Analytical Constraints on the Radius and Bulk Lorentz Factor in the Lepto-Hadronic One-Zone Model of BL Lacs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Derivation of Constraints
2.1. Constraint from Variability Timescale
2.2. Constraint from SSC Luminosity
2.3. Constraint from Optical Depth
2.4. Constraint from the Hadronic Process
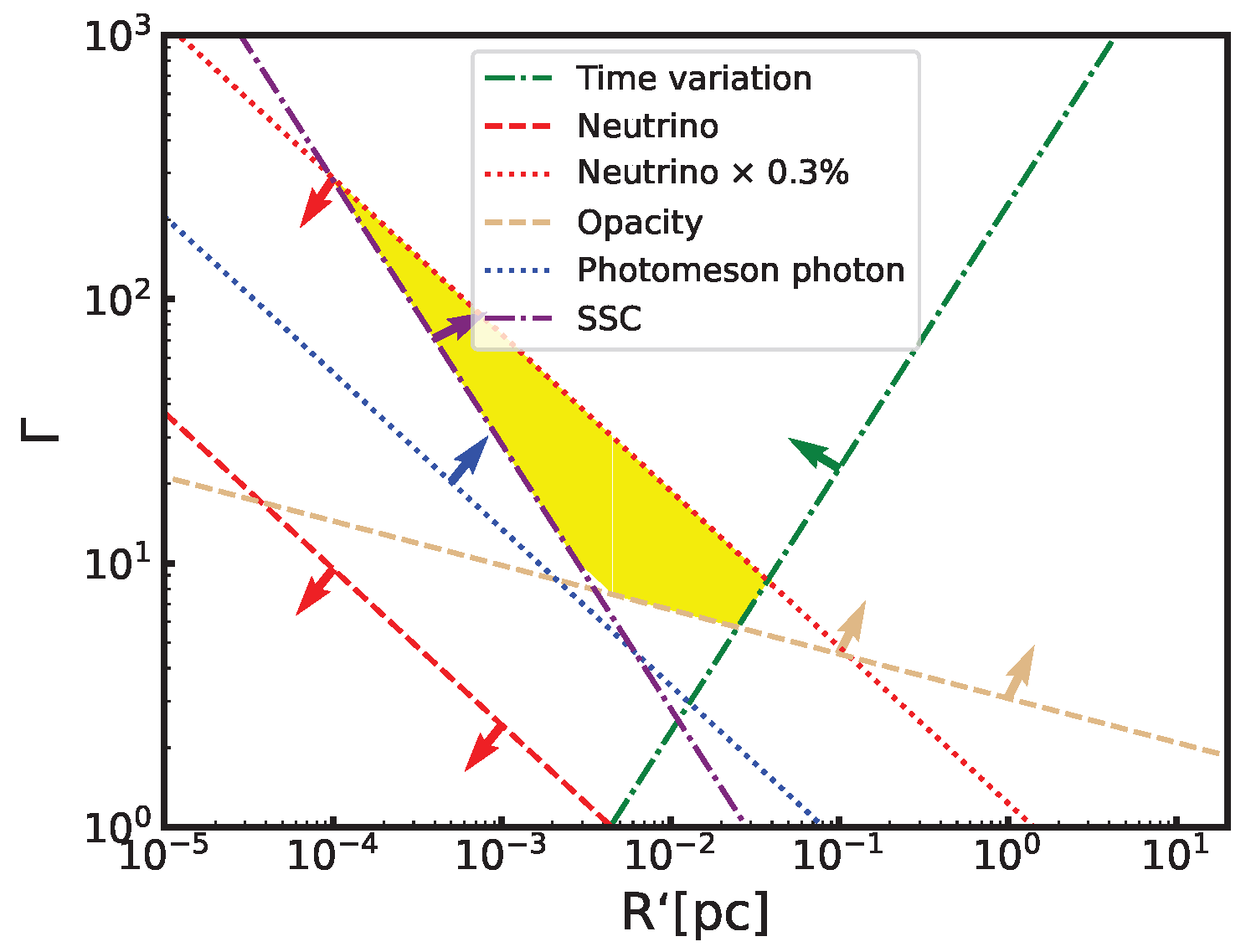
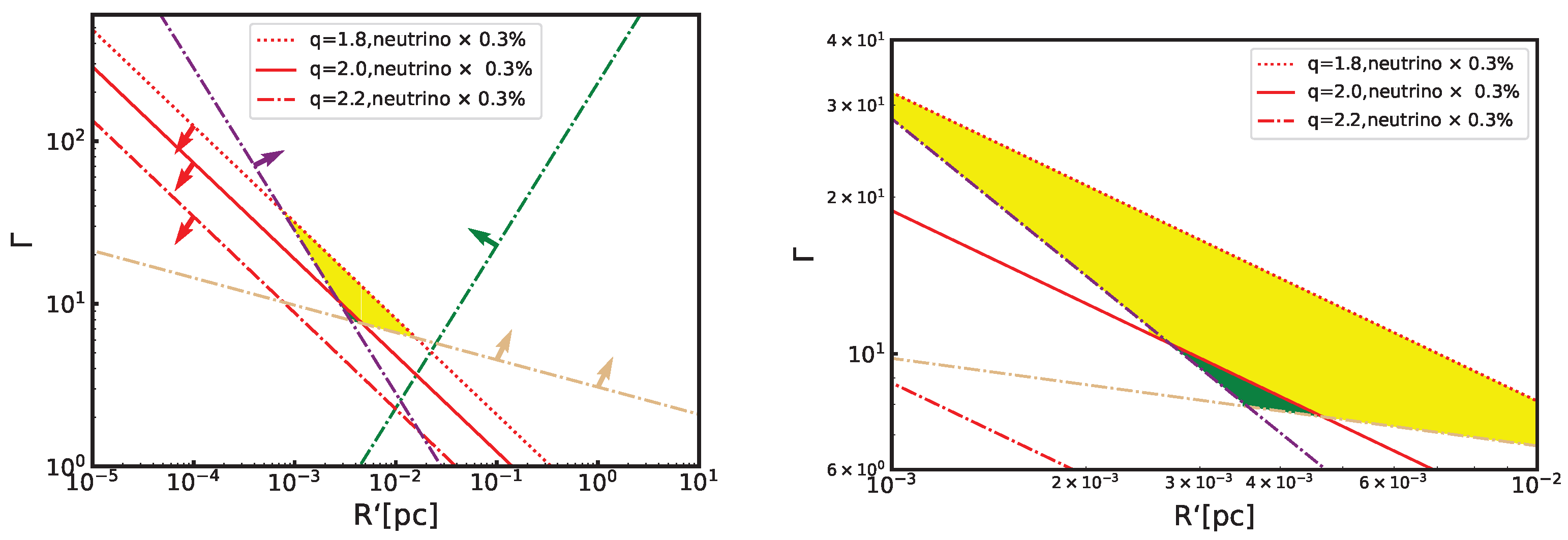
3. Application to TXS 0506+056
4. Application to PKS 0735+178
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aartsen, M.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.A.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Al Samarai, I.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; et al. Multimessenger observations of a flaring blazar coincident with high-energy neutrino IceCube-170922A. Science 2018, 361, eaat1378. [Google Scholar]
- Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Baack, D.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; De Almeida, U.B.; Barrio, J.A.; González, J.B.; et al. The blazar TXS 0506+056 associated with a high-energy neutrino: Insights into extragalactic jets and cosmic-ray acceleration. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 863, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keivani, A.; Murase, K.; Petropoulou, M.; Fox, D.; Cenko, S.; Chaty, S.; Coleiro, A.; DeLaunay, J.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Evans, P.; et al. A multimessenger picture of the flaring blazar TXS 0506+056: Implications for high-energy neutrino emission and cosmic-ray acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E.; Glauch, T.; Arsioli, B.; Sahakyan, N.; Huber, M. Dissecting the region around IceCube-170922A: The blazar TXS 0506+056 as the first cosmic neutrino source. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, N. Lepto-hadronic γ-ray and neutrino emission from the jet of TXS 0506+056. Astrophys. J. 2018, 866, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fang, K.; Li, H. Variability and Optical Polarization Can Probe the Neutrino and Electromagnetic Emission Mechanisms of TXS 0506+056. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.11069. [Google Scholar]
- Banik, P.; Bhadra, A. Describing correlated observations of neutrinos and gamma-ray flares from the blazar TXS 0506+056 with a proton blazar model. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruti, M.; Zech, A.; Boisson, C.; Emery, G.; Inoue, S.; Lenain, J. Leptohadronic single-zone models for the electromagnetic and neutrino emission of TXS 0506+056. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 483, L12–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, R. Constraints on neutrino speed, weak equivalence principle violation, Lorentz invariance violation, and dual lensing from the first high-energy astrophysical neutrino source TXS 0506+056. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 100, 103002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Y.; Wang, K.; Xue, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Hadronuclear interpretation of a high-energy neutrino event coincident with a blazar flare. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 063008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Oikonomou, F.; Petropoulou, M.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E. TXS 0506+056, the first cosmic neutrino source, is not a BL Lac. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 484, L104–L108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, C.; Tavecchio, F.; Inoue, S. Neutrino emission from BL Lac objects: The role of radiatively inefficient accretion flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 483, L127–L131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Liu, R.Y.; Petropoulou, M.; Oikonomou, F.; Wang, Z.R.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.Y. A two-zone model for blazar emission: Implications for TXS 0506+056 and the neutrino event IceCube-170922A. Astrophys. J. 2019, 886, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, J. A self-consistent leptonic–hadronic interpretation of the electromagnetic and neutrino emissions from blazar TXS 0506+056. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 72, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urry, C.M.; Padovani, P. Unified schemes for radio-loud active galactic nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 1995, 107, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, K.; Stanev, T.; Biermann, P. Neutrinos from flat-spectrum radio quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 260, L1–L3. [Google Scholar]
- Atoyan, A.; Dermer, C.D. High-energy neutrinos from photomeson processes in blazars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 221102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murase, K.; Inoue, Y.; Dermer, C.D. Diffuse neutrino intensity from the inner jets of active galactic nuclei: Impacts of external photon fields and the blazar sequence. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 023007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Petropoulou, M.; Giommi, P.; Resconi, E. A simplified view of blazars: The neutrino background. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulou, M.; Dimitrakoudis, S.; Padovani, P.; Mastichiadis, A.; Resconi, E. Photohadronic origin of-ray BL Lac emission: Implications for IceCube neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 2412–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padovani, P.; Resconi, E.; Giommi, P.; Arsioli, B.; Chang, Y. Extreme blazars as counterparts of IceCube astrophysical neutrinos. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 3582–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, X.; Gao, S.; Fedynitch, A.; Palladino, A.; Winter, W. Leptohadronic blazar models applied to the 2014–2015 flare of TXS 0506+056. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 874, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.; Schlickeiser, R.; Mastichiadis, A. High-energy gamma radiation from extragalactic radio sources. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 256, L27–L30. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, S.D.; Marscher, A.P. An analysis of the synchrotron self-compton model for the multi–wave band spectra of blazars. Astrophys. J. 1996, 461, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraschi, L.; Ghisellini, G.; Celotti, A. A jet model for the gamma-ray emitting blazar 3C 279. Astrophys. J. 1992, 397, L5–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastichiadis, A.; Kirk, J. Variability in the synchrotron self-Compton model of blazar emission. arXiv 1996, arXiv:astro-ph/9610058. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, A.; Laor, A. Hadronic production of TeV gamma-ray flares from blazars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 478, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araudo, A.T.; Bosch-Ramon, V.; Romero, G.E. Gamma-ray emission from massive stars interacting with active galactic nuclei jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 436, 3626–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, R.Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Dai, Z.G. Jet Cloud–Star Interaction as an Interpretation of Neutrino Outburst from the Blazar TXS 0506+056. Universe 2022, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.T.; Petropoulou, M.; Murase, K.; Oikonomou, F. A Neutral Beam Model for High-energy Neutrino Emission from the Blazar TXS 0506+056. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparyan, S.; Bégué, D.; Sahakyan, N. Time-dependent lepto-hadronic modeling of the emission from blazar jets with SOPRANO: The case of TXS 0506+056, 3HSP J095507.9+355101 and 3C 279. Monthly Not. R. Astrono. Soc. 2022, 509, 2102–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Fedynitch, A.; Winter, W.; Pohl, M. Interpretation of the coincident observation of a high energy neutrino and a bright flare. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.04275. [Google Scholar]
- Murase, K.; Oikonomou, F.; Petropoulou, M. Blazar flares as an origin of high-energy cosmic neutrinos? Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Liu, R.Y.; Wang, Z.R.; Ding, N.; Wang, X.Y. A Two-zone Blazar Radiation Model for “Orphan” Neutrino Flares. Astrophys. J. 2021, 906, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelner, S.; Aharonian, F. Energy spectra of gamma rays, electrons, and neutrinos produced at interactions of relativistic protons with low energy radiation. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 034013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, M.; Reimer, A.; Sweeney, K.; Prakash, A. Leptonic and hadronic modeling of Fermi-detected blazars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerruti, M.; Zech, A.; Boisson, C.; Inoue, S. A hadronic origin for ultra-high-frequency-peaked BL Lac objects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 448, 910–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zech, A.; Cerruti, M.; Mazin, D. Expected signatures from hadronic emission processes in the TeV spectra of BL Lacertae objects. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, A25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diltz, C.; Boettcher, M.; Fossati, G. Time dependent hadronic modeling of flat spectrum radio quasars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Fernández, B.; van Eerten, H. Katu: A fast open-source full lepto-hadronic kinetic code suitable for Bayesian inference modelling of blazars. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08207. [Google Scholar]
- Baring, M.G.; Böttcher, M. Time-dependent, multi-wavelength shock acceleration models for active flares of 3C 279. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.12358. [Google Scholar]
- Nalewajko, K.; Begelman, M.C.; Sikora, M. Constraining the location of gamma-ray flares in luminous blazars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.; Larson, D.; Weiland, J.; Hinshaw, G. The 1% concordance Hubble constant. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Menon, G. High Energy Radiation from Black Holes; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Stecker, F. Effect of photomeson production by the universal radiation field on high-energy cosmic rays. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1968, 21, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Liu, R.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Yan, H.; Böttcher, M. On the minimum jet power of TeV BL Lac Objects in the p–γ model. Astrophys. J. 2019, 871, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakyan, N.; Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Petropoulou, M.; Bégué, D.; Boccardi, B.; Gasparyan, S. A multi-messenger study of the blazar PKS 0735+178: A new major neutrino source candidate. Monthly Not. R. Astrono. Soc. 2023, 159, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Altmann, D.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. The IceCube realtime alert system. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 92, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhilkibaev, Z.A.; Suvarova, O.; Baikal-GVD Collaboration. Baikal-GVD observation of a high-energy neutrino candidate event from the blazar PKS 0735+17 at the day of the IceCube-211208A neutrino alert from the same direction. Astron. Telegr. 2021, 15112, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Petkov, V.; Novoseltsev, Y.F.; Novoseltseva, R. Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope observation of a GeV neutrino candidate event at the time of a gamma-ray flare of the blazar PKS 0735+17, a possible source of coinciding IceCube and Baikal high-energy neutrinos. Astron. Telegr. 2021, 15143, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Filippini, F.; Illuminati, G.; Heijboer, A.; Gatius, C.; Muller, R.; Dornic, D.; Huang, F.; Le Stum, S.; Palacios González, J.; Celli, S.; et al. Search for neutrino counterpart to the blazar PKS0735+178 potentially associated with IceCube-211208A and Baikal-GVD-211208A with the KM3NeT neutrino detectors. Astron. Telegr. 2022, 15290, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Aartsen, M.; Ackermann, M.; Adams, J.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlers, M.; Ahrens, M.; Alispach, C.; Andeen, K.; Anderson, T.; Ansseau, I.; et al. Time-integrated neutrino source searches with 10 years of IceCube data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 051103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliya, V.S.; Böttcher, M.; Olmo-García, A.; Domínguez, A.; Gil de Paz, A.; Franckowiak, A.; Garrappa, S.; Stein, R. Multifrequency Observations of the Candidate Neutrino-emitting Blazar BZB J0955+3551. Astrophys. J. 2020, 902, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giommi, P.; Padovani, P.; Oikonomou, F.; Glauch, T.; Paiano, S.; Resconi, E. 3HSP J095507.9+355101: A flaring extreme blazar coincident in space and time with IceCube-200107A. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 640, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrappa, S.; Buson, S.; Franckowiak, A.; Fermi-LAT Collaboration; Shappee, B.J.; Beacom, J.F.; Dong, S.; Holoien, T.W.S.; Kochanek, C.S.; Prieto, J.L.; et al. Investigation of Two Fermi-LAT Gamma-Ray Blazars Coincident with High-energy Neutrinos Detected by IceCube. Astrophys. J. 2019, 880, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadler, M.; Krauß, F.; Mannheim, K.; Ojha, R.; Müller, C.; Schulz, R.; Anton, G.; Baumgartner, W.; Beuchert, T.; Buson, S.; et al. Coincidence of a high-fluence blazar outburst with a PeV-energy neutrino event. Nat. Phys. 2016, 12, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franckowiak, A.; Garrappa, S.; Paliya, V.; Shappee, B.; Stein, R.; Strotjohann, N.; Kowalski, M.; Buson, S.; Kiehlmann, S.; Max-Moerbeck, W.; et al. Patterns in the Multiwavelength Behavior of Candidate Neutrino Blazars. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Symbol | TXS 0506+056 | PKS 0735+178 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Syn-radiation peak flux | |||
| Gamma ray peak flux | |||
| Neutrino flux | |||
| Critical photon flux | |||
| Critical photon energy | eV | eV | |
| Maximum photon energy | eV | eV | |
| Low energy peak frequency | |||
| High energy peak frequency | |||
| Redshift | z | ||
| Spectral index | |||
| Time variation | one week | 5000 s | |
| Maximum Lorentz factor | |||
| Minimum Lorentz factor | 1 | 1 | |
| Injection index | q | ||
| Proton luminosity (AGN frame) |
| Conditions | q = 1.8 | q = 2.0 | q = 2.2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [pc] | [pc] | [pc] | ||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| — | — | — | — | |||
| — | — | |||||
| Conditions | q = 1.8 | q = 2.0 | q = 2.2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [pc] | [pc] | [pc] | ||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| — | — | — | — | |||
| — | — | |||||
| — | — | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.-P.; Wang, K. Analytical Constraints on the Radius and Bulk Lorentz Factor in the Lepto-Hadronic One-Zone Model of BL Lacs. Universe 2023, 9, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9070314
Ma Z-P, Wang K. Analytical Constraints on the Radius and Bulk Lorentz Factor in the Lepto-Hadronic One-Zone Model of BL Lacs. Universe. 2023; 9(7):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9070314
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhi-Peng, and Kai Wang. 2023. "Analytical Constraints on the Radius and Bulk Lorentz Factor in the Lepto-Hadronic One-Zone Model of BL Lacs" Universe 9, no. 7: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9070314
APA StyleMa, Z.-P., & Wang, K. (2023). Analytical Constraints on the Radius and Bulk Lorentz Factor in the Lepto-Hadronic One-Zone Model of BL Lacs. Universe, 9(7), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9070314






