T.H.; Williams, J.R.; Endres, M. An Atomic-Array Optical Clock with Single-Atom Readout. Phys. Rev. X 2019, 9, 041052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcia, M.A.; Young, A.W.; Eckner, W.J.; Oelker, E.; Ye, J.; Kaufman, A.M. Seconds-scale coherence on an optical clock transition in a tweezer array. Science 2019, 366, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyka, K.; Herschbach, N.; Keller, J.; Mehlstäubler, T.E. A high-precision segmented Paul trap with minimized micromotion for an optical multiple-ion clock. Appl. Phys. B Laser Opt. 2014, 114, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.; Burgermeister, T.; Kalincev, D.; Kiethe, J.; Mehlstäubler, T.E. Evaluation of trap-induced systematic frequency shifts for a multi-ion optical clock at the 10−19 level. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 723, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derevianko, A.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V. Highly Charged Ions as a Basis of Optical Atomic Clockwork of Exceptional Accuracy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 180801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlov, M.G.; Safronova, M.S.; López-Urrutia, J.R.C.; Schmidt, P.O. Highly charged ions: Optical clocks and applications in fundamental physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2018, 90, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C.; Safronova, M.S.; Porsev, S.G.; Kozlov, M.G.; Tupitsyn, I.I.; Bondarev, A.I. Accurate Prediction of Clock Transitions in a Highly Charged Ion with Complex Electronic Structure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 163001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didier, A.; Millo, J.; Grop, S.; Dubois, B.; Bigler, E.; Rubiola, E.; Lacroûte, C.; Kersalé, Y. Ultra-low phase noise all-optical microwave generation setup based on commercial devices. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3682–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E.; Brochard, P.; Bouchand, R.; Schilt, S.; Südmeyer, T.; Kippenberg, T.J. Ultralow-noise photonic microwave synthesis using a soliton microcomb-based transfer oscillator. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riehle, F. Optical clock networks. Nat. Photonics 2017, 11, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshenboim, S.G.; Peik, E. Astrophysics, atomic clocks and fundamental constants. Eur. Phys. J. Spéc. Top. 2008, 163, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenband, T.; Hume, D.B.; Schmidt, P.O.; Chou, C.W.; Brusch, A.; Lorini, L.; Oskay, W.H.; Drullinger, R.E.; Fortier, T.M.; Stalnaker, J.E.; et al. Frequency Ratio of Al+ and Hg+ Single-Ion Optical Clocks; Metrology at the 17th Decimal Place. Science 2009, 319, 1808–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godun, R.M.; Nisbet-Jones, P.B.R.; Jones, J.M.; King, S.A.; Johnson, L.A.M.; Margolis, H.S.; Szymaniec, K.; Lea, S.N.; Bongs, K.; Gill, P. Frequency Ratio of Two Optical Clock Transitions in 171Yb+ and Constraints on the Time Variation of Fundamental Constants. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 210801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntemann, N.; Lipphardt, B.; Tamm, C.; Gerginov, V.; Weyers, S.; Peik, E. Improved Limit on a Temporal Variation of mp/me from Comparisons of Yb+ and Cs Atomic Clocks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 210802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, R.; Kosteleck’y, V.A.; Lane, C.D.; Russell, N. Clock-Comparison Tests of Lorentz and CPT Symmetry in Space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 090801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, C.; Huntemann, N.; Lange, R.; Tamm, C.; Peik, E.; Safronova, M.S.; Porsev, S.G. Optical clock comparison for Lorentz symmetry testing. Nature 2019, 567, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehlstraubler, T.E.; Grosche, G.; Lisdat, C.; Schmidt, P.O.; Denker, H. Atomic clocks for geodesy. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2018, 81, 064401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarescu, R.; Bondarescu, M.; Hetényi, G.; Boschi, L.; Jetzer, P.; Balakrishna, J. Geophysical applicability of atomic clocks: Direct continental geoid mapping. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkowitz, S.; Pikovski, I.; Langellier, N.; Lukin, M.D.; Walsworth, R.L.; Ye, J. Gravitational wave detection with optical lattice atomic clocks. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 124043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wcisło, P.; Ablewski, P.; Beloy, K.; Bilicki, S.; Bober, M.; Brown, R.; Fasano, R.; Ciuryło, R.; Hachisu, H.; Ido, T.; et al. New bounds on dark matter coupling from a global network of optical atomic clocks. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savalle, E.; Roberts, B.M.; Frank, F.; Pottie, P.E.; Mcallister, B.T.; Dailey, C.; Derevianko, A.; Wolf, P. Novel approaches to dark-matter detection using space-time separated clocks, General relativity and Quantam Cosmology. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.07192. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, N.; Roy, A.; Majhi, S.; Panja, S.; De, S. Singly charged ions for optical clocks. Asian J. Phys. 2017, 25, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Huntemann, N.; Sanner, C.; Lipphardt, B.; Tamm, C.; Peik, E. Single-Ion Atomic Clock with 3 × 10−18 Systematic Uncertainty. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 063001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, M.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Gao, K. A liquid nitrogen-cooled Ca+ optical clock with systematic uncertainty of 3 × 10−18. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.08913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwalla, M.; Benhelm, J.; Kim, K.; Kirchmair, G.; Monz, T.; Riebe, M.; Schindler, P.; Villar, A.S.; Hänsel, W.; Roos, C.F.; et al. Absolute Frequency Measurement of the 40Ca+ 4s 2S1/2 − 3d 2D5/2 Clock Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Liu, P.; Liang, K.; Ou, B.; Guan, H.; Huang, X.; Li, T.; Gao, K. Hertz-level measurement of the 40Ca+ 4s 2S1/2 − 3d 2D5/2 clock transition frequency with respect to the SI second through the Global Positioning System. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 85, 030503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, K.; Hachisu, H.; Li, Y.; Nagano, S.; Locke, C.; Nogami, A.; Kajita, M.; Hayasaka, K.; Ido, T.; Hosokawa, M. Direct comparison of a Ca+ single-ion clock against a Sr lattice clock to verify the absolute frequency measurement. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 22034–22041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, P.; Shang, J.; Cui, K.; Yuan, J.; Chao, S.; Wang, S.; Shu, H.; Huang, X. A compact, transportable single-ion optical clock with 7.8 × 10−17 systematic uncertainty. Appl. Phys. B Laser Opt. 2017, 123, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwood, G.P.; Huang, G.; Klein, H.A.; Johnson, L.A.M.; King, S.A.; Margolis, H.S.; Szymaniec, K.; Gill, P. Agreement between two88Sr+optical clocks to 4 parts in 1017. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 050501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, B.; Dubé, P.; Madej, A.A. Quantum projection noise limited stability of a 88Sr+ atomic clock. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 723, 12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinel, M.; Shao, H.; Filzinger, M.; Lipphardt, B.; Brinkmann, M.; Didier, A.; Mehlstaubler, T.E.; Lindvall, T.; Peik, E.; Huntemann, N. Evaluation of a 88Sr+ optical clock with a drect measurement of the blackbody radiation shift and determination of the clock frequency. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.08687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Liu, T.; Dumke, R.; Stejskal, A.; Zhao, Y.N.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, L.J.; Becker, T.; Walther, H. Improved absolute frequency measurement of the 115 In+ 5 s 2 1 S 0-5 s 5 p 3 P 0 narrowline transition: Progress towards an optical frequency standard. Laser Phys. 2007, 17, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, N.; Li, Y.; Nemitz, N.; Hachisu, H.; Matsubara, K.; Ido, T.; Hayasaka, K. Frequency ratio of an 115In+ ion clock and a 87Sr optical lattice clock. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 5950–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.J.; Kaewuam, R.; Chanu, S.R.; Tan, T.R.; Zhang, Z.; Barrett, M.D. Precision Measurements of the Ba+ 138 6 s S 2 1/2 − 5 d D 2 5/2 Clock Transition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 193001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörscher, S.; Huntemann, N.; Schwarz, R.; Lange, R.; Benkler, E.; Lipphardt, B.; Sterr, U.; Peik, E.; Lisdat, C. Optical frequency ratio of a 171Yb+ single-ion clock and a 87Sr lattice clock. Metrologia 2021, 58, 015005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leute, J.; Huntemann, N.; Lipphardt, B.; Tamm, C.; Nisbet-Jones, P.B.R.; King, S.A.; Godun, R.M.; Jones, J.M.; Margolis, H.S.; Whibberley, P.; et al. Frequency Comparison of 171Yb+ Ion Optical Clocks at PTB and NPL via GPS PPP. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2016, 63, 981–985. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7398135 (accessed on 5 April 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Kyle, J.A.; Rattakorn, K.; Barrett, M.D. 176Lu+ clock comparison at the 10−18 level via correlation spectroscopy. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.04652. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2212.04652.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Diddams, S.A.; Udem, T.; Bergquist, J.C.; Curtis, E.A.; Drullinger, R.E.; Hollberg, L.; Itano, W.M.; Lee, W.D.; Oates, C.W.; Vogel, K.R.; et al. An Optical Clock Based on a Single Trapped 199Hg+ Ion. Science 2001, 293, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friebe, J.; Riedmann, M.; Wübbena, T.; Pape, A.; Kelkar, H.; Ertmer, W.; Terra, O.; Sterr, U.; Weyers, S.; Grosche, G.; et al. Remote frequency measurement of the 1S0→3P1 transition in laser-cooled 24Mg. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 125010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fim, D.B. First Optical Lattice Frequency Standard Based on 24Mg Atoms. Doctoral Dissertation, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität, Hannover, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterr, U.; Degenhardt, C.; Stoehr, H.; Lisdat, C.; Schnatz, H.; Helmcke, J.; Riehle, F.; Wilpers, G.; Oates, C.; Hollberg, L. The optical calcium frequency standards of PTB and NIST. Comptes Rendus Phys. 2004, 5, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilpers, G.; Oates, C.W.; Diddams, S.A.; Bartels, A.; Fortier, T.M.; Oskay, W.H.; Bergquist, J.C.; Jefferts, S.R.; Heavner, T.P.; Parker, T.E.; et al. Absolute frequency measurement of the neutral 40Ca optical frequency standard at 657 nm based on microkelvin atoms. Metrologia 2007, 44, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothwell, T.; Kedar, D.; Oelker, E.; Robinson, J.M.; Bromley, S.L.; Tew, W.L.; Ye, J.; Kennedy, C.J. JILA SrI optical lattice clock with uncertainty of 2.0 × 10−18. Metrologia 2019, 56, 065004. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1360292620234141312 (accessed on 5 April 2023). [CrossRef]
- Le Targat, R.; Lorini, L.; Le Coq, Y.; Zawada, M.; Guéna, J.; Abgrall, M.; Gurov, M.; Rosenbusch, P.; Rovera, D.G.; Nagórny, B.; et al. Experimental realization of an optical second with strontium lattice clocks. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, R.; Dörscher, S.; Al-Masoudi, A.; Benkler, E.; Legero, T.; Sterr, U.; Weyers, S.; Rahm, J.; Lipphardt, B.; Lisdat, C. Long term measurement of the Sr87 clock frequency at the limit of primary Cs clocks. Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemitz, N.; Gotoh, T.; Nakagawa, F.; Ito, H.; Hanado, Y.; Ido, T.; Hachisu, H. Absolute frequency of 87Sr at 1.8 × 10−16 uncertainty by reference to remote primary frequency standards. Metrologia 2021, 58, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, D.; Inaba, H.; Hosaka, K.; Yasuda, M.; Onae, A.; Suzuyama, T.; Amemiya, M.; Hong, F.-L. Spectroscopy and frequency measurement of the87Sr clock transition by laser linewidth transfer using an optical frequency comb. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 7, 012401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushijima, I.; Takamoto, M.; Das, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Katori, H. Cryogenic optical lattice clocks. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baillard, X.; Fouché, M.; Le Targat, R.; Westergaard, P.G.; Lecallier, A.; Le Coq, Y.; Rovera, G.D.; Bize, S.; Lemonde, P. Accuracy evaluation of an optical lattice clock with bosonic atoms. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1812–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Akamatsu, D.; Hosaka, K.; Hisai, Y.; Wada, M.; Inaba, H.; Suzuyama, T.; Hong, F.-L.; Yasuda, M. Demonstration of the nearly continuous operation of an 171Yb optical lattice clock for half a year. Metrologia 2020, 57, 065021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Heo, M.-S.; Park, C.Y.; Yu, D.-H.; Lee, W.-K. Absolute frequency measurement of the 171Yb optical lattice clock at KRISS using TAI for over a year. Metrologia 2021, 58, 055007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzocaro, M.; Bregolin, F.; Barbieri, P.; Rauf, B.; Levi, F.; Calonico, D. Absolute frequency measurement of the 1S0–3P0 transition of 171Yb with a link to international atomic time. Metrologia 2019, 57, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarlo, L.; De Sarlo, L.; Favier, M.G.; Tyumenev, R.; Bize, S. A mercury optical lattice clock at LNE-SYRTE. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 723, 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Ohmae, N.; Ushijima, I.; Takamoto, M.; Katori, H. Frequency Ratio ofHg199andSr87Optical Lattice Clocks beyond the SI Limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 230801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovizin, A.; Tregubov, D.; Fedorova, E.; Mishin, D.; Provorchenko, D.; Khabarova, K.; Sorokin, V.; Kolachevsky, N. Extraordinary low systematic frequency shifts in bi-colour thulium optical clock. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.07468. [Google Scholar]
- Derevianko, A.; Katori, H. Colloquium: Physics of optical lattice clocks. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katori, H.; Ido, T.; Kuwata-Gonokami, M. Optimal Design of Dipole Potentials for Efficient Loading of Sr Atoms. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1999, 68, 2479–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, G.; Marti, G.E.; Hutson, R.B.; Goban, A.; Campbell, S.L.; Poli, N.; Ye, J. Imaging Optical Frequencies with 100 μHz Precision and 1.1 μm Resolution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 103201. [Google Scholar]
- Beloy, K.; Bodine, M.I.; Bothwell, T.; Brewer, S.M.; Bromley, S.L.; Chen, J.-S.; Deschênes, J.-D.; Diddams, S.A.; Fasano, R.J. Frequency ratio measurements at 18-digit accuracy using an optical clock network. Nature 2021, 591, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achariya, A.; Vattikonda, B.; Arora, P.; Yadav, S.; Agarwal, A.; Sen Gupta, A. Systematic uncertainty evaluation of the caesium fountain primary frequency standard at NPL India. Mapan 2017, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotti, J.; Koller, S.; Vogt, S.; Häfner, S.; Sterr, U.; Lisdat, C.; Denker, H.; Voigt, C.; Timmen, L.; Rolland, A.; et al. Geodesy and metrology with a transportable optical clock. Nat. Phys. 2018, 14, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, S.; Pelzer, L.; Scharnhorst, N.; Kramer, J.; Stepanova, M.; Xu, Z.T.; Spethmann, N.; Leroux, I.D.; Mehlstäubler, T.E.; Schmidt, P.O. Towards a transportable aluminium ion quantum logic optical clock. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 053204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, N.; Schioppo, M.; Vogt, S.; Falke, S.; Sterr, U.; Lisdat, C.; Tino, G.M. A transportable strontium optical lattice clock. Appl. Phys. B Laser Opt. 2014, 117, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origlia, S.; Pramod, M.S.; Schiller, S.; Singh, Y.; Bongs, K.; Schwarz, R.; Al-Masoudi, A.; Dörscher, S.; Herbers, S.; Häfner, S.; et al. Towards an optical clock for space: Compact, high-performance optical lattice clock based on bosonic atoms. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 053443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamoto, M.; Ushijima, I.; Ohmae, N.; Yahagi, T.; Kokado, K.; Shinkai, H.; Katori, H. Test of general relativity by a pair of transportable optical lattice clocks. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldous, M.; Viswam, S.; Bass, J.; Menchetti, M.; Ubaid, Q.; Jones, J.; Morris, D.; Molony, P.; Gellesch, M.; Bongs, K.; et al. Route to a Portable Optical Clock. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (IFCS), Olympic Valley, CA, USA, 21–24 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.; Aldous, M.; Gellesch, M.; Jones, J.M.; Kale, Y.B.; Singh, A.; Bass, J.; Bongs, K.; Singh, Y.; Hill, I.R.; et al. Development of a Portable Optical Clock. In Proceedings of the 2019 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and European Frequency and Time Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 14–18 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Delehaye, M.; Lacroûte, C. Single-ion, transportable optical atomic clocks. J. Mod. Opt. 2018, 65, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Hao, Y.; Guan, H.; Zeng, M.; Chen, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; et al. Geopotential measurement with a robust, transportable Ca+ optical clock. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 102, 050802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, T.A.; Seubert, J. Overview of the Deep Space Atomic Clock Technology Demonstration Mission. In Proceedings of the 2019 AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Portland, ME, USA, 11–15 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, W.; Fasano, R.; Fox, R.; McGrew, W.; Hassan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Beloy, K.; Nicolodi, D.; Ludlow, A. Portable Yb Optical Lattice Clock: Towards Precision Measurement Outside the Lab. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the APS Division of Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics APS Meeting, Milwaukee, Wisconsin, May 27–31, 2019. pp. E01–E046.
- Gellesch, M.; Jones, J.; Barron, R.; Singh, A.; Sun, Q.; Bongs, K.; Singh, Y. Transportable optical atomic clocks for use in out-of-the-lab environments. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2020, 9, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.opticlock.de/info/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Available online: https://www.iqclock.eu/ (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Available online: https://www.sussex.ac.uk/research/labs/ion-trap-cavity-qed-and-molecular-physics/research/portable_optical_atomic_clocks (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Rastogi, A.; Batra, N.; Roy, A.; Thangjam, J.; Kalsi, V.P.S.; Panja, S.; De, S. Design of the Ion Trap and Vacuum System for 171Yb-ion Optical Frequency Standard. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc. India 2015, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panja, S.; De, S.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, A.S. Note: Measuring capacitance and inductance of a helical resonator and improving its quality factor by mutual inductance alteration. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2015, 86, 056104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, N.; Panja, S.; De, S.; Roy, A.; Majhi, S.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, A.S. Design and Construction of a Helical Resonator for Delivering Radio Frequency to an Ion Trap. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc. India 2017, 32, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Roy, A.; Panja, S.; Ojha, V.N.; De, S. Estimation of the ion-trap assisted electrical loads and resulting BBR shift. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, N.; Sahoo, B.K.; De, S. An optimized ion trap geometry to measure quadrupole shifts of 171Yb+ clocks. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 113703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Roy, A.; Panja, S.; De, S. Atomic flux distribution from a low-divergent dark wall oven. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 053202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; De, S.; Arora, P.; Gupta, A.S. A universal driver for vibration free operation of mechanical shutters. Measurements 2015, 61, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Batra, N.; Majhi, S.; Panja, S.; Gupta, A.S.; De, S. Design of a Stable DC Voltage Source and Computer Controlling of It Using an Indigenously Developed All-Digital Addressing-Cum-Control Hardware. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc. India 2018, 33, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Sharma, L.; Chakraborty, I.; Panja, S.; Ojha, V.; De, S. An FPGA based all-in-one function generator, lock-in amplifier and auto-relockable PID system. J. Instrum. 2019, 14, P05012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, H.K.; Sharma, L.; Roy, A.; Olaniya, M.P.; De, S.; Panja, S. Studies on Temperature Sensitivity of a White Rabbit Network-Based Time Transfer Link. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc. India 2021, 36, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, H.K.; Roy, A.; Utreja, S.; Sharma, L.; De, S.; Panja, S. A Compact Device for Precise Distribution of Time and Frequency Signal. MAPAN-J. Metrol. Soc. India 2021, 36, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Roy, A.; Panja, S.; De, S. An easy to construct sub-micron resolution imaging system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, C.; Mangaonkar, J.; Patel, K.; Verma, G.; Sarkar, S.; Rapol, U.D. A simple atomic beam oven with a metal thermal break. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 90, 053106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, C.; Patel, K.; Mangaonkar, J.; MacLennan, J.L.; Biswas, K.; Rapol, U.D. Study of loss dynamics of strontium in a magneto-optical trap. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.03202. [Google Scholar]
- Viswakarma, C.; De, S.; Rapol, U.D. A brief introduction to optical atomic clocks. Phys. News 2020, 50, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
| Performance Metric [Unit] | Microwave | Optical | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 133Cs Fountain [28] | Trapped 27Al+ [29] | 171Yb Optical Lattice [30] | |
| νo [GHz] | 9.192631770 | 1,121,138.58639 | 518,672.072664 |
| Δν [Hz] | 0.1 | 8 × 10−3 | 7 × 10−3 |
| Q [×1015] | 91.92 × 10−6 | 140.142 | 74.096 |
| Systematic uncertainty [×10−19] | 1100 | 9.4 | 14 |
| σ at 1s [×10−16] | 1700 | 12 | 1.5 |
| Applications and functionality | Present SI standard, T&F metrology | Ultrahigh-accuracy T&F metrology, quantum metrology, fundamental science, miniaturisation for compact/transportable clock | |
| Species | Clock Transition | Wavelength in Vacuum [nm] | Measured Clock Frequency [Hz] | Fractional Uncertainty [×10−17] | Short-Term Stability | Same-Species Comparison Performed (Yes/No) | Accuracy of the Same-Species Comparison | Lab, Country [Ref.] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singly charged atomic ions in a Paul trap | ||||||||
| 27Al+ | 1S0-3P0 | 267.4 | 1121015393207857.4(7) | 0.094 | 1.2 × 10−15 | No * | NIST, USA [29] | |
| 40Ca+ | 2S1/2-2D5/2 | 729.3 | 411042129776393.2(1.0) 411042129776393.0(1.6) | 240 390 | 2.9 × 10−13 4.0 × 10−13 | No No | SYRTE, France [64] | |
| NIM, China [65] | ||||||||
| 411042129776398.4(1.2) | 300 | 2.4 × 10−14 | No | NICT, Japan [66] | ||||
| 411042129776401.7 (1.1) | 7.7 | 2.3 × 10−14 (20 ms) | Yes | Not reported | WIPM, China [67] | |||
| 88Sr+ | 2S1/2-2D5/2 | 674 | 444779044095486.71(24) | 3 | 2.2 × 10−14 | Yes | 4× 10−17 | NPL, UK [68] |
| 444779044095485.5(9) | 1.2 | 3.0 × 10−15 (1 s) | Yes | Not reported | NRC, Canada [69] | |||
| 444779044095485.271(59) | 1 | 3.3 × 10−15 | No | PTB, Germany [70] | ||||
| 115In+ | 1S0-3P0 | 236.5 | 1267402452900967(63) 1267402452901040.1(1.1) | 5000 85 | − 1.7 × 10−13 | No No | MPIQ, Germany [71] NICT, Japan [72] | |
| 138Ba+ | 2S1/2-2D5/2 | 1762.2 | 170126432449333.00 | 33 | 1.5 × 10−15 (1000 s) | No | NUS, Singapore [73] | |
| 171Yb+ | 2S1/2-2D3/2 | 435.5 | 688358979309307.82(36) 688358979309308.42(42) | 5231.6 | 4.1 × 10−14 1.0 × 10−14 | No Yes | 1.3(1.2) × 10−15 | PTB, Germany [74] NPL, UK [75] |
| 171Yb+ | 2S1/2-2F7/2 | 466.9 | 642121496772645.150(1) 642121496772644.91(37) | 0.2757.9 | 1.0 × 10−15 - | No No | PTB, Germany [74] NPL, UK [52] | |
| 176Lu+ | 1S0-3D1 | 847.7 | 3536399159522(60) | - | 1.2 × 10−15 | Yes | 3.7 × 10−18 | NUS, Singapore [76] |
| 199Hg+ | 2S1/2-2D5/2 | 281.6 | 1064721609899145.30(69) | 69 | 7 × 10−15 (1 s) | No | NIST, USA [77] | |
| Neutral atoms in an optical lattice | ||||||||
| 24Mg | 1S0-3P1 | 457.7 | 655659923839730(48) | 7000 | 2.0 × 10−13 | No | PTB, Germany [78] | |
| 24Mg | 1S0-3P0 | 458.0 | 655 058 646 681 864.1(5.3) | 700 | 1.5 × 10−15 | No | LUH, Germany [79] | |
| 40Ca | 1S0-3P1 | 657.5 | 455986240494144(5.3) 455986240494135.8(3.4) | 1200 750 | 3.0 × 10−15 2 × 10−16 | No No | PTB, Germany [80] NIST, USA [81] | |
| 87Sr | 1S0-3P0 | 698.4 | 429228004229873.65(37) | 0.20 | 4.8 × 10−17 | - | JILA, USA [82] | |
| 429228004229873.10(0.17) | 31 | 3.0 × 10−15 | Yes | 2.8 × 10−16 | SYRTE, France [83] | |||
| 429228004229873.00(07) | 1.5 | 5.0 × 10−17 (120 days) | No | PTB, Germany [84] | ||||
| 429228004229873.082(76) | 18 | 7.0 × 10−15 | No | NICT, Japan [85] | ||||
| 429228004229872.0(1.6) | 370 | 2.4 × 10−13 (8 s) | No | NMIJ, Japan [86] | ||||
| 429228004229873.4(4) | 0.72 | 1.8 × 10−16 | Yes | 2.0 × 10−18 | RIKEN, Japan [87] | |||
| 88Sr | 1S0-3P0 | 698.4 | 429228066418009(32) | 7000 | - | SYRTE, France [88] | ||
| 171Yb | 1S0-3P0 | 578.4 | 518295836590865.2(0.7) 518295836590863.54(26) | 0.2 50 | 1.5 × 10−16 1.0 × 10−14 (1 s) | Yes No | 5× 10−19 | NIST, USA [30] NMIJ, Japan [89] |
| 518295836590863.75(14) | 1.7 | 3.2 × 10−15 | No | KRISS, S. Korea [90] | ||||
| 518295836590863.61(13) | 2.8 | 2.7 × 10−15 (1 s) | No | INRIM, Italy [91] | ||||
| 199Hg | 1S0-3P0 | 265.6 | 1128575290808155.1(6.7) 1128575290808155.4(1.1) | 5707.2 | 1.2 × 10−15 (1s) 3.0 × 10−15 | No No | SYRTE, France [92] RIKEN, Japan [93] | |
| 169Tm | 2F7/2-2F5/2 | 1140 | 262 954 938 269 213(30) | <0.5 | <10−14 | No | LPI, Russia [94] | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De, S.; Sharma, A. Indigenisation of the Quantum Clock: An Indispensable Tool for Modern Technologies. Atoms 2023, 11, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms11040071
De S, Sharma A. Indigenisation of the Quantum Clock: An Indispensable Tool for Modern Technologies. Atoms. 2023; 11(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms11040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe, Subhadeep, and Arijit Sharma. 2023. "Indigenisation of the Quantum Clock: An Indispensable Tool for Modern Technologies" Atoms 11, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms11040071
APA StyleDe, S., & Sharma, A. (2023). Indigenisation of the Quantum Clock: An Indispensable Tool for Modern Technologies. Atoms, 11(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms11040071






