Revise the Phase-Space Analysis of the Dynamical Spacetime Unified Dark Energy Cosmology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Field Equations
3. Analytic Solutions
3.1. Case A: and
3.2. Case B: and
4. Asymptotic Solutions
4.1. Case I: and
4.2. Case II: and
Subcase
4.3. Case III: and
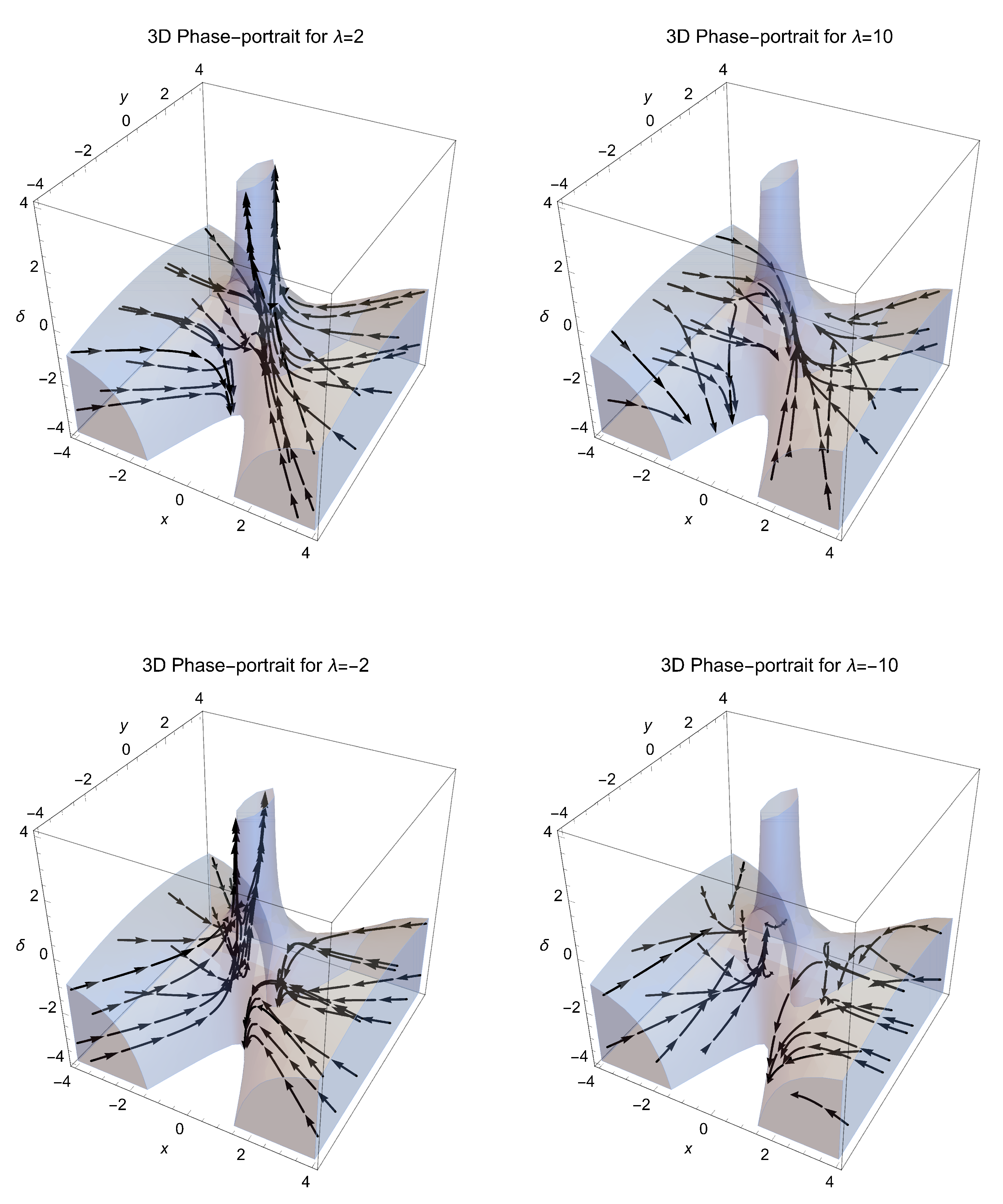
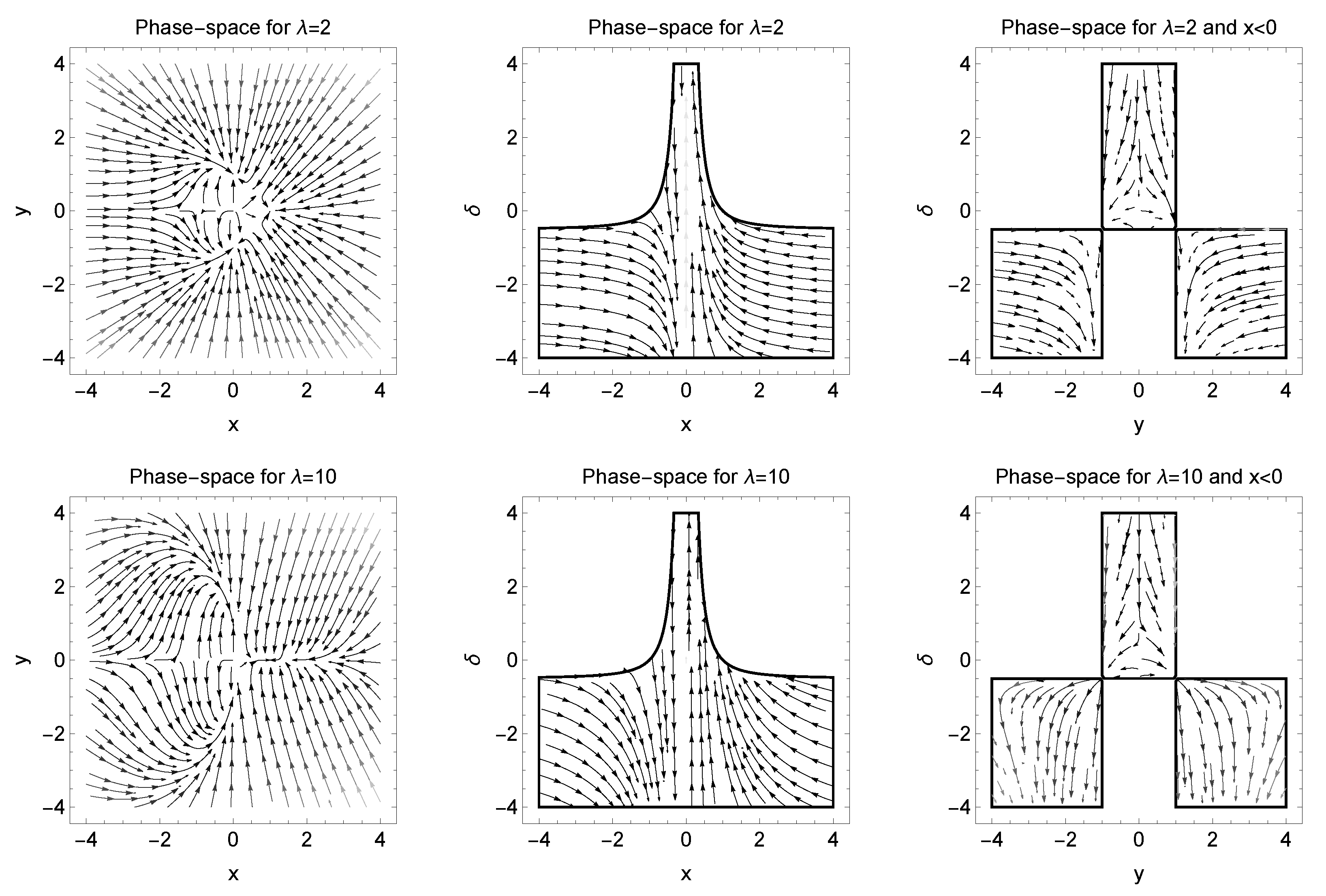
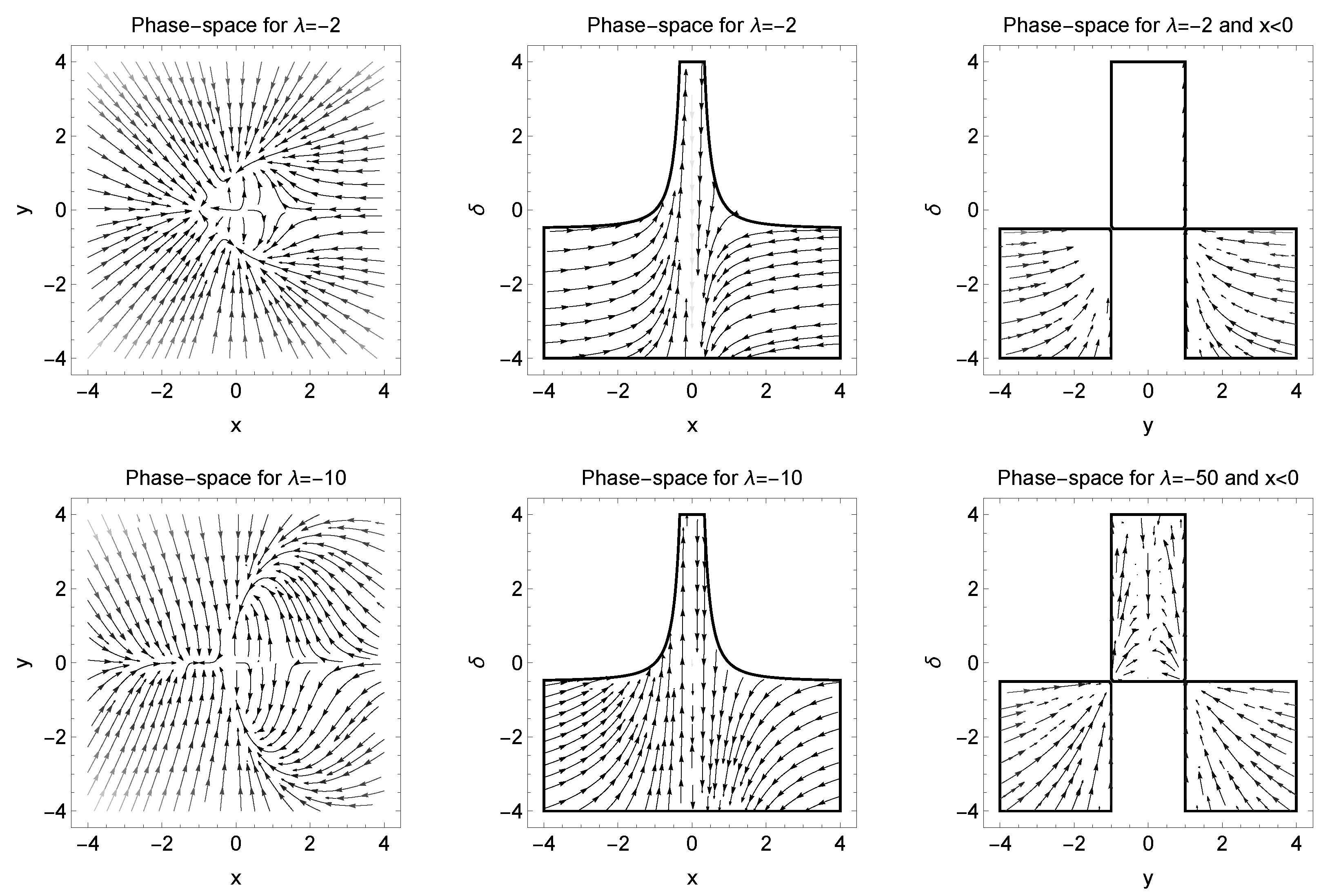
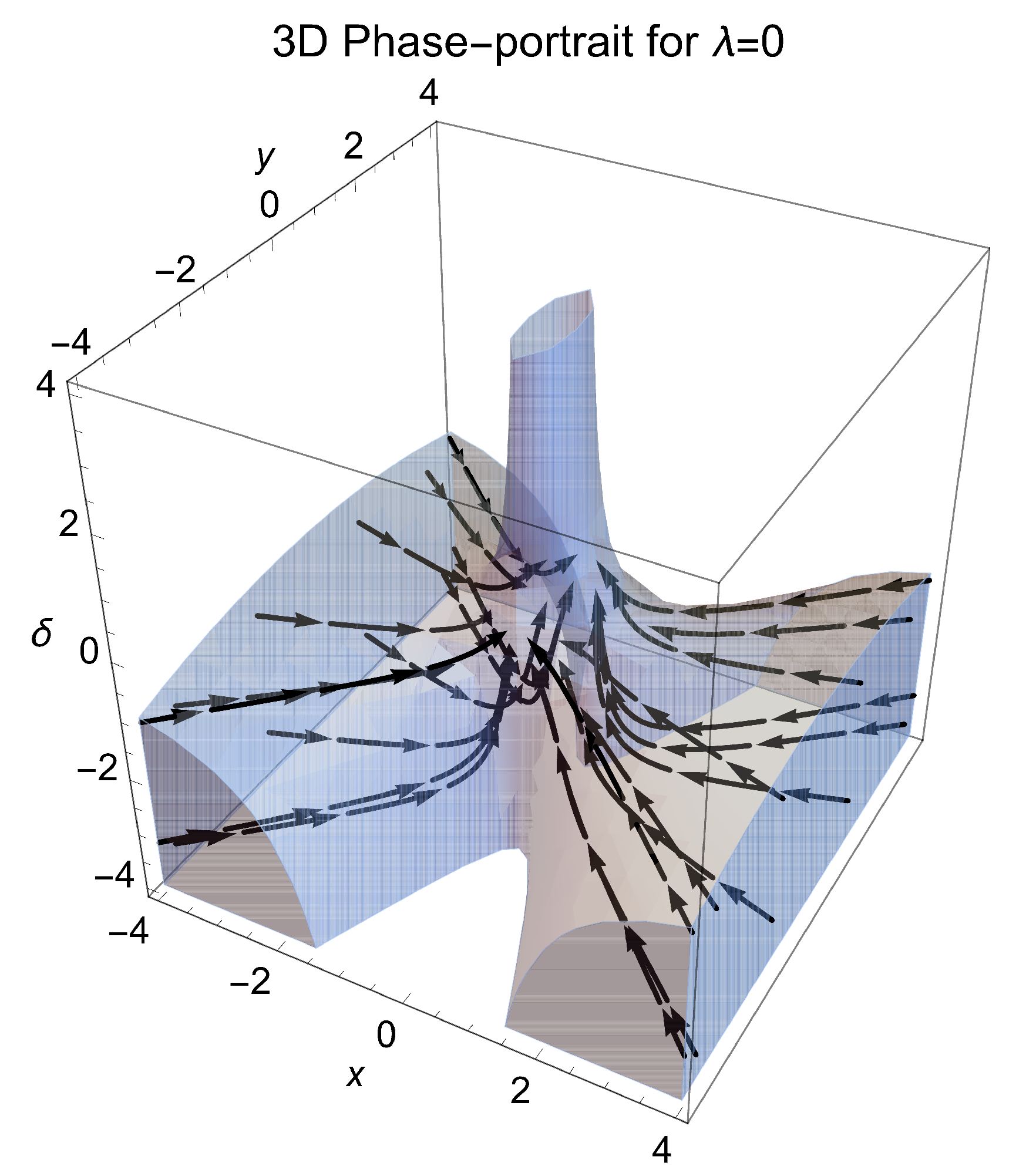
5. Analysis at Infinity
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Persic, M.; Salucci, P.; Stel, F. The universal rotation curve of spiral galaxies—I. The dark matter connection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 281, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, D.H.; Colombi, S.; Davé, R.; Katz, N. Baryon Dynamics, Dark Matter Substructure, and Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2008, 678, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, P.M.; Gilliland, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational evidence from Supernovae for an accelerating universe and cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar]
- Tegmark, M. et al. [SDSS Collaboration] The 3D power spectrum of galaxies from the SDSS. Astrophys. J. 2004, 606, 702–740. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, M.; Rubin, D.; Aldering, G.; Agostinho, R.J.; Amadon, A.; Amanullah, R.; Balland, C.; Barbary, K.; Blanc, G.; Challis, P.J.; et al. Improved Cosmological Constraints from New, Old, and Combined Supernova Data Sets. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, 749. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, J.; Watanabe, Y. Theoretical models of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2012, 21, 1230002. [Google Scholar]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified Gravity and Cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V. Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: Inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraro, R.; Fiorini, F. Modified teleparallel gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 084031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliathanasis, A. Dynamical analysis of f(Q) -cosmology. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 41, 101255. [Google Scholar]
- Krssak, M.; van den Hoogen, R.J.; Pereira, J.G.; Boehmer, C.G.; Coley, A.A. Teleparallel Theories of Gravity. Class. Quantum Grav. 2019, 36, 183001. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, S.; Jawad, A.; Bamba, K.; Malik, I.-U. Cosmological Consequences of New Dark Energy Models in Einstein-Aether Gravity. Symmetry 2019, 11, 509. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Barrow, J.D.; Mota, D.F. Cosmology of modified Gauss-Bonnet gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 044027. [Google Scholar]
- Ratra, B.; Peebles, P.J.E. Cosmological consequences of a rolling homogeneous scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 3406. [Google Scholar]
- Hordenski, G.W. Second-order scalar-tensor field equations in a four-dimensional space. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1975, 10, 363–384. [Google Scholar]
- Socorro, J.; Pérez-Payán, S.; Hernández-Jiménez, R.; Espinoza-García, A.; Díaz-Barrón, L.R. Classical and quantum exact solutions for a FRW in chiral like cosmology. Class. Quantum Grav. 2021, 38, 135027. [Google Scholar]
- von Marttens, R.; Barbosa, D.; Alcaniz, J. One-parameter dynamical dark-energy from the generalized Chaplygin gas. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 2023, 052. [Google Scholar]
- Akrami, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Solomon, A.R.; Vardanyan, V. Multi-field dark energy: Cosmic acceleration on a steep potential. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 819, 136427. [Google Scholar]
- Mamon, A.A.; Paliathanasis, A.; Saha, S. An extended analysis for a generalized Chaplygin gas model. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Cardone, V.F.; Troisi, A.; Capozziello, S. Unified dark energy models: A phenomenological approach. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 083517. [Google Scholar]
- Bento, M.C.; Bertolami, O.; Sen, A.A. Generalized Chaplygin gas, accelerated expansion, and dark-energy-matter unification. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 70, 083519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.; Matarrese, S.; Torki, M. Instability of Chaplygin gas trajectories in unified dark matter models. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 70, 121304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-B.; Li, S.; Lu, J.-B.; Yang, X.-Y. The modified Chaplygin gas as a unified dark sector model. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 22, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, V.; Kamenshchik, A.Y.; Moschella, U.; Piattella, O.F.; Starobinsky, A.A. More about the Tolman-Oppenheimer-Volkoff equations for the generalized Chaplygin gas. Phys. Rev. D 2009, 80, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-H. Generalized Chaplygin gas as a unified scenario of dark matter/energy: Observational constraints. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 423, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Barrow, J.D. Does bulk viscosity create a viable unified dark matter model? Phys. Rev. D 2009, 79, 103521. [Google Scholar]
- Atreya, A.; Bhatt, J.R.; Mishra, A.K. Viscous self interacting dark matter cosmology for small redshift. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 045. [Google Scholar]
- Bertacca, D.; Matarrese, S.; Pietroni, M. Unified Dark Matter in Scalar Field Cosmologies. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2007, 22, 2893–2907. [Google Scholar]
- Bertacca, D.; Bartolo, N.; Matarrese, S. Unified Dark Matter Scalar Field Models. Adv. Astron. 2010, 2010, 904379. [Google Scholar]
- Paliathanasis, A. Dynamics of Chiral Cosmology. Class. Quantum Grav. 2020, 37, 195014. [Google Scholar]
- Leon, G.; Paliathanasis, A.; Saridakis, E.N.; Basilakos, S. Unified dark sectors in scalar-torsion theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 024055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L. Coupled quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterich, C. An asymptotically vanishing time-dependent cosmological “constant”. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 301, 321. [Google Scholar]
- Di Valentino, E.; Melciorri, A.; Mena, O.; Pan, S.; Yang, W. Interacting Dark Energy in a closed universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2021, 502, L23–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonilla, A.; Kumar, S.; Nunes, R.C.; Pan, S. Reconstruction of the dark sectors’ interaction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 512, 4231–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisty, D.; Guendelman, E.I. Interacting diffusive unified dark energy and dark matter from scalar fields. Eur. Phys. J. C 2017, 77, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisty, D.; Guendelman, E.I. Unified dark energy and dark matter from dynamical spacetime. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 023506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopulos, F.K.; Benisty, D.; Basilakos, S.; Guendelman, E.I. Dark energy and dark matter unification from dynamical space time: Observational constraints and cosmological implications. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2019, 2019, 003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, T.; Leon, G.; Quiros, I. Dynamics of quintessence models of dark energy with exponential coupling to dark matter. Class. Quantum Grav. 2006, 23, 3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tot, J.; Yildirim, B.; Coley, A.; Leon, G. The dynamics of scalar-field Quintom cosmological models. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 39, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millano, A.D.; Leon, G.; Paliathanasis, A. Global dynamics in Einstein-Gauss-Bonnet scalar field cosmology with matter. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coley, A.A.; van den Hoogen, R.J. Dynamics of multi-scalar-field cosmological models and assisted inflation. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 023517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Gannouji, R.; Polarski, D.; Tsujikawa, S. Conditions for the cosmological viability of f(R) dark energy models. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 75, 083504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khyllep, W.; Dutta, J.; Saridakis, E.N.; Yesmakhanova, K. Cosmology in f(Q) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2023, 107, 044022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Kunz, M.; Liddle, A.R.; Parkinson, D. Unified dark energy and dark matter from a scalar field different from quintessence. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 043520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendelman, E.I.; Kaganovich, A.B. Dark energy, dark matter and fermion families in the two measures theory. Int. J. Mod. Phys A 2004, 19, 5325–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendelman, E.I.; Kaganovich, A.B. Exotic Low Density Fermion States in the Two Measures Field Theory: Neutrino Dark Energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2006, 21, 4373–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, F.; Muench, U.; Macias, A.; Hehl, F.W. Volume elements of spacetime and a quartet of scalar fields. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 084021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, D. A Way to Dynamically Overcome the Cosmological Constant Problem. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2008, 23, 4133–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendelman, E.I. Gravitational Theory with a Dynamical Time. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2010, 15, 4081–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
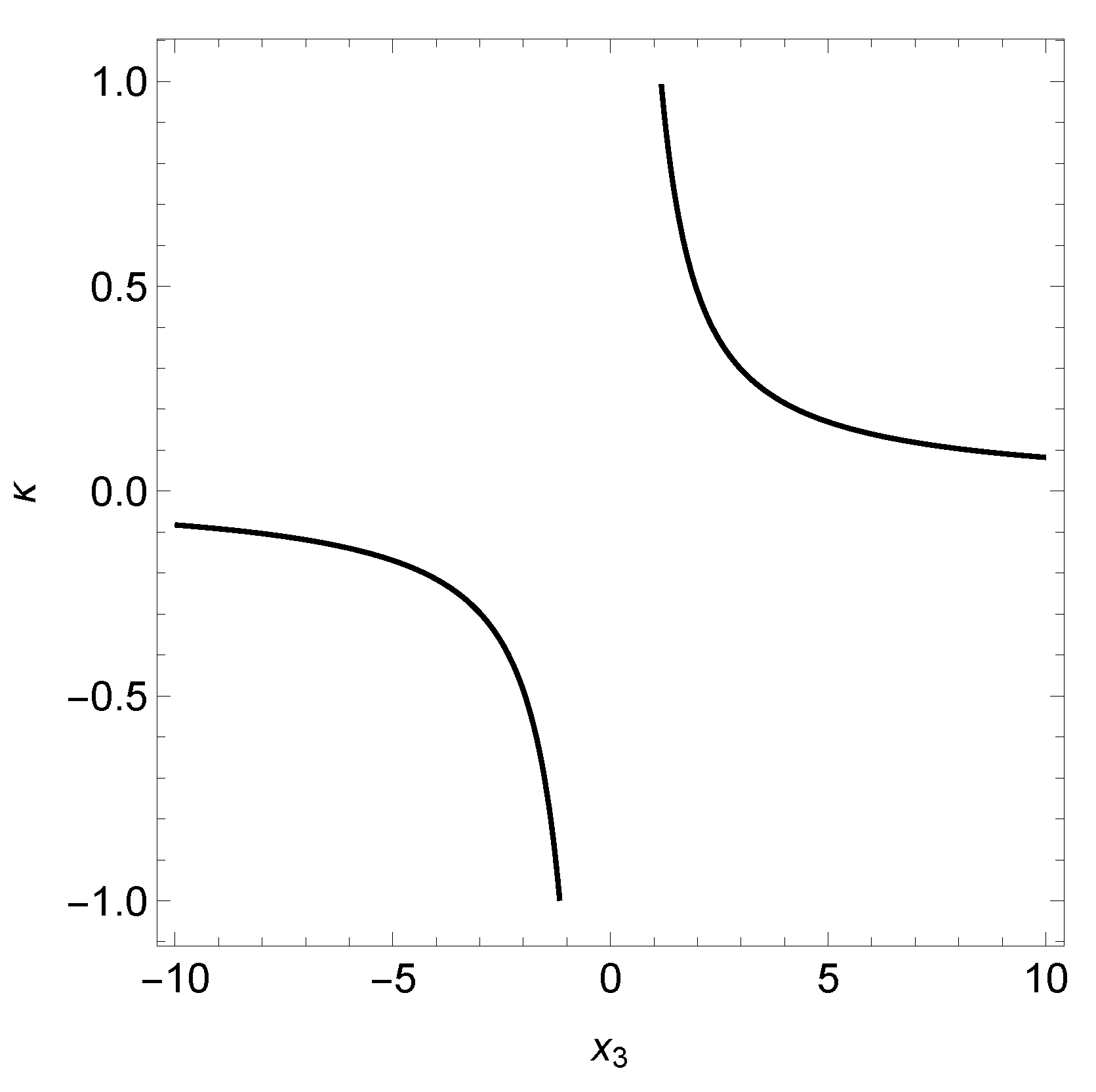

| Model | Point | Acceleration? | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0 | ||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| II | |||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| II | |||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| Yes | |||||
| III | |||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| 0 | No | ||||
| No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paliathanasis, A. Revise the Phase-Space Analysis of the Dynamical Spacetime Unified Dark Energy Cosmology. Universe 2023, 9, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9090406
Paliathanasis A. Revise the Phase-Space Analysis of the Dynamical Spacetime Unified Dark Energy Cosmology. Universe. 2023; 9(9):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9090406
Chicago/Turabian StylePaliathanasis, Andronikos. 2023. "Revise the Phase-Space Analysis of the Dynamical Spacetime Unified Dark Energy Cosmology" Universe 9, no. 9: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9090406
APA StylePaliathanasis, A. (2023). Revise the Phase-Space Analysis of the Dynamical Spacetime Unified Dark Energy Cosmology. Universe, 9(9), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9090406